Marine Natural Products from Flora and Fauna of the Western Australian Coast: Taxonomy, Isolation and Biological Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Discussion
2.1. Porifera
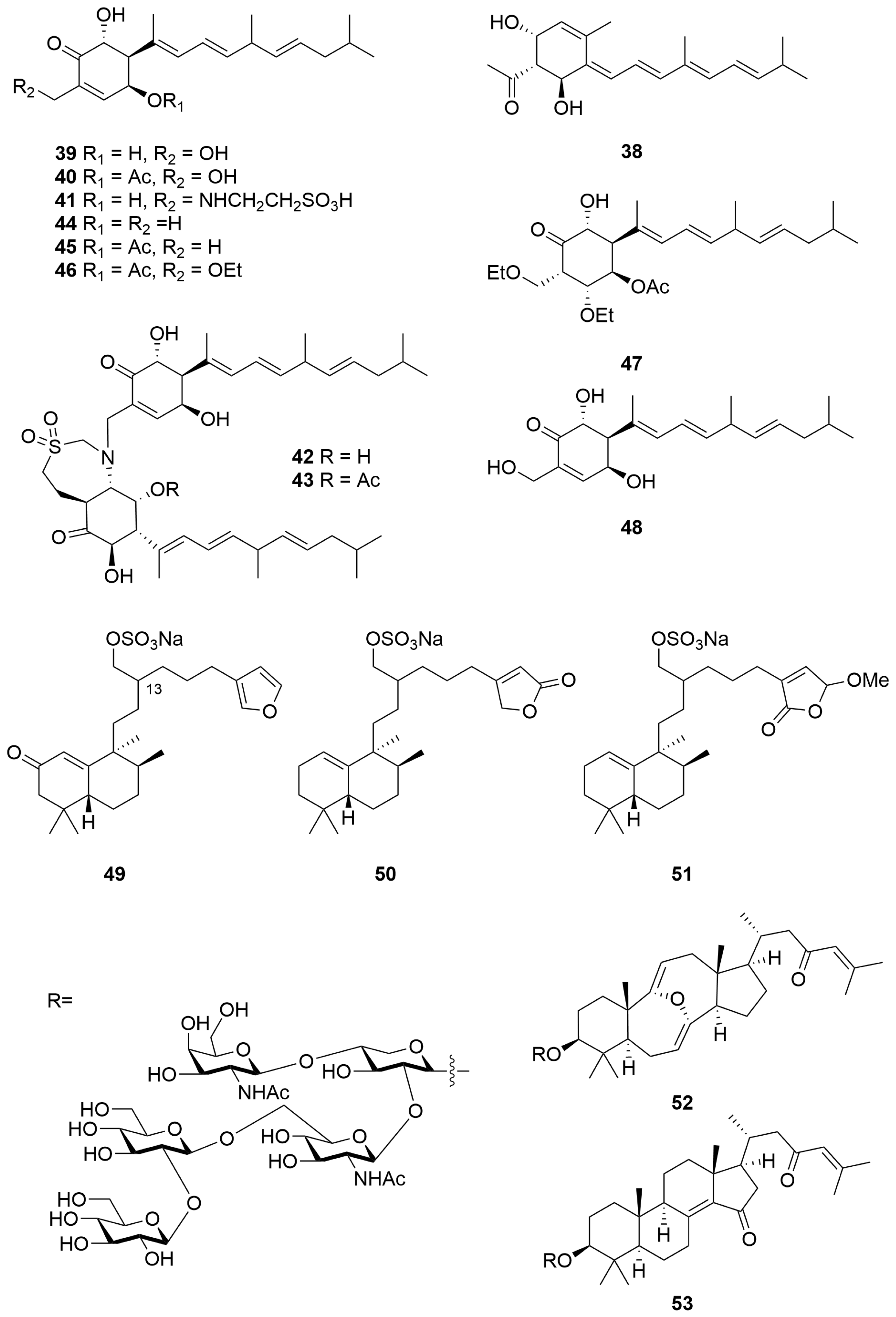
2.1.1. Terpenoids
2.1.2. Alkaloids
2.1.3. Polyketides
2.1.4. Fatty Acids
2.1.5. Peptides
2.1.6. Miscellanea
2.2. Cnidaria
2.3. Tunicata
2.4. Echinodermata
2.5. Plantae
2.6. Ochrophyta
2.7. Rhodophyta
2.8. Chlorophyta
2.9. Cyanophyta
2.10. Dinoflagelatta
2.11. Fungi
2.12. Arsenic Metabolism in the Marine Food Web
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J. Marine Natural Products Chemistry: Past, Present, and Future. Aust. J. Chem. 2010, 63, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromont, J.; Althaus, F.; McEnnulty, F.R.; Williams, A.; Salotti, M.; Gomez, O.; Gowlett-Holmes, K. Living on the edge: The sponge fauna of Australia’s southwestern and northwestern deep continental margin. Hydrobiologia 2012, 687, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönberg, C.H.L.; Fromont, J. Sponge gardens of Ningaloo Reef (Carnarvon Shelf, Western Australia) are biodiversity hotspots. Hydrobiologia 2012, 687, 143–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Phorboxazoles A and B: Potent cytostatic macrolides from marine sponge Phorbas species. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8126–8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.L.; Beutler, J.A.; Cardellina, J.H.; Boyd, M.R. Salicylihalamides A and B, Novel Cytotoxic Macrolides from the Marine Sponge Haliclona sp. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 8188–8192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, M.R.; Farina, C.; Belfiore, P.; Gagliardi, S.; Kim, J.W.; Hayakawa, Y.; Beutler, J.A.; McKee, T.C.; Bowman, B.J.; Bowman, E.J. Discovery of a novel antitumor benzolactone enamide class that selectively inhibits mammalian vacuolar-type (H+)-ATPases. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 114–120. [Google Scholar]
- Lindel, T.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Long, B.H.; Casazza, A.M.; Carboni, J.; Fairchild, C.R. Eleutherobin, a New Cytotoxin that Mimics Paclitaxel (Taxol) by Stabilizing Microtubules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 8744–8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MarineLit. Available online: http://pubs.rsc.org/marinlit (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Capon, R.; Ghisalberti, E.; Jefferies, P. New aromatic sesquiterpenes from a Halichondria sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 2583–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.; Wells, R. Five new C26 tetracyclic terpenes from a sponge (Lendenfeldia sp.). Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Jefferies, P.R. A new furanoterpene from a Spongia sp. Experientia 1982, 38, 1444–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Jenkins, A.; Rooney, F.; Ghisalberti, E.L. Structure Revision and Assignment of Absolute Stereochemistry of a Marine C21 Bisfuranoterpene. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 638–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, M.; Ghisalberti, E.; Jefferies, P.; Skelton, B.; White, A. New Tricyclic Diterpenes from the Sponge Higginsia sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1985, 38, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, M.P.; Ghisalberti, E.L. New Terpene Hydrocarbons from the Sponge Higginsia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Scalemic 12-hydroxyambliofuran and 12-acetoxy-ambliofuran, five tetracyclic furanoditerpenes and a furanosesterterpene from Spongia sp. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 9893–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochfort, S.J.; Atkin, D.; Hobbs, L.; Capon, R.J. Hippospongins A−F: New Furanoterpenes from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge Hippospongia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Miller, M.; Rooney, F. Clathrins A−C: Metabolites from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Clathria Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, D.; Capon, R.J. Phorbasin A: A Novel Diterpene from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Phorbas Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1684–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, M.; Capon, R.J. Phorbasin B and C: Novel Diterpenes from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Phorbas Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Capon, R.J. Phorbasins D−F: Diterpenyl-taurines from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 1959–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Major, J.M.; Lewis, R.J.; Capon, R.J. Phorbasins G–K: New cytotoxic diterpenes from a southern Australian marine sponge, Phorbas sp. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 3811–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Rho, J.-R.; Lee, H.-S.; Santalova, E.A.; Stonik, V.; Shin, J. New Sesterterpene Sulfates from the Sponge Darwinella australensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1010–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santalova, E.A.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Berdyshev, D.V.; Stonik, V.A. Two New Sarasinosides from the Sponge Melophlus sarasinorum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2006, 1, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.; Piggott, A.M.; Capon, R.J. Bistellettazines A−C and Bistellettazole A: New Terpenyl−Pyrrolizidine and Terpenyl−Imidazole Alkaloids from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Stelletta sp. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 4247–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A.; Krasokhin, V.B. Sesquiterpenoid Aminoquinones from the Marine Sponge Dysidea sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Khalil, Z.G.; Capon, R.J. Fascioquinols A–F: Bioactive meroterpenes from a deep-water southern Australian marine sponge, Fasciospongia sp. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 2591–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellar, G.; Djura, P.; Sargent, M.V. Structure and synthesis of a new bromoindole from a marine sponge. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1981, 1679–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.A.; Penn, S.G.; Lebrilla, C.B.; Lam, T.H.; Pessah, I.N.; Molinski, T.F. Bastadin 20 and Bastadin O-Sulfate Esters from Ianthella basta: Novel Modulators of the Ry1R FKBP12 Receptor Complex. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 1121–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.W.; Jímenez, D.R.; Molinski, T.F. Agelastatins C and D, New Pentacyclic Bromopyrroles from the Sponge Cymbastela sp., and Potent Arthropod Toxicity of (−)-Agelastatin A. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovenden, S.P.B.; Capon, R.J. Echinosulfonic Acids A−C and Echinosulfone A: Novel Bromoindole Sulfonic Acids and a Sulfone from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Echinodictyum. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1246–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, S.; Nealon, G.L.; Sobolev, A.N.; Fromont, J.; Gomez, O.; Flematti, G.R. Structure Reassignment of Echinosulfone A and the Echinosulfonic Acids A–D Supported by Single-Crystal X-ray Diffraction and Density Functional Theory Analysis. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, D.C.; Kiefel, M.J.; Carroll, A.R. Structure Revisions of the Sponge-Derived Dibrominated Bis-indole Alkaloids, Echinosulfone A and the Echinosulfonic Acids A to D. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 3490–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neupane, P.; Salim, A.A.; Capon, R.J. Structure revision of the rare sponge metabolite echinosulfone A, and biosynthetically related echinosulfonic acids A–D. Tetrahedron Lett. 2020, 61, 151651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Vuong, D.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H. (−)-Echinobetaine A: Isolation, Structure Elucidation, Synthesis, and SAR Studies on a New Nematocide from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Echinodictyum sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Vuong, D.; McNally, M.; Peterle, T.; Trotter, N.