New Insights into 4-Anilinoquinazolines as Inhibitors of Cardiac Troponin I–Interacting Kinase (TNNi3K)
Abstract
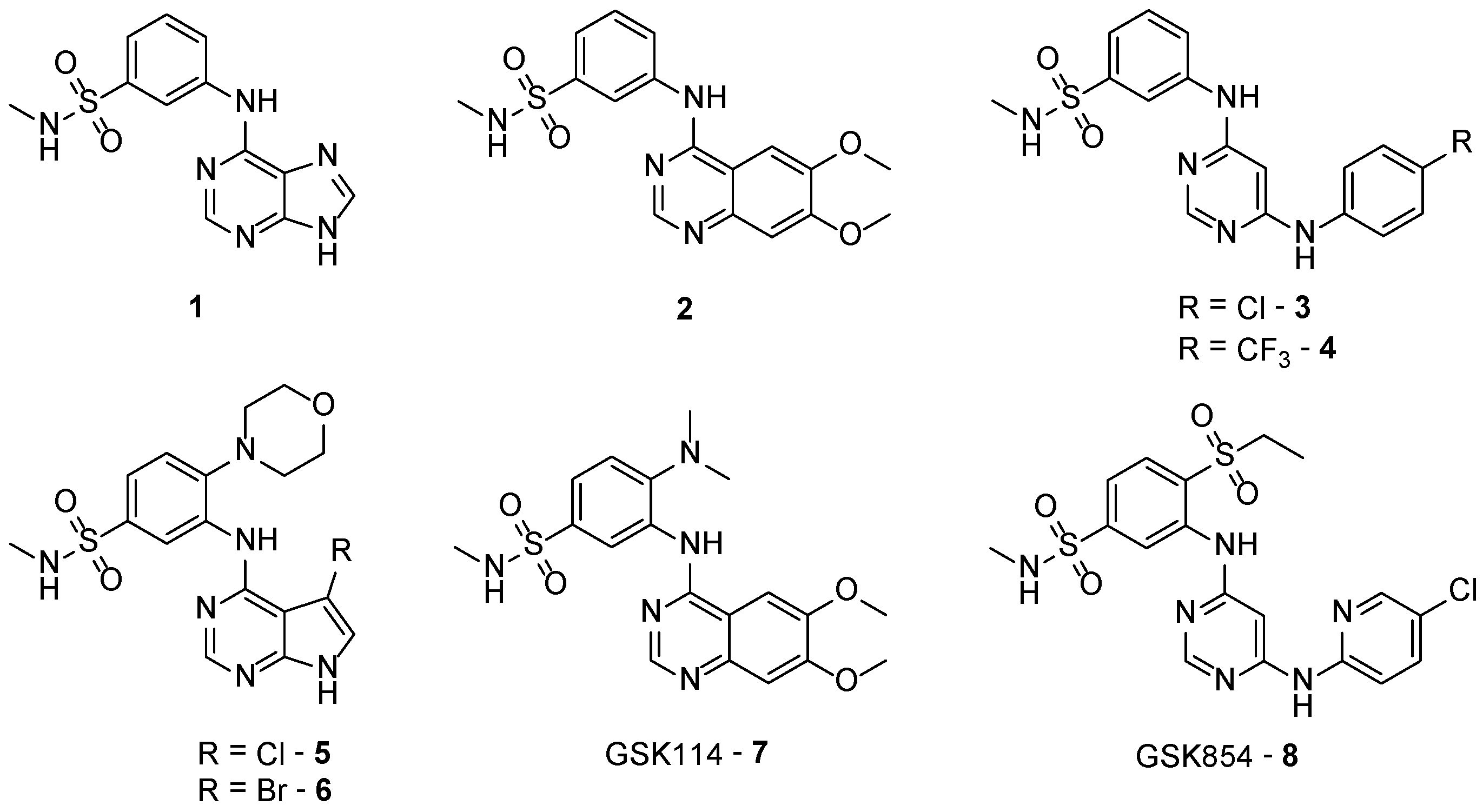
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
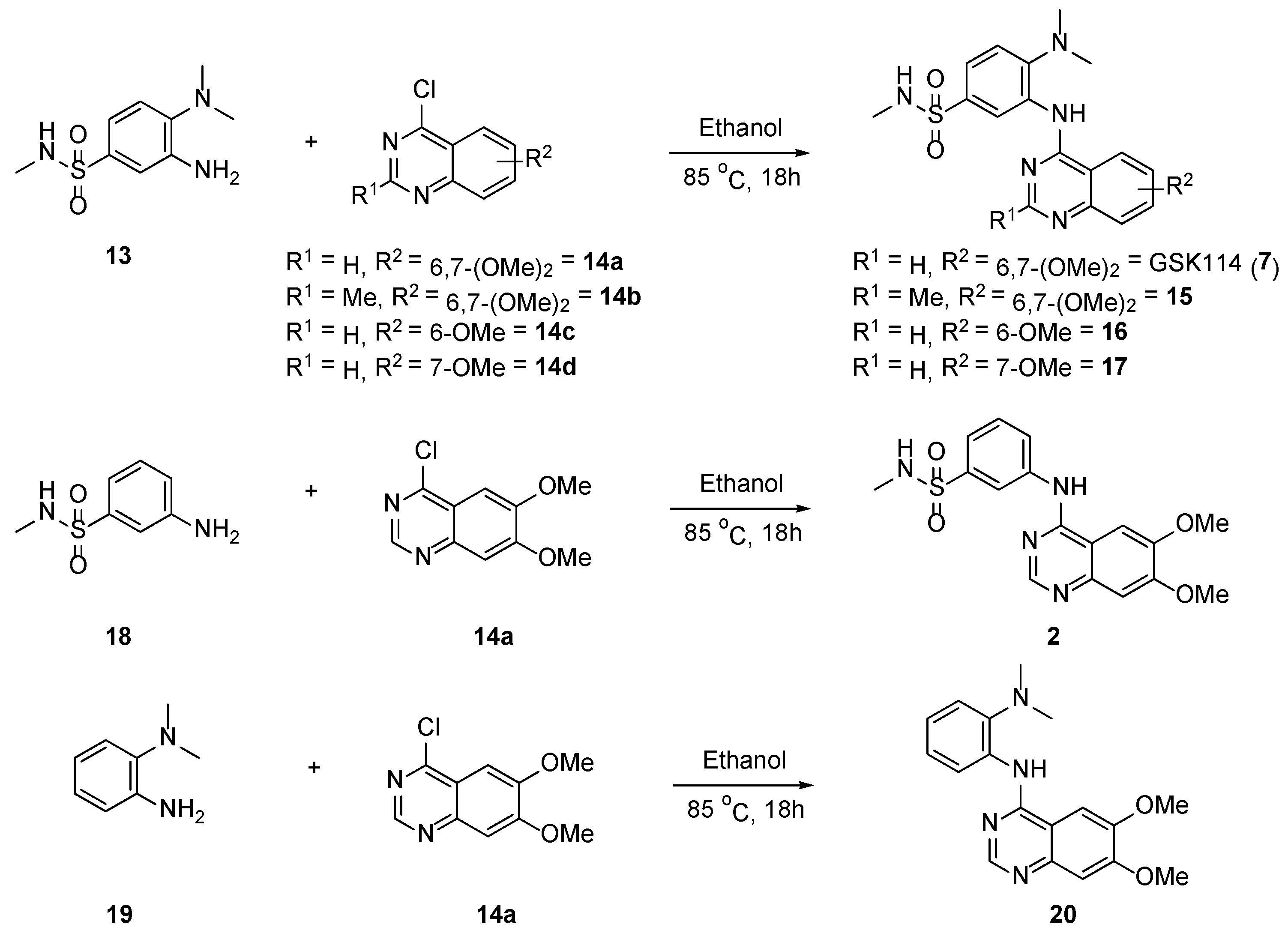
2.1. Synthesis of Aniline 13
2.2. Synthesis of 4-Anilinoquinazolines 2, 7, 15–17 & 20
2.3. Results of 4-Anilinoquinazolines 2, 7, 15–17 & 20 in TNNi3K Binding Assay
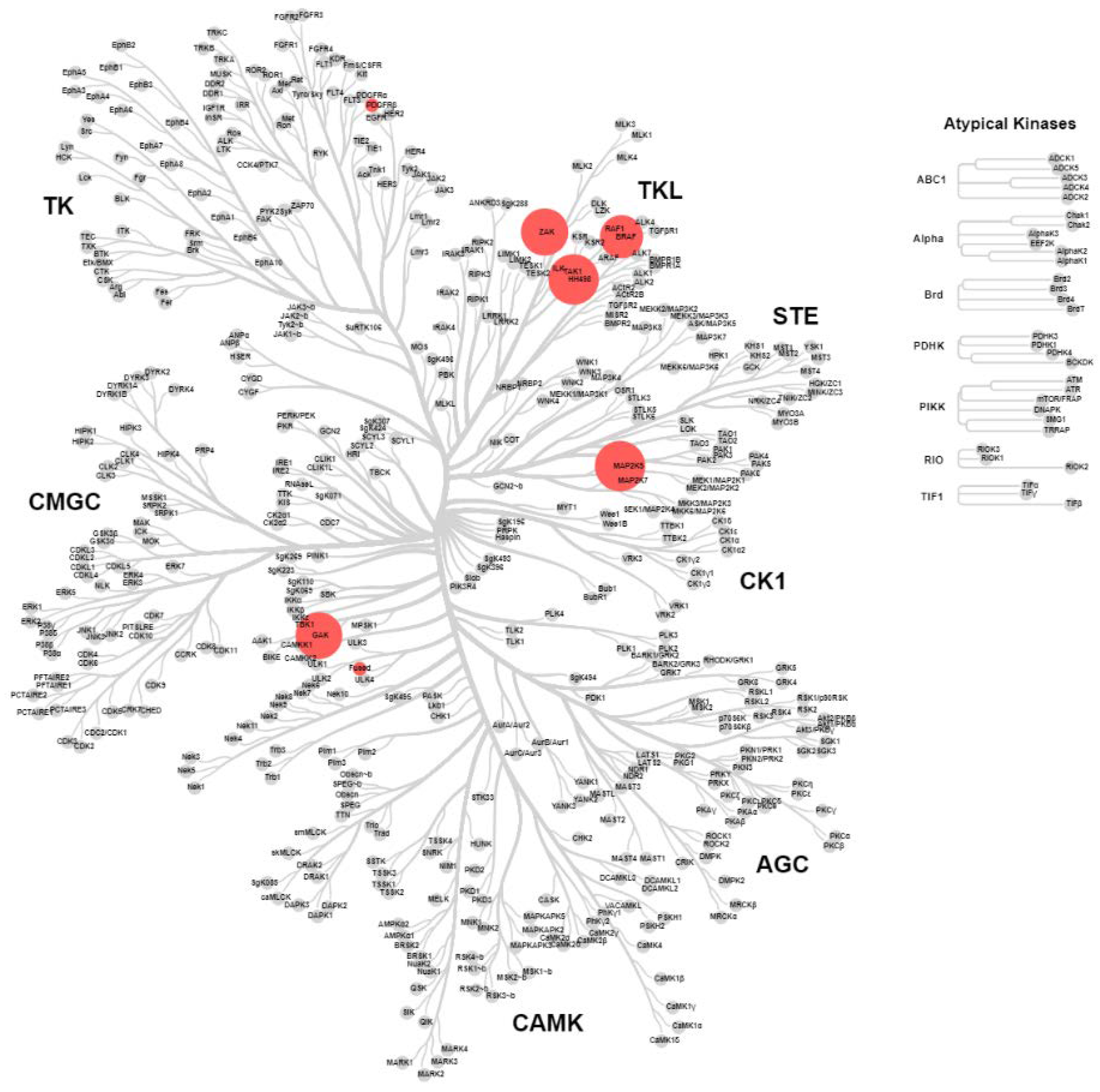
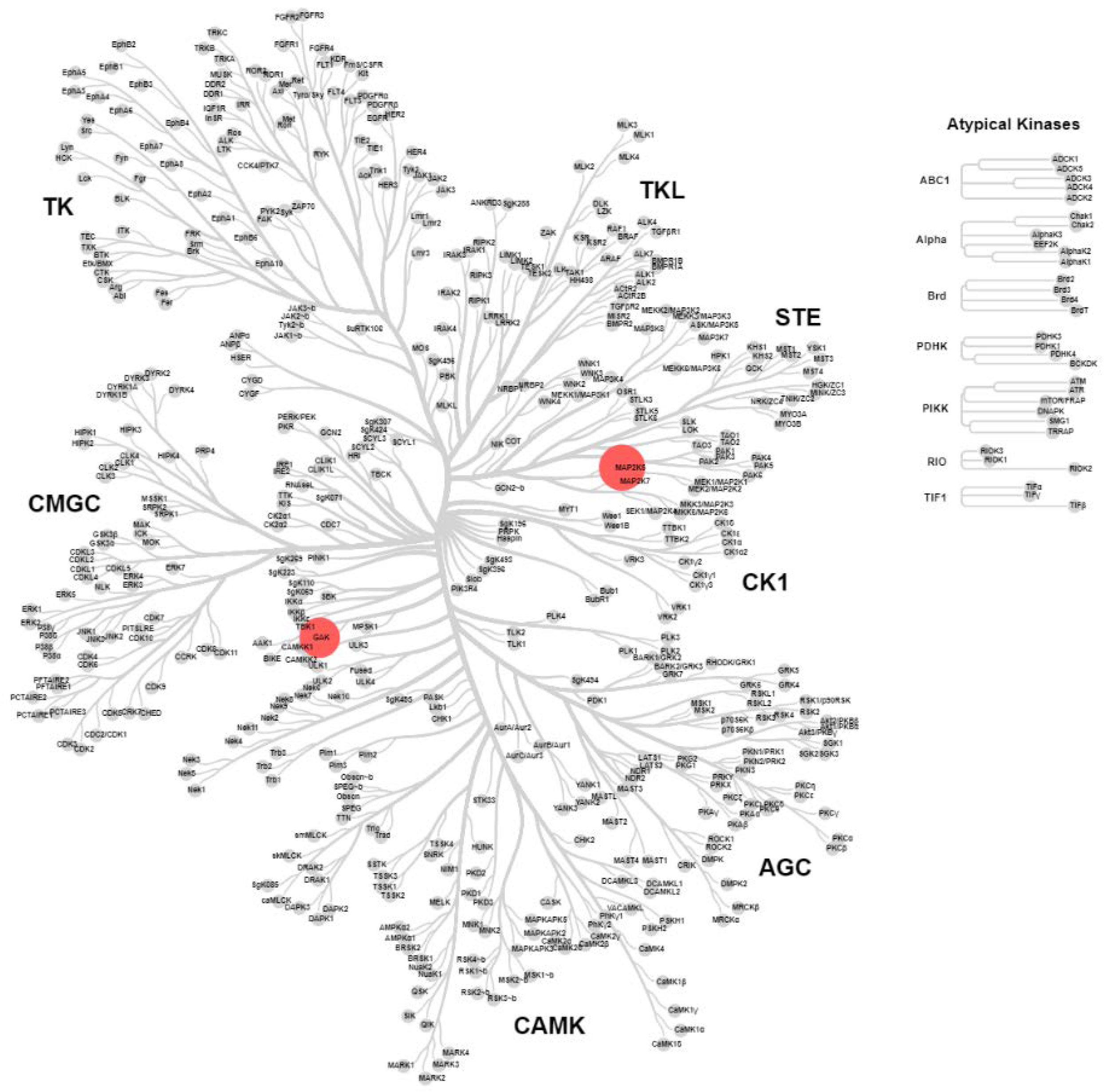
2.4. KinomeScan® of GSK114 (7) and 15
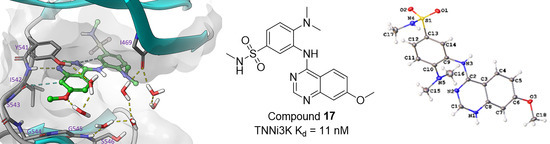
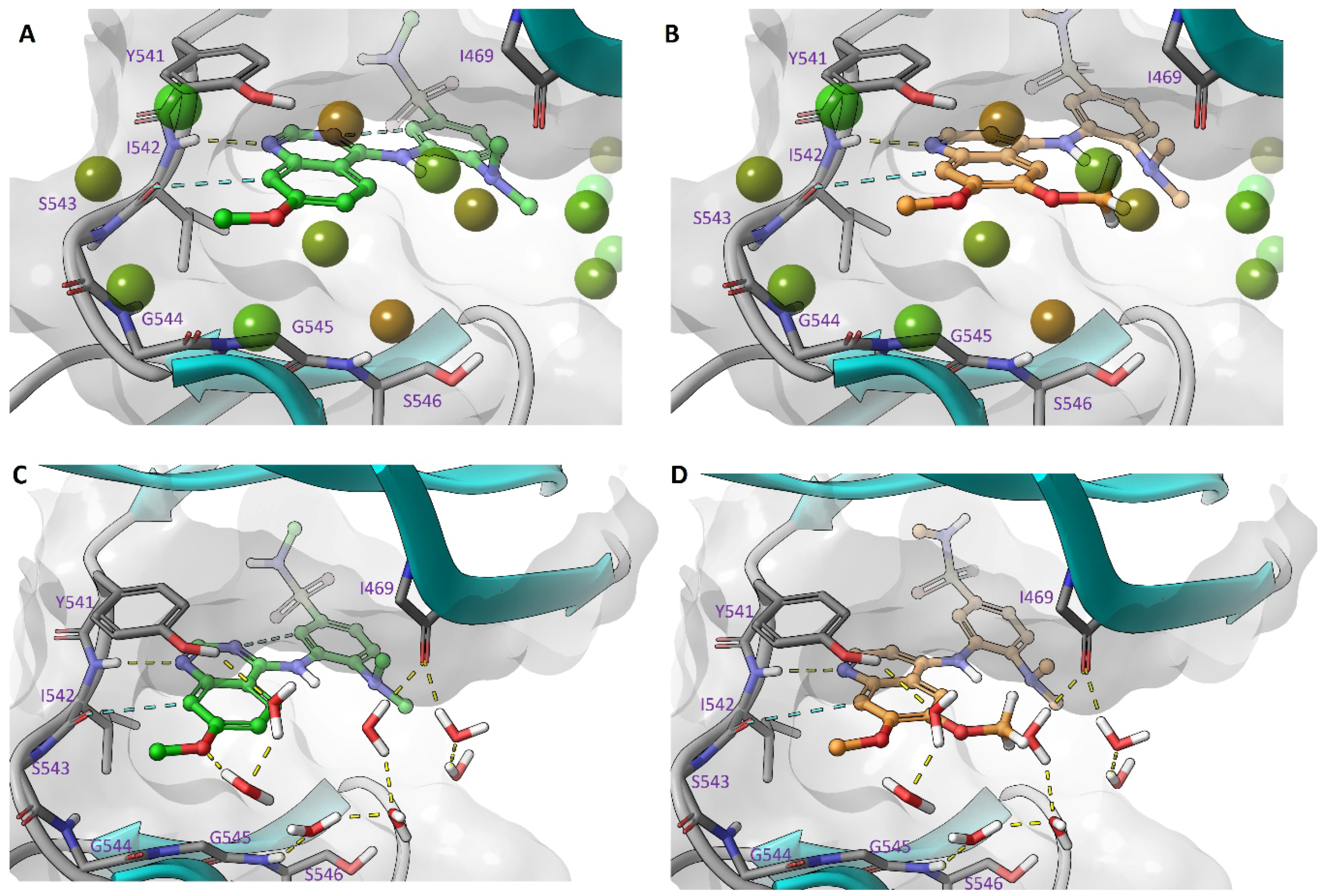
2.5. Modelling of Inhibitors in TNNi3K
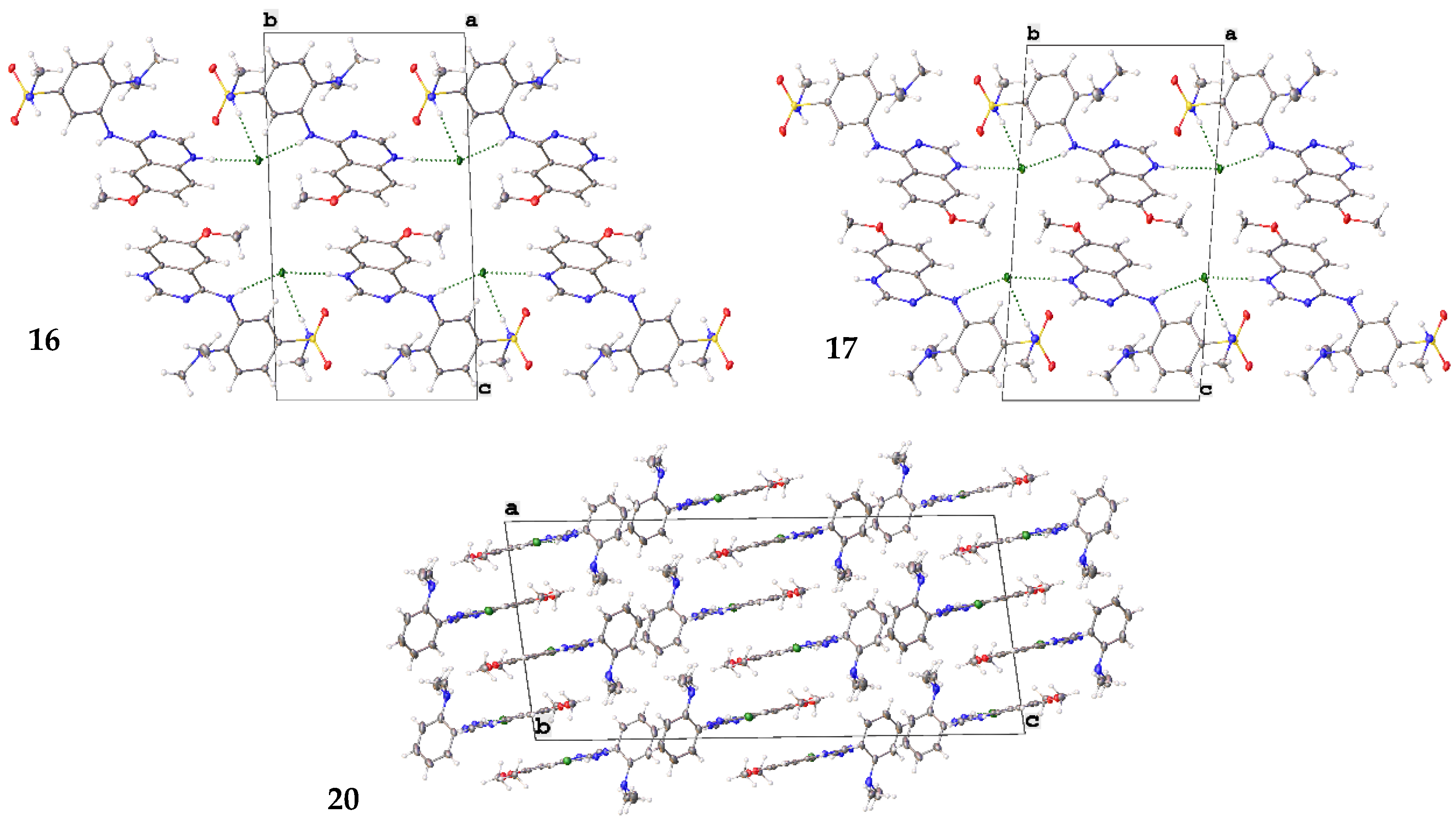
2.6. Small Molecule Crystal Structures of 16, 17 and 20
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Mass Spectrometry
3.3. Molecular Modelling
3.4. Crystallography
3.5. KinomeScan® Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferguson, F.M.; Gray, N.S. Kinase inhibitors: The road ahead. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 353–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, P.; Alessi, D.R. Kinase drug discovery—What’s next in the field? ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The Protein Kinase Complement of the Human Genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, S.; Arruda, P.; Blagg, J.; Burley, S.; Drewry, D.H.; Edwards, A.; Fabbro, D.; Gillespie, P.; Gray, N.S.; Kuster, B.; et al. A public-private partnership to unlock the untargeted kinome. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagnozzi, R.J.; Gatto, G.J., Jr.; Kallander, L.S.; Hoffman, N.E.; Mallilankaraman, K.; Ballard, V.L.T.; Lawhorn, B.G.; Stoy, P.; Philp, J.; Graves, A.P.; et al. Inhibition of the cardiomyocyte-specific TNNI3K limits oxidative stress, injury, and adverse remodeling in the ischemic heart. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 207ra141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Ye, J.; Xu, R.X.; Song, L.; Shi, N.; Zhang, Y.W.; Chen, X.; Meng, X.M. Adenovirus-mediated overexpression of cardiac troponin I-interacting kinase promotes cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2011, 38, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, F.C.; Tang, H.; Marks, O.A.; Hadnott, T.N.; Chu, P.L.; Mao, L.; Rockman, H.A.; Marchuk, D.A. Tnni3k modifies disease progression in murine models of cardiomyopathy. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhorn, B.G.; Philp, J.; Zhao, Y.; Louer, C.; Hammond, M.; Cheung, M.; Fries, H.; Graves, A.P.; Shewchuk, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Identification of Purines and 7-Deazapurines as Potent and Selective Type I Inhibitors of Troponin I-Interacting Kinase (TNNI3K). J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7431–7448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhorn, B.G.; Philp, J.; Graves, A.P.; Holt, D.A.; Gatto, G.J., Jr.; Kallander, L.S. Substituent Effects on Drug-Receptor H-bond Interactions: Correlations Useful for the Design of Kinase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10629–10641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhorn, B.G.; Philp, J.; Graves, A.P.; Shewchuk, L.; Holt, D.A.; Gatto, G.J., Jr.; Kallander, L.S. GSK114: A selective inhibitor for elucidating the biological role of TNNI3K. Bioorg Med. Chem Lett. 2016, 26, 3355–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, J.; Lawhorn, B.G.; Graves, A.P.; Shewchuk, L.; Rivera, K.L.; Jolivette, L.J.; Holt, D.A.; Gatto, G.J., Jr.; Kallander, L.S. 4,6-Diaminopyrimidines as Highly Preferred Troponin I-Interacting Kinase (TNNI3K) Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 3076–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Laitinen, T.; Bennett, J.M.; Godoi, P.H.; East, M.P.; Tizzard, G.J.; Graves, L.M.; Johnson, G.L.; Dornsife, R.E.; Wells, C.I.; et al. Identification and Optimization of 4-Anilinoquinolines as Inhibitors of Cyclin G Associated Kinase. Chem. Med. Chem. 2018, 13, 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Berger, B.T.; Wan, J.; Bennett, J.M.; Capuzzi, S.J.; Crona, D.J.; Drewry, D.H.; East, M.P.; Elkins, J.M.; Fedorov, O.; et al. SGC-GAK-1: A Chemical Probe for Cyclin G Associated Kinase (GAK). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2830–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Treiber, D.K.; Zuercher, W.J. Utilizing comprehensive and mini-kinome panels to optimize the selectivity of quinoline inhibitors for cyclin G associated kinase (GAK). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 1727–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Naegeli, N.; East, M.P.; Laitinen, T.; Havener, T.M.; Wells, C.I.; Johnson, G.L.; Drewry, D.H.; Zuercher, W.J.; Morris, D.C. Design of a cyclin G associated kinase (GAK)/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor set to interrogate the relationship of EGFR and GAK in chordoma. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 4772–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Fleck, N.; Torrice, C.D.; Crona, D.J.; Grundner, C.; Zuercher, W.J. Anti-tubercular activity of novel 4-anilinoquinolines and 4-anilinoquinazolines. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 18, 2695–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Maffuid, K.A.; Laitinen, T.; Torrice, C.D.; Tizzard, G.J.; Crona, D.J.; Zuercher, W.J. Targeting an EGFR water network using novel 4-anilinoquin(az)olines inhibitors for chordoma. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 1693–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Bennett, J.M.; Su, L.; Laitinen, T.; Elkins, J.M.; Pickett, J.E.; Wells, C.I.; Li, Z.; Willson, T.M.; Zuercher, W.J. Development of SGC-GAK-1 as an orally active in vivo probe for cyclin G associated kinase through cytochrome P450 inhibition. Molecules 2019, 24, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asquith, C.R.M.; Tizzard, G.J. 6-Bromo-N-(2-methyl-2H-benzo[d][1,2,3]triazol-5-yl)quinolin-4-amine. Molbank 2019, 2019, M1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimmer, S.G.; Betz, M.; Heine, A.; Klebe, G. Methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl: Futile but not for water, as the correlation of structure and thermodynamic signature shows in a congeneric series of thermolysin inhibitors. Chem. Med. Chem. 2014, 9, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. ShelXT-Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. Olex2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with ShelXL. Acta Crystallogr. 2015, C27, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.A.; Biggs, W.H.; Treiber, D.K.; Atteridge, C.E.; Azimioara, M.D.; Benedetti, M.G.; Carter, T.A.; Ciceri, P.; Edeen, P.T.; Floyd, M.; et al. A small molecule-kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds 2, 7, 15–17, 20 are available from the authors. |



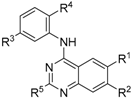 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | TNNi3K (Kd) a (nM) |
| 7 (GSK114) | OMe | OMe | N-SO2NHMe | NMe2 | H | 25 b |
| 15 | OMe | OMe | N-SO2NHMe | NMe2 | Me | 0% Inh. at 1 µM |
| 16 | OMe | H | N-SO2NHMe | NMe2 | H | 90 |
| 17 | H | OMe | N-SO2NHMe | NMe2 | H | 11 |
| 2 | OMe | OMe | N-SO2NHMe | H | H | 120 |
| 20 | OMe | OMe | H | NMe2 | H | 6200 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asquith, C.R.M.; Laitinen, T.; Wells, C.I.; Tizzard, G.J.; Zuercher, W.J. New Insights into 4-Anilinoquinazolines as Inhibitors of Cardiac Troponin I–Interacting Kinase (TNNi3K). Molecules 2020, 25, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071697
Asquith CRM, Laitinen T, Wells CI, Tizzard GJ, Zuercher WJ. New Insights into 4-Anilinoquinazolines as Inhibitors of Cardiac Troponin I–Interacting Kinase (TNNi3K). Molecules. 2020; 25(7):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071697
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsquith, Christopher R. M., Tuomo Laitinen, Carrow I. Wells, Graham J. Tizzard, and William J. Zuercher. 2020. "New Insights into 4-Anilinoquinazolines as Inhibitors of Cardiac Troponin I–Interacting Kinase (TNNi3K)" Molecules 25, no. 7: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071697
APA StyleAsquith, C. R. M., Laitinen, T., Wells, C. I., Tizzard, G. J., & Zuercher, W. J. (2020). New Insights into 4-Anilinoquinazolines as Inhibitors of Cardiac Troponin I–Interacting Kinase (TNNi3K). Molecules, 25(7), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25071697