A Colorimetric Membrane-Based Sensor with Improved Selectivity towards Amphetamine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
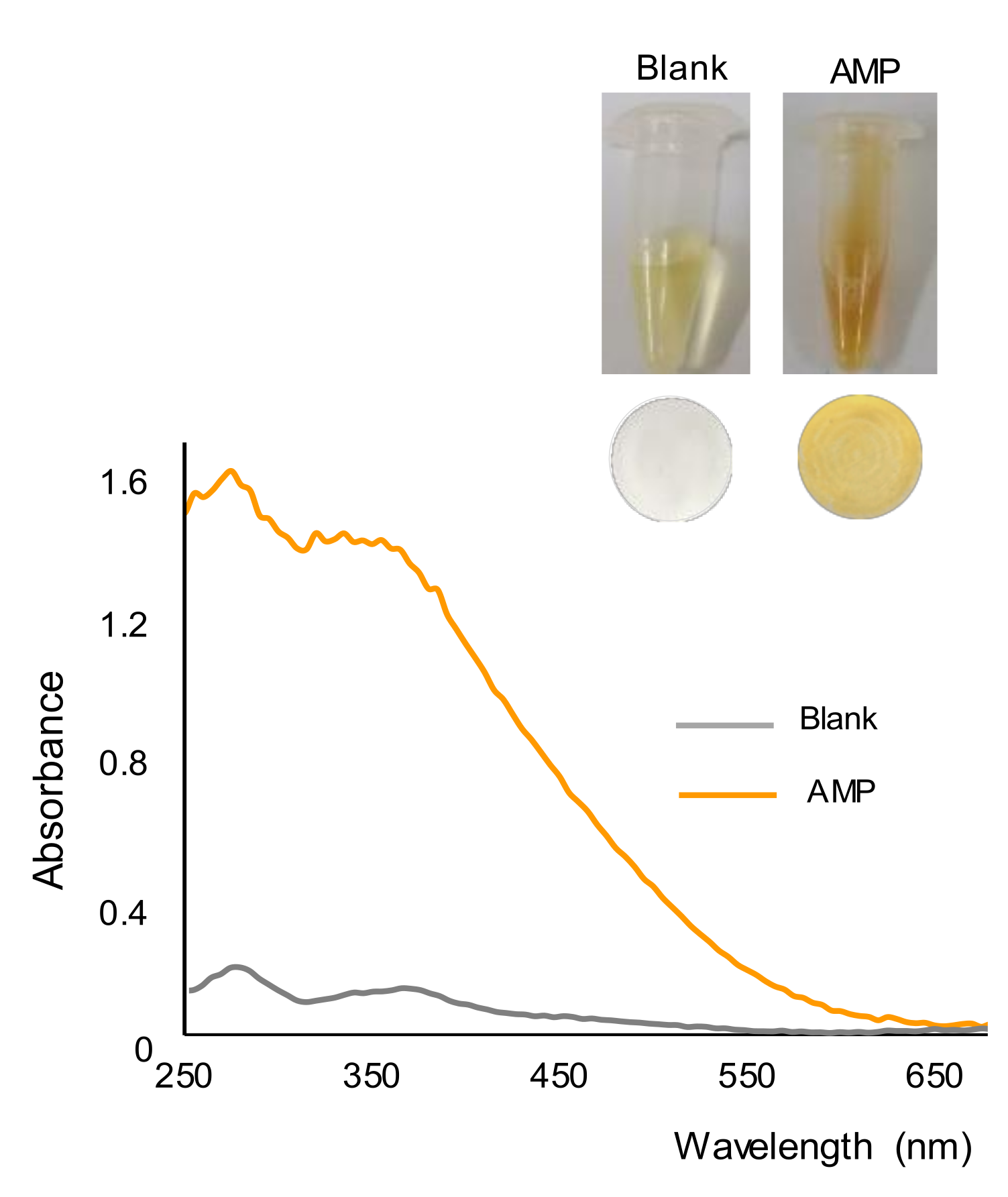
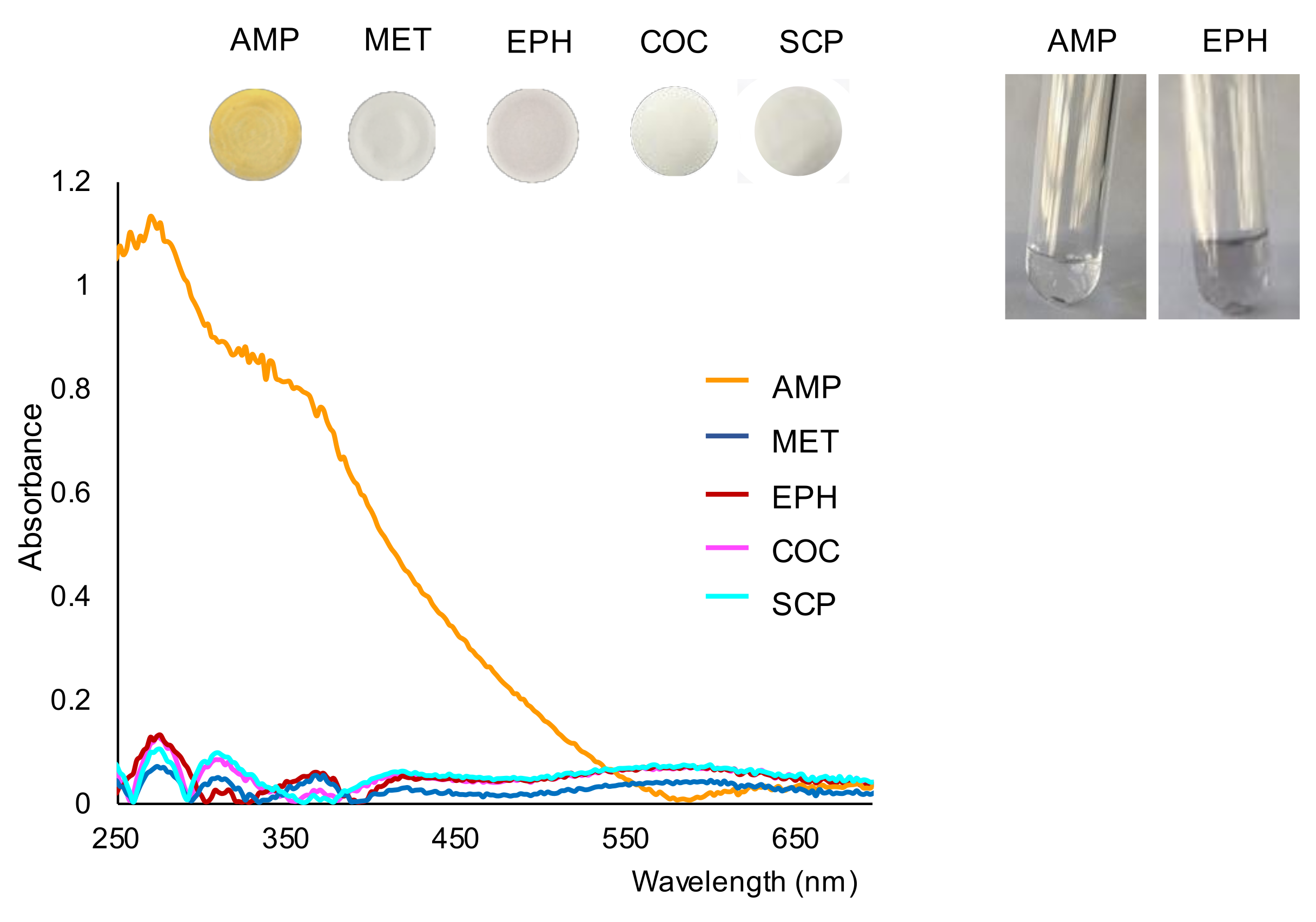