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H. (+)-Echinobetaine B: Isolation, structure elucidation, synthesis and preliminary SAR studies on a new nematocidal betaine from a southern Australian marine sponge, Echinodictyum sp. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijoux, M.-G.; Gamble, W.R.; Hallock, Y.F.; Cardellina, J.H.; van Soest, R.; Boyd, M.R. A New Discorhabdin from Two Sponge Genera. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 636–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groweiss, A.; Newcomer, J.J.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Blackman, A.; Boyd, M.R. Cytotoxic Metabolites from an Australian Collection of the Sponge Jaspis Species. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1691–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovenden, S.P.B.; Nielson, J.L.; Liptrot, C.H.; Willis, R.H.; Tapiolas, D.M.; Wright, A.D.; Motti, C.A. A New Diketopiperazine, Cyclo-(4-S-hydroxy-R-proline-R-isoleucine), from an Australian Specimen of the Sponge Stelletta sp. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2469–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Miller, M.; Rooney, F. Mirabilin G: A New Alkaloid from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Clathria Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.; Conte, M.; Capon, R.J. Mirabilins revisited: Polyketide alkaloids from a southern Australian marine sponge, Clathria sp. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Blees, J.S.; Bayer, M.M.; Colburn, N.H.; Thomas, C.L.; Henrich, C.J.; Peach, M.L.; McMahon, J.B.; Schmid, T.; Gustafson, K.R. Tricyclic Guanidine Alkaloids from the Marine Sponge Acanthella cavernosa that Stabilize the Tumor Suppressor PDCD4. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4593–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.-S.; MacMillan, J.B.; Olmstead, M.M.; Ta, T.A.; Pessah, I.N.; Molinski, T.F. (+)-7S-Hydroxyxestospongin A from the Marine Sponge Xestospongia sp. and Absolute Configuration of (+)-Xestospongin D. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.C.; Otero-Quintero, S.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Bewley, C.A. Batzelline D and Isobatzelline E from the Indopacific Sponge Zyzzya fuliginosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J.; Peng, C.; Dooms, C. Trachycladindoles A–G: Cytotoxic heterocycles from an Australian marine sponge, Trachycladus laevispirulifer. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2008, 6, 2765–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herb, R.; Carroll, A.R.; Yoshida, W.Y.; Scheuer, P.J.; Paul, V.J. Polyalkylated cyclopentindoles: Cytotoxic fish antifeedants from a sponge, Axinella sp. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 3089–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhar, S.; Feng, Y.; Campitelli, M.R.; Quinn, R.J.; Hooper, J.N.A.; Ekins, M.G.; Davis, R.A. Trikentramides A–D, Indole Alkaloids from the Australian Sponge Trikentrion flabelliforme. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2100–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.G.; Goodman, J.M. Assigning Stereochemistry to Single Diastereoisomers by GIAO NMR Calculation: The DP4 Probability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12946–12959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salib, M.N.; Molinski, T.F. Six Trikentrin-like Cyclopentanoindoles from Trikentrion flabelliforme. Absolute Structural Assignment by NMR and ECD. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragini, K.; Fromont, J.; Piggott, A.M.; Karuso, P. Enantiodivergence in the Biosynthesis of Bromotyrosine Alkaloids from Sponges? J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Sorolla, A.; Fromont, J.; Blancafort, P.; Flematti, G.R. Crambescidin 800, Isolated from the Marine Sponge Monanchora viridis, Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F.; Brzezinski, L.J.; Leahy, J.W. Absolute Configuration of Phorboxazoles A and B from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. 