Abstract
Silica nanoparticles (SiO2 NPs) synthesized by the Stober method were used as drug delivery vehicles. Doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX·HCl) is a chemo-drug absorbed onto the SiO2 NPs surfaces. The DOX·HCl loading onto and release from the SiO2 NPs was monitored via UV-VIS and fluorescence spectra. Alternatively, the zeta potential was also used to monitor and evaluate the DOX·HCl loading process. The results showed that nearly 98% of DOX·HCl was effectively loaded onto the SiO2 NPs’ surfaces by electrostatic interaction. The pH-dependence of the process wherein DOX·HCl release out of DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs was investigated as well. For comparison, both the free DOX·HCl molecules and DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs were used as the labels for cultured cancer cells. Confocal laser scanning microscopy images showed that the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs were better delivered to cancer cells which are more acidic than healthy cells. We propose that engineered DOX·HCl-SiO2 systems are good candidates for drug delivery and clinical applications.
1. Introduction
Doxorubicin (DOX) is an anthracycline antibiotic and is one of the most chemotherapeutic antitumor drugs to treat different solid malignant tumors. DOX consists of a planar anthraquinone nucleus attached to an amino sugar through a glycosidic bond [1]. In order to increase aqueous solubility, the amino group of sugar is protonated by forming DOX hydrochloride (DOX·HCl). The flat anthraquinone part of the molecule is highly lipophilic, while the sugar part is hydrophilic. The DOX·HCl molecule contains various functional groups such as phenolic ring, acid, and base functional groups in the amino sugar. These make the DOX·HCl molecule both amphiphilic and amphoteric [1]. Moreover, DOX·HCl is biocompatible. It interacts with DNA by intercalation to inhibit biomacromolecule synthesis. DOX·HCl is an exciting drug delivery research tool in view of its inherent fluorescence associated with the central anthracycline chromophore group. In recent years, DOX·HCl has been widely used to study cancer therapy employing fluorescence properties to visualize the results. However, free DOX·HCl causes severe side effects such as myelosuppression and cardiotoxicity when treating cancer via chemotherapy [2].
Nanotechnology is a promising alternative to overcome these limitations in cancer therapy as it has been shown to reduce the systemic side effects and increase the therapeutic efficacy of drugs [3]. Numerous nanoparticle drug delivery systems, where the chemo-drugs were incorporated inside, have been developed in the last few years. Many types of nanomedicines are currently being investigated in the clinic for cancer treatment, namely proteins drug conjugates, lipid-based, natural or unnatural polymer-based nanocarriers [3,4,5,6,7], viral nanoparticles, and inorganic nanoparticles [8]. SiO2 NPs—the most popular NPs—are intensively investigated for biomedical applications. Their potential applications for drug delivery have been investigated and developed at incredible rates [6,8,9,10,11]. SiO2 NPs constituents are mainly the siloxane groups that can be broken down via hydrolysis to the orthosilicic acid in the human body after the drug delivery process. These products are biocompatible and are excreted well by the urinary system [11,12].
The main advantages of silica nanostructures in biological applications are that they can serve as protection layers or drug delivery vehicles, given that silica in biological media is highly stable. The silica shells possessing no cytotoxicity and outstanding biocompatibility improve the stability of the protected substances in the cores significantly.
Due to the silanols groups (Si-OH) on the pores and surfaces of SiO2 NPs, which confer a very negative zeta potential, the positively charged drugs can be absorbed onto SiO2 NPs pores and surfaces easily by the strong electrostatic interaction [13]. More importantly, knowing this mechanism, one can control the drug-releasing process at the targets [14]. Finally, it is worth mentioning that silica shells can alter the optical properties of the contained dye molecules—in our case, is DOX·HCl.
There are two main types of SiO2 NPs: nonporous and mesoporous silica, which can be obtained from the hydrolysis and condensation of silane alkoxide precursors. The large pore of mesoporous silica nanoparticles can shelter large biomolecules such as proteins and DNA, protecting them from rapid biodegradation. Therefore, many works have focused on drug load onto the mesoporous silica nanoparticles [6,7,9,10,15], which were traditionally created by micelle methods using cationic or anionic template agents. However, these synthesis methods require the use of either surfactant agents or/and toxic solvents, which require great care before applying. Moreover, the nonporous SiO2 NPs can be easily synthesized in non-toxic media, nonsurfactant agents with a precise size-control in the range of 10 to 2000 nm from TEOS by the Stober method [16,17,18]. Furthermore, the encapsulation and conjugation of drugs inside these particles have been reported in [19], where authors realized covalent binding between the drugs and the organic functional silane alkoxide precursors during the SiO2 NPs formation, imposing the drug inside the silica matrix via the formation of bonds between the drug and silane coupling reagent. However, to the best of our knowledge, the adsorption of the drugs onto SiO2 NPs’ surfaces via non-covalent binding after SiO2 NPs have been formed, and its uses for drug delivery vehicles as a controllable drug adsorption/release mechanism has not been reported.
In this work, the optical properties of the free DOX·HCl molecule and of the DOX·HCl adsorbed SiO2 NPs after NPs formation were investigated. The drug loading efficiency was monitored using absorption spectra and zeta potentials. The results showed that nearly 98% of DOX was effectively loaded onto the SiO2 NPs surface by electrostatic interaction. The DOX release from these NPs, depending on the pH of the solution, was simultaneously measured by fluorescence spectra. The free DOX·HCl molecule and DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs were used to label cultured cancer cells. Confocal laser scanning microscopy (LCSM) images showed that the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs were efficiently delivered to cancer cells. These results show that the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs system is an effective method of drug delivery and has great potential for clinical applications.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS, 98%) and ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH, 28–30% in water), penicillin/streptomycin (P/S), and FBS were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Ethanol, hydrochloric acid (HCl, 36.5%), trisodium citrate dehydrate (Na3C6H5O7.2H2O, 99%), potassium carbonate (K2CO3, 99%), and tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (C4H11NO3 99%) were purchased from Merck (Kenilworth, NJ, USA). Doxorubicin hydrochloride solution (2 mg/mL) was obtained from Ebewe Pharma (Unterach am Attersee, Austria). The DMEM medium was purchased from HIMEDIA (Mumbai, India). Deionized water was used in all experiments.
2.2. Cell Culture and Cellular Uptake Assay
The MCF7 breast cancer cell line was maintained in DMEM medium supplemented with 1% penicillin/streptomycin (P/S) and 10% FBS. The cells were incubated at 37 °C under 5% CO2 atmosphere. After thawing, the cells were cultured and passaged 2 or 3 times before performed the cellular uptake assay. For treatment with NPs, cells were counted and aliquoted at a concentration of 5000 cells/mL and 1 mL/well in a 12-well-plate. The plate was incubated overnight for cell attachment. The nucleus of MCF7 cells was stained with the DAPI molecules. Then the cells were treated with 4 µM of DOX·HCl, DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs, and the samples were observed after staining 2 and 6 h using confocal laser scanning microscopy.
