Ligand and Structure-Based Virtual Screening in Combination, to Evaluate Small Organic Molecules as Inhibitors for the XIAP Anti-Apoptotic Protein: The Xanthohumol Hypothesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
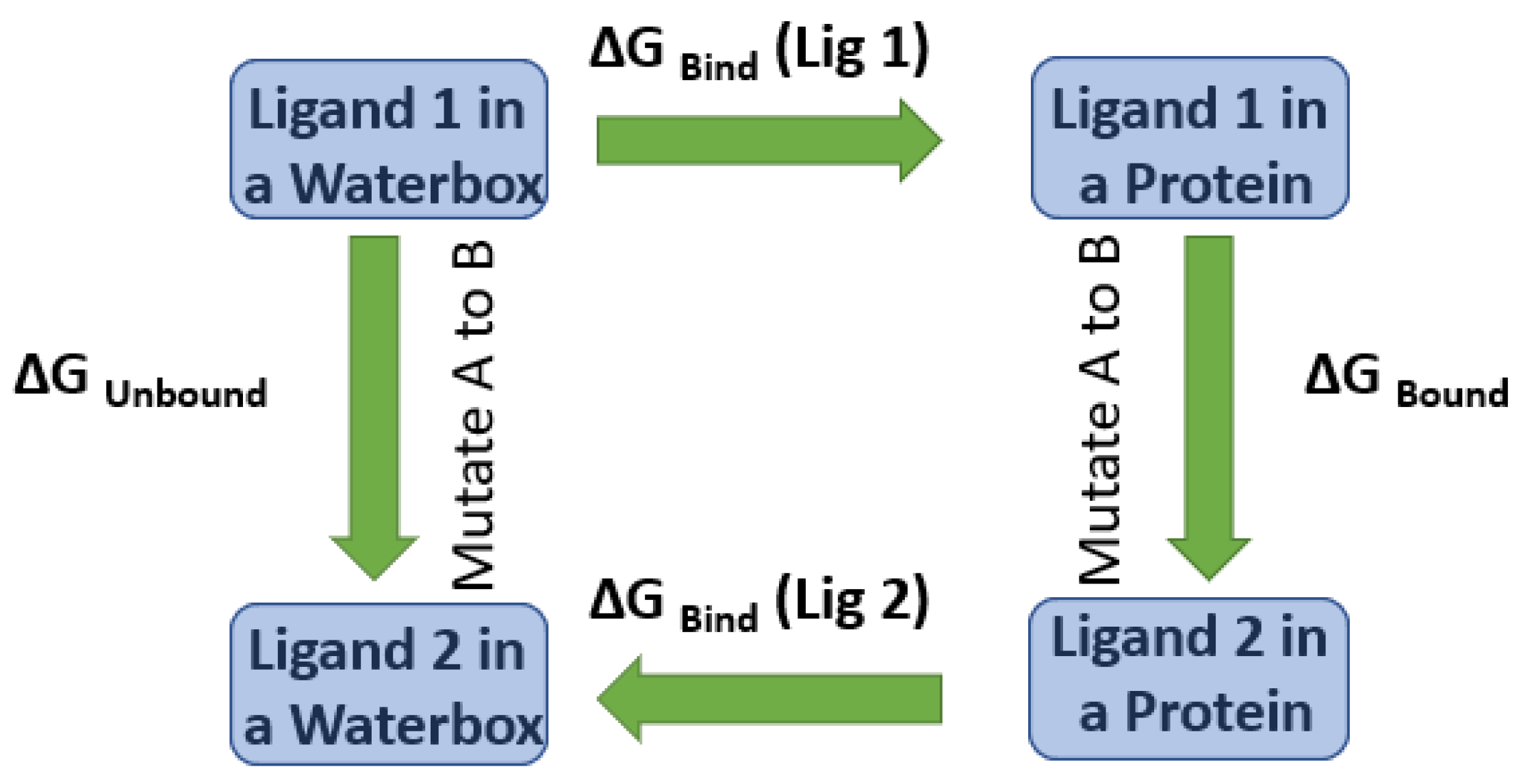
2. Computational Methods
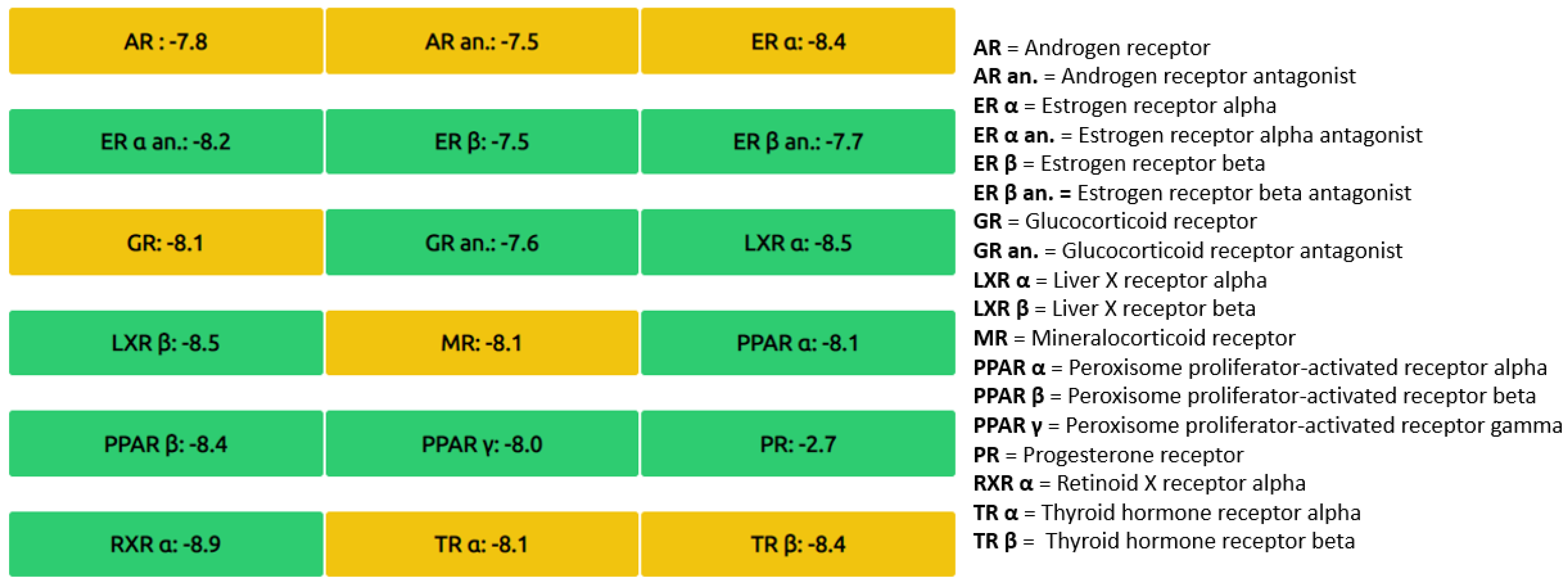
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shikata, Y.; Yoshimaru, T.; Komatsu, M.; Katoh, H.; Sato, R.; Kanagaki, S.; Okazaki, Y.; Toyokuni, S.; Tashiro, E.; Ishikawa, S.; et al. Protein kinase A inhibition facilitates the antitumor activity of xanthohumol, a valosin-containing protein inhibitor. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimaru, T.; Komatsu, M.; Matsuo, T.; Chen, Y.-A.; Murakami, Y.; Mizuguchi, K.; Mizohata, E.; Inoue, T.; Akiyama, M.; Yamaguchi, R.; et al. Targeting BIG3-PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yoshimaru, T.; Komatsu, M.; Tashiro, E.; Imoto, M.; Osada, H.; Miyoshi, Y.; Honda, J.; Sasa, M.; Katagiri, T. Xanthohumol suppresses estrogen-signaling in breast cancer through the inhibition of BIG3-PHB2 interactions. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harish, V.; Haque, E.; Śmiech, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Jamieson, S.; Tewari, D.; Bishayee, A. Xanthohumol for human malignancies: Chemistry, pharmacokinetics and molecular targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasiou, M.C.; Petrou, C.C.; Sarigiannis, Y.; Pafiti, K.S. Density functional theory studies and molecular docking on xanthohumol, 8-prenylnaringenin and their symmetric substitute diethanolamine derivatives as inhibitors for colon cancer-related proteins. Symmetry 2021, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obexer, P.; Ausserlechner, M. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP)—A critical death-resistance regulator and therapeutic target for personalized cancer therapy. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.M.; Metink-Kane, M.S. Changes in genes. NIH Public Access 2012, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, C.; Belunis, C.; Crowther, R.; Danho, W.; Gao, L.; Goggin, B.; Janson, C.A.; Li, S.; Remiszewski, S.; Schutt, A.; et al. The structure of XIAP BIR2: Understanding the selectivity of the BIR domains. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Bai, L.; Sun, H.; Nikolovska-coleska, Z.; Qiu, S.; Miller, R.S.; Yi, H.; Shangary, S.; Sun, Y.; Meagher, J.L.; et al. SM-164: A novel, bivalent Smac mimetic that induces apoptosis and tumor regression by concurrent removal of the blockade of cIAP-1/2 and XIAP. NIH Public Access 2009, 68, 9384–9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Abe, S.; Kurata, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Inoue, M.; Takemura, T.; Suzuki, K.; Kitagawa, M. IAP family protein expression correlates with poor outcome of multiple myeloma patients in association with chemotherapy-induced overexpression of multidrug resistance genes. Am. J. Hematol. 2006, 81, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluger, H.M.; McCarthy, M.M.; Alvero, A.B.; Sznol, M.; Ariyan, S.; Camp, R.L.; Rimm, D.L.; Mor, G. The X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) is up-regulated in metastatic melanoma, and XIAP cleavage by Phenoxodiol is associated with Carboplatin sensitization. J. Transl. Med. 2007, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wang, T.; Wu, F.; Huang, W.; He, G.; Ouyang, L.; Xiang, M.; Peng, C.; Jiang, Q. Combining structure-based pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, and in silico ADMET analysis to discover novel tetrahydro-quinoline based pyruvate kinase isozyme M2 activators with antitumor activity. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2014, 8, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, S.; Luo, M.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lai, Y. Effective virtual screening strategy focusing on the identification of novel Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2015, 60, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhan, S.; Sahoo, S.K. In silico ADMET and molecular docking study on searching potential inhibitors from limonoids and triterpenoids for COVID-19. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 124, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opo, F.A.D.M.; Rahman, M.M.; Ahammad, F.; Ahmed, I.; Bhuiyan, M.A.; Asiri, A.M. Structure-based pharmacophore modeling, virtual screening, molecular docking and ADMET approaches for identification of natural anticancer agents targeting XIAP protein. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlikova, B.; Tasdemir, D.; Golais, F.