Quantitative Analysis of Solar Photovoltaic Panel Performance with Size-Varied Dust Pollutants Deposition Using Different Machine Learning Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
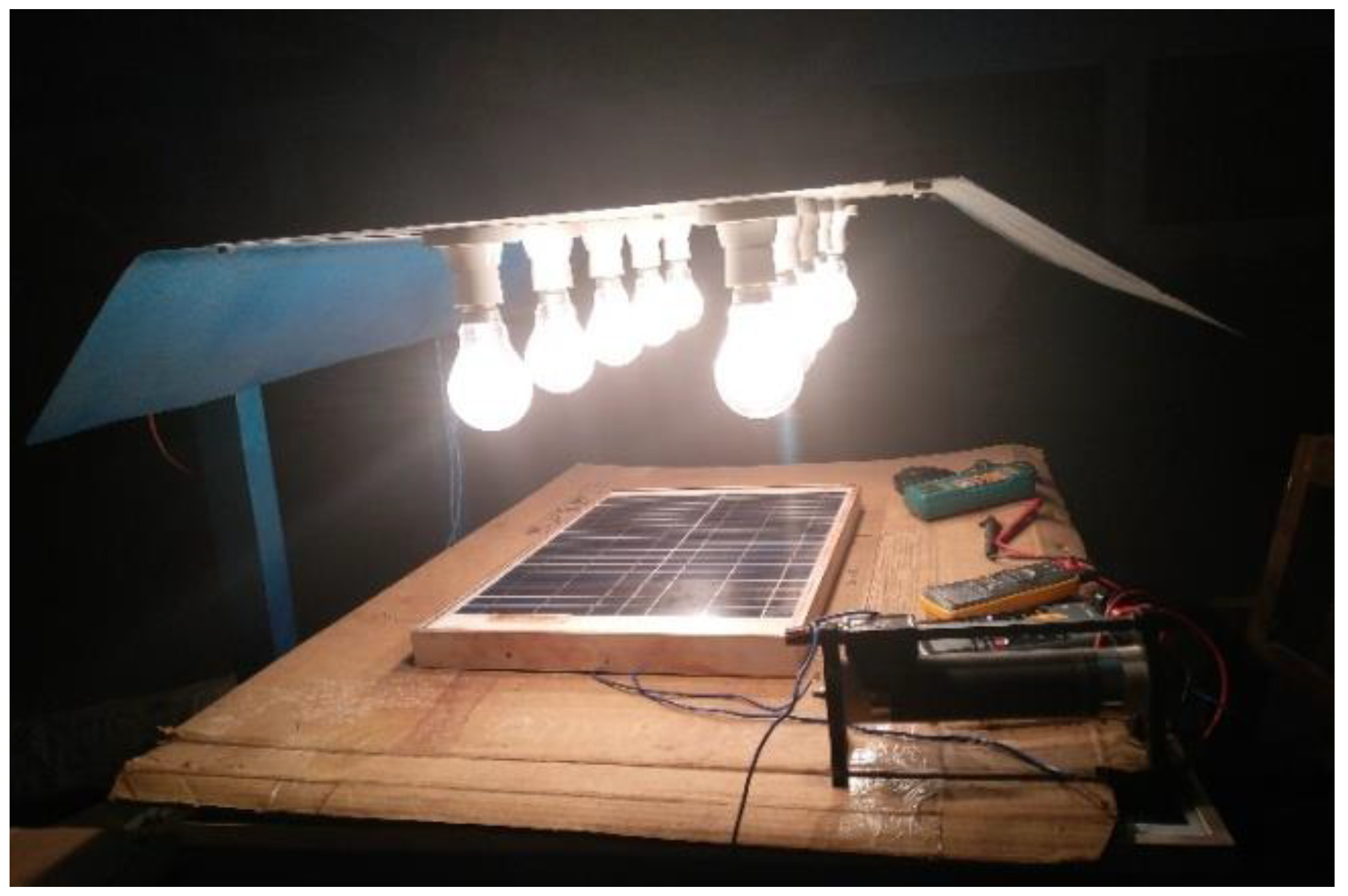
2. Research Method and Experimental Set-Ups
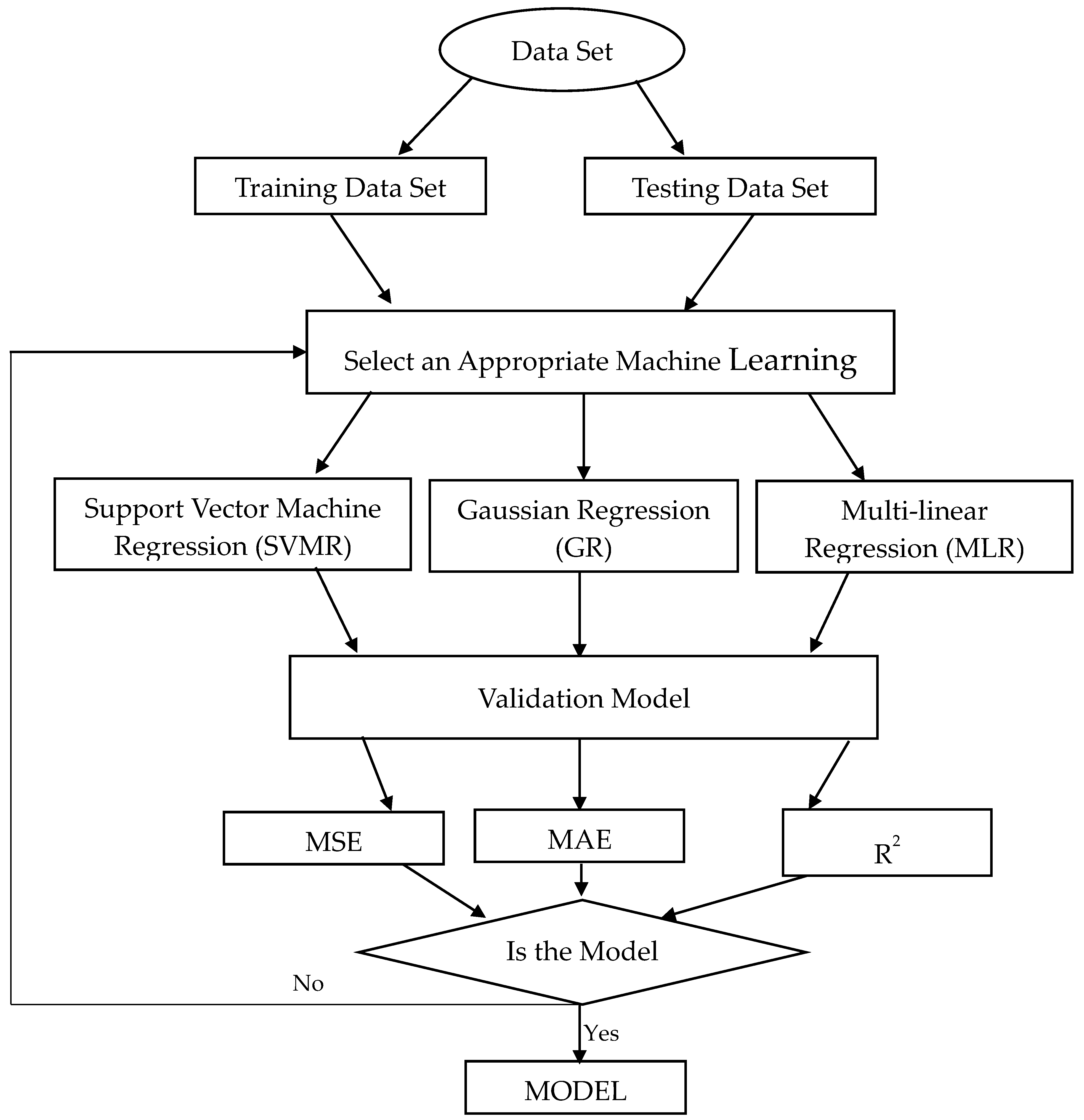
3. Machine Learning Approach for Prediction of Output Power
3.1. Support Vector Machine Regression (SVMR)
3.2. Gaussian Regression (GR)
3.3. Multiple Linear Regression (MLR)
4. Prediction of Output Power Due to Size-Varied Dust Pollutants Deposition
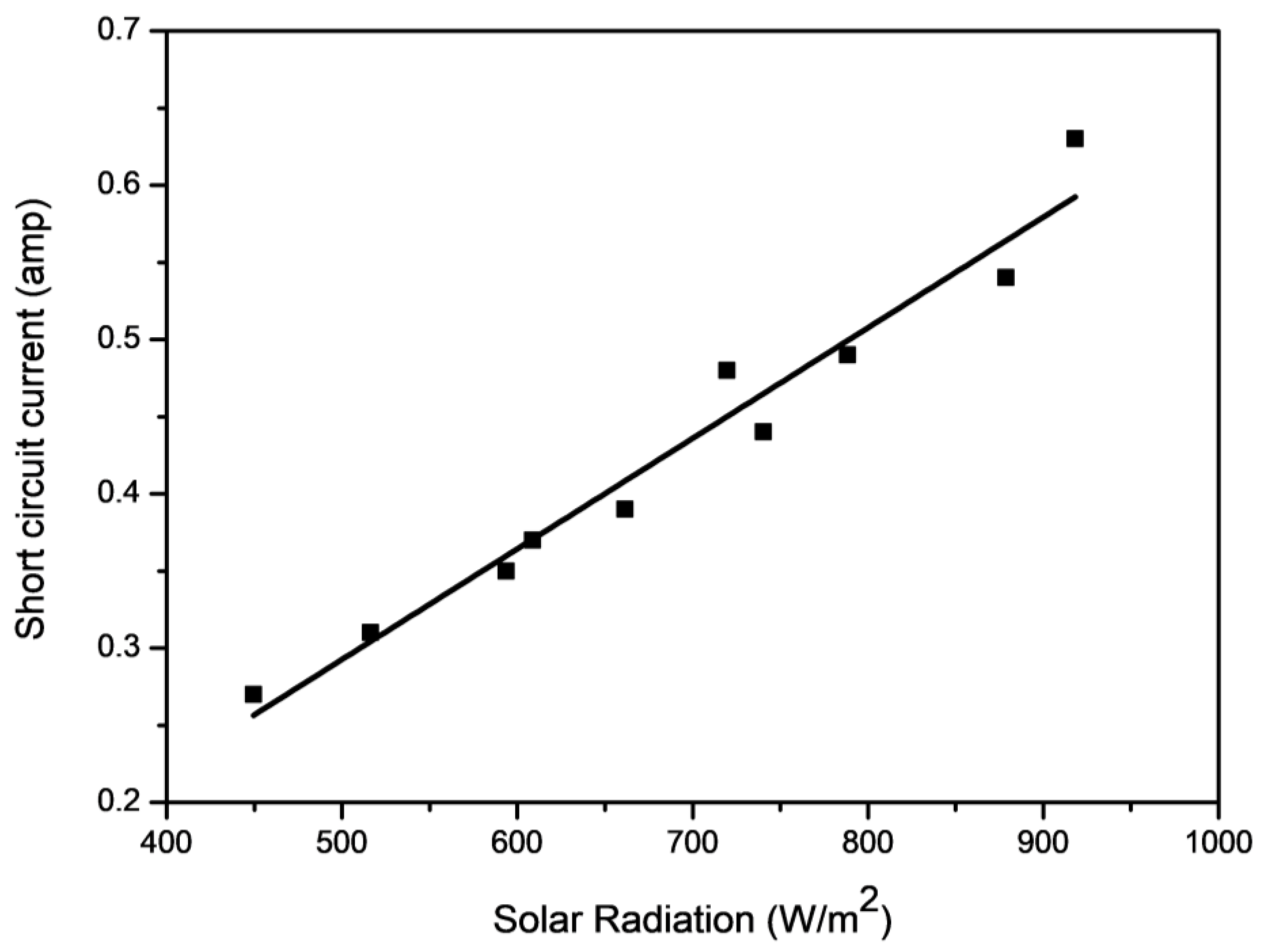
5. Establishing the Relationship between Solar Radiation and Short-Circuit Current
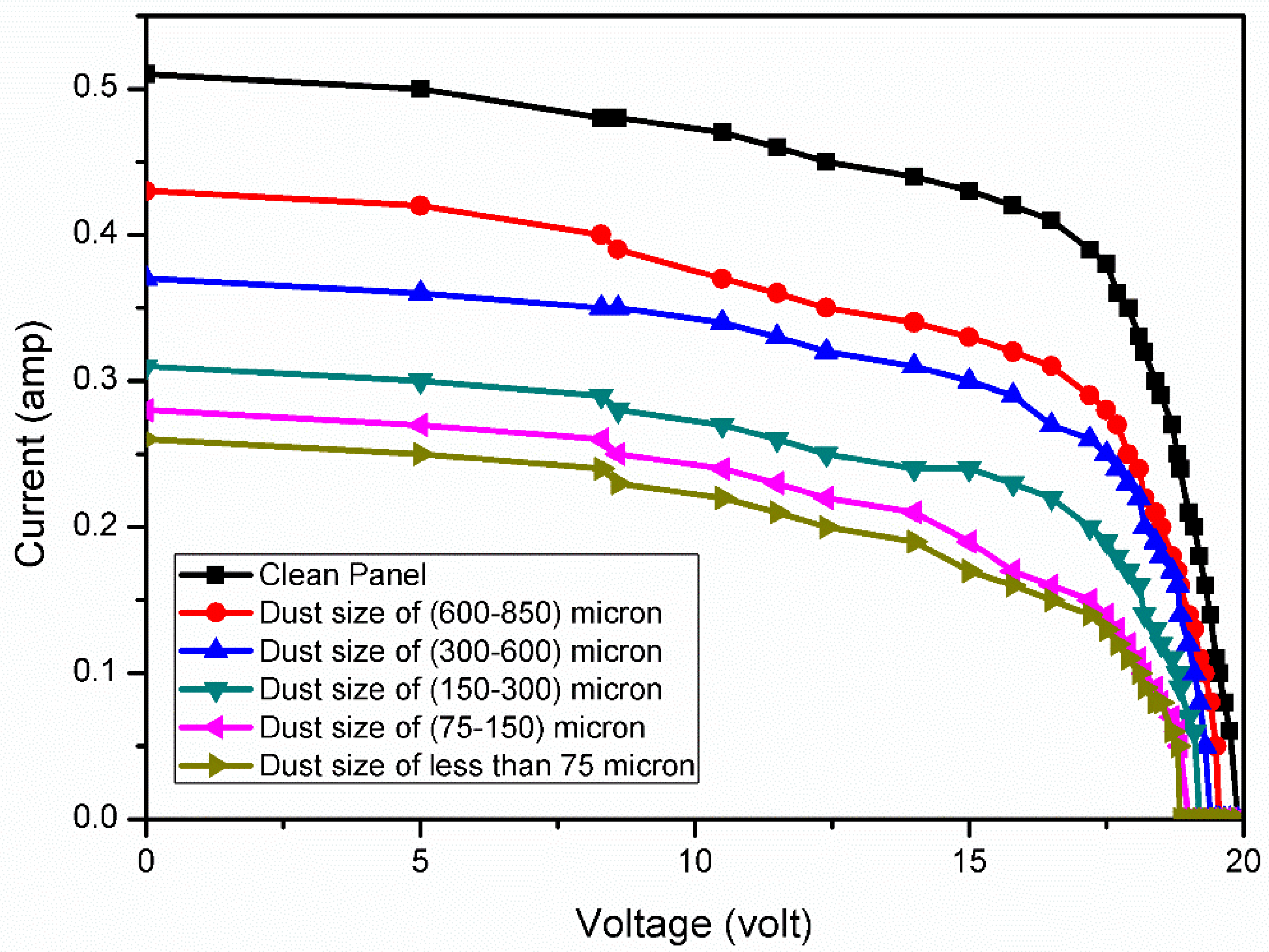
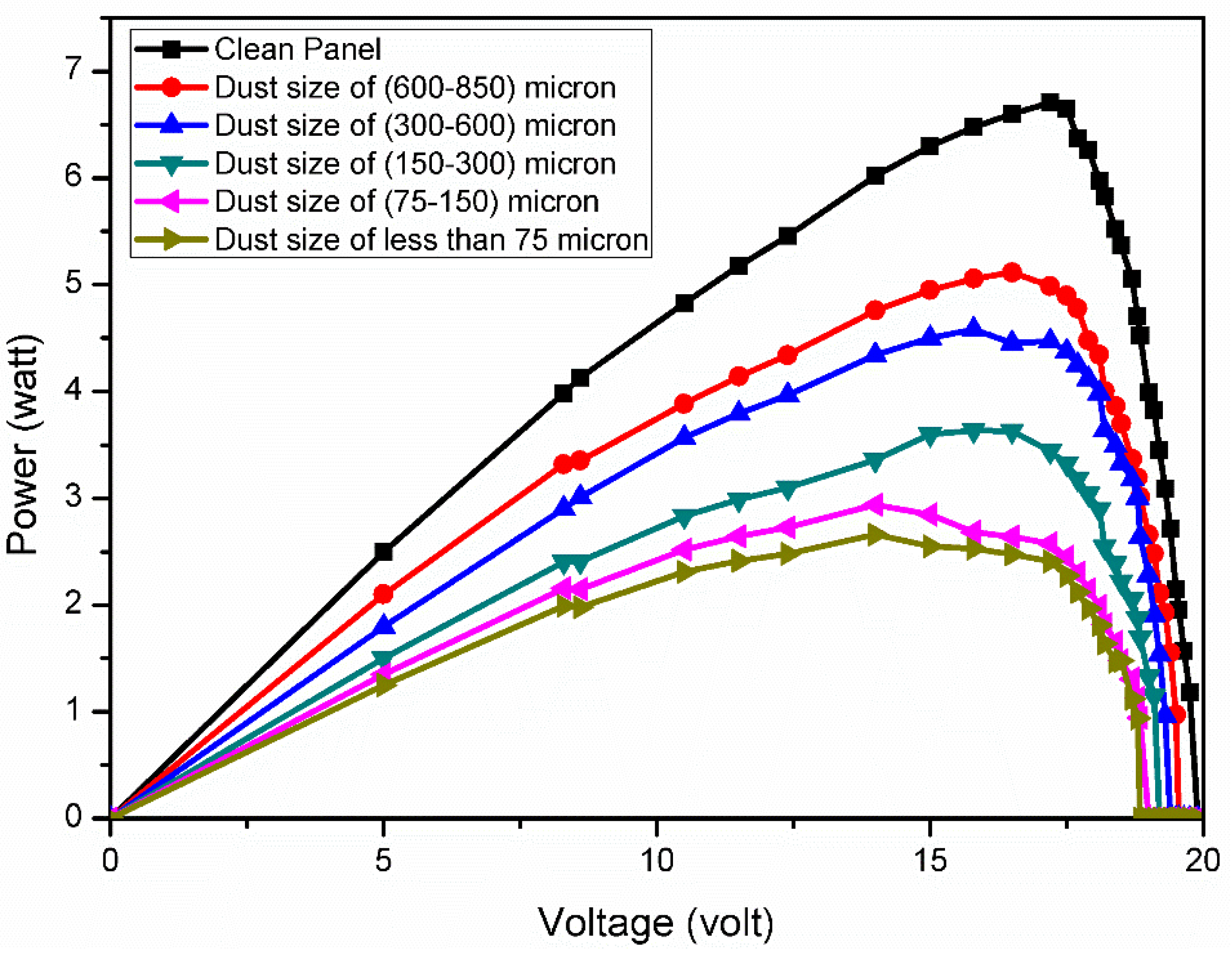
6. Analysis of PV Panel Performance under the Size-Varied Dust Pollutants Deposition
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Jiang, H.; Lin, L.; Sun, K. Experimental Investigation of the Impact of Airborne Dust Deposition on the Performance of Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Modules. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4299–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldellis, J.K.; Fragos, P.; Kapsali, M. Systematic Experimental Study of the Pollution Deposition Impact on the Energy Yield of Photovoltaic Installations. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 2717–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Yim, Y.J.; Lee, J.W.; Heo, Y.J.; Park, S.J. Carbon-filled organic phase-change materials for thermal energy storage: A review. Molecules 2019, 24, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luceño-Sánchez, J.A.; Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Peña Capilla, R. Materials for photovoltaics: State of art and recent developments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darwish, Z.A.; Hussein, A.K.; Kamaruzzaman, S.; Al-Goul, M.A.; Hussain, A. Effect of Dust Pollutant Type on Photovoltaic Performance. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 41, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaifan, R.J.; Ayman, S.; Wafa, S.; Daniel, J.; Wubulikasimu, Y.; Amir, A.A.; Brahim, A. Improved Self-Cleaning Properties of an Efficient and Easy to Scale up TiO2 Thin Films Prepared by Adsorptive Self-Assembly. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobokshy, E.; Mohammad, S.; Fahmy, M.H. Degradation of Photovoltaic Cell Performance Due to Dust Deposition on to Its Surface. Renew. Energy 1993, 3, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, D.S.; Sudhakar, K. Effect of Dust on the Performance of Solar PV Panel. Int. J. ChemTech. Res. 2013, 5, 1083–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Tobnaghi, D.M.; Naderi, D. The effect of solar Irradiance and temperature on solar cells performance. Extensive J. Appl. Sci. 2015, 3, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Arjyadhara, P.; Ali, S.M.; Chitralekha, J. Analysis of solar PV cell performance with changing irradiance and temperature. Int. J. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2013, 2, 214–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hirata, Y.; Tani, T. Output variation of photovoltaic modules with environmental factors—I. The effect of spectral solar Irradiance on photovoltaic module output. Solar Energy 1995, 55, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Aruna, M.; Murthy, S.N. Performance Evaluation of PV Panel Under Dusty Condition. Int. J. Renew. Energy Dev. 2017, 6, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darwish, Z.A.; Kazem, H.A.; Sopian, K.; Alghoul, M.A.; Alawadhi, H. Experimental investigation of dust pollutants and the impact of environmental parameters on PV performance: An experimental study. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 155–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elminir, H.K.; Ghitas, A.E.; Hamid, R.H.; El-Hussainy, F.; Beheary, M.M.; Abdel-Moneim, K.M. Effect of dust on the transparent cover of solar collectors. Energy Convers. Manag. 