2.3. Silica Nanoparticles Preparation
2.3.1. Synthesis of SiO2 NPs
SiO2 NPs with the sizes of 90–100 nm were prepared by an effortless method. Briefly, 2.0 mL of NH4OH were added into 30 mL of ethanol and thoroughly mixed by magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 30 min. After that, 300 µL of TEOS was dropped into the reaction mixture and kept for one day under vigorous stirring. The obtained particles were then washed three times via centrifugation with DI water and redispersed in DI water before DOX·HCl loading.
2.3.2. Doxorubicin Loading onto the SiO2 NPs Surface
In order to determine the maximum loading capacity of DOX·HCl onto SiO2 NPs’ surfaces, different volumes of DOX·HCl solution (2 mg/mL) varying from 0 to 60 µL was added into 1 mL of SiO2 NPs suspension. These mixtures were incubated and shaken gently for 3 h to allow DOX·HCl to get absorbed onto the SiO2 NPs surfaces. The free DOX·HCl molecules and DOX·HCl absorbed on the SiO2 NPs (DOX·HCl-SiO2) were separated using centrifugation. The supernatant was removed from the pellet with a pipette. After that, the pellet was washed twice again and redispersed in DI water. The stock solution of DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs in aqueous was kept in the dark and at low temperature (about 4–8 °C) for future use. The concentration of the residual DOX·HCl in the supernatant was determined by measuring the absorbance. The following equation is used to calculate the DOX·HCl absorption efficiency (EF).
where is the initial DOX·HCl amount used to load on the SiO2 NPs and is the residual DOX·HCl amount in the supernatant.
2.3.3. pH-Dependence of Doxorubicin Release from SiO2 NPs
The following experiment was conducted to determine the rate at which DOX·HCl molecules go off the SiO2 NPs’ surface and how the pH affects this rate. The equal amounts of stored DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs solution were diluted 20 folds in the different pH buffers from 3.0 to 8.0 at an optical density below 0.1. The DOX·HCl content loaded on SiO2 NPs is about 1.5 µg·mL−1. The released DOX·HCl concentration in the supernatant solution was determined by fluorescence spectra. The concentration of the released DOX·HCl was estimated when compare the measured fluorescent spectra with that of the known concentration of free DOX·HCl in an aqueous solution.
2.4. Characterization
The absorption spectra were recorded on a Shimadzu UV-2600 spectrophotometer. The fluorescent spectra were measured on Cary Eclipse fluorescence spectrophotometer. The size, shape, and morphology of SiO2 NPs and DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs were observed through TEM Model Jem JEOL 1010 microscope. The zeta potential values were determined by the dynamic light scattering (DLS) technique (Nano ZS. Malvern). Nikon Laser Scan Microscope TE was used to acquire confocal photoluminescence images. The 488 nm, 2.5 mW laser beam was used to excite the fluorescence of the DOX·HCl. The wavelength of the laser is close to the maximum value of the excitation spectrum of DOX·HCl.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Characterizations of DOX·HCl Molecule
3.1.1. Optical Properties of Free DOX·HCl in Aqueous Solution
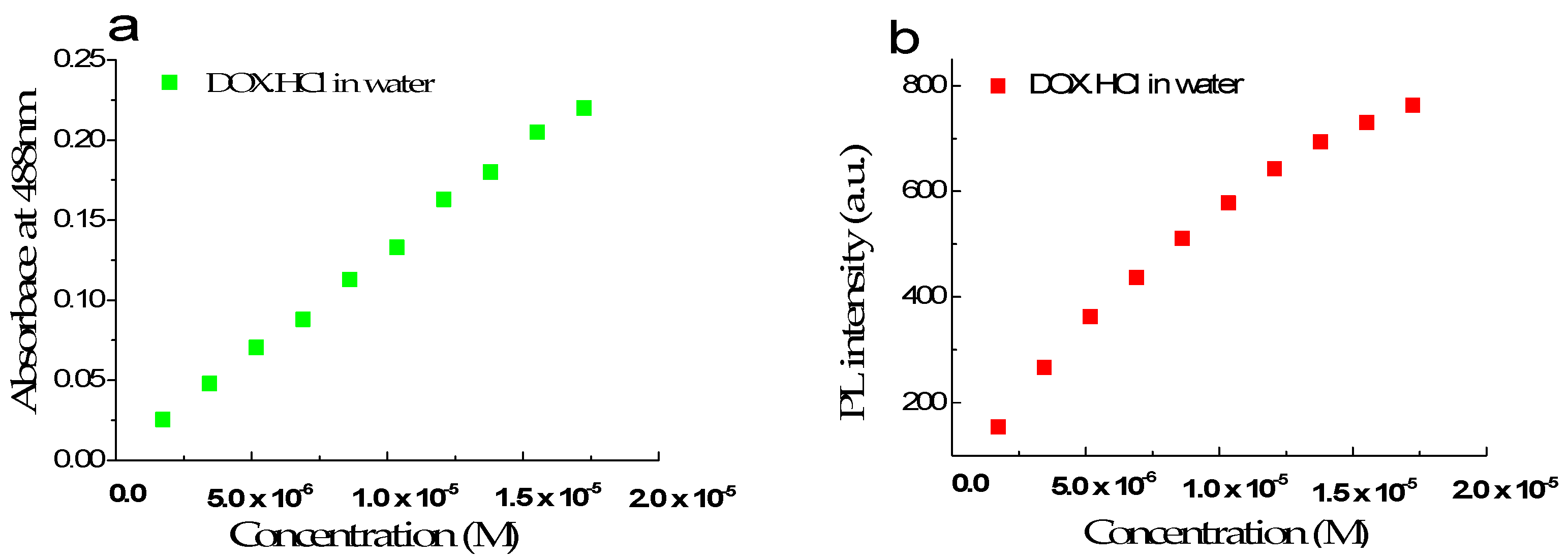
The maximum absorption and fluorescence spectra of free DOX·HCl in an aqueous solution as a function of concentration in the range of 1.72 × 10−6 M to 1.72 × 10−5 M or 1 µg/mL to 10 µg/mL were presented in Figure 1a,b, respectively. This result showed that in this concentration range, the absorbance increases linearly with DOX·HCl’s concentrations. The molar absorption coefficient of DOX·HCl in water at 480 nm is estimated to be 13,500 ± 100 L mol−1 cm−1. Figure 1b shows that the fluorescence intensity at 595 nm is nearly linear when the DOX·HCl ‘s concentrations are lower than 1 × 10−5 M or equivalent to 5 µg/mL.
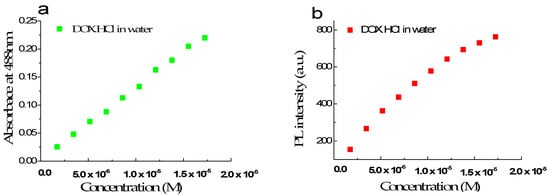
Figure 1.
Absorption and fluorescence intensity spectra of free DOX in aqueous solution at 480 nm (a) and 595 nm (b) with the concentration in the range of 1.72 × 10−6 M to 1.72 × 10−5 M.
