Chiral Monolithic Silica-Based HPLC Columns for Enantiomeric Separation and Determination: Functionalization of Chiral Selector and Recognition of Selector-Selectand Interaction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Monolithic Silica HPLC Columns for Chiral Analysis
2.1. Propoerties of Monolithic-Silica Stationary Phase
2.2. Monolithic Column Coupling
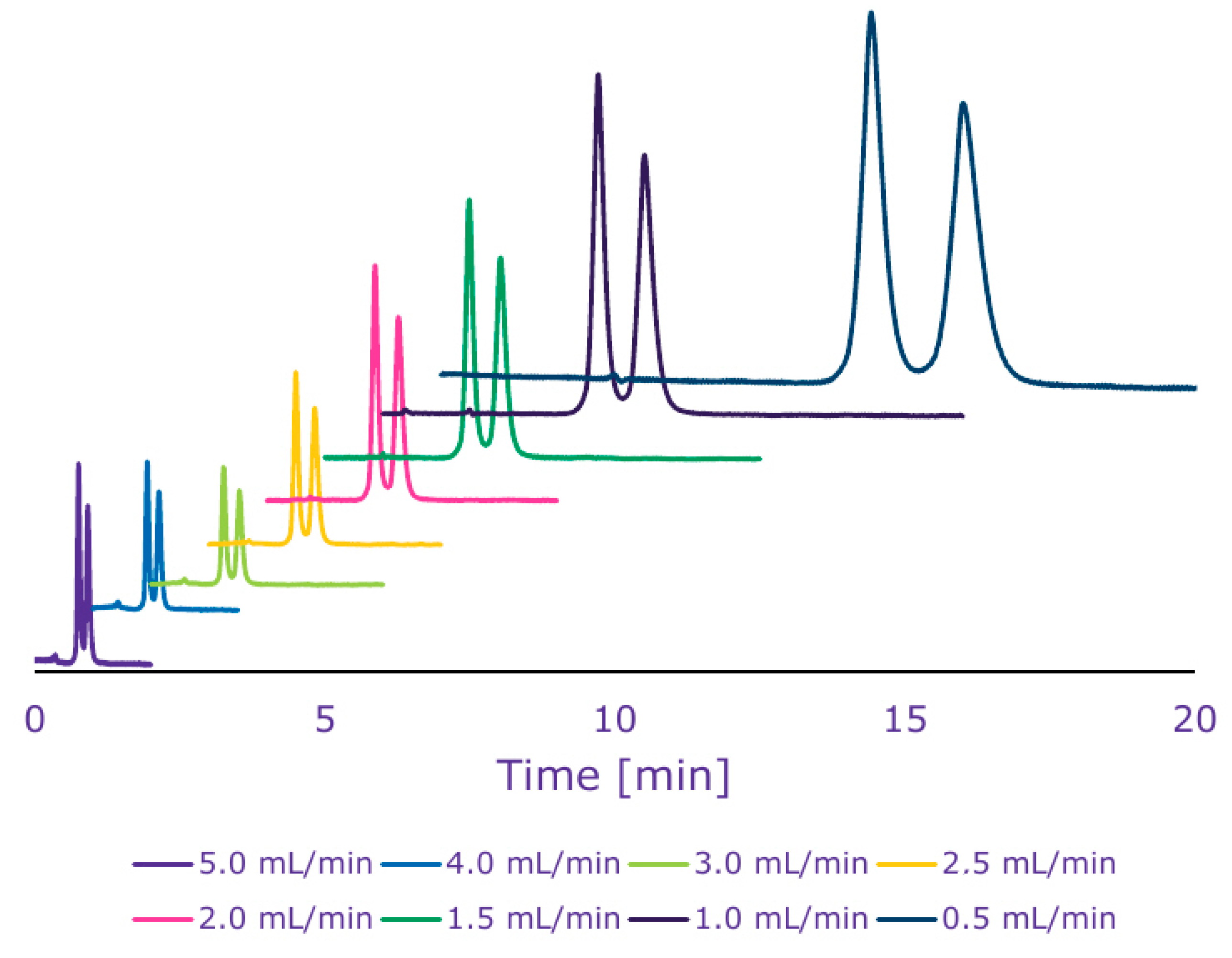
2.3. Flow Programming Elution
2.4. Introducing Chiral Selector into the Monolithic Silica Stationary Phase
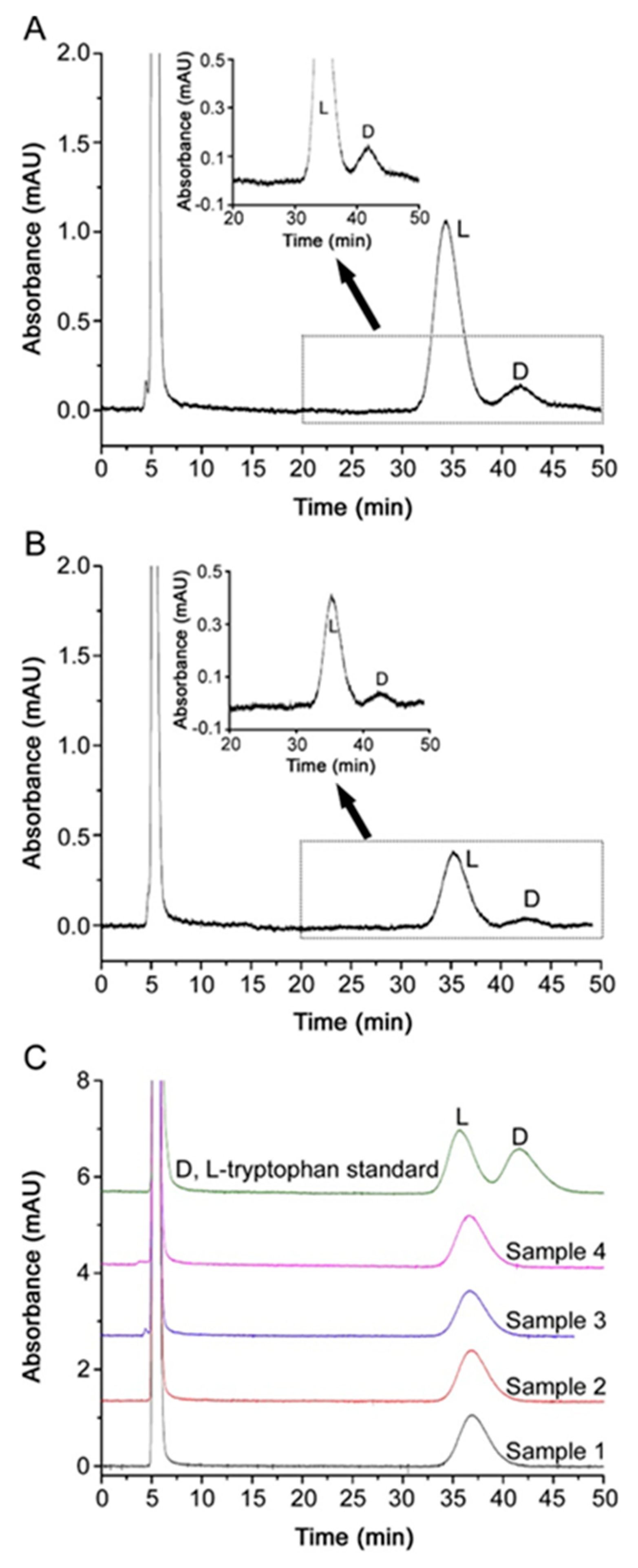
3. Enantiomeric Impurity Determination
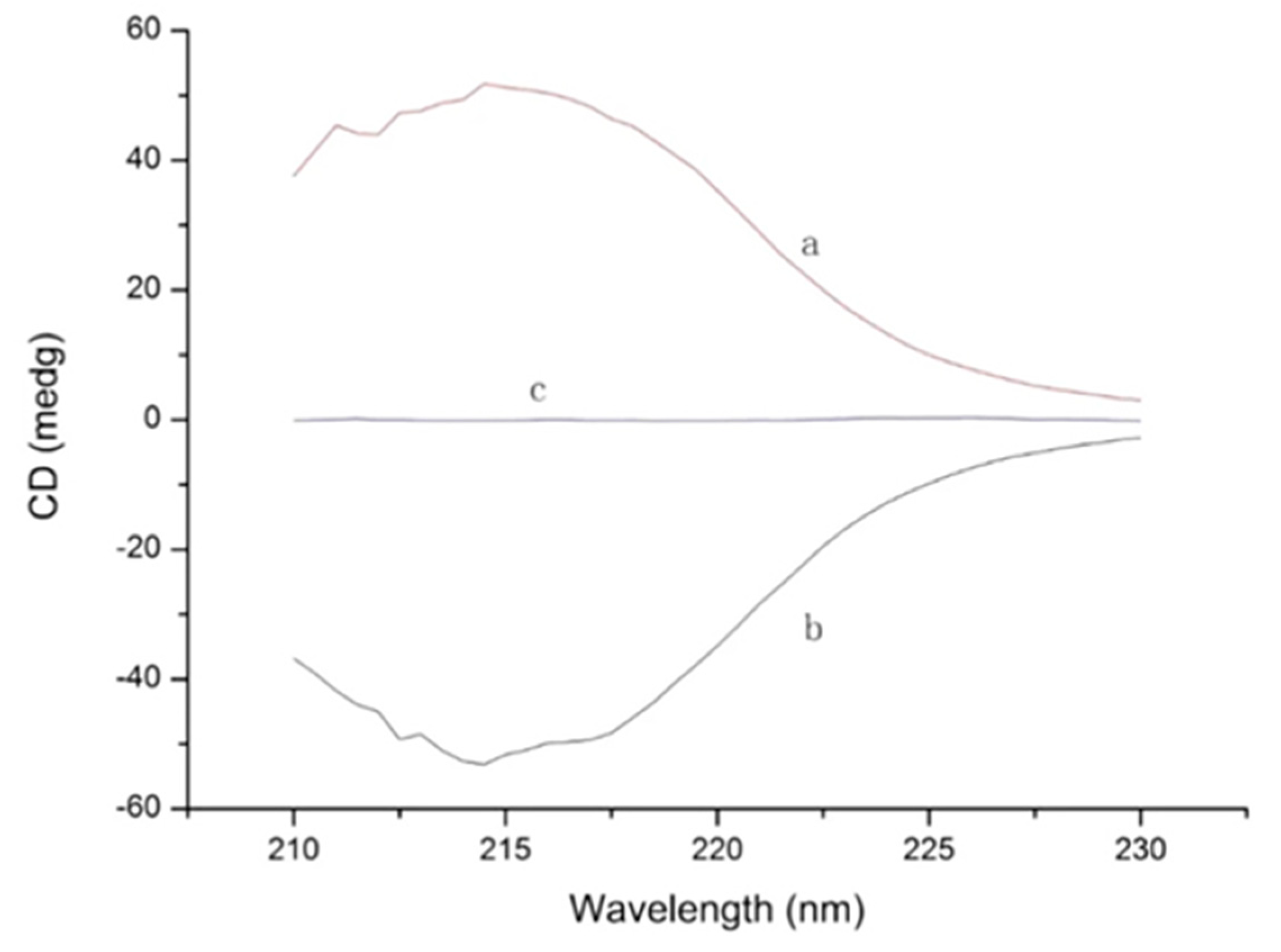
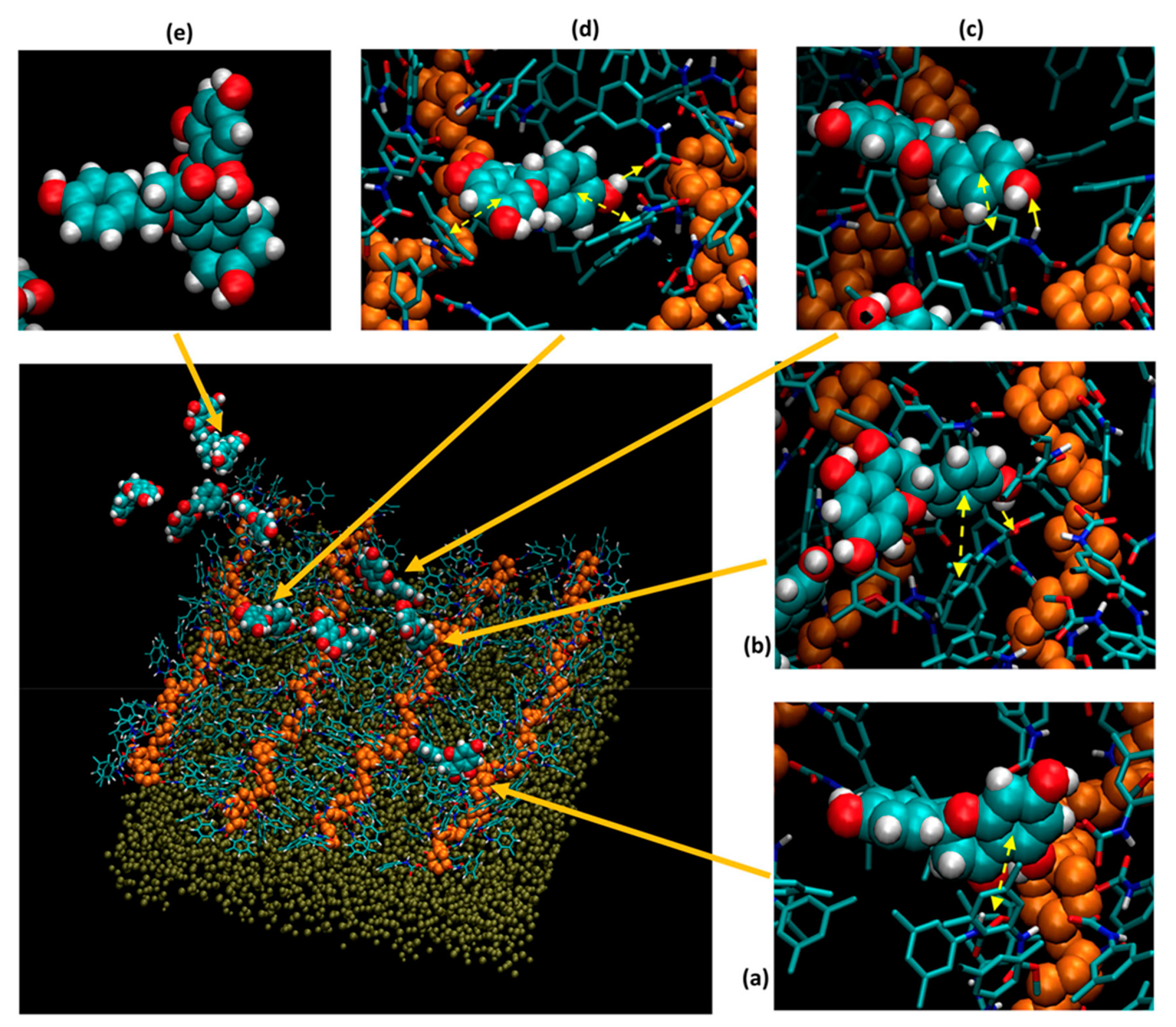
4. Molecular Modeling Applied to Enantioseparations
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribeiro, A.R.; Maia, A.S.; Cass, Q.B.; Tiritan, M.E. Enantioseparation of Chiral Pharmaceuticals in Biomedical and Environmental Analyses by Liquid Chromatography: An Overview. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 968, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, N.; Valimaña-Traverso, J.; García, M.Á.; Marina, M.L. Enantiomeric Determination of Drugs in Pharmaceutical Formulations and Biological Samples by Electrokinetic Chromatography. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2020, 50, 554–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casado, N.; Jiang, Z.; García, M.Á.; Marina, M.L. Enantiomeric Separation of Colchicine and Lacosamide by Nano-LC. Quantitative Analysis in Pharmaceutical Formulations. Separations 2020, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Montealegre, C.; Marina, M.L.; Crego, A.L. Development of Chiral Methodologies by Capillary Electrophoresis with Ultraviolet and Mass Spectrometry Detection for Duloxetine Analysis in Pharmaceutical Formulations. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1363, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, A.; Lipiński, P.F.J.; Karoń, K.; Rode, J.E.; Lyczko, K.; Dobrowolski, J.C.; Donten, M.; Kaczorek, D.; Poszytek, J.; Kawęcki, R.; et al. Enantioselective Sensing of (S)-Thalidomide in Blood Plasma with a Chiral Naphthalene Diimide Derivative. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 167, 112446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhu, P.T.; kurian, M.; Hisham, M.C.; Shrikumar, S. Pharmaceutical review and its importance of chiral chromatography. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Chem. 2016, 6, 476–484. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-López, E.; Castro-Puyana, M.; Marina, M.L.; Crego, A.L. Chiral Separations by Capillary Electrophoresis. In Analytical Separation Science; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2015; pp. 731–775. [Google Scholar]
- Commission Directive 2001/15/EC of 15 February 2001 on Substances That May Be Added for Specific Nutritional Purposes in Foods for Particular Nutritional Uses (Text with EEA Relevance) (Repealed). Available online: https://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/eu-exit/https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX:02001L0015-20091231 (accessed on 5 July 2021).
