High-Throughput Mining of Novel Compounds from Known Microbes: A Boost to Natural Product Screening
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Why Novel Drugs Are Required?
1.2. Conventional and Current Strategies for Drug Discovery
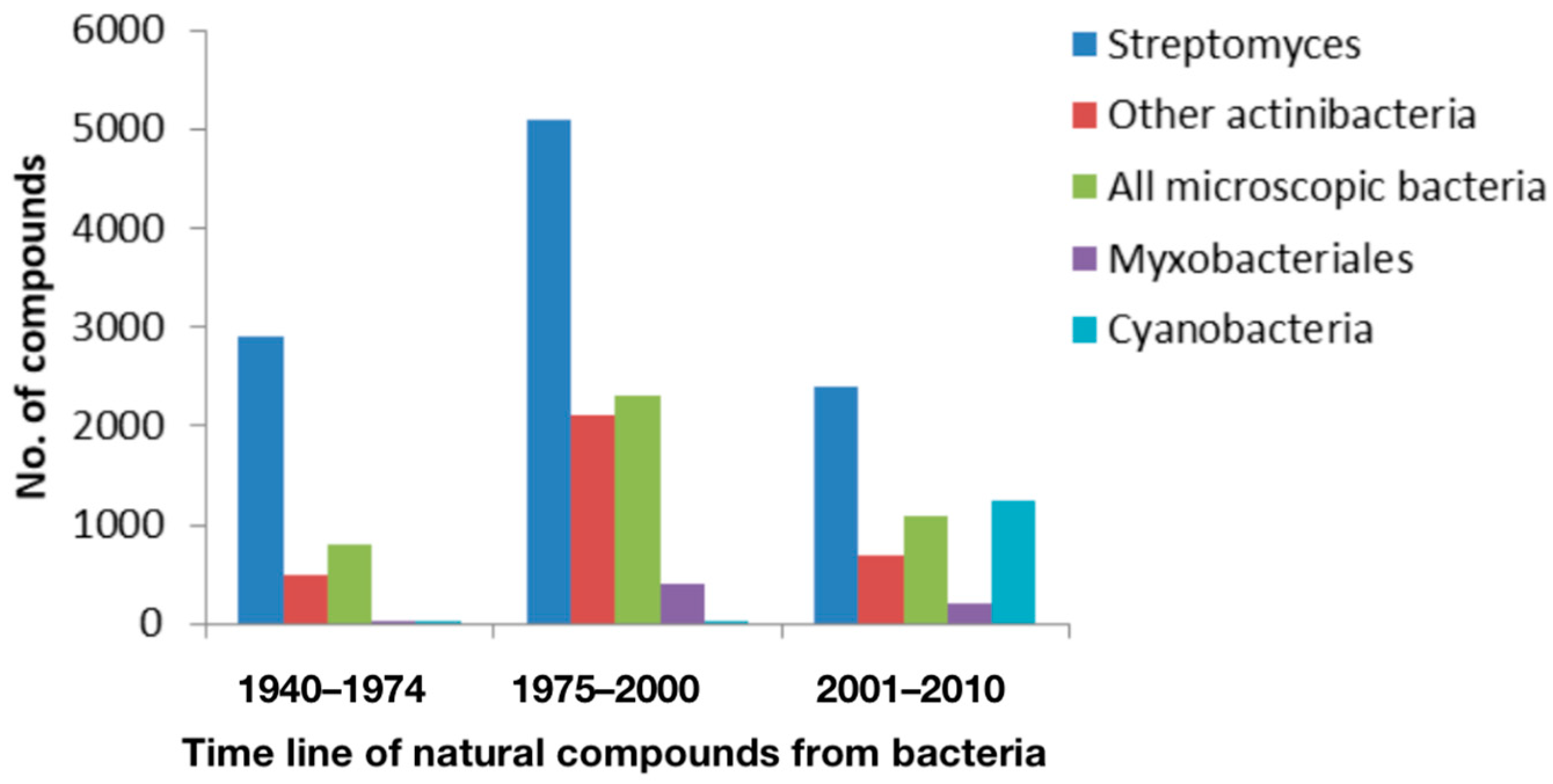
1.3. Novel Sources: Novel Drug Approach
2. Microbial Genome Mining for Cryptic BGCs
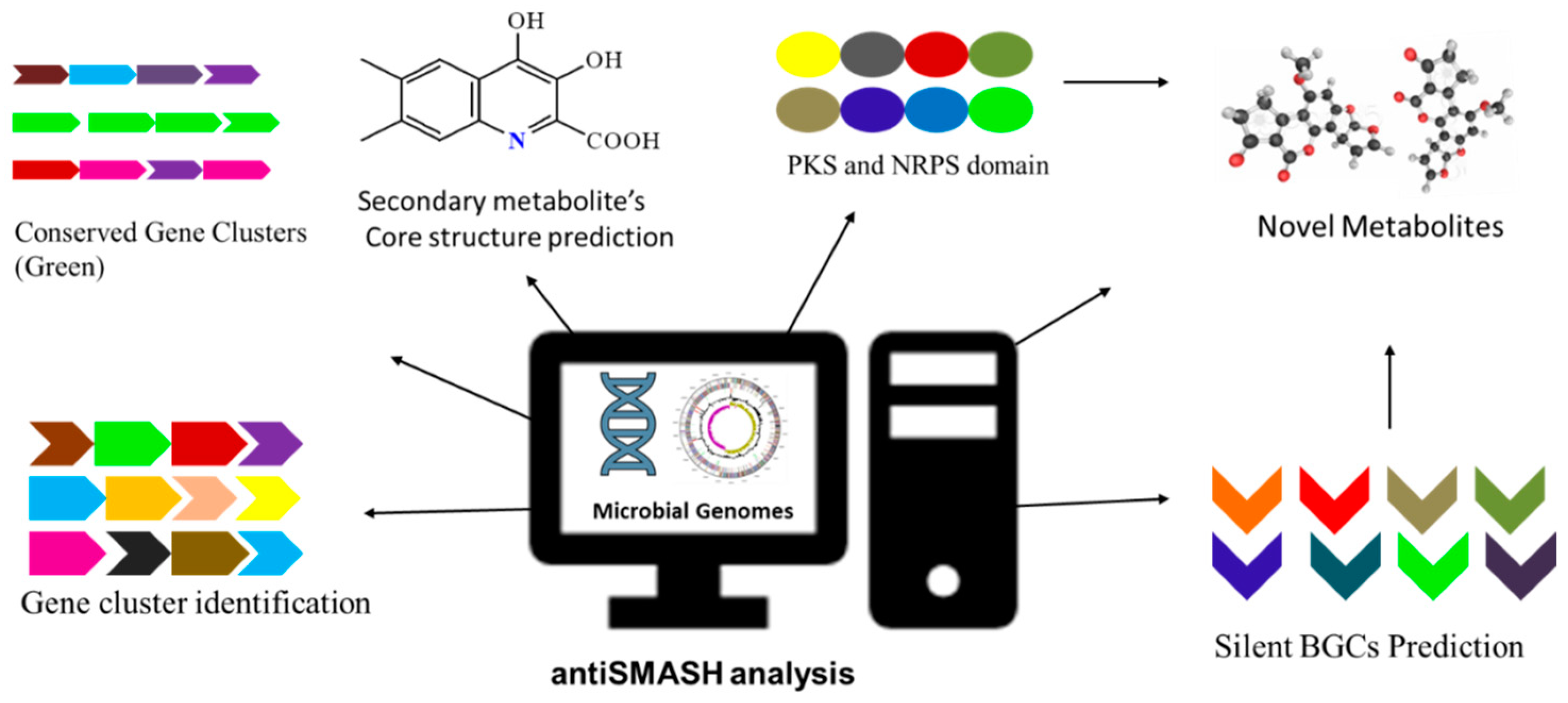
2.1. Bioinformatics Tools for Genome Mining
Workflow of antiSMASH
3. Strategies to Activate the Expression of Silent BGCs
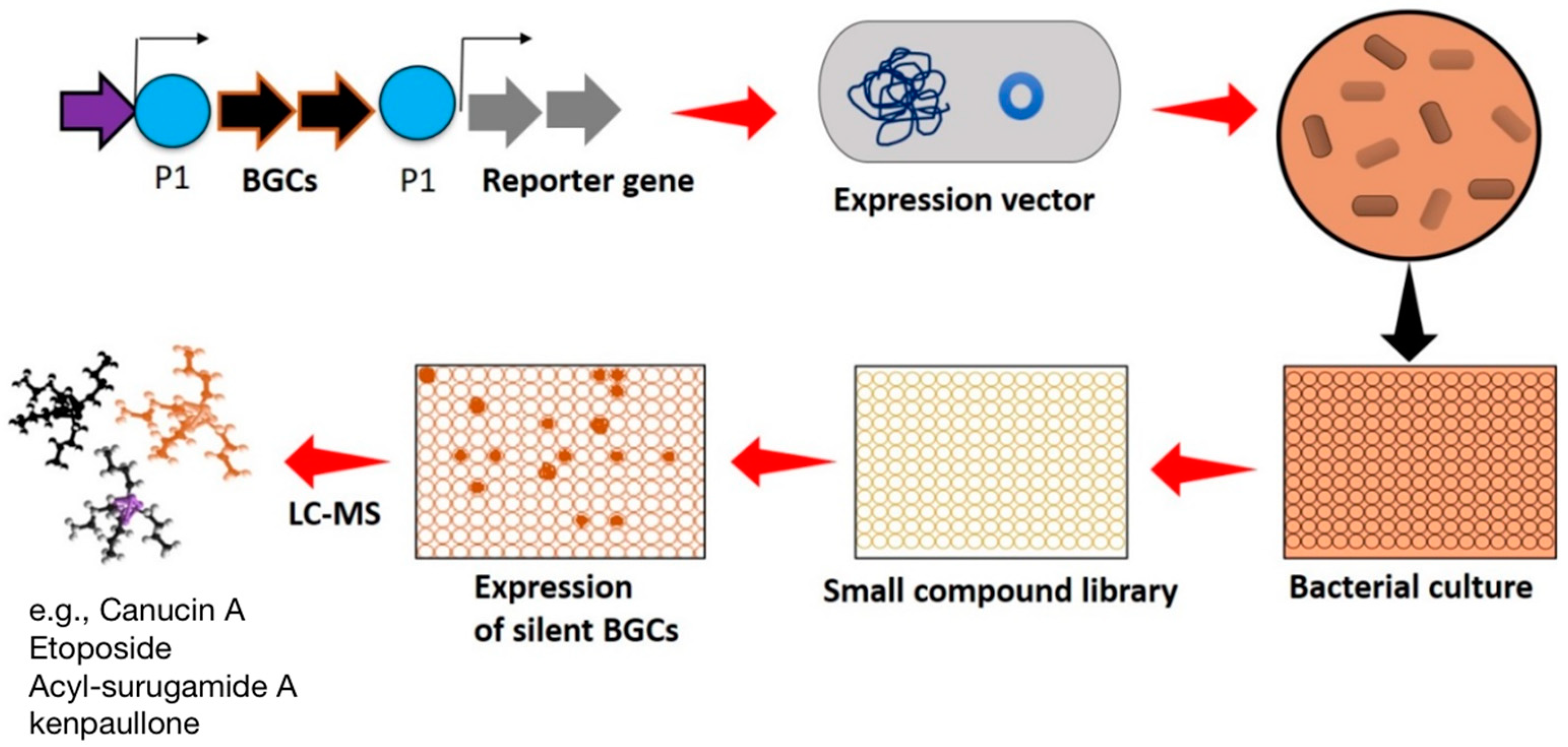
3.1. High-Throughput Expression of Silent BGCs
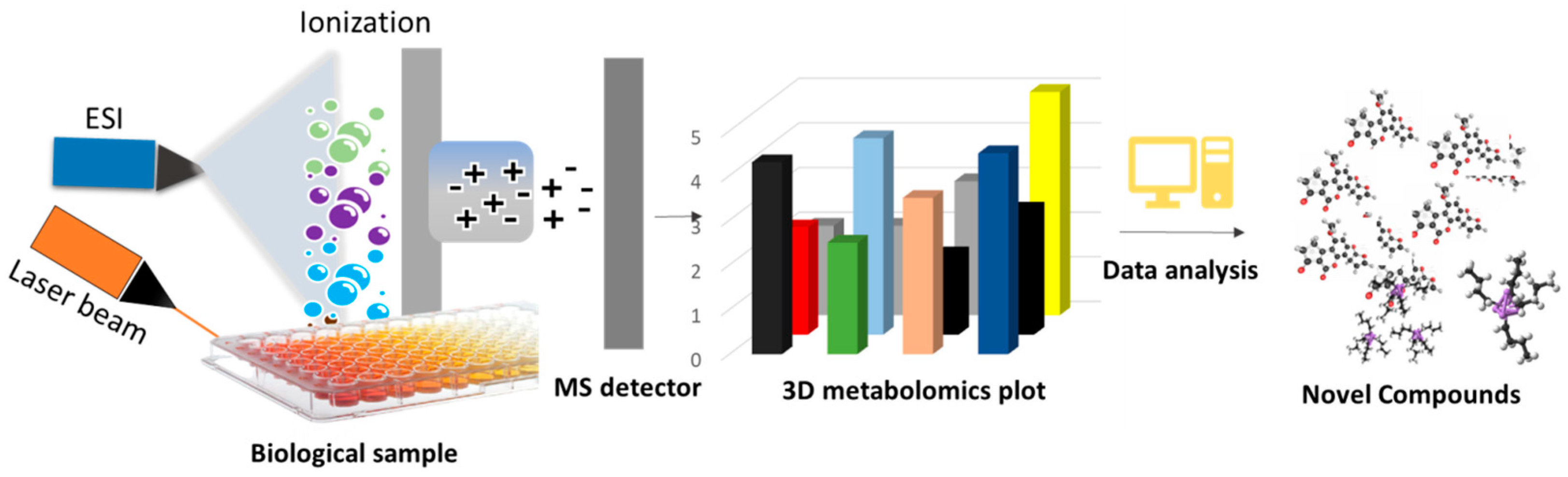
3.1.1. Imaging Mass Spectrometry in High-Throughput Screening of NCs
3.1.2. HiTES Coupled with the IMS Technique in High-Throughput Screening of NCs
Workflow of HiTES-IMS
4. Dereplication of Natural Products
Workflow to Generate MN
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Demain, A.L. Importance of Microbial Natural Products and the Need to Revitalize Their Discovery. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, M.A. Antibiotics from Microbes: Converging to Kill. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubira, C.; de Oliveira Carvalho, P.E.; Cataneo, A.J.; Carvalho, L.R. Antibiotics for Preventing Infection in People Receiving Chest Drains. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2017, CD009165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussmann, M.; Abe Cunha, D.H.; Berciano, S. Bioactive Compounds for Human and Planetary Health. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1193848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Kumar, V.; Rathore, S.; Vyas, A.; Nagarajan, R.; Panwar, H. Natural Bio-Colorant and Pigments: Sources and Applications in Food Processing. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 12, 100628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybczyńska-Tkaczyk, K.; Łopusiewicz, Ł.; Bartkowiak, A.; Horubała, A.; Miazga-Karska, M.; Sołowiej, B. Natural Compounds with Antimicrobial Properties in Cosmetics. Pathogens 2023, 12, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yao, M.; Lv, L.; Ling, Z.; Li, L. The Human