Abstract
Due to their remarkable electronic features, recent years have witnessed the emergence of carbones L2C, which consist in two donating L ligands coordinating a central carbon atom bearing two lone pairs. In this context, the phosphine/sulfoxide-supported carbone 4 exhibits a strong nucleophilic character, and here, we describe its ability to coordinate dichlorogermylene. Two original stable coordination complexes were obtained and fully characterized in solution and in the solid state by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis, respectively. At 60 °C, in the presence of 4, the Ge(II)-complex 5 undergoes a slow isomerization that transforms the bis-ylide ligand into an yldiide.
1. Introduction
The rapid development of homogeneous catalysis in the last decades is highly related to the intensive research that was accomplished toward ligand design. Due to their lone pair(s) and their related nucleophilic character, oxygen-, nitrogen-, sulfur- and phosphorus-containing ligands have been dominating in the field for several decades [1]. In the late 1980s, the discovery of the first stable carbenes represented the milestone leading to the emergence of carbon-based ligands (I, Figure 1) [2,3]. Indeed, the development of these molecules, containing a divalent C(II) atom bearing a vacant orbital and a lone pair, exhibiting a high σ-donation and a strong binding ability toward transition metals, render them essential tools for catalysis. The corresponding organometallic complexes have been proven to be particularly robust and efficient and offering in numerous catalytic processes a larger scope of reaction [4,5,6,7]. The related carbon(0) species (II), also named carbones, bearing two lone pairs on the central carbon atom are a new emerging class of η1-carbon ligands. Even though carbodiphosphoranes (II, L, L′ = PPh3) were discovered in the 1960s by Ramirez [8], these species were at first regarded as two cumulated phosphorus ylide functions on a central carbon atom. It was only in 2006, after the theoretical investigations by Frenking et al. [9,10,11,12], that these molecules were considered as a carbon atom in the zero-oxidation state stabilized by two L-phosphine ligands, in agreement with the description initially used by Kaska in 1973 [13]. Since then, this family of ligands has considerably grown, leading to a large structural diversity of carbones II and a better understanding of their behavior [14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Naturally, owing to the existence of two lone pairs, they are strong σ- and π-donors (two- or four-electron donating ability); they have been used as original ligands for the preparation of organometallic complexes with interesting applications in catalysis [24,25,26,27,28,29].
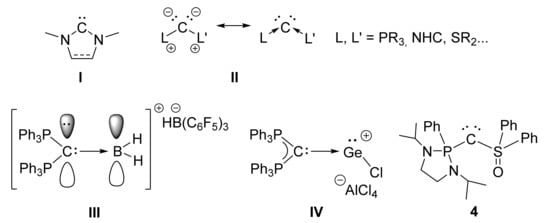
Figure 1.
NHC (I), carbones (II), dihydrido borenium (III) and germyliumylidene (IV) stabilized by carbodiphosphoranes and phosphine/sulfoxide-supported carbone 4 (for a better readability, formal charges in (III,IV) and 4 were omitted).
The strong donor ability of carbones II also enables the synthesis and isolation of novel reactive species. For example, Alcarazo et al. took advantage of the two available lone pairs of carbodiphosphoranes to stabilize reactive molecules such as dihydrido borenium cation III [30]. In the same vein, several groups have used carbones or strong σ-donating ligands to prepare dichlorogermylene adducts giving access to germyliumylidenes (IV) or germylones [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38]. In this context, we report here the coordination ability of a phosphine/sulfoxide-supported carbone 4 [39] towards dichlorogermylene.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
For the preparation of the phosphine/sulfoxide-supported carbone 4, we followed the previously described synthesis [39] but several practical aspects were improved. Indeed, after the complete oxidation of methyldiphenylsulfonium, acidification and filtration of the precipitates (carboxylic acids), the expected methyldiphenylsulfoxonium salt 1 was extracted from the aqueous solution by liquid/liquid extraction using dichloromethane as a solvent (Scheme 1). This extraction avoids the possible thermal degradation of the sulfoxonium salt during the evaporation of water under reduced pressure (if prolonged heating above 50 °C is performed). The yield of this step was improved to 53%, after two successive recrystallizations. The coupling reaction between sulfoxonium salt 1 and chlorophosphonium 2 in the presence of two equivalents of lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) was also improved in terms of reaction time (Scheme 1). It was found that heating the reaction mixture up to 60 °C considerably sped up the reaction since a full conversion was reached in 24 h instead of 96 h at room temperature. Protonated precursor 3 was obtained as a white powder upon concentration (70% yield). The final deprotonation was performed in THF solution at RT with potassium hydride (KH) leading to the selective formation of 4, which was isolated in 69% yield.