Quantum yield (Q.Y.) of free DOX·HCl in aqueous solutions was determined from the data presented in Figure 2 for both absorption and fluorescence measurements. At this concentration range, the OD varies from 0.01 to 0.15. Solution of R6G dye in ethanol was used as the reference sample. From the known value Q.Y. of 94% of the R6G, Q.Y. of free DOX was calculated using the following equation.
where is the Q.Y. of R6G molecule in ethanol, are the refractive indexes of the ethanol and water corresponding. The and terms are the absorption of the sample and reference at the excitation wavelength (488 nm). and are the corrected fluorescence spectra of the sample and reference, respectively. The integrals represent the area under the fluorescence spectra. The determined Q.Y. of free DOX·HCl in aqueous solution is 4.5% which agrees well with Shah’s report [20].
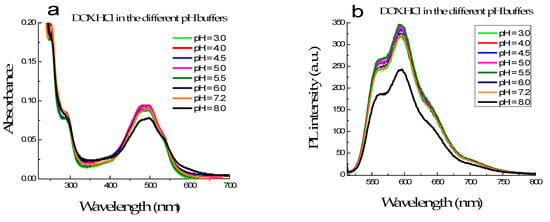
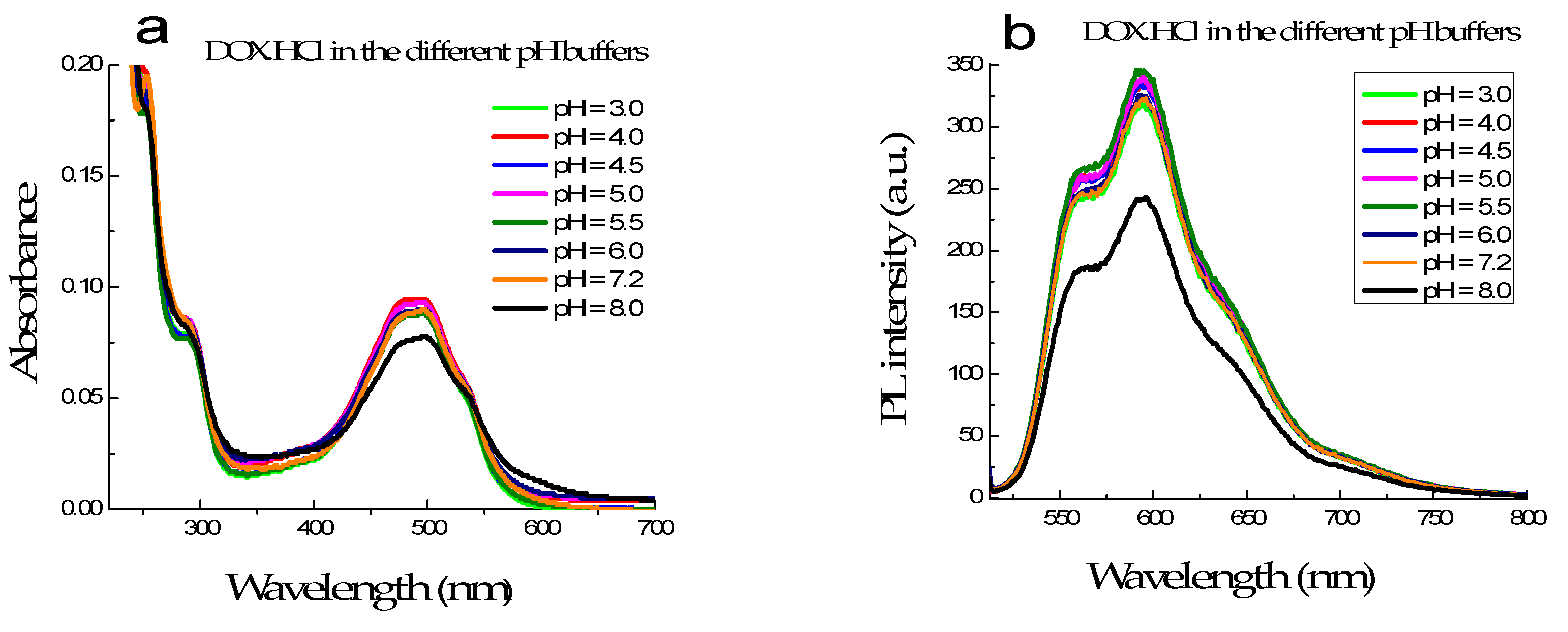
Figure 2.
The absorption (a) and fluorescence (b) spectra of DOX·HCl in varying pH buffer solution from 3.0 to 8.0.
3.1.2. Characterization of DOX·HCl in Different pH Media
The absorption and fluorescence spectra of the DOX·HCl in different buffer solutions with pH varying from 3.0 to 8.0, but the concentration of DOX·HCl was kept constant at 6.8 µM, showed that their intensity and spectral shape have no significant changes when the pH value of buffer solution below 7.2. However, at pH is 8.0 or higher, their absorbances strongly decreased, and the absorption band broadens (Figure 2a). At the same time, Figure 2b shows that their fluorescence intensities are strongly quenched when pH is higher than 8.0. DOX·HCl was found extremely unstable to alkaline hydrolysis, even at room [21]. This explains the substantial decrease of absorbance and intensities of fluorescence spectra of the DOX·HCl when pH is higher than 8.0.
3.2. DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs Characterizations
3.2.1. Zeta Potential of DOX·HCl Loading on the SiO2 NPs
Table 1 shows zeta potential values of the SiO2 NPs loaded with different amounts of DOX·HCl. The zeta potential value of SiO2 NPs in an aqueous solution is highly negatively charged −50 mV while zeta potential of free DOX·HCl is only −27.4 mV. The zeta potential of non loaded SiO2·NPs was −50 mV, whereas the zeta potential of SiO2 NPs increases with the amount of the DOX·HCl loaded on their surfaces (shown in Table 1). This potential reaches the value of the free DOX·HCL when DOX·HCl molecules fully cover the SiO2 NPs surfaces with 120 µg/mL. Based on the measured zeta potential results, we can determine the DOX·HCl loading capacity of the SiO2 NPs in an aqueous solution.

Table 1.
Zeta potential values of bare SiO2 NPs and different quantity DOX·HCl absorbed on SiO2 NPs in an aqueous solution.
