Deactivatable Bisubstrate Inhibitors of Protein Kinases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Deactivatable Bisubstrate Inhibitors of PKAcα
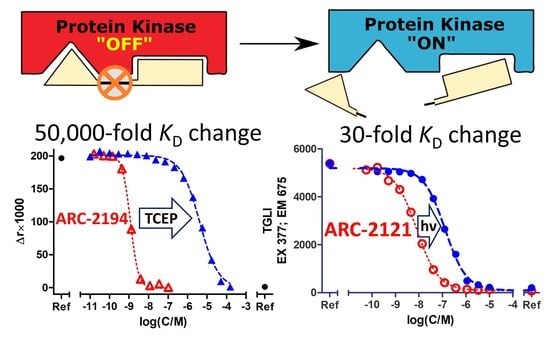
2.2. Characterization of Deactivatable Inhibitors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Equipment and Software
4.2. Reagents
4.3. HPLC-MS Analysis of the Fragmentation of ARC-2121 and ARC-2194
4.4. Biochemical Binding/Displacement Assay
4.5. Kinase Activity Assay
4.6. Chemical Synthesis
4.6.1. Solid Phase Synthesis
4.6.2. Compound 5
4.6.3. Compound 6
4.6.4. Compound 7
4.6.5. Compound 3
4.6.6. Compound 8
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Badeau, B.A.; DeForest, C.A. Programming stimuli-responsive behavior into biomaterials. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 21, 241–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczi, D.; Johnstone, M.D.; Fleming, C.L. Photoresponsive Small Molecule Inhibitors for the Remote Control of Enzyme Activity. Chem. Asian. J. 2022, 17, e202200200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klán, P.; Šolomek, T.; Bochet, C.G.; Blanc, A.; Givens, R.; Rubina, M.; Popik, V.; Kostikov, A.; Wirz, J. Photoremovable protecting groups in chemistry and biology: Reaction mechanisms and efficacy. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 119–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymański, W.; Beierle, J.M.; Kistemaker, H.A.; Velema, W.A.; Feringa, B.L. Reversible photocontrol of biological systems by the incorporation of molecular photoswitches. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 6114–6178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imoto, T.; Minoshima, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Emery, B.P.; Bull, S.D.; Bito, H.; Kikuchi, K. A photodeactivatable antagonist for controlling CREB-dependent gene expression. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1813–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimer, J.; Pávová, M.; Anders, M.; Pachl, P.; Šácha, P.; Cígler, P.; Weber, J.; Majer, P.; Řezáčová, P.; Kräusslich, H.G.; et al. Triggering HIV polyprotein processing by light using rapid photodegradation of a tight-binding protease inhibitor. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toebes, M.; Coccoris, M.; Bins, A.; Rodenko, B.; Gomez, R.; Nieuwkoop, N.J.; van de Kasteele, W.; Rimmelzwaan, G.F.; Haanen, J.B.; Ovaa, H.; et al. Design and use of conditional MHC class I ligands. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, L.L.; Kurutz, J.W.; Kent, S.B.; Kron, S.J. Control of the yeast cell cycle with a photocleavable alpha-factor analogue. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 6322–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, K.; Tsukiji, S.; Furuta, T.; Nagamune, T. A bromocoumarin-based linker for synthesis of photocleavable peptidoconjugates with high photosensitivity. Chem. Commun. 2008, 42, 5399–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagawati, M.; Lata, S.; Tampé, R.; Piehler, J. Native laser lithography of His-tagged proteins by uncaging of multivalent chelators. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5932–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallafuss, A.; Gibson, D.; Morcos, P.; Li, Y.; Seredick, S.; Eisen, J.; Washbourne, P. Turning gene function ON and OFF using sense and antisense photo-morpholinos in zebrafish. Development 2012, 139, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordoukhanian, P.; Taylor, J.S. Design and synthesis of a versatile photocleavable DNA building block. Application to phototriggered hybridization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 9570–9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.L.; Tang, X.; Turetsky, A.; Dmochowski, I.J. RNA bandages for photoregulating in vitro protein synthesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 6255–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boirie, Y.; Dangin, M.; Gachon, P.; Vasson, M.P.; Maubois, J.L.; Beaufrère, B. Slow and fast dietary proteins differently modulate postprandial protein accretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14930–14935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momotake, A.; Lindegger, N.; Niggli, E.; Barsotti, R.J.; Ellis-Davies, G.C. The nitrodibenzofuran chromophore: A new caging group for ultra-efficient photolysis in living cells. Nat. Methods. 2006, 3, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.P.; Gwizdala, C.; Burdette, S.C. Methods for preparing metal ion photocages: Application to the synthesis of crowncast. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 2587–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valant, C.; Robert Lane, J.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. The best of both worlds? Bitopic orthosteric/allosteric ligands of g protein-coupled receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2012, 52, 153–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavogina, D.; Enkvist, E.; Uri, A. Bisubstrate inhibitors of protein kinases: From principle to practical applications. Chem. Med. Chem. 2010, 5, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jencks, W.P. On the attribution and additivity of binding energies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 4046–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauquelin, G.; Charlton, S.J. Exploring avidity: Understanding the potential gains in functional affinity and target residence time of bivalent and heterobivalent ligands. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mammen, M.; Choi, S.K.; Whitesides, G.M. Polyvalent interactions in biological systems: Implications for design and use of multivalent ligands and inhibitors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1998, 37, 2754–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sõrmus, T.; Lavogina, D.; Enkvist, E.; Uri, A.; Viht, K. Efficient photocaging of a tight-binding bisubstrate inhibitor of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 11147–11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R. A historical overview of protein kinases and their targeted small molecule inhibitors. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 100, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niklas, B.; Lapied, B.; Nowak, W. In search of synergistic insect repellents: Modeling of muscarinic GPCR interactions with classical and bitopic photoactive ligands. Molecules 2022, 27, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velema, W.A.; Szymanski, W.; Feringa, B.L. Photopharmacology: Beyond proof of principle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2178–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuil, J.; van Wandelen, L.T.; de Mol, N.J.; Liskamp, R.M. A photoswitchable ITAM peptidomimetic: Synthesis and real time surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis of the effects of cis-trans isomerization on binding. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponader, D.; Igde, S.; Wehle, M.; Märker, K.; Santer, M.; Bléger, D.; Hartmann, L. Photoswitchable precision glycooligomers and their lectin binding. Beilstein. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osswald, U.; Boneberg, J.; Wittmann, V. Photoswitching affinity and mechanism of multivalent lectin ligands. Chemistry 2022, 28, e202200267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hah, J.M.; Lawrence, D.S. Light-mediated liberation of enzymatic activity: “small molecule” caged protein equivalents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10474–10475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Bhattarai, U.; Song, Y.; Liang, F.S. Design, synthesis and activity of light deactivatable microRNA inhibitor. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 80, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivan, T.; Enkvist, E.; Viira, B.; Manoharan, G.; Raidaru, G.; Pflug, A.; Alam, K.A.; Zaccolo, M.; Engh, R.A.; Uri, A. Bifunctional ligands for inhibition of tight-binding protein−protein interactions. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1900–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.; Hu, J.; Liu, S. Disulfide-based self-immolative linkers and functional bioconjugates for biological applications. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2020, 41, e1900531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, J.J.; Davies, T.G.; Donald, A.; McHardy, T.; Rowlands, M.G.; Aherne, G.W.; Hunter, L.K.; Taylor, K.; Ruddle, R.; Raynaud, F.I.; et al. Identification of 4-(4-aminopiperidin-1-yl)-7H-pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidines as selective inhibitors of protein kinase B through fragment elaboration. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2147–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enkvist, E.; Lavogina, D.; Raidaru, G.; Vaasa, A.; Viil, I.; Lust, M.; Viht, K.; Uri, A. Conjugation of adenosine and hexa-(D-arginine) leads to a nanomolar bisubstrate-analog inhibitor of basophilic protein kinases. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 494, 7150–7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavogina, D.; Lust, M.; Viil, I.; König, N.; Raidaru, G.; Rogozina, J.; Enkvist, E.; Uri, A.; Bossemeyer, D. Structural analysis of ARC-type inhibitor (ARC-1034) binding to protein kinase A catalytic subunit and rational design of bisubstrate analogue inhibitors of basophilic protein kinases. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinner, K.; Doughan, B.; Poon, D.J. Scalable synthesis of β-amino esters via reformatsky reaction with N-tert-butanesulfinyl imines. Synlett 2009, 6, 991–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, M.; Moriyama, K.; Togo, H. One-Pot Transformation of methylarenes into aromatic aldehydes under metal-free conditions. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 16, 3402–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkvist, E.; Vaasa, A.; Kasari, M.; Kriisa, M.; Ivan, T.; Ligi, K.; Raidaru, G.; Uri, A. Protein-induced long lifetime luminescence of nonmetal probes. ACS Chem. Biol. 2011, 6, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinijarv, H.; Wu, S.; Ivan, T.; Laasfeld, T.; Viht, K.; Uri, A. Binding assay for characterization of protein kinase inhibitors possessing sub-picomolar to sub-millimolar affinity. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 531, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaasa, A.; Viil, I.; Enkvist, E.; Viht, K.; Raidaru, G.; Lavogina, D.; Uri, A. High-affinity bisubstrate probe for fluorescence anisotropy binding/displacement assays with protein kinases PKA and ROCK. Anal. Biochem. 