Microbiota in Health and Disease. Engineering 2017, 3, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M. The Human Microbiota in Health and Disease: An Ecological and Community-Based Approach; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Methé, B.A.; Nelson, K.E.; Pop, M.; Creasy, H.H.; Giglio, M.G.; Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; Petrosino, J.F.; Abubucker, S.; Badger, J.H.; et al. A Framework for Human Microbiome Research. Nature 2012, 486, 215. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Chen, Y.; Dou, Q.P. Are We Seeing a Resurgence in the Use of Natural Products for New Drug Discovery? Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, A.M. Rediscovering Natural Products. Chem. Eng. News 2003, 81, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Nascimento, I.J.; de Moura, R.O. Ligand and Structure-Based Drug Design (LBDD and SBDD): Promising Approaches to Discover New Drugs. In Applied Computer-Aided Drug Design: Models and Methods; Bentham Science Publihers: Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 2023; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Volochnyuk, D.M.; Ryabukhin, S.V.; Moroz, Y.S.; Savych, O.; Chuprina, A.; Horvath, D.; Zabolotna, Y.; Varnek, A.; Judd, D.B. Evolution of Commercially Available Compounds for HTS. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, A.A.; Iram, F.; Siddiqui, S.; Sahu, K. Role of Natural Products in Drug Discovery Process. Int. J. Drug Dev. Res. 2014, 6, 172–204. [Google Scholar]
- DiMasi, J.A.; Hansen, R.W.; Grabowski, H.G. The Price of Innovation: New Estimates of Drug Development Costs. J. Health Econ. 2003, 22, 151–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, S.; Grootendorst, P.; Lexchin, J.; Cunningham, C.; Greyson, D. The Cost of Drug Development: A Systematic Review. Health Policy 2001, 100, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.M.; Mytelka, D.S.; Dunwiddie, C.T.; Persinger, C.C.; Munos, B.H.; Lindborg, S.R.; Schacht, A.L. How to Improve R&D Productivity: The Pharmaceutical Industry’s Grand Challenge. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 203–214. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, M.L. Changing Patterns of Infectious Disease. Nature 2000, 406, 762–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.F.; Goldberg, M.; Rosenthal, S.; Carlson, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, C.; Ramachandran, S. Global Rise in Human Infectious Disease Outbreaks. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneyama, H.; Katsumata, R. Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria and Its Future for Novel Antibiotic Development. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 1060–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, L.L.; Bostian, K.A. Discovery and Development of New Antibiotics: The Problem of Antibiotic Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1993, 37, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneci, P.; Miertus, S. Combinatorial Chemistry and High-Throughput Screening in Drug Discovery: Different Strategies and Formats. Mol. Divers. 2000, 5, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appell, K.; Baldwin, J.J.; Egan, W.J. Combinatorial Chemistry and High-Throughput Screening in Drug Discovery and Development. In Handbook of Modern Pharmaceutical Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 3, pp. 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- Kodadek, T. The Rise, Fall and Reinvention of Combinatorial Chemistry. Chem. Comm. 2011, 47, 9757–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djaballah, H. Chemical Space, High Throughput Screening and the World of Blockbuster Drugs. DDW Spring. 2013. Available online: https://www.ddw-online.com/chemical-space-high-throughput-screening-and-the-world-of-blockbuster-drugs-1528-201304/ (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Bérdy, J. Thoughts and Facts about Antibiotics: Where We Are Now and Where We Are Heading. J. Antibiot. 2012, 65, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.H. Antimicrobial Drug Development—The Past, the Present, and the Future. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Projan, S.J.; Shlaes, D.M. Antibacterial Drug Discovery: Is It All Downhill from Here? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2004, 10, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, K. Antibiotics: From Prehistory to the Present Day. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokem, J.S.; Lantz, A.E.; Nielsen, J. Systems Biology of Antibiotic Production by Microorganisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 1262–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudêncio, S.P.; Pereira, F.; Barata, T.; Vasconcelos, C. Advanced Methods for Natural Products Discovery: Bioactivity Screening, Dereplication, Metabolomics Profiling, Genomic Sequencing, Databases and Informatic Tools, and Structure Elucidation. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breinbauer, R.; Manger, M.; Scheck, M.; Waldmann, H. Natural Product Guided Compound Library Development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 2129–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayon, N.J. High-Throughput Screening of Natural Product and Synthetic Molecule Libraries for Antibacterial Drug Discovery. Metabolites 2023, 13, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breinbauer, R.; Vetter, I.R.; Waldmann, H. From Protein Domains to Drug Candidates—Natural Products as Guiding Principles in the Design and Synthesis of Compound Libraries. Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 2968–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paululat, T.; Tang, Y.Q.; Grabley, S.; Thiericke, R. Combinatorial Chemistry: The Impact of Natural Products. Chimica Oggi 1999, 17, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Procópio, R.E.L.; Silva, I.R.; Martins, M.K.; Azevedo, J.L.; Araújo, J.M. Antibiotics Produced by Streptomyces. Braz. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 16, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, H.B.; Bethe, B.; Höfs, R.; Zeeck, A. Big Effects from Small Changes: Possible Ways to Explore Nature’s Chemical Diversity. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiewe, H.J.; Zeeck, A. Cineromycins, γ-Butyrolactones and Ansamycins by Analysis of the Secondary Metabolite Pattern Created by a Single Strain of Streptomyces. J. Antibiot. 