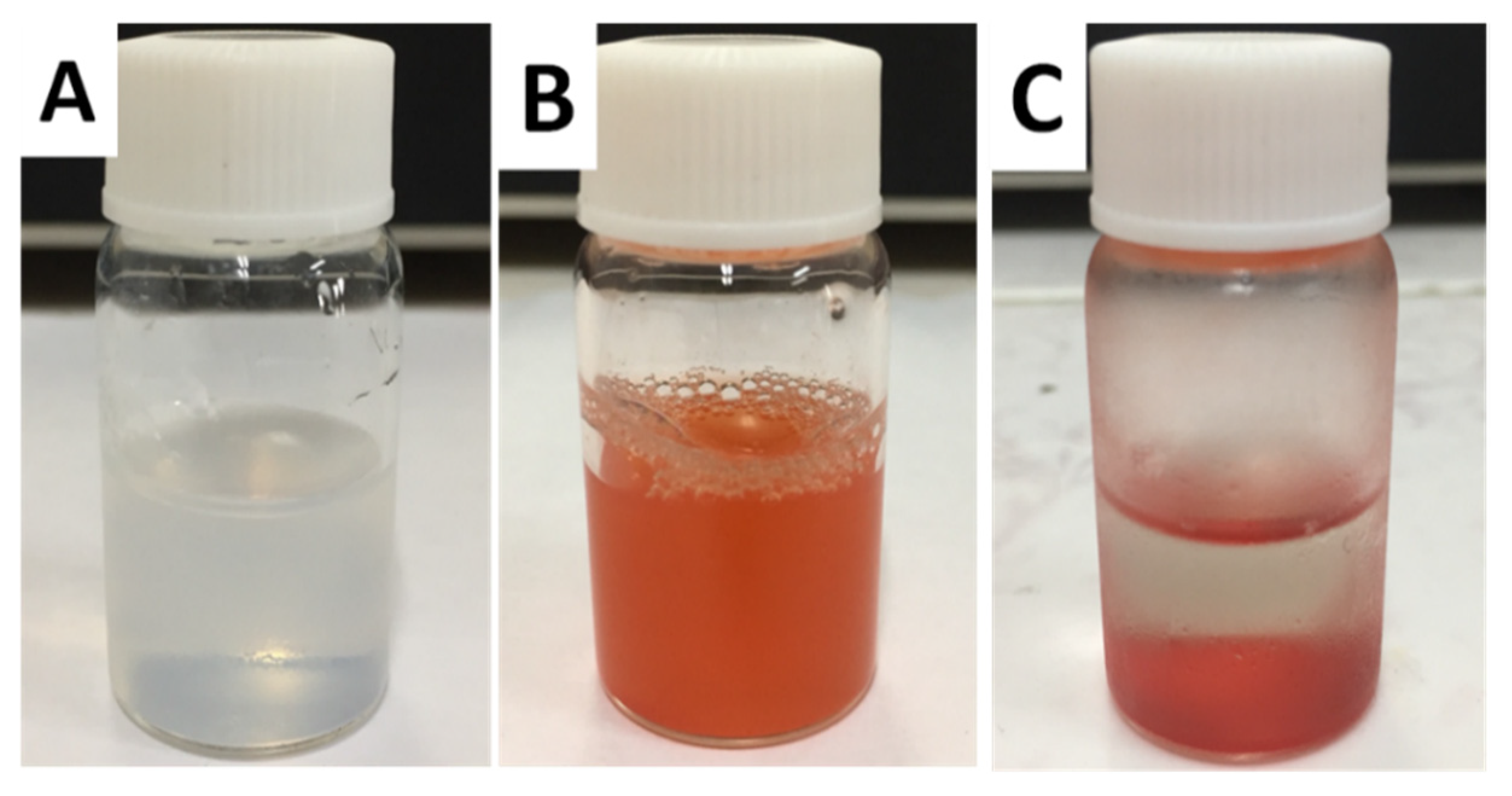
Figure 3A is the bottle containing SiO2 NPs suspension before DOX·HCl loading; the SiO2 NPs are well dispersed in water. In comparison, Figure 3B,C show the freshly prepared and stay-for-some-time DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs suspensions, respectively. All the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs subside and lay at the bottom of the bottle, making the top solution nearly transparent. These images obviously indicate that DOX·HCl molecules are totally loaded onto the SiO2 NPs’surfaces, and no free DOX·HCl molecules are left in the solution. The results presented in Table 1 indicate that the zeta potentials of the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs are below −30 mV. Usually, DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs whose zeta potential is less than −30 mV are considered stable. However, The DOX·HCl-SiO2-120 NPs are not stable, even though they are dispersed in the medium. The instability of the DOX·HCl-SiO2-NPs-120 system in DI water can be treated with bovine serum albumin protein coating the DOX·HCl-SiO2-NPs to form the fort steric stabilization [22,23,24].
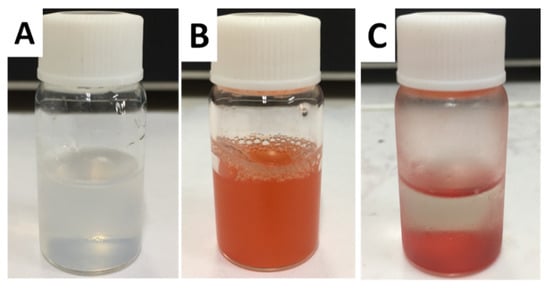
Figure 3.
The SiO2 NPs solutions before (A); freshly prepared and stay-for-some-time DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs (B,C).
3.2.2. Morphology of SiO2 NPs and DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs
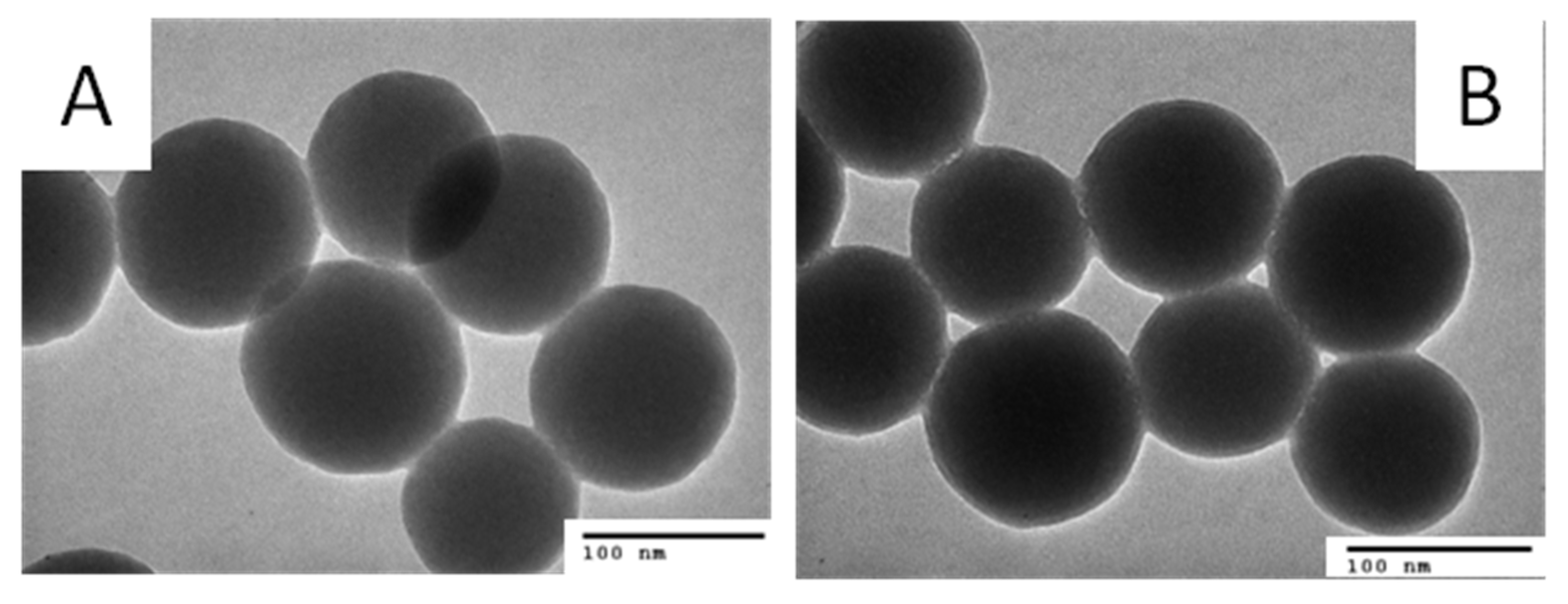
Figure 4A,B show the TEM images of the bare SiO2 NPs and DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs. The bare SiO2 NPs have a spherical shape with an average diameter 90 ± 5 nm. The diameters of the SiO2 NPs stay nearly the same after DOX·HCl loading. The TEM images of the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs are darker than the ones of the bare SiO2 NPs. This higher contrast is due to the absorbed DOX·HCl molecules onto the surfaces of the SiO2 NPs. This result is in good agreement with Min Zhang, and Li Jiang’s work reported in 2016 when they load DOX·HCl onto the mesoporous SiO2 NPs [4].
