Imperatorin Positively Regulates Melanogenesis through Signaling Pathways Involving PKA/CREB, ERK, AKT, and GSK3β/β-Catenin
Abstract
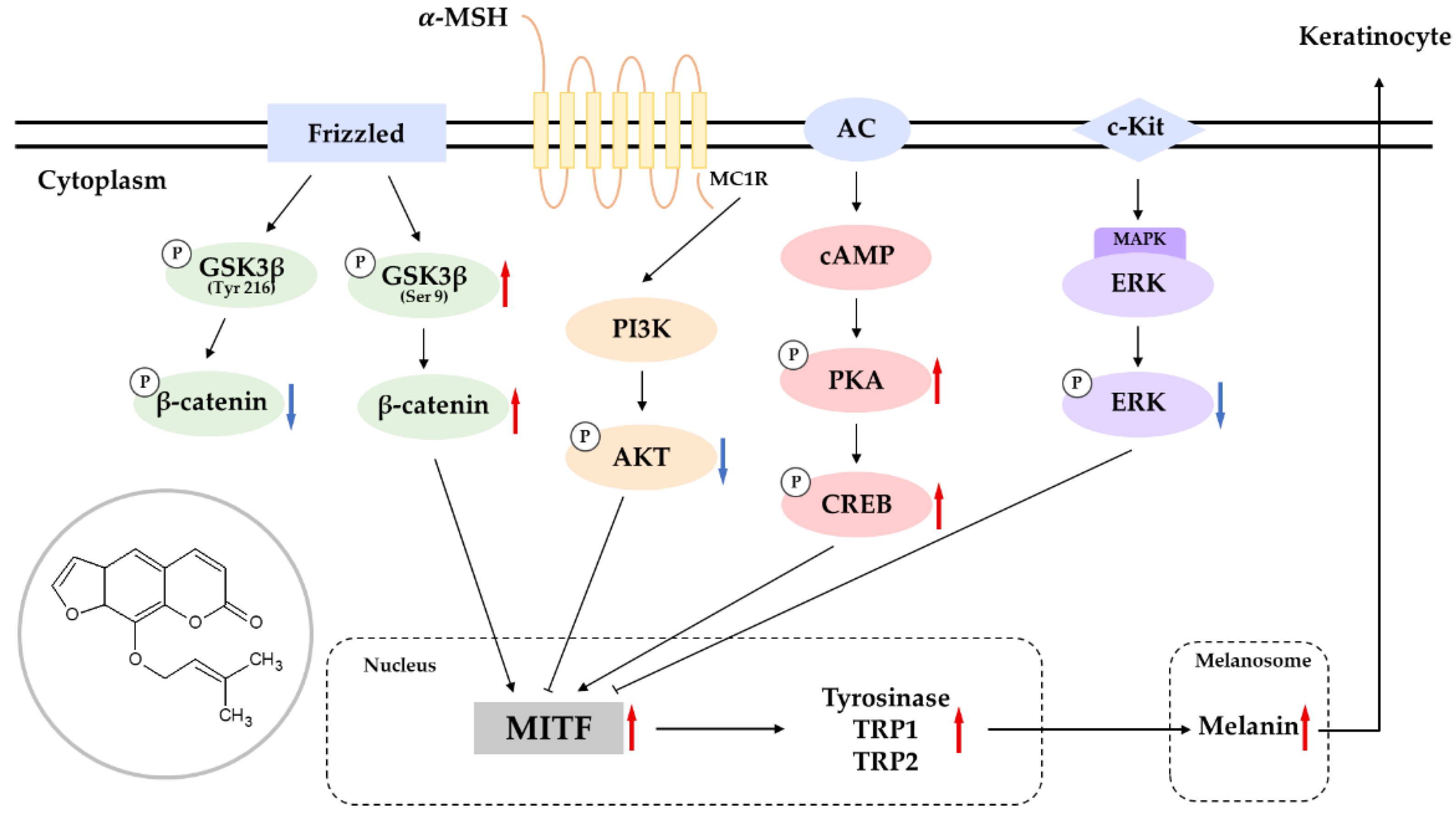
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Imperatorin and Isoimperatorin on the Viability, Melanin Content and Cellular Tyrosinase Activity of B16F10 Cells
2.2. Effects of Imperatorin on the Abundance of Melanogenic Enzymes and MITF
2.3. Effects of Imperatorin on the PKA–CREB Signaling Pathway
2.4. Effects of Imperatorin on the MAPK Signaling Pathway
2.5. Effects of Imperatorin on the AKT/GSK-3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways
2.6. Effects of Imperatorin on Signaling Pathways by Specific Inhibitors
2.7. Primary Skin Irritation Test
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Determination of Melanin Content
4.5. Measurement of Cellular Tyrosinase Activity
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Primary Skin Irritation Test
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ainiwaer, P.; Nueraihemaiti, M.; Li, Z.; Zang, D.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Aisa, H.A. Chemical constituents of Ruta graveolens L. and their melanogenic effects and action mechanism. Fitoterapia 2022, 156, 105094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, Q. Paeonol protects melanocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress through activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway. Drug Dev. Res. 2021, 82, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herraiz, C.; Martínez-Vicente, I.; Maresca, V. The α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone/melanocortin-1 receptor interaction: A driver of pleiotropic effects beyond pigmentation. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2021, 34, 748–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Su, X.; Li, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhuang, W. Schisandrin B inhibits α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced melanogenesis in B16F10 cells via downregulation of MAPK and CREB signaling pathways. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2021, 85, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Yoon, J.H.; Youn, K.; Jun, M. Decursin prevents melanogenesis by suppressing MITF expression through the regulation of PKA/CREB, MAPKs, and PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β cascades. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Wang, L.; Luo, M.; Zhu, W.; Fu, J.; Dong, Z. Molecular and functional analysis of the microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (mitf) gene duplicates in red tilapia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2022, 271, 111257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Hyun, C.G. Inhibitory Effects of Pinostilbene Hydrate on Melanogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells via ERK and p38 Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, G.S.; Lee, J.N.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.G. Pratol, an O-Methylated Flavone, Induces Mel-anogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells via p-p38 and p-JNK Upregulation. Molecules 2017, 22, 1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hyun, C.G. Mechanistic Insights into the Ameliorating Effect of Melanogenesis of Psoralen Derivatives in B16F10 Melanoma Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, W.J.; Ham, Y.M.; Yoon, H.S.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, N.H.; Hyun, C.G. Acanthoic acid inhibits melanogenesis through tyrosinase downregulation and melanogenic gene expression in B16 melanoma cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 1359. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, J.W.; Deng, S.J.; Xue, Z.W.; Liu, P.Y.; Yu, L.J.; Li, J.N.; Xia, S.N.; Gu, Y.; Bao, X.Y.; Lan, Z.; et al. Imperatorin inhibits mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor kappa-B signaling pathways and alleviates neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Hu, S.; Bai, H.; Hou, Y.; Wang, C.; He, H.; He, L. Imperatorin ameliorates mast cell-mediated allergic airway inflammation by inhibiting MRGPRX2 and CamKII/ERK signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 184, 114401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yu, J.; Xiao, X.; Zang, L.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Huang, Q.; Niu, X.; Li, W. Imperatorin reduces the inflammatory response of atherosclerosis by regulating MAPKs signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 90, 107170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, M.; Luo, Y. Imperatorin Relieved Ulcerative Colitis by Regulating the Nrf-2/ARE/HO-1 Pathway in Rats. Inflammation 2021, 44, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, B.; Yang, Z.; Gao, W.; Song, C.; Miao, W.; et al. The Protective Effects of Imperatorin on Acetaminophen Overdose-Induced Acute Liver Injury. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 13, 8026838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Ansari, M.Y.; Bano, S.; Haqqi, T.M. Imperatorin suppresses IL-1β-induced iNOS expression via inhibiting ERK-MAPK/AP1 signaling in primary human OA chondrocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 85, 106612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Z.; Chen, J.H.; Tsai, C.F.; Yeh, W.L. Anti-inflammatory Property of Imperatorin on Alveolar Macrophages and Inflammatory Lung Injury. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1002–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Hsiao, G.; Wang, C.C.; Lee, Y.L. Imperatorin exerts antiallergic effects in Th2-mediated allergic asthma via induction of IL-10-producing regulatory T cells by modulating the function of dendritic cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 110, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.L.; Im, M.; Lee, M.H.; Roh, S.S.; Choi, B.W.; Kim, S.J.; Sohn, K.C.; Lee, Y.; Seo, Y.J.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Inhibitory effect of imperatorin on insulin-like growth factor-1-induced sebum production in human sebocytes cultured in vitro. Life Sci. 2016, 144, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Sun, J.; Jiang, L.; Duan, L.; Huo, M.; Chen, N.; Zhong, W.; Wassy, L.; Yang, Z.; Feng, H. Imperatorin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by suppressing NF-κB and MAPKs activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Inflammation 2012, 35, 1764–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarska, A.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Kiełbus, M.; Dmoszyńska-Graniczka, M.; Miziak, P.; Szumiło, J.; Nowosadzka, E.; Kowalczuk, K.; Khalifa, S.; Smok-Kalwat, J.; et al. Imperatorin as a Promising Chemotherapeutic Agent Against Human Larynx Cancer and Rhabdomyosarcoma Cells. Molecules 2020, 25, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, C.; Yang, Y.; Gao, B. Imperatorin Targets MCL-1 to Sensitize CD133+ Lung Cancer Cells to γδ-T Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, K.S.; Zuo, H.X.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.Y.; Piao, L.X.; Xu, G.H.; Li, X.; Quan, Z.S.; et al. Imperatorin suppresses proliferation and angiogenesis of human colon cancer cell by targeting HIF-1α via the mTOR/p70S6K/4E-BP1 and MAPK pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 203, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Sun, J.; Li, H.; Wu, P.; Fung, K.P.; Liu, F. Imperatorin induces Mcl-1 degradation to cooperatively trigger Bax translocation and Bak activation to suppress drug-resistant human hepatoma. Cancer Lett. 2014, 348, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiba, Y.; Oyama, R.; Misawa, S.; Tanikawa, T.; Kitamura, M.; Suzuki, R. Screening for inhibitory effects of crude drugs on furin-like enzymatic activities. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.W.; Ha, T.K.Q.; Cho, H.M.; An, J.P.