Carotenoid Contents of Lycium barbarum: A Novel QAMS Analyses, Geographical Origins Discriminant Evaluation, and Storage Stability Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
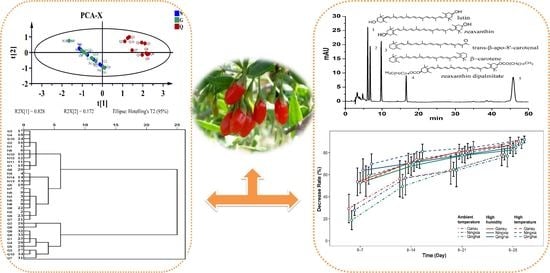
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
2.2. Calculation of Relative Correction Factor
2.3. Validation of the Method
2.3.1. Linearity, LOD and LOQ Tests
2.3.2. Accuracy Tests
2.3.3. Precision Tests
2.3.4. Sample Solution Stability Tests
2.3.5. Ruggedness Tests
2.4. Quantitative Determination of Carotenoids in LB Samples
2.5. Storage Condition and Stable Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents and Chemicals
3.2. Instruments and Chromatographic Conditions
3.3. Preparation of Standard and Sample Solutions
3.4. Calculation of Relative Correction Factor, Relative Retention Time and Quantification of Carotenoids in Different LB Samples
3.5. Stability Evaluation of LB
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
Abbreviations
| BHT | 2,6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol |
| ESM | external standard method |
| HCA | hierarchical cluster analysis |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| OPLS-DA | orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis |
| QAMS | qualitative and quantitative analysis of multi-components by single marker methods |
| RCF | relative correction factor |
| RRT | relative retention time |
| RSD | relative standard deviations |
| SMD | standard method difference |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicines |
References
- Neelam, K.; Dey, S.; Sim, R.; Lee, J.; Au, E.K. Fructus lycii: A Natural Dietary Supplement for Amelioration of Retinal Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Heinrich, M.; Weckerle, C.S. The genus Lycium as food and medicine: A botanical, ethnobotanical and historical review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 212, 50–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, F.; Yan, H.; Qian, D.W.; Wang, H.Q.; Jin, L.; Duan, J.A. Comparison of Functional Components and Antioxidant Activity of Lycium barbarum L. Fruits from Different Regions in China. Molecules 2019, 24, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, R.C.; So, K.F. Use of anti-aging herbal medicine, Lycium barbarum, against aging-associated diseases. What do we know so far? Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 28, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chang, S.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B. Isolation of carotenoids, flavonoids and polysaccharides from Lycium barbarum L. and evaluation of antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhao, J.; Xi, W. Functional constituents and antioxidant activities of eight Chinese native goji genotypes. Food Chem. 2016, 200, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenariu, D.; Fischer-Fodor, E.; Tigu, A.B.; Bunea, A.; Virag, P.; Perde-Schrepler, M.; Toma, V.A.; Mocan, A.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Pintea, A.; et al. Zeaxanthin-Rich Extract from Superfood Lycium barbarum Selectively Modulates the Cellular Adhesion and MAPK Signaling in Melanoma versus Normal Skin Cells In Vitro. Molecules 2021, 26, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.S.; Leung, S.K.; Lai, S.W.; Che, C.M.; Zee, S.Y.; So, K.F.; Yuen, W.H.; Chang, R.C. Neuroprotective effects of anti-aging oriental medicine Lycium barbarum against beta-amyloid peptide neurotoxicity. Exp. Gerontol. 