Antibacterial Effect of Shrimp By-Products Hydrolysate on Specific Spoilage Organisms of Squid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Comparison of Antibacterial Activities among Five Hydrolysates
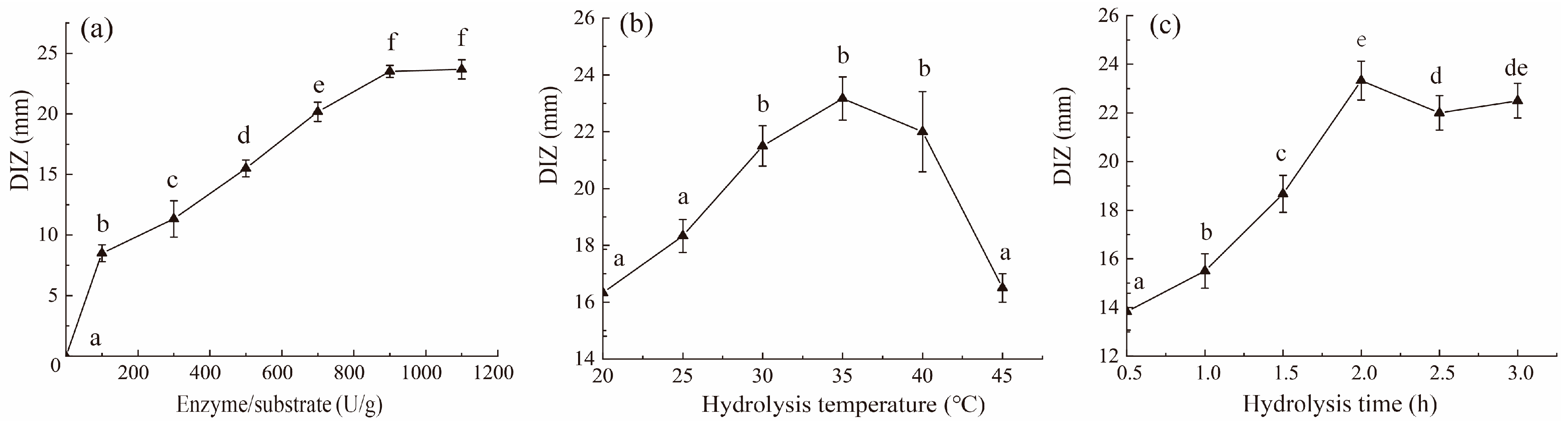
2.2. Effects of Hydrolysis Conditions on Antibacterial Activity of Pepsin Hydrolysate on SE-SSOs
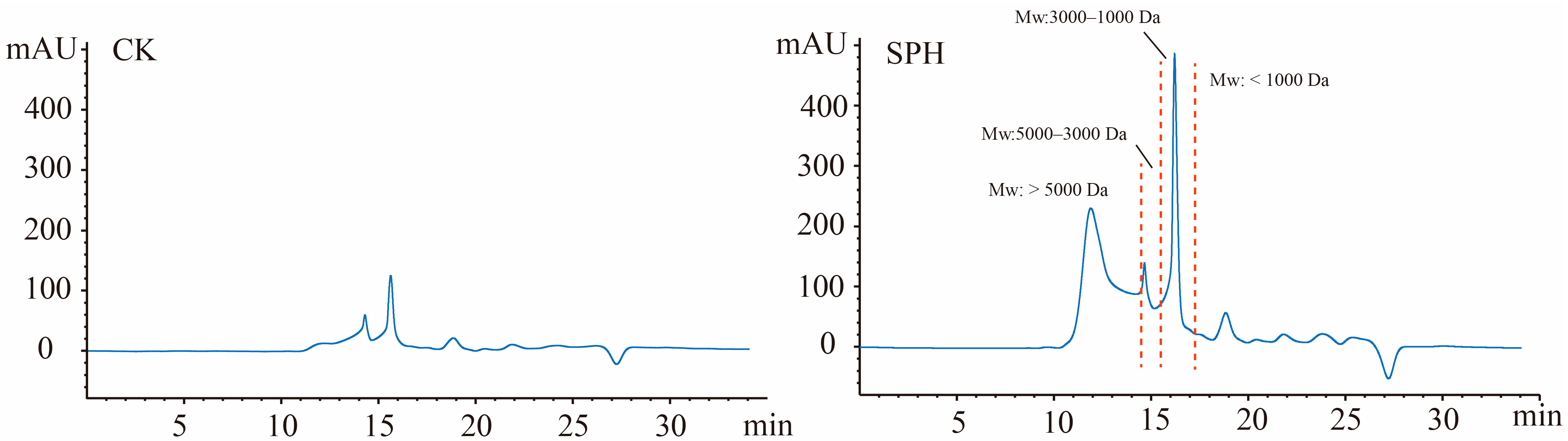
2.3. Molecular Weight (Mw) Distribution of Peptide Fractions in SPH
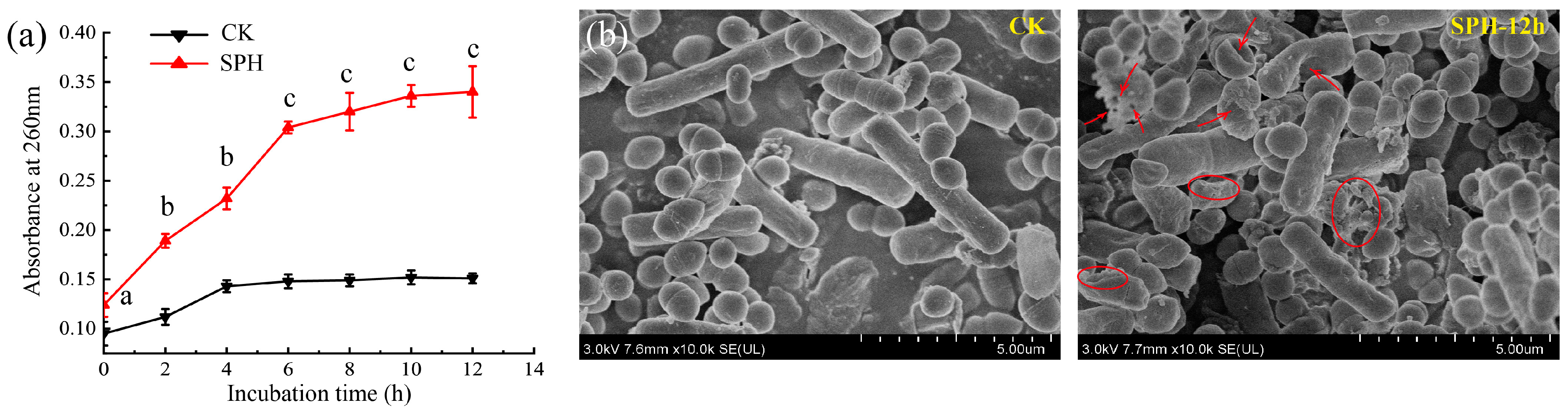
2.4. Antibacterial Effect of SPH on SE–SSOs
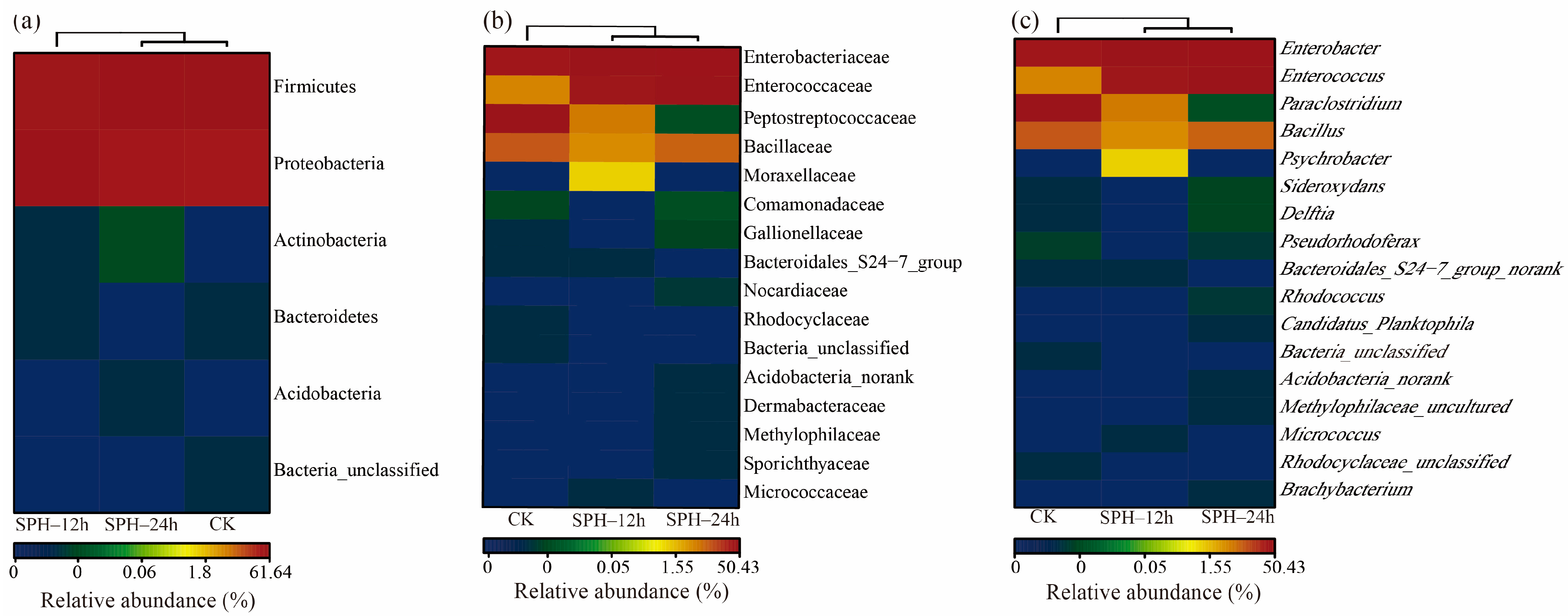
2.5. Effect of SPH on Microbial Structure of SE–SSOs
2.5.1. Alpha Diversity
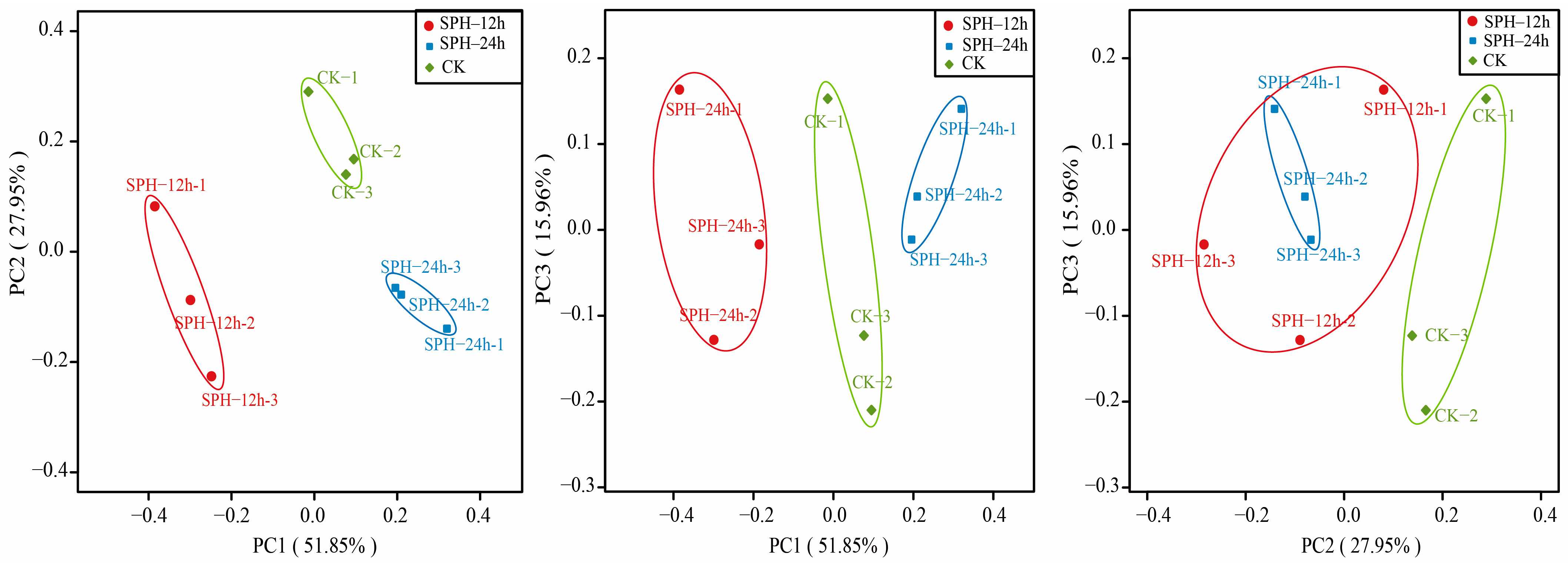
2.5.2. Beta Diversity
2.5.3. Composition of SE–SSOs at the Phylum, Family, and Genus Levels
2.6. LEfSe–Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA)
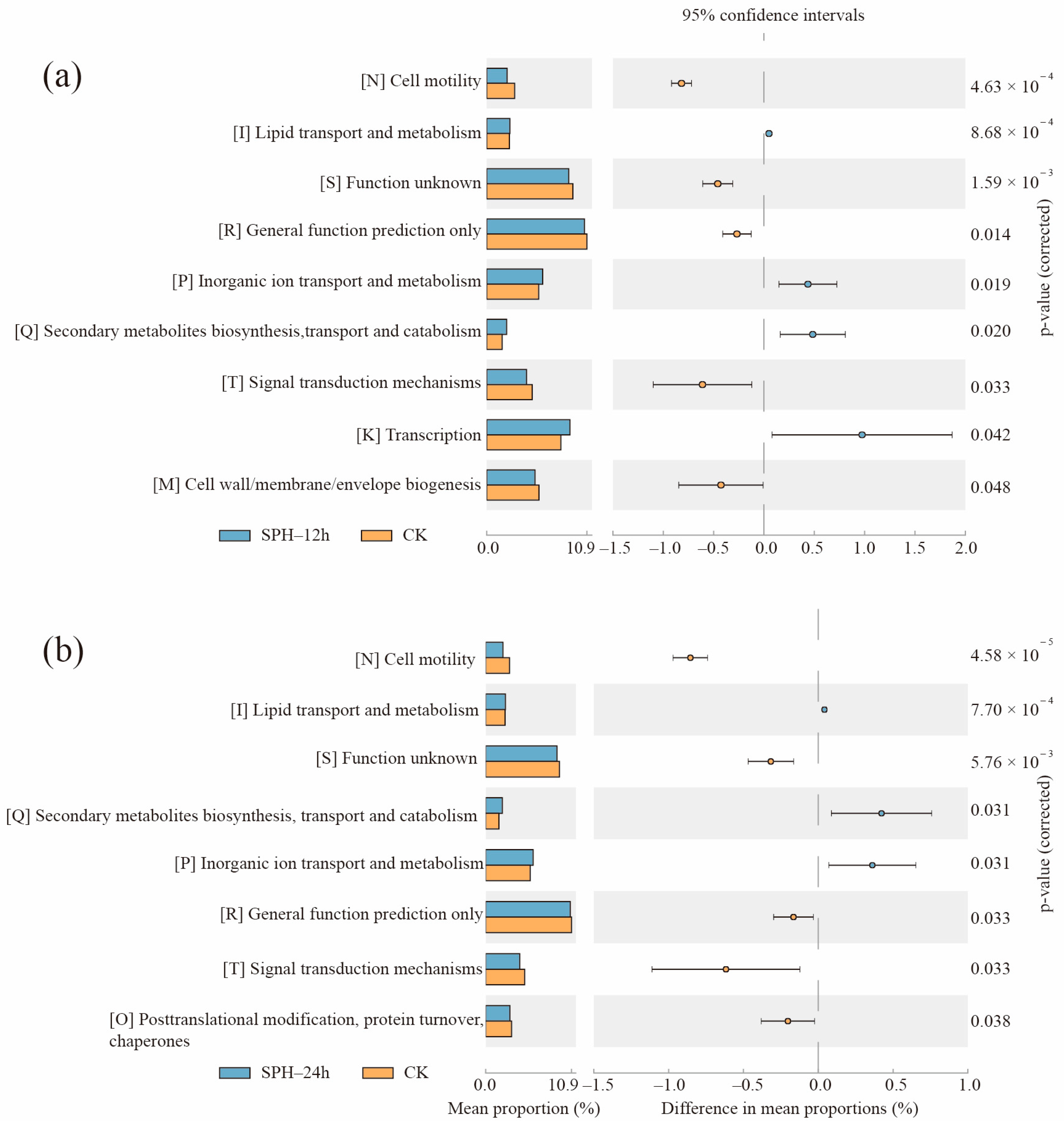
2.7. Changes of Gene Functions of SE–SSOs after SPH Treatment
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Protein Hydrolysates from Shrimp Processing By-Products
3.3. SE–SSOs Collection
3.4. Antibacterial Activity—Agar-Well-Diffusion Method
3.5. Molecular Weight Distribution
3.6. Membrane Permeability
3.7. Microstructure Observation—SEM
3.8. 16S rDNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
3.9. Statistic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Jia, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, J.X.; Song, R. Antioxidant activity and degradation kinetics of astaxanthin extracted from Penaeus sinensis (Solenocera crassicornis) byproducts under pasteurization treatment. LWT 2021, 152, 112336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdollahi, M.; Olofsson, E.; Zhang, J.N.; Alminger, M.; Undeland, I. Minimizing lipid oxidation during pH-shift processing of fish by-products by cross-processing with lingonberry press cake, shrimp shells or brown seaweed. Food Chem. 2020, 327, 127078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, J.Y.; Azwady, A.A.; Rusea, G.; Noormasshela, U.A.; Shaziera, A.G.; Azleen, A.A.; Muskhazli, M. The availability of astaxanthin from shrimp shell wastes through microbial fermentations, Aeromonas hydrophila and cell disruptions. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2014, 16, 277–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadkelayeh, S.; Cheema, S.K.; Hawboldt, K.A. Evaluation of conventional solvent processes for lipid and astaxanthin extraction from shrimp processing by-products. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2022, 210, 398–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, S.; Raju, N.; Nagarajarao, R.C.; Benjakul, S. Oil and pigments from shrimp processing by-products: Extraction, composition, bioactivities and its application—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 100, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh, P.; Moradi, M.; Vaezi, N.; Moosavy, M.H.; Mahmoudi, R. Effects of chitosan edible coating containing grape seed extract on the shelf-life of refrigerated rainbow trout fillet. Vet. Res. Forum. 2018, 9, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Moosazad, S.; Ghajarbeigi, P.; Mahmoudi, R.; Shahsavari, S.; Vahidi, R.; Soltani, A. Antibacterial and antioxidant properties of colorant extracted from red onion skin. J. Chem. Health Risks 2019, 9, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanya, A.; Dhanapal, K.; Sravani, K.; Madhavi, K.R.; Yeshdas, B.; Kumar, G.P. Antioxidant and antibacterial activity of protein hydrolysate prepared from tilapia fish waste by enzymatic treatment. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, L.; Beaulieu, L.; Thibodeau, J.; Bonnet, C.; Bryl, P.; Carbonneau, M. Detection of antibacterial activity in an enzymatic hydrolysate fraction obtained from processing of Atlantic rock crab (Cancer irroratus) by-product. Pharma. Nutr. 2013, 