Fabrication and Evaluation of Alginate/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals–Chitosan–Gelatin Composite Scaffolds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
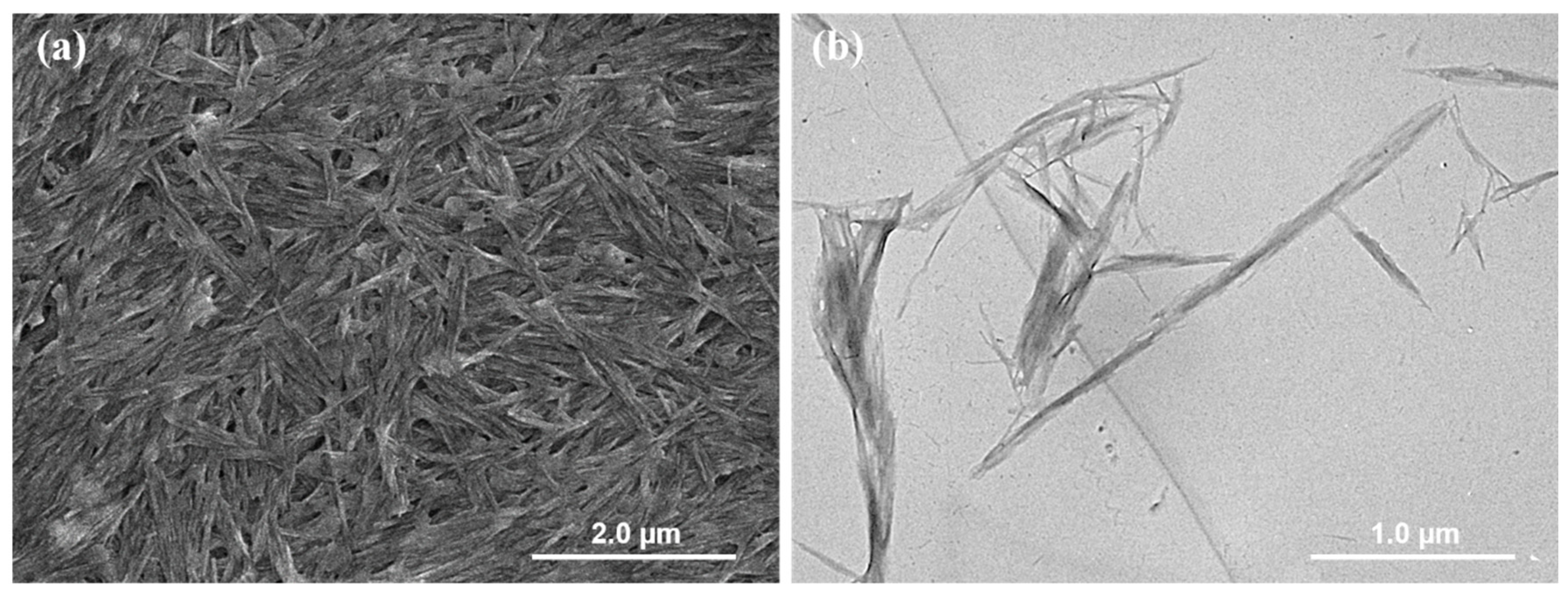
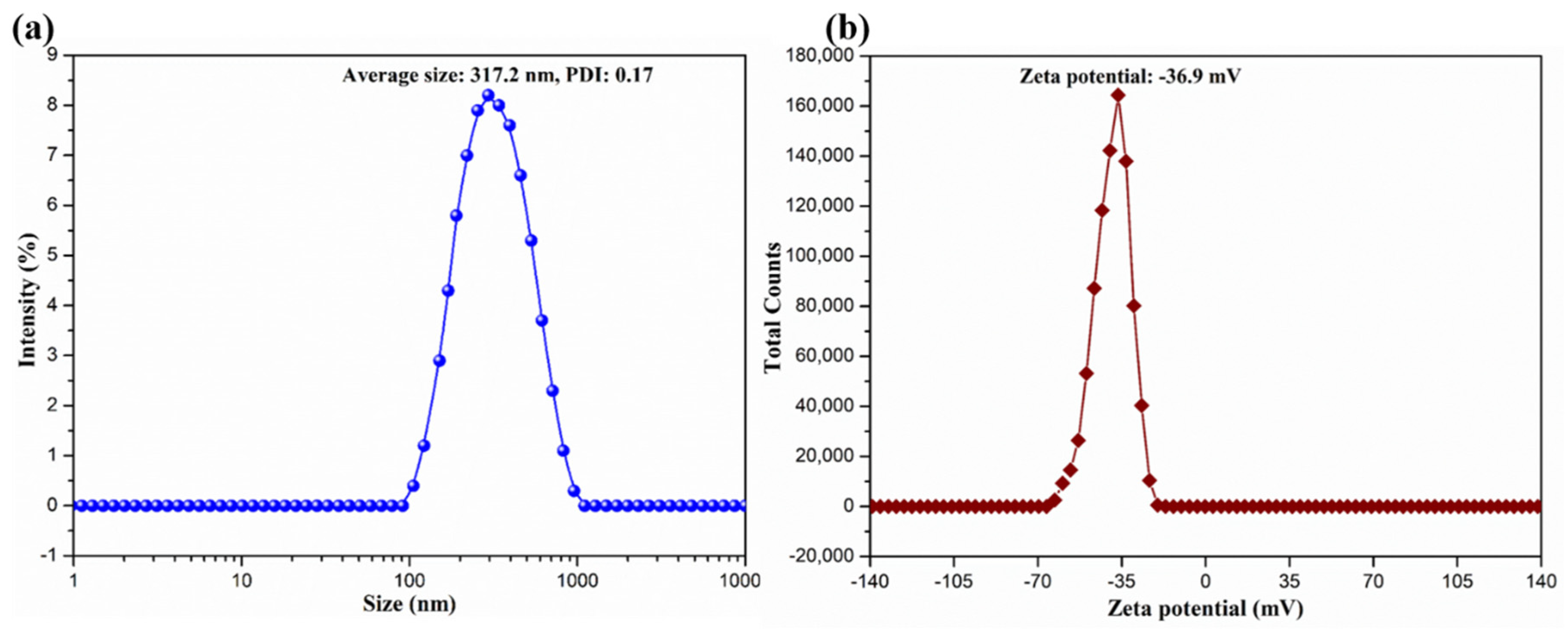
2.1. Colloidal and Interfacial Activity of BCNs
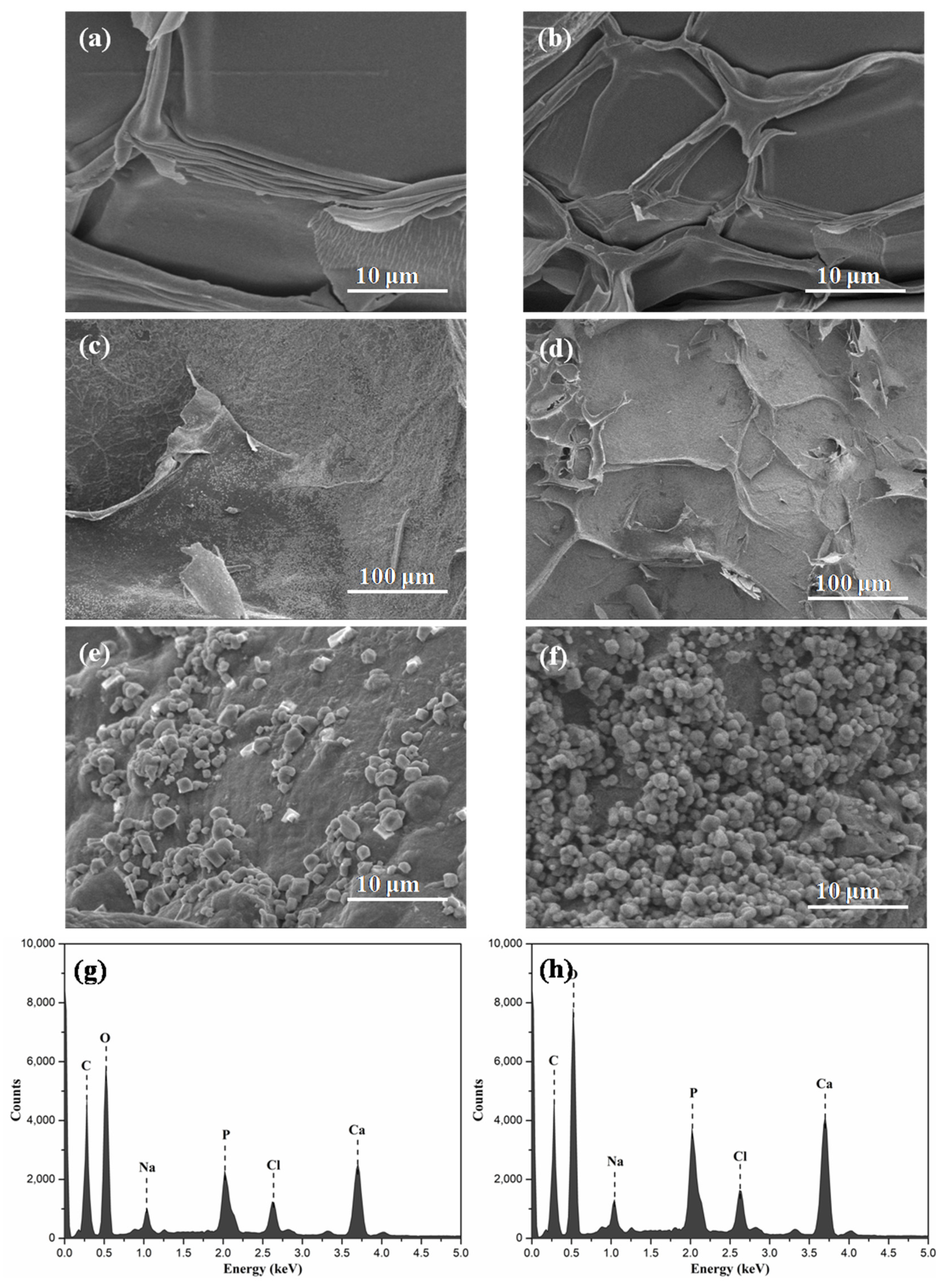
2.2. Morphology of Alg/BCNs-CS-GT Composite Scaffolds
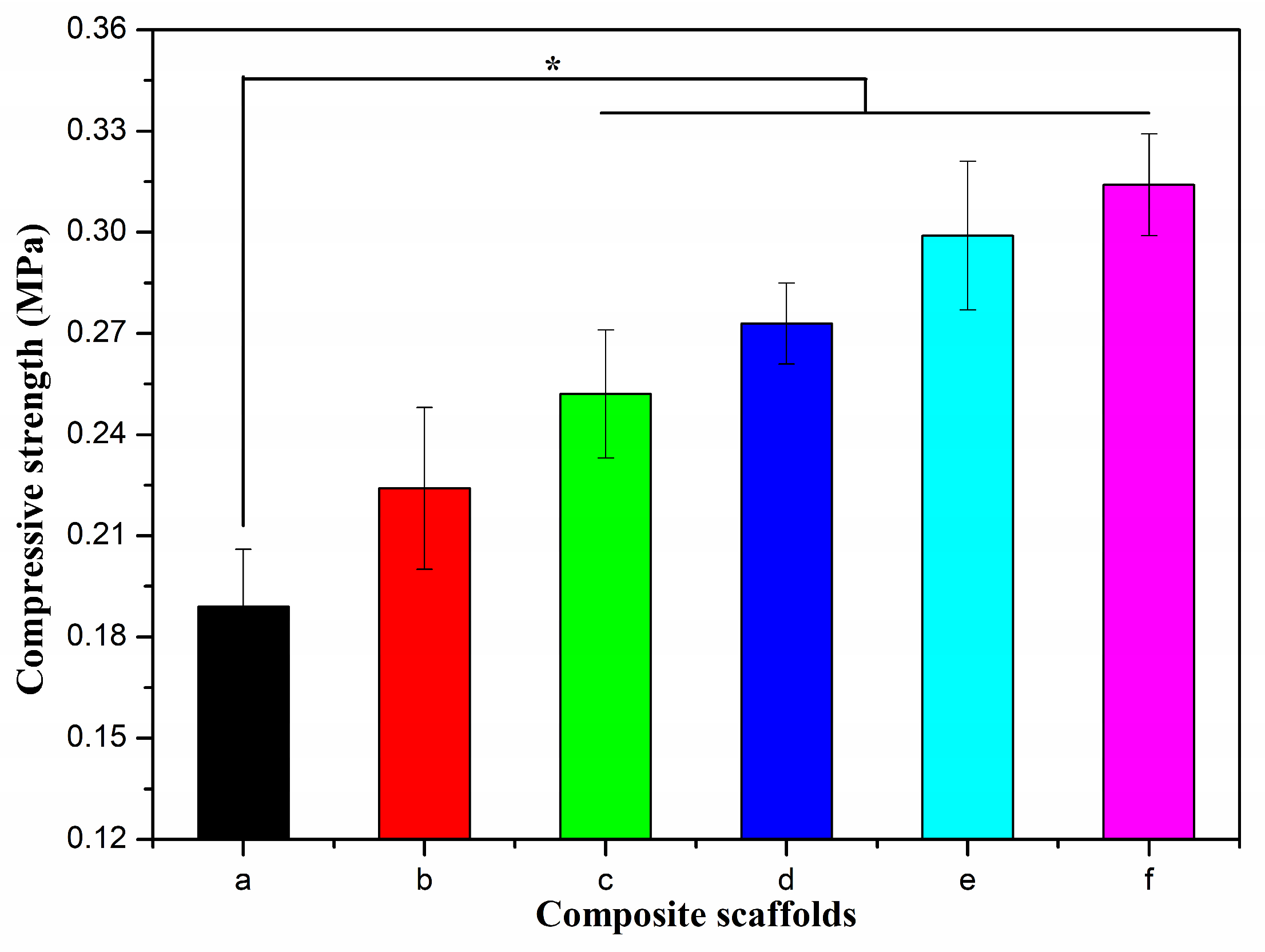
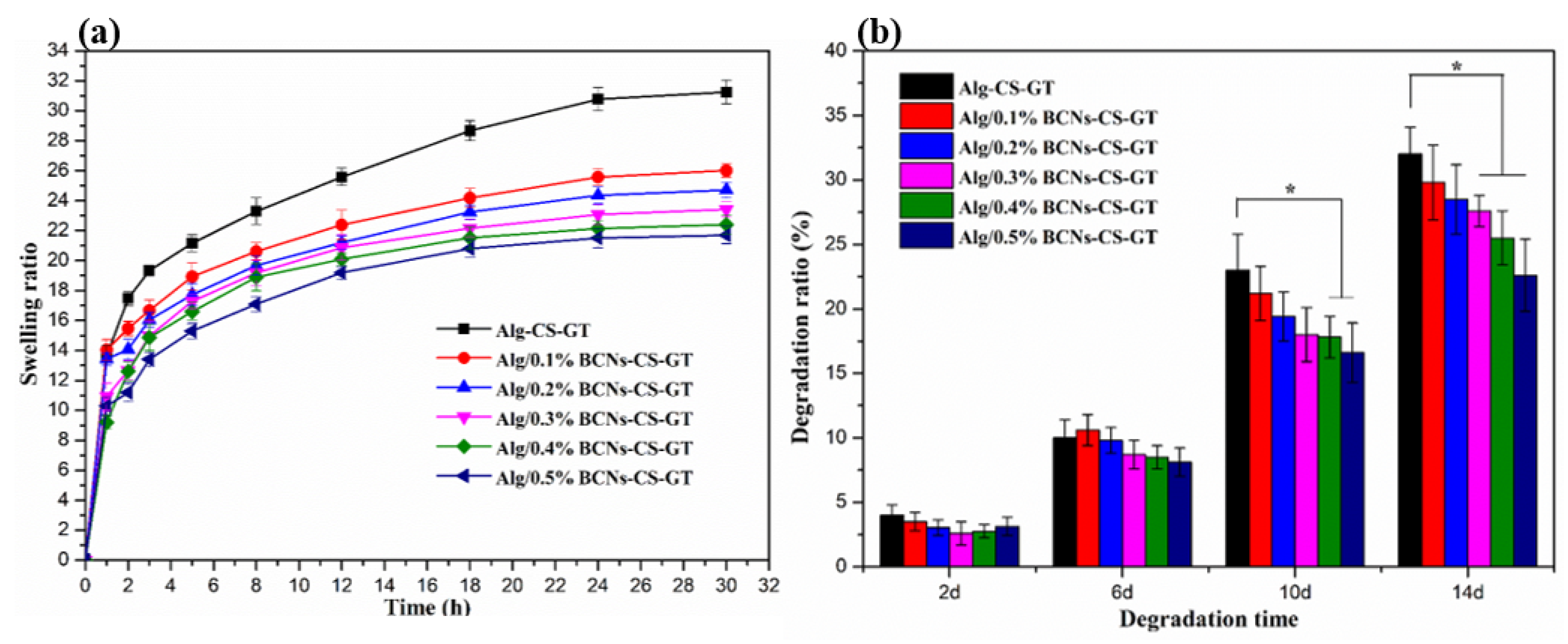
2.3. Characterization of Alg/BCNs-CS-GT Composite Scaffolds
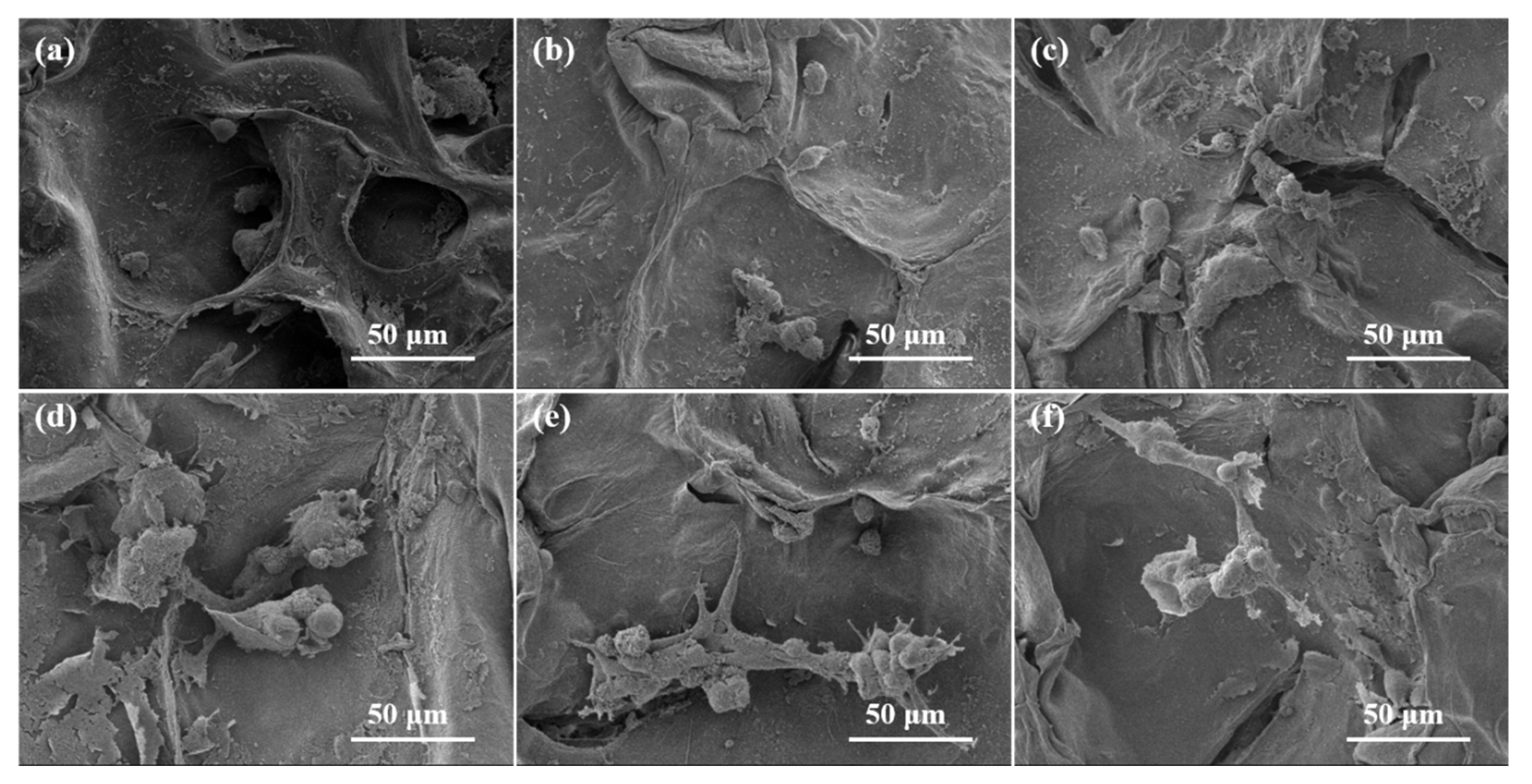
2.4. In Vitro Cytotoxicity of Alg/BCNs-CS-GT Composite Scaffolds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of BCNs
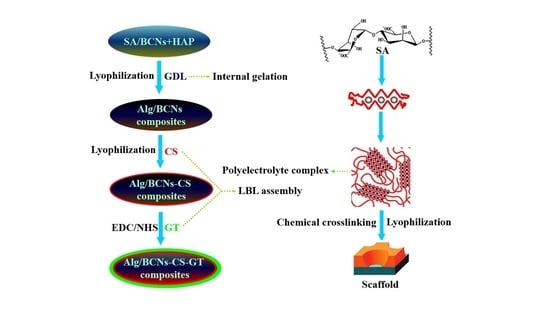
3.3. Fabrication of Alg/BCNs-CS-GT Composite Scaffolds
3.4. Characterization
3.5. In Vitro Swelling, Biodegradation and Biomineralization Studies
3.6. Cytotoxicity Studies
3.6.1. Cell Culture and Seeding
3.6.2. Cell Attachment
3.6.3. Cell Proliferation
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| Sodium alginate | SA |
| Bacterial cellulose nanocrystals | BCNs |
| Chitosan | CS |
| Gelatin | GT |
| Hydroxyapatite | HAP |
| d-glucono-δ-lactone | GDL |
| Layer-by-layer | LBL |
| Alginate/bacterial cellulose nanocrystals-chitosan-gelatin | Alg/BCNs-CS-GT |
| Alginate-chitosan-gelatin | Alg-CS-GT |
| Extracellular matrix | ECM |
| Arg–Gly–Asp | RGD |
| Cell Counting Kit-8 | CCK-8 |
| Alkaline phosphatase | ALP |
| Bacterial cellulose | BC |
| Scanning electron microscope | SEM |
| Energy-dispersive X-ray | EDX |
| Transmission electron microscopy | TEM |
| Phosphate buffer saline | PBS |
| Simulated body fluid | SBF |
References
- Turco, G.; Marsich, E.; Bellomo, F.; Semeraro, S.; Donati, I.; Brun, F.; Grandolfo, M.; Accardo, A.; Paoletti, S. Alginate/hydroxyapatite biocomposite for bone ingrowth: A trabecular structure with high and isotropic connectivity. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gribova, V.; Auzely-Velty, R.; Picart, C. Polyelectrolyte multilayer assemblies on materials surfaces: From cell adhesion to tissue engineering. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 854–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, P.F.; Wu, W.J.; Wei, Y.; Ren, L.; Lin, S.X.; Wu, J.H. Biomimetic gelatin/chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/nano-hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Des. 2021, 207, 109865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Liu, X.; Yeung, K.W.K.; Liu, C.; Yang, X. Biomimetic porous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 80, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.D.; Jin, H.X.; Patel, D.K.; Ganguly, K.; Lim, K.T. 3D-printed bioactive and biodegradable hydrogel scaffolds of alginate/gelatin/cellulose nanocrystals for tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantripragada, V.P.; Lecka-Czernik, B.; Ebraheim, N.A.; Jayasuriya, A.C. An overview of recent advances in designing orthopedic and craniofacial implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 3349–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.J.; Qin, M.; Cheng, Y.Z.; Niu, X.L.; Kong, J.L.; Zhang, X.M.; Huang, D.; Wang, H.N. Alginate microgels as delivery vehicles for cell-based therapies in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 266, 118128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, G.V.Y.; Prabhu, A.; Anil, S.; Venkatesan, J. Preparation and characterization of dexamethasone loaded sodium alginate-graphene oxide microspheres for bone tissue engineering. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102624. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, Q. Synthesis of alginate derivative via the Ugi reaction and itscharacterization. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidarra, S.J.; Barrias, C.C.; Granja, P.L. Injectable alginate hydrogels for cell delivery in tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1646–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, M.; Pandele, M.A.; Iovu, H. Sodium alginate/graphene oxide