2005, 40, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Cai, Y.; Yan, J.; Sun, M.; Corke, H. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects and antioxidant activity of fruit extracts from Lycium barbarum. Life Sci. 2004, 76, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, G.; Qi, C.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y. Immune activities comparison of polysaccharide and polysaccharide-protein complex from Lycium barbarum L. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adadi, P.; Barakova, N.V.; Krivoshapkina, E.F. Selected Methods of Extracting Carotenoids, Characterization, and Health Concerns: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5925–5947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harunobu, A.; Norman, R.F. A review of botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, clinical relevance in efficacy and safety of Lycium barbarum fruit (Goji). Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Inbaraj, B.S.; Lu, H.; Hung, C.F.; Wu, W.B.; Lin, C.L.; Chen, B.H. Determination of carotenoids and their esters in fruits of Lycium barbarum Linnaeus by HPLC-DAD-APCI-MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, Y.; Leung, K.S.; Jiang, Z.H.; Zhao, Z. Quantification of zeaxanthin dipalmitate and total carotenoids in Lycium fruits (Fructus Lycii). Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2005, 60, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hempel, J.; Schadle, C.N.; Sprenger, J.; Heller, A.; Carle, R.; Schweiggert, R.M. Ultrastructural deposition forms and bioaccessibility of carotenoids and carotenoid esters from goji berries (Lycium barbarum L.). Food Chem. 2017, 218, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olech, M.; Kasprzak, K.; Wojtowicz, A.; Oniszczuk, T.; Nowak, R.; Waksmundzka-Hajnos, M.; Combrzynski, M.; Gancarz, M.; Kowalska, I.; Krajewska, A.; et al. Polyphenol Composition and Antioxidant Potential of Instant Gruels Enriched with Lycium barbarum L. Fruit. Molecules 2020, 25, 4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manthey, A.L.; Chiu, K.; So, K.F. Effects of Lycium barbarum on the Visual System. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2017, 135, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Huang, X.Y.; Liu, J.F.; Pei, D.; Sun, X.; Di, D.L. Development of an effective method based upon second-order overlapping repeated sample injections for isolation of carotenoids from Lycium barbarum L. fruits with elution-extrusion counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1645, 462026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patsilinakos, A.; Ragno, R.; Carradori, S.; Petralito, S.; Cesa, S. Carotenoid content of Goji berries: CIELAB, HPLC-DAD analyses and quantitative correlation. Food Chem. 2018, 268, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, X.; Yan, Y.; Ran, L.; Lu, L.; Mi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Cao, Y. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction and high-speed counter-current chromatography purification of zeaxanthin dipalmitate from the fruits of Lycium barbarum L. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Guo, Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, X. Simultaneous determination of seven phenylethanoid glycosides in Cistanches Herba by a single marker using a new calculation of relative correction factor. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 1913–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.M.; Gao, H.M.; Fu, X.T.; Wang, W.H. Multi-components quantitation by one marker new method for quality evaluation of Chinese herbal medicine. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2006, 31, 1925–1928. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaojun, Z.; Chao, S.; Ruru, R.; Bo, Z.; Yingli, W.; Xiaojuan, S.; Fangfang, L.; Rong, Z.; Lingling, Y.; Wannian, Z.; et al. Simultaneous determination of both kavalactone and flavokawain constituents by different single-marker methods in kava. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 2705–2716. [Google Scholar]





| NO | Origin | Batch | NO | Origin | Batch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | Ningxia | 20190917 | G4 | Gansu | 20190974 |
| N2 | Ningxia | 20190918 | G5 | Gansu | 20190970 |
| N3 | Ningxia | 20180920 | G6 | Gansu | 20190924 |
| N4 | Ningxia | 20190921 | G7 | Gansu | 20190910 |
| N5 | Ningxia | 20190922 | G8 | Gansu | 20190115 |
| N6 | Ningxia | 20190935 | G9 | Gansu | 20190956 |
| N7 | Ningxia | 20190904 | G10 | Gansu | 20190957 |
| N8 | Ningxia | 20190908 | Q1 | Qinghai | 20191109 |
| N9 | Ningxia | 20190911 | Q2 | Qinghai | 20190931 |
| N10 | Ningxia | 20190925 | Q3 | Qinghai | 20191041 |
| N11 | Ningxia | 20190927 | Q4 | Qinghai | 20190113 |
| N12 | Ningxia | 20180903 | Q5 | Qinghai | 20191110 |
| N13 | Ningxia | 20170708 | Q6 | Qinghai | 20191044 |
| N14 | Ningxia | 20190950 | Q7 | Qinghai | 20191111 |
| G1 | Gansu | 20190936 | Q8 | Qinghai | 20191045 |
| G2 | Gansu | 20190930 | Q9 | Qinghai | 20191055 |
| G3 | Gansu | 20190952 | Q10 | Qinghai | 20191035 |
| Standard Substance | trans-β-Apo-8′-Carotenal as Reference | β-Carotene as Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCF | RRT | RCF | RRT | |
| Lutein | 40.35 ± 0.11 | 1.34 | 9.28 ± 0.06 | 2.37 |
| Zeaxanthin | 1.18 ± 0.01 | 1.41 | 0.27 ± 0.00 | 2.49 |
| β-Carotene | 4.35 ± 0.02 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Zeaxanthin dipalmitate | 2.60 ±0.03 | 0.20 | 0.6 ± 0.01 | 0.36 |
| Standard Substance | Calibration Curve | R2 | Test Range μg/mL | LOQ μg/mL | LOD μg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lutein | y = 6.2046x − 5.3418 | 0.9996 | 1.14–90.96 | 1.14 | 0.57 |
| Zeaxanthin | y = 139.72x + 34.43 | 0.9995 | 0.082–20.42 | 0.082 | 0.05 |
| β-Carotene | y = 49.31x + 6.046 | 0.9995 | 0.25–6.26 | 0.25 | 0.13 |
| Zeaxanthin dipalmitate | y = 98.505x − 40.763 | 0.9993 | 1.01–91.15 | 1.01 | 0.44 |
| Compound | Repeatability | Reproducibility | Stability | Recovery/RSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lutein | 0 | 0 | 0 | 102.4/7.8 |
| Zeaxanthin | 0.57 | 1.38 | 2.72 | 103.3/6.8 |
| β-Carotene | 1.25 | 3.84 | 4.74 | 105.5/6.1 |
| Zeaxanthin dipalmitate | 0.21 | 1.13 | 2.62 | 96.0/1.9 |
| Factor | Level/Brand | Lutein | Zeaxanthin | β-Carotene | Zeaxanthin Dipalmitate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Different flow rates | 0.8 min/mL | 40.49 | 1.21 | 4.94 | 2.61 |
| 0.9 min/mL | 40.53 | 1.21 | 4.64 | 2.64 | |
| 1.1 min/mL | 40.52 | 1.21 | 4.82 | 2.65 | |
| Different temperatures | 23 °C | 41.04 | 1.24 | 5.30 | 2.83 |
