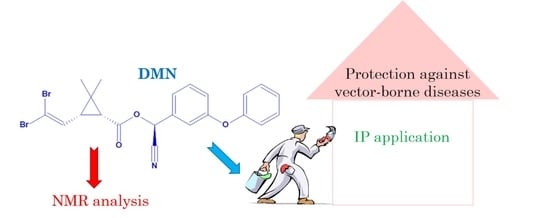
New Insights into the Degradation Path of Deltamethrin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
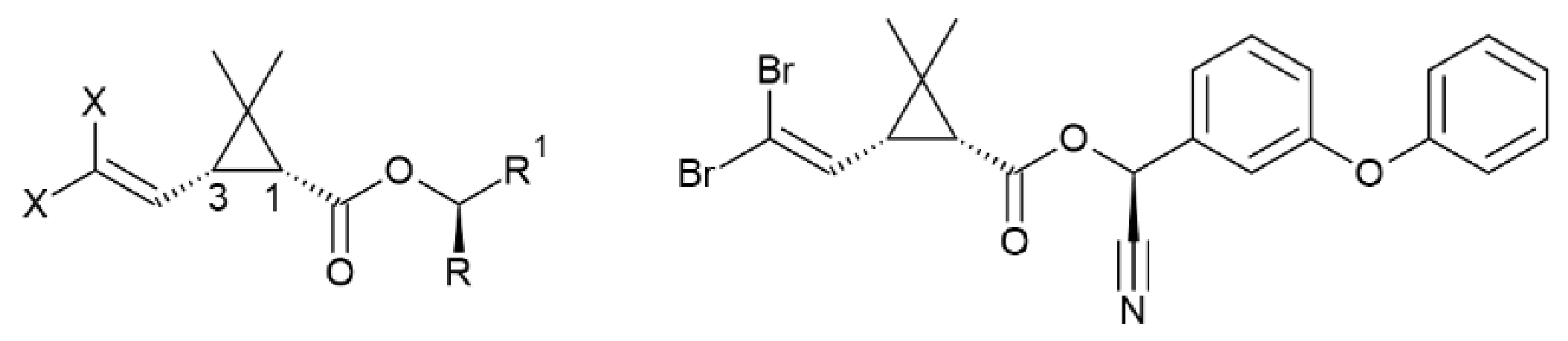
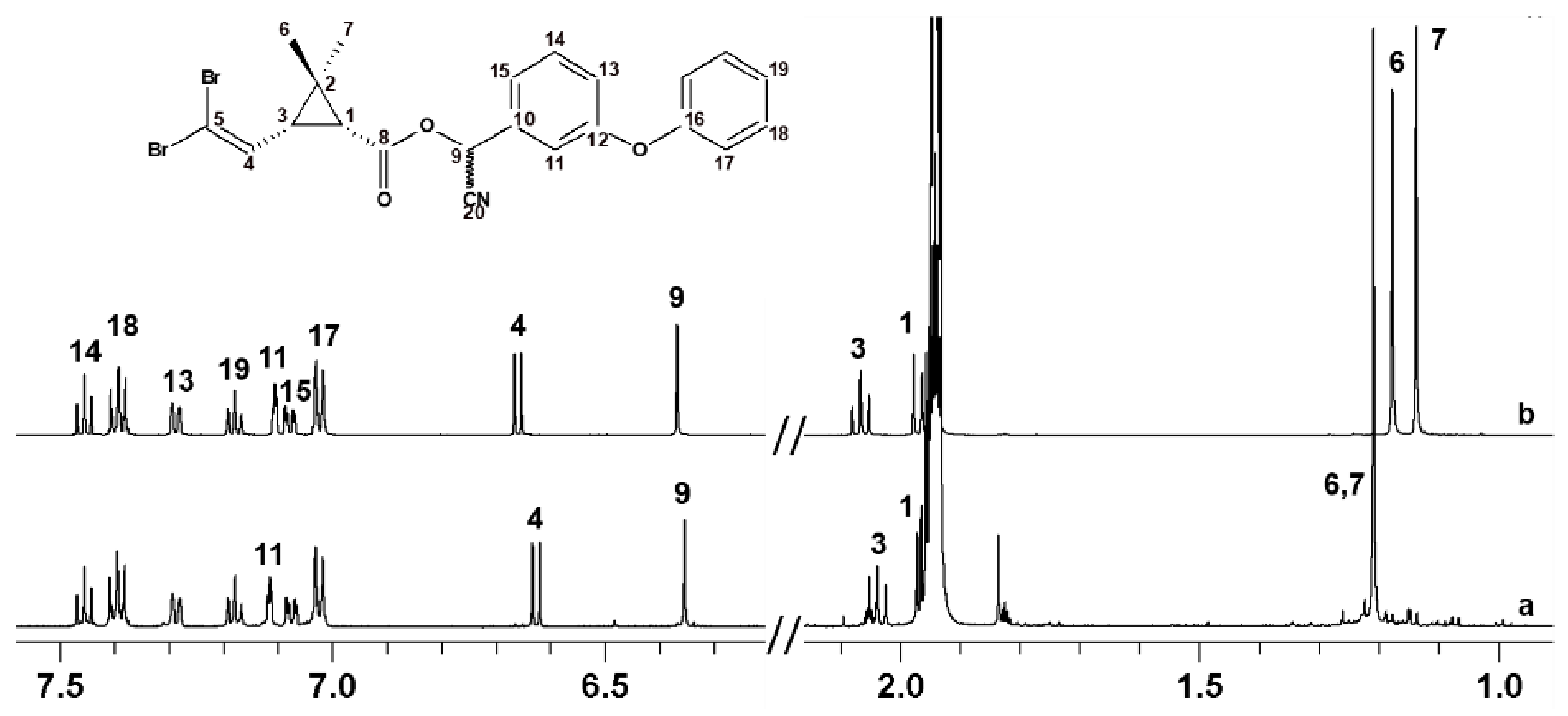
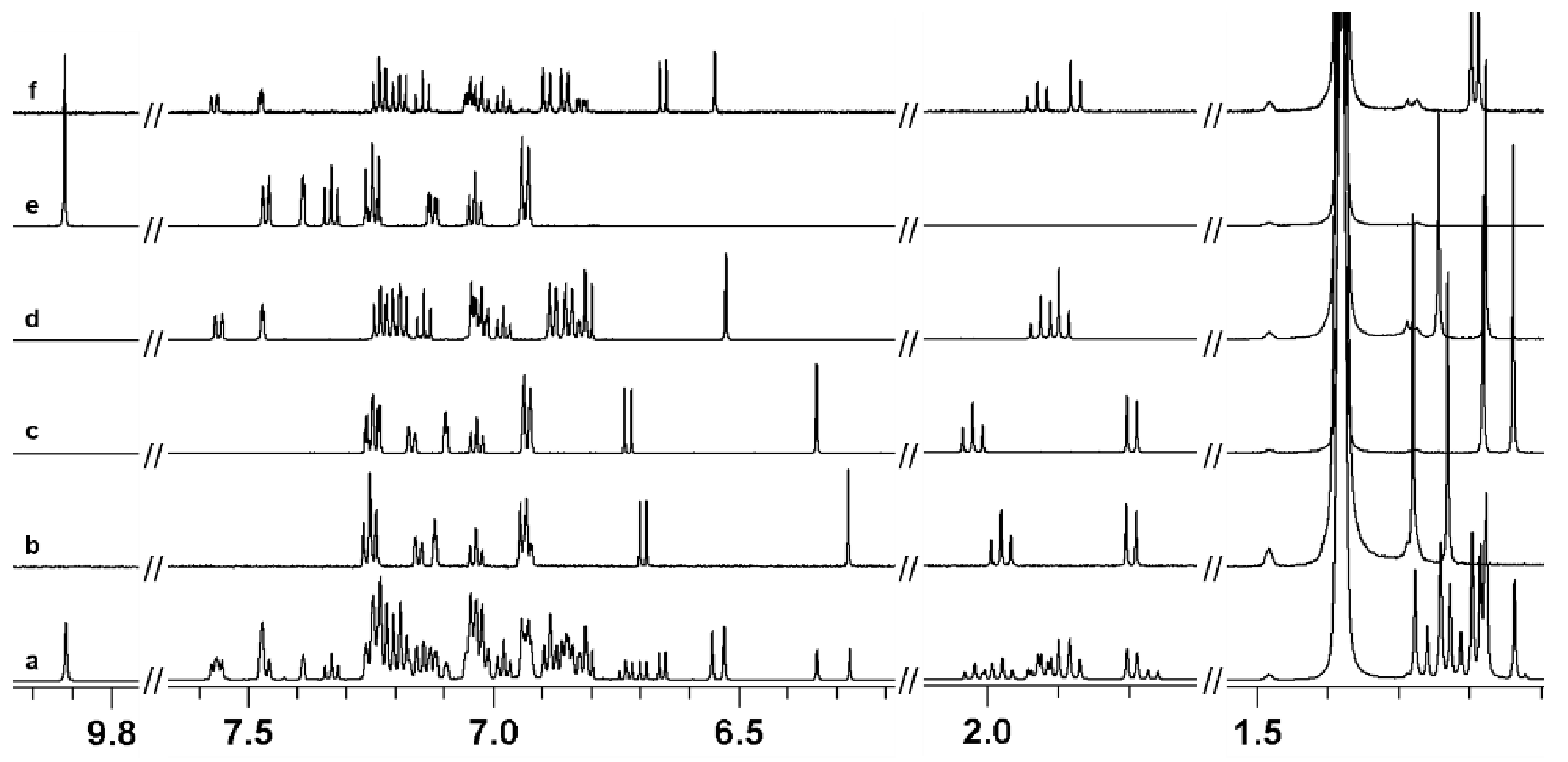
2.1. Analysis of Active and Inactive Deltamethrin
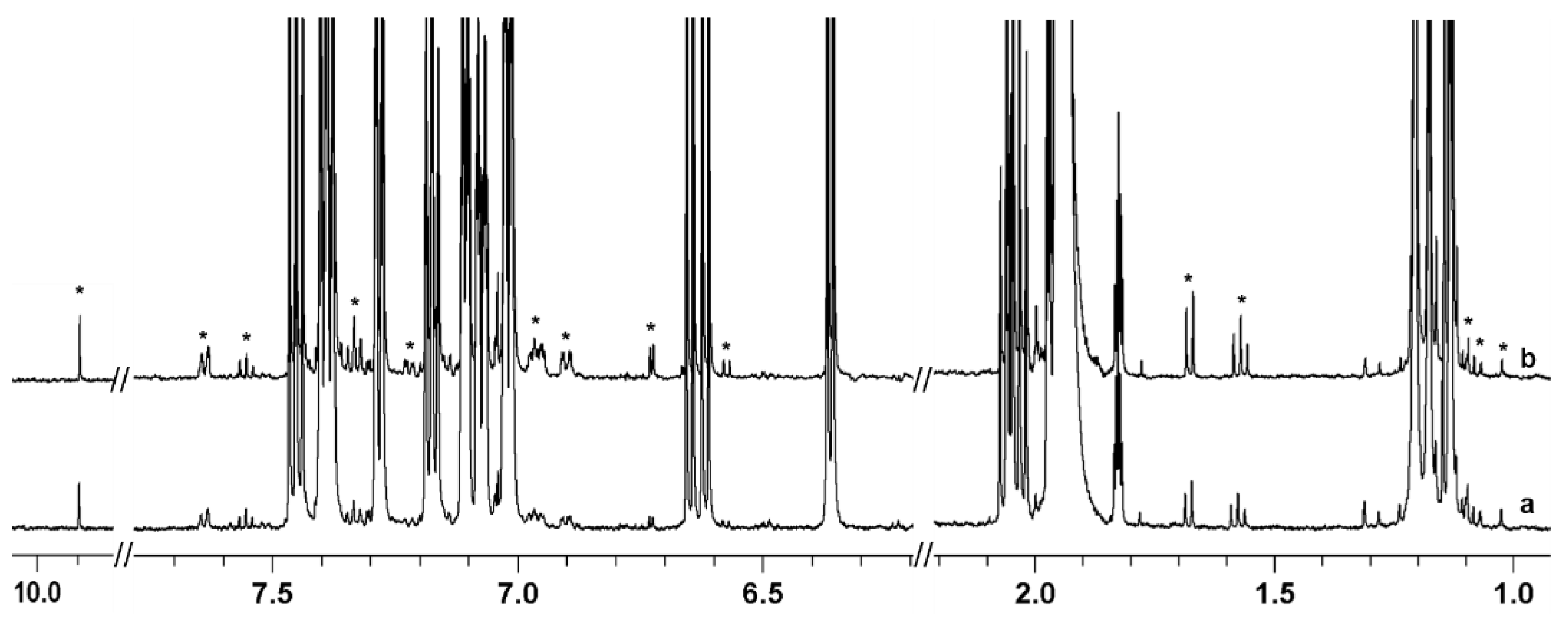
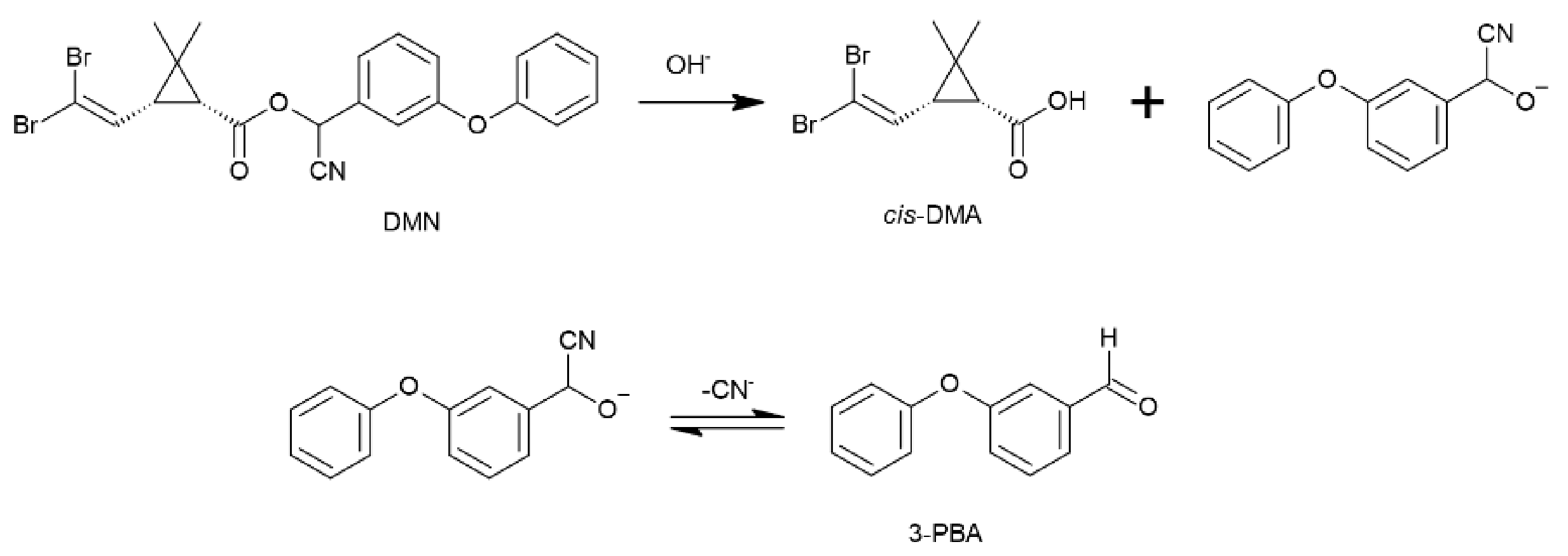
2.2. Stability Studies and Identification of By-Products
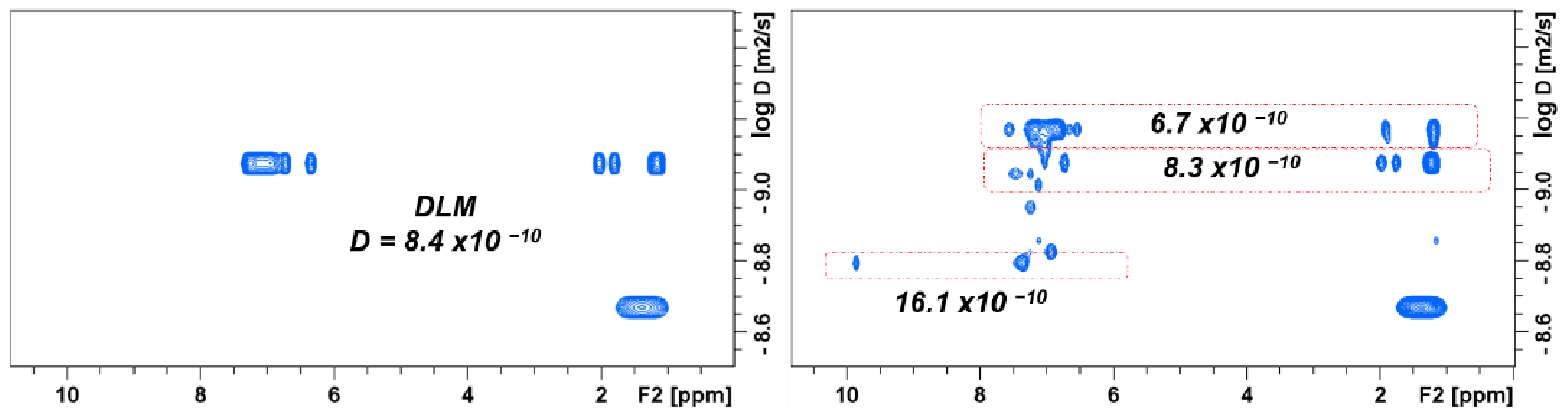
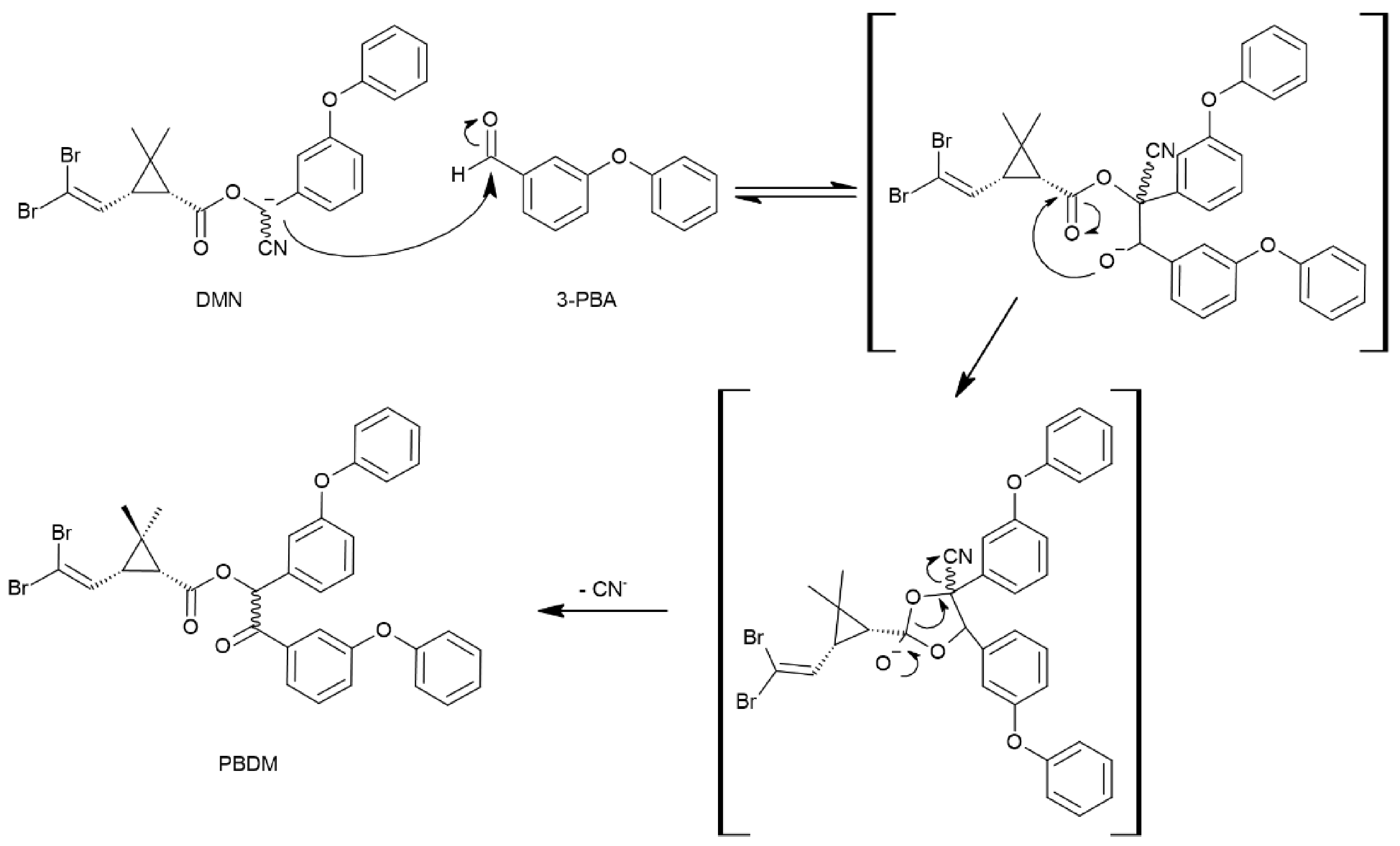
2.3. Identification of Unknown By-Products
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Reagents
3.2. Samples Preparation
3.2.1. Solution A
3.2.2. Solution B
3.3. HPLC Analysis
3.4. MS Analysis
3.5. NMR Analysis
3.6. Characterization of R-PBDM and S-PBDM
3.6.1. R/S-PBDM
3.6.2. S/R-PBDM
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenberg, R.; Lindsey, N.P.; Fischer, M.; Gregory, C.J.; Hinckley, A.F.; Mead, P.S.; Paz-Bailey, G.; Waterman, S.H.; Drexler, N.A.; Kersh, G.J.; et al. Vital Signs: Trends in Reported Vectorborne Disease Cases—United States and Territories, 2004–2016. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherrard-Smith, E.; Griffin, J.T.; Winskill, P.; Corbel, V.; Pennetier, C.; Djenontin, A.; Moore, S.; Richardson, J.H.; Muller, P.; Edi, C.; et al. Systematic review of indoor residual spray efficacy and effectiveness against Plasmodium falciparum in Africa. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, J.C.; Keating, J.; Githure, J.I.; Macdonald, M.B.; Impoinvil, D.E.; Novak, R.J. Integrated vector management for malaria control. Malar. J. 2008, 7, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messenger, L.A.; Rowland, M. Insecticide-treated durable wall lining (ITWL): Future prospects for control of malaria and other vector-borne diseases. Malar. J. 2017, 16, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maloney, K.M.; Ancca-Juarez, J.; Salazar, R.; Borrini-Mayori, K.; Niemierko, M.; Yukich, J.O.; Naquira, C.; Keating, J.A.; Levy, M.Z. Comparison of insecticidal paint and deltamethrin against Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera: Reduviidae) feeding and mortality in simulated natural conditions. J. Vector Ecol. 2013, 38, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, D.K. Pesticidal Paints: An Integral Approach to Colour your Imagination. Biodivers. Int. J. 2018, 2, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schiøler, K.L.; Alifrangis, M.; Kitron, U.; Konradsen, F. Insecticidal Paints: A Realistic Approach to Vector Control? PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.; Mudraboyina, B.; Spence-Elder, C.; Resendes, R.; Cunningham, M.F.; Jessop, P.G. Water-borne coatings that share the mechanism of action of oil-based coatings. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Amo, B.; Romagnoli, R.; Deyá, C.; González, J.A. High performance water-based paints with non-toxic anticorrosive pigments. Prog. Org. Coat. 2002, 45, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.; Lu, J.; McLoughlin, D.; Olsen, J.H. Insecticidal Paints. U.S. Patents 2014/0288026 A1, 25 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. President’s Malaria Initiative FY 2020 Guidance; USAID: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Sibanda, M.M.; Focke, W.W.; Labuschagne, F.J.W.J.; Moyo, L.; Nhlapo, N.S.; Maity, A.; Muiambo, H.; Massinga, P.; Crowther, N.A.S.; Coetzee, M.; et al. Degradation of insecticides used for indoor spraying in malaria control and possible solutions. Malar. J. 2011, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelotti, I.; Catalá, S.S.; Gorla, D.E. Experimental evaluation of insecticidal paints against Triatoma infestans (Hemiptera: Reduviidae), under natural climatic conditions. Parasites Vectors 2009, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M. Properties and applications of pyrethroids. Environ. Health Perspect. 