composite films with enhanced thermal and mechanical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-González, A.C.; Téllez-Jurado, L.; Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.M. Alginate hydrogels for bone tissue engineering, from injectables to bioprinting: A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, C.G.; Huang, Z.H.; Xue, F.F. Preparation and characterization of nanoparticles based on hydrophobic alginate derivative as carriers for sustained release of vitamin D3. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1962–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khattak, W.A.; Park, J.K. Overview of bacterial cellulose composites: A multipurpose advanced material. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1585–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, N.; Dufresne, A. Nanocellulose in biomedicine: Current status and future prospect. Eur. Polym. J. 2014, 59, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dugan, J.M.; Gough, J.E.; Eichhorn, S.J. Bacterial cellulose scaffolds and cellulose nanowhiskers for tissue engineering. Nanomedicine 2013, 8, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedarawatte, S.T.G.; Ravensdale, J.T.; Al-Salami, H.; Dykes, G.A.; Coorey, R. Antimicrobial efficacy of nisin-loaded bacterial cellulose nanocrystals against selected meat spoilage lactic acid bacteria. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 251, 117096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, N.B.; James, R.; Laurencin, C.T.; Kumbar, S.G. Polysaccharidebiomaterials for drug delivery and regenerative engineering. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Wahid, F.; Santos, H.A.; Khan, T. Advances in biomedical and pharmaceutical applications of functional bacterial cellulose-based nanocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 150, 330–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Shi, Q.; Guo, W.; Terrell, L.; Qureshi, A.T.; Hayes, D.J.; Wu, Q. Electrospun bio-nanocomposite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering by cellulose nanocrystals reinforcing maleic anhydride grafted PLA. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3847–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Cheng, F.; Grénman, H.; Spoljaric, S.; Seppälä, J.; Eriksson, J.E.; Willför, S.; Xu, C. Development of nanocellulose scaffolds with tunable structures tosupport 3D cell culture. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 148, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoeck, D.; Moerkerke, B.; Mignon, A.; De Belie, N. In-situ crosslinking of superabsorbent polymers as external curing layer compared to internal curing to mitigate plastic shrinkage. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.G.; Shin, H.; Lim, D.W. Biomimetic scaffolds for tissue engineering. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2446–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, G.; Park, J.; Jo, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Ahn, Y.; Lee, J.Y. Studies on the effects of microencapsulated human mesenchymal stem cells in RGD-modified alginate on cardiomyocytes under oxidative stress conditions using in vitro biomimetic co-culture system. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 123, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammelt, S.; Illert, T.; Bierbaum, S.; Scharnweber, D.; Zwipp, H.; Schneiders, W. Coating of titanium implants with collagen, RGD peptide and chondroitin sulfate. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5561–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, D.; Sola, A.; Gentile, P.; Ciardelli, G.; Cannillo, V. Biomimetic coating on bioactive glass-derived scaffolds mimicking bone tissue. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2012, 100, 3259–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojak-Cwik, I.M.; Hintze, V.; Schnabelrauch, M.; Moeller, S.; Dobrzynski, P.; Pamula, E.; Scharnweber, D. Poly (L-lactide-co-glycolide) scaffolds coated with collagen and glycosaminoglycans: Impact on proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 3109–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rechenmacher, F.; Neubauer, S.