Nitric Acid-Treated Blue Coke-Based Activated Carbon’s Structural Characteristics and Its Application in Hexavalent Chromium-Containing Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
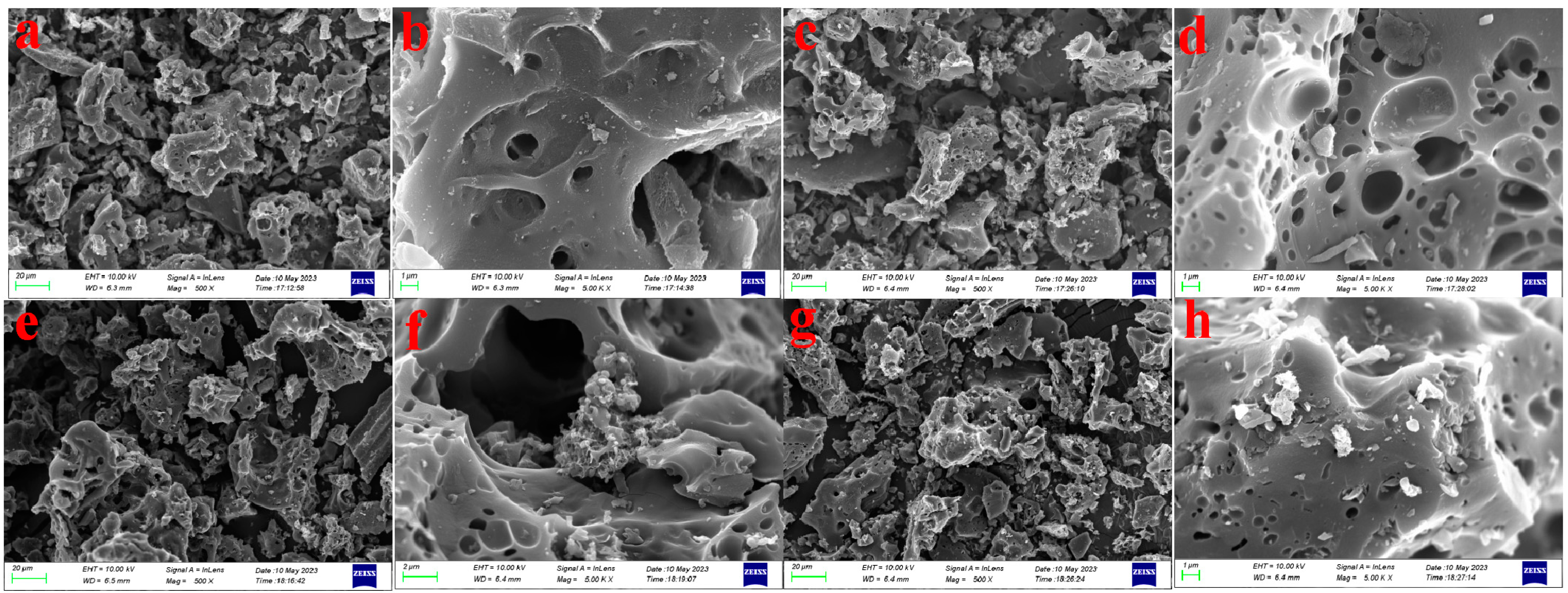
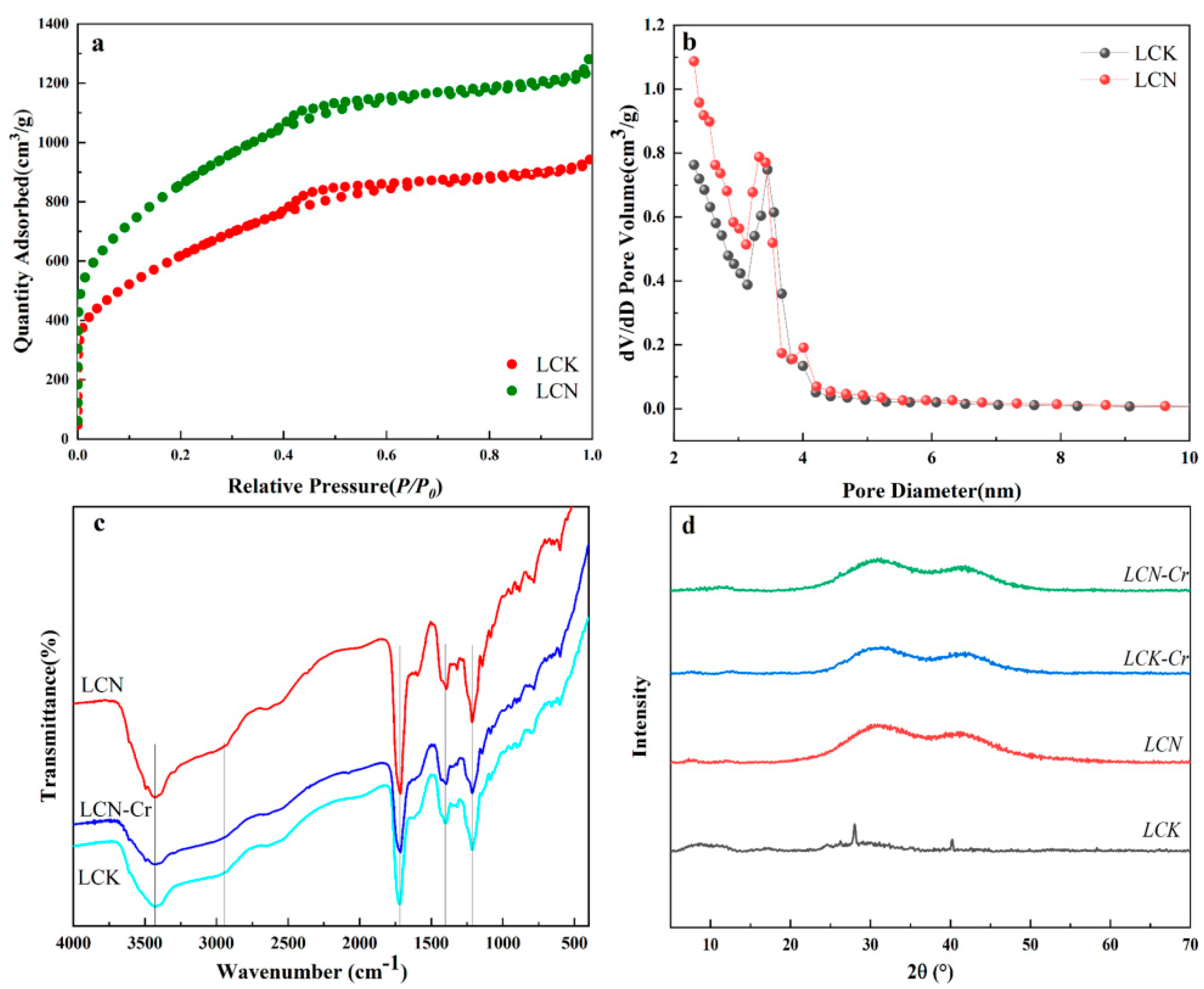
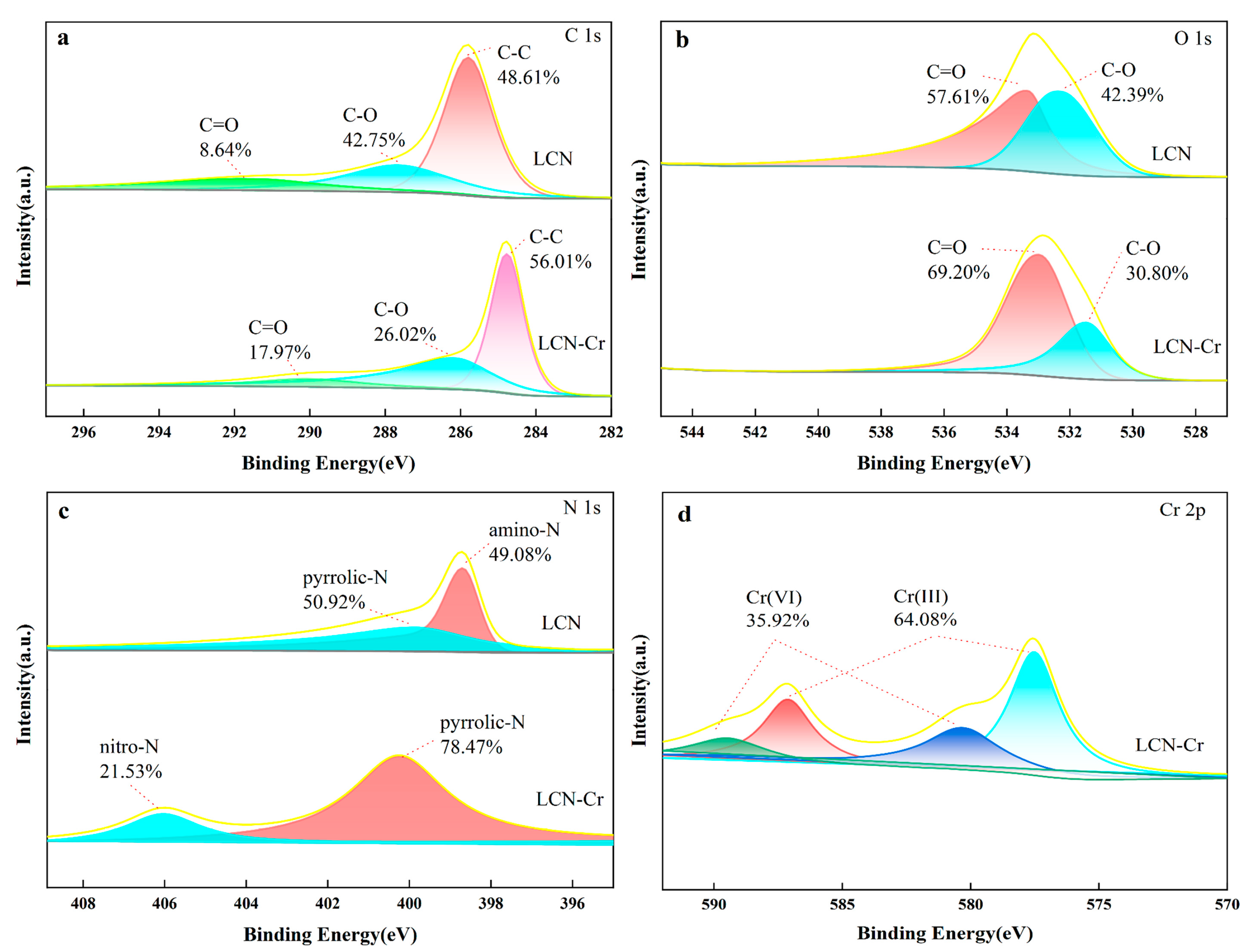
2.1. Sample Characterization
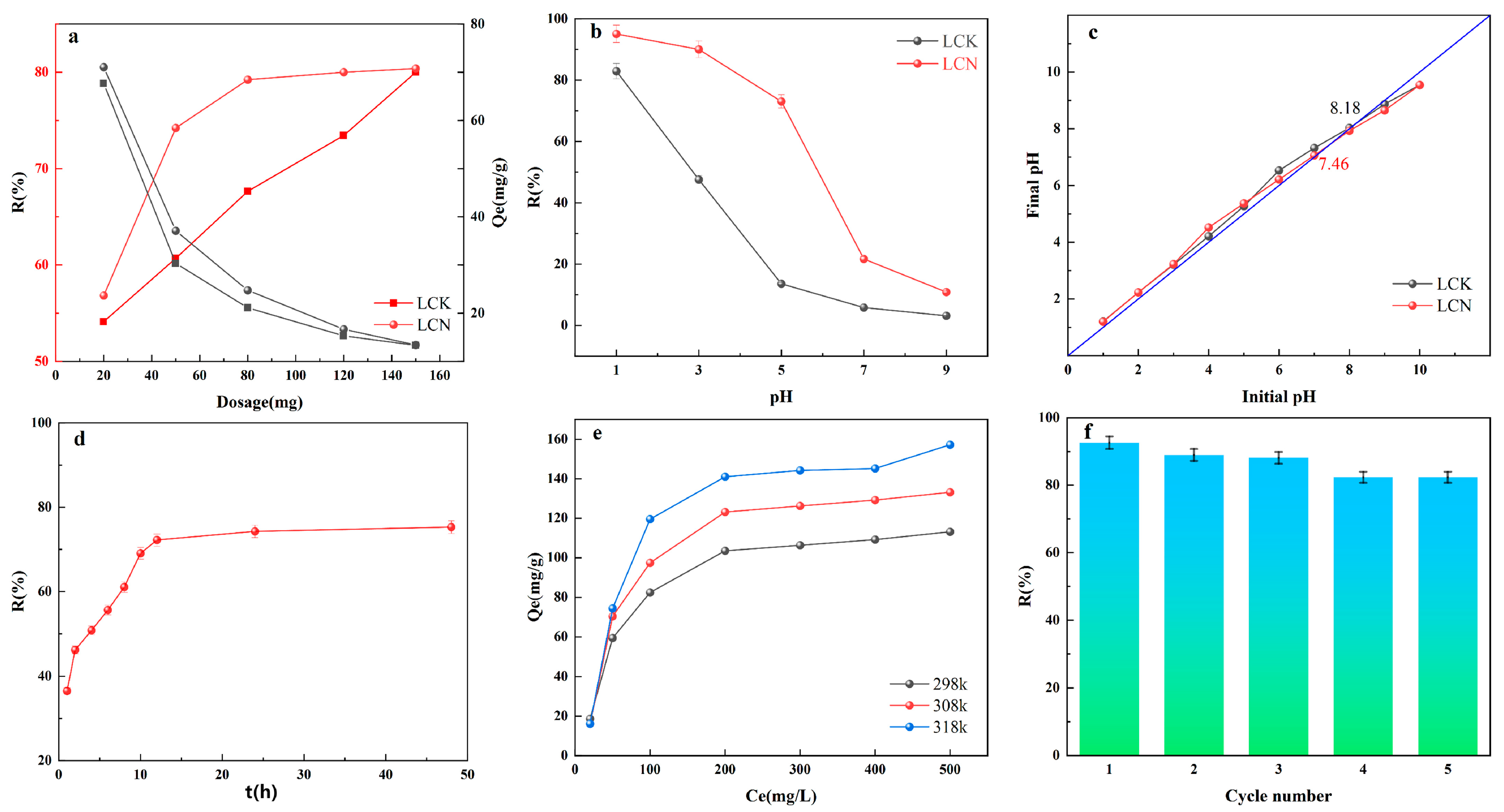
2.2. Adsorptive Property
2.3. Impact of Contact Time and Kinetic Analysis
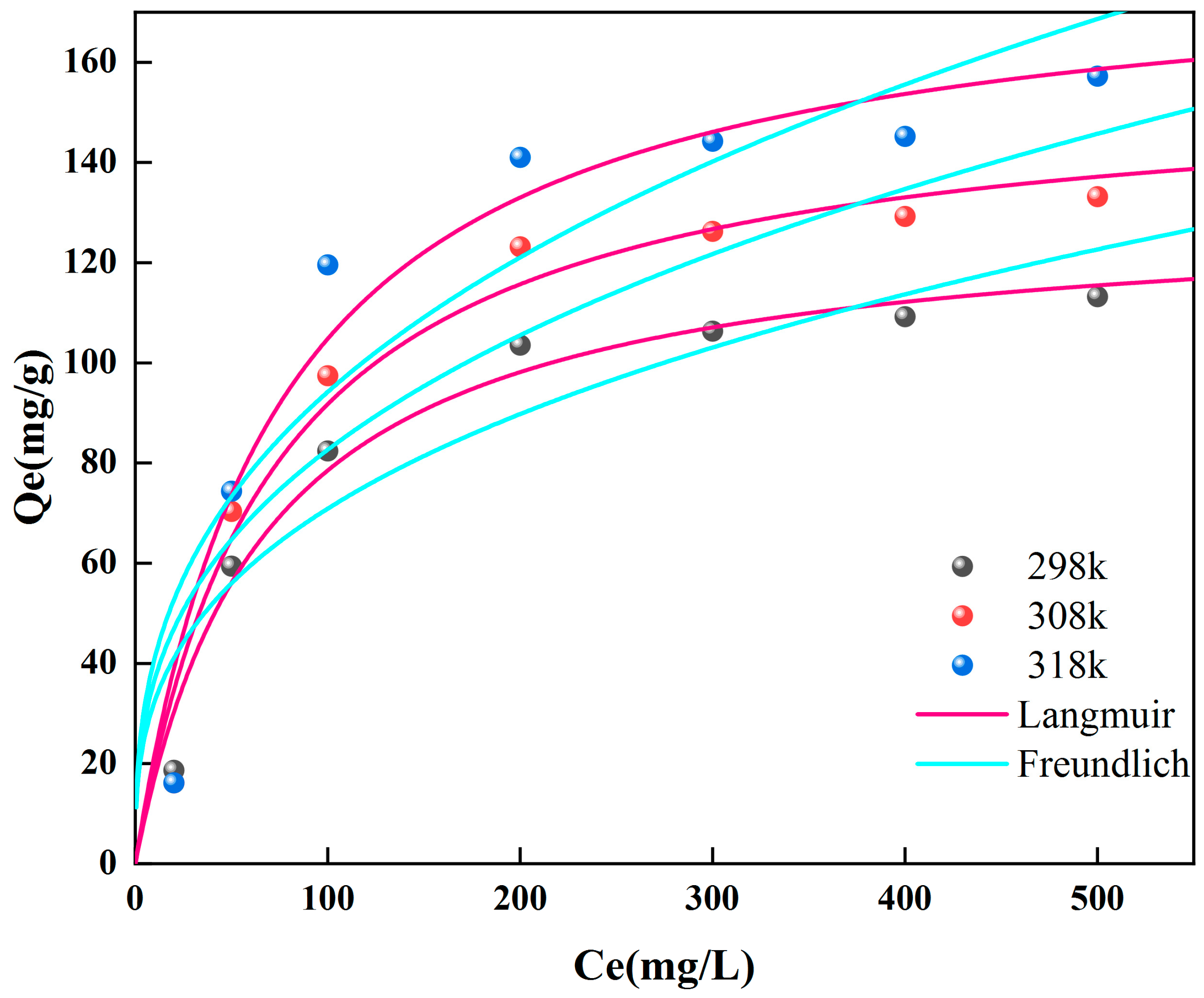
2.4. Effect of Concentration and Adsorption Isotherm
2.5. Temperature and Adsorption Thermodynamics
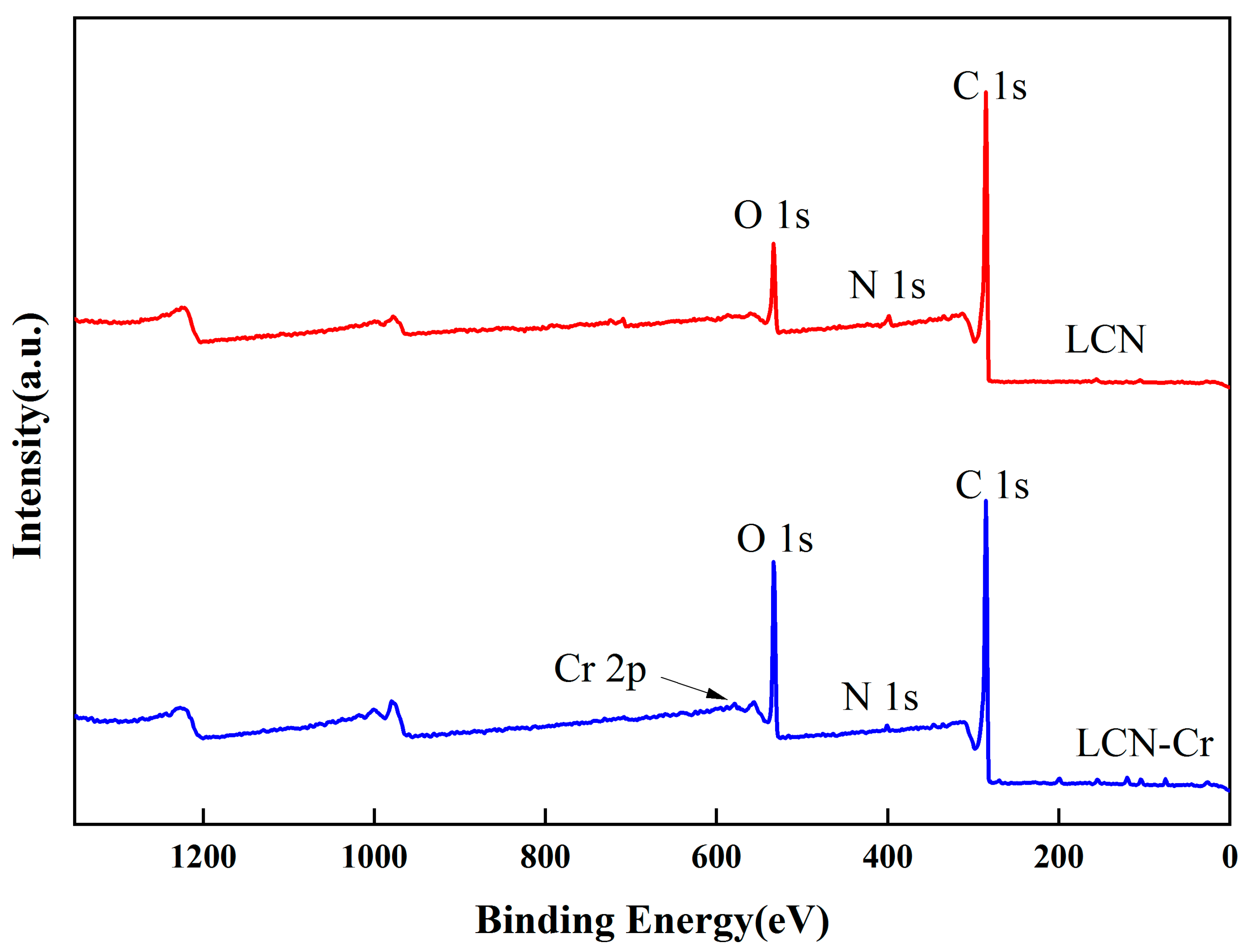
2.6. Adsorbent Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Sorbent Preparation
3.2.1. The Preparation of Alkali-Modified Blue Coke
3.2.2. The Preparation of the Blue Coke Powder through a Two-Step Acid-Base Modification
3.3. Material Characterization
3.4. Adsorption Experiments
3.5. Material Reusability Experiment
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Li, Y.; Cai, G. A novel 3D superelastic polyethyleneimine functionalized chitosan aerogels for selective removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solution: Performance and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kassimi, A.; Naboulsi, A.; Yazid, H.; Achour, Y.; Regti, A.; El Himri, M.; Lazar, S.; Laamari, R.; El Haddad, M. Adsorption of chromium (VI) on low-cost adsorbents derived from agricultural waste material: A comparative study and experimental design. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaraj, M.; Srinivasan, N.R.; Assefa, G.; Adugna, A.T.; Kebede, M. Facile development of sunlit ZnO nanoparticles-activated carbon hybrid from pernicious weed as an operative nano-adsorbent for removal of methylene blue and chromium from aqueous solution: Extended application in tannery industrial wastewater. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, R.; Aslam, Z.; Abbas, A.; Ahmad, W.; Ramzan, N.; Shawabkeh, R. Adsorptive potential of Acacia Nilotica based adsorbent for Chromium(VI) from an aqueous phase. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Tan, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, K.; Peng, C.; Xiao, X.; Huang, W. Enhanced electron transfer pathway of zero-valent iron particles immobilized on coconut shell derived carbon for prolonged Cr (VI) removal. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2023, 132863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, B.; Wen, R.; Wang, K.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, K.; Tao, H. Efficient removal of aqueous hexavalent chromium by activated carbon derived from Bermuda grass. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 560, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yu, L.; Ma, H.; Zhou, F.; Yang, K.; Wu, G. Corn stalk-based activated carbon synthesized by a novel activation method for high-performance adsorption of hexavalent chromium in aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 578, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, N.; Aslam, Z.; Shawabkeh, R.A.; Baig, N.; Aslam, U.; Ihsanullah, I.; Khan, S. Decolorization of multicomponent dye-laden wastewater by modified waste fly ash: A parametric analysis for an anionic and cationic combination of dyes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 77165–77180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, M.; Das, A.; Bose, S. Development of copper-iron bimetallic nanoparticle impregnated activated carbon derived from coconut husk and its efficacy as a novel adsorbent toward the removal of chromium (VI) from aqueous solution. Water Environ. Res. 2021, 93, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ren, Q.; Bai, X.; Liu, B.; Jing, X.; Lan, X. Effect of direct coal liquefaction residue on the properties of fine blue-coke-based activated coke. Green Process. Synth. 2022, 11, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y. Effect of acidic surface functional groups on Cr (VI) removal by activated carbon from aqueous solution. Rare Met. 2010, 29, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitthikhankaew, R.; Chadwick, D.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Laosiripojana, N. Performance of Sodium-Impregnated Activated Carbons toward Low and High Temperature H2S Adsorption. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2014, 201, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Wang, Y.; Tian, X.; Jiang, Z.; Deng, F.