Vitamin D Fortification of Consumption Cow’s Milk: Health, Nutritional and Technological Aspects. A Multidisciplinary Lecture of the Recent Scientific Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Vitamin D
3. Vitamin D and Bone Health
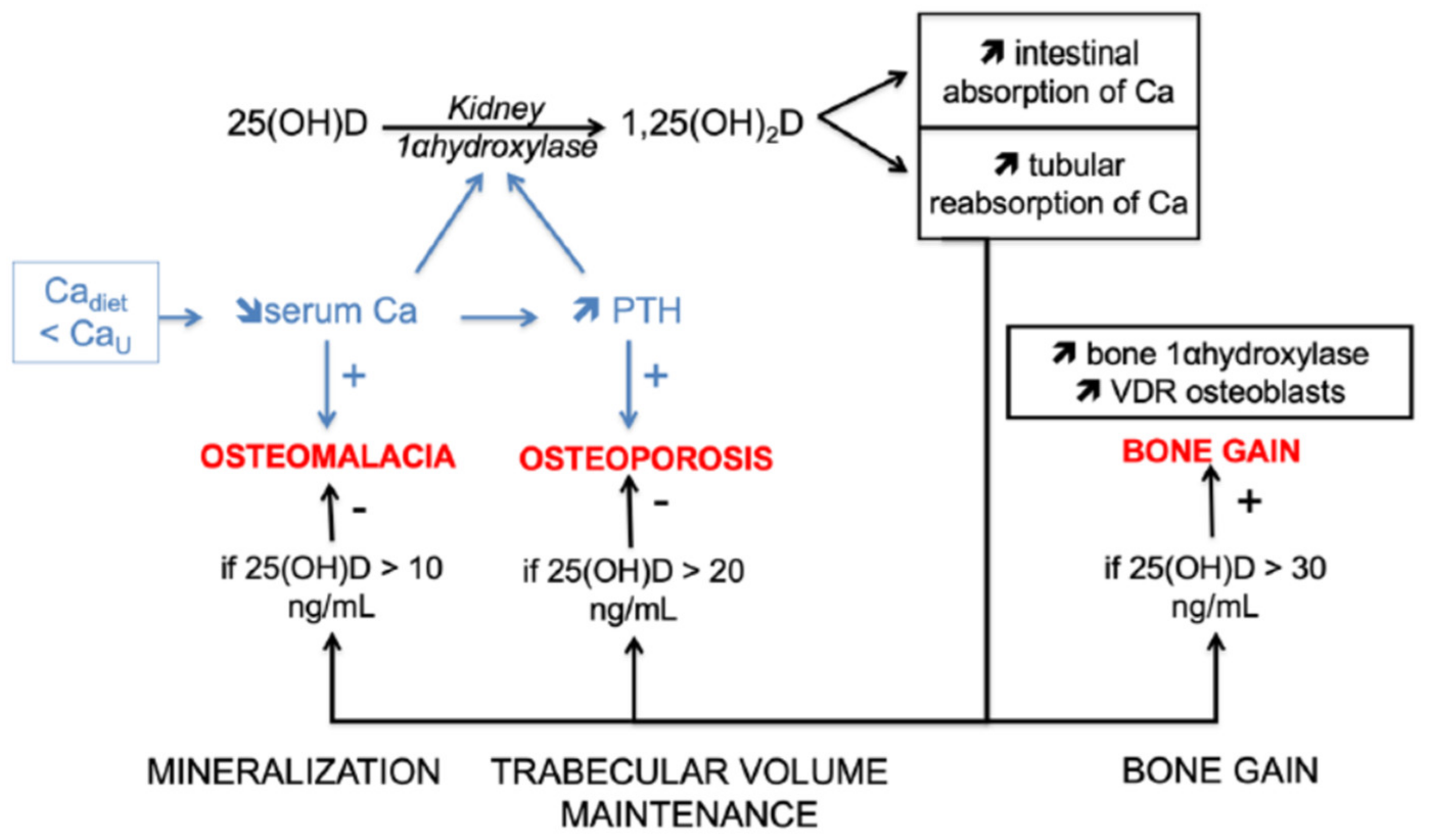
3.1. Biomolecular Effects of Vitamin D on Bone
3.2. Clinical Effects of Vitamin D Deficiency on Bone According to Age
3.3. Bone Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation According to Age
4. Vitamin D and Non-Skeletal Effects
5. Vitamin D Status: Role of the Dietary Intake
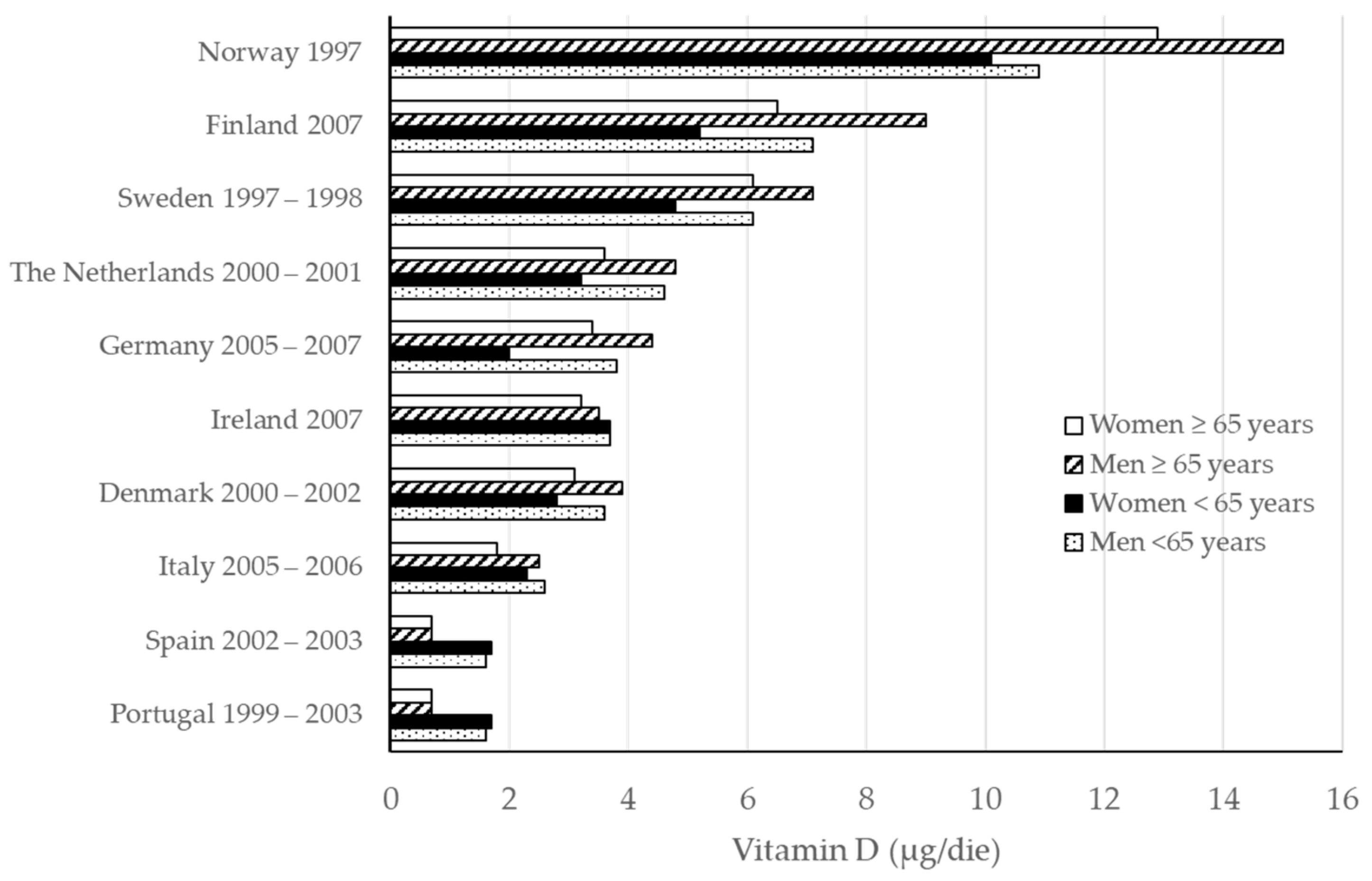
5.1. Epidemiology
5.2. Nutritional Recommendations and Dietary Intake
6. Milk as an Optimal Carrier of Vitamin D
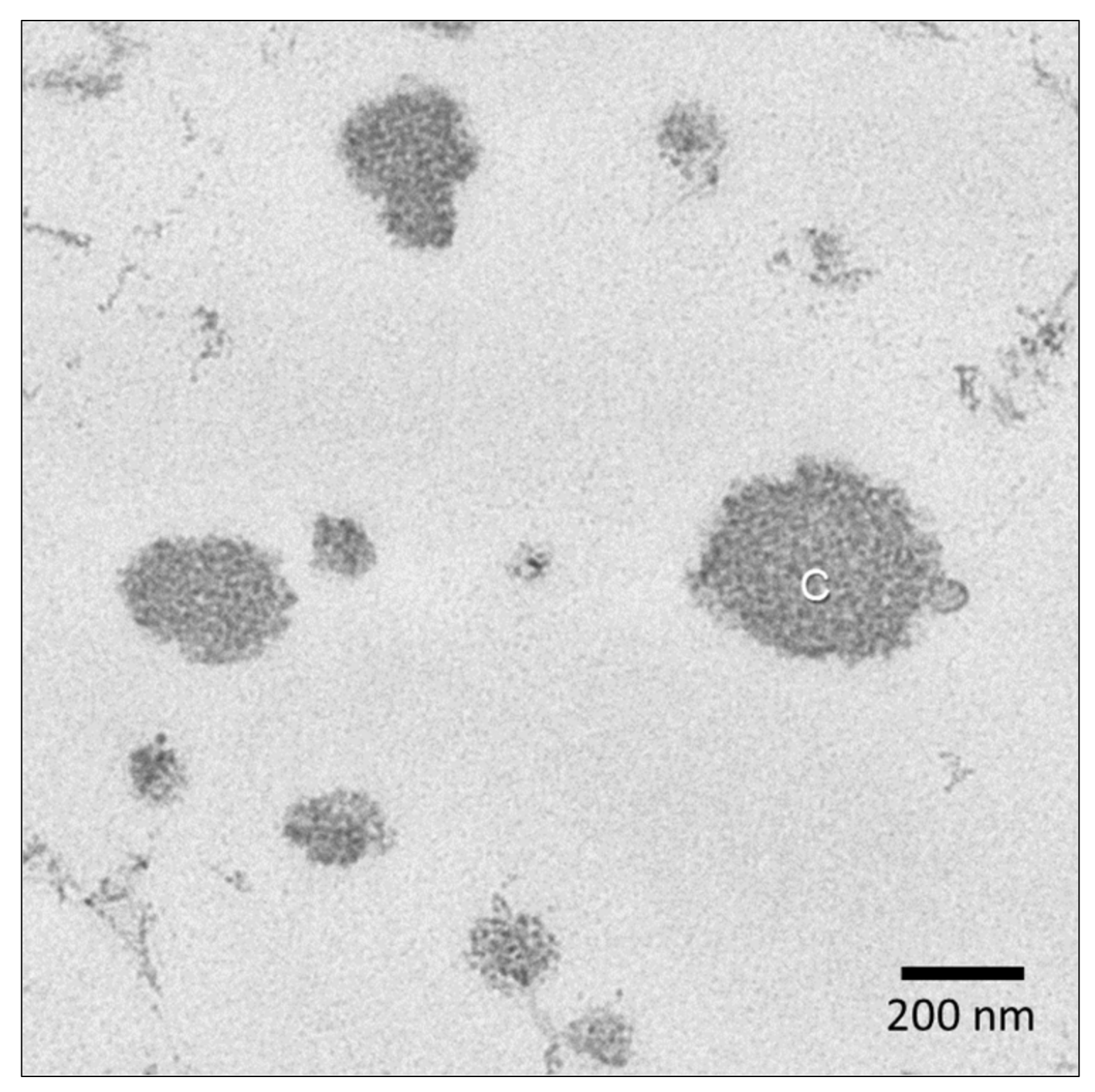
6.1. Casein Micelles and Whey Proteins
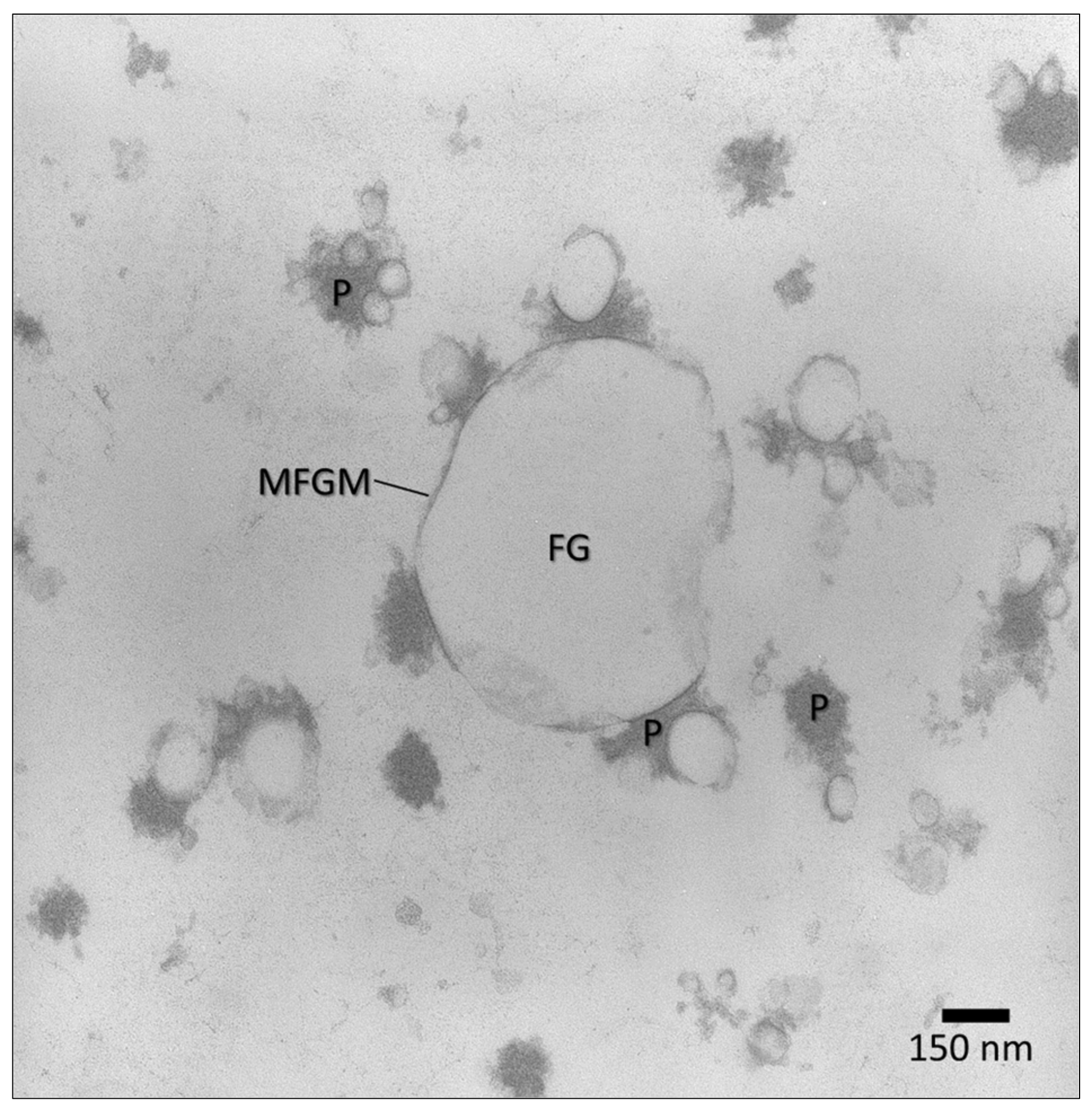
6.2. Fat Globules
6.3. Industrial Processes and Storage of Milk
7. Fortification Policies
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cashman, K.D.; Dowling, K.G.; Škrabáková, Z.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Valtueña, J.; De Henauw, S.; Moreno, L.; Damsgaard, C.T.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mølgaard, C.; et al. Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: Pandemic? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Baylin, A.; Levy, P.D. Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency among US adults: Prevalence, predictors and clinical implications. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, P.; Cashman, K.D.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Obermayer-Pietsch, B.; Bianchi, M.L.; Stepan, J.; El-Hajj Fuleihan, G.; Bouillon, R. Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: A position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA, Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to vitamin D and normal function of the immune system and inflammatory response (ID 154, 159), maintenance of normal muscle function (ID 155) and maintenance of normal cardiovascular function (ID 159) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- EFSA, Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific opinion on the substantiation of a health claim related to vitamin D and contribution to the normal function of the immune system pursuant to Article 14 of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Scientific Advisory Committee on Nutrition (SACN). Vitamin D and Health Report Public Health England. 2016. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/sacn-vitamin-d-and-health-report (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Zahedirad, M.; Asadzadeh, S.; Nikooyeh, B.; Neyestani Tirang, R.; Khorshidian, N.; Yousefi, M.; Mortazavian Amir, M. Fortification aspects of vitamin D in dairy products: A review study. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 94, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Dairy Federation (IDF) Bulletin N° 506/2020: The World Dairy Situation. 2020. Available online: https://fil-idf:newsinsights/idf-world-dairy-situation-report-2020/ (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- FAO, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Gateway to Dairy Production and Products. 2018. Available online: http://www.fao.org/dairy-production-products/production/en/ (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- International Dairy Federation (IDF). Dairy’s Role in Healthy and Sustainable Diets (Version 6 March 2020). Available online: https://fil-idf.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/IDF-position-to-FAO-WHO-guiding-principles-on-sustainable-healthy-diets.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Schmid, A.; Walther, B. Natural Vitamin D Content in Animal Products. Adv. Nutr. 2013, 4, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasalová, E.; Aufartová, J.; Kujovská Krčmová, L.; Solichová, D.; Solich, P. Recent trends in the analysis of vitamin D and its metabolites in milk—A review. Food Chem. 2015, 171, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itkonen, S.; Erkkola, M.; Lamberg-Allardt, C. Vitamin D Fortification of Fluid Milk Products and Their Contribution to Vitamin D Intake and Vitamin D Status in Observational Studies—A Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annweiler, C.; Kabeshova, A.; Callens, A.; Paty, M.L.; Duval, G.T.; Holick, M.F. Self-administered Vitamin D Status Predictor: Older adults are able