1976, 14, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, H. Pesticide use in rice and rice–fish farms in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Crop. Prot. 2001, 20, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, M. Characteristics of pyrethroids for insect pest control in agriculture. Pestic. Sci. 1989, 27, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouters, W.; van den Bercken, J. Action of pyrethroids. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1978, 9, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawa, A.S.; Mali, G.V.; Deshmukh, H.V. Biodegradation of Deltamethrin by using Indigenous Bacteria Isolated from Contaminated Soil. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycoń, M.; Żmijowska, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Enhancement of deltamethrin degradation by soil bioaugmentation with two different strains of Serratia marcescens. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, H.; Aziz, A.T.; Saggu, S.; Abbas, Z.; Mohan, A.; Ansari, A. Systematic review on pyrethroid toxicity with special reference to deltamethrin. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2014, 2, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Mestres, R.; Mestres, G. Deltamethrin: Uses and Environmental Safety. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: Continuation of Residue Reviews; Ware, G.W., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, R.J.; Carey, J.H.; Hart, J.H.; Tkacz, R.J.; Lee, H.B. Persistence and fate of deltamethrin sprayed on a pond. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1989, 37, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perschke, H.; Hussain, M. Chemical isomerization of deltamethrin in alcohols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.R.; Ahmed, D.; Farooq, A.; Rasheed, S.; Mansoor, M. Photodegradation of bifenthrin and deltamethrin-effect of copper amendment and solvent system. Env. Monit Assess. 2017, 189, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahri-Niknafs, B.; Ahmadi, A. Photodegradation of Deltamethrin and Fenvalerate under Simulated Solar Light Irradiation and Identification of Photoproducts. Rev. Chim. 2013, 64, 828–831. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, M. The pyrethroids: Early discovery, recent advances and the future. Pestic. Sci. 1989, 27, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, H. Pyrethroid Chemistry and Metabolism; Elsevier Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1635–1663. [Google Scholar]