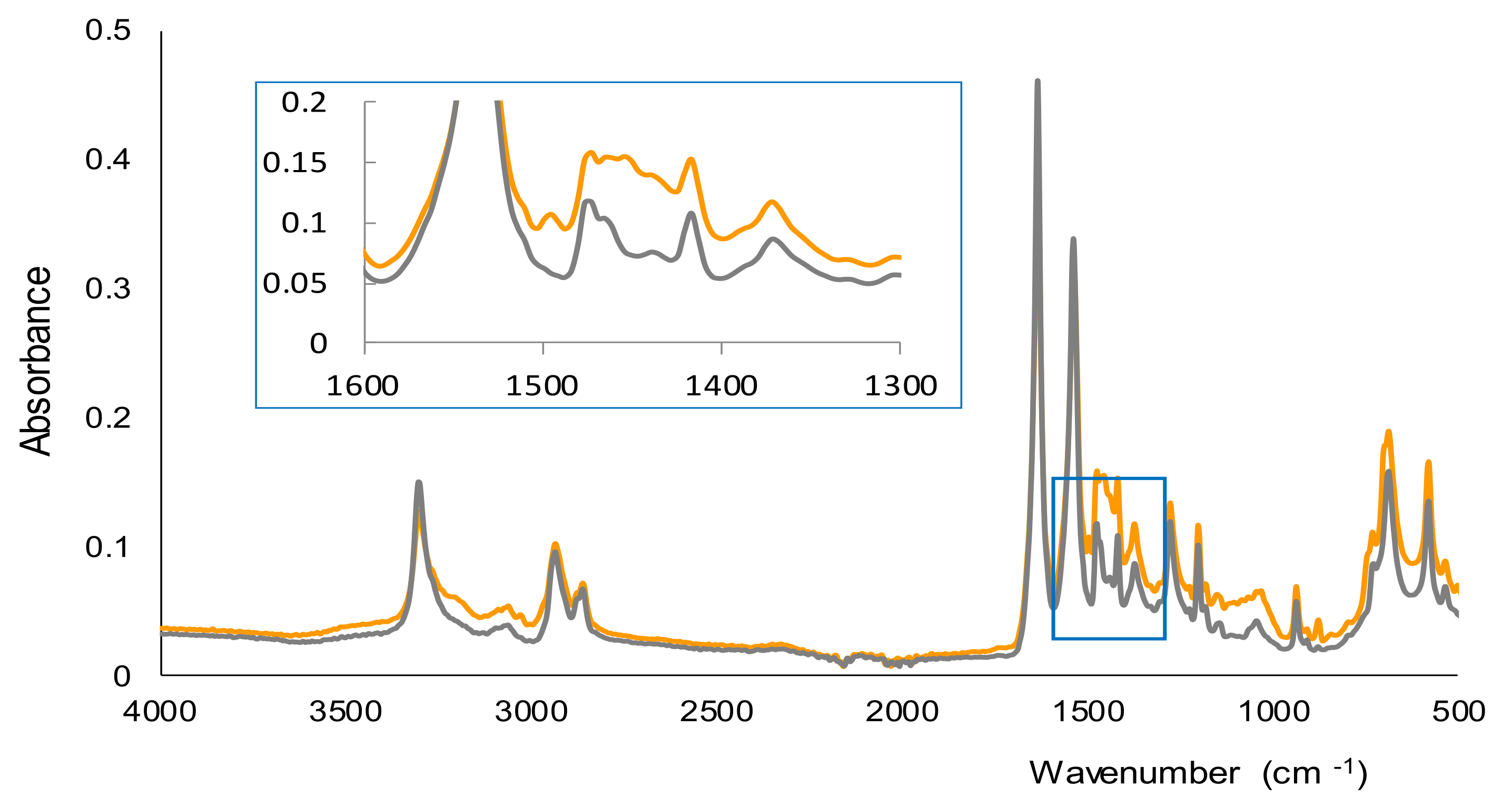
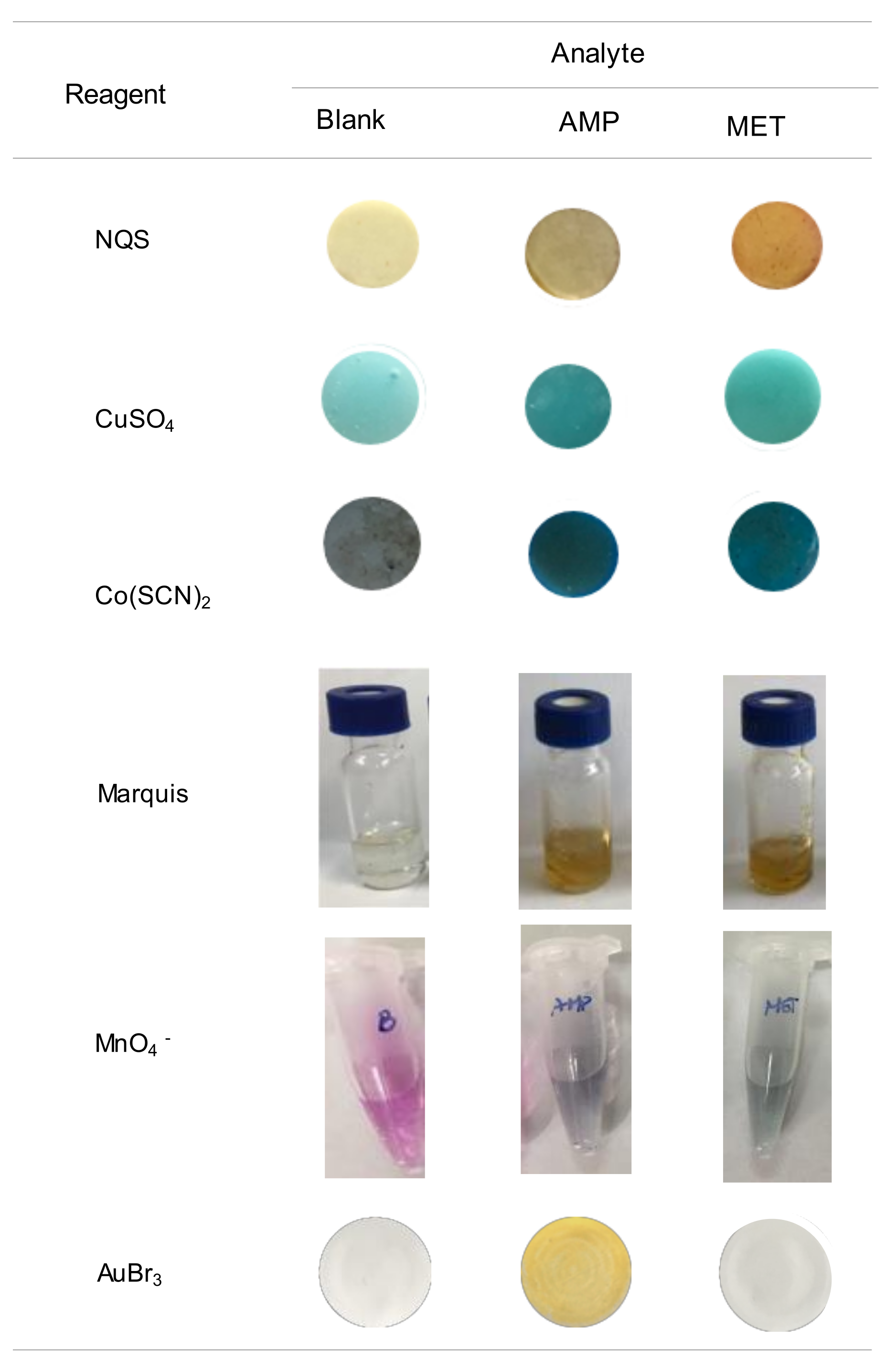
2.1. Study of the Reaction and Selectivity
2.2. Quantitative Performance
2.3. Digital Color Analysis of the Filters
2.4. Application to the Analysis of Drug Street Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Solutions
4.2. Reaction Conditions
4.3. Instrumentation and Conditions
4.4. Application to the Analysis of Drug Street Samples
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- United Nation Office on Drugs and Crime (UNDOC), World Drug Report. Available online: https://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wdr2021.html (accessed on 20 September 2021).
