Ruthenium p-Cymene Complexes Incorporating Substituted Pyridine–Quinoline-Based Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization, and Cytotoxic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
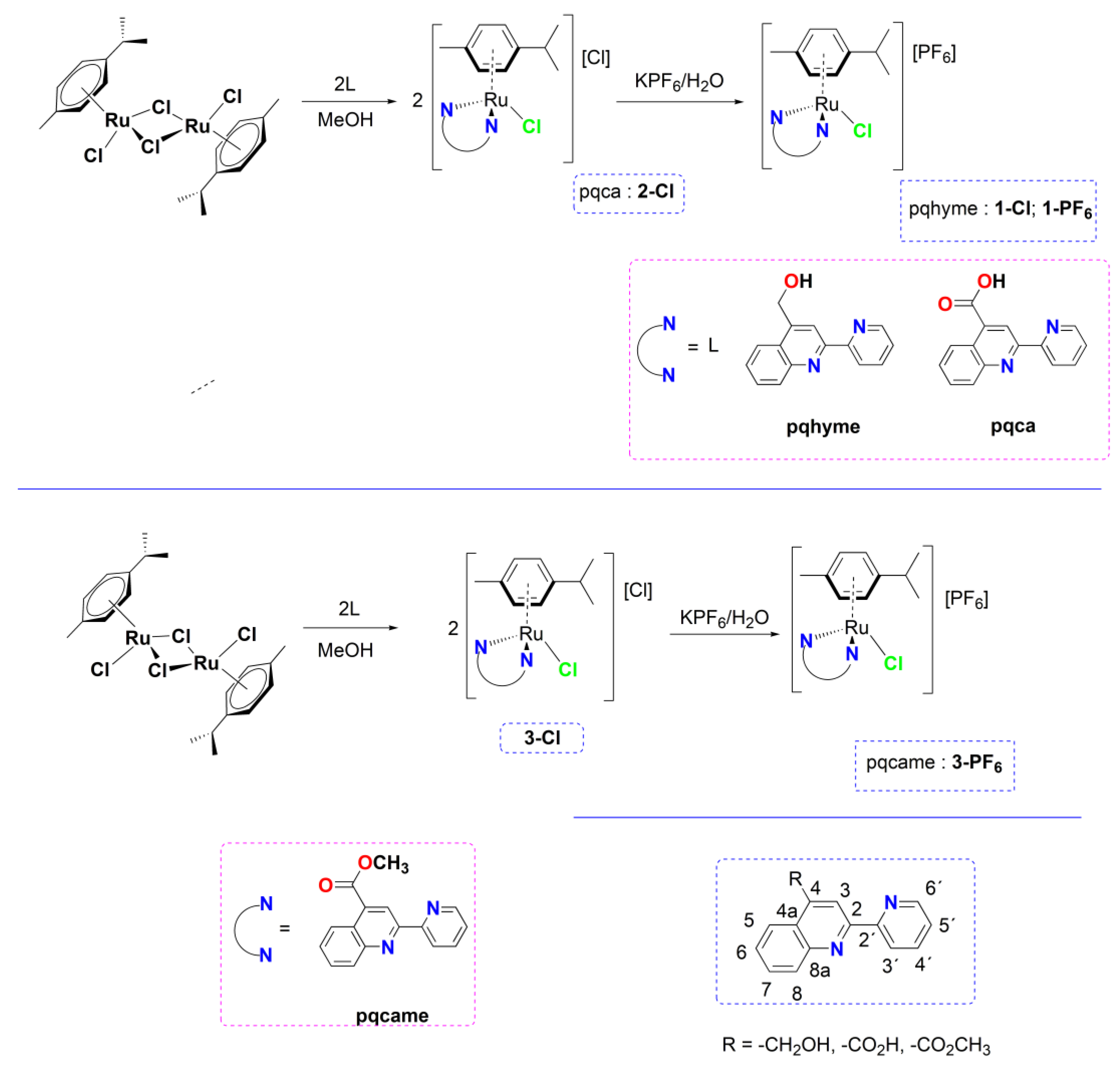
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
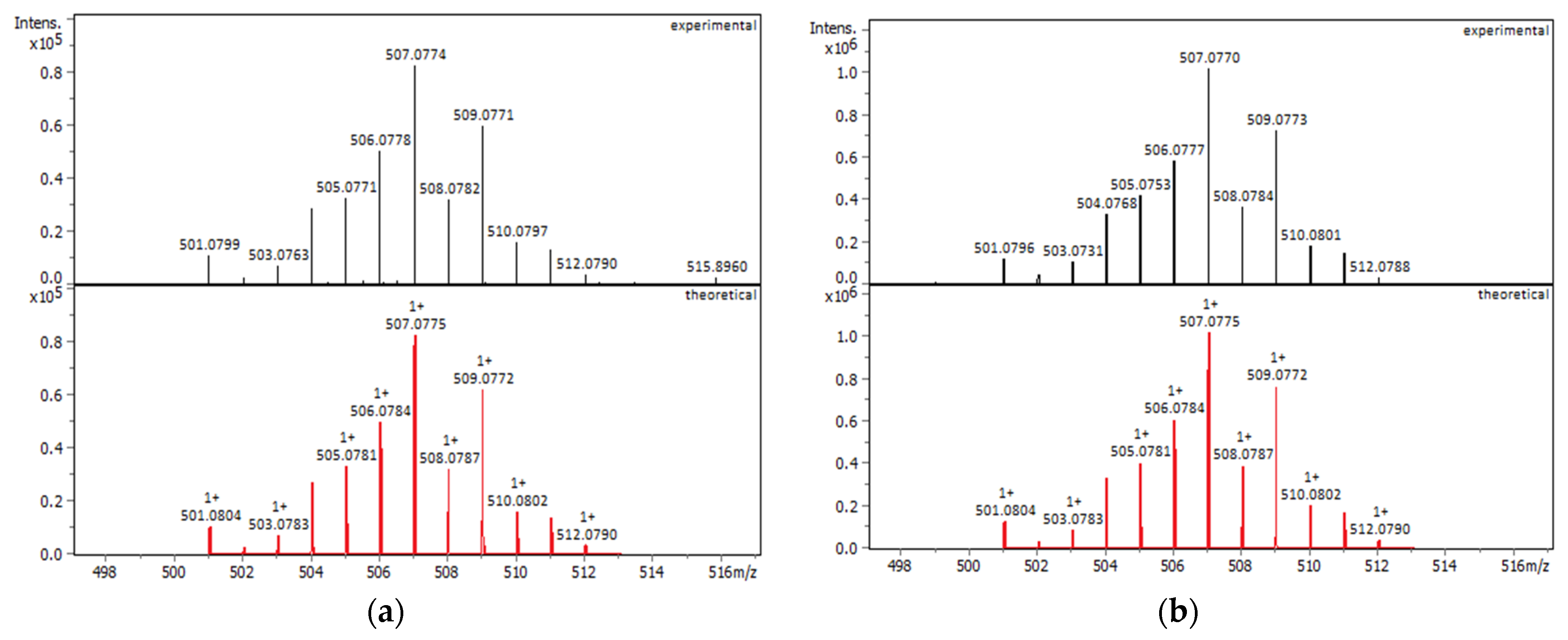
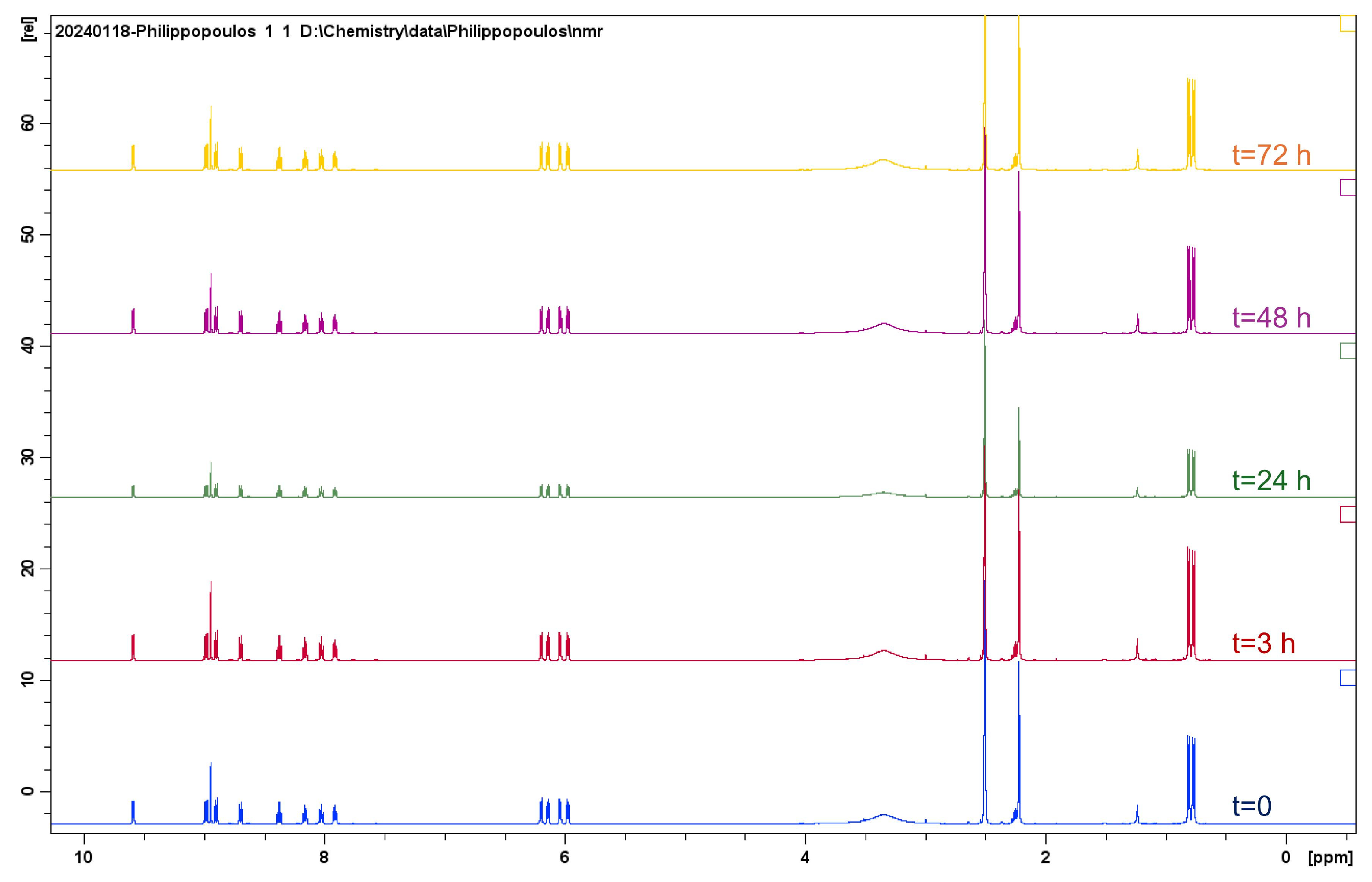
2.1.1. Solution Behavior (UV–Vis Spectroscopy, Conductivity Measurements, and Electrospray Ionization—High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (ESI-HRMS))
2.2. Evaluation of Biological Activity
Cell Viability Assay
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization
3.1.1. Synthesis of complexes 1-Cl, 2-Cl, 3-Cl
3.1.2. Data for Complexes 1-Cl, 2-Cl, and 3-Cl
3.1.3. Synthesis of Complexes 1-PF6, 3-PF6
3.1.4. Data for complexes 1-PF6, 3-PF6
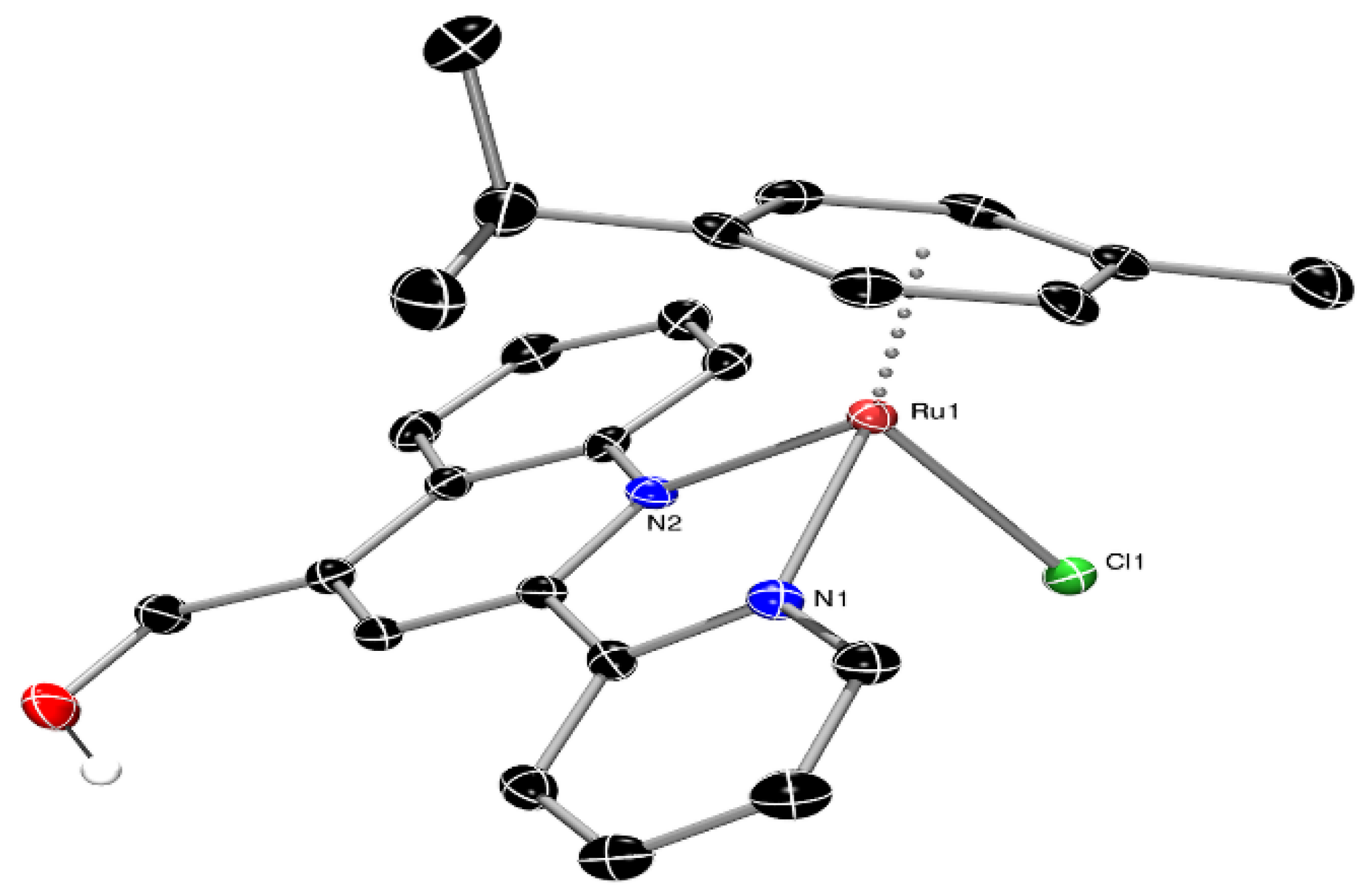
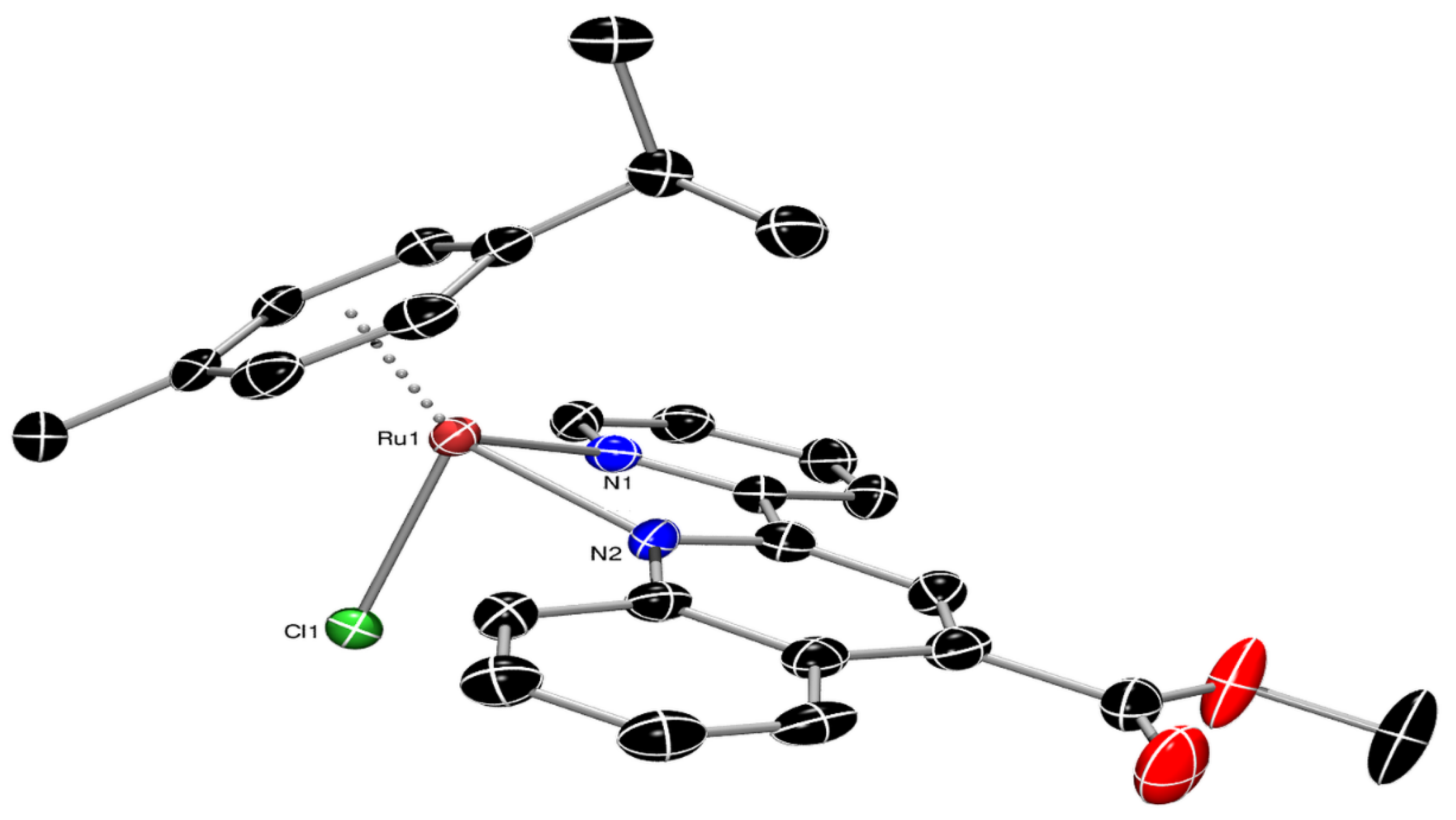
3.2. Single-Crystal X-ray Structural Determination
3.3. Biological Evaluation
3.3.1. Cell Lines
3.3.2. MTT Assay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sava, G.; Bergamo, A.; Dyson, P.J. Metal-based antitumour drugs in the post-genomic era: What comes next? Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 9069–9075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, A.; Mariconda, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Longo, P. Complexes of Ruthenium(II) as Promising Dual-Active Agents against Cancer and Viral Infections. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.; Nath, P.; Das, A.; Datta, A.; Baildya, N.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S. A review on metal complexes and its anti-cancer activities: Recent updates from in vivo studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 171, 116211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q. Ruthenium Complexes as Promising Candidates against Lung Cancer. Molecules 2021, 26, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Le, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W. Ruthenium-based antitumor drugs and delivery systems from monotherapy to combination therapy. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 16339–16375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabec, V.; Nováková, O. DNA binding mode of ruthenium complexes and relationship to tumor cell toxicity. Drug Resist. Updat. 2006, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessio, E. Thirty Years of the Drug Candidate NAMI-A and the Myths in the Field of Ruthenium Anticancer Compounds: A Personal Perspective. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 1549–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simović, A.R.; Masnikosa, R.; Bratsos, I.; Alessio, E. Chemistry and reactivity of ruthenium(II) complexes: DNA/protein binding mode and anticancer activity are related to the complex structure. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 398, 113011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, M.J. Ruthenium metallopharmaceuticals. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2003, 236, 209–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Nandi, U.; Mukherjee, D. Detailed account on activation mechanisms of ruthenium coordination complexes and their role as antineoplastic agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 150, 419–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.J.; Lippard, S.J. Synthetic methods for the preparation of platinum anticancer complexes. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4470–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rademaker-Lakhai, J.; van den Bongard, D.; Pluim, D.; Beijnen, J.H.; Schellens, J.H. A Phase I and pharmacological study withimidazolium-trans-DMSO-imidazole-tetrachloro ruthenate, a novel ruthenium anticancer agent. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 3717–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartinger, C.G.; Jakupec, M.A.; Zorbas-Seifried, S.; Groessl, M.; Egger, A.; Berger, W.; Zorbas, H.; Dyson, P.J.; Keppler, B.K. KP1019, A new redox-active anticancer agent—Preclinical development and results of a clinical phase I study in tumor patients. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trondl, R.; Heffeter, P.; Kowol, C.R.; Jakupec, M.A.; Bergerbd, W.; Keppler, B.K. NKP-1339, the first ruthenium-based anticancer drug on the edge to clinical application. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 2925–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, M.R.; Thomas, J.A. Ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes and DNA—From structural probes to cellular imaging and therapeutics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3179–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Kim, C.Y.; Nam, T.G. Ruthenium Complexes as Anticancer Agents: A Brief History and Perspectives. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 5375–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nongpiur, C.G.L.; Verma, A.K.; Singh, R.K.; Ghate, M.M.; Poluri, K.M.; Kaminsky, W.; Kollipara, M.R. Half-sandwich ruthenium(II), rhodium(III) and iridium(III) fluorescent metal complexes containing pyrazoline based ligands: DNA binding, cytotoxicity and antibacterial activities. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2023, 238, 112059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, M.; Caramés-Méndez, P.; Hofmann, B.J.; Pask, C.M.; Phillips, R.M.; Lord, R.M.; McGowan, P.C. Cytotoxicity of Ruthenium(II) Arene Complexes Containing Functionalized Ferrocenyl β-Diketonate Ligands. Organometallics 2023, 42, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, J.; Shu, L.; Li, T.; Lu, S.; Subarkhan, M.K.M.; Chen, C.; Wang, H. New Organometallic Ruthenium (II) Compounds Synergistically Show Cytotoxic, Antimetastatic and Antiangiogenic Activities for the Treatment of Metastatic Cancer. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 15170–15182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, A.F.; Sadler, P.J. Medicinal organometallic chemistry: Designing metal arene complexes as anticancer agents. Chem. Asian J. 2008, 13, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilpin, K.J.; Cammack, S.M.; Clavel, C.M.; Dyson, P.J. Ruthenium(II) arene PTA (RAPTA) complexes: Impact of enantiomerically pure chiral ligands. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 2008–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolaro, C.; Bergamo, A.; Brescacin, L.; Delfino, R.; Cocchietto, M.; Laurenczy, G.; Geldbach, T.J.; Sava, G.; Dyson, P.J. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of ruthenium(II)-arene PTA complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 4161–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Ong, M.S.; Groessl, M.; Adhireksan, Z.; Hartinger, C.G.; Dyson, P.J.; Davey, C.A. A Ruthenium Antimetastasis Agent Forms Specific Histone Protein Adducts in the Nucleosome Core. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 3562–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougana, S.J.; Sadler, P.J. The Design of Organometallic Ruthenium Arene Anticancer Agents. Chimia 2007, 61, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, A.A.; Hartinger, C.G.; Dyson, P.J. Opening the lid on piano-stool complexes: An account of ruthenium(II)-arene complexes with medicinal applications. J. Organomet. Chem. 2014, 751, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.K.; Melchart, M.; Habtemariam, A.; Dyson, P.J. Organometallic chemistry, biology and medicine: Ruthenium arene anticancer complexes. Chem. Commun. 2005, 4764–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenis-Rojas, O.A.; Robalo, M.P.; Tomaz, A.I.; Carvalho, A.; Fernandes, A.R.; Marques, F.; Folgueira, M.; Yáñez, J.; Vázquez-García, D.; López Torres, M.; et al. RuII p-cymene Compounds as Effective and Selective Anticancer Candidates with No Toxicity in Vivo. Inorg Chem. 2018, 57, 13150–13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolić, S.; Rangasamy, L.; Gligorijević, N.; Aranđelović, S.; Radulović, S.; Gasser, G.; Grgurić-Šipka, S. Synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation of novel Ru(II)-arene complexes containing intercalating ligands. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 160, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süss-Fink, G. Arene ruthenium complexes as anticancer agents. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 1673–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremlett, W.D.J.; Goodman, D.M.; Steel, T.R.; Kumar, S.; Wieczorek-Błauż, A.; Walsh, F.P.; Sullivan, M.P.; Hanif, M.; Hartinger, C.G. Design Concepts of Half-Sandwich Organoruthenium Anticancer Agents Based on Bidentate Bioactive Ligands. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 445, 213950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Sen, U.; Roy, N.; Muthukumar, V.; Sahoo, S.K.; Bose, B.; Paira, P. DNA Targeting Half Sandwich Ru (II)-p-cymene-N,N Complexes as Cancer Cell Imaging and Terminating Agents: Influence of Regioisomers in Cytotoxicity. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 979–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumithaa, G.; Ganeshpandian, M. Half-Sandwich Ruthenium Arene Complexes Bearing Clinically Approved Drugs as Ligands: The Importance of Metal–Drug Synergism in Metallodrug Design. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 1453–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsolis, T.; Papavasileiou, K.D.; Divanis, S.A.; Melissas, V.S.; Garoufis, A. How half sandwich ruthenium compounds interact with DNA while not being hydrolyzed: A comparative study. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2016, 160, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, M.; Mantoo, I.A.; Arjmand, F.; Tabassum, S.; Yousuf, I. An overview of advancement of organoruthenium(II) complexes as prospective anticancer agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 487, 215169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matada, B.S.; Pattanashettar, R.; Yernale, N.G. A comprehensive review on the biological interest of quinoline and its derivatives. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2021, 32, 115973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chancha, S.; Sarkarb, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. RutheniumIJII)–arene complexes as anti-metastatic agents, and related techniques. RSC Med. Chem. 2022, 13, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, A.A.; Pietro, W.J. Telechelic poly(-caprolactones) with tethered mixed ligand ruthenium(II) chromophores. Can. J. Chem. 2004, 82, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamoto, K. Infrared and Raman Spectra of Inorganic and Coordination Compounds: Part B: Applications in Coordination, Organometallic and Bioinorganic Chemistry, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780470405888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, P.; Lu, R.; Qian, Q.; Lei, X.