Solving an Old Puzzle: Elucidation and Evaluation of the Binding Mode of Salvinorin A at the Kappa Opioid Receptor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Salvinorin A Binds above the Morphinan Binding Pocket of the Kappa Opioid Receptor
2.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulations Confirm Salvinorin A Binding Mode Obtained by Docking Experiments but Revealed Additional Interaction with Q115
2.3. Non-Conserved Residues Harboring Salvinorin A at the Kappa Opioid Receptor Lead to Receptor Subtype Selectivity of Salvinorin A
2.4. Salvinorin A Binding Mode Is in Agreement with Previous Published Structure-Activity-Relationship Data
2.4.1. C2-Analogs of SalA
2.4.2. C4-Analogs of SalA
2.4.3. C12-Analogs of SalA (Furan-Analogs)
2.4.4. SalA Derivatives with Modified Scaffolds
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Preparation
4.2. Docking
4.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Generation of Dynophores
4.4. Energy Calculations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yekkirala, A.S.; Roberson, D.P.; Bean, B.P.; Woolf, C.J. Breaking barriers to novel analgesic drug development. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 545–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pierce, M.; van Amsterdam, J.; Kalkman, G.A.; Schellekens, A.; van den Brink, W. Is Europe facing an opioid crisis like the United States? An analysis of opioid use and related adverse effects in 19 European countries between 2010 and 2018. Eur. Psychiatry 2021, 64, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierk, K.A. The Real Antidote: A Critical Review of U.S. and Canadian Drug Treatment Courts and a Call for Public Health Prevention Tools as a Solution to the Opioid Epidemic. Indiana Int. Comp. Law Rev. 2019, 29, 185–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, Ł.; Goryński, K. Pharmacological aspects of over-the-counter opioid drugs misuse. Molecules 2020, 25, 3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C. Opioid Receptors. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mores, K.L.; Cummins, B.R.; Cassell, R.J.; van Rijn, R.M. A review of the therapeutic potential of recently developed G protein-biased kappa agonists. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corder, G.; Castro, D.C.; Bruchas, M.R.; Scherrer, G. Endogenous and exogenous opioids in pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 41, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.M.L.; Filizola, M. Insights from molecular dynamics simulations of a number of G-protein coupled receptor targets for the treatment of pain and opioid use disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chou, R.; Fanciullo, G.J.; Fine, P.G.; Adler, J.A.; Ballantyne, J.C.; Davies, P.; Donovan, M.I.; Fishbain, D.A.; Foley, K.M.; Fudin, J.; et al. Clinical guidelines for the use of chronic opioid therapy in chronic noncancer pain. J. Pain 2009, 10, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albert-Vartanian, A.; Boyd, M.; Hall, A.; Morgado, S.; Nguyen, E.; Nguyen, V.; Patel, S.; Russo, L.; Shao, A.; Raffa, R. Will peripherally restricted kappa-opioid receptor agonists (pKORA s) relieve pain with less opioid adverse effects and abuse potential? J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 41, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasov, A.G.; Zotchev, S.B.; Dirsch, V.M.; Supuran, C.T. Natural products in drug discovery: Advances and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coffeen, U.; Pellicer, F. Salvia divinorum: From recreational hallucinogenic use to analgesic and anti-inflammatory action. J. Pain Res. 2019, 12, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zjawiony, J.K.; Machado, A.S.; Menegatti, R.; Ghedini, P.C.; Costa, E.A.; Pedrino, G.R.; Lukas, S.E.; Franco, O.L.; Silva, O.N.; Fajemiroye, J.O. Cutting-edge search for safer opioid pain relief: Retrospective review of salvinorin A and its analogs. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, J.J.; Shenvi, R.A. A review of salvinorin analogs and their kappa-opioid receptor activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito-da-Costa, A.M.; Dias-da-Silva, D.; Gomes, N.G.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Madureira-Carvalho, Á. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Salvinorin A and Salvia divinorum: Clinical and Forensic Aspects. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooker, J.M.; Xu, Y.; Schiffer, W.; Shea, C.; Carter, P.; Fowler, J.S. Pharmacokinetics of the potent hallucinogen, salvinorin A in primates parallels the rapid onset and short duration of effects in humans. NeuroImage 2008, 41, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Butelman, E.R.; Fry, R.S.; Kimani, R.; Reed, B.; Kreek, M.J. Neuroendocrine effects of naltrexone versus nalmefene in humans. Hum. Psychopharmacol. Clin. Exp. 2020, 35, e2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, J.A.; Weinstein, H. Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure-function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. In Methods in Neurosciences; Sealfon, S.C., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA; London, UK, 1995; Volume 25, pp. 366–428. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wacker, D.; Mileni, M.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Vardy, E.; Liu, W.; Thompson, A.A.; Huang, X.