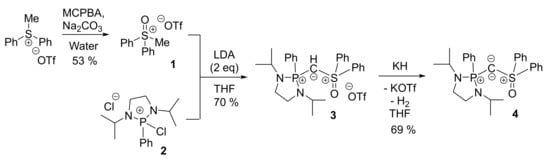
Scheme 1.
Synthetic path of phosphine/sulfoxide-supported carbone 4.
2.2. Dichlorogermylene Coordination
Previous experimental results and DFT calculations have already established that phosphine/sulfoxide-supported carbone 4 exhibits a strong nucleophilic character [39]. The potential usefulness of 4 as a ligand towards transition metals was demonstrated by selective reactions with several organometallic complexes [Au(I), Rh(I)] [39]. Therefore, its coordinating ability toward GeCl2/dioxane should be an interesting approach to access original low-valent germanium derivatives.
Ligand 4 reacts immediately with one equivalent of GeCl2 dioxane leading to the selective formation of complex 5 which has been isolated as colorless crystals from a saturated solution of CH2Cl2/pentane (yield 80%, Scheme 2). In comparison with the hexaphenylcarbodiphosphorane analogue [33], complex 5 exhibits a good solubility in common organic solvent and could be fully characterized by NMR spectroscopy. The 31P NMR spectrum displays a signal at lower field (δ = 49.5 ppm) compared to that of free ligand 4 (δ = 29.0 ppm), reminiscent of the protonated precursor 3 (δ = 45.0 ppm). In the 13C NMR spectrum, the central carbon atom appears as a doublet at δ = 47.0 ppm (JPC = 77.3 Hz). The addition of a second equivalent of GeCl2·dioxane to 5, or the direct use of two equivalents of GeCl2·dioxane with 4, leads to the quantitative formation of bis-germylene complex 6, which has been isolated in the crystalline form from C6D6 solution (yield 75%). It has been fully characterized by NMR spectroscopy, and particularly, the 31P NMR spectrum indicates a signal at δ = 51.2 ppm and the central carbon atom appears in 13C NMR spectrum as a doublet at δ = 46.6 ppm (JPC = 79.1 Hz).
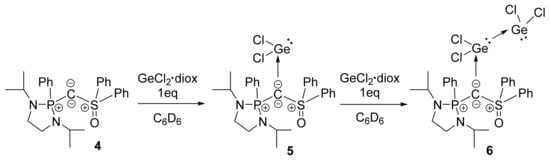
Scheme 2.
Coordination of phosphine/sulfoxide-supported carbone 4 with one or two equivalents of germylene dichloride.
Isolated in the crystalline form, the molecular structures of complexes 5 and 6 were confirmed by X-ray diffraction analysis (Figure 2, see Supplementary Materials). The selected geometrical parameters for experimental structures can be found in Table 1.
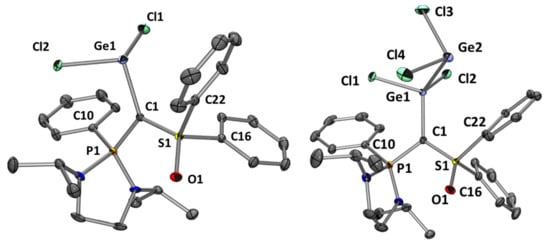
Figure 2.
Molecular structures of 5 (left) and 6 (right). Ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level; hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity. Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (°): 5: C1-Ge1 2.071(2), C1-P1 1.725(2), C1-S1 1.650(2), P1-C10 1.802(3), S1-O1 1.457(2), Ge1-Cl2 2.299(1), Ge1-Cl1 2.331(1), S1-C22 1.780(3), S1-C16 1.784(3). P1-C1-S1 113.73(14), P1-C1-Ge1 128.12(13), Ge1-C1-S1 115.65(13), C1-Ge1-Cl2 96.82(7), Cl2-Ge1-Cl1 95.37(3), Cl1-Ge1-C1 98.81(7); 6: C1-Ge1 1.980(2), C1-P1 1.748(2), C1-S1 1.665(2), Ge1-Ge2 2.582(1), Ge1-Cl1 2.185(1), Ge1-Cl2 2.245(1), Ge2-Cl4 2.267(1), Ge2-Cl3 2.275(1), P1-C10 1.792(2), S1-O1 1.455(1), S1-C22 1.778(2), S1-C16 1.782(2), P1-C1-S1 112.40(10), P1-C1-Ge1 127.01(9), Ge1-C1-S1 117.30(9), C1-Ge1-Cl1 105.44(5), Cl1-Ge1-Cl2 101.33(2), Cl2-Ge1-Ge2 107.25(2), Cl1-Ge1-Ge2 109.25(2), Ge1-Ge2-Cl4 92.09(2), Cl4-Ge2-Cl3 98.84(3), Ge1-Ge2-Cl3 89.41(2).

Table 1.