to use a self-questionnaire for evaluating their vitamin D status. PLoS ONE 2017, 11, 0186578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Altieri, B.; Annweiler, C.; Balercia, G.; Pal, H.B.; Boucher, B.J.; Cannell, J.J.; Foresta, C.; Grübler, M.R.; Kotsa, K.; et al. Vitamin D and chronic diseases: The current state of the art. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christakos, S.; Ajibade, D.V.; Dhawan, P.; Fechner, A.J.; Mady, L.J. Vitamin D: Metabolism. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G. Introduction to Vitamin D: Current evidence and future directions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1491–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, W.B.; Anouti, F.; Moukayed, M. Targeted 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration measurements and vitamin D3 supplementation can have important patient and public health benefits. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lips, P. Vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism in the elderly: Consequences for bone loss and fractures and therapeutic implications. Endocr. Rev. 2001, 22, 477–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover, J.; Egido, J.; Fernández-Giráldez, E.; Praga, M.; Solozábal-Campos, C.; Torregrosa, J.V.; Martínez-Castelao, A. Vitamin D, vitamin D receptor and the importance of its activation in patients with chronic kidney disease. Rev. Nefrol. 2015, 35, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lips, P.; van Schoor, N.M. The effect of vitamin D on bone and osteoporosis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfitt, A.M.; Rao, D.S.; Stanciu, J.; Villanueva, A.R.; Kleerekoper, M.; Frame, B. Irreversible bone loss in osteomalacia. Comparison of radial photon absorptiometry with iliac bone histomorphometry during treatment. J. Clin. Investig. 1985, 76, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Rizzoli, R.; Chevalley, T.; Slosman, D.; Eisman, J.A.; Bonjour, J.P. Vitamin-D- receptor-gene polymorphisms and change in lumbar-spine bone mineral density. Lancet 1995, 345, 423–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allgrove, J.; Shaw, N.J.; Allgrove, J.; Shaw, N.J. A Practical Approach to Vitamin D Deficiency and Rickets. In Calcium and Bone Disorders in Children and Adolescents; Allgrove, J., Shaw, N.J., Eds.; Endocrine Development Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 28, pp. 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Vitamin D: Supplement Use in Specific Population Groups; Public Health Guideline (PH56); National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE): London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- National Health Service (NHS). Treatment of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults. Reviewed June 2020. Available online: https://mm.wirral.nhs.uk/document_uploads/guidelines/Vitamin%20D%20Guidelines%20for%20Adults%20v2.pdf (accessed on 21 June 2021).