-P.; Carroll, F. Structure of the human κ-opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature 2012, 485, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenalti, G.; Zatsepin, N.A.; Betti, C.; Giguere, P.; Han, G.W.; Ishchenko, A.; Liu, W.; Guillemyn, K.; Zhang, H.; James, D.; et al. Structural basis for bifunctional peptide recognition at human δ-opioid receptor. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, T.; Majumdar, S.; Zaidi, S.A.; Ondachi, P.; McCorvy, J.D.; Wang, S.; Mosier, P.D.; Uprety, R.; Vardy, E.; Krumm, B.E.; et al. Structure of the nanobody-stabilized active state of the kappa opioid receptor. Cell 2018, 172, 55–67.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vo, Q.N.; Mahinthichaichan, P.; Shen, J.; Ellis, C.R. How μ-opioid receptor recognizes fentanyl. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, K.; Inan, S.; Siebert, D.; Holzgrabe, U.; Lee, D.Y.; Huang, P.; Li, J.-G.; Cowan, A.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y. Comparison of pharmacological activities of three distinct κ ligands (salvinorin A, TRK-820 and 3FLB) on κ opioid receptors in vitro and their antipruritic and antinociceptive activities in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 312, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, B.E.; Nieto, M.J.; McCurdy, C.R.; Ferguson, D.M. A unique binding epitope for salvinorin A, a non-nitrogenous kappa opioid receptor agonist. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vortherms, T.A.; Mosier, P.D.; Westkaemper, R.B.; Roth, B.L. Differential helical orientations among related G protein-coupled receptors provide a novel mechanism for selectivity: Studies with salvinorin A and the κ-opioid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 3146–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J. Salvinorin A, a kappa-opioid receptor agonist hallucinogen: Pharmacology and potential template for novel pharmacotherapeutic agents in neuropsychiatric disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, B.L.; Baner, K.; Westkaemper, R.; Siebert, D.; Rice, K.C.; Steinberg, S.; Ernsberger, P.; Rothman, R.B. Salvinorin A: A potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11934–11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacLean, K.A.; Johnson, M.W.; Reissig, C.J.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Griffiths, R.R. Dose-related effects of salvinorin A in humans: Dissociative, hallucinogenic, and memory effects. Psychopharmacology 2012, 226, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivell, B.M.; Ewald, A.W.; Prisinzano, T.E. Salvinorin A analogs and other kappa-opioid receptor compounds as treatments for cocaine abuse. Adv. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 481–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsujikawa, K.; Kuwayama, K.; Miyaguchi, H.; Kanamori, T.; Iwata, Y.; Inoue, H. In vitro stability and metabolism of salvinorin A in rat plasma. Xenobiotica 2009, 39, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Tidgewell, K.; Harding, W.; Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J.; Murry, D.J. Determination of Salvinorin A in body fluids by high performance liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 818, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teksin, Z.S.; Lee, I.J.; Nemieboka, N.N.; Othman, A.A.; Upreti, V.V.; Hassan, H.E.; Syed, S.S.; Prisinzano, T.E.; Eddington, N.D. Evaluation of the transport, in vitro metabolism and pharmacokinetics of Salvinorin A, a potent hallucinogen. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCurdy, C.R.; Sufka, K.J.; Smith, G.H.; Warnick, J.E.; Nieto, M.J. Antinociceptive profile of salvinorin A, a structurally unique kappa opioid receptor agonist. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 83, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.D.; Schmidt, M.S.; Butelman, E.R.; Harding, W.W.; Tidgewell, K.; Murry, D.J.; Kreek, M.J.; Prisinzano, T.E. Pharmacokinetics of the plant-derived κ-opioid hallucinogen salvinorin A in nonhuman primates. Synapse 2005, 58, 208–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, D.J. Salvia divinorum and salvinorin A: New pharmacologic findings. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 43, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prisinzano, T.E.; Rothman, R.B. Salvinorin A analogs as probes in opioid pharmacology. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 1732–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Béguin, C.; Richards, M.R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Ma, Z.; Lee, D.Y.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B.M. Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological evaluation of salvinorin A analogues modified at C (2). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beguin, C.; Potter, D.N.; DiNieri, J.A.; Munro, T.A.; Richards, M.R.; Paine, T.A.; Berry, L.; Zhao, Z.; Roth, B.L.; Xu, W. N-methylacetamide analog of salvinorin A: A highly potent and selective κ-opioid receptor agonist with oral efficacy. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2008, 324, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erli, F.; Guerrieri, E.; Ben Haddou, T.; Lantero, A.; Mairegger, M.; Schmidhammer, H.; Spetea, M. Highly potent and selective new diphenethylamines interacting with the κ-opioid receptor: Synthesis, pharmacology, and structure-activity relationships. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7579–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Béguin, C.; Duncan, K.K.; Munro, T.A.; Ho, D.M.; Xu, W.