Biotechnological Innovations from Ocean: Transpiring Role of Marine Drugs in Management of Chronic Disorders
Abstract
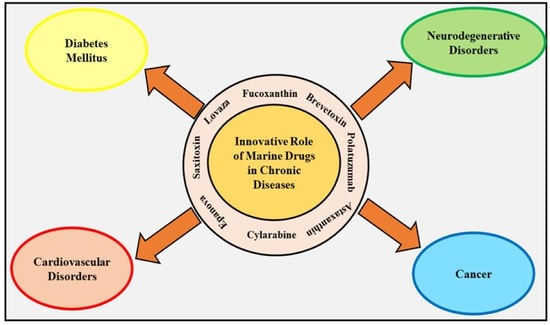
:1. Introduction
2. Identification and Isolation of Bioactive Compound from Marine Natural Extract
3. Marine Drugs in the Management of Cancer
3.1. Cytarabine (Cytosar)
3.2. Trabectedin
3.3. Eribulin Mesylate
3.4. Brentuximab Vedotin
4. Marine Drugs in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus
5. Marine Natural Products and Cardiovascular Diseases
5.1. Fucoxanthin
5.2. Saponins
5.3. Astaxanthin
5.4. Xyloketal B
6. Marine Drugs in Neurodegeneration
6.1. Fucoidan
6.2. Seaweeds
6.3. Cerebrosides
7. Future Prospects of Marine Drugs and Drug Candidates Obtained from the Ocean
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiménez, C. Marine Natural Productsin Medicinal Chemistry. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Productsas Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patridge, E.; Gareiss, P.; Kinch, M.S.; Hoyer, D. An Analysis of FDA-Approved Drugs: Natural Products and Their Derivatives. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Sarkar, T.; Pati, S.; Kari, Z.A.; Edinur, H.A.; Chakraborty, R. Novel Bioactive Compounds From Marine Sourcesas a Tool for Functional Food Development. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 76, 832957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Hu, W.P.; Munro, M.H.G.; Northcote, P.T.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 170–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Drugs and Drug Candidates from Marine Sources: An Assessment of the Current “StateofPlay”. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glevitzky, I.; Dumitrel, G.A.; Glevitzky, M.; Pasca, B.; Otrisal, P.; Bungau, S.; Cioca, G.; Pantis, C.; Popa, M. Statistical Analysis of the Relationship between Antioxidant Activity and the Structure of Flavonoid Compounds. Rev. De Chim. 2019, 70, 3103–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, K.H. Drugs from the Oceans: Marine Natural Products as Leads for Drug Discovery. Chimia 2017, 71, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Costantini, M.; Sansone, C.; Lauritano, C.; Ruocco, N.; Ianora, A. Marine Microorganisms as a Promising and Sustainable Source of Bioactive Molecules. Mar. Environ. Res. 2017, 128, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, K.; Abbas, S.Q.; Shah, S.A.A.; Akhter, N.; Batool, S.; Hassan, S.S.U. Marine Sponges as a Drug Treasure. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moumbock, A.F.A.; Li, J.; Mishra, P.; Gao, M.; Günther, S. Current Computational Methods for Predicting Protein Interactions of Natural Products. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moumbock, A.F.A.; Simoben, C.V.; Wessjohann, L.; Sippl, W.; Günther, S.; Ntie-Kang, F. Computational studies and biosynthesis of natural products with promising anticancer properties. In Natural Products and Cancer Drug Discovery; InTech Open: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tirumala, M.G.; Anchi, P.; Raja, S.; Rachamalla, M.; Godugu, C. Novel Methods and Approaches for Safety Evaluation of Nanoparticle Formulations: A Focus towards in Vitro Models and Adverse Outcome Pathways (AOP). Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, C.T.; Fischbach, M.A. Natural Products Version 2.0: Connecting Genes to Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2469–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grover, M.; Behl, T.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Virmani, T.; Rachamalla, M.; Farasani, A.; Chigurupati, S.; Alsubayiel, A.; et al. In Vitro Phytochemical Screening, Cytotoxicity Studies of Curcuma Longa Extracts with Isolation and Characterisation of Their Isolated Compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puppala, E.R.; Jain, S.; Saha, P.; Rachamalla, M.; Syamprasad, N.P.; Yalamarthi, S.S.; Abubakar, M.; Chaudhary, A.; Chamundeswari, D.; Murty, U.S.N.; et al. Perillyl Alcohol Attenuates Rheumatoid Arthritis via Regulating TLR4/NF-Κ Band Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways: A Comprehensive Study On in-Vitro and in-Vivo Experimental Models. Phytomedicine 2022, 97, 153926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug Development from Marine Natural Products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinarvand, M.; Spain, M. Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Marine Natural Products and Exploration of Structure—Activity Relationships (Sar). Antibiotics 2021, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, F.; Aires-de-Sousa, J. Computational Methodologies in the Exploration of Marine Natural Product Leads. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Masi, J.A.; Grabowski, H.G.; Hansen, R.W. Innovation in the Pharmaceutical Industry: New Estimates of R&D Costs. J. Health Econ. 2016, 47, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nantasenamat, C.; Prachayasittikul, V. Maximizing Computational Tools for Successful Drug Discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasteiger, J. Chemoinformatics: Achievements and Challenges, a Personal View. Molecules 2016, 21, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, R.; Dawson, E.S.; Meiler, J.; Rodriguez, A.L.; Chauder, B.A.; Bates, B.S.; Felts, A.S.; Lamb, J.P.; Menon, U.N.; Jadhav, S.B.; et al. Discovery of (2-(2-Benzoxazoyl Amino)-4-Aryl-5-Cyanopyrimidine MGlu 5NAMs: From Artificial Neural Network Virtual Screen to in Vivo Tool Compound. Chem. Med. Chem 2012, 7, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leelananda, S.P.; Lindert, S. Computational Methods in Drug Discovery. BeilsteinJ. Org. Chem. 2016, 12, 2694–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katsila, T.; Spyroulias, G.A.; Patrinos, G.P.; Matsoukas, M.T. Computational Approaches in Target Identification and Drug Discovery. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, A.L.; Grier, M.D.; Jones, C.K.; Herman, E.J.; Kane, A.S.; Smith, R.L.; Williams, R.; Zhou, Y.; Marlo, J.E.; Days, E.L.; et al. Discovery of Novel Allosteric Modulators of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype5 Reveals Chemical and Functional Diversity and in Vivo Activity in Rat Behavioral Models of Anxiolytic and Antipsychotic Activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 2010, 78, 1105–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudêncio, S.P.; Pereira, F. Dereplication: Racing to Speed up the Natural Products Discovery Process. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 779–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Victoria, I.; Martín, J.; Reyes, F. Combined LC/UV/MS and NMR Strategies for the Dereplication of Marine Natural Products. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijayakrishnan, R. Structure-Based Drug Design and Modern Medicine. J. Postgrad. Med. 2009, 55, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talele, T.; Khedkar, S.; Rigby, A. Successful Applications of Computer Aided Drug Discovery: Moving Drugs from Concept to the Clinic. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.A.; Baylin, S.B. The Epigenomics of Cancer. Cell 2007, 128, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauthe, S.K.; Mahajan, S.; Rachamalla, M.; Tikoo, K.; Singh, I.P. Synthesis and Evaluation of Linear Furanocoumarinsas Potential Anti-Breast and Anti-Prostate Cancer Agents. Med. Chem. Res. 2015, 24, 2476–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varun, K.; Mahesh, R.; Prajwal, N.L.; Khatik, G.T.; Sangamwar, A.; Kulbhushan, T.A.; Nair, V. Design and Synthesis of Optically Pure3-Aryl-6-Methyl-2-Thioxotetrahydropyrimidin-4(1H)-Ones as Anti-ProstateCancerAgents. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 37868–37877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujambio, A.; Lowe, S.W. The Microcosmos of Cancer. Nature 2012, 482, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchet, B.P.; Galmarini, C.M. Cabazitaxel, a New Taxane with Favorable Properties. Drugs Today 2010, 46, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.; Peixe, L.; Gomes, N.C.M.; Calado, R. Cnidarians as a Source of New Marine Bioactive Compounds An Overview of the Last Decade and Future Steps for Bioprospecting. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1860–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Marine microorganisms and drug discovery: Current status and future potential. In Drugs from the Sea; Karger: Basel, Switzerland, 2000; pp. 6–29. [Google Scholar]