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, S.; Liu, L.; Huang, C.; Su, W. Synthesis, X-ray Diffraction Study, and Cytotoxicity of a Cationic p-Cymene Ruthenium Chloro Complex Containing a Chelating Semicarbazone Ligand. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2013, 639, 943–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milton, A.; Benial, F.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Murugesan, R. Infrared and laser Raman studies of [Ni(II)(dppe)Cl2] and [Co(III)(dppe)2Cl2]PF6 (dppe=1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane). Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2002, 58, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkosi, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Ruthenium(ΙΙ) Complexes of the Type Ru(p-cymene)ClL]X, where X (X = Cl−, PF6−) and L (L = 2,2′-pyridyl-4-(hydroxymethyl)quinoline). Cell Viability Experiments of the New Compounds, on HEK293T and on HeLa Cancer Cell Lines. Master’s Thesis, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2023. Available online: https://pergamos.lib.uoa.gr/uoa/dl/object/3329312 (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Stebler-Rothlisberger, M.; Hummel, W.; Pittet, P.-A.; Biirgi, H.-B.; Ludi, A.; Merbach, A.E. Triaqua(benzene)ruthenium(II) and Triaqua(benzene)osmium(II):Synthesis, Molecular Structure and Water-Exchange Kinetics. Inorg. Chem. 1988, 27, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, O.; Demirmen, S.; Özdemir, N. Heteroleptic ruthenium(II) complexes of 2-(2-pyridyl)benzimidazoles: A study of catalytic efficiency towards transfer hydrogenation of acetophenone. Polyhedron 2015, 85, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małecki, J.G. Half-sandwich ruthenium(II) complexes with N- and N,(N,O)-donor ligands: Molecular, electronic structures, and computational study. Struct. Chem. 2012, 23, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüther, T.; Woodward, C.P.; Jones, T.W.; Coghlan, C.J.; Hebting, Y.; Cordiner, R.L.; Dawson, R.E.; Robinson, D.E.; Wilson, G.J. Synthesis, characterisation, and properties of p-cymene Ruthenium(II) tetracarboxylate bipyridine complexes [(η6-p-cymene)Ru(Rn,Rn′-tcbpy)Cl][Cl]. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 823, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillinger, A.; Parkinson, B.A. The Adsorption Behavior of a Ruthenium-Based Sensitizing Dye to Nanocrystalline TiO2 Coverage Effects on the External and Internal Sensitization Quantum Yields. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1999, 146, 4559–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.A.; Huang, T.N.; Matheson, T.W.; Smith, K. Inorganic Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1982; Volume 21, pp. 