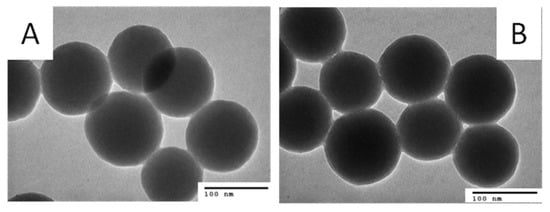
Figure 4.
TEM images of SiO2·NPs at scale bare of 100 nm before (A) and after (B) absorbed DOX·HCl molecules.
3.2.3. Optical Properties of DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs
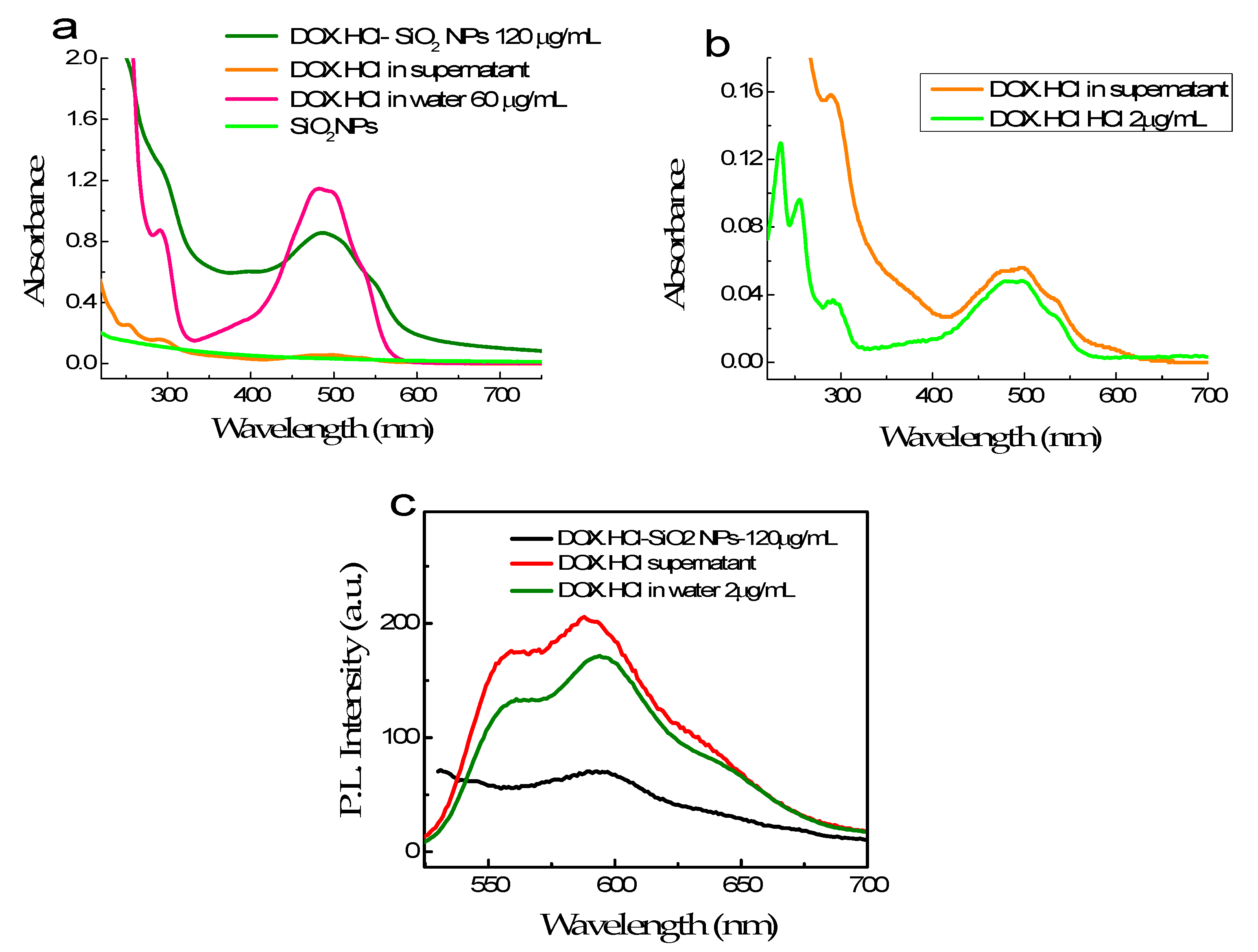
The loading capacity of SiO2 NPs is evaluated by measuring DOX·HCl concentration in solution before and after loading into SiO2 NPs using absorbance measured at 480 nm. Figure 5a,b shows the absorption spectra of DOX·HCl bond on the SiO2 NPs and excessive DOX·HCl in the supernatant compared to those of free DOX·HCl in an aqueous solution. The absorption band of the DOX·HCl bond on SiO2 NPs is broader than those of free DOX·HCl in an aqueous solution (Figure 5). Moreover, the molar absorption coefficient at 480 nm of DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs decrease three folds. The silanol group on the SiO2 NPs attracts the daunosamine head of the DOX·HCl molecule via electrostatic force. Therefore, DOX·HCl molecules can anchor onto the surface of the SiO2 NPs, making the flat anthraquinone head sticks outwards from the NPs’ surface. This alignment of the DOX·HCl molecules make the absorption cross-section of the DOX·HCl molecules changed.