2006, 47, 3192–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, S.A.; Walwil, H.M. Fundamental studies on dust fouling effects on PV module performance. Sol. Energy 2014, 107, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldellis, J.K.; Kapsali, M. Simulating the dust effect on the energy performance of photovoltaic generators based on experimental measurements. Energy 2011, 36, 5154–5161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnasser, T.M.; Mahdy, A.M.; Abass, K.I.; Chaichan, M.T.; Kazem, H.A. Impact of dust ingredient on photovoltaic performance: An experimental study. Sol. Energy 2020, 195, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazem, H.A.; Chaichan, M.T. The effect of dust accumulation and cleaning methods on PV panels’ outcomes based on an experimental study of six locations in Northern Oman. Sol. Energy 2019, 187, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoukis, C.; Figgis, B.; Ackermann, L.; Ayoub, M.A. Effects of atmospheric dust deposition on Solar PV energy production in a desert environment. Sol. Energy 2018, 164, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepak; Malvi, C.S. Experimental investigation of Effect of Dust Accumulation and Discoloration on Photovoltaic Panel Material. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 4427–4441. [Google Scholar]
- Kazem, H.A.; Chaichan, M.T.; Al-Waeli, A.H.; Sopian, K. Effect of dust and cleaning methods on mono and polycrystalline solar photovoltaic performance: An indoor experimental study. Sol. Energy 2022, 236, 626–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Revilla, S.A.; Milón Guzmán, J.J.; Navarrete Cipriano, K.; Braga, S.L. Influence of dust deposition, wind and rain on photovoltaic panels efficiency in Arequipa–Peru. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2022, 41, 1369–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadat, S.A.; Faraji, J.; Nazififard, M.; Ketabi, A. The experimental analysis of dust deposition effect on solar photovoltaic panels in Iran’s desert environment. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2021, 47, 101542. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, Z.A.; Sopian, K.; Fudholi, A. Reduced output of photovoltaic modules due to different types of dust particles. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 280, 124317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazem, H.A.; Chaichan, M.T.; Al-Waeli, A.H.; Sopian, K. A novel model and experimental validation of dust impact on grid-connected photovoltaic system performance in Northern Oman. Sol. Energy 2020, 206, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanchangi, Y.N.; Ghosh, A.; Sundaram, S.; Mallick, T.K. An analytical indoor experimental study on the effect of soiling on PV, focusing on dust properties and PV surface material. Sol. Energy 2020, 203, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, D.P.; Parida, S.; Khandu, L. Safety risk assessment and risk prediction in underground coal mines using machine learning techniques. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. D 2021, 102, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, L.; Shukla, T.; Huang, X.; Ussery, D.W.; Wang, S. Machine learning methods in drug discovery. Molecules 2020, 25, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Aruna, M.; Murthy, C.S. Output power enhancement of solar PV panel using solar tracking system. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. (Former. Recent Pat. Electr. Electron. Eng.) 2019, 12, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Dash, P. Short term wind power forecasting using Chebyshev polynomial trained by ridge extreme learning machine. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Power, Communication and Information Technology Conference (PCITC), Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India, 15–17 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Netsanet, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, D.; Agrawal, R.K.; Muchahary, F. An aggregative machine learning approach for output power prediction of wind turbines. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Texas Power and Energy Conference (TPEC), College Station, TX, USA, 8–9 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zazoum, B. Solar photovoltaic power prediction using different machine learning methods. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, I.; Pandey, D.S. Incorporating uncertainty in data driven regression models of fluidized bed gasification: A Bayesian approach. Fuel Process. Technol. 2016, 142, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devi, Y.S.S.; Prasad, T.K.D.; Saladi, K.; Nandan, D. Analysis of precision agriculture technique by using machine learning and IoT. In Soft Computing: Theories and Applications; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 859–867. [Google Scholar]