Selected geometrical parameters for 3, 4, 5 and 6 1.
As expected, the S1-C1 (1.650 Å) and P1-C1 (1.725 Å) bond lengths in 5 are very similar to those observed in the protonated precursor 3 (1.653 Å and 1.719 Å respectively), because of their similar environments. The repulsion between the pπ-lone pair at the carbon and the one at the Ge atom explains the long C1-Ge1 bond length (2.071 Å). It is slightly longer than the one observed by Alcarazo et al. with carbodiphosphoranes (2.063 Å) but much longer than a typical C-Ge bond (1.95 Å) [40]. The P1-C1-S1 angle decreased significantly upon complexation with GeCl2 (from 121° in 3 or 4 to 113.7° in 5). The introduction of a third heteroatom (Ge) around the carbon, which is less electronegative than P and S, influences the atomic orbital distribution with a pronounced s character toward the C-Ge bond and increased p-character in the C-P and C-S bonds. This phenomenon together with the covalent radius of the germanium atom justify the narrowing of the P1-C1-S1 angle in 5 [41]. Nevertheless, the C1 atom environment remains almost planar (∑°= 357.5°). In 6, with the coordination of the second GeCl2 unit, the previously discussed repulsion disappears, leading to a shortening of the C1-Ge1 bond length to 1.980 Å. The other bond lengths and angles (P1-C1, C1-S1, PCS) remain almost unchanged (Table 1). The dative nature of the Ge1-Ge2 bond is confirmed by its length (2.582 Å), way longer than classical Ge-Ge σ-bonds (2.40–2.50 Å) [42]. The same tendency was observed for carbodiphosphoranes [33] or NHC [43].
Contrary to the carbodiphosphorane analogues, chloride abstraction from 5 using AlCl3 or KB(C6F5)4 in order to prepare germyliumylidene derivatives only led to complex mixtures. Nevertheless, when 5 is treated in the presence of one equivalent of 4 at 60 °C for 60 h, we observed the gradual consumption of 5 with the concomitant formation of a new compound that exhibits a signal at δ = 56.3 ppm in 31P NMR (this reaction does not occur in the absence of 4) (Scheme 3). In fact, the process is base-catalyzed, but with 10 mol % of 4, the reaction time is slower and needs 90 h [Note: catalytic amounts (15 mol %) of alternative Lewis bases such as DMAP or Et3N can be used but the reactions are less selective, see Supplementary Materials for more details]. The structure of the new product 7, determined by X-ray diffraction analysis (Figure 3), involves the 1,3-migration of a phenyl group from the sulfur to the germanium atom. Considering the ligand moiety, this isomerization transforms a bis-ylide (carbone) to an original yldiide [44]. Unfortunately, because of the presence of 4 in the media, product 7 could not be isolated in pure form for complete characterization despite several attempts.
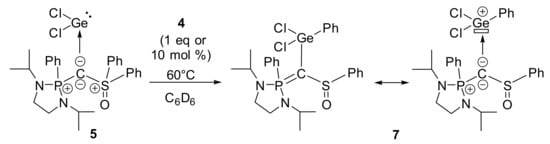
Scheme 3.
Evolution of 5 in presence of 4 upon heating at 60 °C.
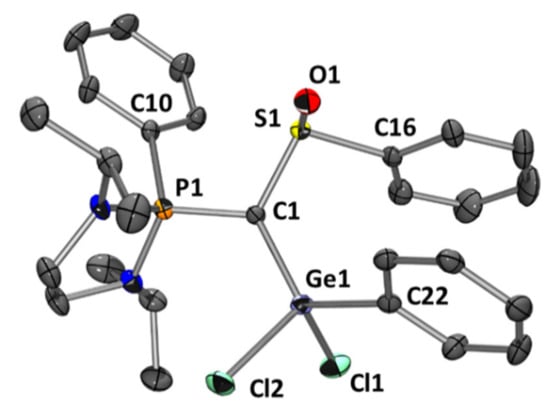
Figure 3.
Molecular structure of 7. Ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level; hydrogen atoms are omitted for clarity. Selected bond lengths (Å) and angles (°): P1-C1 1.707(3), C1-S1 1.744(3), C1-Ge1 1.891(3), Ge1-C22 1.927(3), Ge1-Cl2 2.172(1), Ge1-Cl1 2.173(1), P1-C10 1.805(3), S1-O1 1.499(2), S1-C16 1.800(4), P1-C1-S1 114.48(18), S1-C1-Ge1 120.89(17), Ge1-C1-P1 122.37(19), C1-Ge1-C22 119.52(14), C1-Ge1-Cl2 111.27(10), C22-Ge1-Cl2 104.77(10), C1-Ge1-Cl1 111.72(10), C22-Ge1-Cl1 106.65(11), Cl2-Ge1-Cl1 101.15(4), O1-S1-C1 112.64(15), O1-S1-C16 105.28(16), C1-S1-C16 100.04(16).