- Bidlingmaier, B.; Unger, K.K.; von Doehren, N. Comparative Study on the Column Performance of Microparticulate 5-Μm C18-Bonded and Monolithic C18-Bonded Reversed-Phase Columns in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 832, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Rapid Development of Core–Shell Column Technology: Accurate Measurements of the Intrinsic Column Efficiency of Narrow-Bore Columns Packed with 4.6 down to 1.3μm Superficially Porous Particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1333, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano, J.J.; Schuster, S.A.; Lawhorn, J.M.; Kirkland, J.J. Performance Characteristics of New Superficially Porous Particles. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1258, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gritti, F. Introduction to “Comparison between the Efficiencies of Columns Packed with Fully and Partially Porous C18-Bonded Silica Materials” by F. Gritti, A. Cavazzini, N. Marchetti, G. Guiochon [J. Chromatogr. A 1157 (2007) 289–303]. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1446, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Minakuchi, H.; Soga, N.; Tanaka, N. Double Pore Silica Gel Monolith Applied to Liquid Chromatography. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1997, 8, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Soga, N. Phase Separation in Gelling Silica-Organic Polymer Solution: Systems Containing Poly(Sodium Styrenesulfonate). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 2518–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Minakuchi, H.; Ishizuka, N. Peer Reviewed: Monolithic LC Columns. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 420 A–429 A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minakuchi, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Soga, N.; Ishizuka, N.; Tanaka, N. Octadecylsilylated Porous Silica Rods as Separation Media for Reversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1996, 68, 3498–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, K.; Hira, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Nishimura, M.; Tanaka, N. High-Performance Polymer-Based Monolithic Capillary Column. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 5729–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydoğan, C.; Gökaltun, A.; Denizli, A.; El-Rassi, Z. Organic Polymer-based Monolithic Capillary Columns and Their Applications in Food Analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 962–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Ou, J.; Ye, M.; Zou, H. Functionalization of Hybrid Monolithic Columns via Thiol-Ene Click Reaction for Proteomics Analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1498, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ou, J.; Ye, M.; Wei, Y. Fast Preparation of Hybrid Monolithic Columns via Photo-Initiated Thiol-Yne Polymerization for Capillary Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1538, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Ou, J.; Lin, H.; Dong, J.; Zou, H. Preparation of a Butyl–Silica Hybrid Monolithic Column with a “One-Pot” Process for Bioseparation by Capillary Liquid Chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 2265–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chankvetadze, B.; Kubota, T.; Ikai, T.; Yamamoto, C.; Kamigaito, M.; Tanaka, N.; Nakanishi, K.; Okamoto, Y. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Enantioseparations on Capillary Columns Containing Crosslinked Polysaccharide Phenylcarbamate Derivatives Attached to Monolithic Silica. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1988–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chankvetadze, B.; Yamamoto, C.; Kamigaito, M.; Tanaka, N.; Nakanishi, K.; Okamoto, Y. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Enantioseparations on Capillary Columns Containing Monolithic Silica Modified with Amylose Tris(3,5-Dimethylphenylcarbamate). J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1110, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chankvetadze, B.; Yamamoto, C.; Tanaka, N.; Nakanishi, K.; Okamoto, Y. High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Enantioseparations on Capillary Columns Containing Monolithic Silica Modified with Cellulose Tris(3,5-Dimethylphenylcarbamate). J. Sep. Sci. 2004, 27, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Ghanem, A. Chiral β-Cyclodextrin Functionalized Polymer Monolith for the Direct Enantioselective Reversed Phase Nano Liquid Chromatographic Separation of Racemic Pharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1345, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Lin, H.; Tang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, J.; Zou, H. Hybrid Monolithic Columns Coated with Cellulose Tris(3,5-Dimethylphenyl-Carbamate) for Enantioseparations in Capillary Electrochromatography and Capillary Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1269, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, A.; Marzouk, A.A.; Shaykoon, M.S.A.; Ibrahim, S.M.; El-Adl, S.M.; Ghanem, A. Daptomycin: A Novel Macrocyclic Antibiotic as a Chiral Selector in an Organic Polymer Monolithic Capillary for the Enantioselective Analysis of a Set of Pharmaceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanem, A.; Ahmed, M.; Ishii, H.; Ikegami, T. Immobilized β-Cyclodextrin-Based Silica vs Polymer Monoliths for Chiral Nano Liquid Chromatographic Separation of Racemates. Talanta 2015, 132, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Guo, J.; Wang, F.; Crommen, J.; Jiang, Z. Preparation of a β-Cyclodextrin Functionalized Monolith via a Novel and Simple One-Pot Approach and Application to Enantioseparations. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1325, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A New Generation of Silica-Based Monoliths HPLC Columns with Improved Performance. Available online: https://www.chromatographyonline.com/view/new-generation-silica-based-monoliths-hplc-columns-improved-performance (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- El Deeb, S.; Ma, B.N.; Baecker, D.; Gust, R. Studies on the Stability of the Anticancer-Active [N,N′-Bis(Salicylidene)-1,2-Phenylenediamine]Chloridoiron(III) Complex under Pharmacological-like Conditions. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2019, 487, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Measurement of the Eddy Dispersion Term in Chromatographic Columns: III. Application to New Prototypes of 4.6mm I.D. Monolithic Columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1225, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sklenářová, H.; Chocholouš, P.; Koblová, P.; Zahálka, L.; Šatínský, D.; Matysová, L.; Solich, P. High-Resolution Monolithic Columns—A New Tool for Effective and Quick Separation. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Tara, A.; Sharma, V.D. Advances in Monolithic Silica Columns for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Ishizuka, N.; Minakuchi, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Hosoya, K.; Ikegami, T. Monolithic Silica Columns for High-Efficiency Chromatographic Separations. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 965, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deeb, S.; Schepers, U.; Wätzig, H. Evaluation of Monolithic C18 HPLC Columns for the Fast Analysis of Pilocarpine Hydrochloride in the Presence of Its Degradation Products. Pharmazie 2006, 61, 751–756. [Google Scholar]