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Dorfner, P.M.; Polleux, J.; Guasch, J.; Conings, B.; Boyen, H.G.; Bochen, A.; Sobahi, T.R.; et al. A molecular toolkit for the functionalization of titanium-based biomaterials that selectively control integrin-mediated cell adhesion. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 9218–9223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mas-Moruno, C.; Dorfner, P.M.; Manzenrieder, F.; Neubauer, S.; Reuning, U.; Burgkart, R.; Kessler, H. Behavior of primary human osteoblasts on trimmed and sandblasted Ti6Al4V surfaces functionalized with integrin αvβ3-selective cyclic RGD peptides. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumya, S.; Sreerekha, P.R.; Menon, D.; Nair, S.V.; Chennazhi, K.P. Generation of a biomimetic 3D microporous nano-fibrous scaffold on titanium surfaces for better osteointegration of orthopedic implants. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1904–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Dellatore, S.M.; Miller, W.M.; Messersmith, P.B. Mussel-inspired surface chemistry for multifunctional coatings. Science 2007, 318, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Poon, Y.F.; Li, W.; Zhu, H.Y.; Yeap, S.H.; Cao, Y.; Qi, X.B.; Zhou, C.C.; Lamrani, M.; Beuerman, R.W.; et al. A polycationic antimicrobial and biocompatible hydrogel with microbe membrane suctioning ability. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Fleming, K.E.; Chuang, H.F.; Chau, T.M.; Loose, C.R.; Stephanopoulos, G.N.; Hammond, P.T. Controlling the release of peptide antimicrobial agents from surfaces. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2348–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepthi, S.