2.3. Conclusions
In summary, the excellent coordination ability of the phosphine/sulfoxide-supported carbone ligand 4 allows the preparation of Ge(II)-complex 5. The strong donation of 4 results in an enriched germylene 5, which becomes sufficiently nucleophilic to coordinate a second GeCl2 unit. The two original and stable coordination complexes 5 and 6 were fully characterized by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction analysis. Interestingly, the Ge(II)-complex 5 shows an original isomerization in the presence of 4 that transforms the bis-ylide ligand into an yldiide, thanks to a phenyl migration. Efforts are currently underway to extend the diversity of organometallic complexes that can be obtained with 4 to consider its application in catalysis.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Comments
All manipulations were performed under an inert atmosphere of argon by using standard Schlenk techniques or high-pressure NMR tube techniques. Dry and oxygen-free solvents were used. 1H, 13C, 19F and 31P NMR spectra were recorded on Brucker Avance II 300 MHz, Avance III HD 400 MHz and Avance I and II 500 MHz spectrometers (Brucker, Karlsruhe, Germany). Chemical shifts are expressed in parts per million with residual solvent signals as internal reference (1H and 13C{1H}). 19F and 31P NMR chemical shifts were reported in ppm relative to CFCl3 and 85% H3PO4, respectively. The following abbreviations and their combinations are used: br, broad; s, singlet; d, doublet; t, triplet; q, quartet; hept, heptuplet; m, multiplet. 1H and 13C resonance signals were attributed by means of 2D COSY, HSQC and HMBC experiments. Mass spectra were recorded on a Hewlett Packard 5989A spectrometer (Hewlett-Packard, Palo Alto, CA, USA). All commercially available reagents were used without further purification otherwise noted. Preparation of diphenylsulfonium, 2 and 4 were prepared following previously reported procedures [39].
3.2. Synthesis
Diphenylmethylsulfoxonium triflate 1: A suspension of diphenylmethylsulfonium triflate (14.96 g, 42.7 mmol, 1 eq.), Na2CO3 (13.58 g, 128.1 mmol, 3 eq.) and meta-chloroperbenzoic acid (MCPBA) (22.13 g, 128.1 mmol, 3 eq.) in water (400 mL) was stirred at RT for three days. Na2CO3 (4.53 g, 42.7 mmol, 1 eq.) and MCPBA (7.28 g, 42.7 mmol, 1 eq.) were added and the mixture was stirred at RT for one additional day. A 37% aqueous solution of HCl was added to the solution until pH = 1. White solid was filtrated off and washed with an aqueous solution of HCl at pH = 1 (3 × 20 mL). The product was then extracted with CH2Cl2 (3 × 20 mL). The solution was dried then the solvent was removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by successive crystallizations in acetone/pentane, yielding 1 as colorless crystals (8.30 g, 22.6 mmol, 53%). 1H NMR (300 MHz, 298 K, Acetone-d6): δ = 4.86 (s, 3H, CH3), 7.91–7.98 (m, 4H, CHar), 8.04–8.11 (m, 2H, CHpara), 8.31–8.37 (m, 4H, CHar). 13C{1H} NMR (75 MHz, 298 K, Acetone-d6): δ = 39.7 (s, CH3), 128.4 (s, CHar), 132.0 (s, CHar), 132.9 (s, Cipso), 138.1 (s, CHpara). The signal of the triflate could not be detected. 19F NMR (282 MHz, 298 K, DMSO-d6) δ = −77.7 (s). Mp = 157 °C. HRMS (ES +): m/z [M]+ calculated for C13H13OS = 217.0687, found = 217.0690.