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B.M. Modification of the furan ring of salvinorin A: Identification of a selective partial agonist at the kappa opioid receptor. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, D.S.; Katavic, P.L.; Lozama, A.; Harding, W.W.; Parrish, D.; Deschamps, J.R.; Dersch, C.M.; Partilla, J.S.; Rothman, R.B.; Navarro, H. Synthetic studies of Neoclerodane diterpenes from Salvia divinorum: Preparation and opioid receptor activity of Salvinicin analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3596–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, K.G.; Tidgewell, K.; Marquam, A.; Rothman, R.B.; Navarro, H.; Prisinzano, T.E. Synthetic studies of neoclerodane diterpenes from Salvia divinorum: Exploration of the 1-position. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 6111–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harding, W.W.; Schmidt, M.; Tidgewell, K.; Kannan, P.; Holden, K.G.; Gilmour, B.; Navarro, H.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Synthetic studies of Neoclerodane diterpenes from Salvia divinorum: Semisynthesis of Salvinicins A and B and other chemical transformations of Salvinorin A. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bikbulatov, R.V.; Stewart, J.; Jin, W.; Yan, F.; Roth, B.L.; Ferreira, D.; Zjawiony, J.K. Short synthesis of a novel class of salvinorin A analogs with hemiacetalic structure. Tetrahedron Lett. 2008, 49, 937–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowley, R.S.; Riley, A.P.; Alder, A.F.; Anderson III, R.J.; Luo, D.; Kaska, S.; Maynez, P.; Kivell, B.M.; Prisinzano, T.E. Synthetic studies of neoclerodane diterpenes from salvia divinorum: Design, synthesis, and evaluation of analogues with improved potency and G-protein activation bias at the μ-opioid receptor. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tidgewell, K.; Groer, C.E.; Harding, W.W.; Lozama, A.; Schmidt, M.; Marquam, A.; Hiemstra, J.; Partilla, J.S.; Dersch, C.M.; Rothman, R.B. Herkinorin analogues with differential β-arrestin-2 interactions. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keasling, A.W.; Pandey, P.; Doerksen, R.J.; Pedrino, G.R.; Costa, E.A.; da Cunha, L.C.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Fajemiroye, J.O. Salvindolin elicits opioid system-mediated antinociceptive and antidepressant-like activities. J. Psychopharm. 2019, 33, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardy, E.; Mosier, P.D.; Frankowski, K.J.; Wu, H.; Katritch, V.; Westkaemper, R.B.; Aubé, J.; Stevens, R.C.; Roth, B.L. Chemotype-selective modes of action of κ-opioid receptor agonists. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34470–34483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roach, J.J.; Sasano, Y.; Schmid, C.L.; Zaidi, S.; Katritch, V.; Stevens, R.C.; Bohn, L.M.; Shenvi, R.A. Dynamic strategic bond analysis yields a ten-step synthesis of 20-nor-Salvinorin A, a potent κ-OR agonist. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polepally, P.R.; Huben, K.; Vardy, E.; Setola, V.; Mosier, P.D.; Roth, B.L.; Zjawiony, J.K. Michael acceptor approach to the design of new salvinorin A-based high affinity ligands for the kappa-opioid receptor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 85, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, D.L.; Mosier, P.D.; Roth, B.L.; Westkaemper, R.B. CoMFA analyses of C-2 position Salvinorin A analogs at the kappa-opioid receptor provides insights into epimer selectivity. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2010, 28, 612–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vortherms, T.A.; Roth, B.L. Salvinorin A. Mol. Interv. 2006, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Mosier, P.D.; Westkaemper, R.B.; Stewart, J.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Vortherms, T.A.; Sheffler, D.J.; Roth, B.L. Identification of the molecular mechanisms by which the diterpenoid salvinorin A binds to κ-opioid receptors. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8643–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Bikbulatov, R.V.; Mocanu, V.; Dicheva, N.; Parker, C.E.; Wetsel, W.C.; Mosier, P.D.; Westkaemper, R.B.; Allen, J.A.; Zjawiony, J.K. Structure-based design, synthesis, and biochemical and pharmacological characterization of novel salvinorin A analogues as active state probes of the κ-opioid receptor. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 6898–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bock, A.; Bermudez, M.; Krebs, F.; Matera, C.; Chirinda, B.; Sydow, D.; Dallanoce, C.; Holzgrabe, U.; Amici, M.d.; Lohse, M.J.; et al. Ligand binding ensembles determine graded agonist efficacies at a G protein-coupled receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16375–16389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sydow, D. Dynophores: Novel Dynamic Pharmacophores Implementation of Pharmacophore Generation Based on Molecular Dynamics Trajectories and Their Graphical Representation; Freie Universität Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.Y.; He, M.; Kondaveti, L.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.-G.; Beguin, C.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological studies of C (4) modified salvinorin A analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 4169–4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; He, M.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.-G.; Xu, W.; Ma, Z.