1, 49–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Sun, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, B.J.; Jiang, K.Y.; Sun, S.J.; Meng, X.L.; Luo, Z.Y.; Wang, L. Molecular Cloning of Hemocyanin cDNA from Fenneropenaeus chinensis and Antimicrobial Analysis of Two C-terminal Fragments. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, M.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C.; Fournier, V.; Corre, E.; Le Corguillé, G.; Bernay, B.; Henry, J. Transcriptomic and peptidomic analysis of protein hydrolysates from the white shrimp (L. vannamei). J. Biotechnol. 2014, 186, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Sillero, J.; Gharsallaoui, A.; Prentice, C. Peptides from fish by-product protein hydrolysates and its functional properties: An overview. Mar. Biotechnol. 2018, 20, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boziaris, I.S.; Parlapani, F.F. Chapter 3—Specific Spoilage Organisms (SSOs) in Fish; Woodhead Publishing: Volos, Greece, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, W.Q.; Sun, Y.Q.; Zhang, N.N.; Xie, J. Effects of ε-polylysine and rosemary extract on quality attributes and microbial communities in vacuum-packaged large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) during ice storage. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 30, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaszab, E.; Farkas, M.; Radó, J.; Micsinai, A.; Nyírő-Fekete, B.; Szabó, I.; Kriszt, B.; Urbányi, B.; Szoboszlay, S. Novel members of bacterial community during a short-term chilled storage of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Folia Microbiol. 2022, 67, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Qiu, J.X.; Wang, X. Exploring the dynamic of bacterial communities in manila clam (Ruditapes philippinarum) during refrigerated storage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 