Abstract
The aim of this study was to characterize hydrolyzable tannins in Polygonaceous plants, as only a few plants have previously been reported to contain ellagitannins. From Persicaria chinensis, a new hydrolyzable tannin called persicarianin was isolated and characterized to be 3-O-galloyl-4,6-(S)-dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl-d-glucose. Interestingly, acid hydrolysis of this compound afforded ellagic acid, despite the absence of a hexahydroxydiphenoyl group. From the rhizome of Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense, a large amount of granatin A, along with minor ellagitannins, helioscpoinin A, davicratinic acids B and C, and a new ellagitannin called polygonanin A, were isolated. Based on 2D nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopic examination, the structure of polygonanin A was determined to be 1,6-(S)-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-2,4-hydroxychebuloyl-β-d-glucopyranose. These are the second and third hydrolyzable tannins isolated from Polygonaceous plants. In addition, oligomeric proanthocyanidins of Persicaria capitatum and P. chinensis were characterized by thiol degradation. These results suggested that some Polygonaceous plants are the source of hydrolyzable tannins not only proanthocyanidins.
1. Introduction
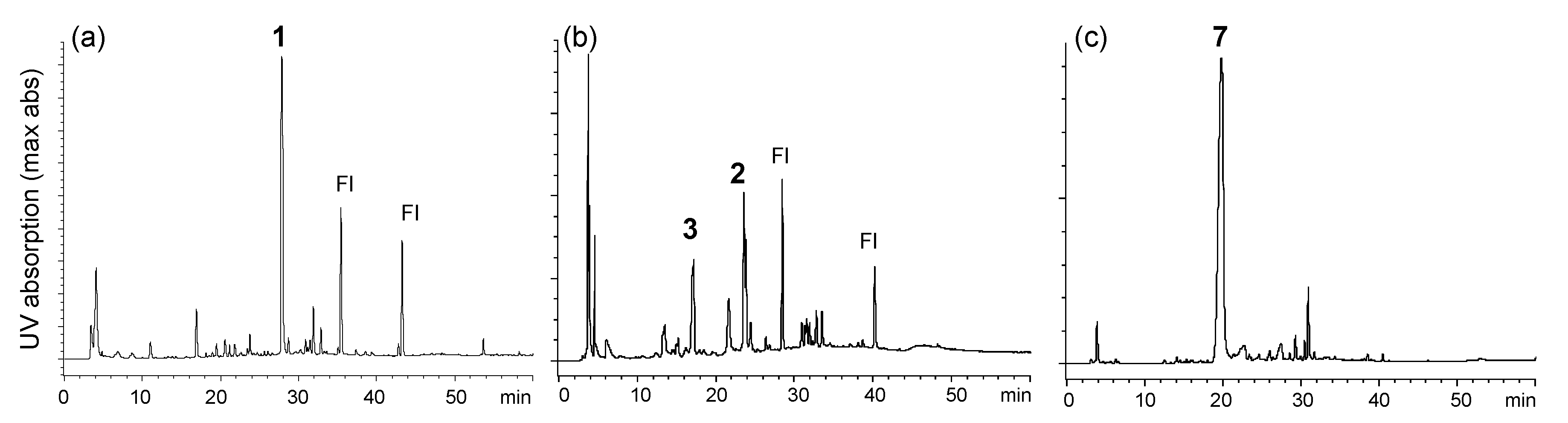
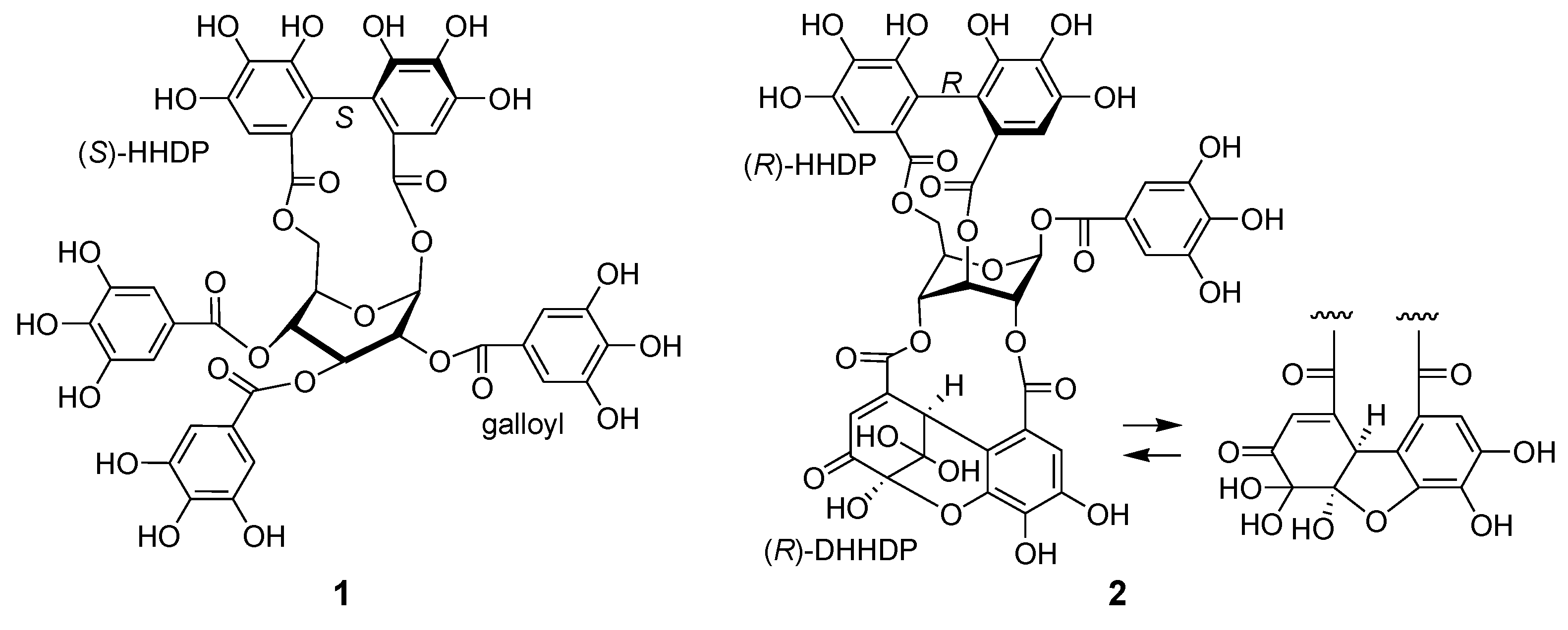
Ellagitannins are hydrolyzable tannins containing hexahydroxydiphenoyl (HHDP) groups and related acyl groups. Recently, their high structural diversity and biological activities have attracted intense interest amongst natural product chemists [1,2,3,4,5]. Compared to proanthocyanidins (synonym (syn.) condensed tannins), distribution of ellagitannins in the plant kingdom is relatively limited. Among Polygonaceous plants, only 2,3,4-tri-O-galloyl-1,6-(S)-HHDP-β-d-glucose (davidiin, 1) has been isolated from Persicaria capitatum (syn. Polygonum capitatum) [6]; its biological activity and metabolism have also been reported [7,8,9]. More recently, the presence of geraniin and chebulagic acid in the aerial parts of Persicaria chinense var. hispidum was suggested by the use of high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)-mass spectroscopy (MS) [10]. In the course of chemical studies on ellagitannins, we analyzed aqueous CH3CN extracts of eight Polygonaceous plants, Reynoutria japonica, Persicaria perfoliata, P. longiseta, P. lapathifolia, P. capitata, P. chinensis, P. filiformis, and P. thunbergii, by HPLC-diode array detector (DAD) analysis (Figure S1, Supplementary Materials). In the study, only the extracts of P. capitata and P. chinensis showed peaks with UV absorption characteristic to ellagitannins (Figure 1). The results were consistent with the above-mentioned studies; the major ellagitannin of P. capitata was davidiin (1), and P. chinensis contains geraniin (2) (Figure 2). In addition, we found that the rhizome of Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense, a Chinese perennial plant used as a folk medicine for detoxification and hemostasis, contains ellagitannins as the major constituents. This paper describes the isolation of phenolic substances from these three plants and structural determination of the two new ellagitannins obtained from Persicaria chinensis and Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense. In addition, proanthocyanidin oligomers from Persicaria capitata and Persicaria chinensis were chemically characterized.