1. Macrolide and Hemiketal Rings. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 9422–9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F. Absolute configuration of phorboxazoles A and B from the marine sponge, Phorbas sp. 2. C43 and complete stereochemistry. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7879–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skepper, C.K.; MacMillan, J.B.; Zhou, G.-X.; Masuno, M.N.; Molinski, T.F. Chlorocyclopropane Macrolides from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. Assignment of the Configurations of Phorbasides A and B by Quantitative CD. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4150–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacMillan, J.B.; Xiong-Zhou, G.; Skepper, C.K.; Molinski, T.F. Phorbasides A−E, Cytotoxic Chlorocyclopropane Macrolide Glycosides from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. CD Determination of C-Methyl Sugar Configurations. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 3699–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Morinaka, B.I.; Skepper, C.K.; Molinski, T.F. A Tetrachloro Polyketide Hexahydro-1H-isoindolone, Muironolide A, from the Marine Sponge Phorbas sp. Natural Products at the Nanomole Scale. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7552–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F. Structure Elucidation at the Nanomole Scale. 2. Hemi-phorboxazole A from Phorbas sp. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 1967–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F. NMR Quantitation of Natural Products at the Nanomole Scale. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalisay, D.S.; Molinski, T.F. Structure Elucidation at the Nanomole Scale. 3. Phorbasides G−I from Phorbas sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Young, K.; Zakarian, A. Total Synthesis and Structural Revision of (+)-Muironolide A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5907–5910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Liu, E.H.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K.; Friedel, T. Esmodil: An Acetylcholine Mimetic Resurfaces in a Southern Australian Marine Sponge Raspailia (Raspailia) sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2004, 18, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdo, D.A.; Motti, C.A.; Battershill, C.N.; Harvey, E.S. Temperature and Spatiotemporal Variability of Salicylihalamide A in the Sponge Haliclona sp. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovenden, S.P.B.; Capon, R.J.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Friedel, T.; Wadsworth, D. Amphilactams A−D: Novel Nematocides from Southern Australian Marine Sponges of the Genus Amphimedon. J. Org. Chem. 1999, 64, 1140–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Wadsworth, D.; Friedel, T. Geodin A Magnesium Salt: A Novel Nematocide from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge, Geodia. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Sorolla, A.; Fromont, J.; Blancafort, P.; Flematti, G.R. Aurantoside C Targets and Induces Apoptosis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, S.E.; Molinski, T.F.; Preston, C.M.; DeLong, E.F. Brominated acetylenic fatty acids from Xestospongia sp., a marine sponge bacteria association. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 7667–7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Liu, E.H.-T.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K.; Friedel, T. The Isolation and Synthesis of Novel Nematocidal Dithiocyanates from an Australian Marine Sponge, Oceanapia sp. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 7765–7769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Skene, C.; Liu, E.H.-T.; Lacey, E.; Gill, J.H.; Heiland, K.; Friedel, T. Nematocidal Thiocyanatins from a Southern Australian Marine Sponge Oceanapia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Guzii, A.G.; Santalova, E.A.; Stonik, V.A.; MacMillan, J.B.; Molinski, T.F. Oceanalin A, a Hybrid α,ω-Bifunctionalized Sphingoid Tetrahydroisoquinoline β-Glycoside from the Marine Sponge Oceanapia sp. Org. Lett. 2005, 7, 2897–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Svetashev, V.I.; Rodkina, S.