- Maguire, R.J. Aquatic Environmental Fate of Deltamethrin. Water Sci. Technol. 1992, 25, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, R.J. Chemical and photochemical isomerization of deltamethrin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990, 38, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzo, L.O.; Casida, J.E. Degradation of decamethrin on cotton plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1979, 27, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Z.; Khan, S.U.; Akhtar, M.H.; Ivarson, K.C. Persistence, degradation, and distribution of deltamethrin in an organic soil under laboratory conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1984, 32, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, M.K.; MacMillan, D.K.; Zehr, D.; Sobus, J.R. Pyrethroid insecticides and their environmental degradates in repeated duplicate-diet solid food samples of 50 adults. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.N.; Nivsarkar, M.; Saxena, C.; Kaushik, M.P. Effects of the process of the incorporation of deltamethrin on slow release property of insecticidal paint. Pigment. Resin Technol. 2004, 33, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.L.; Ahmad, N.W.; Ghani, A.A. Paint Composition. U.S. Patent 6,881,248 B2, 19 April 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Phyo, P.; Zhao, X.; Templeton, A.C.; Xu, W.; Cheung, J.K.; Su, Y. Understanding Molecular Mechanism of Biologics Drug Delivery and Stability from NMR Spectroscopy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 174, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.-J.; Park, K.; Kim, W.-J.; Rhee, J.-K.; Son, W.S. Spectroscopic methods to analyze drug metabolites. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2018, 41, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Guo, Y. Insecticidal paint containing deltamethrin and manufacture method. Chinese Patent Office 2014/104194510, 10 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, M.A.; Marei, A.E.-S.M.; Casida, J.E. alpha-Cyano-3-phenoxybenzyl pyrethroids: Derivatizations at the benzylic position. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1980, 28, 592–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.S.; Vázquez, P.P.; Frenich, A.G.; Vidal, J.L.M.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Chiral Separation of Several Pyrethroids on Polysaccharide-Based Chiral Stationary Phases Under Normal and Reversed Phase Modes. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2004, 27, 1507–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|