- El Deeb, S. High Efficiency Separation Techniques: Fast HPLC Using Monolithic Silica Columns and Chiral Separation Using Capillary Zone Electrophoresis. Doctoral Thesis, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany, June 2007. [Google Scholar]
- El Deeb, S.; Preu, L.; Wätzig, H. Evaluation of Monolithic HPLC Columns for Various Pharmaceutical Separations: Method Transfer from Conventional Phases and Batch to Batch Repeatability. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- el Kurdi, S.; Muaileq, D.A.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Al Bratty, M.; El Deeb, S. Comparing Monolithic and Fused Core HPLC Columns for Fast Chromatographic Analysis of Fat-Soluble Vitamins. Acta Pharm. 2017, 67, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gritti, F.; Guiochon, G. Mass Transfer Kinetic Mechanism in Monolithic Columns and Application to the Characterization of New Research Monolithic Samples with Different Average Pore Sizes. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4752–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizuka, N.; Kobayashi, H.; Minakuchi, H.; Nakanishi, K.; Hirao, K.; Hosoya, K.; Ikegami, T.; Tanaka, N. Monolithic Silica Columns for High-Efficiency Separations by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 960, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-T.; Zeng, H.; Deng, Y.; Unger, S.E. High-Speed Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry Using a Monolithic Column for High-Throughput Bioanalysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2001, 15, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- al Bratty, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Javed, S.A.; Lalitha, K.G.; Asmari, M.; Wölker, J.; El Deeb, S. Development and Validation of LC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Metformin and Four Gliptins in Human Plasma. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deeb, S.; Waetzig, H. Performance Comparison between Monolithic C18 and Conventional C18 Particle-Packed Columns in the Liquid Chromatographic Determination of Propranolol HCl. Turk J Chem 2006, 30, 543–552. [Google Scholar]
- El Deeb, S. Monolithic Silica for Fast HPLC: Current Success and Promising Future. Chromatographia 2011, 74, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, K.; Minakuchi, H.; Soga, N.; Tanaka, N. Structure Design of Double-Pore Silica and Its Application to HPLC. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 1998, 13, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, M.; Abed, A.; El Deeb, S. Quality Control of Drugs. In Monolithic Silicas in Separation Science; Unger, K.K., Tanaka, N., Machtejevas, E., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; ISBN 9783527633241. [Google Scholar]
- León-González, M.E.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; Pérez-Arribas, L.V.; Guillén-Casla, V. Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography for Direct Chiral Separations: A Review. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.; Suhail, M.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y.; Kon’kova, T. Recent Trends in Chiral Separations by 2D-HPLC. Chromatographia 2021, 84, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, L.; El Deeb, S.; Wätzig, H. Repeatability of Monolithic HPLC Columns While Using a Flow Program. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Deeb, S.; Schepers, U.; Wätzig, H. Fast HPLC Method for the Determination of Glimepiride, Glibenclamide, and Related Substances Using Monolithic Column and Flow Program. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jandera, P.; Hájek, T.; Staňková, M. Monolithic and Core–Shell Columns in Comprehensive Two-Dimensional HPLC: A Review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deeb, S.; Preu, L.; Wätzig, H. A Strategy to Develop Fast RP-HPLC Methods Using Monolithic Silica Columns. J. Sep. Sci. 2007, 30, 1993–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deeb, S.; Ma, B.N.; Gust, R. Development and Validation of a LC Method for the Separation and Determination of the Anticancer-Active Fe III (4-Methoxy-Salophene) Using the New Second-Generation Monolith. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 3434–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Deeb, S.; Ma, B.N.; Gust, R. Determination of NiII(3-OMe-Salophene) in MCF7 and HT29 Cancer Cell Lines Using HR-CS-AAS and in Serum Albumin Using LC with Monolithic Silica. Microchem. J. 2012, 101, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, C.; Fanali, S.; Chankvetadze, B. HPLC Separation of Enantiomers of Some Flavanone Derivatives Using Polysaccharide-Based Chiral Selectors Covalently Immobilized on Silica. Chromatographia 2016, 79, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Ding, G. Enantioseparations in Capillary Electrochromatography Using Sulfated Poly β-Cyclodextrin-Modified Silica-Based Monolith as Stationary Phase. In Chiral Separation Methods and Protocols; Gerhard, K., Scriba, E., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2013; Volume 970, pp. 489–503. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.; Xue, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M. Preparation of a Novel Hydroxypropyl-γ-cyclodextrin Functionalized Monolith for Separation of Chiral Drugs in Capillary Electrochromatography. Chirality 2021, 33, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ji, Y. Monoliths with Proteins as Chiral Selectors for Enantiomer Separation. Talanta 2012, 91, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ji, Y. A Protein-Based Mixed Selector Chiral Monolithic Stationary Phase in Capillary Electrochromatography. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 13520–13528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Hendrickx, A.; Mangelings, D.; Smeyers-Verbeke, J.; vander Heyden, Y. Monolithic Silica Capillary Columns with Immobilized Cellulose Tris(3,5-Dimethylphenylcarbamate) for Enantiomer Separations in CEC. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 3796–3803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, A.; Marzouk, A.A.; Ibrahim, S.M.; El-Adl, S.M.; Ghanem, A. Functionalized Polymer Monoliths with Carbamylated Amylose for the Enantioselective Reversed Phase Nano-Liquid Chromatographic Separation of a Set of Racemic Pharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1515, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhenqun, L.; Li, J. Research Progress of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Separation of Chiral Drugs by Capillary Electrochromatography. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2020, 38, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-H.; Dong, Q.; Ying, L.-L.; Chi, S.-S.; Lan, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-P.; Liu, Z.