882629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sheng, J.; Chen, Y.X.; Xu, J.K. Microbial diversity and dominant bacteria causing spoilage during storage and processing of the Antarctic krill, Euphausia superba. Polar Biol. 2021, 44, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Lee, N.H.; Hong, S.P.; Bang, H.Y. Effects of propolis treatment on the quality of dried squid. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 31, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, N.U.; Sadzali, N.L.; Hassan, M. Effects of squid ink as edible coating on squid sp. (Loligo duvauceli) spoilage during chilled storage. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 23, 1895–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.C.; Cui, L.; Du, F.X.; Xiao, H.; Li, J.R. Impacts of ε-polylysine hydrochloride with thymol on biogenic amines formation and biochemical changes of squid (Illex argentinus). J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Wei, R.B.; Zhang, B.; Wang, D.F. Optimization of the antibacterial activity of half-fin anchovy (Setipinna taty) hydrolysates. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 1979–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardini, R.D.; Harnedy, P.A.; Bolton, D.J.; Kerry, J.P.; O’Neill, E.E.; Mullen, A.M.; Hayes, M. Antioxidant and antimicrobial peptidic hydrolysates from muscle protein sources and by-products. Food Chem. 2011, 4, 1296–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, L.; Bondu, S.; Doiron, K.; Rioux, L.; Turgeon, S.L. Characterization of antibacterial activity from protein hydrolysates of the macroalga Saccharina longicruris and identification of peptides implied in bioactivity. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 17, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennaas, N.; Hammami, R.; Beaulieu, L.; Fliss, I. Production of antibacterial fraction from Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) and its processing by-products using commercial enzymes. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, M.; Schwarz, K.; Rehbein, H.; Bußmann, B.; Beermann, C. Detection of antibacterial activity of an enzymatic hydrolysate generated by processing rainbow trout by-products with trout pepsin. Food Chem. 2016, 205, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Zhu, S.G.; Xu, C.F. Biochemistry (Volume a.); China Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Brogden, K.A. Antimicrobial peptides: Pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, R.; MubarakAli, D.; Mehboob Nousheen, M.G.; Vasimalai, N.; Thajuddin, N.; Kim, J.W. An investigation of pepsin hydrolysate of short antibacterial peptides derived from Limnospira sp. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 5580–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.H.; Lee, D.S.; Jung, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Choi, J.I.; Yim, M.J.; Jeon, J.M.; Kim, H.W.; Son, K.T.; Je, J.Y.; et al. The mechanism of antibacterial activity of phlorofucofuroeckol-A against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 9795–9804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauson, A.J.; He, J.; Wimley, W.C. Determining the mechanism of membrane permeabilizing peptides: Identification of potent, equilibrium pore-formers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Z.; Cooper, S.L. Interactions between dendrimer biocides and bacterial membranes. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 3359–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Xu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.X. Integration of intestinal microbiota and metabonomics to elucidate different alleviation impacts of non-saponification and saponification astaxanthin pre-treatment on paracetamol induced oxidative stress in rats. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byerley, L.O.; Samuelson, D.; Blanchard, E.; Luo, M.; Lorenzen, B.N.; Banks, S.; Ponder, M.A.; Welsh, D.A.; Taylor, C.M. Changes in the gut microbial communities following addition of walnuts to the diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 48, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, W.F.; Yue, Q.Q.; Han, Q.H.; Wang, H.X.; Zhou, M.; Ding, M.; Pan, S.Y. Inhibition of ε-poly-lysine on dominant spoilage bacteria in grass carp and its effect on microbial diversity during cold storage. Food Sci. 2020, 41, 223–230. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Zurek, L. Chapter 9 Antibiotic Resistance in Enterococci: A Food Safety Perspective; Academic Press: Manhattan, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Esteves, E.; Whyte, P.; Mills, J.; Brightwell, G.; Gupta, T.B.; Bolton, D. An investigation into the anaerobic spoilage microbiota of beef carcass and rump steak cuts using high- throughput sequencing. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2021, 368, fnab109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, K.; Noseda, B.; Heyndrickx, M.; Vlaemynck, G.; Devlieghere, F. Volatile compounds associated with Psychrobacter spp. and Pseudoalteromonas spp. the dominant microbiota of brown shrimp (Crangon crangon) during aerobic storage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 16, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urvashi; Choksket, S.; Jain, A.; Sharma, D.; Grover, V.; Korpole, S. Paraclostridium dentum, a novel species with pathogenic features isolated from human dental plaque sample. Anaerobe 2020, 65, 102239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, R.U.; Biswas, R.; Raja, S.; Sistla, S.; Gopalakrishnan, M.S.; Saxena, S.K. Brain abscess and cervical lymphadenitis due to Paraclostridium bifermentans: A report of two cases. Anaerobe 2018, 51, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, B.C.; Esteves, C.T.; Palazzo, I.C.; Darini, A.L.; Felis, G.E.; Sechi, L.A.; Franco, B.D.; De Martinis, E.C. Prevalence and characterization of Enterococcus spp. isolated from Brazilian foods. Food Microbiol. 