Protonated phosphine/sulfoxide precursor 3: In situ prepared LDA (18.2 mmol, 2 eq.) in THF (20 mL) was added dropwise to a suspension of 1 (4 g, 10.9 mmol, 1.2 eq.) in THF (100 mL) at −80 °C and the reaction was stirred at this temperature for 2 h. A suspension of 2 (2.92 g, 9.1 mmol, 1 eq.) in THF (50 mL) was then added dropwise to the solution at −80 °C. The solution was allowed to warm up to RT then heated at 60 °C for two days. The solution was concentrated (2/3 of the solvent removed) and a white precipitate was observed. The solvent was filtered off and the white solid was washed with small volumes of THF (4 × 2 mL). The remaining solid was extracted in CH2Cl2 then dried under a high vacuum. Ylide 3 was obtained as a white powder (3.9 g, 6.37 mmol, 70%). 31P{1H} NMR (202 MHz, 298 K, CDCl3): δ = 45.0 ppm (s). 1H NMR (300 MHz, 298 K, CDCl3): δ = 0.76 (d, JHH = 6.5 Hz, 12H, CH3iPr), 3.08–3.24 (m, 4H, CH2), 3.40 (hept, JHH = 6.5 Hz, 1H, CHiPr), 3.43 (hept, JHH = 6.5 Hz, 1H, CHiPr), 3.80 (d, JPH = 13.7 Hz, 1H, PCHS), 7.57 (m, 9H, CHar), 8.05–8.16 (m, 2H, CHar), 8.18–8.25 (m, 4H, CHar). 13C{1H} NMR (75 MHz, 298 K, CDCl3): δ = 19.9–20.1 (m, CH3iPr), 31.6 (d, JCP = 137.2 Hz, PCHS), 39.1 (d, JPC = 8.6 Hz, CH2), 45.1 (d, JPC = 5.7 Hz, CHiPr), 121.2 (q, JCF = 318.9 Hz, CF3), 126.7 (d, JPC = 121.1 Hz, Cipso P side), 127.1 (s, CHar), 130.0 (d, JPC = 13.7 Hz, CHar), 130.4 (s, CHar), 132.8 (d, JPC = 11.7 Hz, CHar), 134.4 (s, CHar), 134.5 (d, JPC = 3.1 Hz, CHar), 140.4 ppm (d, JPC = 2.4 Hz, Cipso S side). 19F NMR (282 MHz, 298 K CDCl3): δ = −78.1 (s). HRMS (ES +): m/z [M]+ calculated for C27H34ON2PS = 465.2130, found = 465.2133. The elemental analysis calculated (%) for C28H34F3N2O4PS2: C 54.71, H 5.58, N 4.56; found: C 54.63, H 5.47, N 4.51.
Phosphine/sulfoxide-carbone-GeCl2 complex 5: To a solution of 4 (37.1 mg, 0.08 mmol, 1 eq.) in C6D6 (0.6 mL), GeCl2•dioxane (9 mg, 0.08 mmol, 1 eq.) was added. The reaction is complete after a few minutes. C6D6 was removed under reduced pressure and the residue afforded crystals (38.9 mg, 0.064 mmol, 80% yield) from a saturated solution of CH2Cl2/pentane. 31P {1H} NMR (202 MHz, 298 K, C6D6): δ = 49.5 ppm (s). 31P {1H} NMR (162 MHz, 298 K, CD2Cl2): δ = 50.9 ppm (s). 1H NMR (500 MHz, 298 K, CD2Cl2): δ = 0.70 (d, JHH = 6.5 Hz, 6H, CH3iPr), 0.81 (d, JHH = 6.5 Hz, 6H, CH3iPr), 3.08–3.18 (m, 2H, CH2), 3.19–3.28 (m, 2H, CH2), 3.58–3.69 (m, 2H, CHiPr), 7.59–7.71 (m, 9H, CHar), 8.07–8.14 (m, 6H, CHar). 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, 298 K, CD2Cl2): δ = 19.9 (m, CH3iPr), 39.3 (d, JPC = 8.9 Hz, CH2), 46.0 (d, JPC = 4.6 Hz, CHiPr), 47.0 (d, JPC = 77.3 Hz, PCS), 129.1 (s, CHar) 129.9 (d, JPC = 125.5 Hz, Cipso P side), 130.1 (d, JPC = 13.9 Hz CHar), 130.3 (s, CHar) 132.9 (d, JPC = 11.8 Hz, CHar), 134.2 (d, JPC = 3.1 Hz, CHar), 134.7(s, CHar), 140.7 (d, JPC = 3.1 Hz, Cipso S side). HRMS (DCI-CH4): m/z [M + H]+ calcd for C27H34Cl2GeN2OPS: 609.0713; found: 609.0715.
Phosphine/sulfoxide-carbone-GeCl2-GeCl2 complex 6: To a solution of 4 (37.1 mg, 0.08 mmol, 1 eq.) in C6D6 (0.6 mL), GeCl2•dioxane (18 mg, 0.16 mmol, 2 eq.) was added. Product 6 directly crystallized in C6D6 (45.0 mg, 0.06 mmol, 75% yield). 31P {1H} NMR (202 MHz, 298 K, C6D6): δ = 51.2 ppm (s). 31P {1H} NMR (202 MHz, 298 K, CD2Cl2): δ = 51.2 ppm (s). 1H NMR (300 MHz, 298 K, CD2Cl2): δ = 0.70 (d, JHH = 6.4 Hz, 6H, CH3iPr), 0.82 (d, JHH = 6.5 Hz, 6H, CH3iPr), 3.09–3.18 (m, 2H, CH2), 3.18–3.28 (m, 2H, CH2), 3.60–3.70 (m, 2H, CHiPr), 7.60–7.71 (m, 9H, CHar), 8.06–8.13 (m, 3H, 6CHar). 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, 298 K, CD2Cl2): δ = 19.7–20.3 (m, CH3iPr), 39.3 (d, JPC = 9.2 Hz, CH2), 46.1 (d, JPC = 5.3 Hz, CHiPr), 46.6 (d, JPC = 79.1 Hz, PCS), 129.1 (s, CHar), 129.7 (d, JPC = 125.0 Hz, Cipso deduced from J-Mod), 130.2 (d, JPC = 13.9 Hz, CHar), 130.4 (s, CHar), 132.8 (d, JPC = 11.8 Hz, CHar), 134.4 (d, JPC = 3.1 Hz, CHar), 134.8 (s, CHar), 140.5 (d, JPC = 2.95 Hz, Cipso S side). HRMS for 6 did not afford satisfactory results.
