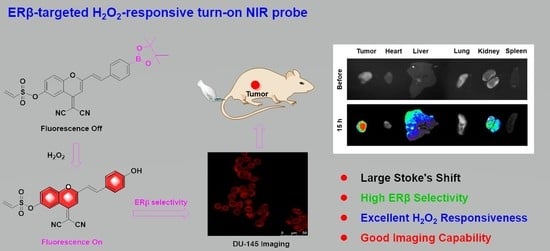
Development of Highly Efficient Estrogen Receptor β-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescence Probes Triggered by Endogenous Hydrogen Peroxide for Diagnostic Imaging of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Probes
2.2. Optical Properties of Probes
2.3. Interference Resistance of Probe
2.4. ERβ Selectivity of Probes
2.5. Imaging of Probe in Living Cells
2.6. In Vivo Imaging
2.7. The Mechanism of Response towards H2O2
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Measurements
3.2. Chemical Synthesis
3.2.1. (E)-2-(6-Methoxy-2-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)styryl)-4H-chromen-4-ylidene)malononitrile (3)
3.2.2. (E)-2-(6-Hydroxy-2-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)styryl)-4H-chromen-4-ylidene)malononitrile (P1)
3.2.3. (E)-4-(Dicyanomethylene)-2-(4-(4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolan-2-yl)styryl)-4H-chromen-6-yl ethenesulfonate (P2)
3.3. Optical Properties
3.4. ER Binding Affinity Assay
3.5. CCK-8 Assay
3.6. Cell Imaging
3.7. Animal Imaging
3.8. DFT Calculation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Kuiper, G.G.J.M.; Enmark, E.; PeltoHuikko, M.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Cloning of a novel estrogen receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5925–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. Estrogen receptor transcription and transactivation Estrogen receptor alpha and estrogen receptor beta: Regulation by selective estrogen receptor modulators and importance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2000, 2, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Xu, X.L.; Liang, C.L.; Chen, X.; Yu, X.W.; Zhong, H.F.; Xu, W.X.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.D.; et al. ER beta modulates genistein’s cisplatin-enhancing activities in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells via P53-independent pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 456, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, K.; Yu, H.; Xie, B.; Meng, Q.; Dong, C.; Shen, K.; Zhou, H.-B. Anticancer or carcinogenic? The role of estrogen receptor β in breast cancer progression. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 242, 108350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, I.; Coutermarsh-Ott, S.; Morrison, R.G.; Allen, I.C.; Davalos, R.V.; Verbridge, S.S.; Bickford, L.R. Irreversible electroporation inhibits pro-cancer inflammatory signaling in triple negative breast cancer cells. Bioelectrochemistry 2017, 113, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piperigkou, Z.; Bouris, P.; Onisto, M.; Franchi, M.; Kletsas, D.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Estrogen receptor beta modulates breast cancer cells functional properties, signaling and expression of matrix molecules. Matrix Biol. 2016, 56, 4–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.C.; Zhao, D.; Spring, D.J.; DePinho, R.A. Genetics and biology of prostate cancer. Gene Dev. 2018, 32, 1105–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.P.; Chen, X.; Langbein, B.J.; Giganti, F.; Kasivisvanathan, V.; Emberton, M.; Moore, C.M.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Keating, N.L.; Trinh, Q.D. Geographic Variability, Time Trends and Association of Preoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging with Surgical Outcomes for Elderly United States Men with Prostate Cancer: A Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results-Medicare Analysis. J. Urol. 2022, 208, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandrika, L.; Kumar, B.; Koul, S.; Maroni, P.; Koul, H.K. Oxidative stress in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009, 282, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoforou, P.; Christopoulos, P.F.; Koutsilieris, M. The Role of Estrogen Receptor beta in Prostate Cancer. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, D.L. Selective estrogen receptor modulators contribute to prostate cancer treatment by regulating the tumor immune microenvironment. J. Immunother Cancer 2022, 10, e002944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.D.; Huang, B.W.; Tsuji, Y. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) homeostasis and redox regulation in cellular signaling. Cell Signal. 2012, 24, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, J.R.; Yang, S.P. Hydrogen peroxide: A signaling messenger. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, P.; Kossmann, S.; Munzel, T.; Daiber, A. Redox regulation of cardiovascular inflammation—Immunomodulatory function of mitochondrial and Nox-derived reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 109, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgio, M.; Trinei, M.; Migliaccio, E.; Pelicci, P.G. Hydrogen peroxide: A metabolic by-product or a common mediator of ageing signals? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippert, A.R.; De Bittner, G.C.V.; Chang, C.J. Boronate Oxidation as a Bioorthogonal Reaction Approach for Studying the Chemistry of Hydrogen Peroxide in Living Systems. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, D.; Baxter, B.; Campbell, B.C.V.; Carpenter, J.S.; Cognard, C.; Dippel, D.; Eesa, M.; Fischer, U.; Hausegger, K.; Hirsch, J.A.; et al. Multisociety Consensus Quality Improvement Revised Consensus Statement for Endovascular Therapy of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 13, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galadari, S.; Rahman, A.; Pallichankandy, S.; Thayyullathil, F. Reactive oxygen species and cancer paradox: To promote or to suppress? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 104, 144–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.P.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Liu, F.; Tian, H.Y.; Chen, X.S. A Strategy of Killing Three Birds with One Stone for Cancer Therapy through Regulating the Tumor Microenvironment by H2O2-Responsive Gene Delivery System. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2019, 11, 47785–47797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Xiao, W.Y.; Song, X.J.; Wang, W.J.; Dong, X.C. Recent Advances in Tumor Microenvironment Hydrogen Peroxide-Responsive Materials for Cancer Photodynamic Therapy. Nano-Micro Lett. 2020, 12, 212–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.Y.; Huang, C.S.; Jia, N.Q. A new mitochondria-targeting fluorescent probe for ratiometric detection of H2O2 in live cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1097, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Shen, Y.M. A Novel ESIPT Phthalimide-Based Fluorescent Probe for Quantitative Detection of H2O2. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 16242–16246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, B.; Van Laer, K.; Owusu, T.N.E.; Ezerina, D.; Pastor-Flores, D.; Amponsah, P.S.; Tursch, A.; Dick, T.P. Real-time monitoring of basal H2O2 levels with peroxiredoxin-based probes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.B.; Duan, S.Z.; Zhu, R.Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L.C. Recent Advances on Reactive Oxygen Species-Responsive Delivery and Diagnosis System. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2441–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Shi, W.; Li, H.Y.; Li, X.H.; Ma, H.M. H2O2-Responsive Organosilica-Doxorubicin Nanoparticles for Targeted Imaging and Killing of Cancer Cells Based on a Synthesized Silane-Borate Precursor. ChemMedChem 2019, 14, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Jiao, C.P.; Lu, W.J.; Zhang, P.P.; Wang, Y.F. Research progress in the development of organic small molecule fluorescent probes for detecting H2O2. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 18027–18041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.B.; Fan, H.L.; Balakrishnan, K.; Lin, Z.C.; Cao, S.; Chen, W.B.; Fan, Y.K.; Guthrie, Q.A.; Sun, H.B.; Teske, K.A.; et al. Hydrogen peroxide activated quinone methide precursors with enhanced DNA cross-linking capability and cytotoxicity towards cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 133, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, S.K.; Das, A. Fluorescent probes for imaging bioactive species in subcellular organelles. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 12058–12073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, T.S.; Lu, R.; Liu, B.T. Reversibly monitoring oxidation and reduction events in living biological systems: Recent development of redox-responsive reversible NIR biosensors and their applications in in vitro/in vivo fluorescence imaging. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Lin, W.Y.; Zheng, K.B.; He, L.W.; Huang, W.M. Far-red to near infrared analyte-responsive fluorescent probes based on organic fluorophore platforms for fluorescence imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 622–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Li, B.; Zhao, W.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Luo, X.; Corkins, M.E.; Cole, S.L.; Wang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Bi, X.M.; et al. Two-Photon Near Infrared Fluorescent Turn-On Probe Toward Cysteine and Its Imaging Applications. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.C.; Xia, L.L.; Li, L.S.; Cui, M.Y.; Gu, Y.Q.; Wang, P. An acetate-based NIR fluorescent probe for selectively imaging of hydrogen peroxide in living cells and in vivo. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2019, 288, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ren, W.X.; Hou, J.T.; Won, M.; An, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Shu, J.; Kim, J.S. Fluorescence imaging of pathophysiological microenvironments. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8887–8902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.H.; Tian, H.; Zang, Y.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Li, J.; Sessler, J.L.; He, X.P.; James, T.D. Small-molecule fluorescence-based probes for interrogating major organ diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 9391–9429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Q.Y.; Xie, B.H.; Yu, H.G.; Shen, K.; Deng, X.P.; Zhou, H.B.; Dong, C.N. Estrogen Receptor beta-Targeted Near-Infrared Inherently Fluorescent Probe: A Potent Tool for Estrogen Receptor beta Research. ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.H.; Meng, Q.Y.; Yu, H.G.; Shen, K.; Cheng, Y.; Dong, C.E.; Zhou, H.B. Estrogen receptor beta-targeted hypoxia-responsive near-infrared fluorescence probes for prostate cancer study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 238, 114506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, T.-L.; Tzeng, C.-R.; Yu, C.-L.; Wang, Y.-P.; Kao, S.-H. Estrogen receptor-β in mitochondria: Implications for mitochondrial bioenergetics and tumorigenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1350, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinge, C.M. Estrogenic control of mitochondrial function. Redox Biol. 2020, 31, 101435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-H.; Sarkar, S.N.; Liu, R.; Perez, E.J.; Wang, X.; Wen, Y.; Yan, L.-J.; Simpkins, J.W. Estrogen receptor β as a mitochondrial vulnerability factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9540–9548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lei, P.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Ji, A.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Qu, C.; Min, J.; et al. Development of a Novel 18F-Labeled Probe for PET Imaging of Estrogen Receptor β. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 1210–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.X.; Jiang, W.L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.Y. Near-infrared fluorescence probe with a large stokes shift for visualizing hydrogen peroxide in ulcerative colitis mice. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 320, 128296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, J.X.; Yang, X.J.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhou, J.P. A near-infrared fluorescent probe based on nucleophilic substitution-cyclization for selective detection of hydrogen sulfide and bioimaging. Dyes Pigment 2018, 153, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the Damping Function in Dispersion Corrected Density Functional Theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassolov, V.A.; Ratner, M.A.; Pople, J.A.; Redfern, P.C.; Curtiss, L.A. 6-31G*basis set for third-row atoms. J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Cmpd. | λex a (nm) | λem b (nm) | Stokes Shift (nm) | ε | Φfl c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 410 | 653 | 243 | 1.41 × 104 | 0.33 |
| P2 | 413 | 655 | 242 | 1.82 × 104 | 0.37 |
| Cmpd. | Structure | Ki (μM) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERα | ERβ | β/α Ratio b | ||
| P1 |  | 4.36 ± 0.01 | 1.42 ± 0.02 | 3 |
| P2 |  | 8.73 ± 0.01 | 1.21 ± 0.03 | 7.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, P.; Deng, X.; Xu, B.; Xie, B.; Zou, W.; Zhou, H.; Dong, C. Development of Highly Efficient Estrogen Receptor β-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescence Probes Triggered by Endogenous Hydrogen Peroxide for Diagnostic Imaging of Prostate Cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052309
He P, Deng X, Xu B, Xie B, Zou W, Zhou H, Dong C. Development of Highly Efficient Estrogen Receptor β-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescence Probes Triggered by Endogenous Hydrogen Peroxide for Diagnostic Imaging of Prostate Cancer. Molecules. 2023; 28(5):2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052309
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Pei, Xiaofei Deng, Bin Xu, Baohua Xie, Wenting Zou, Haibing Zhou, and Chune Dong. 2023. "Development of Highly Efficient Estrogen Receptor β-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescence Probes Triggered by Endogenous Hydrogen Peroxide for Diagnostic Imaging of Prostate Cancer" Molecules 28, no. 5: 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052309
APA StyleHe, P., Deng, X., Xu, B., Xie, B., Zou, W., Zhou, H., & Dong, C. (2023). Development of Highly Efficient Estrogen Receptor β-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescence Probes Triggered by Endogenous Hydrogen Peroxide for Diagnostic Imaging of Prostate Cancer. Molecules, 28(5), 2309. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28052309