- Gershman, S.J.; Blei, D.M. A tutorial on Bayesian nonparametric models. J. Math. Psychol. 2012, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui, R.; Bajpai, U. Correlation between thicknesses of dust collected on photovoltaic module and difference in efficiencies in composite climate. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2012, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darlington, R.B.; Hayes, A.F. Regression Analysis and Linear Models: Concepts, Applications, and Implementation; Guilford Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 603–611. [Google Scholar]
- Topp, R.; Gómez, G. Residual analysis in linear regression models with an interval-censored covariate. Stat. Med. 2004, 23, 3377–3391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hasan, A.Y. A new correlation for direct beam solar Irradiance received by photovoltaic panel with sand dust accumulated on its surface. Sol. Energy 1998, 63, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakubu, M.; Yilbas, B.S.; Abubakr, A.A.; Al-Qahtani, H. Droplet rolling and spinning in V-shaped hydrophobic surfaces for environmental dust mitigation. Molecules 2020, 25, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adıgüzel, E.; Özer, E.; Akgündoğdu, A.; YıLMAZ, A.E. Prediction of dust particle size effect on the efficiency of photovoltaic modules with ANFIS: An experimental study in Aegean region, Turkey. Sol. Energy 2019, 177, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazem, H.A.; Chaichan, M.T. Experimental analysis of the effect of dust’s physical properties on photovoltaic modules in Northern Oman. Sol. Energy 2016, 139, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhao, W. Effects of particle sizes and tilt angles on dust deposition characteristics of a ground-mounted solar photovoltaic system. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanesab, J.; Parlevliet, D.; Whale, J.; Urmee, T. The effect of dust with different morphologies on the performance degradation of photovoltaic modules. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2019, 31, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Nature of Study | Work | Measure Parameter | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outdoor | Effect of dust discoloration on PV panel material | Glass Transmittance | 15% degradation | [20] |
| Indoor | Effect of various types of dust deposition on mono and poly PV panel performance | Output power | Mono—12% degradation Poly—5% degradation For Ash deposition | [21] |
| Indoor | Type of dust impact on PV panel performance | Efficacy | Dust degrades the panel efficacy | [22] |
| Outdoor | Effect of desert dust on PV panels | Output power | 98.13% reduction | [23] |
| Indoor | Investigation of PV efficacy under the deposition of different types of dust pollutants | Power | 99.76% Performance reduction due to carbon dust | [24] |
| Outdoor | Proposed a model to encounter the impact of dust on grid-connected PV system | Inverter efficacy (IE) and performance efficacy (PE) | 94% IE 73% PE | [25] |
| Indoor | Study the impact of coal dust | Output power | 62.05% degradation | [26] |
| Sl. No. | Particle Size Range | Symbolic Representation | Designated As |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 600 µ to 850 µ | T1 | Larger size |
| 2 | 300 µ to 600 µ | T2 | Moderate larger size |
| 3 | 150 µ to 300 µ | T3 | Medium size |
| 4 | 75 µ to 150 µ | T4 | Moderate medium size |
| 5 | less than 75 µ | T5 | Smaller size |
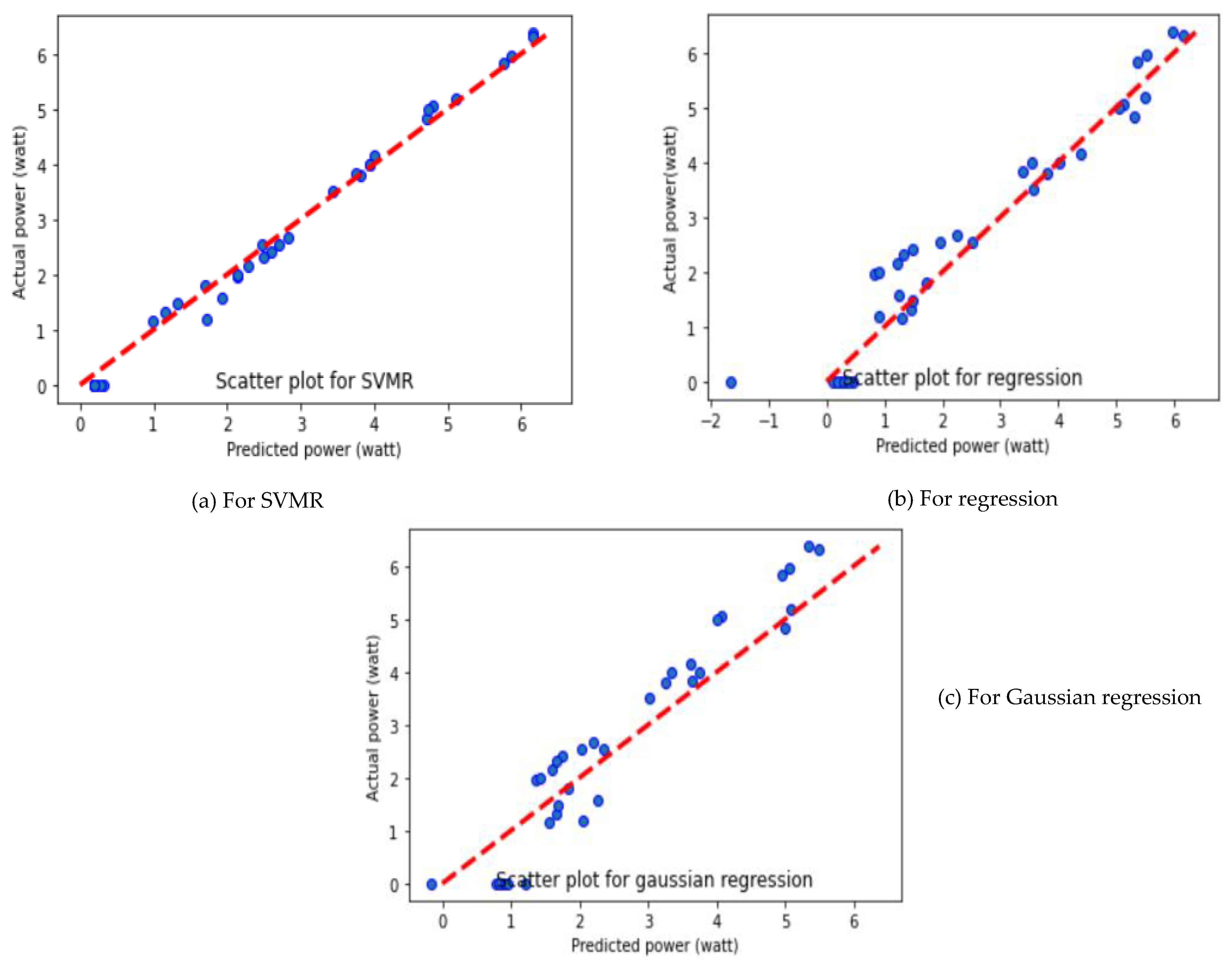
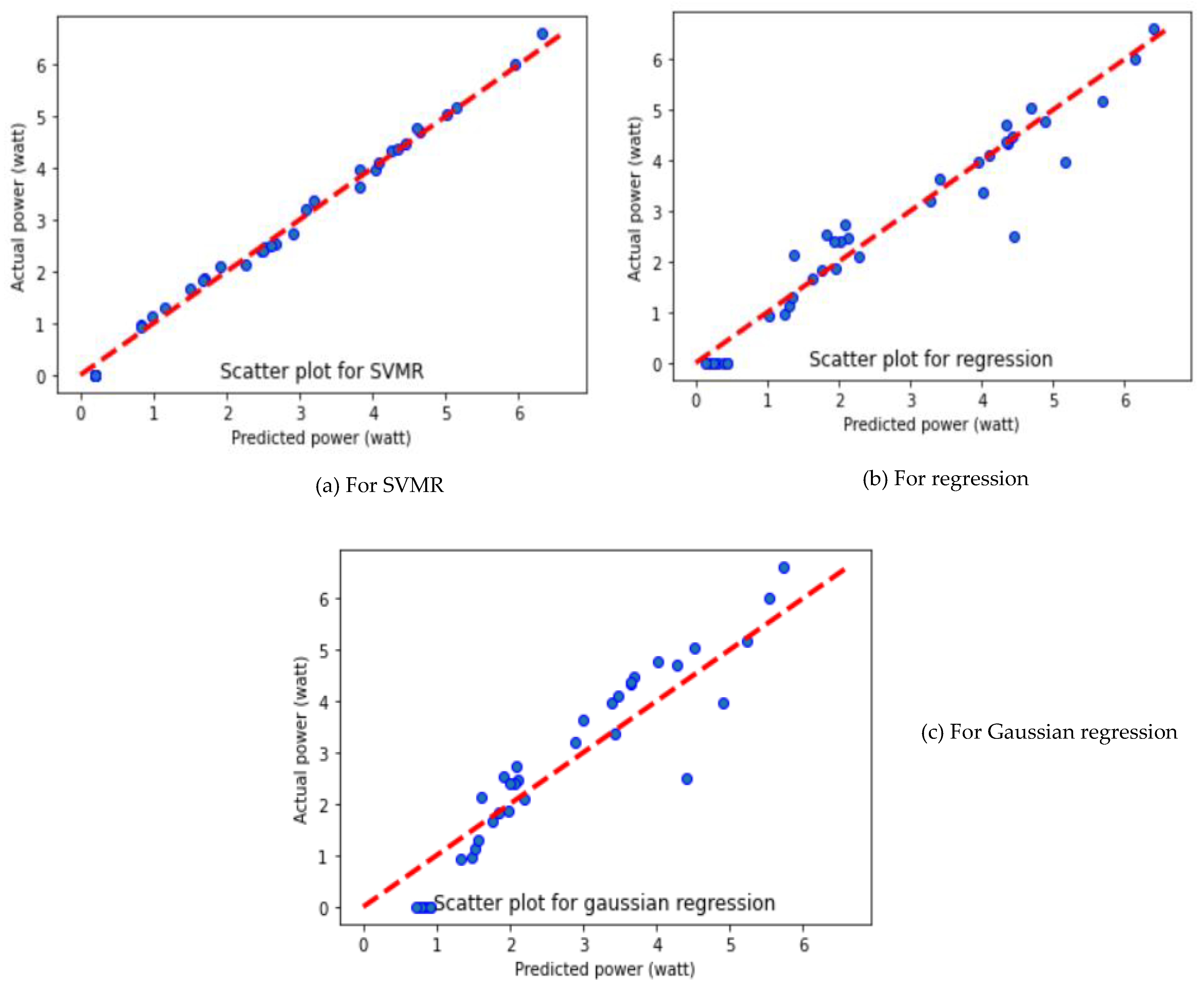
| Algorithms | Performance Parameters | Fold-1 | Fold-2 | Fold-3 | Average Value of Performance Parameters |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVMR | MAE | 0.1708 | 0.1708 | 0.1351 | 0.1589 |
| MSE | 0.0381 | 0.0381 | 0.0224 | 0.0328 | |
| R2 | 0.9910 | 0.9910 | 0.9937 | 0.9919 | |
| MLR | MAE | 0.3926 | 0.3926 | 0.3256 | 0.3702 |
| MSE | 0.2833 | 0.2833 | 0.2377 | 0.2681 | |
| R2 | 0.9334 | 0.9334 | 0.9334 | 0.9334 | |