- Schilling, S. Epidemic vitamin D deficiency among patients in an elderly care rehabilitation facility. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2012, 109, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F.; Matsuoka, L.Y.; Wortsman, J. Age, vitamin D, and solar ultraviolet. Lancet 1989, 334, 1104–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, G.T.; Rolland, G.Y.; Schott, A.M.; Blain, H.; Dargent-Molina, P.; Walrand, S.; Duque, G.; Annweiler, C. Association of hypovitaminosis D with triceps brachii muscle fatigability among older women: Findings from the EPIDOS cohort. Maturitas 2018, 111, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Staehelin, H.B.; Orav, J.E.; Stuck, A.E.; Theiler, R.; Wong, J.B.; Egli, A.; Kiel, D.P.; Henschkowski, J. Fall prevention with supplemental and active forms of vitamin D: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2009, 339, b3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Resurrection of vitamin D deficiency and rickets. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 2062–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, Y.; Mathieu, C.; Piau, C.; Cayla, F.; Bouget, C.; Vellas, B.; De Souto Barreto, P. Improving the Quality of Care of Long-Stay Nursing Home Residents in France. J. Am. Geriat. Soc. 2016, 64, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Willett, W.C.; Wong, J.B.; Giovannucci, E.; Dietrich, T.; Dawson-Hughes, B. Fracture prevention with vitamin D supplementation: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. JAMA 2005, 293, 2257–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Willett, W.C.; Wong, J.B.; Stuck, A.E.; Staehelin, H.B.; Orav, E.J.; Thoma, A.; Kiel, D.P.; Henschkowski, J. Prevention of nonvertebral fractures with oral vitamin D and dose dependency: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annweiler, C.; Beauchet, O. Questioning vitamin D status of elderly fallers and nonfallers: A meta-analysis to address a ‘forgotten step’. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 277, 16–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Bennett, D.; Mafham, M.; Lin, X.; Chen, Z.; Armitage, J.; Clarke, R. Vitamin D and calcium for the prevention of fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1917789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, I.R.; Bolland, M.J.; Grey, A. Effects of vitamin D supplements on bone mineral density: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2014, 383, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Mitri, J.; Mathieu, C.; Badenhoop, K.; Tamer, G.; Orio, F.; Mezza, T.; Vieth, R.; Colao, A.; Pittas, A. Mechanisms in endocrinology: Vitamin D as a potential contributor in endocrine health and disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 171, R101–R110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, B.; Grant, W.B.; Della Casa, S.; Orio, F.; Pontecorvi, A.; Colao, A.; Sarno, G.; Muscogiuri, G. Vitamin D and pancreas: The role of sunshine vitamin in the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus and pancreatic cancer. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3472–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Scannapieco, M.; Di Somma, C.; Scacchi, M.; Aimaretti, G.; Savastano, S.; Colao, A.; Marzullo, P. The lullaby of the sun: The role of vitamin D in sleep disturbance. Sleep Med. 2019, 54, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenngam, N.; Holick, M.F. Immunologic effects of vitamin D on human health and disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K. A review of the critical role of vitamin D in the functioning of the immune system and the clinical implications of vitamin D deficiency. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, D.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.; Bergeron, G.; Bourassa, M.W.; Brown, K.H.; Calvo, M.S.; Cashman, K.D.; Combs, G.; De-Regil, L.M.; et al. Global prevalence and disease burden of vitamin D deficiency: A roadmap for action in low- and middle-income countries. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2018, 1430, 44–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ODIN (Food-Based Solutions for Optimal Vitamin D Nutrition and Health through the Life Cycle). Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/613977/reporting/it (accessed on 5 June 2021).