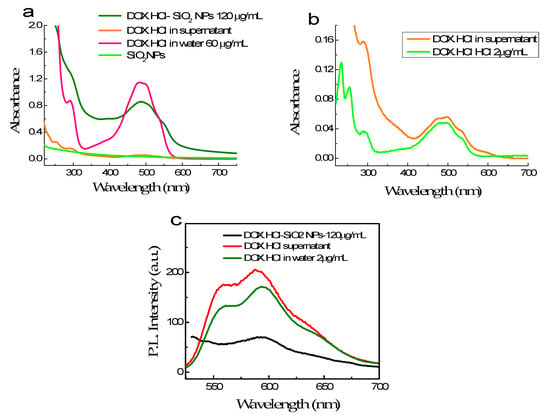
Figure 5.
The absorption spectra of SiO2 NPs, 120 µg/mL DOX·HCl absorbing on SiO2 NPs and residual DOX·HCl content in supernatant compared with those of free DOX·HCl at 60 µg/mL, and the residual DOX·HCl in the supernatant (a); the absorption of DOX·HCl in supernatant compared with those of free DOX·HCl at 2 µg/mL in aqueous solution (b); and the fluorescence spectra of three above solutions (c).
Figure 5b compares the spectra of DOX·HCl in the supernatant and free DOX·HCl at a 2 µg/mL concentration. Their absorbances at 488 nm are roughly the same. Based on this, we can estimate that the DOX·HCl concentration in the supernatant is close to 2 µg/mL and hence quantify the amount of DOX·HCl absorbed on the SiO2 NPs. The loading efficiency of DOX·HCl molecules into SiO2·NPs can reach up to 98%. For the 90 ± 5 nm NPs, the estimated loading content is 30 µg of DOX·HCl per mg of SiO2 NPs. Reducing the sizes of the NPs, makes the surface area/volume increase. As a consequence, the DOX·HCl storage of SiO2 NPs becomes bigger.
Figure 5c presents the fluorescence spectra of 120 µg DOX·HCl binding with 1 mL SiO2 NPs suspension, excess DOX·HCl content in the supernatant and DOX·HCl in water at 2 µg/mL. It is clear that the fluorescence of DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs is weak, while those of the supernatant and 2 µg/mL DOX·HCl solution in water are comparable. Especially, this result demonstrates that free DOX·HCl molecules fluoresce much better than DOX·HCl bound to SiO2 NPs.
3.2.4. pH-Dependence of DOX·HCl Release from DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs
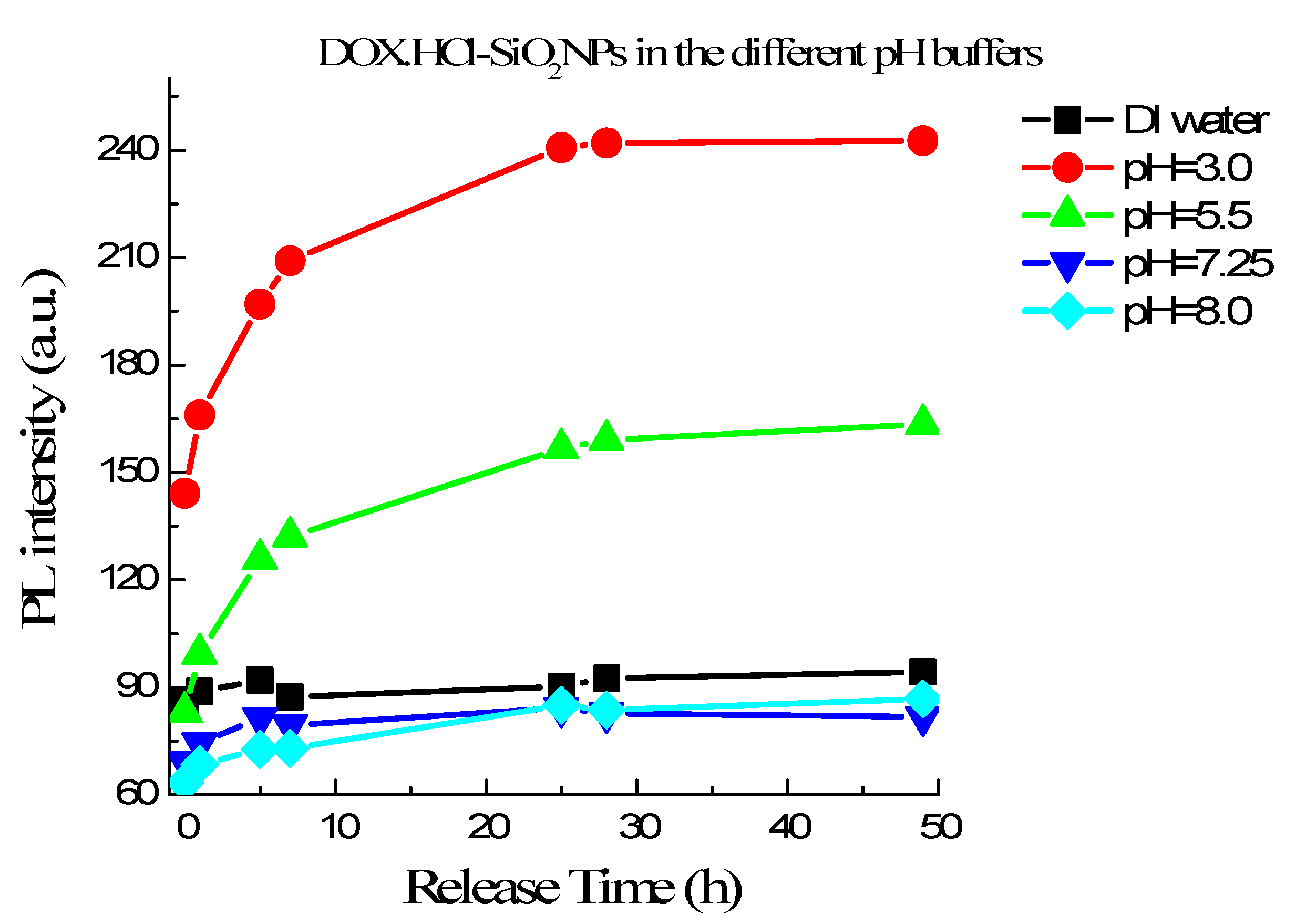
As mentioned above, DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs do not fluoresce well while free DOX·HCl molecules in an aqueous solution fluoresce with a Q.Y. of 4.5%. Therefore, we can observe the DOX·HCl release via fluorescent measurement. Figure 6 shows the fluorescence intensities of DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs in different buffer solutions as a function of time. These curves show the efficiencies of DOX·HCl release from DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs in the different buffers having pH range from 3.0 to 8.0. This result reveals that in the water or the buffer with pH higher than 7.25 the DOX·HCl gets off DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs very slowly. We recall that the pH values of the blood and physiologic media are around 7.25–7.50. In the first 5 h, the release rate increase with decreasing pH. The curves go flat after 24 h, hinting that there is almost no release afterward (shown in Figure 6). In comparison, the accumulative content of DOX·HCl release attains 90% at pH = 3.0 and 50% at pH = 5. These pH values are similar to the extracellular pH of tumors and in the liposome of cellular [5]. This pH dependence is very interesting. It allows us to realize the drug delivery schema so that DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs are stable in the blood and follow the circulation system to reach the targeted tumors. At the tumor tissues, DOX·HCl molecules release from the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs and attack them.