| 2-OH deltamethrin | 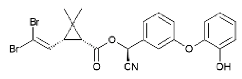 |
| 4-OH deltamethrin | 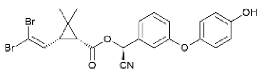 |
| α-hydroxy-3-phenoxy-benzeneacetonitrile | 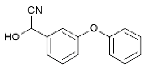 |
| 3-phenoxybenzaldehyde |  |
| 2-hydroxy-4-methoxy benzophenone |  |
| 3-phenoxybenzoic acid | 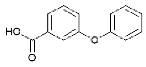 |
| cis-decamethrinic acid | 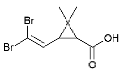 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aiello, F.; Simons, M.G.; van Velde, J.W.; Dani, P. New Insights into the Degradation Path of Deltamethrin. Molecules 2021, 26, 3811. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133811
Aiello F, Simons MG, van Velde JW, Dani P. New Insights into the Degradation Path of Deltamethrin. Molecules. 2021; 26(13):3811. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133811
Chicago/Turabian StyleAiello, Federica, Marcel G. Simons, Jan W. van Velde, and Paulo Dani. 2021. "New Insights into the Degradation Path of Deltamethrin" Molecules 26, no. 13: 3811. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133811
APA StyleAiello, F., Simons, M. G., van Velde, J. W., & Dani, P. (2021). New Insights into the Degradation Path of Deltamethrin. Molecules, 26(13), 3811. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26133811