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Anastyuk, S.D.; Stonik, V.A. New cerebrosides from the marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2006, 55, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Svetashev, V.I.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Pokanevich, E.V.; Santalova, E.A.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Stonik, V.A. New ceramides from sea sponge Oceanapia sp. Russ. J. Bioorganic Chem. 2006, 32, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Guzii, A.G.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. New two-headed sphingolipid-like compounds from the marine sponge Oceanapia sp. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2008, 57, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, S.; Fromont, J.; Gomez, O.; Vuong, D.; Lacey, E.; Flematti, G.R. Albanitriles A–G: Antiprotozoal Polyacetylene Nitriles from a Mycale Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3450–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulavita, N.K.; Pomponi, S.A.; Wright, A.E.; Yarwood, D.; Sills, M.A. Isolation and structure elucidation of perthamide B, a novel peptide from the sponge Theonella sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1994, 35, 6815–6818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Rashid, M.A.; Cartner, L.K.; Bokesch, H.R.; Wilson, J.A.; McMahon, J.B.; Gustafson, K.R. Stellettapeptins A and B, HIV-inhibitory cyclic depsipeptides from the marine sponge Stelletta sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 4215–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.; Wells, R.; Jamieson, D. Halogenated pyrrolo [2,3-d]pyrimidine nucleosides from marine organisms. Aust. J. Chem. 1983, 36, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Isolation of Spongosine and 2′-Deoxyspongosine from a Western Australian Sponge of the Order Hadromerida (Tethyidae). J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1452–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Jefferies, P.R. New tetrahydropyrans from a marine sponge. Tetrahedron 1982, 38, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, K.L.; Beutler, J.A.; Cardellina, J.H.; Boyd, M.R. Rottnestol, a new hemiketal from the sponge Haliclona sp. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 11953–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czuba, I.R.; Rizzacasa, M.A. Total synthesis of (+)-rottnestol. Chem. Commun. 1999, 1419–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, P.A.; Molinski, T.F. Trachycladines A and B: 2′-C-methyl-5′-deoxyribofuranosyl nucleosides from the marine sponge Trachycladus laevispirulifer. J. Org. Chem. 1995, 60, 4296–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Trotter, N.S. N3,5′-Cycloxanthosine, the First Natural Occurrence of a Cyclonucleoside. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saludes, J.P.; Lievens, S.C.; Molinski, T.F. Occurrence of the α-Glucosidase Inhibitor 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-imino-D-arabinitol and Related Iminopentitols in Marine Sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capon, R.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Jefferies, P.R.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Structural studies of halogenated diphenyl ethers from a marine sponge. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1981, 2464–2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A.; Scholokova, O.V.; Virovaya, M.V.; Gerasimenko, A.V.; Popov, D.Y.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Popov, A.M. Spongiadioxins A and B, Two New Polybrominated Dibenzo-p-dioxins from an Australian Marine Sponge Dysidea dendyi. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkina, N.K.; Denisenko, V.A.; Virovaya, M.V.; Scholokova, O.V.; Prokof’eva, N.G. Two New Minor Polybrominated Dibenzo-p-dioxins from the Marine Sponge Dysidea dendyi. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1213–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussis, V.; Fenical, W.; Harvala, C. Pectinoacetals A–C: Novel sterol hemiacetals from the gorgonian Ctenocella pectinata. Experientia 1993, 49, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, J.E.; McCool, B.J.; Bowden, B.F. Excavatolides N–T, New Briaran Diterpenes from the Western Australian Gorgonian Briareum excavatum. Aust. J. Chem. 1999, 52, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.B.; Butler, M.S.; Healy, P.C.; Quinn, R.J. Anthoptilides A–E, New Briarane Diterpenes from the Australian Sea Pen Anthoptilum cf. kukenthali. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlotkowski, K.; Hewitt, W.M.; Yan, P.; Bokesch, H.R.; Peach, M.L.; Nicklaus, M.C.; O’Keefe, B.R.; McMahon, J.B.; Gustafson, K.R.; Schneekloth, J.S. Macrophilone A: Structure Elucidation, Total Synthesis, and Functional Evaluation of a Biologically Active Iminoquinone from the Marine Hydroid Macrorhynchia philippina. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1726–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Ritt, D.A.; Zlotkowski, K.; Bokesch, H.R.; Reinhold, W.C.; Schneekloth, J.S.; Morrison, D.K.; Gustafson, K.R. Macrophilones from the Marine Hydroid Macrorhynchia philippina Can Inhibit ERK Cascade Signaling. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1666–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Marwood, J.; Murphy, P.; Wells, R. A blue pigment from a compound ascidian. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 215–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, H.H.; Friedland, D.J.; Morrison, D.A. A novel dipyrrolyldipyrromethene prodigiosin analog from Serratia marcescens. Tetrahedron Lett. 1968, 9, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.A.; Gustafson, K.R.; Cardellina, J.H.; Boyd, M.R. Patellamide F, a New Cytotoxic Cyclic Peptide from the Colonial Ascidian Lissoclinum patella. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Fenical, W. Polycarpine dihydrochloride: A cytotoxic dimeric disulfide alkaloid from the Indian ocean ascidian Polycarpa clavata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 2369–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochfort, S.; Metzger, R.; Hobbs, L.; Capon, R. New Chromenols from a Southern Australian Tunicate, Aplidium solidum. Aust. J. Chem. 1996, 49, 1217–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Isolation of Microbial Antibiotics from a Marine Ascidian of the Genus Didemnum. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Fenical, W. Ningalins A–D: Novel Aromatic Alkaloids from a Western Australian Ascidian of the Genus Didemnum. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 3254–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Fenical, W. Aplidiamine, a unique zwitterionic benzyl hydroxyadenine from the Western Australian marine ascidian Aplidiopsis sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinis, D.L.; McKee, T.C.; Pannell, L.K.; Cardellina, J.H.; Boyd, M.R. Lobatamides A and B, Novel Cytotoxic Macrolides from the Tunicate Aplidium lobatum. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 8968–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.C.; Galinis, D.L.; Pannell, L.K.; Cardellina, J.H.; Laakso, J.; Ireland, C.M.; Murray, L.; Capon, R.J.; Boyd, M.R. The Lobatamides, Novel Cytotoxic Macrolides from Southwestern Pacific Tunicates. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 7805–7810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.; Lim, T.; Currie, G.; Capon, R. Aplidites (A–G): Macrocyclic Orthonitrites from an Australian Tunicate, Aplidium sp. Aust. J. Chem. 1995, 48, 1253–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Lin, C.T.; Porco, J.A. Total Synthesis and Stereochemical Assignment of the Salicylate Antitumor Macrolide Lobatamide C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 5650–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K. Pigments of some echinoderms collected from Western Australian waters. Aust. J. Chem. 1980, 33, 2781–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, R.W. Diterpenoid hydrocarbons in the sea grass Amphibolis antartica. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 977–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Jefferies, P.R. Isoprenoid dihydroquinones from a brown alga, Cystophora sp. Phytochemistry 1981, 20, 2598–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlop, R.; Ghisalberti, E.; Jefferies, P.; Skelton, B.; White, A. Structure of a New Dolastane Diterpene from Dictyota furcellata. Aust. J. Chem. 1989, 42, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amico, V.; Biondi, D.; Cunsolo, F.; Ruberto, G. Three Acetogenins from the Brown Alba Caulocystis cephalornithos. J. Nat. Prod. 1990, 53, 1379–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussis, V.; King, R.L.; Fenical, W. Secondary metabolite chemistry of the Australian brown alga Encyothalia cliftonii: Evidence for herbivore chemical defence. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.W.; Poole, R.; Wikström, M.; van Altena, I.A. Pycnanthuquinone C, an Unusual 6,6,5-Tricyclic Geranyltoluquinone from the Western Australian Brown Alga Cystophora harveyi. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Jefferies, P.R.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Sesquiterpene metabolites from Laurencia filiformis. Tetrahedron 1981, 37, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.; Ghisalberti, E.; Jefferies, P. Synthesis of the thermolysis product of 6β-hydroxyaplysistatin. J. Chem. Res. Synop. 1987, 4, 118–119. [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas, R.; Murphy, P.; Wells, R. A brominated metabolite from the red alga Vidalia spiralis. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 219–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.R.; Erickson, K.L. Austradiol acetate and austradiol diacetate, 4,6-dihydroxy-(+)-selinane derivatives from an Australian Laurencia sp. J. Org. Chem. 1982, 47, 3917–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.; Engelhardt, L.; Ghisalberti, E.; Jefferies, P.; Patrick, V.; White, A. Structural studies of polyhalogenated monoterpenes from Plocamium species. Aust. J. Chem. 1984, 37, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Mori, T.A.; Jefferies, P.R. Sesquiterpenes from Laurencia spp. J. Nat. Prod. 1988, 51, 1302–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.; Ghisalberti, E.; Jefferies, P. New sesquiterpenes from Caulerpa flexilisvar. muelleri. Aust. J. Chem. 1981, 34, 1775–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Jefferies, P.R. Metabolites of the green algae, Caulerpa species. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 1465–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Dunlop, R.W.; Ghisalberti, E.L.; Jefferies, P.R. Poly-3-hydroxyalkanoates from marine and freshwater cyanobacteria. Phytochemistry 1983, 22, 1181–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkman, J.K.; Rijpstra, W.I.C.; de Leeuw, J.W.; Mansour, M.P.; Jackson, A.E.; Blackburn, S.I. Sterols of four dinoflagellates from the genus Prorocentrum. Phytochemistry 1999, 52, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fremlin, L.J.; Piggott, A.M.; Lacey, E.; Capon, R.J. Cottoquinazoline A and Cotteslosins A and B, Metabolites from an Australian Marine-Derived Strain of Aspergillus versicolor. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanamge, S.; Khalil, Z.G.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Capon, R.J. Noonindoles A–F: Rare Indole Diterpene Amino Acid Conjugates from a Marine-Derived Fungus, Aspergillus noonimiae CMB-M0339. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A.; Cannon, J.R.; Raston, C.L.