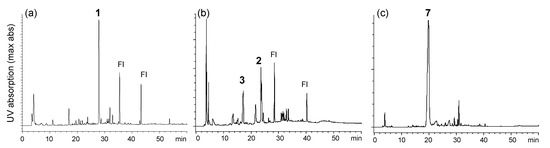
Figure 1.
HPLC profiles of 60% CH3CN extracts of (a) Persicaria capitata, (b) Persicaria chinensis and (c) Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense. 1: davidiin, 2: geraniin, 3: persicarianin, 7: granatin A and Fl: flavonoid glycosides.
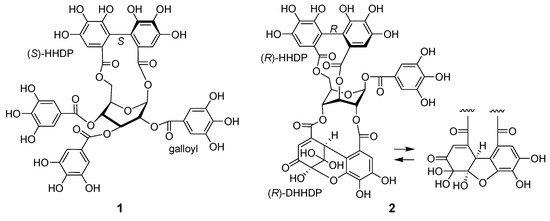
Figure 2.
Structures of davidiin (1) from Persicaria capitata and geraniin (2) from Persicaria chinensis.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Polyphenols of Persicaria capitata
The EtOH extract of Persicaria capitata whole plant, collected in Shui Cheng, Guizhou, China, was fractionated by Diaion HP20SS and further separated using Sephadex LH-20 and Chromatorex ODS to give davidiin (1) as the major constituent (7% from the extract), along with minor compounds, which were identified as 2,3-di- [11], 2,4-di- [12], 2,3,4-tri- [13], and 2,3,6-tri-O-galloyl glucoses [14], 6’-O-galloyl arbutin [15], 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenol 1-O-β-d-(6’-O-galloyl)-glucopyranoside [16], 4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenol 1-O-β-d-(6’-O-galloyl)-glucopyranoside [16], quercetin 3-O-β-d-glucoside [17], quercetin 3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranoside [17], quercetin 3-O-α-L-(3’’-O-galloyl)-rhamnopyranoside [18], ellagic acid, and quercetin.
2.2. Polyphenols from Persicaria Chinensis
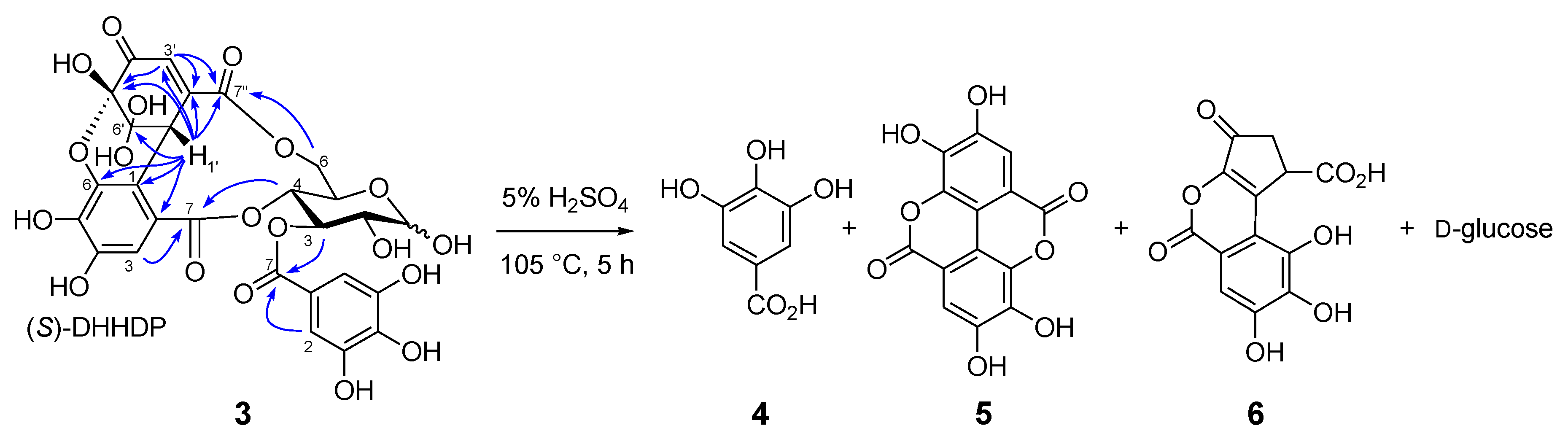
Similar separation of an aqueous acetone extract of the fresh aerial part of Persicaria chinensis collected in Nagasaki, Japan, afforded 1-O- [19] and 1,2,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-d-glucoses [20], geraniin (2) [21], quercetin 3-O-(2’’-α-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-glucuronopyranoside [22], and a new ellagitannin called persicarianin. Persicarianin (3) was obtained as a brown amorphous powder, and high-resolution electrospray ionization time of flight (HRESITOF) MS indicated a molecular formula of C27H22O19 (m/z: 673.0689, calculated for C27H22O19Na: 673.0653). The 1H NMR spectrum showed signals arising from α- and β-hexopyranoses, and it is apparent that the sugar is a 4C1-glucopyranose based on the large coupling constants of the pyranose ring proton signals (J2,3, J3,4, J4,5 = 8–10 Hz). The low field shifts of H-3 [δ 5.63 (α-H-3), 5.40 (β-H-3)], H-4 [5.40 (α-H-4), 3.94 (β-H-4)], and H-6 [4.94, 3.95 (α-H-6), 5.40, 3.92 (β-H-6)] indicates acylation of these positions. The acyl groups were shown to be a galloyl and a dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl (DHHDP) group by 13C NMR spectroscopy, which exhibited signals attributable to an aliphatic methine (δ 43.0), a double bond (δ 151.7 and 130.8), a ketone (δ 192.0), and two acetal carbons (δ 91.5 and 96.5), constructing a hydrated cyclohexenetrione ring of the DHHDP group. The large chemical shift differences of the glucose H-6 methylene proton signals in the 1H NMR spectrum suggested that the DHHDP esters bridges between the C-4 and C-6 hydroxy groups [23]. This was confirmed by heteronuclear multiple bond coherence (HMBC) correlations of the glucose H-6 and H-4 to the DHHDP C-7’ and C-7 ester carbonyl carbons, respectively (Figure 3). The configuration of the DHHDP methine carbon (C-1’) was concluded to be S, based on the appearance of negative and positive Cotton effects at 213 nm and 234 nm, respectively [24]. The location of the galloyl group was determined to be at the glucose C-3 hydroxy group by observation of HMBC correlations between the glucose H-3 and galloyl C-7. The D configuration of the glucosyl moiety was determined via acid hydrolysis followed by HPLC analysis of the thiazolidine derivatives prepared by reaction with L-cysteine and o-tolylisothiocyanate [25,26]. Based on this evidence, persicarianin was characterized to be 3-O-galloyl-4,6-(S)-DHHDP-d-glucose (3). HPLC analysis of the aforementioned hydrolysis products, before condensation with cysteine, revealed production of gallic acid (4), ellagic acid (5), and brevifolin carboxylic acid (6) (Figure S2, Supplementary Materials). Ellagic acid is a bislactone form of the HHDP group, and therefore, a reduction product of the DHHDP ester of 3. Similar production of 5 from DHHDP groups on acid hydrolysis have been also observed for 2 and related ellagitannins, and the reaction was deduced to be a redox disproportionation [27,28]. Ellagitannins were originally defined as hydrolyzable tannins which afford 5 upon hydrolysis, and 5 is usually considered to be originated from HHDP groups. In this context, despite the absence of a HHDP group, 3 is also an ellagitannin.