- Dayanidhi, D.L.; Thomas, B.C.; Osterberg, J.S.; Vuong, M.; Vargas, G.; Kwartler, S.K.; Schmaltz, E.; Dunphy-Daly, M.M.; Schultz, T.F.; Rittschof, D.; et al. Exploring the Diversity of the Marine Environment for New Anti-Cancer Compounds. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 7, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, A.F.U.H.; Su, J.; Ouyang, S. Marine-Derived Drugs: Recent Advances in Cancer Therapy and Immune Signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.S.; Rachamalla, M.; Chary, N.R.; Shera, F.Y.; Tikoo, K.; Jena, G. Cytarabine Induced Cerebellar Neuronal Damage in Juvenile Rat: Correlating Neurobehavioral Performance with Cellular and Genetic Alterations. Toxicology 2012, 293, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Honecker, F. Marine Compounds and Cancer: The First Two Decades of XXI Century. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Honecker, F. Marine Compounds and Cancer: Updates 2020. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, P.C.; Wilke, D.V.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Marine Drugs for Cancer: Surfacing Biotechnological Innovations from the Oceans. Clinics 2018, 73, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Donk, N.W.C.J.; Dhimolea, E. Brentuximab Vedotin. mAbs 2012, 4, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newsholme, P.; Cruzat, V.F.; Keane, K.N.; Carlessi, R.; de Bittencourt, P.I.H. Molecular Mechanisms of ROS Production and Oxidative Stress in Diabetes. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 4527–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barde, S.R.; Sakhare, R.S.; Kanthale, S.B.; Chandak, P.G.; Jamkhande, P.G. Marine Bioactive Agents: A Short Review on New Marine Antidiabetic Compounds. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 5, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skyler, J.S. Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 4113–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lordan, S.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Marine Bioactives as Functional Food Ingredients: Potential to Reduce the Incidence of Chronic Diseases. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1056–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imada, C. Enzyme Inhibitors and Other Bioactive Compounds from Marine Actinomycetes. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2005, 87, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbab, A.; Aly, A.H.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Bacteria and Fungi: Mini review. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 544–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carotenuto, Y.; Esposito, F.; Pisano, F.; Lauritano, C.; Perna, M.; Miralto, A.; Ianora, A. Multi-Generation Cultivation of the Copepod Calanus Helgolandicusina Re-Circulating System. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2012, 418, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianora, A.; Miralto, A.; Poulet, S.A.; Carotenuto, Y.; Buttino, I.; Romano, G.; Casotti, R.; Pohnert, G.; Wichard, T.; Colucci-D’Amato, L.; et al. Aldehyde Suppression of Copepod Recruitmentin Blooms of a Ubiquitous Planktonic Diatom. Nature 2004, 429, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Peng, X.; Liu, J.; Fan, K.W.; Wang, M.; Chen, F. Inhibitory Effects of Microalgal Extracts on the Formation of Advanced Glycation Endproducts (AGEs). Food Chem. 2010, 120, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.; Huangfu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, F. Astaxanthin Is Responsible for Antiglycoxidative Properties of Microalga Chlorella zofingiensis. Food Chem. 2011, 126, 1629–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Zeng, X.; Huangfu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, F. Protective Actions of Microalgae against Endogenous and Exogenous Advanced Glycation Endproducts (AGEs) in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. Food Funct. 2011, 2, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifuddin, Y.; Chin, Y.X.; Lim, P.E.; Phang, S.M. Potential Bioactive Compounds from Seaweed for Diabetes Management. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5447–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, D.; Guo, S.; Jiang, B.; Guo, C.; Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, J. HPN, a Synthetic Analogue of Bromophenol from Red Alga Rhodomela Confervoides: Synthesis and Anti-Diabetic Effects in C57BL/KsJ-Db/Db Mice. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaziano, T.; Reddy, K.S.; Paccaud, F.; Horton, S.; Chaturvedi, V. Cardiovascular Disease. Dis. Control. Priorities Dev. Ctries. 2006, 2, 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Cao, Q.; Xing, M.; Xiao, H.; Cheng, Z.; Song, S.; Ji, A. Advances in the Study of Marine Products with Lipid-Lowering Properties. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Cai, X.-Y.; Gu, N. Marine Natural Products and Coronary Artery Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 739932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xing, M.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liang, H.; Ji, A.; Song, S. Current Research Landscape of Marine-Derived Anti-Atherosclerotic Substances. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kondo, K. Potential Anti-Atherosclerotic Properties of Astaxanthin. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.L.; Qian, Y.; Meng, W.F.; Pang, J.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Guan, Y.Y.; Chen, S.P.; Liu, J.; Pei, Z.; Wang, G.L. A Novel Marine Compound Xyloketal B Protects against Oxidized LDL-Induced Cell Injury in Vitro. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, M.; Rachamalla, M.; Niyogi, S.; Datusalia, A.K.; Flora, S.J.S. Molecular Mechanism of Arsenic-Induced Neurotoxicity Including Neuronal Dysfunctions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, G. Promise from the Sea. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhardwaj, S.; Kesari, K.K.; Rachamalla, M.; Mani, S.; Ashraf, G.M.; Jha, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Ambasta, R.K.; Dureja, H.; Devkota, H.P.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing: New Hope for Alzheimer’s Disease Therapeutics. J. Adv. Res. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehni, A.K.; Singh, N.; Rachamalla, M.; Tikoo, K. Modulation of Histone Deacetylase AttenuatesNaloxone-Precipitated Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, D.; Castro, A.; Martinez, A. Marine Compounds for the Therapeutic Treatment of Neurological Disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2005, 15, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, C.; Valentão, P.; Ferreres, F.; Andrade, P.B. Review: Bioactive Marine Drugs and Marine Biomaterials for Brain Diseases. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Catanesi, M.; Caioni, G.; Castelli, V.; Benedetti, E.; d’Angelo, M.; Cimini, A. Benefits under the Sea: The Role of Marine Compounds in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olasehinde, T.A.; Olaniran, A.O.; Okoh, A.I. Sulfated Polysaccharides of Some Seaweeds Exhibit Neuroprotection via Mitigation of Oxidative Stress, Cholinergic Dysfunction and Inhibition of Zn-Induced Neuronal Damage in HT-22 Cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2020, 20, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Cui, Y.; Sun, Z.; Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Jia, J.; Yu, F.; Wang, X.; et al. Fucoidan Protects against Dopaminergic Neuron Death in Vivo and in Vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 617, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Dash, R.; Haque, M.N.; Mohibbullah, M.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Uddin, M.J.; Alam, M.; Moon, I.S. Neuroprotective Potentials of Marine Algae and Their Bioactive Metabolites: Pharmacological Insights and Therapeutic Advances. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celikler, S.; Vatan, O.; Yildiz, G.; Bilaloglu, R. Evaluation of Anti-Oxidative, Genotoxic and Antigenotoxic Potency of Codium Tomentosum Stackhouse Ethanolic Extract in Human Lymphocytes in Vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2009, 47, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Possede Chaves, E.; Sipione, S. Sphingolipids and Gangliosides of the Nervous System in Membrane Function and Dysfunction. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1748–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, R.; Kanie, Y.; Kanie, O.; Shimizu, Y. A Unique Structural Distribution Pattern Discovered for the Cerebrosides from Starfish Asterias Amurensis. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 473, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, J.; Rodriguez, L.P.; Blanco, L.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Tetrodotoxin, an Extremely Potent Marine Neurotoxin: Distribution, Toxicity, Origin and Therapeutical Uses. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6384–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bane, V.; Lehane, M.; Dikshit, M.; O’Riordan, A.; Furey, A. Tetrodotoxin: Chemistry, Toxicity, Source, Distribution and Detection. Toxins 2014, 6, 693–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nieto, F.R.; Cobos, E.J.; Tejada, M.Á.; Sánchez-Fernández, C.; González-Cano, R.; Cendán, C.M. Tetrodotoxin (TTX) as a Therapeutic Agent for Pain. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 281–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoh, K.; Kohno, S.; Asari, T.; Harada, T.; Katada, J.; Muramatsu, M.; Kawashima, H.; Sekiya, H.; Uno, I. (−)-Phenylahistin: A New Mammalian Cell Cycle Inhibitor Produced by Aspergillus ustus. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 1997, 7, 2847–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.G.M.; Lefranc, F.; Kijjoa, A.; Kiss, R. Can Some Marine-Derived Fungal Metabolites Become Actual Anticancer Agents? Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3950–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Rachamalla, M.; Najda, A.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Sharma, N.; Bhatia, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Chigurupati, S.; Vargas-De-La-Cruz, C.; et al. Applications of Adductomics in Chemically Induced Adverse Outcomes and Major Emphasis on DNA Adductomics: A Pathbreaking Tool in Biomedical Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, B.; Lloyd, G.K.; Miller, B.R.; Palladino, M.A.; Kiso, Y.; Hayashi, Y.; Neuteboom, S.T.C. NPI-2358 Is a Tubulin-Depolymerizing Agent: In-Vitro Evidence for Activity as a Tumor Vascular-Disrupting Agent. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2006, 17, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.V.; Bandi, M.; Raje, N.; Richardson, P.; Palladino, M.A.; Chauhan, D.; Anderson, K.C. A Novel Vascular Disrupting Agent Plinabulin Triggers JNK-Mediated Apoptosis and Inhibits Angiogenesisin Multiple Myeloma Cells. Blood 2011, 117, 5692–5700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feling, R.H.; Buchanan, G.O.; Mincer, T.J.; Kauffman, C.A.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Salinosporamide A: A Highly Cytotoxic Proteasome Inhibitor from a Novel Microbial Source, a Marine Bacterium of the New Genus Salinospora. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulder, T.A.M.; Moore, B.S. Salinosporamide Natural Products: Potent 20S Proteasome Inhibitors as Promising Cancer Chemotherapeutics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9346–9367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Mohan, R.; Kwok, B.H.B.; Elofsson, M.; Sin, N.; Crews, C.M. Epoxomicin, a Potent and Selective Proteasome Inhibitor, Exhibits in Vivo Antiinflammatory Activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10403–10408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauhan, D.; Catley, L.; Li, G.; Podar, K.; Hideshima, T.; Velankar, M.; Mitsiades, C.; Mitsiades, N.; Yasui, H.; Letai, A.; et al. A Novel Orally Active Proteasome Inhibitor Induces Apoptosis in Multiple Myeloma Cells with Mechanisms Distinct from Bortezomib. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richardson, P.G.; Spencer, A.; Cannell, P.; Harrison, S.J.; Catley, L.; Underhill, C.; Zimmerman, T.M.; Hofmeister, C.C.; Jakubowiak, A.J.; Laubach, J.P.; et al. Phase 1 Clinical Evaluation of Twice-Weekly Marizomib (NPI-0052), a Novel Proteasome Inhibitor, in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma (MM). Blood 2011, 118, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.J. Sponging off Nature for New Drug Leads. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 13, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Salvador, L.A.; Byeon, S.; Ying, Y.; Kwan, J.C.; Law, B.K.; Hong, J.; Luesch, H. Anticolon Cancer Activity of Largazole, a Marine-Derived Tunable Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010, 335, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, Y.; Taori, K.; Kim, H.; Hong, J.; Luesch, H. Total Synthesis and Molecular Target of Largazole, a Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8455–8459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Luesch, H. Largazole: From Discovery to Broad-Spectrum Therapy. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Engene, N.; Tronholm, A.; Salvador-Reyes, L.A.; Luesch, H.; Paul, V.J. Caldora Penicillata Gen. Nov., Comb. Nov. (Cyanobacteria), a Pantropical Marine Species with Biomedical Relevance. J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salvador-Reyes, L.A.; Engene, N.; Paul, V.J.; Luesch, H. Targeted Natural Products Discovery from Marine Cyanobacteria Using Combined Phylogenetic and Mass Spectrometric Evaluation. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.Y.; Chaturvedi, P.R.; Luesch, H. Process Development and Scale-up Total Synthesis of Largazole, a Potent Classi Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybdal-Hargreaves, N.F.; Risinger, A.L.; Mooberry, S.L. Eribulin Mesylate: Mechanism of Action of a Unique Microtubule Targeting Agent. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Name | Structure |
|---|---|
| Cytarabine |  |
| Trabectedin |  |
| Eribulin Mesylate |  |
| Brentuximab vedotin |  |
| Name | Structure |
|---|---|
| Pyrostatins A and B |  |
| N-carboxymethyllysine |  |
| Pentosidine |  |
| neoxanthin |  |
| antheraxanthin |  |
| violaxanthin |  |
| Lutein |  |
| Name | Structure |
|---|---|
| Fucoxanthin |  |
| adiponectin |  |
| Astaxanthin |  |
| Xyloketal B |  |
| Name | Structure |
|---|---|
| Fucoidan |  |
| Phlorotannins |  |
| Cerebrosides |  |
| Name of the Compound | Source | Scientific Name | Uses | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ziconotide | Cone snails | Conidae | Management of spinal cord injury-mediated chronic pain | [4] |
| Hemiasterlin, discodermolide | Marine sponges | Spongia officinalis | Anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antibiotic | [11] |
| Cytarabine | Caribbean sponge | Cryptotethya crypta | Anticancer | [32,33,34] |
| Trabectedin | Caribbean ascidian | Ecteinascidia turbinate | Anticancer | [35] |
| Eribulin Mesylate | Sponge | Halichondria okadai | Anticancer | [36] |
| Brentuximab vedotin | Gastropod mollusk | Dolabella auriculria | Anticancer | [36,37] |
| marine sponge bacterium | Coralliphaga | Antidiabetic | [43] | |
| Aquastatin B | Marine fungi | Cosmospora species SF-5060 | Antidiabetic | [44] |
| Chlorella and diatom | Nitzschia laevis | Antidiabetic | [47] | |
| Astaxanthin | Chlorella zofingiensis | Antidiabetic | [48] | |
| Green, red and brown algae | Palmaria, Ecklonia cava, Alaria, Rhodomela confervoides and Ascophyllum | Antidiabetic | [40,51] | |
| Fucoxanthin | Brown algae | Phaeophyceae | Antihyperlipidemic | [53] |
| Spirostaneand triterpene aglycone compounds | Sea cucumber saponins | Holothurialessoni | Anti-atherosclerotic | [55] |
| Xyloketal B | Xylaria species | Antioxidant, antihyperlipidemic | [57] | |
| Fucoidan | Brown algae | Saccharina japonica | Parkinson disease, anti-inflammation | [63] |
| Seaweed | Codium Tomentosum | Neuroprotective, anti-apoptotic | [64,65] | |
| Aplidin | Marine tunicate | Aplidium albicans | Anticancer | [76] |
| Tetrodotoxin | Puffer fish | Tetraodontidae | Analgesic | [79,80] |
| Plinabulin | Marine fungus | belonging to species of Aspergillus | Under investigation in clinical trials phase III as antitumor | [81,82,83,84] |
| Salinosporamide A or Marizomib | Marine bacteria | Salinispora arenicola and Salinispora tropica | Proteasome inhibitor | [85,86,87] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhatia, S.; Makkar, R.; Behl, T.; Sehgal, A.; Singh, S.; Rachamalla, M.; Mani, V.; Iqbal, M.S.; Bungau, S.G. Biotechnological Innovations from Ocean: Transpiring Role of Marine Drugs in Management of Chronic Disorders. Molecules 2022, 27, 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051539
Bhatia S, Makkar R, Behl T, Sehgal A, Singh S, Rachamalla M, Mani V, Iqbal MS, Bungau SG. Biotechnological Innovations from Ocean: Transpiring Role of Marine Drugs in Management of Chronic Disorders. Molecules. 2022; 27(5):1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051539
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhatia, Saurabh, Rashita Makkar, Tapan Behl, Aayush Sehgal, Sukhbir Singh, Mahesh Rachamalla, Vasudevan Mani, Muhammad Shahid Iqbal, and Simona Gabriela Bungau. 2022. "Biotechnological Innovations from Ocean: Transpiring Role of Marine Drugs in Management of Chronic Disorders" Molecules 27, no. 5: 1539. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27051539