- Wahl, D.A.; Cooper, C.; Ebeling, P.R.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Hilger, J.; Hoffmann, K.; Josse, R.; Kanis, J.A.; Mithal, A.; Pierroz, D.D.; et al. A global representation of vitamin D status in healthy populations. Arch. Osteoporos. 2012, 7, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiro, A.; Buttriss, J.L. Vitamin D: An overview of vitamin D status and intake in Europe. Nutr. Bull. 2014, 39, 322–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schoor, N.; Lips, P. Global Overview of Vitamin D Status. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 845–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Anagnostis, P.; Annweiler, C.; Naughton, D.P.; Petroczi, A.; Bili, E.; Harizopoulou, V.; Tarlatzis, B.C.; Persinaki, A.; Papadopoulou, F.; et al. Maternal vitamin D status during pregnancy: The Mediterranean reality. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braegger, C.; Campoy, C.; Colomb, V.; Decsi, T.; Domellof, M.; Fewtrell, M.; Hojsak, I.; Mihatsch, W.; Molgaard, C.; Shamir, R.; et al. Vitamin D in the Healthy European Paediatric Population. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrick, K.A.; Storandt, R.J.; Afful, J.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Schleicher, R.L.; Gahche, J.J.; Potischman, N. Vitamin D status in the United States, 2011–2014. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calame, W.; Street, L.; Hulshof, T. Vitamin D Serum Levels in the UK Population, including a Mathematical Approach to Evaluate the Impact of Vitamin D Fortified Ready-to-Eat Breakfast Cereals: Application of the NDNS Database. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 October 2011 on the provision of food information to consumers, amending Regulations (EC) No 1924/2006 and (EC) No 1925/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council, and repealing Commission Directive 87/250/EEC, Council Directive 90/496/EEC, Commission Directive 1999/10/EC, Directive 2000/13/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Commission Directives 2002/67/EC and 2008/5/EC and Commission Regulation (EC) No 608/2004. Off. J. Eur. Un. L. 2011, 304, 18–63.
- EFSA, Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on the Tolerable Upper Intake Level of vitamin D. EFSA J. 2012, 10, 2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresson, J.L.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.; Naska, A.; Neuhäuser-Berthold, M.; et al. Dietary reference values for vitamin D. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.; Adler, R.A.; Binkley, N.; Bollerslev, J.; Bouillon, R.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Ebeling, P.R.; Feldman, D.; Formenti, A.M.; Lazaretti-Castro, M.; et al. Consensus statement from 2nd International Conference on Controversies in Vitamin D. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2020, 21, 89–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freisling, H.; Fahey, M.T.; Moskal, A.; Ocké, M.C.; Ferrari, P.; Jenab, M.; Norat, T.; Naska, A.; Welch, A.A.; Navarro, C.; et al. Region-specific nutrient intake patterns exhibit a geographical gradient within and between European countries. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1280–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmadfa, I.; Meyer, A.; Nowak, V.; Hasenegger, V.; Putz, P.; Verstraeten, R.; Remaut-DeWinter, A.M.; Kolsteren, P.; Dostálová, J.; Dlouhý, P.; et al. European Nutrition and Health Report 2009. Forum Nutr. 2009, 62, 1–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelli, V.; D’Incecco, P.; Pellegrino, L. Vitamin D incorporation in foods: Formulation strategies, stability and bioaccessibility as affected by the food matrix. Foods 2021, 10, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, F.; Pellegrino, L.; Verduci, E.; Ghiselli, A.; Bernabei, R.; Calvani, R.; Irene, C.; Michelangelo, G.; Francesco, P.; Luca, P.; et al. Cow’s milk consumption and health: A health professional’s guide. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. Regulation of fluid flow through the mammary gland of dairy cows and its effect on milk production: A systematic review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo-Fani, A.; Dave, A.; Singh, H. Nature-assembled structures for delivery of bioactive compounds and their potential in functional foods. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 564021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huppertz, T.; Gazi, I.; Luyten, H.; Nieuwenhuijse, H.; Alting, A.; Schokker, E. Hydration of casein micelles and caseinates: Implications for casein micelle structure. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 74, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, R.; Dokland, T.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.; Harte, F. Cryo-transmission electron tomography of native casein micelles from bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5770–5775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Y.; Margier, M.; Lesmes, U.; Reboul, E.; Livney, Y.D.D. Mechanisms of Absorption of Vitamin D3 Delivered in Protein Nanoparticles in the Absence and Presence of Fat. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 4935–4946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Incecco, P.; Rosi, V.; Cabassi, G.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Pellegrino, L. Microfiltration and ultra-high-pressure homogenization for extending the shelf-storage stability of UHT milk. Food Res. Int. 2018, 107, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, L. β-Lactoglobulin, Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 211–259. [Google Scholar]