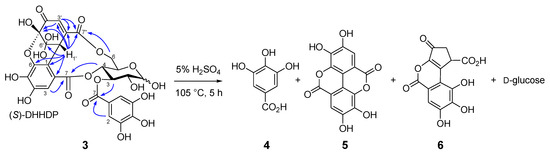
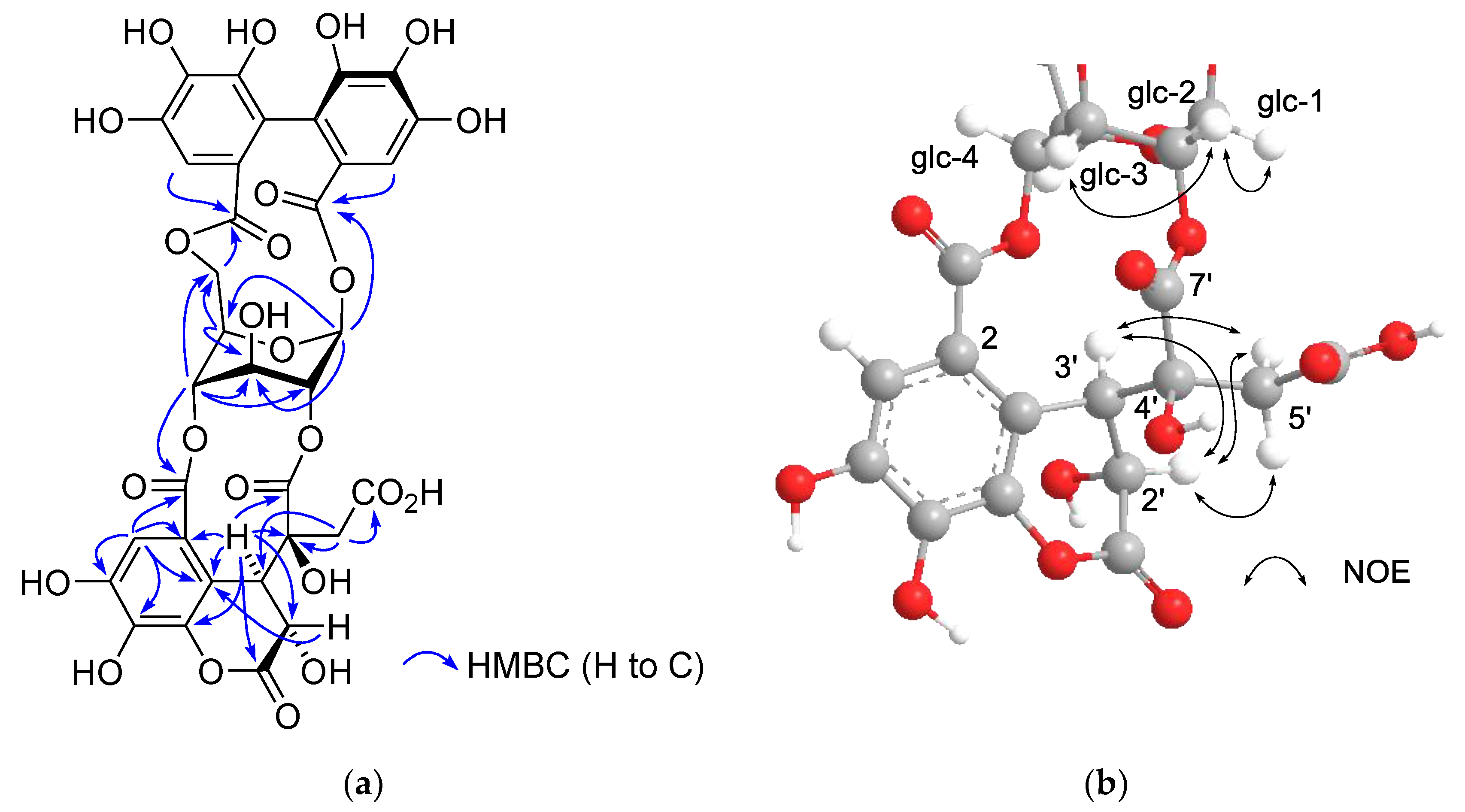
Figure 3.
Selected heteronuclear multiple bond coherence (HMBC) correlations and acid hydrolysis of 3-O-galloyl-4,6-(S)-DHHDP-d-glucose (3).
2.3. Hydrolyzable Tannin from Polygonum Runcinatum var. Sinense
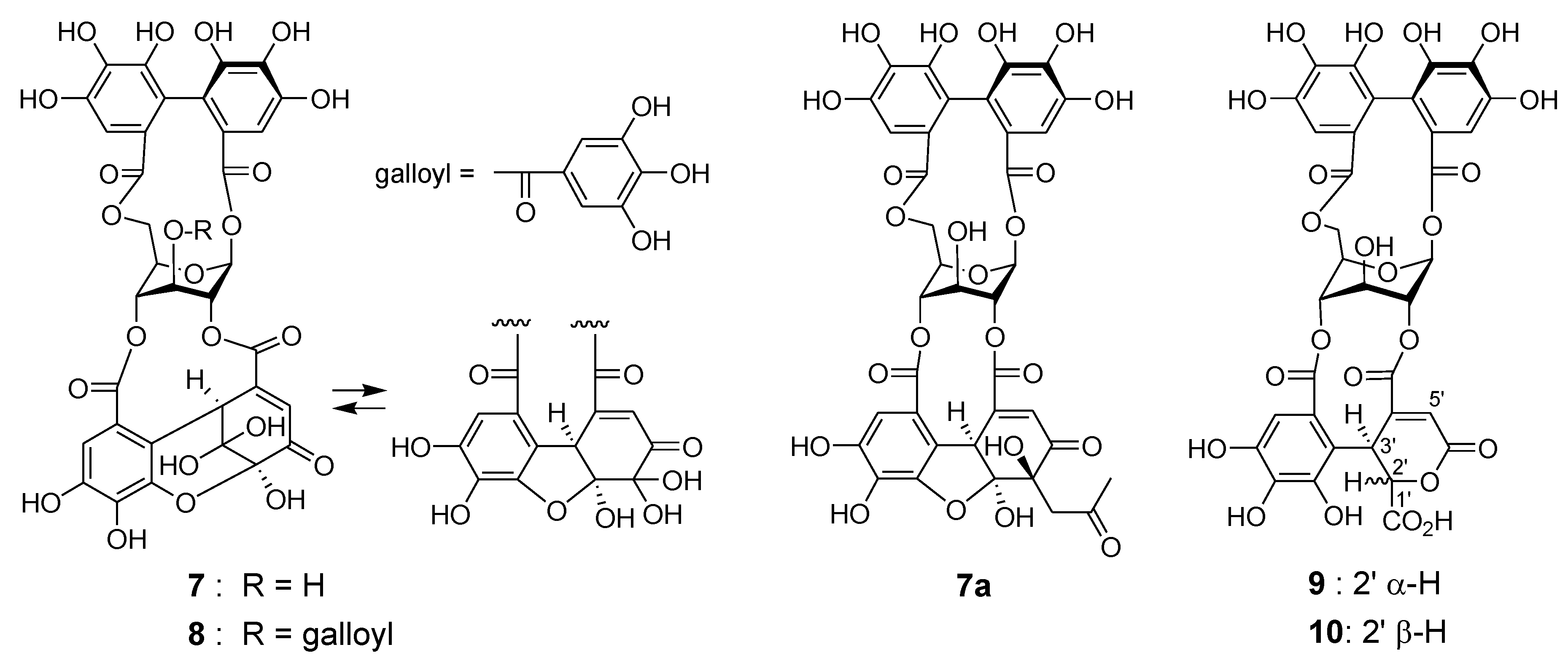
Reverse-phase HPLC analysis of the rhizome of Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense showed a prominent peak arising from a principal phenolic component (Figure 1c), which was isolated by Diaion HP20SS column chromatography and identified as granatin A (7) by 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopic analysis [29]. Furthermore, the acetonyl derivative 7a was prepared by treatment of 7 with aqueous acetone containing HCO2NH4, and spectroscopic comparison of 7a with those of an authentic sample provided further evidence for the structure of 7 [30]. In the purification process of 7 (Figure 4), four minor ellagitannins were isolated by a combination of column chromatography using Chromatorex ODS and Toyopearl Butyl-650M to give helioscopinin A (8) [31], davicratinic acids B (9) and C (10) [32], and a new ellagitannin called polygonanin A.
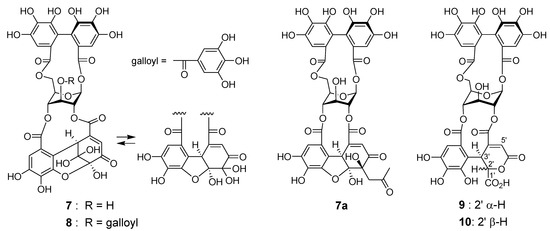
Figure 4.