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Dietary chalcones with chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic potential. Genes Nutr. 2011, 6, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, T.; Lungu, C.N. Anticancer activity of natural and synthetic chalcones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, T.; Hackl, C.; Freese, K.; Dietrich, P.; Mahli, A.; Thasler, R.M.; Thasler, W.E.; Lang, S.A.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Hellerbrand, C. Xanthohumol, a prenylated chalcone derived from hops, inhibits growth and metastasis of melanoma cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sławińska-Brych, A.; Zdzisińska, B.; Dmoszyńska-Graniczka, M.; Jeleniewicz, W.; Kurzepa, J.; Gagoś, M.; Stepulak, A. Xanthohumol inhibits the extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) signalling pathway and suppresses cell growth of lung adenocarcinoma cells. Toxicology 2016, 357, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, I.S.; Moon, A. 2-Hydroxychalcone and xanthohumol inhibit invasion of triple negative breast cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2013, 203, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, A. Software News and Updates Gabedit—A Graphical User Interface for Computational Chemistry Softwares. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 32, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitin, A.M.; Milchevskiy, Y.V.; Lyubartsev, A.P. A new AMBER-compatible force field parameter set for alkanes. J. Mol. Modeling 2014, 20, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitin, A.; Milchevskiy, Y.; Lyubartsev, A. AMBER-II: New Combining Rules and Force Field for Perfluoroalkanes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 14563–14573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.M.; Chen, C.C. GEMDOCK: A Generic Evolutionary Method for Molecular Docking. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 2004, 55, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasiou, M.C.; Pafti, K.S. Screening possible drug molecules for Covid-19. The example of vanadium (III/IV/V) complex molecules with computational chemistry and molecular docking. Comput. Toxicol. 2021, 18, 100157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasiou, M.; Pafiti, K.S. Dft studies and molecular dynamics of the molecular and electronic structure of cu (Ii) and zn (ii) complexes with the symmetric ligand (z)-2-((3,5-dimethyl-2h-pyrrol-2-yl) methylene)-3,5-dimethyl-2h-pyrrole. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 5953–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlasiou, M.C. Structural characterization of two novel, biological active chalcone derivatives, using density functional theory studies. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chemistry 2021, 11, 15051–15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Hassan, S.S.; Abbas, S.Q.; Ali, F.; Ishaq, M.; Bano, I.; Hassan, M.; Jin, H.Z.; Bungau, S.G. A Comprehensive in Silico Exploration of Pharmacological Properties, Bioactivities, Molecular Docking, and Anticancer Potential of Vieloplain F from Xylopia vielana Targeting B-Raf Kinase. Molecules 2022, 27, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, P.; Chen, D.; Lian, C.; Zhang, C.; Meng, S. First-principles dynamics of photoexcited molecules and materials towards a quantum description. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2021, 11, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhang, W. The effects of different substitution heterocycles on ESIPT processes for three 2-(2′-hydroxybenzofuran)-benzoxazole compounds. Chem. Phys. 2021, 543, 111081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasiou, C.; Vasilakaki, S.; Dellis, D.; Cournia, Z. Using physics-based pose predictions and free energy perturbation calculations to predict binding poses and relative binding affinities for FXR ligands in the D3R Grand Challenge 2. J. Comput. -Aided Mol. Design. 2018, 32, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavitsanou, S.; Tsengenes, A.; Papadourakis, M.; Amendola, G.; Chatzigoulas, A.; Dellis, D.; Cosconati, S.; Cournia, Z. FEPrepare: A Web-Based Tool for Automating the Setup of Relative Binding Free Energy Calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Modeling 2021, 61, 4131–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeifman, A.A.; Stroylov, V.V.; Novikov, F.N.; Stroganov, O.V.; Kulkov, V.; Chilov, G.G. Alchemical FEP calculations of ligand conformer focusing in explicit solvent. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

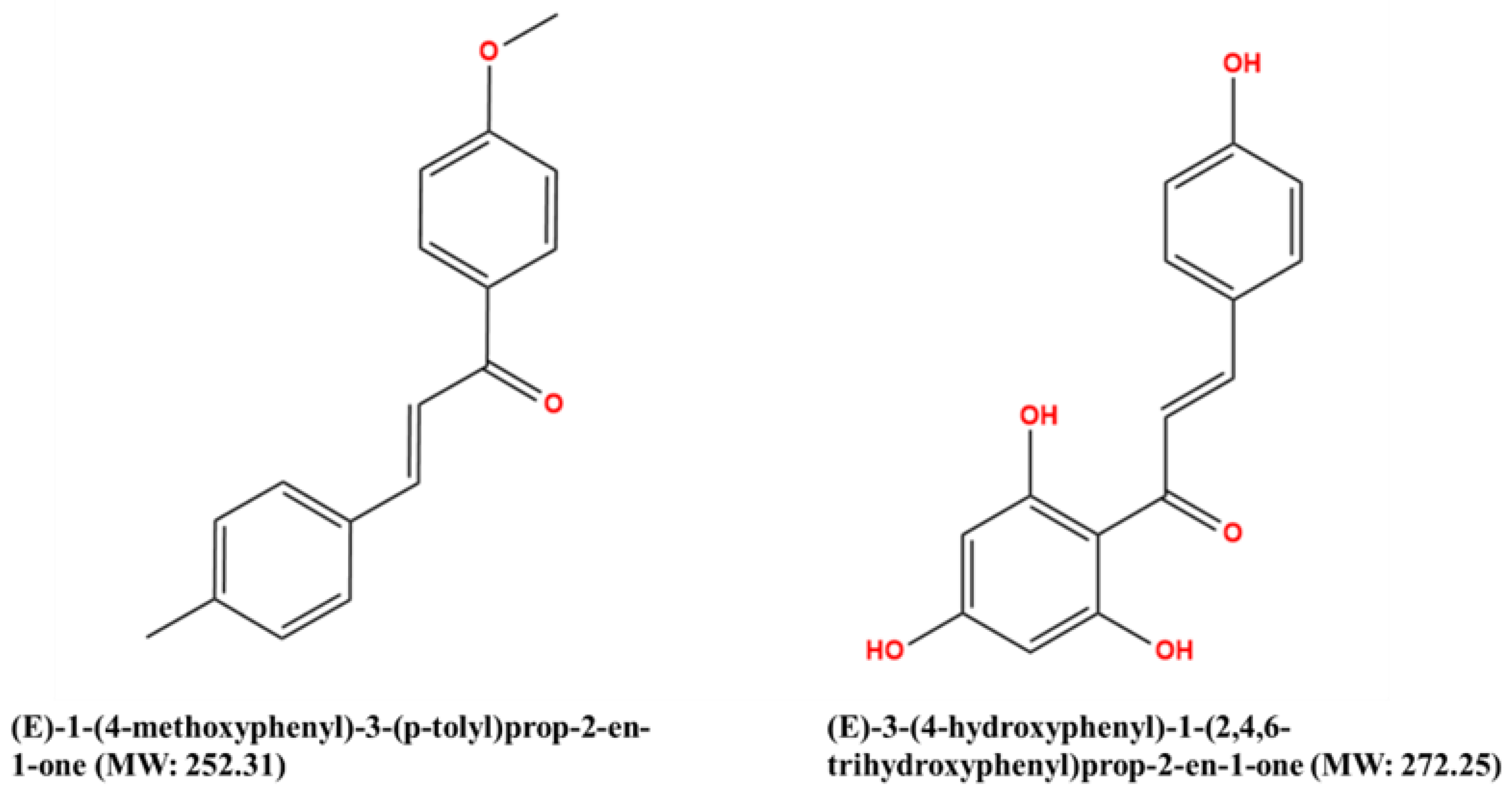
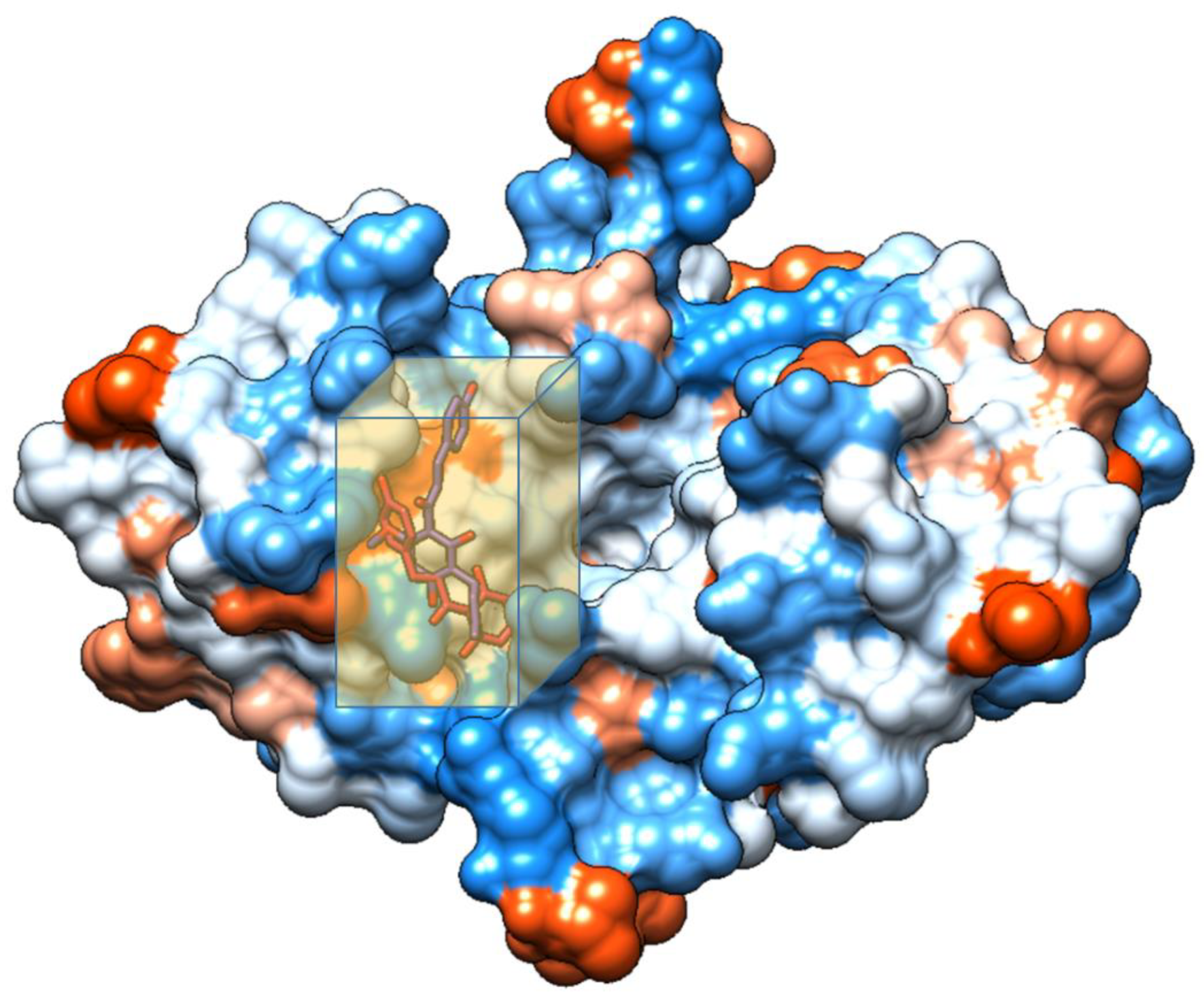
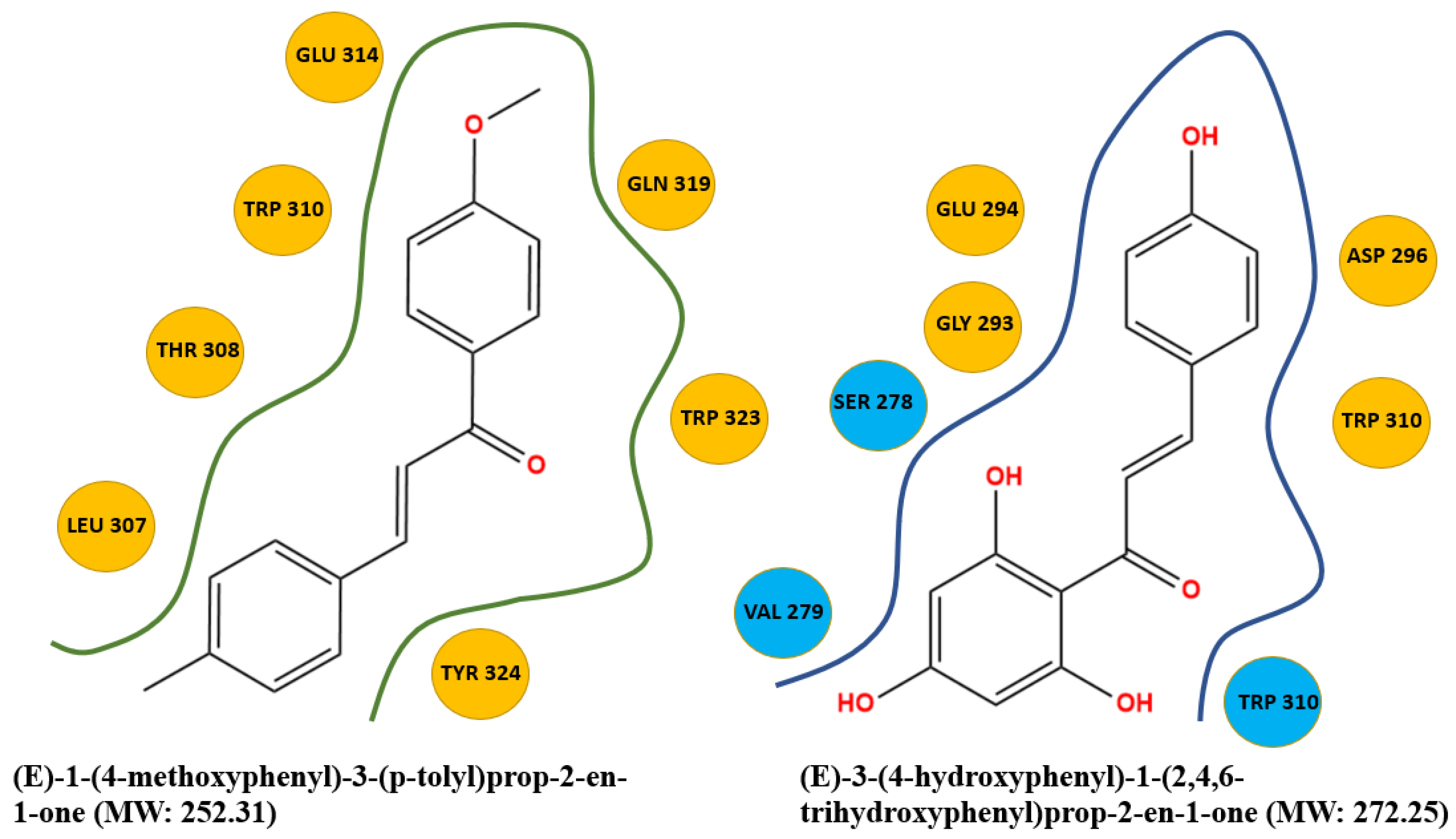
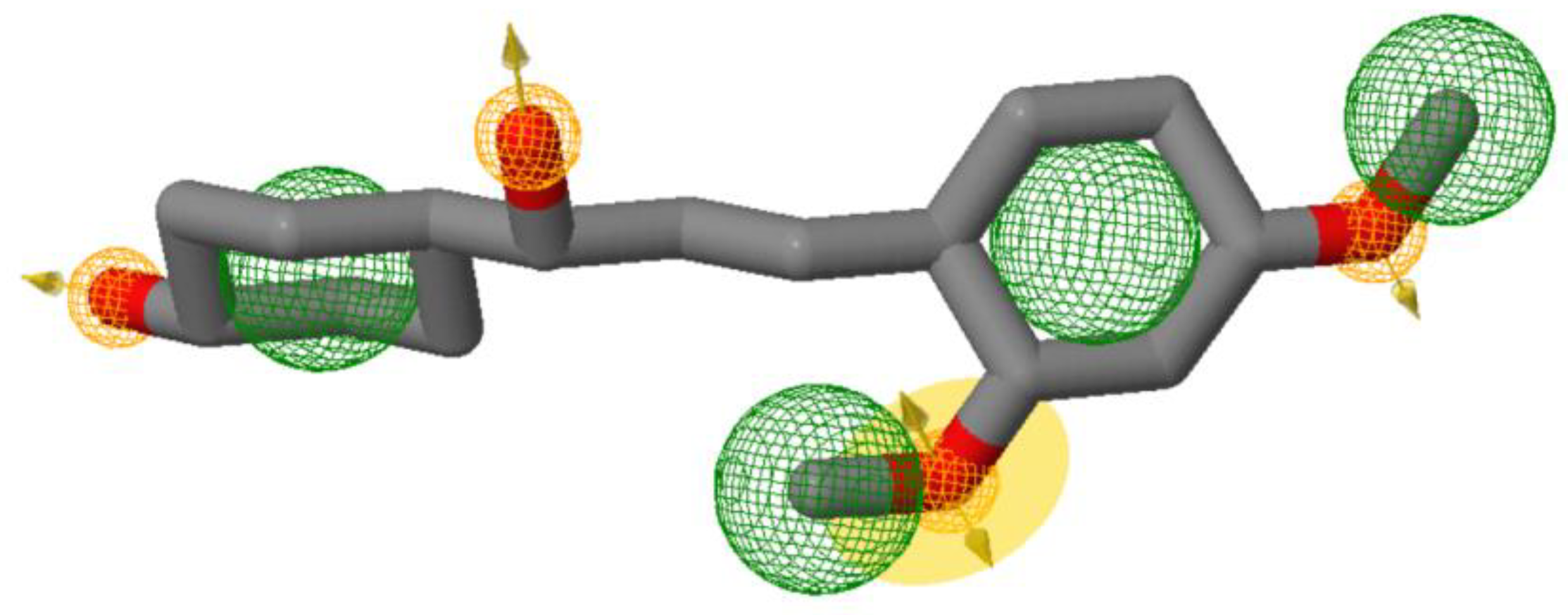
| Quantum Chemical Descriptor | (E)-1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-3-(p-tolyl) prop-2-en-1-one | (E)-3-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-1-(2,4,6-trihydroxyphenyl) prop-2-en-1-one |