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B. Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological studies of new C (4)-modified salvinorin A analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 5498–5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egyed, A.; Kelemen, Á.A.; Vass, M.; Visegrády, A.; Thee, S.A.; Wang, Z.; de Graaf, C.; Brea, J.; Loza, M.I.; Leurs, R. Controlling the selectivity of aminergic GPCR ligands from the extracellular vestibule. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 111, 104832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tröger, T.; Langenberg, M.; Zhong, S.; Ambrosini, D.; Enzensperger, C. Fishing for accessory binding sites at GPCRs with ‘Loop-Hooks’–An approach towards selectivity? Part I. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldhoer, M.; Bartlett, S.E.; Whistler, J.L. Opioid receptors. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 953–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Manglik, A.; Venkatakrishnan, A.J.; Laeremans, T.; Feinberg, E.N.; Sanborn, A.L.; Kato, H.E.; Livingston, K.E.; Thorsen, T.S.; Kling, R.C.; et al. Structural insights into µ-opioid receptor activation. Nature 2015, 524, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claff, T.; Yu, J.; Blais, V.; Patel, N.; Martin, C.; Wu, L.; Han, G.W.; Holleran, B.J.; van der Poorten, O.; White, K.L.; et al. Elucidating the active δ-opioid receptor crystal structure with peptide and small-molecule agonists. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax9115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puls, K.; Schmidhammer, H.; Wolber, G.; Spetea, M. Mechanistic characterization of the pharmacological profile of HS-731, a peripherally acting opioid analgesic, at the µ-, δ-, κ-opioid and nociceptin receptors. Molecules 2022, 27, 919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolber, G.; Langer, T. LigandScout: 3-D pharmacophores derived from protein-bound ligands and their use as virtual screening filters. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolber, G.; Dornhofer, A.A.; Langer, T. Efficient overlay of small organic molecules using 3D pharmacophores. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2006, 20, 773–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polepally, P.R.; White, K.; Vardy, E.; Roth, B.L.; Ferreira, D.; Zjawiony, J.K. Kappa-opioid receptor-selective dicarboxylic ester-derived salvinorin A ligands. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2860–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munro, T.A.; Duncan, K.K.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B.M.; Béguin, C. Standard protecting groups create potent and selective κ opioids: Salvinorin B alkoxymethyl ethers. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prevatt-Smith, K.M.; Lovell, K.M.; Simpson, D.S.; Day, V.W.; Douglas, J.T.; Bosch, P.; Dersch, C.M.; Rothman, R.B.; Kivell, B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Potential drug abuse therapeutics derived from the hallucinogenic natural product salvinorin A. MedChemComm 2011, 2, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.Y.; Karnati, V.V.; He, M.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Kondaveti, L.; Ma, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Beguin, C.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Synthesis and in vitro pharmacological studies of new C (2) modified salvinorin A analogues. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2005, 15, 3744–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavkin, C.; Sud, S.; Jin, W.; Stewart, J.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Siebert, D.J.; Toth, B.A.; Hufeisen, S.J.; Roth, B.L. Salvinorin A, an active component of the hallucinogenic sage Salvia divinorum is a highly efficacious κ-opioid receptor agonist: Structural and functional considerations. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béguin, C.; Richards, M.R.; Li, J.-G.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B.M. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of salvinorin A analogues: Effect of configuration at C (2) and substitution at C (18). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4679–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, T.A.; Duncan, K.K.; Staples, R.J.; Xu, W.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; Béguin, C.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr.; Cohen, B.M. 8-epi-Salvinorin B: Crystal structure and affinity at the κ opioid receptor. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2007, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lovell, K.M.; Vasiljevik, T.; Araya, J.J.; Lozama, A.; Prevatt-Smith, K.M.; Day, V.W.; Dersch, C.M.; Rothman, R.B.; Butelman, E.R.; Kreek, M.J. Semisynthetic neoclerodanes as kappa opioid receptor probes. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 3100–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozama, A.; Cunningham, C.W.; Caspers, M.J.; Douglas, J.T.; Dersch, C.M.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Opioid receptor probes derived from cycloaddition of the hallucinogen natural product salvinorin A. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munro, T.A.; Rizzacasa, M.A.; Roth, B.L.; Toth, B.A.; Yan, F. Studies toward the pharmacophore of salvinorin A, a potent κ opioid receptor agonist. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sherwood, A.M.; Crowley, R.S.; Paton, K.F.; Biggerstaff, A.; Neuenswander, B.; Day, V.W.; Kivell, B.M.; Prisinzano, T.E. Addressing structural flexibility at the A-ring on salvinorin A: Discovery of a potent kappa-opioid agonist with enhanced metabolic stability. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 3866–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.Y.; Yang, L.; Xu, W.; Deng, G.; Guo, L.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y. Synthesis and biological evaluation of C-2 halogenated analogs of salvinorin A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 5749–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fichna, J.; Lewellyn, K.; Yanc, F.; Roth, B.L.; Zjawiony, J.K. Synthesis and biological evaluation of new salvinorin A analogues incorporating natural amino acids. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Crowley, R.S.; Riley, A.P.; Sherwood, A.M.; Groer, C.E.; Shivaperumal, N.; Biscaia, M.; Paton, K.; Schneider, S.; Provasi, D.; Kivell, B.M. Synthetic studies of neoclerodane diterpenes from salvia divinorum: Identification of a potent and centrally acting μ opioid analgesic with reduced abuse liability. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 11027–11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simpson, D.S.; Lovell, K.M.; Lozama, A.; Han, N.; Day, V.W.; Dersch, C.M.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Synthetic studies of neoclerodane diterpenes from Salvia divinorum: Role of the furan in affinity for opioid receptors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2009, 7, 3748–3756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, K.L.; Robinson, J.E.; Zhu, H.; DiBerto, J.F.; Polepally, P.R.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Nichols, D.E.; Malanga, C.; Roth, B.L. The G protein–biased κ-opioid receptor agonist RB-64 is analgesic with a unique spectrum of activities in vivo. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2015, 352, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D E Shaw Research. Desmond Molecular Dynamics System; 2022–1; D E Shaw Research: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bowers, K.J.; Chow, D.E.; Xu, H.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Gregersen, B.A.; Klepeis, J.L.; Kolossvary, I.; Moraes, M.A.; Sacerdoti, F.D.; et al. Scalable algorithms for molecular dynamics simulations on commodity clusters. In Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing (SC06), Tampa, FL, USA, 11–17 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Gowers, R.J.; Alibay, I.; Swenson, D.W.H.; Henry, M.M. Open Free Energy (OpenFE), version 0.21. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzi, A.; Grinaway, P.B.; Parton, D.L.; Shirts, M.R.; Wang, K.; Eastman, P.; Friedrichs, M.; Pande, V.S.; Branson, K.; Mobley, D.L.; et al. YANK: A GPU-Accelerated Platform for Alchemical Free Energy Calculations. Available online: http://getyank.org/latest/ (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Riley, A.P.; Groer, C.E.; Young, D.; Ewald, A.W.; Kivell, B.M.; Prisinzano, T.E. Synthesis and κ-opioid receptor activity of furan-substituted salvinorin A analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10464–10475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harding, W.W.; Tidgewell, K.; Byrd, N.; Cobb, H.; Dersch, C.M.; Butelman, E.R.; Rothman, R.B.; Prisinzano, T.E. Neoclerodane diterpenes as a novel scaffold for μ opioid receptor ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4765–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H. Announcing the worldwide Protein Data Bank. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molecular Operating Environment (MOE); Chemical Computing Group: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2021; Available online: https://www.chemcomp.com/Products.htm (accessed on 10 April 2022).
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D480–D489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, G.N.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Sasisekharan, V. Stereochemistry of polypeptide chain configurations. J. Mol. Biol. 1963, 7, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S. Validation of the generalized force fields GAFF, CGenFF, OPLS-AA, and PRODRGFF by testing against experimental osmotic coefficient data for small drug-like molecules. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 4239–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labute, P. Protonate3D: Assignment of ionization states and hydrogen coordinates to macromolecular structures. Proteins 2009, 75, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, A.; Hessler, G.; Matter, H.; Klabunde, T. Virtual screening of biogenic amine-binding G-protein coupled receptors: Comparative evaluation of protein- and ligand-based virtual screening protocols. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5448–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonk, M.L.; Cole, J.C.; Hartshorn, M.J.; Murray, C.W.; Taylor, R.D. Improved protein-ligand docking using GOLD. Proteins 2003, 52, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Zhang, K.Y.J. Advances in the development of shape similarity methods and their application in drug discovery. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.A.; Pickup, B. A Gaussian description of molecular shape. J. Phys. Chem. 1995, 99, 3503–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Release-4: Maestro, version 2020-4; Schrödinger LLC.: New York, NY, USA, 2020.