Structures of 7–10 and acetonyl derivative 7a.
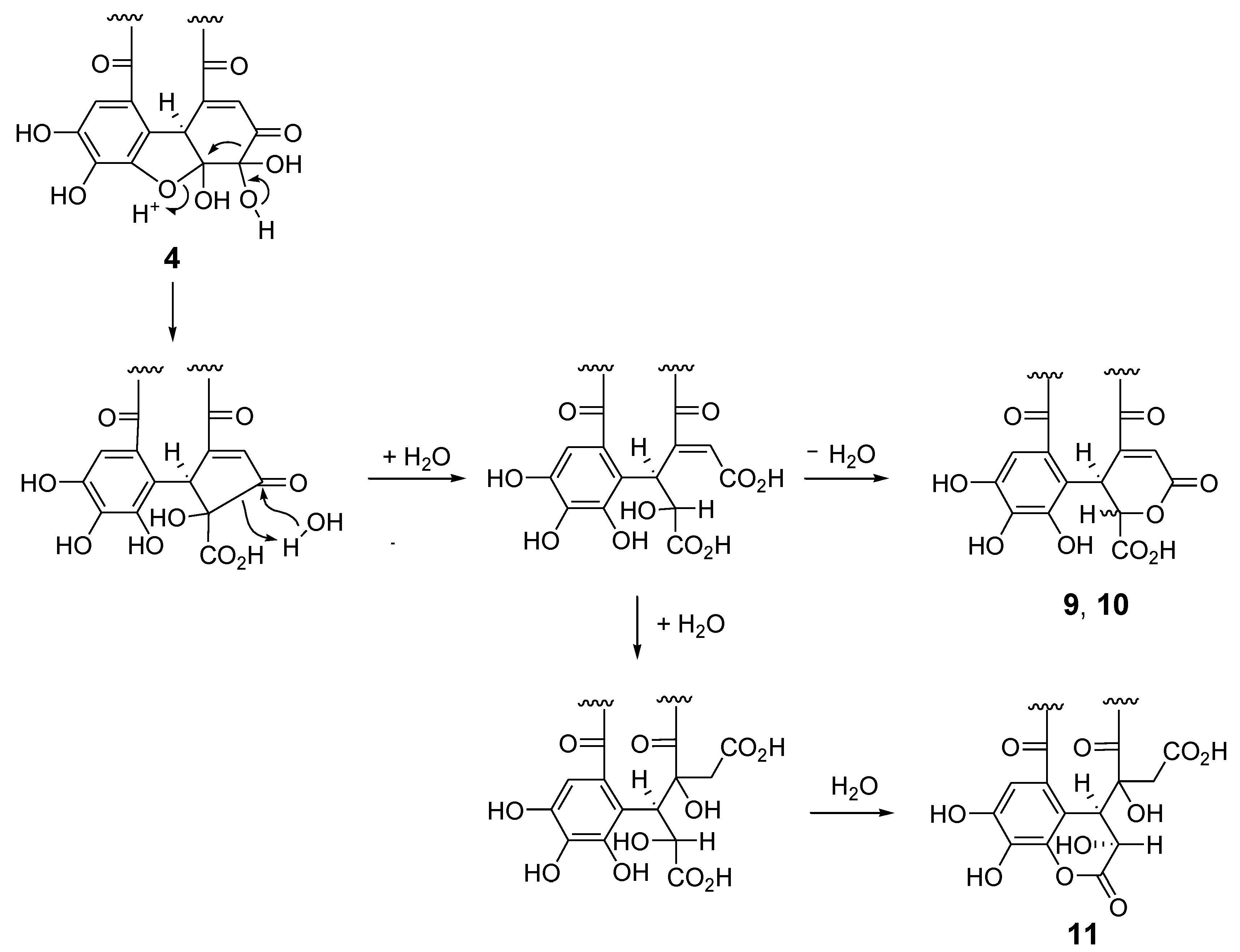
The 1H and 13C NMR spectra of polygonanin A (11) was related to those of 9 and 10, indicating 1,2,4,6-acylated glucopyranose with a HHDP group. The location of the HHDP group at the 1,6-positions of glucose was confirmed by HMBC correlations of glucose H-1 (δH 5.95, s) and H-6 [δH 4.99 (t, J = 11.1 Hz), 4.08 (dd, J = 5.3, 11.1 Hz)] with the HHDP ester carbonyl carbons (δC 166.4, 168.2). The atropisomerism of the HHDP was shown to be an S configuration by appearance of positive and negative Cotton effects at 242 nm and 262 nm, respectively, in the electronic circular dichroism (ECD) spectrum. The configuration is the same as that of 1, 7, 9, and 10. Coupling constants of the pyranose ring protons (J1,2, J2,3, J3,4, and J4,5) were <2 Hz. This was similar to those of 7, 9, and 10, but different to those of 1 (J1,2 = 3.2 Hz, J2,3 = 8.5 Hz, J3,4 = 7.7 Hz, and J4,5 = 2.9 Hz), suggesting that the glucopyranoses of 7, 9, 10, and 11 adopt a 1C4 conformation, whereas the glucopyranose core of 1 with a 2,3,4-trigalloyl structure adopts a boat conformation (Figure 1). The NMR signals indicated that the 2,4-acyl group of 11 was composed of 3 carboxyl carbons (δC 172.3 (C-1’), 172.0 (C-6’), 166.1 (C-7’)), an oxygenated tertiary carbon (δC 76.3 (C-4’)), an oxygenated methine (δC 66.3 (C-2’)), a methylene (δC 41.6 (C-5’)), and a benzylic methine (δC 49.2 (C-3’)), along with a trihydroxy benzoyl moiety. Taking the molecular formula C34H26O24 indicated by HR-fast atom bombardment (FAB) MS into account, these building blocks of the 2,4-acyl group suggested that 8 is generated by addition of H2O to the double bond of 9 or 10 and rearrangements of lactone formation. This was supported by HMBC correlations, as illustrated in Figure 5. The planar structure of this acyl group is the same as the 4’-hydroxychebuloyl group of an ellagitannin isolated from a Euphorbiaceous plant [33], and the chemical shifts of the aliphatic proton and carbon signals in the literature (δH 4.84 (d, J = 5 Hz, H-2’), 4.90 (d, J = 5 Hz, H-3’), 3.28 and 3.43 (each d, J = 18 Hz, H-5’); δC 68.5 (C-2’), 47.3 (C-3’), 77.6 (C-4’), 42.5 (C-5’)) are similar to those of 11 (δH 4.83 (br s, HChe H-2’) and 4.88 (d, J = 2.8 Hz, HChe H-3’), 3.35 and 2.78 (each d, J = 15.9 Hz, HChe H-5’); δC 66.3 (C-2’), 49.2 (C-3’), 76.3 (C-4’), 41.6 (C-5’)). The configuration of C-2’, C-3’, and C-4’ was concluded to be S*, R*, and S* based on the nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) correlations between the H-2’, H-3’ and H-5’ of 11. The most stable conformation of 11 obtained by computational calculation along with NOESY correlations is shown in Figure 5b. The NOESY correlation between H-2’ and one of the H-5’ methylene protons confirmed the relative configurations of C-2’ – C-5’. From the biogenesis illustrated Scheme 1, the configuration of the benzylic methines of the acyl groups of 11 was deduced to be the same as that of the DHHDP group of 7. Interestingly, the glucose H-3 of 11 (δH 5.14) resonated at a much lower field compared to those of 7a (δH 4.58), 9 (δH 4.40) and 10 (δH 4.44). This could be due to the deshielding effect of the ester carbonyl group attached to the glucose C-2 hydroxy group (Figure 5b), suggesting that hydroxylation at C-4’ of the 2,4-acyl group affects the conformation of the macrocyclic ester structure.