Isomer 7: To a solution of 5 (48.6 mg, 0.08 mmol, 1 eq.) in C6D6 (0.6 mL), one equivalent of 4, 37.1 mg, 0.08 mmol, 1 eq.) was added. The reaction was heated at 60 °C until complete consumption of 5 (after 60 h). Crystals of 7 could be obtained from the crude mixture. Unfortunately, despite several attempts, 7 was only analyzed by spectroscopy as a mixture. The spectroscopic data were extracted from a mixture containing 7 and 4 in a 51% to 45% ratio (4% of protonated phosphine/sulfoxide precursor 3). The reaction can also be performed with 10 mol% of 4 (3.7 mg, 0.008 mmol). 31P {1H} NMR (121 MHz, 298 K, C6D6): δ = 56.3 ppm (s). 1H NMR (300 MHz, 298 K, C6D6): δ = 0.45 (d, JHH = 6.5 Hz, 3H, CH3iPr), 0.83 (d, JHH = 6.6 Hz, 3H, CH3iPr),1.34–1.50 (m, 6H, CH3iPr), 2.40–2.70 (m, 2H, CH2), 3.05–3.15 (m, 2H, CH2), 4.10–4.40 (m, 2H, CHiPr), 6.75–7.25 (m, 9H, CHar), 7.75–7.85 (m, 2H, CHar), 7.85–8.15 (m, 4H, CHar). 13C{1H} NMR (126 MHz, 298 K, C6D6): δ = 20.6 (d, JPC = 2.4 Hz, CH3iPr), 20.7 (d, JPC = 5.7 Hz, CH3iPr), 21.7 (d, JPC = 6.1 Hz, CH3iPr), 38.0 (d, JPC = 12.3 Hz, CH2), 38.1 (d, JPC = 12.7 Hz, CH2), 44.5 (d, JPC = 7.4 Hz, CHiPr), 44.9 (d, JPC = 5.0 Hz, CHiPr), 59.1 (d, JPC = 121.5 Hz, PCS), 127.2 (s, CHar), 128.0 (s, CHar), 128.3 (s, CHar), 128.7 (d, JPC = 12.1 Hz), 128.9 (s, CHar), 130.2 (d, JPC = 109.6 Hz Cipso P side), 130.3 (s, CHar), 132.6 (d, JPC = 2.9 Hz, CHar), 133.4 (s, CHar), 133.8 (d, JPC = 10.3 Hz, CHar), 140.4 (d, JPC = 6.2 Hz, Cipso S side), 147.8 (d, JPC = 21.9 Hz, Cipso Ge side). HRMS (DCI-CH4): m/z [M + H]+ calcd for C27H34Cl2GeN2OPS: 609.0713; found: 609.0721.
3.3. X-ray Data
The data of the structures for 5, 6 and 7 were collected at 193 K on a Bruker-AXS APEX II CCD Quazar diffractometer (7) equipped with a 30 W air-cooled microfocus source or on a Brucker-AXS D8-Venture diffractometer (5 and 6) equipped with a CMOS area detector with MoKα radiation (wavelength = 0.71073 Å) by using phi- and omega-scans. The data were integrated with SAINT, and an empirical absorption correction with SADABS was applied [45]. The structures were solved using an intrinsic phasing method (ShelXT) [46] and refined using the least–squares method on F2 (ShelXL-2014) [47]. All non-H atoms were treated anisotropically. All H atoms attached to C atoms were fixed geometrically and treated as riding on their parent atoms with C-H = 0.95 Å (aromatic), 0.98 Å (CH3), 0.99 Å (CH2) or 1.0 Å (CH) with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(CH, CH2) or Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(CH3).