| GR | MAE | 0.6301 | 0.6301 | 0.5773 | 0.6125 |
| MSE | 0.4906 | 0.4906 | 0.4523 | 0.4778 | |
| R2 | 0.8847 | 0.8847 | 0.8732 | 0.8808 |
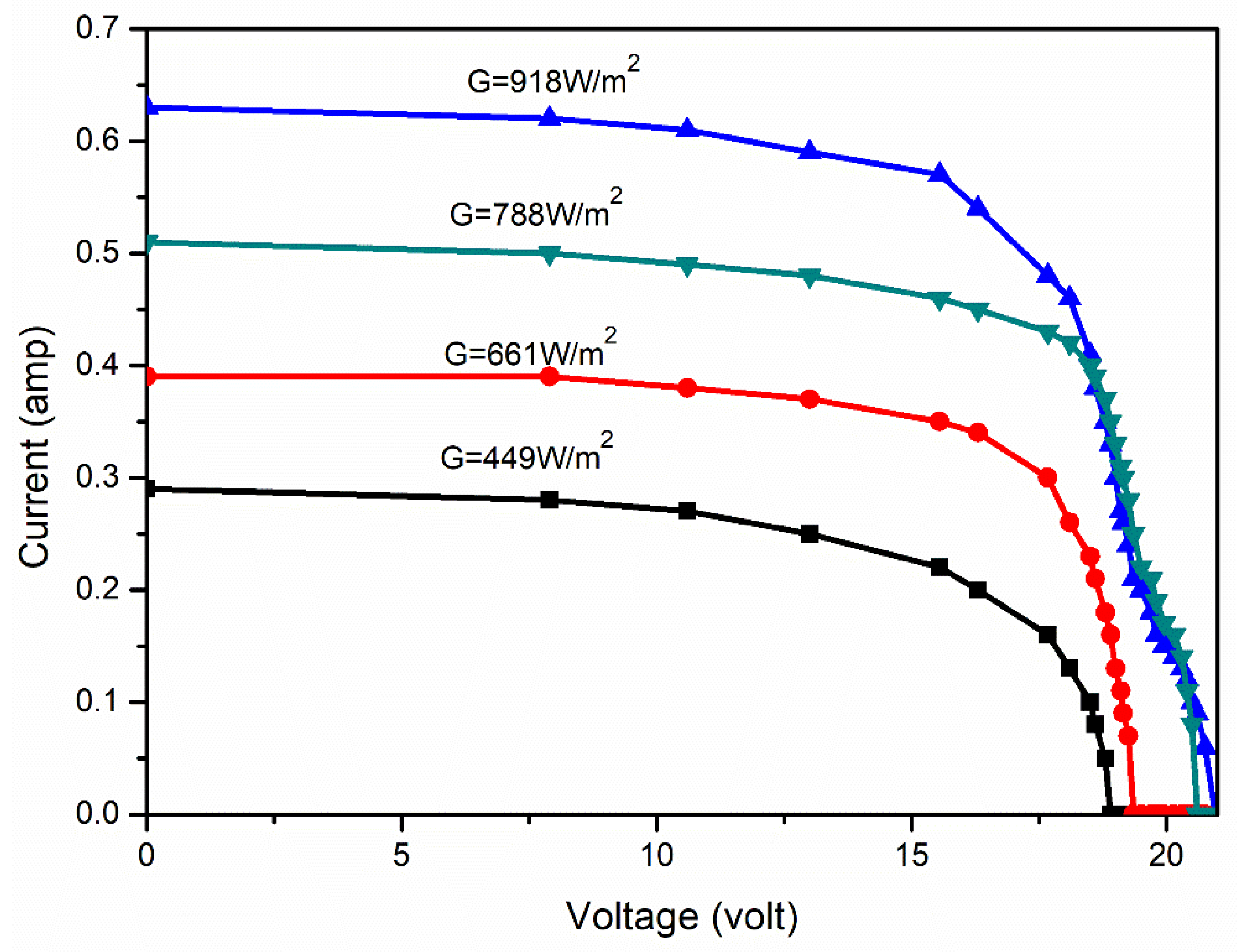
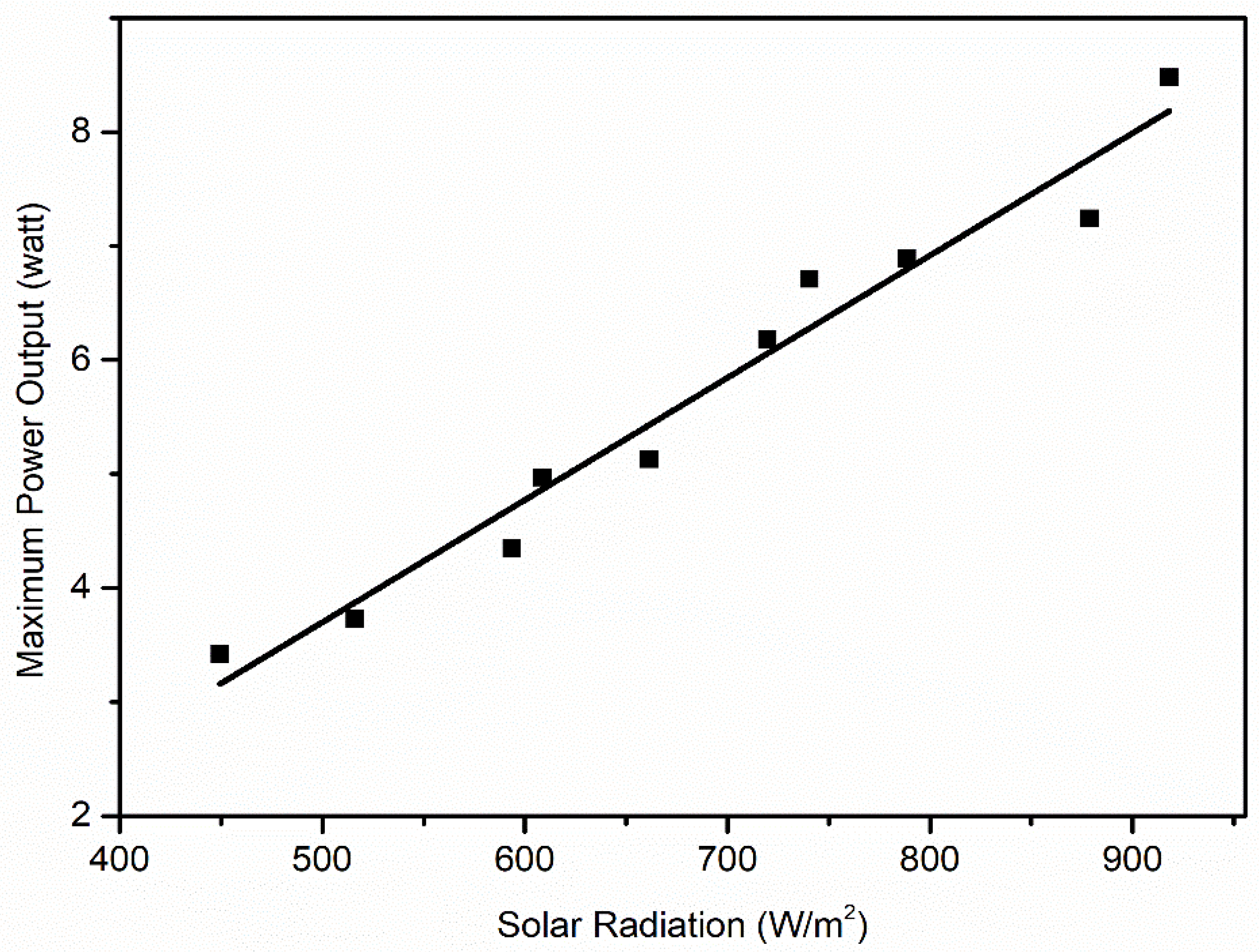
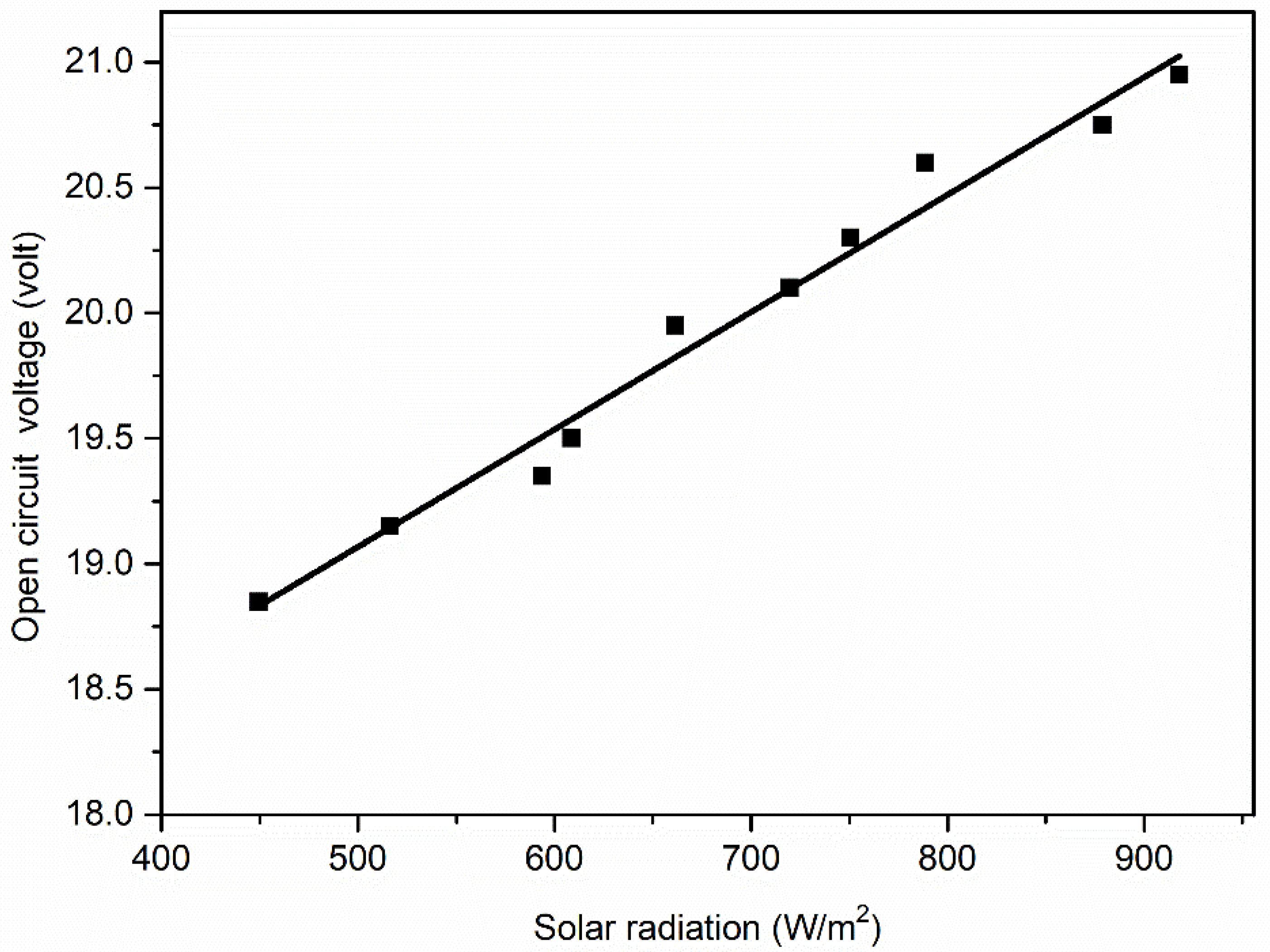
| Solar Irradiance (W/m2) | Maximum Power Output (W) | Short-Circuit Current (A) | Open-Circuit Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 449.58 | 3.42 | 0.27 | 18.85 |
| 516.22 | 3.73 | 0.31 | 19.15 |
| 593.70 | 4.35 | 0.35 | 19.35 |
| 608.63 | 4.97 | 0.37 | 19.50 |
| 661.49 | 5.13 | 0.39 | 19.95 |
| 719.60 | 6.18 | 0.44 | 20.10 |
| 750.50 | 6.71 | 0.48 | 20.30 |
| 788.49 | 6.89 | 0.49 | 20.60 |
| 878.67 | 7.24 | 0.54 | 20.75 |
| 918.10 | 8.48 | 0.63 | 20.95 |
| Solar Irradiance (G) | Short-Circuit Current (ISC) | G2 | ISC × G |
|---|---|---|---|
| 449.58 | 0.27 | 202,122.20 | 160.03 |
| 516.22 | 0.31 | 266,483.10 | 207.80 |
| 593.70 | 0.35 | 352,479.70 | 225.19 |
| 608.63 | 0.37 | 370,430.50 | 257.98 |
| 661.49 | 0.39 | 437,569.00 | 386.36 |
| 719.60 | 0.44 | 517,824.20 | 474.48 |
| 750.00 | 0.48 | 548,147.70 | 325.76 |
| 788.49 | 0.49 | 621,716.50 | 121.39 |
| 878.67 | 0.54 | 772,061.00 | 345.41 |
| 918.10 | 0.63 | 842,907.60 | 578.40 |
| ∑G = 6884.48 | ∑ISC = 4.27 | ∑G2 = 493,1742 | ∑ISC × G = 3082.8 |
| Sl. No | Parameter | Values |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Coefficient of determination | 0.96124 |
| 2 | Standard error | 0.0230 |
| 4 | Standard deviation of residual | 0.0217 |
| Observation | Observed Value | Predicted Value | Residuals (Observed Value-Predicted Value) | Standard Residuals (Residual/Standard Deviationof the Residual) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.27 | 0.256448069 | 0.013551931 | 0.623200484 |
| 2 | 0.31 | 0.304221679 | 0.005778321 | 0.265722458 |
| 3 | 0.35 | 0.359766386 | −0.009766386 | −0.449118053 |
| 4 | 0.37 | 0.370469568 | −0.000469568 | −0.021593587 |
| 5 | 0.39 | 0.408364421 | −0.018364421 | −0.84450815 |
| 6 | 0.44 | 0.464912776 | −0.024912776 | −1.145641458 |
| 7 | 0.48 | 0.450022951 | 0.029977049 | 1.378527641 |
| 8 | 0.49 | 0.499409566 | −0.009409566 | −0.432709265 |