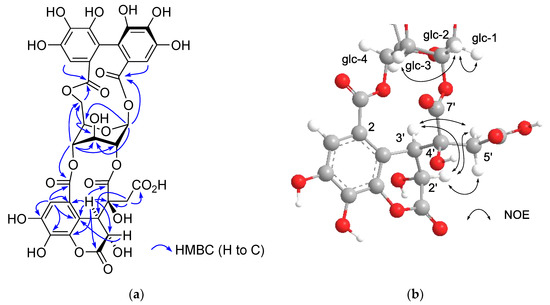
Figure 5.
(a) Structure and selected HMBC correlations for 11. (b) A partial structure of the most stable conformer of 11 and nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy (NOESY) correlations of the glucose and 2,4-acyl group.
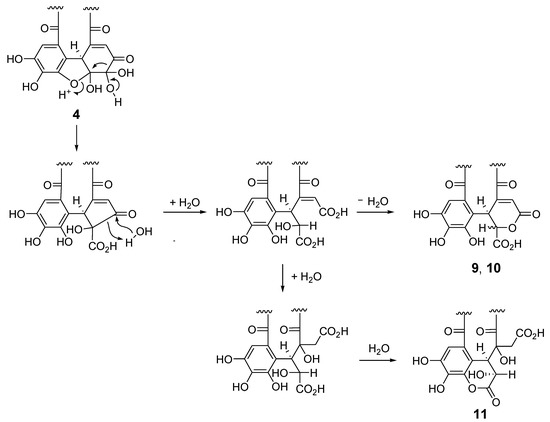
Scheme 1.
Plausible production mechanism of 9–11 from 4.
2.4. Proanthocyanidins of Persicaria Capitata and Persicaria Chinensis
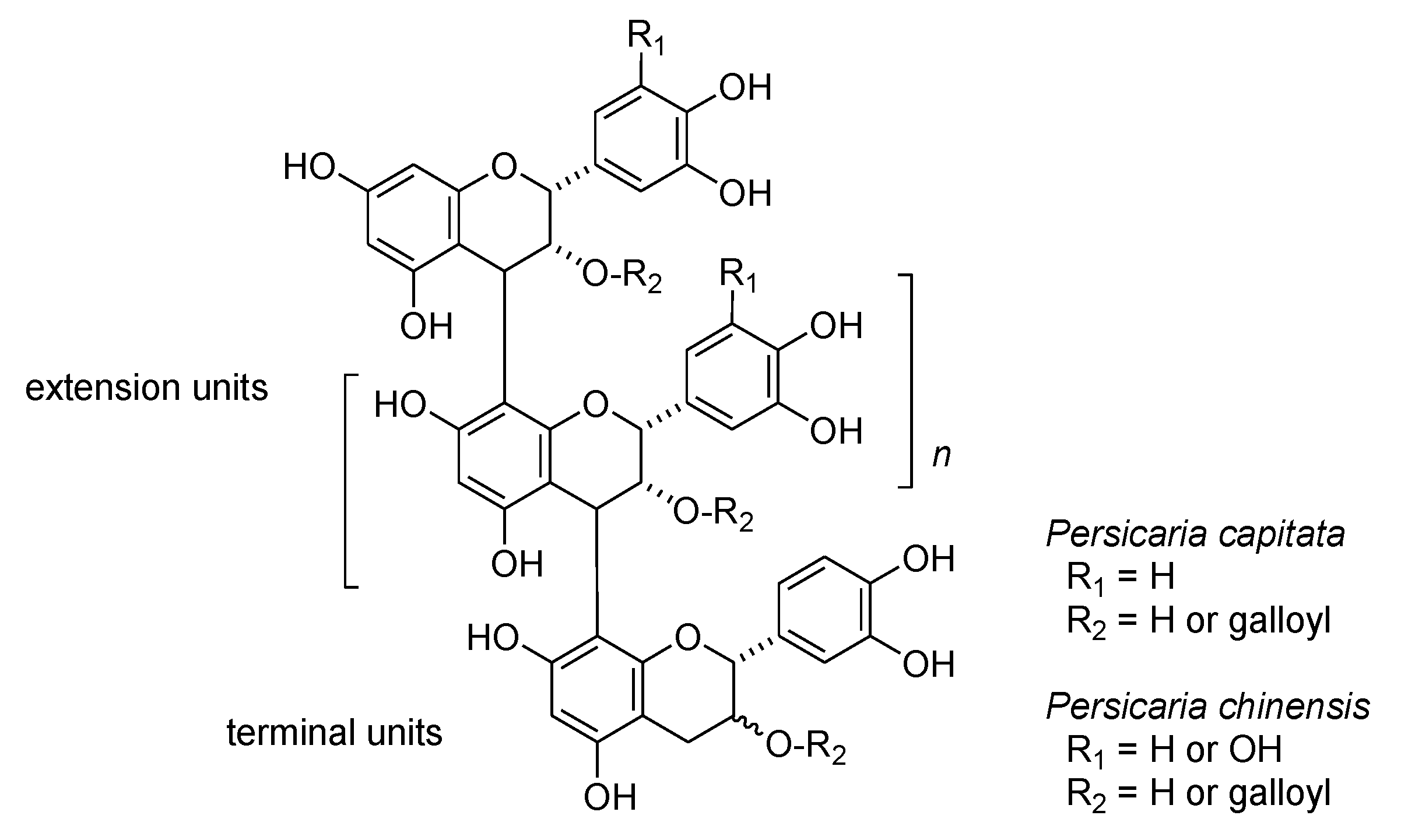
In addition to hydrolyzable tannins, oligomeric proanthocyanidins are also important constituents of Persicaria capitata and Persicaria chinensis. The oligomers were detected as broad humps on the HPLC baseline; thiol degradation using 2-mercaproethanol was used to characterize the structural components [34] (Figure S3, Supplementary Materials). HPLC analysis of the degradation products obtained from proanthocyanidins of Persicaria capitata exhibited peaks attributable to 4β-(2-hydroxyethylsulfanyl) derivatives of epicatechin and epicatechin-3-O-gallate originating from extension units, accompanied by small peaks of catechin, epicatechin, and epicatechin gallate arising from terminal units. Oligomeric proanthocyanidins of P. chinensis yielded 2-hydroxyethylsulfanyl derivatives of epicatechin, epigallocatechin, epicatechin-3-O-gallate and epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate originating from extension units, along with the free form of epicatechin-3-O-gallate originating from the terminal unit. The results indicates that proanthocyanidins in these two plants belonging the same genus Persicaria are composed of different flavan-3-ol units (Figure 6). In contrast, high-molecular weight polyphenols obtained from the rhizome of Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense did not yield 2-hydroxyethylsulfanyl derivatives on thiol degradation, indicating that the polyphenols are not proanthocyanidins. The 13C NMR spectrum suggested that the polyphenols are oligomeric hydrolyzable tannins. Further investigations are now underway.
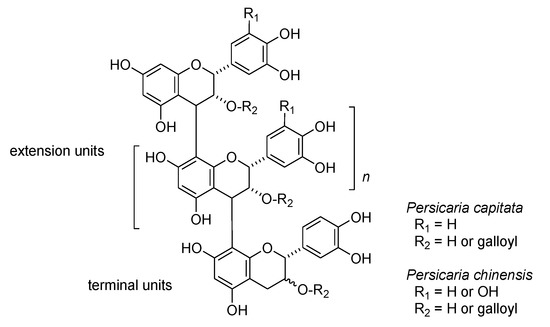
Figure 6.