|---|---|---|
| μ | −8.723 eV | −8.171 eV |
| n | 4.959 eV | 5.386 eV |
| I | 11.202 eV | 10.855 eV |
| A | 6.243 eV | 5.487 eV |
| ω | 7.672 eV | 6.198 eV |
| χ | 8.732 eV | 8.171 eV |
| ζ | 0.202 eV | 0.186 eV |
| Egap | 4.959 eV | 5.386 eV |
| Complex | Total Energy (KJ/mole) | Energy HBond (KJ/mole) | Energy VDW (KJ/mole) | Amino Acid Residue HBond | Amino Acid Residue VDW Interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-5OQW | −69.10 | 0 | −69.10 | None | Leu 307, Thr 308, Trp 310, Glu 314, Gln 319, Trp 323, Tyr 324 |
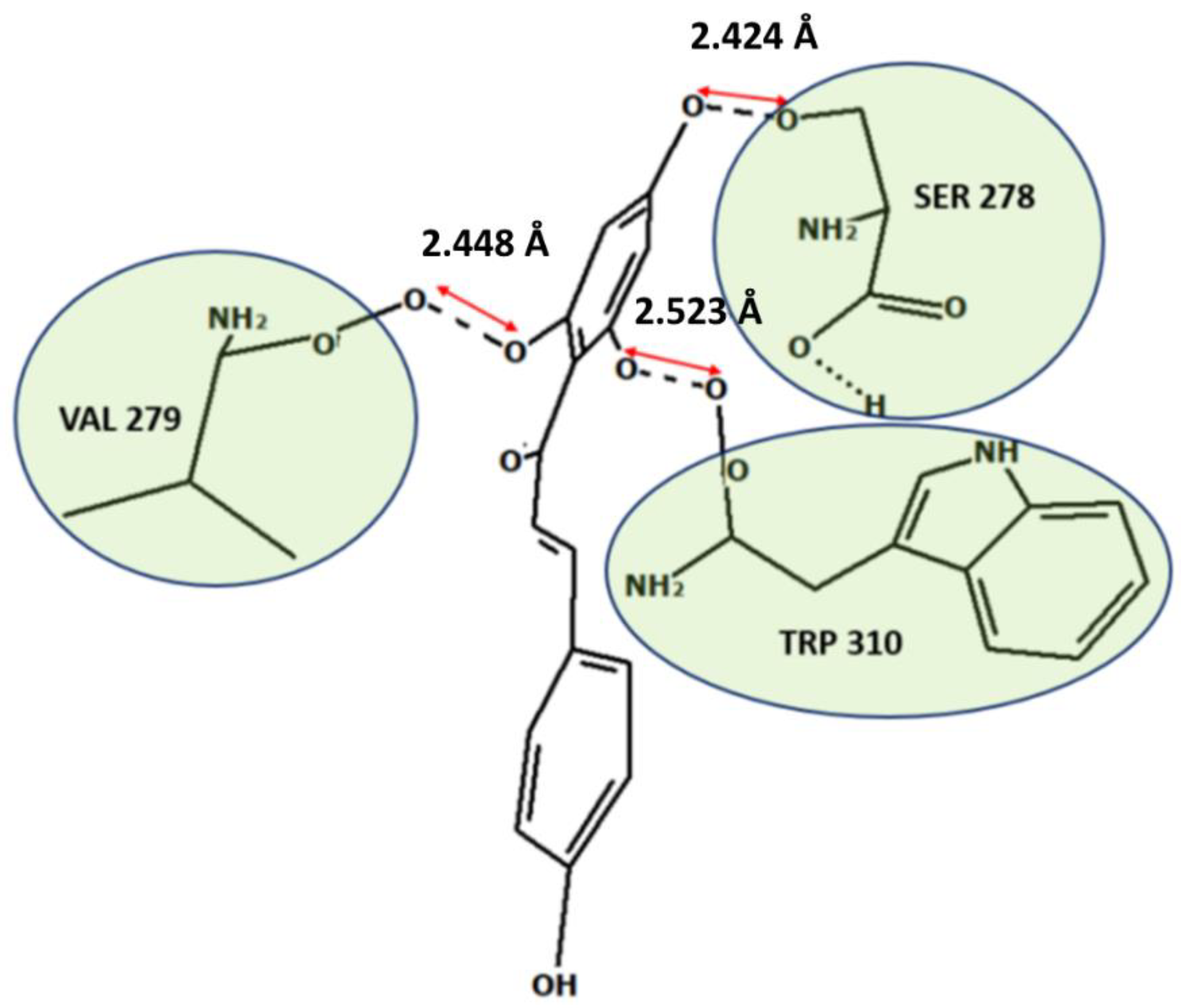
| B-5OQW | −74.13 | −12.08 | −62.05 | Ser 278, Val 279, Trp 310 | Val 279, Gly 293, Glu 294, Asp 296, Trp 310 |
| ADME Characteristics | Value-Answer |
|---|---|
| Formula | C15H12O5 |
| Molecular weight | 272.25 g/mol |
| Number of heavy atoms | 20 |
| Number of rotatable bonds | 3 |
| Number of Hydrogen bond acceptors | 5 |
| Number of Hydrogen bond donors | 4 |
| Molar refractivity | 74.34 |
| Log Po/w | 1.90 |
| Log S | −3.55 |
| GI absorption | High |
| BBB permeant | No |
| CYP1A2 Inhibitor | Yes |
| CYP2C19 Inhibitor | No |
| CYP2C9 Inhibitor | Yes |
| CYP2D6 Inhibitor | No |
| CYP3A4 Inhibitor | Yes |
| Log Kp | −5.96 cm/s |
| Lipinski | Yes, 0 violation |
| Bioavailability Score | 0.55 |
| Lead-likeness | Yes |
| Synthetic accessibility | 2.56 |
| Pg Substrate | No |
| Description | Prediction |
|---|---|
| AMES Toxicity | No |
| Maximum Tolerated Dose | 0.373 (log mg/Kg/day) |
| hERG I Inhibitor | No |
| hERG II Inhibitor | Yes |