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K.; Bumgardner, J.D.; Jayakumar, R. An overview of chitin or chitosan/nano ceramic composite scaffoldsfor bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1338–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha, R.; Sreeram, K.J.; Rajaram, A. Stabilization of collagen with EDC/NHS in the presence of l-lysine: A comprehensive study. Colloids Surf. B 2012, 90, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Ballinger, S.; Pelton, R.; Cranston, E.D. Surfactant-enhanced cellulose nanocrystal Pickering emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 439, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Chen, X.; Song, H.; Li, J.; Feng, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, Q. Synthesis of bacterial cellulose and bacterial cellulose nanocrystals for their applications in the stabilization of olive oil Pickering emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 75, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.Q.; Chen, X.Q.; Feng, M.X.; Shi, Z.F.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Ke, C.R.; Lin, Q. Entrapment of bacterial cellulose nanocrystals stabilized Pickering emulsions droplets in alginate beads for hydrophobic drug delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 177, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Chen, M.; Xue, Q.; Liu, W. Preparation and self-assembly of carboxylic acid-functionalized silica. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 311, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Dai, L.; Shi, H.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, C. In vitro evaluation of alginate/halloysite nanotube composite scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valente, J.F.A.; Valente, T.A.M.; Alves, P.; Ferreira, P.; Silva, A.; Correia, I.J. Alginate based scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mat. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2596–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Guo, H.J.; Xiong, L.; Wang, B.; Shi, S.L.; Chen, X.F.; Lin, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.D. Using wastewater after lipid fermentation as substrate for bacterialcellulose production by gluconacetobacter xylinus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zhai, X.; Fu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhong, C. Surfactant-free emulsions stabilized by tempo-oxidized bacterial cellulose. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriana, R.; Vilaplana, F.; Ek, M. Cellulose nanocrystals from forest residues as reinforcing agents for composites: A study from macro- to nano-dimensions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 139, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Karim, M.R. Fabrication and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)/alginate blend nanofibers by electrospinning method. Colloids Surf. A 2010, 366, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowjanya, J.A.; Singh, J.; Mohita, T.; Sarvanan, S.; Moorthi, A.; Srinivasan, N.; Selvamurugan, N. Biocomposite scaffolds containing chitosan/alginate/nano-silica for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 109, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Ren, L.; Zhao, N.; Gong, Y.; Wang, D.A. Novel mesoporous silica-based antibiotic releasing scaffold for bone repair. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowska-Łańcucka, J.; Mystek, K.; Mignon, A.; Vlierberghe, S.V.; Łatkiewicz, A.; Nowakowska, M. Alginate- and gelatin-based bioactive photocross-linkable hybridmaterials for bone tissue engineering. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1714–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, R.M.A.; Gomes, M.E.; Reis, R.L. The potential of cellulose nanocrystals in tissue engineering strategies. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 2327–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paximada, P.; Tsouko, E.; Kopsahelis, N.; Koutinas, A.A.; Mandala, I. Bacterial cellulose as stabilizer of o/w emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 53, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Fu, S.; Peng, X.; Zhan, H.; Sun, R. Colloidal stability of negatively charged cellulose nanocrystalline in aqueous systems. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Y.; Guo, R.; Liu, J.; Lan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, W.; Zhang, Y. Preparation and properties of PLGA nanofiber membranes reinforced with cellulose nanocrystals. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 132, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajesh, K.M.; Jayakumar, R.; Nair, S.V.; Chennazhi, K.P. Biocompatible conducting chitosan/polypyrrole–alginate compositescaffold for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

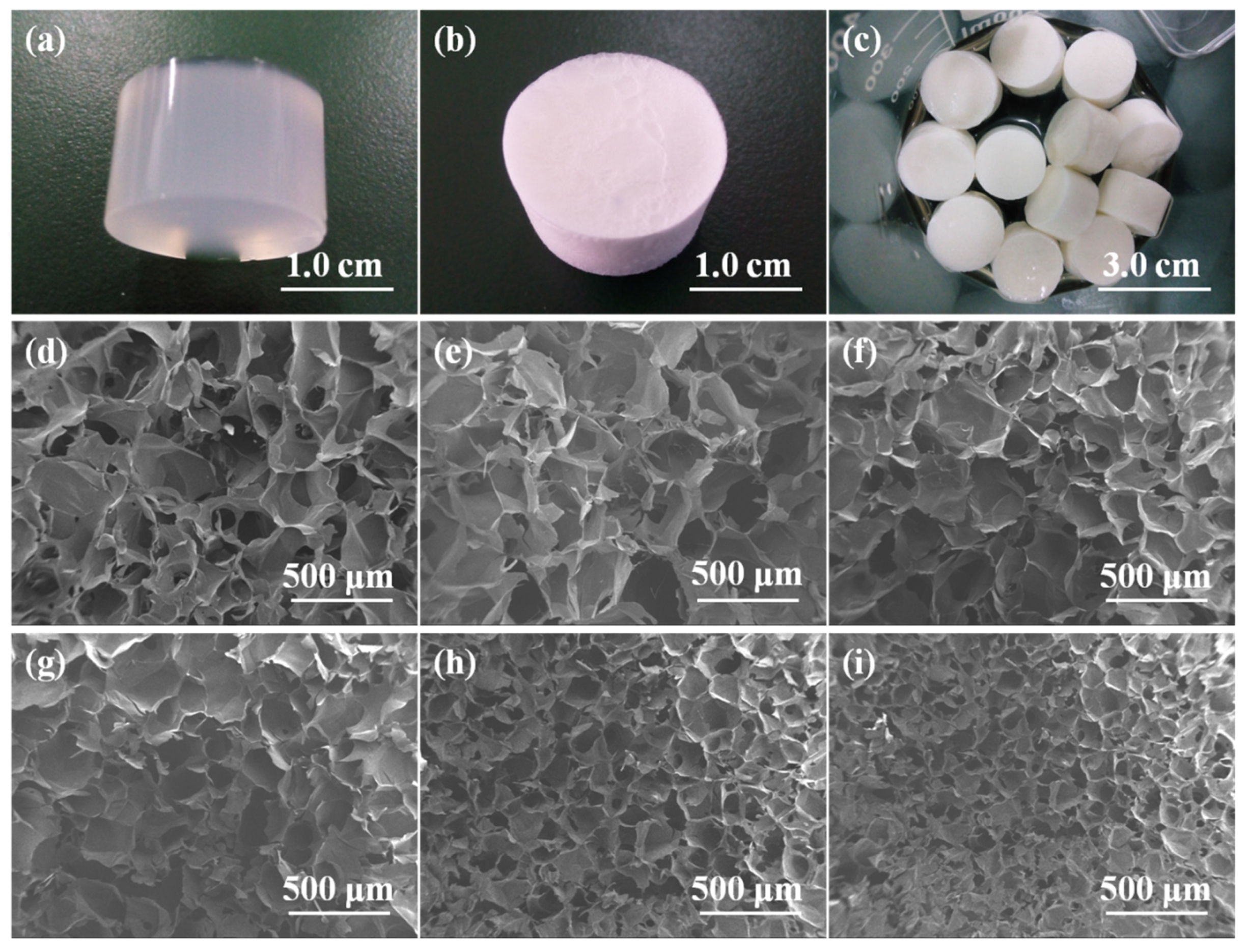





| Samples | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|
| Alg/0.1%BCNs-CS-GT | 86.2 ± 2.8 |
| Alg/0.2%BCNs-CS-GT | 83.6 ± 3.1 |
| Alg/0.3%BCNs-CS-GT | 79.8 ± 2.9 |
| Alg/0.4%BCNs-CS-GT | 75.6 ± 2.3 |
| Alg/0.5%BCNs-CS-GT | 73.2 ± 3.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Bao, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, C.; Li, D.; Yan, H.; Lin, Q. Fabrication and Evaluation of Alginate/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals–Chitosan–Gelatin Composite Scaffolds. Molecules 2021, 26, 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165003
Li Z, Chen X, Bao C, Liu C, Liu C, Li D, Yan H, Lin Q. Fabrication and Evaluation of Alginate/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals–Chitosan–Gelatin Composite Scaffolds. Molecules. 2021; 26(16):5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhengyue, Xiuqiong Chen, Chaoling Bao, Chang Liu, Chunyang Liu, Dongze Li, Huiqiong Yan, and Qiang Lin. 2021. "Fabrication and Evaluation of Alginate/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals–Chitosan–Gelatin Composite Scaffolds" Molecules 26, no. 16: 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165003
APA StyleLi, Z., Chen, X., Bao, C., Liu, C., Liu, C., Li, D., Yan, H., & Lin, Q. (2021). Fabrication and Evaluation of Alginate/Bacterial Cellulose Nanocrystals–Chitosan–Gelatin Composite Scaffolds. Molecules, 26(16), 5003. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26165003