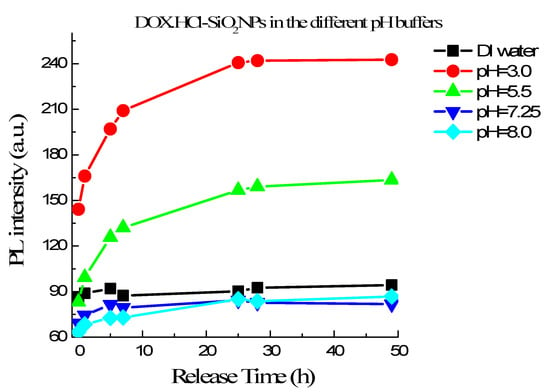
Figure 6.
DOX·HCl release profiles from DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs in the different pH buffers varying from 3.0 to 8.0 in time.
3.2.5. Intracellular Uptake of DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs
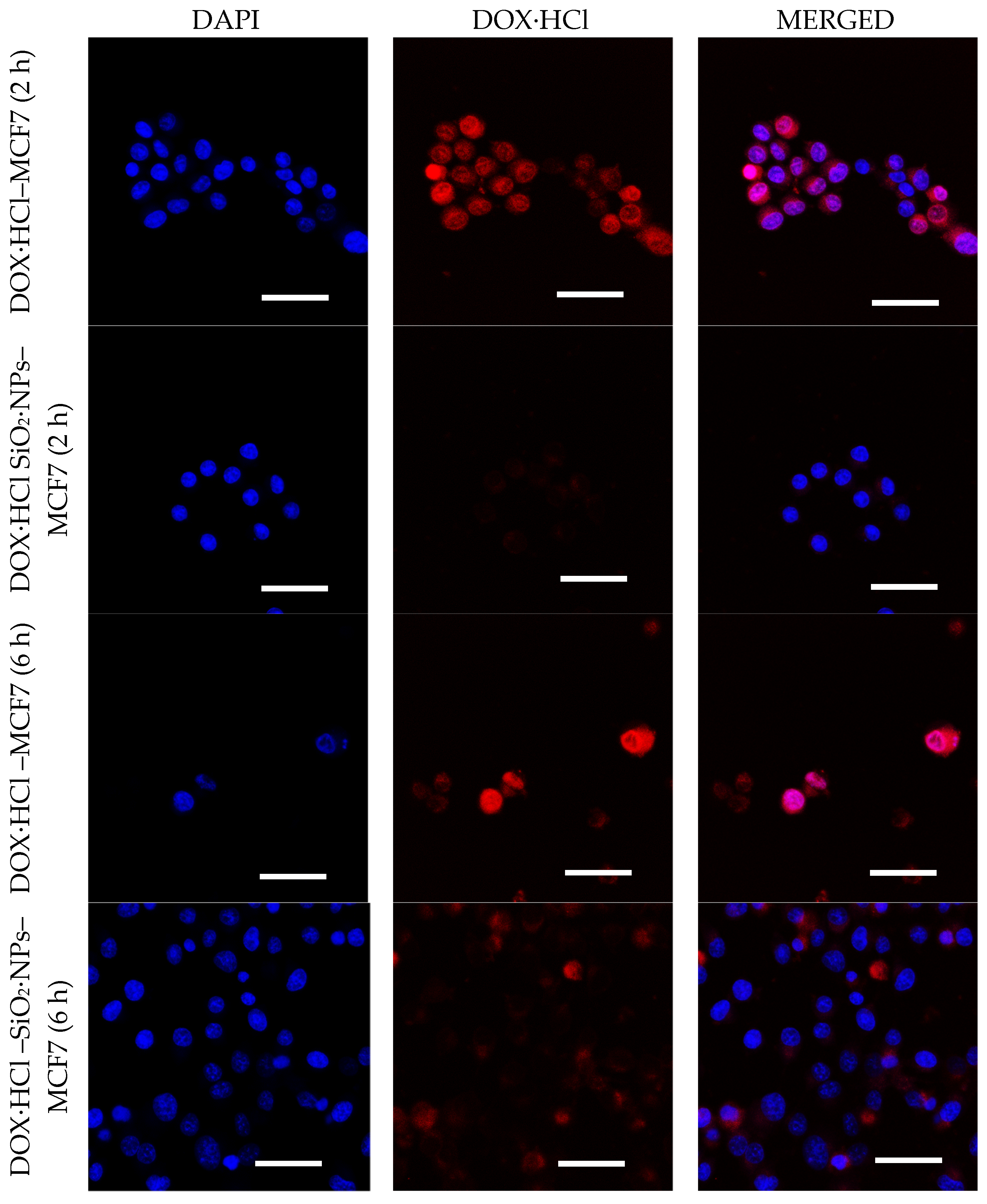
The cellular uptake of DOX·HCl and DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs was further studied with MCF7 cells. DAPI was used for nuclear staining and the DOX·HCl fluorescence was monitored in cells by a laser scanning confocal microscope. Figure 7 shows the fluorescent images of DOX·HCl and DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs treated cells. After treatment with DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs, the intracellular delivery was significantly enhanced compared with cells treated with DOX·HCl molecules. An apparent increase in the amount of drug passed through the cell membrane was obviously observed after two hours of incubation with DOX·HCl. Cellular uptake and the LCSM analyses showed that the free DOX·HCl started to enter the nuclei of MCF7 cells after two hours and totally concentrated in the nuclei after six hours. In contrast, after two hours of incubation with DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs system, the nuclear almost have the DAPI‘s color. However, after six hours of incubation with DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs, the similar results with the free DOX·HCl, the superposing of the red color with the blue color in the nuclear of MCF7 cells, was observed. This phenomenon can be explained that the pH media around cells is close to pH 7.4 of DMEM medium in the early time. Over time, the pH of media becomes more acidic [25,26], increasing the release of DOX·HCl from the DOX·HCl-SiO2·NPs. This result agrees with Guan‘s report where authors observed that after two hours of incubation, cells with DOX·HCl or their DOX·HCl nanocarrier system, DOX·HCl was found in the nuclear [5], especially in acidic media at pH of 6.8. These results demonstrated that the acid-sensitivity property of the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs boosted the DOX·HCl release in the tumors, which led to a significant killing effect on the cancer cells. More importantly, the system showed remarkable cytotoxicity against MCF7 cancer cells. In our experiment, Figure 7 showed the positions where DOX·HCl accumulates and the positions of DAPI in the nucleus of the MCF7 cancer cells. These results confirmed that DOX·HCl molecules release from DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs inside cells and the DOX·HCl molecules bind to DNA which is the main cause of cells’ death [2,27,28].