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y. KOH-activated porous biochar with high specific surface area for adsorptive removal of chromium (VI) and naphthalene from water: Affecting factors, mechanisms and reusability exploration. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, G.; Gao, X. Research on the performance of modified blue coke in adsorbing hexavalent chromium. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benaddi, H.; Bandosz, T.J.; Jagiello, J.; Schwarz, J.A.; Rouzaud, J.N.; Legras, D.; Béguin, F. Surface functionality and porosity of activated carbons obtained from chemical activation of wood. Carbon 2000, 38, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulina, S.; Mentari, V.A. Comparison of Functional Group and Morphological Surface of Activated Carbon from Oil Palm Fronds Using Phosphoric Acid (H3PO4) and Nitric Acid (HNO3) as an Activator. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering, Medan, Indonesia, 16–17 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, C.; Dong, L.; Jia, B.; Chen, G. Eupatorium adenophorum derived adsorbent by hydrothermal-assisted HNO3 modification and application to Pb2+ adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, G.; Deng, Q.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y. Synthesis, characterization and removal performance of Cr (VI) by orange peel-based activated porous biochar from water. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2023, 193, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, R.; Arjmand, O.; Tehrani, N.H.M.H.; Ghorbani, A.; Rashidi, A.; Esrafili, M.D.; Hamyali, H. Anthracite based activated carbon impregnated with HMTA as an effectiveness adsorbent could significantly uptake gasoline vapors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, F.F.; Marrakchi, F.; Barati, B.; Yuan, C.; Cao, B.; Wang, S. Highly efficient adsorption of Bisphenol A using NaHCO3/CO2 activated carbon composite derived from shrimp shell@cellulose. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 68724–68734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.E.; Ibrahim, G.A.A. Cr (VI) and doxorubicin adsorptive capture by a novel bionanocomposite of Ti-MOF@TiO2 incorporated with watermelon biochar and chitosan hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya-Roncancio, S.; Torres-Ceron, D.A.; Velasquez-Tamayo, J.P.; Mercado, D.F.; Arellano-Ramirez, I.D.; Restrepo-Parra, E. Experimental and theoretical study of Cr (VI) photoreduction and adsorption onto SO42−doped TiO2 obtained by plasma electrolytic oxidation. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 31, 101620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, D.; Cheng, R.; Zheng, M.; Sun, Y.; Ye, J.; Zhou, B.; Li, J.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, D. Fabrication of a carbon cloth-based FeS nanosystem for simultaneous removal of Cr (VI) and microplastics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 323, 124432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Huang, Y.; Liu, H. Fabrication of Chitin microspheres supported sulfidated nano zerovalent iron and their performance in Cr (VI) removal. Chemosphere 2023, 338, 139609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M.; Abd El-Monaem, E.M.; Abd El-Latif, M.M.; El-Subruiti, G.M.; Eltaweil, A.S. Facile fabrication of novel magnetic ZIF-67 MOF@aminated chitosan composite beads for the adsorptive removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 265, 118084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, H.; Zeng, C.; Zhao, C.; Zhan, H. Iron oxides decorated graphene oxide/chitosan composite beads for enhanced Cr (VI) removal from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, E.d.S.; Gorza, F.D.S.; Pedro, G.d.C.; Maciel, B.G.; Silva, R.J.d.; Ratkovski, G.P.; Melo, C.P.d. (Maghemite/Chitosan/Polypyrrole) nanocomposites for the efficient removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous media. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Xie, Z.; Ye, H.; Li, W.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y. Magnetic cross-linked chitosan for efficient removing anionic and cationic dyes from aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 193, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xue, Q.; Chen, H.; Guo, H.; Carroll, K.C.; Wang, S. Mechanistic insight into Cr (VI) retention by Si-containing ferrihydrite. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 139, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, B.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, P.; Su, R.; Liu, D. Nano iron oxides impregnated chitosan beads towards aqueous Cr (VI) elimination: Components optimization and performance evaluation. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Guan, Z.; Li, J.; Ao, M.; Sun, S.; Deng, T.; Wang, S.; Tang, Y.; Lin, Q.; Ni, Z.; et al. Nano zero-valent iron enhances the absorption and transport of chromium in rice (Oryza sativa L.): Implication for Cr risks management in paddy fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, C.; Shuai, K.; Hashan, D.; Liu, J.; She, D. Performance and mechanism of starch-based porous carbon capture of Cr (VI) from water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awais; Ali, N.; Khan, A.; Asiri, A.M.; Kamal, T. Potential application of in-situ synthesized cobalt nanoparticles on chitosan-coated cotton cloth substrate as catalyst for the reduction of pollutants. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Zhao, S.; Wei, K.; Sun, H.; Zhang, L. Precise decomplexation of Cr(III)-EDTA and in-situ Cr(III) removal with oxalated zero-valent iron. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2023, 330, 122619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; He, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Song, Z. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide/chitosan composite aerogel with high adsorption performance for Cr (VI) by a new crosslinking route. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 625, 126832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Zhang, N.; Hu, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Y. Preparation of a novel citric acid-crosslinked Zn-MOF/chitosan composite and application in adsorption of chromium(VI) and methyl orange from aqueous solution. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 258, 117644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Zhao, H.; Gao, L.; Qin, Z.; Ma, J.; Han, Y.; Jiao, T. Preparation of carboxymethyl chitosan/phytic acid composite hydrogels for rapid dye adsorption in wastewater treatment. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 628, 127355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Dai, H.; Zhan, P.; Tan, C.; Ning, Z.; Hu, F.; Xu, X.; Peng, X. Rapid reduction of aqueous Cr (VI) by oxalic acid on N-doped lignin charcoal: A significant contribution of structural defects and electronic shuttle effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, X.; Li, M. Removal of Cr (VI) by glutaraldehyde-crosslinked chitosan encapsulating microscale zero-valent iron: Synthesis, mechanism, and longevity. J. Environ. Sci. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masinga, T.; Moyo, M.; Pakade, V.E. Removal of hexavalent chromium by polyethyleneimine impregnated activated carbon: Intra-particle diffusion, kinetics and isotherms. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Xi, M.; Jiang, Z. Removal/adsorption mechanisms of Cr (VI) and natural organic matter by nanoscale zero-valent iron-loaded biochar in their coexisting system. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J. Research on the removal of Cr (VI) ions from wastewater by Mg/Al-layered double oxides. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 29, 101466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicomel, N.R.; Otero-Gonzalez, L.; Folens, K.; Mees, B.; Hennebel, T.; Du Laing, G. Selective and enhanced nickel adsorption from sulfate- and calcium-rich solutions using chitosan. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 276, 119283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavithra, S.; Thandapani, G.; Sugashini, S.; Sudha, P.N.; Alkhamis, H.H.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Almutairi, M.H. Batch adsorption studies on surface tailored chitosan/orange peel hydrogel composite for the removal of Cr (VI) and Cu(II) ions from synthetic wastewater. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamali, M.; Akbari, A. Facile fabrication of magnetic chitosan hydrogel beads and modified by interfacial polymerization method and study of adsorption of cationic/anionic dyes from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Feng, X. Selective removal of Cr (VI) by tannic acid and polyethyleneimine modified zero-valent iron particles with air stability. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 132018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, L.; Lashanizadegan, A.; Sharififard, H. Chestnut oak shells activated carbon: Preparation, characterization and application for Cr (VI) removal from dilute aqueous solutions. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 185, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gao, P.; Cui, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, F.; Cheng, J. Preparation and Cr (VI) removal performance of corncob activated carbon. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20743–20755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, A.; Ocampo, R.; Giraldo, S.; Padilla, E.; Florez, E.; Acelas, N. Removal of Cr (VI) from an aqueous solution using an activated carbon obtained from teakwood sawdust: Kinetics, equilibrium, and density functional theory calculations. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploychompoo, S.; Liang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wei, C.; Luo, H. Fabrication of Zn-MOF-74/polyacrylamide coated with reduced graphene oxide (Zn-MOF-74/rGO/PAM) for As(III) removal. Phys. e-Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2021, 125, 114377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Luo, H.; Cai, Y.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H. Selective removal of total Cr from a complex water matrix by chitosan and biochar modified-FeS: Kinetics and underlying mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Fu, L.; Zhang, L. The one-step synthesis of a novel metal-organic frameworks for efficient and selective removal of Cr (VI) and Pb(II) from wastewater: Kinetics, thermodynamics and adsorption mechanisms. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 640, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Sun, T.; Jia, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, X. The performance and mechanism of Cr (VI) adsorption by biochar derived from Potamogeton crispus at different pyrolysis temperatures. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 167, 105662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, M.A.O.; Frade, T.; Bordonhos, M.; Castellino, M.; Bocchini, S.; Pinto, M.L. N-doped sponge-like biochar: A promising CO2 sorbent for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 gas separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Precursor | Activating Agent | Maximal Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chestnut shells | H3PO4 | 85.47 | [47] |
| Corncob | H3PO4 | 9.62 | [48] |
| Acacia nilotica (keekar) sawdust | HCl | 6.34 | [5] |
| Teakwood sawdust | KOH | 72.46 | [49] |
| Corn stalk | KOH | 89.5 | [7] |
| Coconut husk | Copper–iron bimetallic nanoparticle-impregnated | 173.9 | [9] |
| Medlar | H3PO4 | 34.12 | [2] |
| Cucumis melo | H3PO4 | 54.28 | [2] |
| Blue coke | KOH | 181.96 | This |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Luoyang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gao, X.; Li, J.; Li, X.; He, M. Nitric Acid-Treated Blue Coke-Based Activated Carbon’s Structural Characteristics and Its Application in Hexavalent Chromium-Containing Wastewater Treatment. Molecules 2023, 28, 7986. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247986
Wang W, Wang H, Luoyang Y, Zhang G, Gao X, Li J, Li X, He M. Nitric Acid-Treated Blue Coke-Based Activated Carbon’s Structural Characteristics and Its Application in Hexavalent Chromium-Containing Wastewater Treatment. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):7986. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247986
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wencheng, Hua Wang, Yunxuan Luoyang, Guotao Zhang, Xuchun Gao, Jian Li, Xia Li, and Miao He. 2023. "Nitric Acid-Treated Blue Coke-Based Activated Carbon’s Structural Characteristics and Its Application in Hexavalent Chromium-Containing Wastewater Treatment" Molecules 28, no. 24: 7986. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247986
APA StyleWang, W., Wang, H., Luoyang, Y., Zhang, G., Gao, X., Li, J., Li, X., & He, M. (2023). Nitric Acid-Treated Blue Coke-Based Activated Carbon’s Structural Characteristics and Its Application in Hexavalent Chromium-Containing Wastewater Treatment. Molecules, 28(24), 7986. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28247986