| 25 °C | 40.95 | 1.21 | 5.36 | 2.72 | |
| 30 °C | 43.10 | 1.19 | 5.23 | 2.65 | |
| Different columns | YMC C30 | 40.35 | 1.18 | 4.35 | 2.60 |
| UG17546250W C30 | 40.11 | 1.15 | 4.26 | 2.58 | |
| Different instruments | Hitachi2000 | 38.00 | 1.23 | 5.83 | 3.03 |
| Waters2998 | 38.47 | 1.09 | 4.01 | 2.86 | |
| Shimadzu 2030C | 42.73 | 1.23 | 5.46 | 2.93 |
| Sample | Zeaxanthin Dipalmitate (mg/g) | Zeaxanthin (μg/g) | β-Carotene (μg/g) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ESM | QAMS1 | QAMS2 | ESM | QAMS1 | QAMS2 | ESM | QAMS1 | QAMS2 | |
| N1 | 1.05 | 1.11 | 1.09 | 14.32 | 14.25 | 14.54 | –– | –– | –– |
| N2 | 1.71 | 1.74 | 1.71 | 10.77 | 10.94 | 11.16 | –– | –– | –– |
| N3 | 1.58 | 1.61 | 1.58 | 6.87 | 6.84 | 6.98 | –– | –– | –– |
| N4 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.84 | –– | –– | –– | –– | –– | –– |
| N5 | 1.20 | 1.22 | 1.20 | 6.82 | 6.79 | 6.93 | –– | –– | –– |
| N6 | 1.18 | 1.20 | 1.18 | 19.50 | 18.97 | 19.36 | –– | –– | –– |
| N7 | 1.46 | 1.48 | 1.45 | 6.60 | 6.57 | 6.70 | –– | –– | –– |
| N8 | 1.16 | 1.18 | 1.16 | 5.88 | 5.72 | 5.84 | –– | –– | –– |
| N9 | 1.46 | 1.49 | 1.46 | 7.24 | 7.21 | 7.36 | –– | –– | –– |
| N10 | 1.29 | 1.31 | 1.28 | 19.94 | 19.39 | 19.79 | –– | –– | –– |
| N11 | 1.75 | 1.78 | 1.75 | 17.97 | 17.47 | 17.83 | –– | –– | –– |
| N12 | 0.93 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 18.18 | 17.68 | 18.04 | –– | –– | –– |
| N13 | 1.22 | 1.24 | 1.22 | –– | –– | –– | –– | –– | –– |
| N14 | 0.87 | 0.91 | 0.89 | –– | –– | –– | –– | –– | –– |
| G1 | 1.75 | 1.78 | 1.75 | 19.86 | 19.32 | 19.71 | –– | –– | –– |
| G2 | 1.40 | 1.48 | 1.45 | 15.66 | 15.23 | 15.54 | –– | –– | –– |
| G3 | 1.29 | 1.31 | 1.28 | 13.54 | 13.17 | 13.44 | –– | –– | –– |
| G4 | 1.28 | 1.30 | 1.27 | 13.62 | 13.24 | 13.51 | –– | –– | –– |
| G5 | 1.37 | 1.39 | 1.36 | –– | –– | –– | –– | –– | –– |
| G6 | 2.07 | 2.11 | 2.07 | 20.62 | 20.05 | 20.46 | –– | –– | –– |
| G7 | 2.35 | 2.39 | 2.34 | 9.92 | 9.87 | 10.07 | –– | –– | –– |
| G8 | 1.19 | 1.25 | 1.23 | 8.63 | 8.59 | 8.77 | –– | –– | –– |
| G9 | 1.97 | 2.01 | 1.97 | 7.30 | 7.26 | 7.41 | –– | –– | –– |
| G10 | 1.32 | 1.35 | 1.32 | 13.11 | 13.05 | 13.32 | –– | –– | –– |
| Q1 | 2.94 | 3.03 | 2.97 | 26.76 | 26.64 | 27.18 | 6.08 | 5.93 | 6.59 |
| Q2 | 4.05 | 4.17 | 4.09 | 16.56 | 16.48 | 16.82 | 6.11 | 5.96 | 6.62 |
| Q3 | 2.50 | 2.58 | 2.53 | 16.19 | 16.11 | 16.44 | 7.21 | 7.03 | 7.81 |
| Q4 | 2.57 | 2.65 | 2.60 | 27.30 | 26.55 | 27.09 | 6.78 | 6.61 | 7.34 |
| Q5 | 2.81 | 2.89 | 2.83 | 23.16 | 22.52 | 22.98 | 8.04 | 7.84 | 8.71 |
| Q6 | 3.84 | 3.95 | 3.87 | 21.86 | 21.26 | 21.69 | 7.81 | 7.62 | 8.47 |
| Q7 | 2.54 | 2.62 | 2.57 | 22.01 | 21.40 | 21.84 | 5.62 | 5.48 | 6.09 |
| Q8 | 3.04 | 3.13 | 3.07 | 28.17 | 27.40 | 27.96 | 6.97 | 6.80 | 7.56 |
| Q9 | 3.08 | 3.17 | 3.11 | 28.06 | 27.29 | 27.85 | 6.73 | 6.56 | 7.29 |
| Q10 | 2.74 | 2.82 | 2.76 | 16.11 | 15.67 | 15.99 | 6.89 | 6.72 | 7.47 |
| Sample | Zeaxanthin Dipalmitate | Zeaxanthin | β-Carotene | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMD1 | SMD2 | SMD1 | SMD2 | SMD1 | SMD2 | |
| N1 | 5.7 | 3.6 | 0.5 | 1.5 | –– | –– |
| N2 | 1.8 | 0.2 | 1.6 | 3.7 | –– | –– |
| N3 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.6 | –– | –– |
| N4 | 6.2 | 4.1 | –– | –– | –– | –– |
| N5 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 1.6 | –– | –– |