-S. Enhancement of Selective Separation on Molecularly Imprinted Monolith by Molecular Crowding Agent. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, A.-N.; Wang, X.-N.; Ding, G.-S.; Yan, X.-P. On-Line Preconcentration and Enantioseparation of Thalidomide Racemates by CEC with the Hyphenation of Octyl and Norvancomycin Monoliths. Electrophoresis 2009, 30, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, J.H. Enantioseparation of Chiral Acids and Bases on a Clindamycin Phosphate-Modified Zirconia Monolith by Capillary Electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1251, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, A.; Shaykoon, M.; Ibrahim, S.; El-Adl, S.; Ghanem, A. Colistin Sulfate Chiral Stationary Phase for the Enantioselective Separation of Pharmaceuticals Using Organic Polymer Monolithic Capillary Chromatography. Molecules 2019, 24, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmid, M.G.; Koidl, J.; Wank, P.; Kargl, G.; Zöhrer, H.; Gübitz, G. Enantioseparation by Ligand-Exchange Using Particle-Loaded Monoliths: Capillary-LC versus Capillary Electrochromatography. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 2007, 70, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Correa, E.J.; Ferri, M.; Woiwode, U.; Ma, Y.; Herrero-Martínez, J.M.; Ramis-Ramos, G.; Lindner, W.; Lämmerhofer, M. Zwitterionic Codeine-Derived Methacrylate Monoliths for Enantioselective Capillary Electrochromatography of Chiral Acids and Chiral Bases. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2558–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, M.; Lämmerhofer, M. In-Situ Functionalized Monolithic Polysiloxane-Polymethacrylate Composite Materials from Polythiol-Ene Double Click Reaction in Capillary Column Format for Enantioselective Nano-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1497, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novell, A.; Méndez, A.; Minguillón, C. Effects of Supercritical Fluid Chromatography Conditions on Enantioselectivity and Performance of Polyproline-Derived Chiral Stationary Phases. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1403, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, D.; Crommen, J.; Jiang, Z. Recent Advances in Preparation and Applications of Monolithic Chiral Stationary Phases. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 123, 115774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Lee, W.; Hyun, M.H.; Park, J.H. Enantioseparation of α-Amino Acids on an 18-Crown-6-Tetracarboxylic Acid-Bonded Silica by Capillary Electrochromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Tian, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, Z. Terminal-Vinyl Liquid Crystal Crown Ether-Modified, Vinyl-Functionalized Hybrid Silica Monolith for Capillary Electrochromatography. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 1975–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Otsuka, K.; Terabe, S.; Motokawa, M.; Tanaka, N. Physically Adsorbed Chiral Stationary Phase of Avidin on Monolithic Silica Column for Capillary Electrochromatography and Capillary Liquid Chromatography. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 2973–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Crommen, J.; Jiang, Z. Recent Developments in Cyclodextrin Functionalized Monolithic Columns for the Enantioseparation of Chiral Drugs. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 130, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Rao, L.; He, T.; Crommen, J.; Sun, P.; Jiang, Z. A Facile and Efficient One-Step Strategy for the Preparation of β-Cyclodextrin Monoliths. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2441–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, M.D.; Fréchet, J.M.J.; Svec, F. In-Column Preparation of a Brush-Type Chiral Stationary Phase Using Click Chemistry and a Silica Monolith. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ran, D.; Crommen, J.; Jiang, Z. One-Step Strategy for the Synthesis of a Derivatized Cyclodextrin-Based Monolithic Column. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratih, R.; Wätzig, H.; Azminah, A.; Asmari, M.; Peters, B.; El Deeb, S. Immobilization of Chondroitin Sulfate A onto Monolithic Epoxy Silica Column as a New Chiral Stationary Phase for High-Performance Liquid Chromatographic Enantioseparation. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai-Kato, K.; Kato, M.; Nakakuki, H.; Toyo’oka, T. Investigation of Structure and Enantioselectivity of BSA-Encapsulated Sol–Gel Columns Prepared for Capillary Electrochromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2003, 31, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, M.; Sakai-Kato, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Toyo’oka, T. A Protein-Encapsulation Technique by the Sol−Gel Method for the Preparation of Monolithic Columns for Capillary Electrochromatography. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Ghanem, A. Enantioselective Nano Liquid Chromatographic Separation of Racemic Pharmaceuticals: A Facile One-Pot In Situ Preparation of Lipase-Based Polymer Monoliths in Capillary Format. Chirality 2014, 26, 754–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, O.; Nakanishi, K.; Tanaka, N. Preparation of Monolithic Silica Columns for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1191, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoo, H.T.; Leow, C.H. Advancements in the Preparation and Application of Monolithic Silica Columns for Efficient Separation in Liquid Chromatography. Talanta 2021, 224, 121777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, R.; Xuan, H.; Hage, D.S. Development of an Affinity Silica Monolith Containing A1-Acid Glycoprotein for Chiral Separations. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1149, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mallik, R.; Hage, D.S. Development of an Affinity Silica Monolith Containing Human Serum Albumin for Chiral Separations. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pittler, E.; Schmid, M.G. Enantioseparation of Dansyl Amino Acids by HPLC on a Monolithic Column Dynamically Coated with a Vancomycin Derivative. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, Q.; Sánchez-López, E.; Jiang, Z.; Marina, M.L. Preparation of an O-[2-(Methacryloyloxy)-Ethylcarbamoyl]-10,11-Dihydroquinidine-Silica Hybrid Monolithic Column for the Enantioseparation of Amino Acids by Nano-Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1593, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Sánchez-López, E.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Marina, M.L. Determination of L-Norvaline and l-Tryptophan in Dietary Supplements by Nano-LC Using an O-[2-(Methacryloyloxy)-Ethylcarbamoyl]-10,11-Dihydroquinidine-Silica Hybrid Monolithic Column. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH Q3B (R2) Impurities in New Drug Products | European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-q3b-r2-impurities-new-drug-products (accessed on 7 May 2021).