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gichumbi, J.M.; Friedrich, H.B.; Omondi, B.; Singh, M.; Naicker, K.; Chenia, H.Y. Synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities of ruthenium(II) arene complexes with N,N-bidentate ligands. J. Coord. Chem. 2016, 69, 3531–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalrempuia, R.; Kollipara, M.R. Reactivity studies of η6-arene ruthenium (II) dimers with polypyridyl ligands: Isolation of mono, binuclear p-cymene ruthenium (II) complexes and bisterpyridine ruthenium (II) complexes. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 3155–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dömötör, O.; Pape, V.F.S.; May, N.V.; Szakacs, G.; Enyedy, E.A. Comparative solution equilibrium studies of antitumor ruthenium(η6 -p-cymene) and rhodium(η5-C5Me5) complexes of 8- hydroxyquinolines. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 4382–4396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsierkezos, N.G.; Ritter, U.; Philippopoulos, A.I.; Schröder, D. Electrochemical studies of the bis (triphenyl phosphine) ruthenium(II) complex, cis-[RuCl2(L)(PPh3)2], with L = 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline. J. Coord. Chem. 2010, 63, 3517–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, W. The use of conductivity measurements in organic solvents for the characterisation of coordination compounds. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1971, 7, 81–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, E.J.; Gao, X.N.; Guan, F.; Zhu, M.C.; Liu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Synthesis and crystal structure of two new dinuclear cobalt(II) complexes interaction with HeLa cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margariti, A.; Papakonstantinou, V.D.; Stamatakis, G.M.; Demopoulos, C.A.; Machalia, C.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Schnakenburg, G.; Nika, M.-C.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Philippopoulos, A.I. First-Row Transition Metal Complexes Incorporating the 2-(2′-pyridyl)quinoxaline Ligand (pqx), as Potent Inflammatory Mediators: Cytotoxic Properties and Biological Activities against the Platelet-Activating Factor (PAF) and Thrombin. Molecules 2023, 28, 6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujante-Galián, M.A.; Pérez, S.A.; Montalbán, M.G.; Carissimi, G.; Fuster, M.G.; Víllora, G.; García, G. p-Cymene Complexes of Ruthenium(II) as Antitumor Agents. Molecules 2020, 25, 5063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuster, M.G.; Moulefera, I.; Montalbán, M.G.; Pérez, J.; Víllora, G.; García, G. Synthesis and Characterization of New Ruthenium (II) Complexes of Stoichiometry [Ru(p-Cymene)Cl2L] and Their Cytotoxicity against HeLa-Type Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtemariam, A.; Melchart, M.; Fernández, R.; Parsons, S.; Oswald, I.D.; Parkin, A.; Fabbiani, F.P.; Davidson, J.E.; Dawson, A.; Aird, R.E.; et al. Structure-activity relationships for cytotoxic ruthenium(II) arene complexes containing N,N-, N,O-, and O,O-chelating ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6858–6868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralisankar, M.; Chen, J.-R.; Haribabu, J.; Ke, S.-C. Effective and Selective Ru(II)-Arene Complexes Containing 4,4′-Substituted 2,2′ Bipyridine Ligands Targeting Human Urinary Bladder Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, Y.; Morgan, R.J.; Donovan, R.J.; Baker, A.D. A simple preparation of a functioalized diimine ligand: 2-(2-pyridyl)-4- carboxyquinoline. Synth. Commun. 1997, 27, 2165–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Homoleptic Copper(I) Complexes. Application in Third Generation Solar Cells (Gratzel Type). Master’s Thesis, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2015. Available online: https://pergamos.lib.uoa.gr/uoa/dl/object/1320032 (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Peppas, A.; Papadaki, E.; Schnakenburg, G.; Magrioti, V.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Heteroleptic copper(I) complexes incorporating sterically demanding diazabutadiene ligands (DABs). Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and solid state structural analysis. Polyhedron 2019, 171, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT—Integrated space-group and crystal structure determination. Acta Cryst. 2015, A71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Cryst. 2008, A64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Cryst. 2015, C71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement, and analysis program. J. Appl. Cryst. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

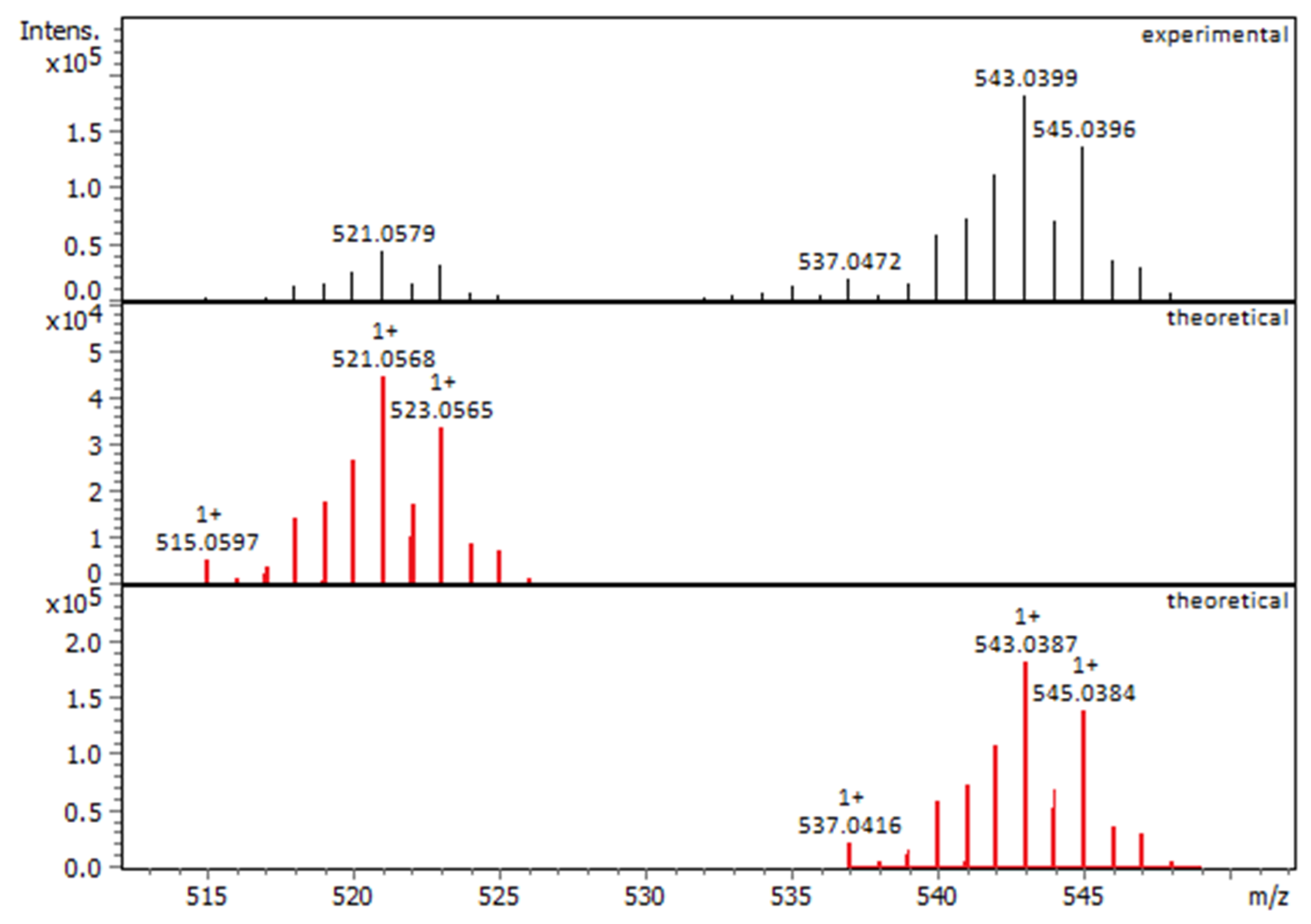
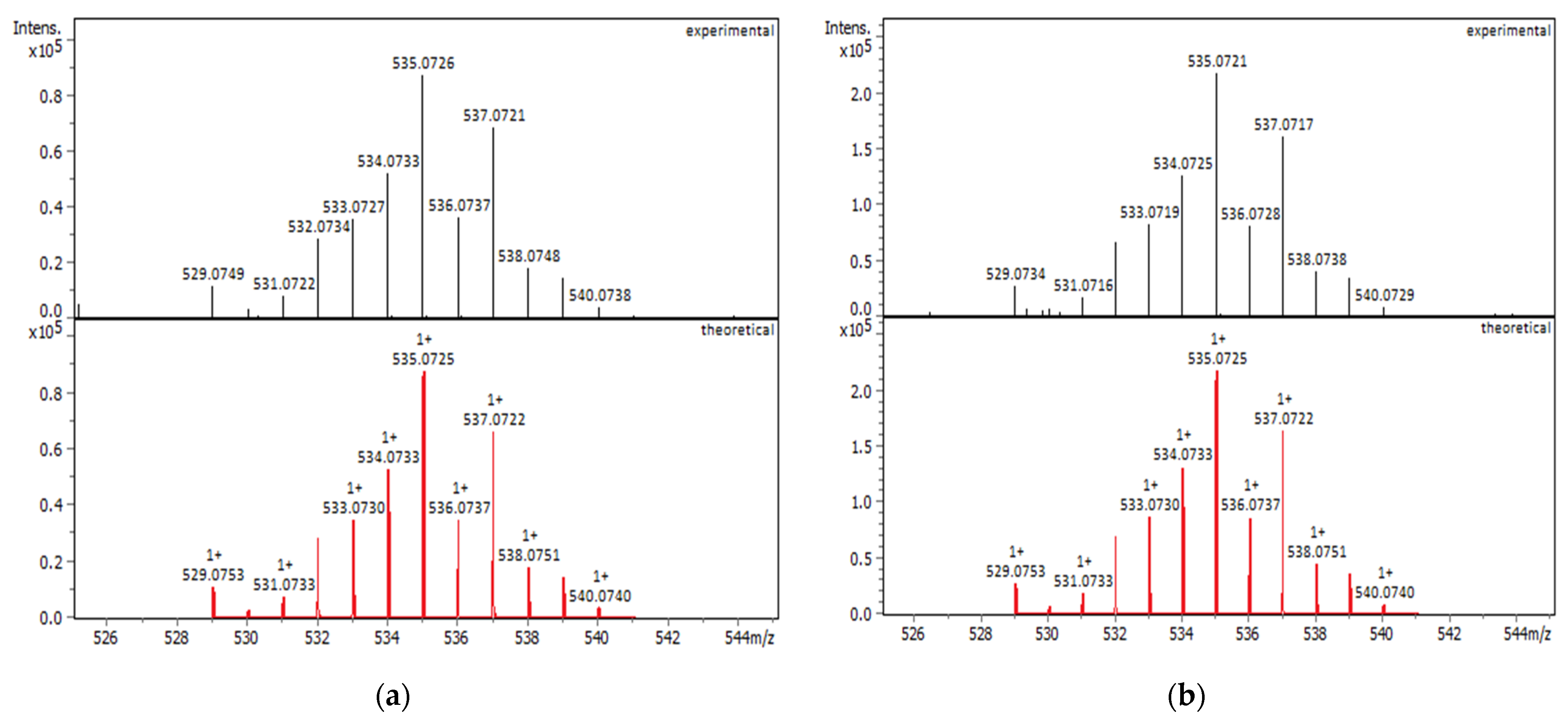
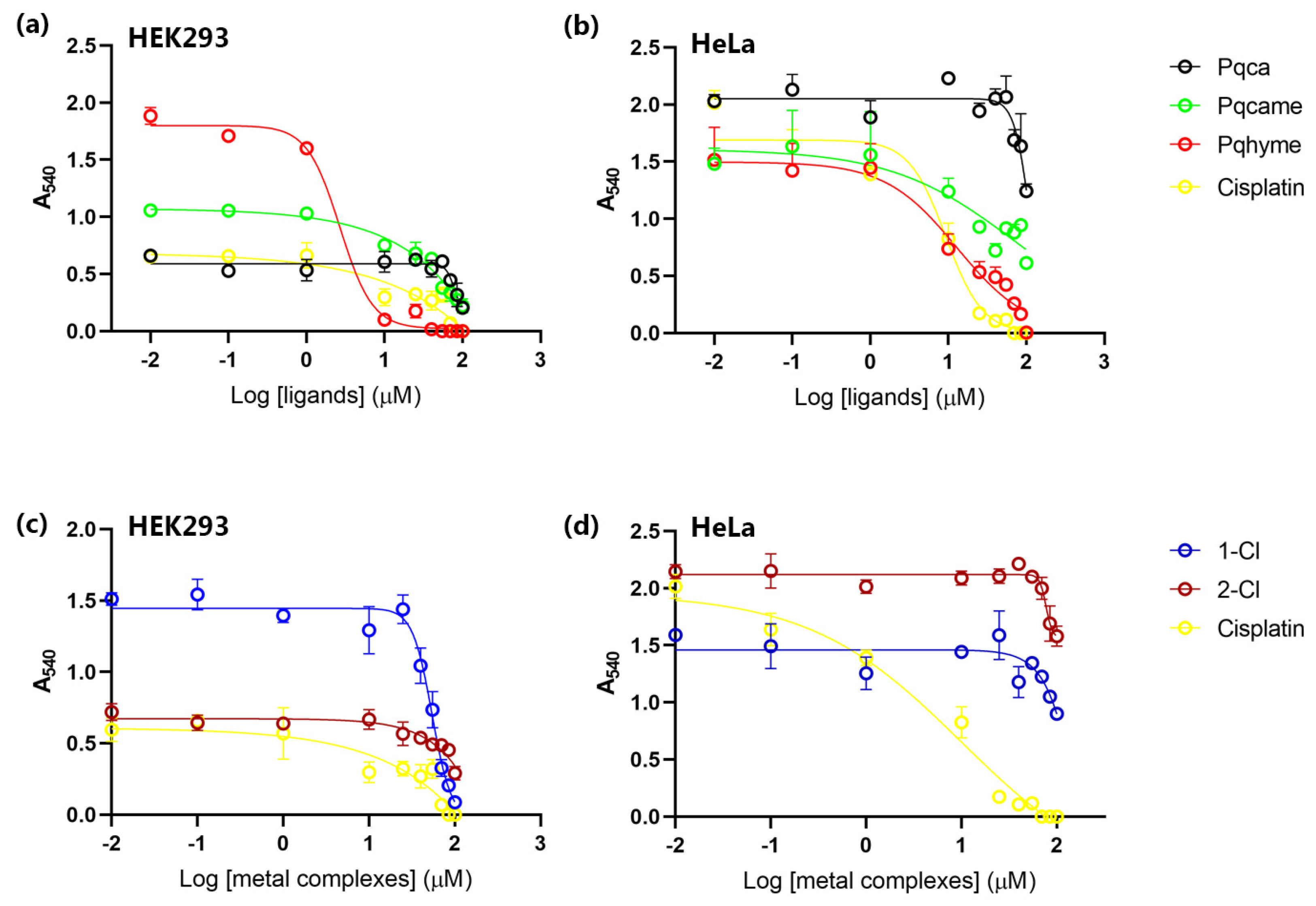

| Compounds | IC50 for HEK293T Cells (μM) | IC50 for HeLa Cells (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| pqhyme | 2.67 ± 1.23 | 12.84 ± 1.01 |
| [Ru(p-cymene)Cl2]2 | 48.33 ± 1.66 | 48.90 ± 1.73 |
| 1-Cl | 54.39 ± 1.53 | 119.40 ± 1.29 |
| pqca | 87.48 ± 1.30 | 100.00 ± 3.47 |
| 2-Cl | 179.60 ± 49.12 | 162.00 ± 21.30 |
| pqcame | 48.85 ± 3.19 | 56.44 ± 12.68 |
| 3-Cl | >115 | >80 |
| 3-PF6 | 145.30 ± 16.20 | 134.40 ± 3.30 |
| cis-platin | 16.41 ± 7.62 | 9.26 ± 1.09 |
| Compound | 1-PF6 | 3-PF6 |
|---|---|---|
| Color, habit | Yellow, block | Yellow, plate |
| Size/mm | 0.044 × 0.043 × 0.037 | 0.106 × 0.04 × 0.02 |