Structures of oligomeric proanthocyanidins of Persicaria capitata and P. chinensis suggested by thiol degradation.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Information
Optical rotations were measured on a JASCO P-1020 digital polarimeter (JASCO, Tokyo, Japan). IR spectra were measured on a JASCO FT/IR 410 spectrophotometer. Ultraviolet (UV) spectra were obtained on a JASCO V-560 UV/VIS spectrophotometer. ECD spectra were measured with a JASCO J-725N spectrophotometer. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were recorded on a Varian Unity plus 500 spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) operating at 500 MHz and 126 MHz for the 1H and 13C nuclei, respectively. 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra were also recorded on a JEOL JNM-AL400 spectrometer (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) operating at 400 and 100 MHz for the 1H and 13C nuclei, respectively. Coupling constants (J) were expressed in hertz and chemical shifts (δ) are reported in ppm with the solvent signal used as a standard (pyridine-d5: δH 7.19, δC 123.5 and methanol-d4: δH 3.31, δC 49.0). FAB-MS data were recorded on a JMS700N spectrometer (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) using m-nitrobenzyl alcohol or glycerol as the matrix. ESI-TOF-MS data were recorded on a quadrupole (Q)-TOF LC/MS (Agilent 6550, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Column chromatography was performed using Sephadex LH-20 (25–100 μm, GE Healthcare UK Ltd., Little Chalfont, UK), Diaion HP20PSS (Mitsubishi Chemical Co., Tokyo, Japan), Chromatorex ODS (Fuji Silysia Chemical Ltd., Kasugai, Japan), and Toyopearl butyl-650M (Tosoh Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) columns. TLC was performed on precoated Kieselgel 60 F254 plates (0.2 mm thick, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) with CHCl3-MeOH-H2O (10:3:0.5 or 7:3:0.5, v/v) and toluene-ethyl formate-formic acid (1:7:1, v/v) mixtures being used as the eluents. The spots were detected using UV illumination and by spraying with a 5% H2SO4 solution followed by heating. Analytical HPLC was performed on a Cosmosil 5C18-ARII (Nacalai Tesque, Kyoto, Japan) column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, i.d.) with a gradient elution of 4–30% (39 min) and 30–75% (15 min) CH3CN in 50 mM H3PO4 at 35 °C (flow rate, 0.8 mL/min; detection, JASCO photodiode array detector MD-2010).
3.2. Plant Material
The whole plant of Persicaria capitata was collected in Shui Cheng, China, in 2014, and in Nagasaki, Japan, in 2017. The aerial part of Persicaria chinensis were collected in Nagasaki, Japan, in 2014. Voucher specimens were deposited at the Nagasaki University Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences. Fresh rhizome of Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense were purchased in a medicinal plant market in Guangxi, China. A voucher specimen was deposited at the Guangxi Institute of Botany. Aerial parts of Reynoutria japonica, Persicaria perfoliata, P. longiseta, P. lapathifolia, P. filiformis, and P. thunbergii were collected in Nagasaki, Japan.
3.3. HPLC Analysis
Fresh aerial parts (1.0 g) of Reynoutria japonica, Persicaria perfoliata, P. longiseta, P. lapathifolia, P. capitata (syn. Polygonum capitatum), P. chinensis (syn. Polygonum chinense), P. filiformis, and P. thunbergii were extracted with 60% CH3CN (20 mL) and analyzed by HPLC (Figure S1, Supplementary Materials).
3.4. Extraction and Separation
3.4.1. Persicaria Capitata
The EtOH extract (200 g) of P. capitata was suspended in 50% MeOH and insoluble material was removed by filtration. The soluble part (132 g) was fractionated by Diaion HP20SS column chromatography (8 cm i.d. × 35 cm) with 0–100% MeOH (10% stepwise gradient elution, each 500 mL) to give 8 fractions (fr.): fr. 1 (84.5 g), fr. 2 (2.2 g), fr. 3 (3.9 g), fr. 4 (9.5 g), fr. 1–5 (14 g), fr. 1–6 (4.3 g), fr. 1–7 (6.9 g), and fr. 1–8 (2.1 g). Fr. 3 was subjected to a combination of column chromatography using Sephadex LH-20 (0–100% MeOH), Avicel cellulose (2% AcOH), and Diaion HP20SS (0–50% MeOH) to give 2,3-di-O-galloyl-d-glucose (719 mg) and 2,4-di-O-galloyl-d-glucose (101 mg). Similar separation of fr. 4 by chromatography using Sephadex LH-20 and Chromatorex ODS (0–50% MeOH, 5% stepwise gradient) to yield 2,3,4-tri-O-galloyl-d-glucose (2.26 g), 6-O-galloyl arbutin (79 mg), 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenol 1-O-β-d-(6′-O-galloyl)-glucopyranoside (37 mg), 4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenol 1-O-β-d-(6′-O-galloyl)-glucopyranoside (46 mg). Fr. 6 was purified by precipitation from water to give davidiin (1) (13 g). Fr. 7 was subjected to a column chromatography on Sephadex LH-20 (60–100% MeOH), Diaion HP20SS, and Chromatorex ODS to give quercetin 3-O-α-rhamnoside (2.5 g), quercetin (719 mg), quercetin 3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (182 mg), quercetin 3-O-α-L-(3”-O-galloyl)-rhamnoside (6.7 mg). The insoluble part of the extract (68 g) was washed with CHCl3–MeOH (1:1, v/v) to remove non-polar substances and a part (5 g) of the residue (31.5 g) was subjected to size-exclusion column chromatography using a Sephadex LH-20 column (4 cm i.d. × 45 cm) with 7 M urea:acetone (2:3, v/v, containing conc. HCl at 5 mL/L) to give fractions containing oligomeric polyphenols and compounds with low-molecular weight [35]. The fractions were separated by Diaion HP20SS column chromatography to give oligomeric proanthocyanidins (707 mg) and ellagic acid (54 mg).
3.4.2. Persicaria Chinensis
The fresh aerial part of P. chinensis (1.18 kg) was extracted with 60% aqueous acetone (3 L) three times. The extract was concentrated and the resulting insoluble precipitates were removed by filtration. The aqueous filtrate was applied to a column of Diaion HP20SS (7 cm i.d. × 50 cm) with 0–100% MeOH (10% stepwise gradient elution, each 500 mL) to give 11 fractions. Crystallization of fr. 3 from H2O yielded 1-O-galloyl-β-d-glucopyranose (301 mg). Separation of fr. 7 (4.61 g) by Sephadex LH-20 (0–100% MeOH) gave polymeric proanthocyanidins (1.37 g), 3 (1.37 g), and 1,2,6-tri-O-galloyl-β-d-glucopyranose (76 mg). Fr. 8 (11.2 g) was subjected to Sephadex LH-20 (0–100% MeOH and then MeOH–H2O–acetone, 8:1:1 and 3:1:1) to give quercetin 3-O-(2’’-α-rhamnopyranosyl)-β-glucuronopyranoside (481 mg) and 2 (553 mg).
3.4.3. Polygonum Runcinatum var. Sinense
The dried root of Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense (805 g) was extracted with 60% acetone (4 L) twice and then MeOH. The extracts were combined and concentrated, and the aqueous solution was applied to a Diaion HP20SS column (8 cm i.d. × 35 cm) with 0–100% MeOH (10% stepwise gradient elution, each 500 mL) to give 13 fractions. HPLC analysis showed that fr. 4–10 (total 159 g) contained 7 as the major component. Fr. 3 (29.7 g) was separated by Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography (6 cm i.d. × 31 cm) with 0–100% MeOH to give 7 (6.68 g), 10 (1.44 g), and a subfraction containing 9 and 11. Further chromatography of the subfraction using Chromatorex ODS (0–50% MeOH) and Toyopearl butyl-650M (0–50% MeOH) to yield 9 (490 mg) and 11 (19 mg). Fr. 11 (40.2 g) was separated by Sephadex LH-20 (60–100% MeOH), Sephadex LH-20 [7 M urea:acetone (2:3, v/v, containing conc. HCl at 5 mL/L)], and Diaion HP20SS column chromatography to afford 8 (990 mg) and a mixture of oligomeric polyphenols detected at origin on TLC plate.