2008, 25, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrighetto, C.; Knijff, E.; Lombardi, A.; Torriani, S.; Vancanneyt, M.; Kersters, K.; Swings, J.; Dellaglio, F. Phenotypic and genetic diversity of enterococci isolated from Italian cheeses. J. Dairy Res. 2001, 68, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Zadernowska, A.; Łaniewska-Trokenheim, Ł. Virulence factors of Enterococcus spp. presented in food. LWT 2017, 75, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haslam, D.B.; St Geme, J.W. 120—Enterococcus Species; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2022; p. 748. [Google Scholar]
- Coughlan, L.M.; Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A. New weapons to fight old enemies: Novel strategies for the (Bio)control of bacterial biofilms in the food industry. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, M.H.; Chen, Y.; Ou-Yang, J.H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.X.; Luo, X.J.; Zhang, D.D.; Ye Lu, Y.; Yu, H.N.; et al. Antimicrobial, anti-biofilm properties of three naturally occurring antimicrobial peptides against spoilage bacteria, and their synergistic effect with chemical preservatives in food storage. Food Control 2020, 123, 107729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhauser, M.; Renz, P.F.; Tsikrika, P.; Freimann, R.; Wutz, A.; Wrana, J.L.; Beyer, T.A. Gaining insights into the function of post-translational protein modification using genome engineering and molecular cell biology. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3920–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, F.C.; Swaisgood, H.E.; Porter, D.H.; Catignani, G.L. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk proteins. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Shi, M.; Gu, L. Digestive properties of half-fin anchovy hydrolysates/glucose Maillard reaction products and modulation effects on intestinal microbiota. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 2584–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A flexible tool for aligning sequences to a template alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
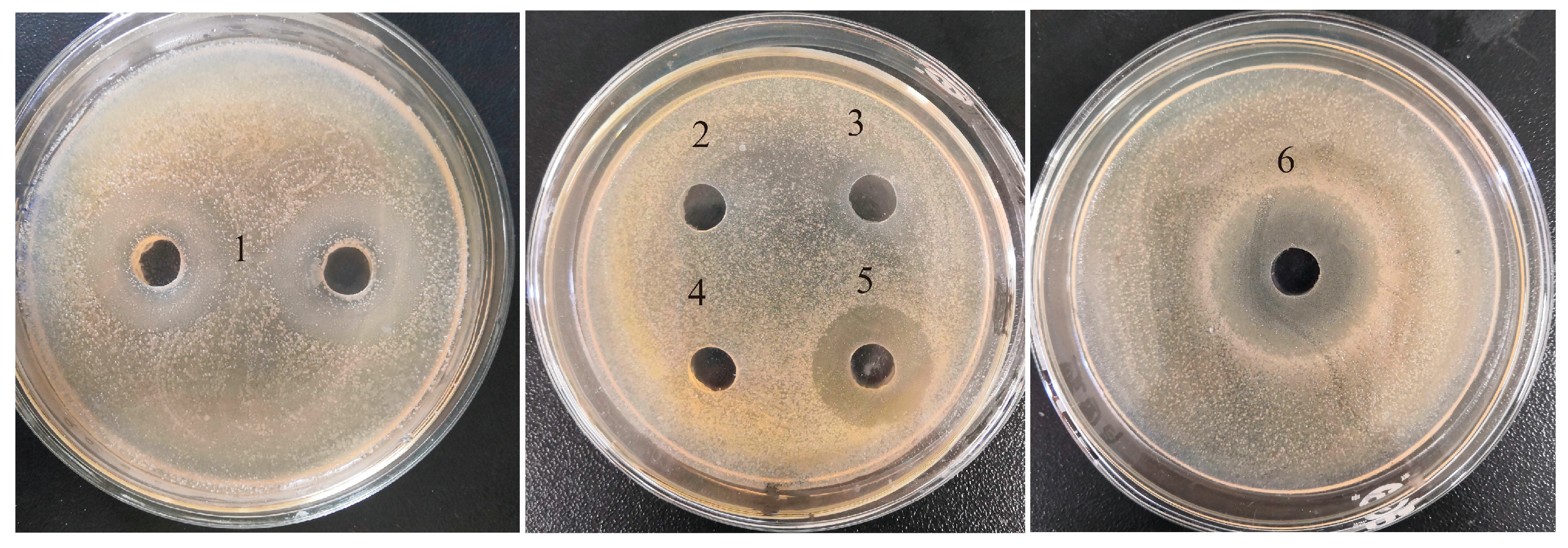


| Proteases | Hydrolysis pH | Hydrolysis Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Neutral protease | 7.0 | 50 |
| Flavourzyme | 8.0 | 50 |
| Trypsin | 8.0 | 37 |
| Alcalase | 9.0 | 45 |
| Pepsin | 2.0 | 35 |
| Group | Ace Index | Chao1 Index | Shannon Index | Simpson Index | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.50 ± 2.12 a,b | 7.67 ± 1.15 a,b | 1.15 ± 0.04 b | 0.37 ± 0.01 a | 0.9999 |
| SPH–12 h | 5.67 ± 0.58 a | 5.67 ± 0.58 a | 0.88 ± 0.13 a | 0.46 ± 0.04 b | 1.0000 |
| SPH–24 h | 10.33 ± 1.53 b | 10.67 ± 1.53 b | 0.91 ± 0.05 a | 0.43 ± 0.00 a,b | 0.9999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gu, L.; Zhu, Q.; Zou, X.; Song, R. Antibacterial Effect of Shrimp By-Products Hydrolysate on Specific Spoilage Organisms of Squid. Molecules 2023, 28, 4105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104105
Gu L, Zhu Q, Zou X, Song R. Antibacterial Effect of Shrimp By-Products Hydrolysate on Specific Spoilage Organisms of Squid. Molecules. 2023; 28(10):4105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104105
Chicago/Turabian StyleGu, Luo, Qiuyu Zhu, Xiaoyu Zou, and Ru Song. 2023. "Antibacterial Effect of Shrimp By-Products Hydrolysate on Specific Spoilage Organisms of Squid" Molecules 28, no. 10: 4105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104105
APA StyleGu, L., Zhu, Q., Zou, X., & Song, R. (2023). Antibacterial Effect of Shrimp By-Products Hydrolysate on Specific Spoilage Organisms of Squid. Molecules, 28(10), 4105. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28104105