- Lomize, M.A.; Pogozheva, I.D.; Joo, H.; Mosberg, H.I.; Lomize, A.L. OPM database and PPM web server: Resources for positioning of proteins in membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D370–D376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, S.; Onck, P.R.; van der Giessen, E. CHARMM TIP3P water model suppresses peptide folding by solvating the unfolded state. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 3692–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; MacKerell, A.D., Jr. CHARMM36 all-atom additive protein force field: Validation based on comparison to NMR data. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tucker, M.R.; Piana, S.; Tan, D.; LeVine, M.V.; Shaw, D.E. Development of force field parameters for the simulation of single-and double-stranded DNA molecules and DNA–protein complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2022, 126, 4442–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullingsrud, J. DEShawResearch. Viparr-Ffpublic. Available online: https://github.com/DEShawResearch/viparr-ffpublic (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastman, P.; Pande, V. OpenMM: A hardware-independent framework for molecular simulations. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2010, 12, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Showalter, S.A.; Brüschweiler, R. Validation of molecular dynamics simulations of biomolecules using NMR spin relaxation as benchmarks: Application to the AMBER99SB force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2007, 3, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothroyd, S.; Behara, P.K.; Madin, O.; Hahn, D.; Jang, H.; Gapsys, V.; Wagner, J.; Horton, J.; Dotson, D.; Thompson, M. Development and benchmarking of open force field 2.0.0—The sage small molecule force field. In preparation. [CrossRef]
- Zielkiewicz, J. Structural properties of water: Comparison of the SPC, SPCE, TIP4P, and TIP5P models of water. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 123, 104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Maxwell, D.S.; Tirado-Rives, J. Development and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11225–11236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponder, J.W.; Case, D.A. Force fields for protein simulations. Adv. Protein Chem. 2003, 66, 27–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Horn, H.W.; Swope, W.C.; Pitera, J.W.; Madura, J.D.; Dick, T.J.; Hura, G.L.; Head-Gordon, T. Development of an improved four-site water model for biomolecular simulations: TIP4P-Ew. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 9665–9678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toukmaji, A.Y.; Board, J.A., Jr. Ewald summation techniques in perspective: A survey. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1996, 95, 73–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the accuracy of protein side chain and backbone parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Man, V.H.; Yang, W.; Lee, T.-S.; Wang, J. A fast and high-quality charge model for the next generation general AMBER force field. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
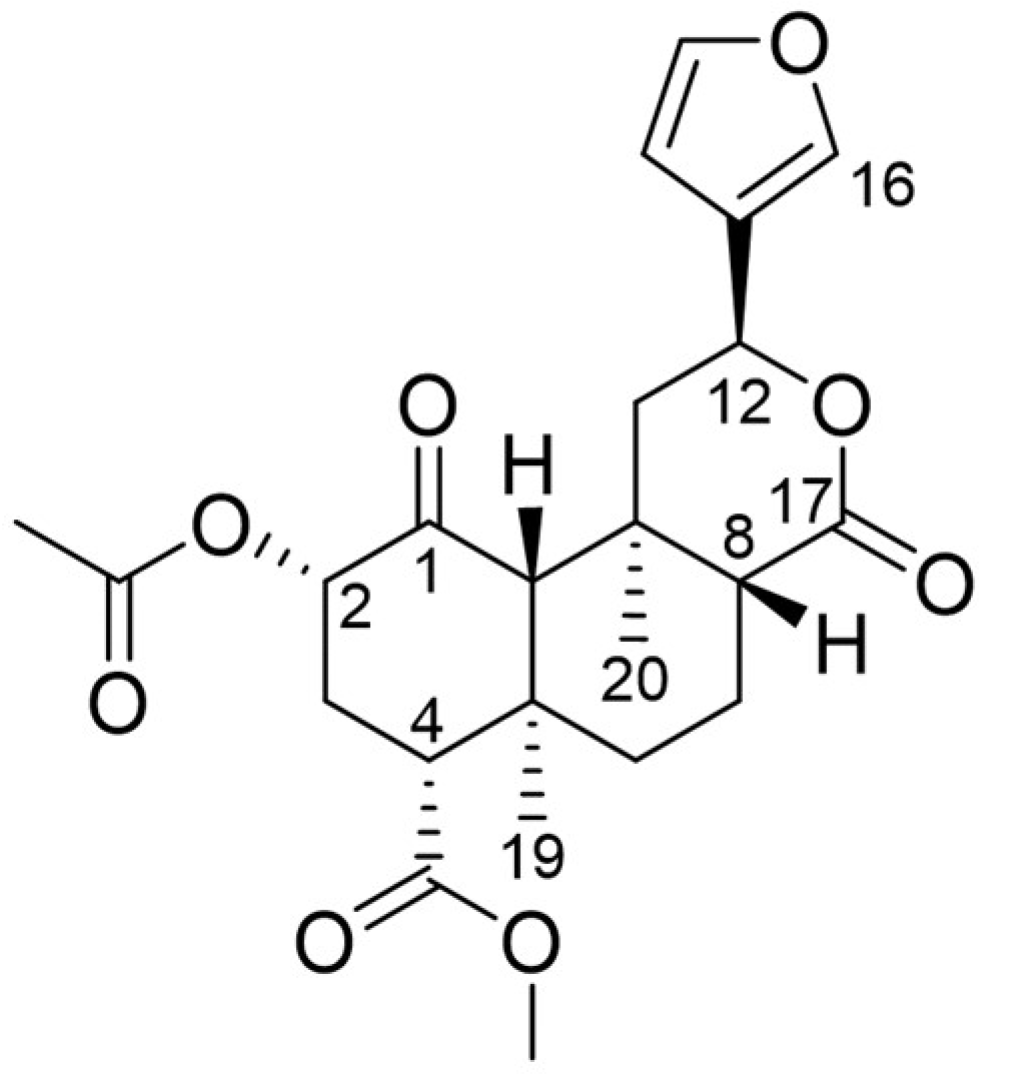
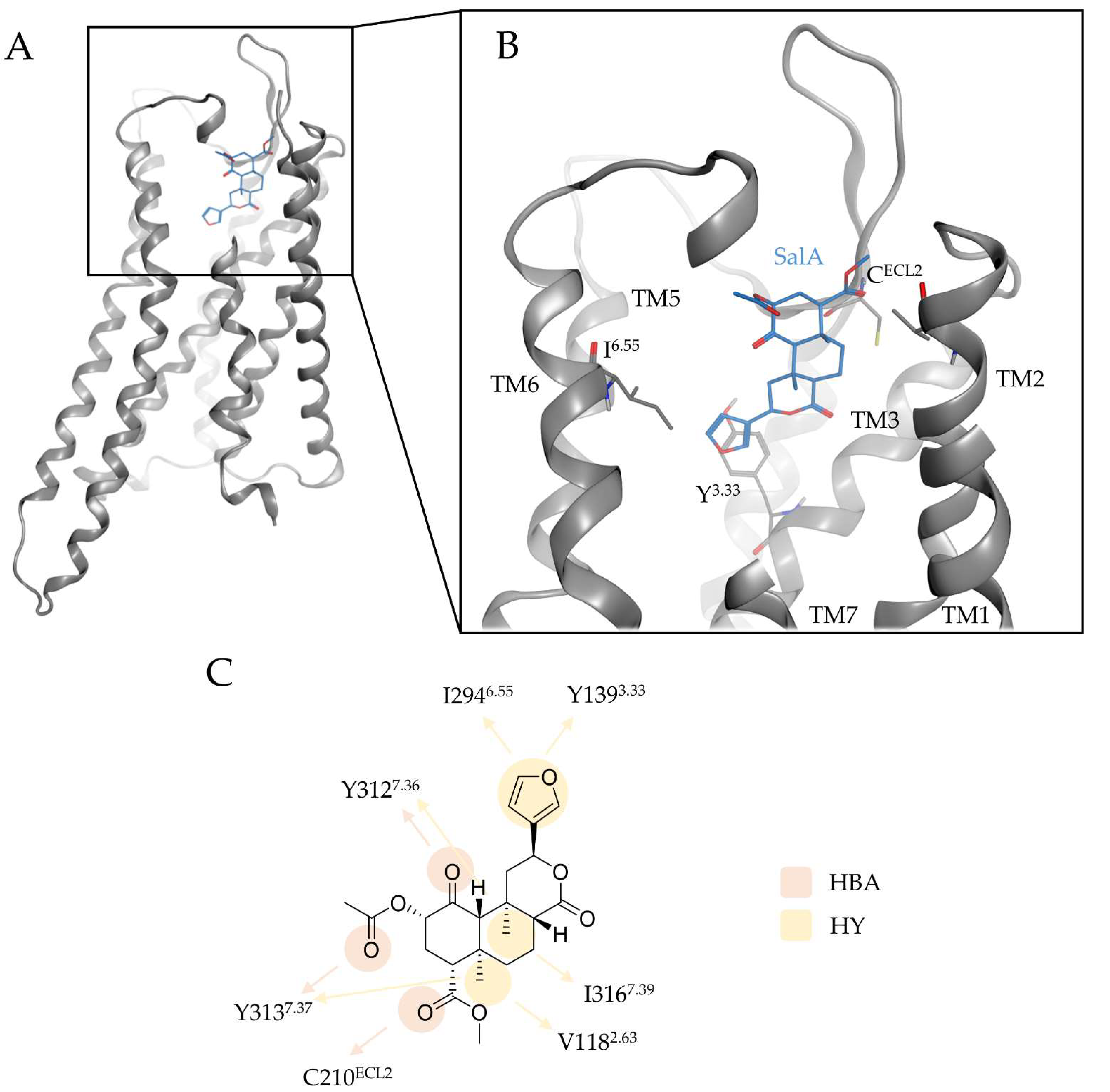



| Interaction | Functional Group | Residue |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen bond | C1-carbonyl | Y3127.35 |
| Hydrogen bond | C2-carbonyl | Y3137.36 |
| Hydrogen bond | C4-carbonyl | C210ECL2 |
| Hydrophobic contact | C19 | V1182.63, Y3137.36 |
| Hydrophobic contact | C20 | I3167.39 |
| Hydrophobic contact | Furan | I2946.55; Y1393.33 |
| Interaction | Functional Group | Residue | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen bond | C2-carbonyl | Y3127.35, Y3137.36 | 17.6 |
| Hydrogen bond | C4-carbonyl | C210ECL2 | 94.1 |
| Hydrogen bond | C1-carbonyl | Y3127.35 | 79.0 |
| Hydrogen bond | C17-carbonyl | Q1152.60 | 54.0 |
| Hydrophobic contact | C19 | V1182.63, Y3137.36 | 97.3 |
| Hydrophobic contact | C20 | I3167.39, Y3127.35 | 76.0 |
| Hydrophobic contact | Furan | I1353.29, L212ECL2; Y1393.33 | 99.5 |
| Residue | KOR | MOR | DOR | NOP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.63 | V118 | N129 | K108 | D110 |
| 6.55 | I294 | V302 | V281 | V283 |
| 7.35 | Y312 | W320 | L300 | L301 |
| 7.36 | Y313 | H321 | H301 | R302 |
| 7.39 | I316 | I324 | I304 | T305 |
| Ligand | Affinity (Ki) [nM] | Ki [ligand]/Ki [SalA] | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 (SalB) | 155 ± 23 c | 119 | [38] |
| >10,000 a | - | [72] | |
| 111 ± 12 c | 85 | [71] | |
| 155 ± 23 c | 119 | [73] | |