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, E.; Oh, W.K. Antiviral activity of furanocoumarins isolated from Angelica dahurica against influenza a viruses H1N1 and H9N2. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 259, 112945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, R.; Márquez, N.; Gómez-Gonzalo, M.; Calzado, M.A.; Bettoni, G.; Coiras, M.T.; Alcamí, J.; López-Cabrera, M.; Appendino, G.; Muñoz, E. Imperatorin inhibits HIV-1 replication through an Sp1-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37349–37359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.X.; Zhang, K.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Yue, Y.S.; Xia, S.Z.; Li, Y.; Deng, H.H.; Jing, H.L.; Cao, Y.J. Imperatorin ameliorates learning and memory deficits through BDNF/TrkB and ERK/CaMKIIα/CREB signaling in prenatally-stressed female offspring. Phytother. Res. 2020, 34, 2408–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Liu, P.; Wei, J.; Zhao, M.; Yao, X.; Luo, X.; Xu, S. Imperatorin alleviated endometriosis by inhibiting the activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in rats. Life Sci. 2021, 274, 119291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunbupha, S.; Prasarttong, P.; Poasakate, A.; Maneesai, P.; Pakdeechote, P. Imperatorin alleviates metabolic and vascular alterations in high-fat/high-fructose diet-fed rats by modulating adiponectin receptor 1, eNOS, and p47phox expression. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 899, 174010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.; Siddiqui, E.M.; Mehan, S. Involvement of adenylate cyclase/cAMP/CREB and SOX9/MITF in melanogenesis to prevent vitiligo. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.E.; Yoo, H.; Lee, H.R.; Moon, I.J.; Lee, W.J.; Song, Y.; Chang, S.E. Carvedilol, an Adrenergic Blocker, Suppresses Melanin Synthesis by Inhibiting the cAMP/CREB Signaling Pathway in Human Melanocytes and Ex Vivo Human Skin Culture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Huang, J.A. Anti-melanogenic effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), epicatechin-3-gallate (ECG) and gallocatechin-3-gallate (GCG) via down-regulation of cAMP/CREB /MITF signaling pathway in B16F10 melanoma cells. Fitoterapia 2020, 145, 104634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qomaladewi, N.P.; Kim, M.Y.; Cho, J.Y. Rottlerin Reduces cAMP/CREB-Mediated Melanogenesis via Regulation of Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eom, Y.S.; Jeong, D.; Ryu, A.R.; Song, K.H.; Im, D.S.; Lee, M.Y. Daphne odora Exerts Depigmenting Effects via Inhibiting CREB/MITF and Activating AKT/ERK-Signaling Pathways. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2022, 44, 3312–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, G.; An, S.K.; Park, I.C.; Bae, S.; Lee, J.H. Daphnetin inhibits α-MSH-induced melanogenesis via PKA and ERK signaling pathways in B16F10 melanoma cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2022, 86, 596–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.M. The effect of emodin on melanogenesis through the modulation of ERK and MITF signaling pathway. Nat. Prod. Res. 2022, 36, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xie, Y.; Wu, Z. Astragaloside IV Enhances Melanogenesis via the AhR-Dependent AKT/GSK-3β/β-Catenin Pathway in Normal Human Epidermal Melanocytes. Evid.-Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 8838656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, D.; Niu, C.; Aisa, H.A. Amine derivatives of furocoumarin induce melanogenesis by activating Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signal pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molagoda, I.M.N.; Karunarathne, W.A.H.M.; Park, S.R.; Choi, Y.H.; Park, E.K.; Jin, C.Y.; Yu, H.; Jo, W.S.; Lee, K.T.; Kim, G.Y. GSK-3β-Targeting Fisetin Promotes Melanogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells and Zebrafish Larvae through β-Catenin Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, B.; Li, K.