Construction and Activity Study of a Natural Antibacterial Patch Based on Natural Active Substance-Green Porous Structures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
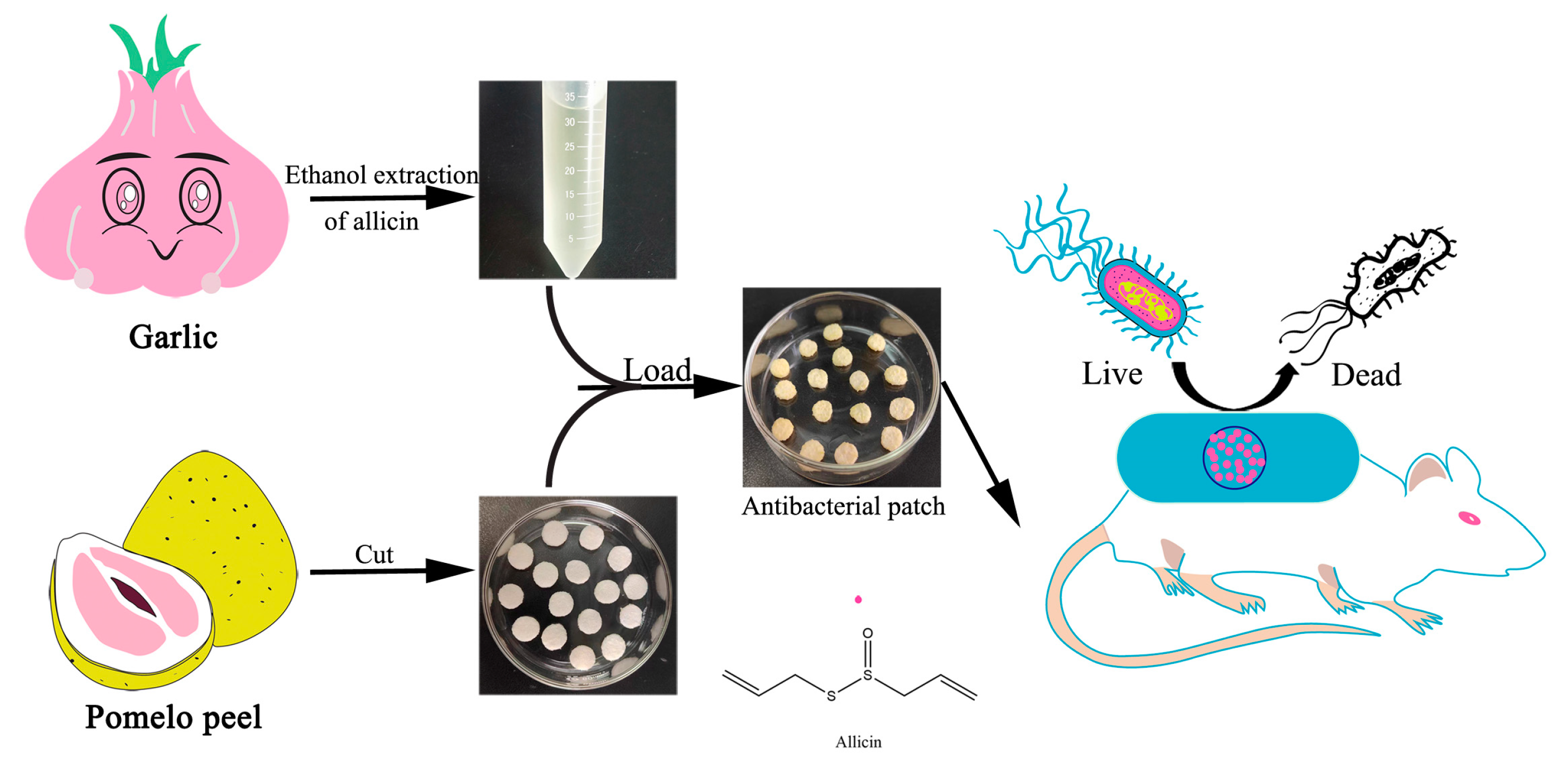
2.1. Extraction of Allicin
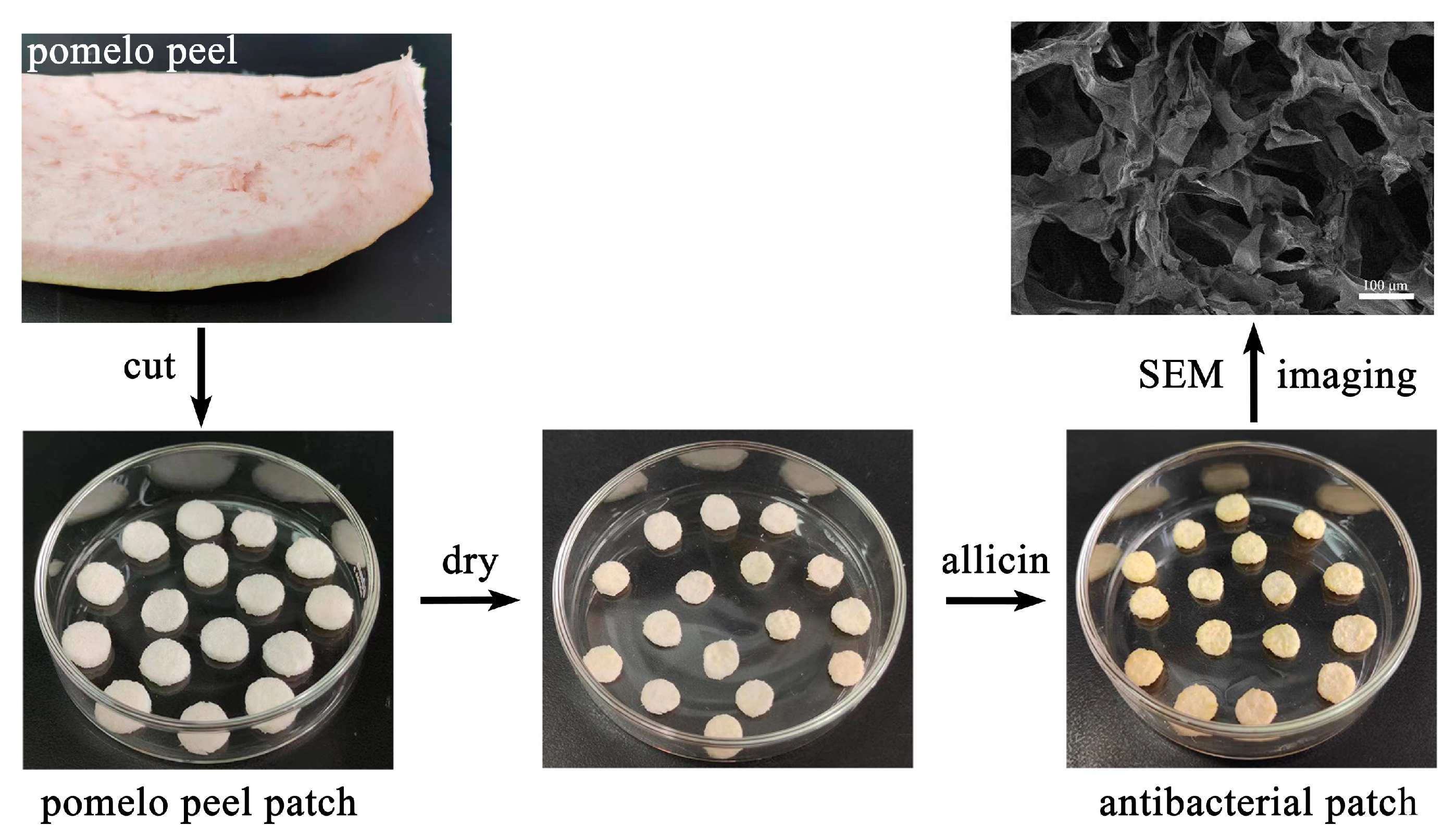
2.2. Preparation of Antibacterial Patches
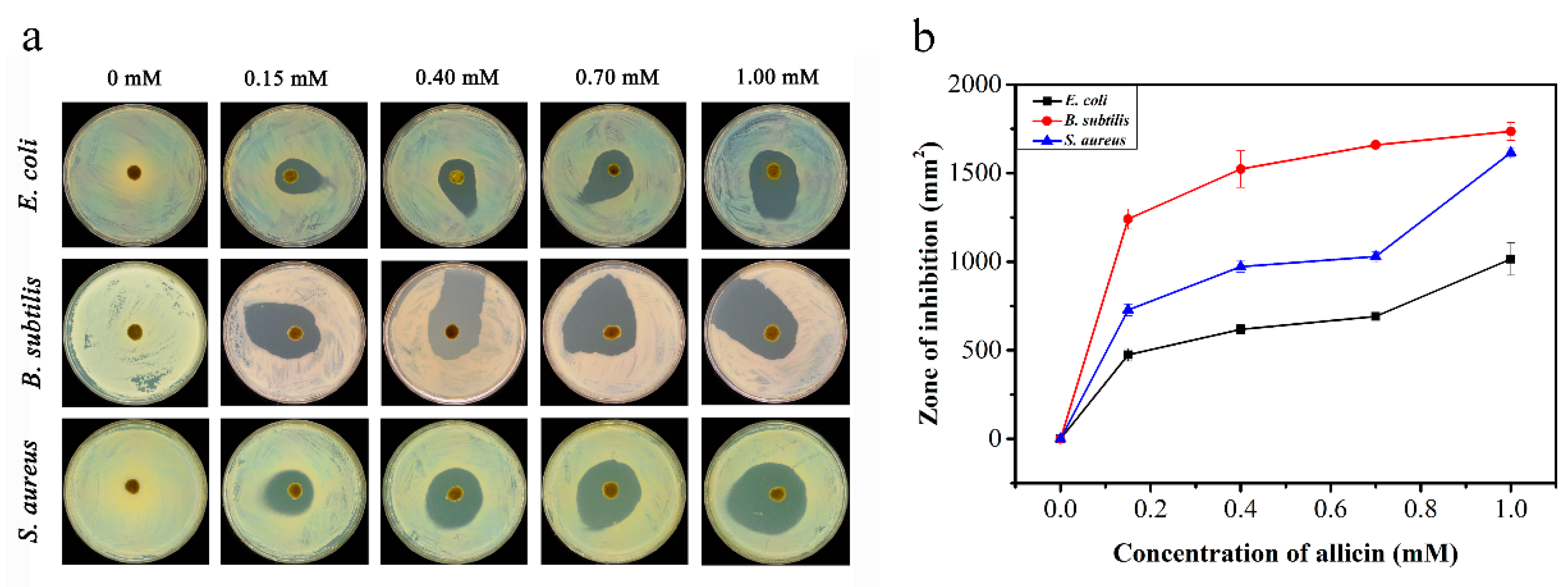
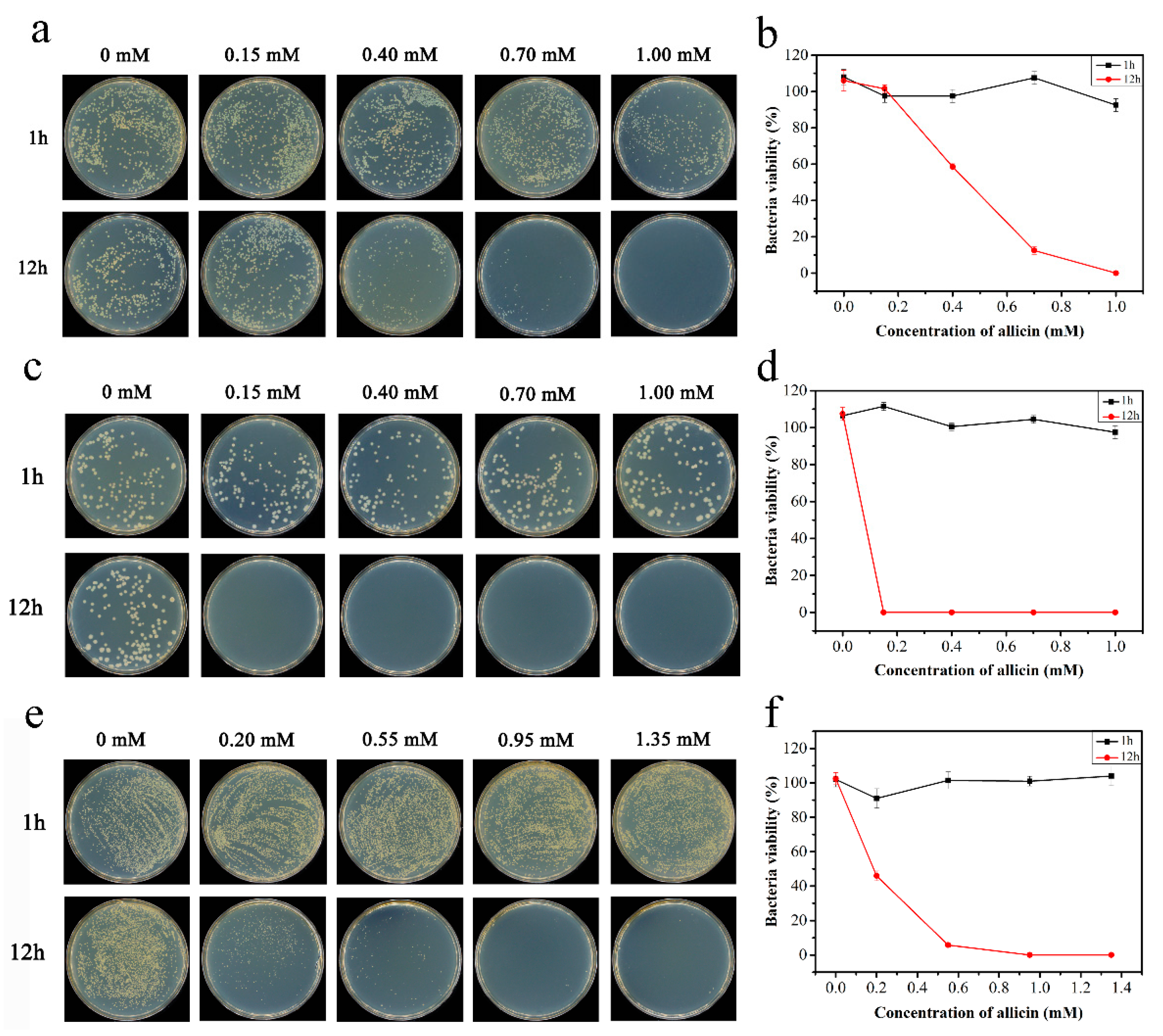
2.3. Antibacterial Activity
2.3.1. Bacteriostatic Ring Test
2.3.2. Plate Counting Method
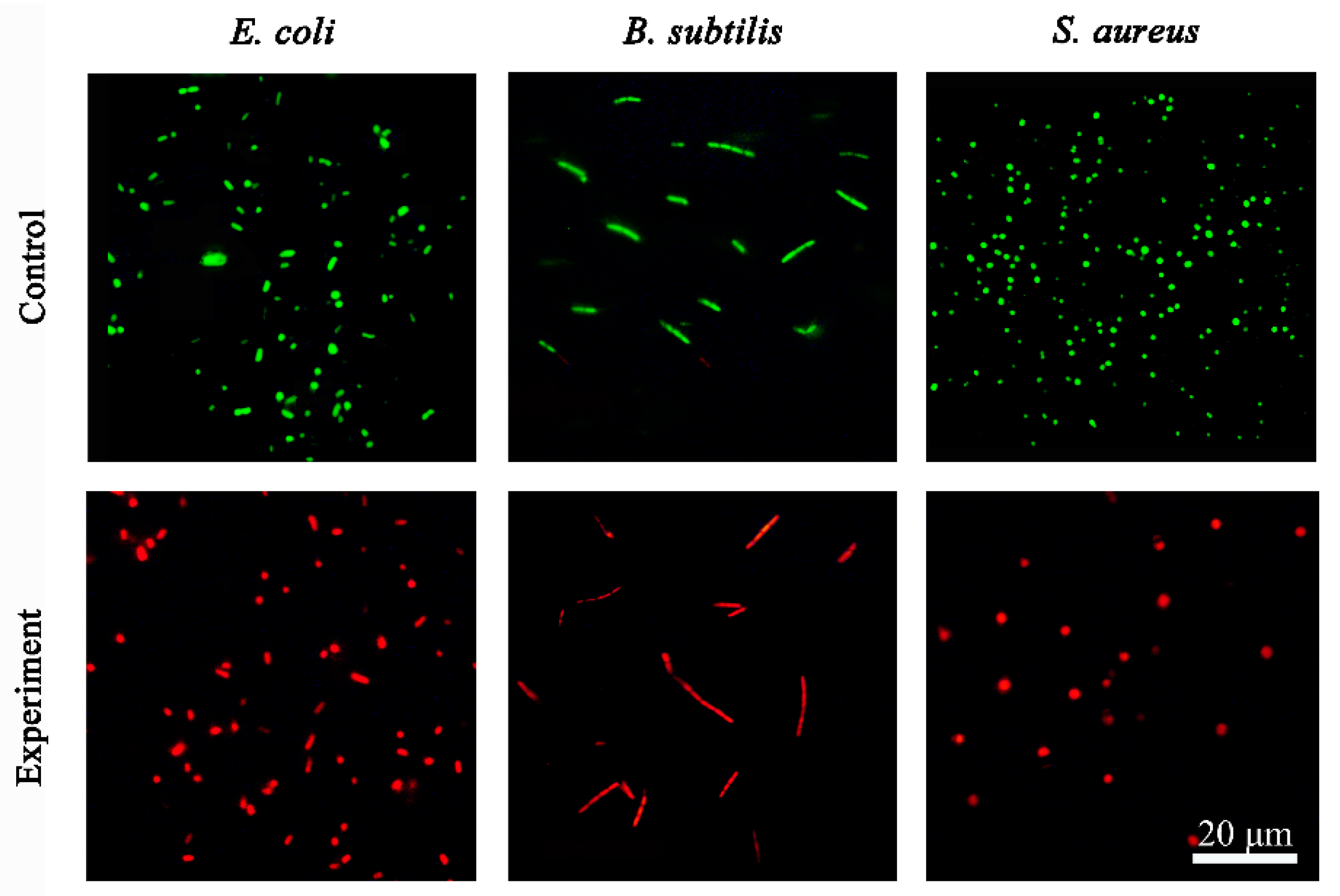
2.4. Live/Dead Staining
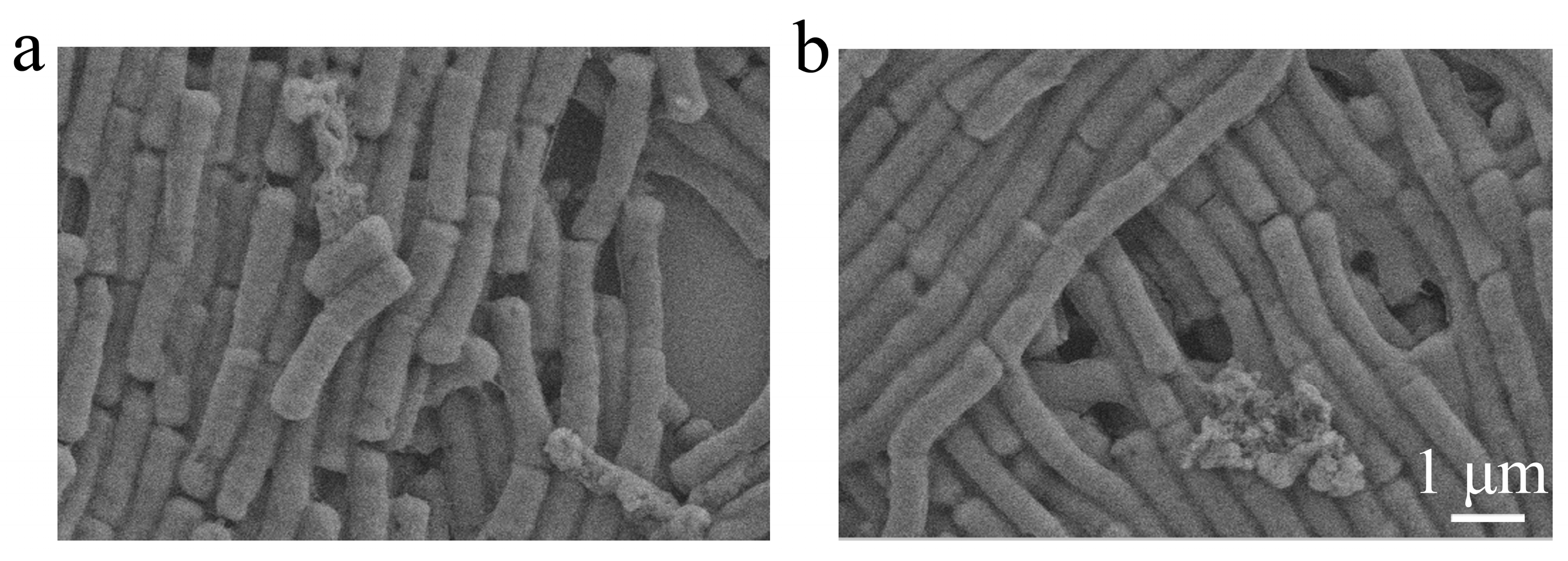
2.5. Bacterial Morphological Changes
2.6. Cytotoxicity Study
2.7. Therapeutic Effect against Mouse Wound Infection
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Measurement
3.2. Allicin Extract
3.3. Quantitative Determination of Allicin
3.4. Preparation of Pomelo Peel Patches
3.5. Water Absorption of Pomelo Peel
3.6. Antibacterial Activity
Bacterial Culture Medium Configuration
- Agar plating method
- 2.
- Plate counting method
3.7. Live/Dead Staining
3.8. Morphology of Bacteria
3.9. Cytotoxicity Study
3.10. In Vivo Antibacterial Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Fuchtbauer, S.; Mousavi, S.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. Antibacterial properties of capsaicin and its derivatives and their potential to fight antibiotic resistance—A literature survey. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2021, 11, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, N.; Gayen, K.; Ghosh, S.; Bhunia, D.; Kirkham, S.; Sen, S.K.; Ghosh, S.; Hamley, I.W.; Banerjee, A. Amphiphilic Peptide-Based Supramolecular, Noncytotoxic, Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Antibacterial Activity. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 3621–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Ai, J.Y.; Cai, H.H.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.L.; Li, Z.; Dai, F.Y. Antibacterial gauze based on the synergistic antibacterial mechanism of antimicrobial peptides and silver nanoparticles. J. Polym. Res. 2021, 28, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernousova, S.; Epple, M. Silver as Antibacterial Agent: Ion, Nanoparticle, and Metal. Angew. Chem. -Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 1636–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, M.; Su, S.; He, Y.; Huang, Q.; Hu, W.B.; Li, D.; Fan, C.H.; Lee, S.T. Long-Term Antimicrobial Effect of Silicon Nanowires Decorated with Silver Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyun, D.G.; Yoon, H.S.; Chung, H.Y.; Choi, H.J.; Thambi, T.; Kimd, B.S.; Lee, D.S. Evaluation of AgHAP-containing polyurethane foam dressing for wound healing: Synthesis, characterization, in vitro and in vivo studies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 7752–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, P.M.; Narchonai, G.; Dhanasekaran, D.; Ranjani, A.; Thajuddin, N. Mycosynthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of AgNPs against multidrug resistant (MDR) bacterial pathogens of female infertility cases. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawson, L.D.; Gardner, C.D. Composition, Stability, and Bioavailability of Garlic Products Used in a Clinical Trial. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 6254–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahman, M.S. Allicin and other functional active components in garlic: Health benefits and bioavailability. Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 10, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, H.; Suma, K.; Origuchi, K.; Kumagai, H.; Seki, T.; Ariga, T. Biological and chemical stability of garlic-derived allicin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 4229–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankri, S.; Mirelman, D. Antimicrobial properties of allicin from garlic. Microbes Infect. 1999, 1, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakri, I.M.; Douglas, C.W.I. Inhibitory effect of garlic extract on oral bacteria. Arch. Oral Biol. 2005, 50, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, R.T.M.; Fawzi, E.M.; Alkhalf, M.I.; Alansari, W.S.; Aleya, L.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Anti-Inflammatory, Immunomodulatory, and Antioxidant Activities of Allicin, Norfloxacin, or Their Combination against Pasteurella multocida Infection in Male New Zealand Rabbits. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1780956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Metwally, D.M.; Al-Olayan, E.M.; Alanazi, M.; Alzahrany, S.B.; Semlali, A. Antischistosomal and anti-inflammatory activity of garlic and allicin compared with that of praziquantel in vivo. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, J.Y.; Yuen, A.C.; Chan, R.Y.; Chan, S.W. A review of the cardiovascular benefits and antioxidant properties of allicin. Phytother. Res. PTR 2013, 27, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyod, S.; Wu, W.K.; Ho, C.T.; Lu, K.H.; Liu, C.T.; Chu, Y.L.; Lai, Y.S.; Chen, W.C.; Lin, Y.E.; Lin, S.H.; et al. Diet Supplementation with Allicin Protects against Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Mice by Improving Anti-inflammation and Antioxidative Functions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 7104–7113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilic, D.P.; Nikolic, V.D.; Nikolic, L.B.; Stankovic, M.Z.; Stanojevic, L.P. Thermal Degradation, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of The Synthesized Allicin and Allicin Incorporated In Gel. Hem. Ind. 2010, 64, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, S.; Chin, V.K.; Wong, E.H.; Madhavan, P.; Tay, S.T.; Yong, P.V.C.; Chong, P.P. Review: Antimicrobial properties of allicin used alone or in combination with other medications. Folia Microbiol. 2020, 65, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, C.H.; Cai, J.; Zhang, W.; Qi, W.L.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Z.B.; Yang, Y. Broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, chemical composition and mechanism of action of garlic (Allium sativum) extracts. Food Control 2018, 86, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldberg, R.S.; Chang, S.C.; Kotik, A.N.; Nadler, M.; Neuwirth, Z.; Sundstrom, D.C.; Thompson, N.H. In vitro mechanism of inhibition of bacterial cell growth by allicin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1988, 32, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, J.; Hubbers, A.M.; Albrecht, F.; Leichert, L.I.O.; Slusarenko, A.J. Allicin, a natural antimicrobial defence substance from garlic, inhibits DNA gyrase activity in bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, K.C.; Viswanathan, R. Combined action of streptomycin and chloramphenicol with plant antibiotics against tubercle bacilli. I. Streptomycin and chloramphenicol with cepharanthine. II. Streptomycin and allicin. Antibiot. Chemother. 1955, 5, 24–27. [Google Scholar]
- Olad, A.; Eslamzadeh, M.; Katiraee, F.; Mirmohseni, A. Evaluation of in vitro anti-fungal properties of allicin loaded ion cross-linked poly (AA-co-AAm)/PVA/Cloisite 15A Nanocomposite hydrogel films as wound dressing materials. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.T.; Karthika, M.; Balaji, U.; Muthappan, A.; Subramanian, B. Functional finishing of medical fabrics using CeO2/allicin nanocomposite for wound dressings. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 695, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Ding, L.X.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, S.Q.; Lu, X.H.; Wang, H.H. Nitrogen-doped porous carbon derived from residuary shaddock peel: A promising and sustainable anode for high energy density asymmetric supercapacitors. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Ye, F.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G.H. Utilization of pomelo peels to manufacture value-added products: A review. Food Chem. 2021, 351, 129247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Peng, X.; Feng, N.; Yan, L.K.; Liu, Q.Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, J.C.; Wang, W.Q.; Chen, T. Converting Pomelo Peel into Eco-friendly and Low-Consumption Photothermic Biomass Sponge toward Multifunctioal Solar-to-Heat Conversion. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5328–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Lv, P.M.; Yang, L.M.; Xing, S.Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, Z.M. Biodiesel synthesis over biochar-based catalyst from biomass waste pomelo peel. Energy Convers. Manag. 2018, 160, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Two-Dimensional Metal–Organic Framework/Enzyme Hybrid Nanocatalyst as a Benign and Self-Activated Cascade Reagent for in Vivo Wound Healing. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 5222–5230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlinghaus, J.; Albrecht, F.; Gruhlke, M.C.H.; Nwachukwu, I.D.; Slusarenko, A.J. Allicin: Chemistry and Biological Properties. Molecules 2014, 19, 12591–12618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavallito, C.J.; Bailey, J.H. Allicin, the Antibacterial Principle of Allium sativum. I. Isolation, Physical Properties and Antibacterial Action. JOurnal Am. Chem. Soc. 1944, 66, 1950–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, A.; Seebeck, E. Chemical investigations on alliin, the specific principle of garlic. Adv. Enzymol. Relat. Subj. Biochem. 1951, 11, 377–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cavallito, C.J.; Bailey, J.H.; Buck, J.S. The Antibacterial Principle of Allium sativum. III. Its Precursor and “Essential Oil of Garlic”1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1945, 67, 1032–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallock-Richards, D.; Doherty, C.J.; Doherty, L.; Clarke, D.J.; Place, M.; Govan, J.R.W.; Campopiano, D.J. Garlic Revisited: Antimicrobial Activity of Allicin-Containing Garlic Extracts against Burkholderia cepacia Complex. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Erande, K.B.; Bhambar, R.S. Garlic Powder Preparation Methodology to Improve Allicin Content. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2019, 10, 4717–4723. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, H.; Watanabe, K.; Suma, K.; Origuchi, K.; Matsufuji, H.; Seki, T.; Ariga, T. Antibacterial Potential of Garlic-Derived Allicin and Its Cancellation by Sulfhydryl Compounds. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1948–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cirkovic, I.; Jovalekic, M.; Jegorovic, B. In Vitro antibacterial activity of garlic and synergism between garlic and antibacterial drugs. Arch. Biol. Sci. 2012, 64, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Li, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Fei, X.; Tian, J.; Li, Y. A reusable ionic liquid-grafted antibacterial cotton gauze wound dressing. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 7598–7612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Hu, X.; Chao, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.; Yan, X.; Yang, F.; Li, Q. Quantitation of Allicin in Garlic-based Products: Comparisons among Spectrophotometry, GC and HPLC. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 9, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Sen, D.; Bhattacharjee, C. In vitro antibacterial effect analysis of stabilized PEGylated allicin-containing extract from Allium sativum in conjugation with other antibiotics. Process Biochem. 2019, 87, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Zhu, W.S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Q.S.; Jiao, L.Z.; Qiu, H.; Bing, W.; Zhang, Z.J. A biodegradable and near-infrared light-activatable photothermal nanoconvertor for bacterial inactivation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 3834–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Construction and Activity Study of a Natural Antibacterial Patch Based on Natural Active Substance-Green Porous Structures. Molecules 2023, 28, 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031319
Gao X, Zhou Y, Gu J, Liu X, Zhang Z. Construction and Activity Study of a Natural Antibacterial Patch Based on Natural Active Substance-Green Porous Structures. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031319
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xiangfan, Yuan Zhou, Jinhui Gu, Xinping Liu, and Zhijun Zhang. 2023. "Construction and Activity Study of a Natural Antibacterial Patch Based on Natural Active Substance-Green Porous Structures" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031319
APA StyleGao, X., Zhou, Y., Gu, J., Liu, X., & Zhang, Z. (2023). Construction and Activity Study of a Natural Antibacterial Patch Based on Natural Active Substance-Green Porous Structures. Molecules, 28(3), 1319. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031319