- Rhumorbarbe, D.; Staehli, L.; Broséus, J.; Rossy, Q.; Esseiva, P. Buying drugs on a Darknet market: A better deal? Studying the online illicit drug market through the analysis of digital, physical and chemical data. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 267, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, M.H.Y.; Ching, D.K.; Lee, C.Y.W.; Lam, Y.-H.-; Mak, T.W.L. Simultaneous detection of 93 conventional and emerging drugs of abuse and their metabolites in urine by UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr B 2014, 969, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepyala, D.; Tsai, I.-L.-; Liao, H.-W.; Chen, G.-Y.; Chao, H.-C.; Kuo, C.-H. Sensitive screening of abused drugs in dried blood samples using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-ion booster-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1491, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musile, G.; Mazzola, M.; Shestakova, K.; Savchuk, S.; Appolonova, S.; Tagliaro, F. A simple and robust method for broad range screening of hair samples for drugs of abuse using a high-throughput UHPLC-Ion Trap MS instrument. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 1152, 122263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philp, M.; Fu, S. A review of chemical ‘spot’ tests: A presumptive illicit drug identification technique. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, E.; Pla, L.; Lozano-Torres, B.; El Sayed, S.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F. Chromogenic and fluorogenic probes for the detection of illicit drugs. Chem. Open 2018, 7, 401–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, L.; Powell, J.; Pijl, E.M. An overview of forensic drug testing methods and their suitability for harm reduction point-of-care services. Harm Reduct. J. 2017, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; He, X.; Xu, F.; Li, F. Pen-on-paper strategies for point-of-care testing of human health. Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 108, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, W.R.; Cardoso, T.M.G.; da Rocha, R.G.; Santana, M.H.P.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; Richter, E.M.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Coltro, W.K.T. Portable analytical platforms for forensic chemistry: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1034, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musile, G.; Wang, L.; Bottoms, J.; Tagliaro, F.; McCord, B. The development of paper microfluidic devices for presumptive drug detection. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 8025–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, S.T.; Woolf, M.S.; Hadley, K.C.; Collins, N.M.; Nauman, A.Q.; Landers, J.P. Centrifugal microfluidic devices using low-volume reagent storage and inward fluid displacement for presumptive drug detection. Sensor Actuat. B-Chem. 2019, 284, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choodum, A.; Daeid, N.N. Digital image-based colourimetric tests for amphetamine and methamphetamine. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choodum, A.; Daeid, N.N. Rapid and semi-quantitative presumptive tests for opiate drugs. Talanta 2011, 86, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choodum, A.; Parabun, K.; Klawach, N.; Daeid, N.N.; Kanatharana, P.; Wongniramaikul, W. Real time quantitative colourimetric test for methamphetamine detection using digital and mobile phone technology. Forensic Sci. Int. 2014, 235, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argente-García, A.; Jornet-Martínez, N.; Herráez-Hernández, R.; Campíns-Falcó, P. A solid colorimetric sensor for the analysis of amphetamine-like street samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 943, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argente-García, A.; Jornet-Martínez, N.; Herráez-Hernández, R.; Campíns-Falcó, P. Passive solid sensor for in-situ colorimetric estimation of the presence of ketamine in illicit drug samples. Sensor Actuat. B-Chem. 2017, 253, 1137–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jornet-Martínez, N.; Herráez-Hernández, R.; Campíns-Falcó, P. Stabilization of formaldehyde into polydimethylsiloxane composite: Application to the in-situ determination of illicit drugs. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2141–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jornet-Martínez, N.; Samper-Avilés, M.; Herráez-Hernández, R.; Campíns-Falcó, P. Modifying the reactivity of copper (II) by its encapsulation into polydimethylsiloxane: A selective sensor for ephedrine-like compounds. Talanta 2019, 196, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.R.; Chand, R.; Kumar, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R. Recent biosensing advances in the rapid detection of illicit drugs. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 131, 116006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, T.-L.E.; Leong, T.X.; Bliese, S.L.; Helmke, A.; Richard, A.; Merga, G.; Rorabeck, J.; Lieberman, M. idPAD: Paper analytical device for presumptive identification of illicit drugs. J. Forensic Sci. 2020, 65, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornet-Martínez, N.; Herráez-Hernández, R.; Campíns-Falcó, P. Scopolamine analysis in beverages: Bicolorimetric device vs portable nanoliquid chromatography. Talanta 2021, 232, 122406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, M. A new, highly specific color tests for ketamine. Microgram J. 2006, 4, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Herráez-Hernández, R.; Jornet-Martínez, N.; Fernández-Ortiz, N.; Campíns-Falcó, P. On-site detection and quantification of ketamine in illicit samples by digital color analysis. In Ketamine: History, Uses and Health Effects; McBride, L.A., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 185–205. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, Y.J.; Page, Z.A.; Knight, A.S.; Treat, N.J.; Hemmer, J.; Hawker, C.J.; de Alaniz, J.R. A Versatile and highly selective colorimetric sensor for the detection of amines. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 3562–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, P.; Leung, H.T.; Sun, G. Colorimetric detection of carcinogenic alkylating fumigants on nylon-6 nanofibrous membrane. Part I: Investigation of 4-(p-nitrobenzyl)pyridine as a “new” sensing agent with ultrahigh sensitivity. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 14593–14601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Leung, H.T.; Gomez, M.T.; Sun, G. Sensitivity-tunable colorimetric detection of chloropicrin vapor on nylon-6 nanofibrous membrane based on a detoxification reaction with biological thiols. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moliner-Martínez, Y.; Muñoz-Ortuño, M.; Herráez-Hernández, R.; Campíns-Falcó, P. Rapid analysis of effluents generated by the dairy industry for fat determination by preconcentration in nylon membranes and attenuated total reflectance infrared spectroscopy measurement. Talanta 2014, 119, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, R.M.; Domingos, E.; Tosato, F.; dos Santos, N.A.; Leite, J.A.; da Silva, M.; Marcelo, M.C.A.; Ortiz, R.S.; Filgueiras, P.R.; Romão, W. Portable near infrared spectroscopy applied to abuse drugs and medicine analyses. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Liu, H.; Meng, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. Portable kit for identification and detection of drugs in human urine using surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 9500–9506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.W.; Xie, X.; Pham, M.; Peaden, P.A.; Patil, M.L.; Tolley, L.T.; Farnsworth, P.B.; Tolley, H.D.; Lee, M.L.; Grinias, J.P. Portable capillary liquid chromatography for pharmaceutical and illicit drug analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2020, 43, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Linearity, y = ax + b (n = 15) | Precision, RDS (n = 3) (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a ± Sa | b ± Sb | R2 | ||
| Absorbance | 0.0011 ± 0.0001 | −0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.990 | 9 1 |
| 8 2 | ||||
| Color Image Analysis | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.42 ± 0.08 | 0.993 | 3 1 |
| 4 2 | ||||
| Sample | Percentage of AMP in the Sample (%) | Percentage of AMP Found (%) | Er (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AMP + EPH | 25 | 24 ± 4 | −4 |
| 75 | 76 ± 8 | +1 | |
| AMP + Caffeine | 25 | 26 ± 2 | +4 |
| 75 | 77 ± 4 | +3 |
| Analytical Signal | Found Concentration, (n = 3) (ppm) | Er (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | 420 ± 40 | −4 |
| Color Coordinate (Blue) | 448 ± 18 | +12 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jornet-Martínez, N.; Campíns-Falcó, P.; Herráez-Hernández, R. A Colorimetric Membrane-Based Sensor with Improved Selectivity towards Amphetamine. Molecules 2021, 26, 6713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216713
Jornet-Martínez N, Campíns-Falcó P, Herráez-Hernández R. A Colorimetric Membrane-Based Sensor with Improved Selectivity towards Amphetamine. Molecules. 2021; 26(21):6713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216713
Chicago/Turabian StyleJornet-Martínez, Neus, Pilar Campíns-Falcó, and Rosa Herráez-Hernández. 2021. "A Colorimetric Membrane-Based Sensor with Improved Selectivity towards Amphetamine" Molecules 26, no. 21: 6713. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26216713