| N6 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 0.7 | –– | –– |
| N7 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 1.6 | –– | –– |
| N8 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 0.7 | –– | –– |
| N9 | 2.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.6 | –– | –– |
| N10 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 2.8 | 0.8 | –– | –– |
| N11 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 2.8 | 0.8 | –– | –– |
| N12 | 5.4 | 3.3 | 2.8 | 0.8 | –– | –– |
| N13 | 1.6 | 0.4 | –– | –– | –– | –– |
| N14 | 4.6 | 2.5 | –– | –– | –– | –– |
| G1 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 2.7 | 0.7 | –– | –– |
| G2 | 5.7 | 3.6 | 2.7 | 0.8 | –– | –– |
| G3 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 2.7 | 0.7 | –– | –– |
| G4 | 1.6 | 0.4 | 2.8 | 0.8 | –– | –– |
| G5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | –– | –– | –– | –– |
| G6 | 1.9 | 0.1 | 2.8 | 0.8 | –– | –– |
| G7 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.5 | –– | –– |
| G8 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 0.5 | 1.6 | –– | –– |
| G9 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.5 | –– | –– |
| G10 | 2.3 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 1.6 | –– | –– |
| Q1 | 3.1 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 2.5 | 8.4 |
| Q2 | 3.0 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 8.4 |
| Q3 | 3.2 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 8.3 |
| Q4 | 3.1 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 8.3 |
| Q5 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 8.3 |
| Q6 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 8.4 |
| Q7 | 3.1 | 1.1 | 2.8 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 8.3 |
| Q8 | 3.0 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.7 | 2.4 | 8.4 |
| Q9 | 2.9 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 8.3 |
| Q10 | 2.9 | 0.9 | 2.7 | 0.7 | 2.5 | 8.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, R.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Su, C.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, X. Carotenoid Contents of Lycium barbarum: A Novel QAMS Analyses, Geographical Origins Discriminant Evaluation, and Storage Stability Assessment. Molecules 2021, 26, 5374. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175374
Ren R, Li Y, Chen H, Wang Y, Yang L, Su C, Zhao X, Chen J, Ma X. Carotenoid Contents of Lycium barbarum: A Novel QAMS Analyses, Geographical Origins Discriminant Evaluation, and Storage Stability Assessment. Molecules. 2021; 26(17):5374. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175374
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Ruru, Yanting Li, Huan Chen, Yingli Wang, Lingling Yang, Chao Su, Xiaojun Zhao, Jianyu Chen, and Xueqin Ma. 2021. "Carotenoid Contents of Lycium barbarum: A Novel QAMS Analyses, Geographical Origins Discriminant Evaluation, and Storage Stability Assessment" Molecules 26, no. 17: 5374. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175374
APA StyleRen, R., Li, Y., Chen, H., Wang, Y., Yang, L., Su, C., Zhao, X., Chen, J., & Ma, X. (2021). Carotenoid Contents of Lycium barbarum: A Novel QAMS Analyses, Geographical Origins Discriminant Evaluation, and Storage Stability Assessment. Molecules, 26(17), 5374. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175374