Supplementary crystallographic data for CCDC-2068304 (5), CCDC-2068305 (6), CCDC-2068306 (7) can be obtained free of charge from The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre via https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/ accessed on 25 March 2021.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online. NMR spectra and crystallographic data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H., E.M. and D.M.; Investigation, U.A., S.H. and A.D.; X-ray structural studies: N.S.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, U.A. and E.M.; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, A.B., D.M. and E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Agence Nationale de la Recherche, ANR-19-CE07-0013.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR-16-CE07-0018-01) and the Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur et de la Recherche are gratefully acknowledged for Ph.D. grant to U.A. The authors would like to thank the CNRS and the Université de Toulouse, UPS for financial support. The authors would like to thank the reviewers for all their useful and helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Sample Availability
Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors.
References
- Mortreux, A.; Petit, F. Industrial Applications of Homogeneous Catalysis; Springer: Dordrecht/Holland, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Igau, A.; Grützmacher, H.; Baceiredo, A.; Bertrand, G. Analogous α,α’-Bis-Carbenoid Triply Bonded Species: Synthesis of a Stable λ3-Phosphinocarbene-λ5-Phosphaacetylene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 6463–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduengo, A.J.; Harlow, R.L.; Kline, M. A Stable Crystalline Carbene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 361–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorius, F. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Transition Metal Catalysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 21. [Google Scholar]
- Nolan, S.P. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes in Synthesis; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann, W.A. N-Heterocyclic Carbenes: A New Concept in Organometallic Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1290–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- César, V.; Bellemin-Laponnaz, S.; Gade, L.H. Chiral N-heterocyclic carbenes as stereodirecting ligands in asymmetric catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, F.; Desai, N.B.; Hansen, B.; McKelvie, N. Hexaphenylcarbodiphosphorane, (C6H5)3PCP(C6H5)3. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 3539–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonner, R.; Öxler, F.; Neumüller, B.; Petz, W.; Frenking, G. Carbodiphosphoranes: The Chemistry of Divalent Carbon(0). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 8038–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonner, R.; Frenking, G. C(NHC)2: Divalent Carbon(0) Compounds with N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands—Theoretical Evidence for a Class of Molecules with Promising Chemical Properties. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8695–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonner, R.; Frenking, G. Divalent Carbon(0) Chemistry, Part 1: Parent Compounds. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3260–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonner, R.; Frenking, G. Divalent Carbon(0) Chemistry, Part 2: Protonation and Complexes with Main Group and Transition Metal Lewis Acids. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 3273–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaska, W.C.; Mitchell, D.K.; Reichelderfer, R.F. Transition metal complexes of hexaphenylcarbodiphosphorane. J. Organomet. Chem. 1973, 47, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, T.; Ikeda, T.; Mikami, T.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshimura, T. Synthesis and structure of (MeN)Ph2S=C=SPh2(NMe). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2576–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcarazo, M.; Lehmann, C.W.; Anoop, A.; Thiel, W.; Fürstner, A. Coordination chemistry at carbon. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellus, N.; Kato, T.; Bagan, X.; Saffon, N.; Branchadell, V.; Baceiredo, A. An isolable mixed P,S-bis(ylide) as an asymmetric carbon atom source. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6798–6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcarazo, M.; Radkowski, K.; Mehler, G.; Goddard, R.; Fürstner, A. Chiral heterobimetallic complexes of carbodiphosphoranes and phosphinidene–carbene adducts. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3140–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidbaur, H.; Schier, A. Coordination Chemistry at Carbon: The Patchwork Family Comprising (Ph3P)2C, (Ph3P)C(C2H4), and (C2H4)2C. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morosaki, T.; Suzuki, T.; Wang, W.W.; Nagase, S.; Fujii, T. Syntheses, Structures, and Reactivities of Two Chalcogen-Stabilized Carbones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9569–9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morosaki, T.; Wang, W.-W.; Nagase, S.; Fujii, T. Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivities of Iminosulfane- and Phosphane-Stabilized Carbones Exhibiting Four-Electron Donor Ability. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 15405–15411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-C.; Shen, J.-S.; Juca, T.; Peng, C.-J.; Lin, Y.-H.; Wang, Y.-P.; Shih, W.-C.; Yap, G.P.A.; Ong, T.-G. Expanding the Ligand Framework Diversity of Carbodicarbenes and Direct Detection of Boron Activation in the Methylation of Amines with CO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 15207–15212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troadec, T.; Wasano, T.; Lenk, R.; Baceiredo, A.; Saffon-Merceron, N.; Hashizume, D.; Saito, Y.; Nakata, N.; Branchadell, V.; Kato, T. Donor-Stabilized Silylene/Phosphine-Supported Carbon(0) Center with High Electron Density. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 6891–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corberan, R.; Marrot, S.; Dellus, N.; Merceron-Saffon, N.; Kato, T.; Peris, E.; Baceiredo, A. First Cyclic Carbodiphosphoranes of Copper(I) and Gold(I) and Their Application in The Catalytic Cleavage of X-H bonds (X = N and O). Organometallics 2009, 28, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldfogel, M.J.; Roberts, C.C.; Meek, S.J. Intermolecular hydroamination of 1,3-dienes catalyzed by bis(phosphine)carbodicarbene-rhodium complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6227–6230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.-C.; Shen, J.-S.; Lin, B.-C.; Chen, W.-C.; Chan, Y.-T.; Ching, W.-M.; Yap, G.P.A.; Hsu, C.-P.; Ong, T.-G. Synthesis and isolation of an acyclic tridentate bis(pyridine)carbodicarbene and studies on its structural implications and reactivities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2420–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.C.; Matias, D.M.; Goldfogel, M.J.; Meek, S.J. Lewis Acid Activation of Carbodicarbene Catalysts for Rh-Catalyzed Hydroarylation of Dienes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 6488–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranckevicius, C.; Fan, L.; Stephan, D.W. Cyclic Bent Allene Hydrido-Carbonyl Complexes of Ruthenium: Highly Active Catalysts for Hydrogenation of Olefins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5582–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcum, J.S.; Roberts, C.C.; Manan, R.S.; Cervarich, T.N.; Meek, S.J. Chiral Pincer Carbodicarbene Ligands for Enantioselective Rhodium-Catalyzed Hydroarylation of Terminal and Internal 1,3-Dienes with Indoles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15580–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberman-Martin, A.L.; Grubss, R.H. Ruthenium Olefin Metathesis Catalysts Featuring a Labile Carbodicarbene Ligand. Organometallics 2017, 36, 4091–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inés, B.; Patil, M.; Carreras, J.; Goddard, R.; Thiel, W.; Alcarazo, M. Synthesis, Structure, and Reactivity of a Dihydrido Borenium Cation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8400–8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Yao, S.; Tan, G.; Inoue, S.; Driess, M. A cyclic Germadicarbene (“Germylone”) from Germyliumylidene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5004–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mondal, C.; Roesky, H.W.; Zhu, H.; Stollberg, P.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Stalke, D.; Andrada, D. Acyclic Germylones: Congeners of Allenes with a CentralGermanium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12422–12428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Gopakumar, G.; Thiel, W.; Alcarazo, M. Stabilization of a two-Coordinate [GeCl]+ Cation by Simultaneous s and p Donation from a Monodentate Carbodiphosphorane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5644–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, M.M.D.; Lummis, P.A.; Ferguson, M.J.; McDonald, R.; Rivard, E. Accessing Low-Valent Inorganic Cations by Using an Extremely Bulky N-Heterocyclic Carbene. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 11249–11252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, T.; Belding, L.; Van der Est, A.; Dudding, T.; Korobkov, I.; Nikonov, G.I. A coordination Compound of Ge0 Stabilized by a Diiminopyridine Ligand. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 2711–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.-L.; Yim, W.-L.; So, C.-W. An N-Heterocyclic Silylene-Stabilized Digermanium(0) Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13155–13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-P.; Karni, M.; Yao, S.; Apeloig, Y.; Driess, M. A Bis(silylenyl)pyridine Zero-Valent Germanium Complex and Its Remarkable Reactivity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 15096–15099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.T.; Gusev, D.; Dmitrienko, A.; Gabidullin, B.M.; Spasyuk, D.; Pilkington, M.; Nikonov, G.I. Ge(0) Compound Stabilized by a Diimino-Carbene Ligand: Synthesis and Ambiphilic Reactivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5852–5861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, M.L.; Bousquet, L.; Hameury, S.; Alvarez Toledano, C.; Saffon-Merceron, N.; Branchadell, V.; Maerten, E.; Baceiredo, A. Phosphine/Sulfoxide-Supported Carbon(0) Complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2018, 24, 2570–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiners, F.; Saak, W.; Weidenbruch, M. Reaction of a diarylgermylene with a phosphaalkyne: Formation of a germadiphosphacyclobutene with an exocyclic C=Ge double bond. Chem. Commun. 2001, 215–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabugin, I.V.; Bresch, S.; Manoharan, M. Hybridization Trends for Main Group Elements and Expanding the Bent’s Rule beyond Carbon: More than Electronegativity. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 3663–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadoruge, M.L.; Weinert, C.S. Singly Bonded Catenated Germanes: Eighty Years of Progress. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 4253–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim Al-Rafia, S.M.; Momeni, M.R.; McDonald, R.; Ferguson, M.J.; Brown, A.; Rivard, E. Controlled Growth of Dichlorogermanium Oligomers from Lewis Basic Hosts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 6390–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fustier-Boutignon, M.; Nebra, N.; Mézailles, N. Geminal Dianions Stabilized by Main Group Elements. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 8555–8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SADABS. Program for Data Correction, Version 2016/2; Bruker−AXS: Madison, WI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).