- Yu, X.; Yao, Z.-P. Chiral Recognition and Determination of Enantiomeric Excess by Mass Spectrometry: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 968, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kang, Y.; Zeng, S. Analysis of Stereoisomers of Chiral Drug by Mass Spectrometry. Chirality 2018, 30, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.V.; Kawai, T.; Wang, L.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Sweedler, J.V. Chiral Measurement of Aspartate and Glutamate in Single Neurons by Large-Volume Sample Stacking Capillary Electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12375–12382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, L.; Yang, B.; Jin, Y.; Zheng, K.; He, Z. A Novel Potential Primary Method for Quantification of Enantiomers by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Circular Dichroism. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, Y.; Kaida, Y. Resolution by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Using Polysaccharide Carbamates and Benzoates as Chiral Stationary Phases. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 666, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y. Significance of Mobile Phase Composition in Enantioseparation of Chiral Drugs by HPLC on a Cellulose-Based Chiral Stationary Phase. Chirality 1996, 8, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-M.; Nakagama, T.; Uchiyama, K.; Hobo, T. Temperature Effect on Chiral Recognition of Some Amino Acids with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Filled Capillary Electrochromatography. Biomed. Chromatogr. 1997, 11, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, S.; Schön, A.; Isaksson, R.; Pettersson, C.; Pettersson, G. An Unexpected Temperature Effect Obtained on Enantiomer Separation Using CBH I-Silica as a Chiral Stationary Phase: Increase in Retention and Enantioselectivity at Elevated Column Temperature: A Chromatographic and Microcalorimetric Study. Chirality 1992, 4, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haginaka, J.; Wakai, J.; Takahashi, K.; Yasuda, H.; Katagi, T. Chiral Separation of Propranolol and Its Ester Derivatives on an Ovomucoid-Bonded Silica: Influence of PH, Ionic Strength and Organic Modifier on Retention, Enantioselectivity and Enantiomeric Elution Order. Chromatographia 1990, 29, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, J.; Arnell, R.; Fornstedt, T. Potential of Adsorption Isotherm Measurements for Closer Elucidating of Binding in Chiral Liquid Chromatographic Phase Systems. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 1491–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelander, H.; Andersson, S.; Öhlén, K. Evaluation of the Chiral Recognition Properties as Well as the Column Performance of Four Chiral Stationary Phases Based on Cellulose (3,5-Dimethylphenylcarbamate) by Parallel HPLC and SFC. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 9397–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easson, L.H.; Stedman, E. Studies on the Relationship between Chemical Constitution and Physiological Action. Biochem. J. 1933, 27, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.K.; Bai, S.; Vyas, S.; Wirth, M.J. NMR and Computational Studies of Chiral Discrimination by Amylose Tris(3,5-Dimethylphenylcarbamate). J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasat, R.B.; Franses, E.I.; Wang, N.-H.L. Experimental and Computational Studies of Enantioseparation of Structurally Similar Chiral Compounds on Amylose Tris(3,5-Dimethylphenylcarbamate). Chirality 2009, 22, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godschalk, F.; Genheden, S.; Söderhjelm, P.; Ryde, U. Comparison of MM/GBSA Calculations Based on Explicit and Implicit Solvent Simulations. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 7731–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Z. Computational Study of Enantioseparation by Amylose Tris(3,5-Dimethylphenylcarbamate)-Based Chiral Stationary Phase. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3245–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; House, D.W.; Oroskar, P.A.; Oroskar, A.; Oroskar, A.; Jameson, C.J.; Murad, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Chiral Recognition Mechanism for a Polysaccharide Chiral Stationary Phase in Enantiomeric Chromatographic Separations. Mol. Phys. 2019, 117, 3569–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Oroskar, P.A.; Wang, X.; House, D.; Oroskar, A.; Oroskar, A.; Jameson, C.; Murad, S. The Composition of the Mobile Phase Affects the Dynamic Chiral Recognition of Drug Molecules by the Chiral Stationary Phase. Langmuir 2017, 33, 11246–11256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Jameson, C.J.; Murad, S. Modeling Enantiomeric Separations as an Interfacial Process Using Amylose Tris(3,5-Dimethylphenyl Carbamate) (ADMPC) Polymers Coated on Amorphous Silica. Langmuir 2020, 36, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, C.J.; Wang, X.; Murad, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Enantiomeric Separations as an Interfacial Process in HPLC. AIChE J. 2021, 67, e17143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jameson, C.J.; Murad, S. Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Chiral Recognition of Drugs by Amylose Polymers Coated on Amorphous Silica. Mol. Phys. 2021, e1922772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggeri, R.; Rossi, D.; Collina, S.; Mannucci, B.; Baierl, M.; Juza, M. Quick Development of an Analytical Enantioselective High Performance Liquid Chromatography Separation and Preparative Scale-up for the Flavonoid Naringenin. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 5414–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asmari, M.; Wang, X.; Casado, N.; Piponski, M.; Kovalenko, S.; Logoyda, L.; Hanafi, R.S.; El Deeb, S. Chiral Monolithic Silica-Based HPLC Columns for Enantiomeric Separation and Determination: Functionalization of Chiral Selector and Recognition of Selector-Selectand Interaction. Molecules 2021, 26, 5241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175241
Asmari M, Wang X, Casado N, Piponski M, Kovalenko S, Logoyda L, Hanafi RS, El Deeb S. Chiral Monolithic Silica-Based HPLC Columns for Enantiomeric Separation and Determination: Functionalization of Chiral Selector and Recognition of Selector-Selectand Interaction. Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175241
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsmari, Mufarreh, Xiaoyu Wang, Natalia Casado, Marjan Piponski, Sergiy Kovalenko, Liliya Logoyda, Rasha Sayed Hanafi, and Sami El Deeb. 2021. "Chiral Monolithic Silica-Based HPLC Columns for Enantiomeric Separation and Determination: Functionalization of Chiral Selector and Recognition of Selector-Selectand Interaction" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175241
APA StyleAsmari, M., Wang, X., Casado, N., Piponski, M., Kovalenko, S., Logoyda, L., Hanafi, R. S., & El Deeb, S. (2021). Chiral Monolithic Silica-Based HPLC Columns for Enantiomeric Separation and Determination: Functionalization of Chiral Selector and Recognition of Selector-Selectand Interaction. Molecules, 26(17), 5241. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175241