3.5. Spectroscopic Data
3.5.1. Persicarianin (3)
Brown amorphous powder, [α]D +43.8 (c 0.1, MeOH), IR νmax cm−1: 3412, 1728, 1708, 1614, 1533, 1450, UV λmax (MeOH) nm (log ε): 271 (4.06), 218 (4.59), HRESIMS m/z: 673.0690 (Calculated for C27H22O19Na: 673.0653), ECD (MeOH) Δε (nm): −25.16 (213), +6.68 (234), −5.47 (283), +2.36 (374). 1H-NMR (acetone-d6, 500 MHz) δH: 7.19 (s, α-galloyl-2,6), 7.18 (s, β-galloyl-2,6), 6.76 (s, α,β-DHHDP-6”), 6.38 (s, α-DHHDP-3), 6.37 (s, β-DHHDP-3), 5.63 (dd, J = 9.8, 9.5 Hz, α-glc H-3), 5.42 (t, J = 9.4 Hz, β-glc H-3), 5.40 (t, J = 9.4, α,β-glc H-4), 5.32 (d, J = 3.4 Hz, α-glc H-1), 5.01 (dd, J = 4.8, 10.7 Hz, α-glc H-6), 4.94 (dd, J = 4.8, 10.7 Hz, α-glc H-6), 4.88 (d, J = 7.8 Hz, β-glc H-1), 4.65 (s, α-DHHDP-1’), 4.63 (s, β-DHHDP-1’), 4.25 (m, α-glc H-5), 3.95 (m, α-glc H-5, α-glc H-6, β-glc H-6), 3.89 (dd, J = 9.8, 3.4 Hz, α-glc H-2), 3.66 (dd, J = 9.4, 7.8 Hz, β-glc H-2), 13C NMR (acetone-d6, 125 MHz) δC: 192.0 (α,β-DHHDP-4’), 168.1 (α,β-DHHDP-7), 166.9 (galloyl-7), 164.6 (α,β-DHHDP-7’), 151.7 (α,β-DHHDP-2’), 146.0 (α,β-DHHDP-4), 145.9 (galloyl-3,5), 142.3 (α,β-DHHDP-6), 138.8 (galloyl-4), 135.4 (α,β-DHHDP-5), 130.8 (α,β-DHHDP-3’), 124.1 (α,β-DHHDP-2), 121.7 (galloyl-1), 112.7 (α,β-DHHDP-1), 110.1 (galloyl-2,6), 107.7 (β-DHHDP-3), 107.6 (α-DHHDP-3), 97.8 (β-glc H-1), 96.5 (α,β-DHHDP-5’), 93.6 (α-glc C-1), 91.5 (α,β-DHHDP-6’), 75.6 (β-glc C-3), 74.1 (α-glc C-4), 74.0 (β-glc C-4), 73.7 (β-glc C-2), 73.3 (α-glc C-3), 71.2 (α-glc C-2), 68.3 (β-glc C-5), 66.9 (α-glc C-6), 66.4 (β-glc C-6), 64.4 (α-glc C-5), 43.0 (α,β-DHHDP-1’).
3.5.2. Polygonanin A (11)
Tan amorphous powder, [α]D −51.3° (c 0.1, MeOH), FABMS m/z: 841 (M + Na)+, 819 (M + H)+, HRFABMS m/z: 819.0891 (M + H)+ (Calcd for C34H27O24: 819.0887), IR νmax cm-1 (neat): 3412, 1719, 1616, 1445, 1313, 1223, 1190. UV λmax (MeOH) nm (log ε): 266 (4.40), 230 (4.70). ECD (MeOH) λmax (Δε): 316 (−2.4), 283 (+12.6), 261 (−8.9), 241 (+17.9), 227 (+0.6), 217 (+5.5). 1H NMR (500 MHz, acetone-d6) δH: 7.46 (1H, s, hydroxychebuloyl (HChe) H-3), 6.83 (1H, s, HHDP-3), 6.79 (1H, s, HHDP-3’), 5.95 (1H, s, glc H-1), 5.14 (1H, br s, glc H-3), 5.10 (1H, br s, glc H-4), 4.99 (1H, t, J = 11.1 Hz, glc H-6), 4.88 (1H, d, J = 2.8 Hz, HChe H-3’), 4.83 (1H, br s, HChe H-2’), 4.72 (1H, br s, glc H-2), 4.48 (1H, dd, J = 5.3, 11.1 Hz, glc H-5), 4.08 (1H, dd, J = 5.3, 11.1 Hz, glc H-6), 3.35 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, HChe H-5’), 2.78 (1H, d, J = 15.9 Hz, HChe H-5’). 13C NMR (125 MHz, acetone-d6) δC: 172.3 (HChe-1’), 172.0 (C-6’), 168.2 (HHDP-7’), 166.7 (HChe-7), 166.4 (HHDP-7), 166.1 (HChe-7’), 146.0 (HChe-4), 145.3 (HHDP-4’), 144.5, 144.9 (HHDP-6, 6’), 143.0 (HChe-6), 144.7 (HHDP-4), 138.5 (HChe-5), 136.9 (HHDP-5), 136.3 (HHDP-5’), 125.9 (HHDP-2), 125.7 (HHDP-2’), 121.0 (HChe-2), 116.7 (HHDP-1), 116.2 (HChe-3), 115.4 (HHDP-1’), 114.5 (HChe-1), 109.8 (HHDP-3), 108.7 (HHDP-3’), 90.4 (glc C-1), 76.3 (HChe-4’), 71.7 (glc C-2), 70.9 (glc C-5), 69.2 (glc C-4), 66.3 (HChe-2’), 64.2 (glc C-6), 59.1 (glc C-3), 49.2 (HChe-3’), 41.6 (HChe-5’).
3.6. Acid Hydrolysis of 3
Persicarianin (3) (10 mg) was hydrolyzed by heating in 5% H2SO4 (1 mL) at 105 °C for 5 h in a screw capped vial. The precipitates (2.7 mg) formed in the mixture were collected by filtration. HPLC analysis of the filtrate showed peaks assignable to gallic acid (8.94 min), brevifolin carboxylic acid (21.36 min), and ellagic acid (30.66 min), which were identified by comparison of tR and UV absorption with those of authentic samples. HPLC analysis of the precipitates showed only a peak for ellagic acid. The filtrate was neutralized with saturated Ba(OH)2 and resulting precipitate of BaSO4 was removed by filtration. The filtrate was concentrated and the residue was dissolved in 0.5 mL of pyridine containing L-cysteine HCl (5.0 mg), and heated at 60 °C for 1 h. To the mixture was added o-tolylisothiocyanate (20 μL) and this mixture heated at 60 °C for 1 h. The final mixture was then cooled to ambient temperature and directly analyzed using HPLC. The retention time of the peak at 34.8 min coincided with that of the thiazolidine derivatives of D-glucose (L-glucose: 35. 6 min).
3.7. Computational Calculation of 8
A conformational search was performed using the Monte Carlo method and the MMFF94 force field with Spartan ′14 (Wavefunction, Irvine, CA). The low-energy conformers within a 6 kcal/mol window were optimized at the B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level in acetone (SMD). The vibrational frequencies were also calculated at the same level to confirm their stability, and no imaginary frequencies were found. The magnetic shielding constants (σ) of the low-energy conformers with Boltzmann populations greater than 1% were calculated using the gauge-independent atomic orbital (GIAO) method at the mPW1PW91/6-311+G(2d,p) level in acetone (PCM) and were weight-averaged [36,37,38].
3.8. Thiol Degradation
Polymeric polyphenols obtained from the three plants (5 mg) were dissolved in a solution containing 4% 2-mercaptoethanol and 0.1% HCl in 60% EtOH (1 mL). The mixture was heated at 70 °C for 7 h and analyzed by HPLC. The standard thiol degradation products were obtained from persimmon proanthocyanidins [34].
4. Conclusions
Distribution of hydrolyzable tannins in the plant kingdom is much more limited compared with that of proanthocyanidins. In Polygonaceous plants, a hydrolyzable tannin had only been isolated from Persicaria capitatum. In this study, we reinvestigated P. capitatum and showed the presence of minor gallotannins and proanthocyanidin oligomers comprised of epicatechin and epicatechin-3-O-gallate. From Persicaria chinensis, a new hydrolyzable tannin called persicarianin (3) was isolated together with an ellagitannin geraniin and proanthocyanidin oligomers mainly comprising epicatechin, epigallocatechin and their galloyl esters. The rhizome of Polygonum runcinatum var. sinense contained granatin A (7) as the major constituent along with minor ellagitannins, including a new ellagitannin polygonanin A (11). These results prompted us to continue investigations into hydrolyzable tannins in this plant family.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online, Figure S1: HPLC of extracts of Polygonaceous plants, Figure S2: HPLC analysis of acid hydrolysis products of 3, Figure S3: Thiol degradation of proanthocyanidin oligomers, Figures S4–S8: 1D and 2D NMR spectra of 3, Figures S9–S14: 1D and 2D NMR spectra of 11. Figures S15 and S16: 1H and 13C NMR spectra of 7, Figures S17 and S18: 1H and 13C NMR spectra of 7a.