| Oral Rat Acute Toxicity (LD50) | 2.193 (mol/Kg) |
| Oral Rat Chronic Toxicity (LOAEL) | 2.690 (log mg/Kg_bw/day) |
| Hepatotoxicity | No |
| Skin Sensitization | No |
| T. Pyriformis Toxicity | 0.318 (log ug/L) |
| Minnow Toxicity | 0.752 (log mM) |
| Non Cardiotoxic | 70% Confidence |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mavra, A.; Petrou, C.C.; Vlasiou, M.C. Ligand and Structure-Based Virtual Screening in Combination, to Evaluate Small Organic Molecules as Inhibitors for the XIAP Anti-Apoptotic Protein: The Xanthohumol Hypothesis. Molecules 2022, 27, 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154825
Mavra A, Petrou CC, Vlasiou MC. Ligand and Structure-Based Virtual Screening in Combination, to Evaluate Small Organic Molecules as Inhibitors for the XIAP Anti-Apoptotic Protein: The Xanthohumol Hypothesis. Molecules. 2022; 27(15):4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154825
Chicago/Turabian StyleMavra, Angeliki, Christos C. Petrou, and Manos C. Vlasiou. 2022. "Ligand and Structure-Based Virtual Screening in Combination, to Evaluate Small Organic Molecules as Inhibitors for the XIAP Anti-Apoptotic Protein: The Xanthohumol Hypothesis" Molecules 27, no. 15: 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154825
APA StyleMavra, A., Petrou, C. C., & Vlasiou, M. C. (2022). Ligand and Structure-Based Virtual Screening in Combination, to Evaluate Small Organic Molecules as Inhibitors for the XIAP Anti-Apoptotic Protein: The Xanthohumol Hypothesis. Molecules, 27(15), 4825. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27154825