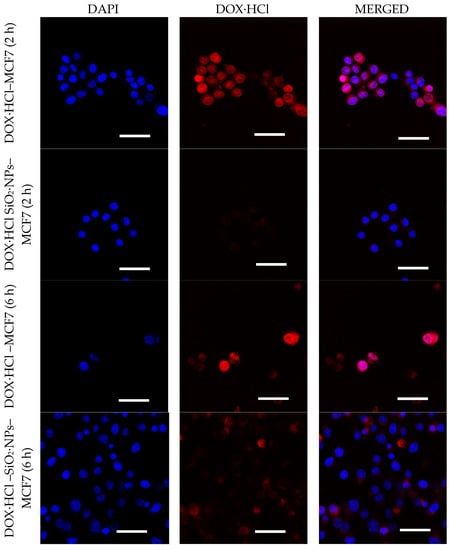
Figure 7.
CLSM images of MCF7 cells incubated with DOX·HCL molecule (on top), DOX·HCl–SiO2 NPs system (bottom) at DOX·HCl concentration of 4 µM. Images were acquired after 2 and 6 h. (Nuclei of these cells incubated with DAPI molecules). Scale bar 50 μm.
4. Conclusions
DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs is a drug delivery system that exhibited dual functions. The zeta potential analysis confirms the charge change of DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs complexes to determine the maximum DOX·HCl loading. The optical characterization was used to monitor the loading and release of DOX·HCl on the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs. CLSM results showed that the DOX·HCl released from DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs was delivered efficiently to the nucleus of cancer cells. These results show that the DOX·HCl-SiO2 NPs system is a promising candidate for drug delivery and has potential in clinical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.H.L.N. and T.M.H.N.; methodology, T.N.N.; validation, T.T.H.T., and V.T.N. and T.B.N.N.; formal analysis, T.N.N.; investigation, T.T.N.; resources, T.H.L.N. and T.M.H.N.; data curation, D.T.N. and T.T.H.T.; writing—original draft preparation, T.N.N.; writing—review and editing, M.H.N. and T.H.L.N.; visualization, D.V.; supervision, T.H.L.N.; project administration, T.H.L.N. and T.N.N.; funding acquisition, T.N.N. and T.H.L.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors are grateful for the financial support for this work from the project ĐTĐLCN.05/17 of the Physics Development Program 2020 of Vietnam and the project number 103.03-2016.72 of the National Foundation for Science and Technology Development of Vietnam (NAFOSTED).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this article are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are available from the authors.
References
- Mohan, P.; Rapoport, N. Doxorubicin as a Molecular Nanotheranostic Agent: Effect of Doxorubicin Encapsulation in Micelles or Nanoemulsions on the Ultrasound-Mediated Intracellular Delivery and Nuclear Trafficking. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1959–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tacar, O.; Sriamornsak, P.; Dass, C.R. Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and novel drug delivery systems. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 65, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados, J.; Melguizo, C.; Ortiz, R.; Vélez, C.; Alvarez, P.J.; Arias, J.L.; Ruíz, M.A.; Gallardo, V.; Aranega, A. Doxorubicin-Loaded Nanoparticles: New Advances in Breast Cancer Therapy. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jiang, L. Doxorubicin Hydrochloride-Loaded Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Inhibit Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Metastasis by Suppressing VEGF-Mediated Angiogenesis. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2016, 12, 1975–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, Z.; Tian, H.; Chen, X. A pH-sensitive charge-conversion system for doxorubicin delivery. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 7672–7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Colilla, M.; Izquierdo-Barba, I.; Manzano, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Current Insights. Molecules 2017, 23, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Quan, G.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Niu, B.; Wu, B.; Huang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wu, C. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug and gene delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.; DeGiovanni, P.; Piel, B.; Rai, P. Cancer nanomedicine: A review of recent success in drug delivery. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, S.A. Incredible pace of research on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2014, 1, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Almalik, A.; Khashab, N.M. Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanoparticles: Physical Chemistry, Biosafety, Delivery Strategies, and Biomedical Applications. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseinpour, S.; Walsh, L.J.; Xu, C. Biomedical application of mesoporous silica nanoparticles as delivery systems: A biological safety perspective. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 9863–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croissant, J.G.; Fatieiev, Y.; Khashab, N.M. Degradability and Clearance of Silicon, Organosilica, Silsesquioxane, Silica Mixed Oxide, and Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, S.V.; Emami, F.S.; Berry, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Naik, R.R.; Deschaume, O.; Heinz, H.; Perry, C.C. Chemistry of Aqueous Silica Nanoparticle Surfaces and the Mechanism of Selective Peptide Adsorption. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6244–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Cheng, S.H.; Huang, I.P.; Souris, J.S.; Yang, C.S.; Mou, C.Y.; Lo, L.W. Intracellular pH-Responsive Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for the Controlled Release of Anticancer Chemotherapeutics. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 8390–8395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monem, A.S.; Elbialy, N.; Mohamed, N. Mesoporous silica coated gold nanorods loaded doxorubicin for combined chemo–photothermal therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 470, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nghiem, T.H.L.; Le, T.N.; Do, T.H.; Vu, T.T.D.; Do, Q.H.; Tran, H.N. Preparation and characterization of silica–gold core–shell nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.S.; El-Hami, K.; Kodaki, T.; Matsushige, K.; Makino, K. A novel method for synthesis of silica nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 289, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Cheng, J. Nonporous silica nanoparticles for nanomedicine application. Nano Today 2013, 8, 290–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, S.; Chandra, A.; Kaur, A.; Sabnis, N.; Lacko, A.; Gryczynski, Z.; Fudala, R.; Gryczynski, I. Fluorescence properties of doxorubicin in PBS buffer and PVA films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 170, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaushik, D.; Bansal, G. Four new degradation products of doxorubicin: An application of forced degradation study and hyphenated chromatographic techniques. J. Pharm. Anal. 2015, 5, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariam, J.; Sivakami, S.; Dongre, P.M. Albumin corona on nanoparticles—A strategic approach in drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2668–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Lee, B.-J. Protein corona: A new approach for nanomedicine design. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3137–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nooney, R.I.; White, A.; O’Mahony, C.; O’Connell, C.; Kelleher, S.M.; Daniels, S.; McDonagh, C. Investigating the colloidal stability of fluorescent silica nanoparticles under isotonic conditions for biomedical applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 456, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Ozawa, S.; Miyamoto, C.; Maehata, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Maeda, T.; Baba, Y. Acidic extracellular microenvironment and cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boedtkjer, E.; Pedersen, S.F. The Acidic Tumor Microenvironment as a Driver of Cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2020, 82, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mobaraki, M.; Faraji, A.; Zare, M.; Manshadi, H.R.D. Molecular Mechanisms of Cardiotoxicity: A Review on Major Side-effect of Doxorubicin. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 79, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-López, A.; Battino, M.; Navarro-Hortal, M.D.; Giampieri, F.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Romero-Márquez, J.M.; Collado, R.; Quiles, J.L. An update on the mechanisms related to cell death and toxicity of doxorubicin and the protective role of nutrients. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 134, 110834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).