| 280 ± 20 d | 147 | [47] | |
| >10,000 b | - | [68] | |
| 3 | >10,000 a | - | [72] |
| 4 | >10,000 a | - | [72] |
| >10,000 c | - | [71] | |
| 5 | 17.6 ± 3.1 c | 14 | [73] |
| 6 | 0.32 ± 0.02 c | 0.133 | [69] |
| 3.13 ± 0.40 b | 0.423 | [70] | |
| 7 (RB-64) | 0.59 ± 0.21 b | 0.328 | [55] |
| 39 ± 11 c | 2 | [55] | |
| 0.6 ± 0.2 b | 0.097 | [68] | |
| 8 | >10,000 c | - | [74] |
| >1000 c | - | [58] | |
| >1000 c | - | [59] | |
| 9 | >10,000 c | - | [73] |
| 10 | 28.5 ± 0.9 c | 22 | [58] |
| 11 | >1000 c | - | [58] |
| 12 | 3400 ± 150 d | 1789 | [42] |
| 13 | 55 ± 23 c | 22 | [41] |
| 14 | 40 ± 1 b | 5 | [75] |
| 15 | 2.9 ± 0.3 c | 1 | [41] |
| 3.0 ± 0.2 d | 2 | [42] | |
| 16 | >8000 b | - | [76] |
| 17 | 6 ± 1 b | 2 | [77] |
| 18 | 18 ± 2 b | 5 | [77] |
| 19 | 1125 ± 365 b | 281 | [77] |
| Interaction | Functional Group | Residue | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen bond | C2-carbonyl | Y3137.36 (Y3127.35) | 22.2 |
| Hydrogen bond | C2-thiocyanate | Y3137.36 | 8.6 |
| Hydrogen bond | C4-carbonyl | C210ECL2 | 93.9 |
| Hydrogen bond | C1-carbonyl | Y3127.35 | 80.1 |
| Hydrogen bond | C17-carbonyl | Q1152.60 | 57.4 |
| Hydrophobic contact | C19 | V1182.63 | 94.4 |
| Hydrophobic contact | C20 | I3167.39 | 51.7 |
| Hydrophobic contact | Furan | I1353.29, L212ECL2; Y1393.33 | 99.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puls, K.; Wolber, G. Solving an Old Puzzle: Elucidation and Evaluation of the Binding Mode of Salvinorin A at the Kappa Opioid Receptor. Molecules 2023, 28, 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020718
Puls K, Wolber G. Solving an Old Puzzle: Elucidation and Evaluation of the Binding Mode of Salvinorin A at the Kappa Opioid Receptor. Molecules. 2023; 28(2):718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020718
Chicago/Turabian StylePuls, Kristina, and Gerhard Wolber. 2023. "Solving an Old Puzzle: Elucidation and Evaluation of the Binding Mode of Salvinorin A at the Kappa Opioid Receptor" Molecules 28, no. 2: 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020718
APA StylePuls, K., & Wolber, G. (2023). Solving an Old Puzzle: Elucidation and Evaluation of the Binding Mode of Salvinorin A at the Kappa Opioid Receptor. Molecules, 28(2), 718. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28020718