- Kimpel, F.; Schmitt, J.J. Review: Milk Proteins as Nanocarrier Systems for Hydrophobic Nutraceuticals. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, 2361–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, P.C.; Sheehy, P.A. Minor Proteins, Including Growth Factors. Advanced Dairy Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 317–335. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.; Gallier, S. Nature’s complex emulsion: The fat globules of milk. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 68, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Incecco, P.; Ong, L.; Pellegrino, L.; Faoro, F.; Barbiroli, A.; Gras, S. Effect of temperature on the microstructure of fat globules and the immunoglobulin-mediated interactions between fat and bacteria in natural raw milk creaming. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2984–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshehab, M.; Reis, M.G.; Day, L.; Nitin, N. Milk fat globules, a novel carrier for delivery of exogenous cholecalciferol. Food Res. Int. 2019, 126, 108579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunick, M.H.; Ren, D.X.; Van Hekken, D.L.; Bonnaillie, L.; Paul, M.; Kwoczak, R.; Tomasula, P.M. Effect of heat and homogenization on in vitro digestion of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeid, S.; Guyomarc’h, F.G.; Tanguy Leconte, N.; Rousseau, F.; Dolivet, A.; Leduc, A.; Wu, X.; Cauty, C.; Jan, G.; Gaucheron, F.; et al. The adhesion of homogenized fat globules to proteins is increased by milk heat treatment and acidic pH: Quantitative insights provided by AFM force spectroscopy. Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, A.L.; Metzger, L.E. Evaluation of increased vitamin D fortification in high-temperature, short-time–processed 2% milk, UHT-processed 2% fat chocolate milk, and low-fat strawberry yogurt. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, A.; Cashman, K.D. Food-based solutions for vitamin D deficiency: Putting policy into practice and the key role for research. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrein, K.; Scherkl, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Neuwersch-Sommeregger, S.; Köstenberger, M.; Tmaya-Berisha, A.; Martucci, G.; Pilz, S.; Malle, O. Vitamin D deficiency 2.0: An update on the current status worldwide. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 74, 1498–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakur, Y.A.; Lou, W.; L’Abbe, M.R. Examining the effects of increased vitamin D fortification on dietary inadequacy in Canada. Can. J. Public Health 2014, 105, e127–e132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jääskeläinen, T.; Itkonen, S.T.; Lundqvist, A.; Erkkola, M.; Koskela, T.; Lakkala, K.; Dowling, K.G.; Hull, G.L.; Kröger, H.; Karppinen, J.; et al. The positive impact of general vitamin D food fortification policy on vitamin D status in a representative adult Finnish population: Evidence from an 11-y follow-up based on standardized 25-hydroxyvitamin D data. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, S.; Eloranta, A.M.; Lindi, V.; Venäläinen, T.; Zaproudina, N.; Mahonen, A.; Lakka, T.A. Determinants of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration in Finnish children: The Physical Activity and Nutrition in Children (PANIC) study. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duus, K.S.; Moos, C.; Frederiksen, P.; Andersen, V.; Heitmann, B.L. Prenatal and Early Life Exposure to the Danish Mandatory Vitamin D Fortification Policy Might Prevent Inflammatory Bowel Disease Later in Life: A Societal Experiment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pellegrino, L.; Marangoni, F.; Muscogiuri, G.; D’Incecco, P.; Duval, G.T.; Annweiler, C.; Colao, A. Vitamin D Fortification of Consumption Cow’s Milk: Health, Nutritional and Technological Aspects. A Multidisciplinary Lecture of the Recent Scientific Evidence. Molecules 2021, 26, 5289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175289
Pellegrino L, Marangoni F, Muscogiuri G, D’Incecco P, Duval GT, Annweiler C, Colao A. Vitamin D Fortification of Consumption Cow’s Milk: Health, Nutritional and Technological Aspects. A Multidisciplinary Lecture of the Recent Scientific Evidence. Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175289
Chicago/Turabian StylePellegrino, Luisa, Franca Marangoni, Giovanna Muscogiuri, Paolo D’Incecco, Guillaume T. Duval, Cedric Annweiler, and Annamaria Colao. 2021. "Vitamin D Fortification of Consumption Cow’s Milk: Health, Nutritional and Technological Aspects. A Multidisciplinary Lecture of the Recent Scientific Evidence" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175289
APA StylePellegrino, L., Marangoni, F., Muscogiuri, G., D’Incecco, P., Duval, G. T., Annweiler, C., & Colao, A. (2021). Vitamin D Fortification of Consumption Cow’s Milk: Health, Nutritional and Technological Aspects. A Multidisciplinary Lecture of the Recent Scientific Evidence. Molecules, 26(17), 5289. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175289