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Huang, P.; Pan, Y. Isoimperatorin (ISO) reduces melanin content in keratinocytes via miR-3619/CSTB and miR-3619/CSTD axes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2020, 84, 1436–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, S.M.; Lee, B.C.; Pyo, H.B.; Park, H.D. New cosmetic agents for skin whitening from Angelica dahurica. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 57, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Goenka, S.; Simon, R.S. Inhibitory Effects of the Bioactive Thermorubin Isolated from the Fungus Thermoactinomyces antibioticus on Melanogenesis. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilles, J.C.; Dos Santos, F.L.; Kulkamp-Guerreiro, I.C.; Contri, R.V. Biological activities and safety data of kojic acid and its derivatives—A review. Exp. Dermatol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merecz-Sadowska, A.; Sitarek, P.; Kowalczyk, T.; Zajdel, K.; Kucharska, E.; Zajdel, R. The Modulation of Melanogenesis in B16 Cells Upon Treatment with Plant Extracts and Isolated Plant Compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 4360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Dong, C. MITF-M regulates melanogenesis in mouse melanocytes. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 90, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, H.; Guan, D.; Meng, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; Jia, H.; Dou, K.; Liu, C.; et al. MITF-siRNA formulation is a safe and effective therapy for human melasma. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sakamoto, K. Citric acid promoted melanin synthesis in B16F10 mouse melanoma cells, but inhibited it in human epidermal melanocytes and HMV-II melanoma cells via the GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goenka, S.; Simon, S.R. Depigmenting effect of Xanthohumol from hop extract in MNT-1 human melanoma cells and normal human melanocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 100955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, S.B.; Bae, S.; Hyun, C.G. Antioxidant Activities of Jeju Wax Apple (Syzygium samarangense) and Safety of Human Keratinocytes and Primary Skin Irritation Test. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hyun, C.G. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Psoralen Derivatives on RAW264.7 Cells via Regulation of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| No. | Test Sample | No. of Respondents | 20 min after Removal | 24 h after Removal | Reaction Grade (R) * | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | 24 h | 48 h | Mean | |||
| 1 | Imperatorin (25 μM) | 2 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | 0 | 2 | 0.8 |
| 2 | Imperatorin (50 μM) | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 0 | 1 | 0.4 |
| 3 | Squalene | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.; Hyun, C.-G. Imperatorin Positively Regulates Melanogenesis through Signaling Pathways Involving PKA/CREB, ERK, AKT, and GSK3β/β-Catenin. Molecules 2022, 27, 6512. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196512
Kim T, Hyun C-G. Imperatorin Positively Regulates Melanogenesis through Signaling Pathways Involving PKA/CREB, ERK, AKT, and GSK3β/β-Catenin. Molecules. 2022; 27(19):6512. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196512
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Taejin, and Chang-Gu Hyun. 2022. "Imperatorin Positively Regulates Melanogenesis through Signaling Pathways Involving PKA/CREB, ERK, AKT, and GSK3β/β-Catenin" Molecules 27, no. 19: 6512. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196512
APA StyleKim, T., & Hyun, C.-G. (2022). Imperatorin Positively Regulates Melanogenesis through Signaling Pathways Involving PKA/CREB, ERK, AKT, and GSK3β/β-Catenin. Molecules, 27(19), 6512. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196512