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Isolation, crystal structure and synthesis of arsenobetaine, the arsenical constituent of the western rock lobster Panulirus longipes cygnus George. Tetrahedron Lett. 1977, 18, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A. Arseno-sugars from brown kelp (Ecklonia radiata) as intermediates in cycling of arsenic in a marine ecosystem. Nature 1981, 289, 602–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A.; Hansen, J.A. Dimethyloxarsylethanol from anaerobic decomposition of brown kelp (Ecklonia radiata): A likely precursor of arsenobetaine in marine fauna. Experientia 1982, 38, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A. Arsenic-containing ribofuranosides: Isolation from brown kelp Ecklonia radiata and nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1983, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmonds, J.S.; Francesconi, K.A.; Healy, P.C.; White, A.H. Isolation and crystal structure of an arsenic-containing sugar sulphate from the kidney of the giant clam, Tridacna maxima. X-Ray crystal structure of (2S)-3-[5-deoxy-5-(dimethylarsinoyl)-β-D-ribofuranosyloxy]-2-hydroxypropyl hydrogen sulphate. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1982, 2989–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A.; Edmonds, J.S.; Stick, R.V.; Skelton, B.W.; White, A.H. Arsenic-containing ribosides from the brown alga Sargassum lacerifolium: X-ray molecular structure of 2-amino-3-[5′-deoxy-5′-(dimethylarsinoyl)ribosyloxy]propane-1-sulphonic acid. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1991, 2707–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, K.A.; Edmonds, J.S.; Stick, R.V. Arsenic compounds from the kidney of the giant clam Tridacna maxima: Isolation and identification of an arsenic-containing nucleoside. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1992, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 362–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 1122–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Lin, Z.; Torres, J.P.; Hill, E.A.; Li, D.; Townsend, C.A.; Schmidt, E.W. Sea Urchin Polyketide Synthase SpPks1 Produces the Naphthalene Precursor to Echinoderm Pigments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 9363–9371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkendale, L.; Hosie, A.M.; Richards, Z. Defining biodiversity gaps for North West Shelf marine invertebrates. J. R. Soc. West. Aust. 2019, 102, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Fromont, J.; Abdul Wahab, M.A.; Gomez, O.; Ekins, M.; Grol, M.; Hooper, J.N. Patterns of Sponge Biodiversity in the Pilbara, Northwestern Australia. Diversity 2016, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Wahab, M.A.; Radford, B.; Fromont, J.; Hosie, A.M.; Miller, K.; Heyward, A. The diversity and distribution of mesophotic benthic invertebrates at Ningaloo Reef, Western Australia. Mar. Biodivers. 2019, 49, 2871–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; El-Hossary, E.M.; Oelschlaeger, T.A.; Donia, M.S.; Quinn, R.J.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Potential of marine natural products against drug-resistant bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e237–e245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.T.; Zhu, H.J.; Cao, F. Marine Natural Products as a Source of Drug Leads against Respiratory Viruses: Structural and Bioactive Diversity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 3568–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, P.; Banerjee, P.; Mandhare, A. Marine natural products as source of new drugs: A patent review (2015–2018). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sala, S.; Micke, S.K.; Flematti, G.R. Marine Natural Products from Flora and Fauna of the Western Australian Coast: Taxonomy, Isolation and Biological Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031452
Sala S, Micke SK, Flematti GR. Marine Natural Products from Flora and Fauna of the Western Australian Coast: Taxonomy, Isolation and Biological Activity. Molecules. 2023; 28(3):1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031452
Chicago/Turabian StyleSala, Samuele, Scott K. Micke, and Gavin R. Flematti. 2023. "Marine Natural Products from Flora and Fauna of the Western Australian Coast: Taxonomy, Isolation and Biological Activity" Molecules 28, no. 3: 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031452
APA StyleSala, S., Micke, S. K., & Flematti, G. R. (2023). Marine Natural Products from Flora and Fauna of the Western Australian Coast: Taxonomy, Isolation and Biological Activity. Molecules, 28(3), 1452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28031452