Author Contributions
Y.-Q.L., M.K., J.T. performed experiments including extraction, chromatographic separation, and spectroscopic analyses. T.T., Y.-L.H., D.-P.L., Z.-H.J. and G.-i.N. conceived and designed the experiments. Z.-H.J., Y.-F.W., Y.-L.H., T.T. and G.-i.N. collected plant materials. Y.M. performed the computational calculation. Y.-Q.L., M.K., Y.S. and Y.M. analyzed the data. Y.M. and T.T. wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers 20K07102, and 17K08338.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to N. Tsuda, K. Chifuku and H. Iwata, Center for Industry, University and Government Cooperation, Nagasaki University, for recording NMR and MS data. Some computations were carried out using the computer facilities at the Research Institute for Information Technology, Kyushu University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Samples are not available from the authors.
References
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T. Hydrolyzable tannins and related polyphenols. In Progress in the chemistry of organic natural products; Herz, W., Kirby, G.W., Moore, R.E., Steglich, W., Tamm, C., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 66, pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Haslam, E.; Cai, Y. Plant polyphenols (vegetable tannins): Gallic acid metabolism. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1994, 11, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H.; Okuda, T. Structural diversity and antimicrobial activities of ellagitannins. In Chemistry and Biology of Ellagitannins, An Underestimated Class of Bioactive Plant Polyphenols; Quideau, S., Ed.; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2009; pp. 55–93. [Google Scholar]
- Quideau, S.; Feldman, K.S. Ellagitannin chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1996, 96, 475–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quideau, S.; Deffieux, D.; Douat-Casassus, C.; Pouységu, L. Plant Polyphenols: Chemical Properties, Biological Activities, and Synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 586–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Ma, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-F.; Wang, Y.; Feng, R.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tan, X.-S.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Sun, Y.-P.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Identification of metabolites of FR429, a potential antitumor ellagitannin, transformed by rat intestinal bacteria in vitro, based on liquid chromatography-ion trap-time of flight mass spectrometry analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 71, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.-M.; Yau, L.-F.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Xia, Y.; Wang, J.-R. Sphingolipidomic study of davidiin-treated HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells using UHPLC-MS. RSC Advances 2017, 7, 55249–55256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.-Y.; Zhou, X.; Fu, J.; He, C.-Y.; Feng, R.; Huang, M.; Shou, J.-W.; Zhao, Z.-X.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. In vivo metabolite profiling of a purified ellagitannin isolated from Polygonum capitatum in rats. Molecules 2016, 21, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, J.; Chow, S.-C.; Li, C.-H.; Xiao, Z.; Feng, R.; Fu, J.; Chen, Y. A potential antitumor ellagitannin, davidiin, inhibited hepatocellular tumor growth by targeting EZH2. Tumor Biology 2014, 35, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, M.; Jia, H.; Zhang, T.; Shang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Z.; Zou, Z. Comprehensive identification of potential antioxidant components in the aerial parts of Polygonum chinense L. var. hispidum using ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 2380–2392. [Google Scholar]
- Hatano, T.; Ogawa, N.; Kira, R.; Yasuhara, T.; Okuda, T. Tannins of Cornaceous plants. I. Cornusiins A, B and C, dimeric monomeric and trimeric hydrolyzable tannins from Cornus officinalis, and orientation of valoneoyl group in related tannins. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989, 37, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Phillipson, J.D.; Greengrass, P.M.; Bowery, N.E.; Cai, Y. Plant polyphenols: Biologically active compounds or non-selective binders to protein? Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Nakazawa, T.; Hatano, T.; Yang, R.C.; Yang, L.L.; Yen, K.Y.; Okuda, T. A dimeric hydrolysable tannin from Camellia oleifera. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes, G.A.C.; da Silva, A.J.R.; Ferri, P.H.; Santos, S.C. Phenolic compounds from the leaves of Eucalyptus microcorys F. Muell. Rec. Nat. Prod 2015, 9, 292–296. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Fukushima, M.; Okuda, T. Tannins and related polyphenols of the Saxifragaceae. Part, I. Galloylarbutin and other polyphenols from Bergenia purpurascens. Phytochemistry 1987, 26, 515–517. [Google Scholar]
- Saijo, R.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. Part 82. Phenol glucoside gallates from Mallotus japonicus. Phytochemistry 1989, 28, 2443–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markham, K.R.; Ternai, B.; Stanley, R.; Geiger, H.; Mabry, T.J. Carbon-13 NMR studies of flavonoids. III. Naturally occurring flavonoid glycosides and their acylated derivatives. Tetrahedron 1978, 34, 1389–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharram, F.A.; Marzouk, M.S.A.; Ibrahim, M.T.; Mabry, T.J. Antioxidant galloylated flavonol glycosides from Calliandra haematocephala. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I.; Miyahara, K.; Kawasaki, T. Tannins and related compounds. part 37. Isolation and structure elucidation of elaeocarpusin, a novel ellagitannin from Elaeocarpus sylvestris var. ellipticus. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1986, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. Part 14. 7-O-Galloyl-(+)-catechin and 3-O-galloylprocyanidin B-3 from Sanguisorba officinalis. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 2575–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T. Constituents of Geranium thunbergii Sieb. et Zucc. Part 12. Hydrated stereostructure and the equilibration of geraniin. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1982, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, M.; Tanaka, T.; Ito, T.; Nakaya, K.; Iliya, I.; Ohyama, M.; Iinuma, M.; Murata, H.; Inatomi, Y.; Inada, A.; et al. Flavonol glycosides in leaves of two Diospyros Species. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 53, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nonaka, G.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nishioka, I. Trapain, a new hydrolyzable tannin from Trapa japonica Flerov. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Koga, T.; Tho, N.; Kuriyama, K. Circular dichroism of hydrolysable tannins-II dehydroellagitannins. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 3941–3944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nakashima, T.; Ueda, T.; Tomii, K.; Kouno, I. Facile discrimination of aldose enantiomers by reversed-phase HPLC. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 899–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Era, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Shii, T.; Saito, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Jiang, Z.H. Diastereomeric Ellagitannin Isomers from Penthorum chinense. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2104–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Era, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tanaka, T. Production of ellagitannin hexahydroxydiphenoyl ester by spontaneous reduction of dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl ester. Molecules 2020, 25, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kojima, D.; Shimizu, K.; Aritake, K.; Era, M.; Matsuo, Y.; Saito, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G. Highly oxidized ellagitannins of Carpinus japonica and their oxidation-reduction disproportionation. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 3424–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. Part 30. Punicafolin, an ellagitannin from the leaves of Punica granatum. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 2075–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Fujisaki, H.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. CXVIII. Structures, preparation, high-performance liquid chromatography and some reactions of dehydroellagitannin-acetone condensates. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1992, 40, 2937–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Tanaka, T.; Nonaka, G.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. XCV. Isolation and characterization of helioscopinins and helioscopins, four new hydrolyzable tannins from Euphorbia helioscopia L. (1). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 1518–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esumi, A.; Aoyama, H.; Shimozu, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Hatano, T. Modified dehydroellagitannins from Davidia involucrata leaves. Heterocycles 2019, 98, 895–903. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.-H. Studies on tannins from the bark of Macaranga sinensis (Baill.) Muell.-Arg. J. Food Drug Anal. 1994, 2, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Takahashi, R.; Kouno, I.; Nonaka, G. Chemical evidence for the de-astringency (insolubilization of tannins) of persimmon fruit. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1994, 3013–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, A.; Shoji, T.; Shibusawa, Y. Separation of proanthocyanidins by degree of polymerization by means of size-exclusion chromatography and related techniques. J. Biochem. Biophy. Meth. 2003, 56, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyk, M.W.; Siebert, M.R.; Tantillo, D.J. Computational prediction of 1H and 13C chemical shifts: A useful tool for natural product, mechanistic, and synthetic organic chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1839–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimblat, N.; Sarotti, A.M. Computational chemistry to the rescue: Modern toolboxes for the assignment of complex molecules by GIAO NMR calculations. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 12246–12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardi, M.M.; Marcarino, M.O.; Sarotti, A.M. Redefining the impact of boltzmann analysis in the stereochemical assignment of polar and flexible molecules by NMR calculations. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).