2009, 385, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viht, K.; Schweinsberg, S.; Lust, M.; Vaasa, A.; Raidaru, G.; Lavogina, D.; Uri, A.; Herberg, F.W. Surface-plasmon-resonance-based biosensor with immobilized bisubstrate analog inhibitor for the determination of affinities of ATP-and protein-competitive ligands of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 362, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasari, M.; Ligi, K.; Williams, J.A.; Vaasa, A.; Enkvist, E.; Viht, K.; Pålsson, L.O.; Uri, A. Responsive microsecond-lifetime photoluminescent probes for analysis of protein kinases and their inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013, 1834, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, J.C.; Dempsey, G.T.; Sun, E.; Zhuang, X. Phosphine quenching of cyanine dyes as a versatile tool for fluorescence microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1197–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amano, Y.; Umezawa, N.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, H.; Umehara, T.; Higuchi, T. Activation of lysine-specific demethylase 1 inhibitor peptide by redox-controlled cleavage of a traceless linker. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, J.J.; Wang, H.; Vilela, M.; Danuser, G.; Hahn, K.M. Manipulation of endogenous kinase activity in living cells using photoswitchable inhibitory peptides. ACS Synth. Biol. 2014, 3, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.S.; Koszelak, M.; Liu, J.; Lawrence, D.S. A caged protein kinase inhibitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 7145–7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schehr, M.; Ianes, C.; Weisner, J.; Heintze, L.; Müller, M.P.; Pichlo, C.; Charl, J.; Brunstein, E.; Ewert, J.; Lehr, M.; et al. 2-Azo-, 2-diazocine-thiazols and 2-azo-imidazoles as photoswitchable kinase inhibitors: Limitations and pitfalls of the photoswitchable inhibitor approach. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2019, 18, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deiters, A. Principles and applications of the photochemical control of cellular processes. Chembiochem 2010, 11, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchter, M.J. On the promise of photopharmacology using photoswitches: A medicinal chemist’s perspective. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 11436–11447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulègue, C.; Löweneck, M.; Renner, C.; Moroder, L. Redox potential of azobenzene as an amino acid residue in peptides. Chembiochem 2007, 8, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, G.; Heckel, A. Biologically active molecules with a “light switch”. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2006, 45, 4900–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.M.; Xu, W.; Lawrence, D.S. Construction of a photoactivatable profluorescent enzyme via propinquity labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2331–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roehrl, M.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Wagner, G. A general framework for development and data analysis of competitive high-throughput screens for small-molecule inhibitors of protein-protein interactions by fluorescence polarization. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 16056–16066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.X. An exact mathematical expression for describing competitive binding of two different ligands to a protein molecule. FEBS Lett. 1995, 360, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Compound | Assay 1 | Parameter | Value ± SD/nM |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARC-1411 | TGLI (A) | KD | 0.003 ± 0.001; (0.003 [31]) |
| H-89 | TGLI (A), FA | KD | 13 ± 3; (9 ± 1 [41]) |
| PhosphoSens® | IC50 | 670 ± 70 | |
| ARC-2121 | TGLI (B) | KD | 0.019 ± 0.007 |
| ARC-2121, irradiated 2 | TGLI (B) | KDapp | 0.6 ± 0.3 |
| ARC-2194 | TGLI (A) | KD | 0.007 ± 0.001 |
| PhosphoSens® | IC50 | 2.9 ± 0.5 | |
| ARC-2194 + TCEP | FA | KDapp | 350 ± 30 |
| PhosphoSens® | IC50 | 48,000 ± 7000 | |
| 10 | FA | KD | 650 ± 130 |
| 11a:10 (1:1) | FA | KDapp | 190 ± 60 |
| 11a | FA | KD | 460 ± 210 |
| 2a | FA | KD | 550 ± 150 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sõrmus, T.; Lavogina, D.; Enkvist, E.; Uri, A.; Viht, K. Deactivatable Bisubstrate Inhibitors of Protein Kinases. Molecules 2022, 27, 6689. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196689
Sõrmus T, Lavogina D, Enkvist E, Uri A, Viht K. Deactivatable Bisubstrate Inhibitors of Protein Kinases. Molecules. 2022; 27(19):6689. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196689
Chicago/Turabian StyleSõrmus, Tanel, Darja Lavogina, Erki Enkvist, Asko Uri, and Kaido Viht. 2022. "Deactivatable Bisubstrate Inhibitors of Protein Kinases" Molecules 27, no. 19: 6689. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196689
APA StyleSõrmus, T., Lavogina, D., Enkvist, E., Uri, A., & Viht, K. (2022). Deactivatable Bisubstrate Inhibitors of Protein Kinases. Molecules, 27(19), 6689. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196689