| Empirical formula | C25H26ClF6N2OPRu | C26H26ClF6N2O2PRu |
| FW | 651.97 | 679.98 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Triclinic |
| Space group | P21/c | P-1 |
| a/Å | 11.0604(10) | 10.9647(7) |
| b/Å | 20.486(2) | 11.4231(7) |
| c/Å | 10.9695(12) | 22.0613(13) |
| α/° | 90 | 102.738(3) |
| β/° | 93.802(4) | 90.100(3) |
| γ/° | 90 | 90.030(3) |
| V/Å3 | 2480.1(4) | 2695.2(3) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| μ/mm−1 | 0.873 | 6.815 |
| T/K | 100 | 100 |
| θmin/max/full (°) | 1.988/28.247/25.242 | 2.053/72.383/67.679 |
| Completeness to θmax/full (%) | 99.0/99.6 | 99.4/100 |
| Reflections total/ Independent | 20955/4275 | 129500/10164 |
| Parameters/restraints | 391/12 | 795/24 |
| Rint | 0.1199 | 0.0603 |
| Final R1, wR2 | 0.0477/0.1104 | 0.0347/0.0881 |
| Goodness-of-fit | 0.994 | 1.074 |
| Largest peak, hole/e.Å−3 | 0.9/-1.2 | 1.6/−0.9 |
| ρcalc/g·cm−3 | 1.746 | 1.676 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kokkosi, A.; Garofallidou, E.; Zacharopoulos, N.; Tsoureas, N.; Diamanti, K.; Thomaidis, N.S.; Cheilari, A.; Machalia, C.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Philippopoulos, A.I. Ruthenium p-Cymene Complexes Incorporating Substituted Pyridine–Quinoline-Based Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization, and Cytotoxic Properties. Molecules 2024, 29, 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133215
Kokkosi A, Garofallidou E, Zacharopoulos N, Tsoureas N, Diamanti K, Thomaidis NS, Cheilari A, Machalia C, Emmanouilidou E, Philippopoulos AI. Ruthenium p-Cymene Complexes Incorporating Substituted Pyridine–Quinoline-Based Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization, and Cytotoxic Properties. Molecules. 2024; 29(13):3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133215
Chicago/Turabian StyleKokkosi, Afroditi, Elpida Garofallidou, Nikolaos Zacharopoulos, Nikolaos Tsoureas, Konstantina Diamanti, Nikolaos S. Thomaidis, Antigoni Cheilari, Christina Machalia, Evangelia Emmanouilidou, and Athanassios I. Philippopoulos. 2024. "Ruthenium p-Cymene Complexes Incorporating Substituted Pyridine–Quinoline-Based Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization, and Cytotoxic Properties" Molecules 29, no. 13: 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133215
APA StyleKokkosi, A., Garofallidou, E., Zacharopoulos, N., Tsoureas, N., Diamanti, K., Thomaidis, N. S., Cheilari, A., Machalia, C., Emmanouilidou, E., & Philippopoulos, A. I. (2024). Ruthenium p-Cymene Complexes Incorporating Substituted Pyridine–Quinoline-Based Ligands: Synthesis, Characterization, and Cytotoxic Properties. Molecules, 29(13), 3215. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133215