| 9 | 0.54 | 0.564058788 | −0.024058788 | −1.106369887 |
| 10 | 0.63 | 0.592325796 | 0.037674204 | 1.732489817 |
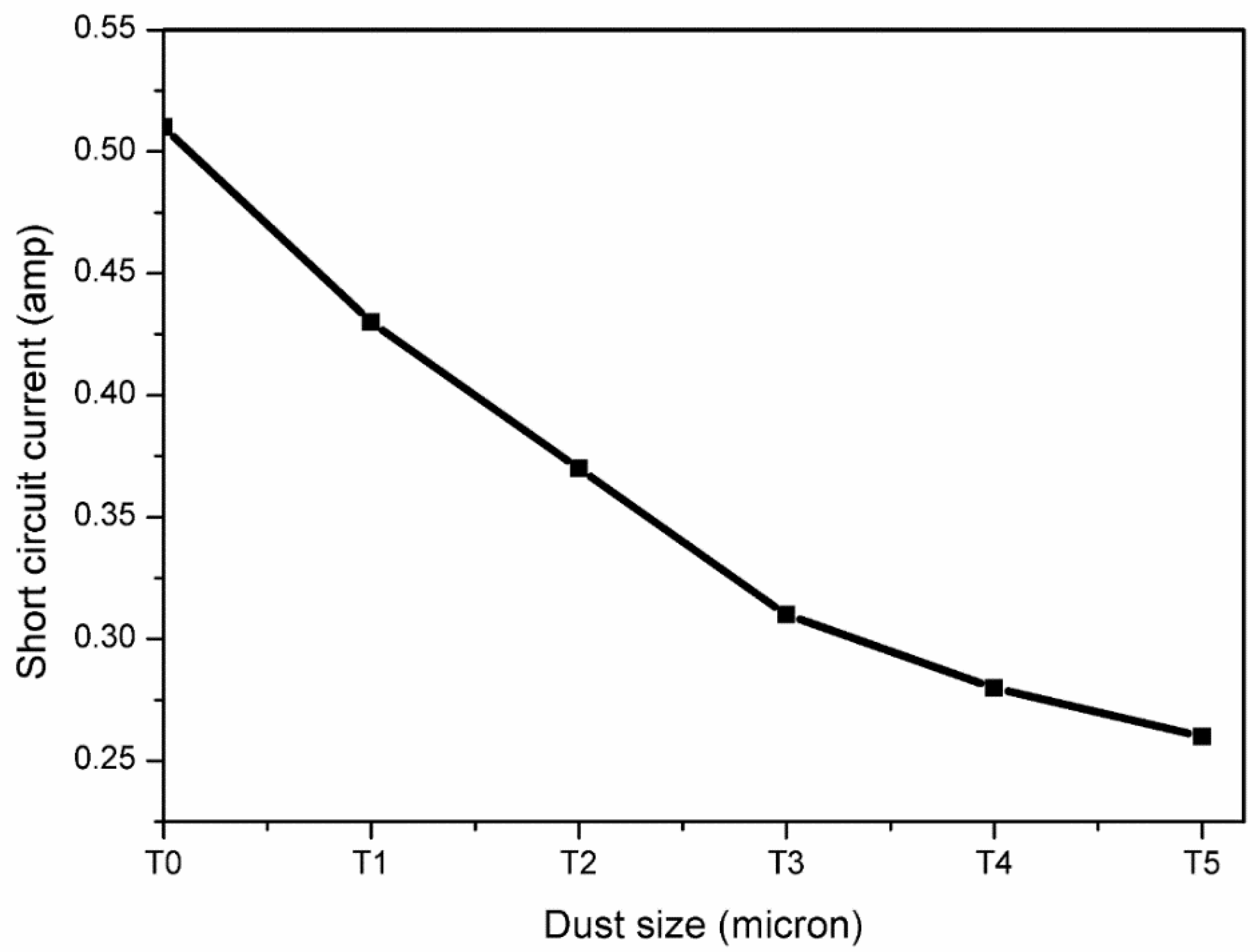
| Dust Particle Size (micron) | Short-Circuit Current (amp) | Reduction in Short-Circuit Current (%) |
|---|---|---|
| T0 | 0.50 | NA |
| T1 | 0.43 | 15.68 |
| T2 | 0.37 | 27.45 |
| T3 | 0.31 | 39.21 |
| T4 | 0.28 | 45.09 |
| T5 | 0.26 | 49.01 |
| Pollutant Size (µ) | Simulated Solar Irradiance GS (W/m2) | Reduction in Solar Irradiance RSI (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 600–850 µ | 702.85 | 12.14 |
| 300–600 µ | 617.14 | 22.85 |
| 150–300 µ | 531.43 | 33.57 |
| 75–150 µ | 488.57 | 38.92 |
| Less than 75 µ | 460.00 | 42.50 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tripathi, A.K.; Aruna, M.; Venkatesan, E.P.; Abbas, M.; Afzal, A.; Shaik, S.; Linul, E. Quantitative Analysis of Solar Photovoltaic Panel Performance with Size-Varied Dust Pollutants Deposition Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Molecules 2022, 27, 7853. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227853
Tripathi AK, Aruna M, Venkatesan EP, Abbas M, Afzal A, Shaik S, Linul E. Quantitative Analysis of Solar Photovoltaic Panel Performance with Size-Varied Dust Pollutants Deposition Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Molecules. 2022; 27(22):7853. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227853
Chicago/Turabian StyleTripathi, Abhishek Kumar, Mangalpady Aruna, Elumalai Perumal Venkatesan, Mohamed Abbas, Asif Afzal, Saboor Shaik, and Emanoil Linul. 2022. "Quantitative Analysis of Solar Photovoltaic Panel Performance with Size-Varied Dust Pollutants Deposition Using Different Machine Learning Approaches" Molecules 27, no. 22: 7853. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227853
APA StyleTripathi, A. K., Aruna, M., Venkatesan, E. P., Abbas, M., Afzal, A., Shaik, S., & Linul, E. (2022). Quantitative Analysis of Solar Photovoltaic Panel Performance with Size-Varied Dust Pollutants Deposition Using Different Machine Learning Approaches. Molecules, 27(22), 7853. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27227853