1999, 52, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardt, I.H.; Steinmetz, H.; Gerth, K.; Sasse, F.; Reichenbach, H.; Höfle, G. New Natural Epothilones from Sorangium cellul osum, Strains So ce90/B2 and So ce90/D13: Isolation, Structure Elucidation, and SAR Studies. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wink, M. Genes of Secondary Metabolism: Differential Expression in Plants and in Vitro Cultures and Functional Expression in Genetically Transformed Microorganisms. In Primary and Secondary Metabolism of Plant Cell Cultures II; Kurz, W.G.W., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.F.; Liras, P. Organization and Expression of Genes Involved in the Biosynthesis of Antibiotics and Other Secondary Metabolites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1989, 43, 173–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Koonin, E.V. Searching for Drug Targets in Microbial Genomes. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1999, 10, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, L.H. DNA and Associated Targets for Drug Design. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Saitou, A.; Wang, C.M.; Toyoda, A.; Minakuchi, Y.; Sekiguchi, Y.; Ueda, K.; Takano, H.; Sakai, Y.; Abe, K.; et al. Genome Features and Secondary Metabolites Biosynthetic Potential of the Class Ktedonobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bok, J.W.; Hoffmeister, D.; Maggio-Hall, L.A.; Murillo, R.; Glasner, J.D.; Keller, N.P. Genomic Mining for Aspergillus Natural Products. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H. Advances in Mining and Expressing Microbial Biosynthetic Gene Clusters. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 49, 18–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, D.; Okada, B.K.; Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. Recent Advances in Activating Silent Biosynthetic Gene Clusters in Bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reen, F.J.; Romano, S.; Dobson, A.D.; O’Gara, F. The Sound of Silence: Activating Silent Biosynthetic Gene Clusters in Marine Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4754–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wang, B.; Zhao, H. Breaking the Silence: New Strategies for Discovering Novel Natural Products. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 48, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Meij, A.; Worsley, S.F.; Hutchings, M.I.; van Wezel, G.P. Chemical Ecology of Antibiotic Production by Actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 392–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.N.M. Biosynthetic Gene Cluster Evaluation-Genome Mining for Natural Product Formation. Ph.D. Dissertation, Technische Universität München, Munich, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, H.A.; Feng, Z.; Brady, S.F. Biocatalysts and Small Molecule Products from Metagenomic Studies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012, 16, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Fewer, D.P.; Holm, L.; Rouhiainen, L.; Sivonen, K. Atlas of Nonribosomal Peptide and Polyketide Biosynthetic Pathways Reveals Common Occurrence of Nonmodular Enzymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 9259–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, J.J.; Bader, C.D.; Remškar, M.; Cirnski, K.; Müller, R. Concepts and Methods to Access Novel Antibiotics from Actinomycetes. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L.; Baltz, R.H. Natural Product Discovery: Past, Present, and Future. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 43, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Kong, L.; Wang, T.; Chu, Y.; Deng, Z.; You, D. Unveiling the Post-PKS Redox Tailoring Steps in Biosynthesis of the Type II Polyketide Antitumor Antibiotic Xantholipin. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, V.; Coeffet-LeGal, M.F.; Brian, P.; Brost, R.; Penn, J.; Whiting, A.; Martin, S.; Ford, R.; Parr, I.; Bouchard, M.; et al. Daptomycin Biosynthesis in Streptomyces roseosporus: Cloning and Analysis of the Gene Cluster and Revision of Peptide Stereochemistry. Microbiology 2005, 151, 1507–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.R.; Yoo, Y.J.; Ban, Y.H.; Yoon, Y.J. Biosynthesis of Rapamycin and Its Regulation: Past Achievements and Recent Progress. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staunton, J.; Weissman, K.J. Polyketide Biosynthesis: A Millennium Review. J. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 380–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meesil, W.; Sermwittayawong, N.; Intra, B.; Kitani, S.; Thancharoen, A.; Duangrattanalert, K.; Igarashi, Y. Genome Mining Reveals Novel Biosynthetic Gene Clusters in Entomopathogenic Bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamek, M.; Spohn, M.; Stegmann, E.; Ziemert, N. Mining Bacterial Genomes for Secondary Metabolite Gene Clusters. In Antibiotics; Sass, P., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 23–47. [Google Scholar]
- Medema, M.H.; Blin, K.; Cimermancic, P.; De Jager, V.; Zakrzewski, P.; Fischbach, M.A.; Weber, T.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. antiSMASH: Rapid Identification, Annotation and Analysis of Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis Gene Clusters in Bacterial and Fungal Genome Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39 (Suppl. 2), W339–W346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, D.; Shen, Y. Discovery of Novel Bioactive Natural Products Driven by Genome Mining. Drug Discov. Ther. 2018, 12, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaldi, N.; Seifuddin, F.T.; Turner, G.; Haft, D.; Nierman, W.C.; Wolfe, K.H.; Fedorova, N.D. SMURF: Genomic Mapping of Fungal Secondary Metabolite Clusters. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.H.; Ung, P.M.; Zajkowski, J.; Garneau-Tsodikova, S.; Sherman, D.H. Automated Genome Mining for Natural Products. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, T.; Rausch, C.; Lopez, P.; Hoof, I.; Gaykova, V.; Huson, D.H.; Wohlleben, W. CLUSEAN: A Computer-Based Framework for the Automated Analysis of Bacterial Secondary Metabolite Biosynthetic Gene Clusters. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 140, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starcevic, A.; Zucko, J.; Simunkovic, J.; Long, P.F.; Cullum, J.; Hranueli, D. ClustScan: An Integrated Program Package for the Semi-Automatic Annotation of Modular Biosynthetic Gene Clusters and In Silico Prediction of Novel Chemical Structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 6882–6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umemura, M.; Koike, H.; Nagano, N.; Ishii, T.; Kawano, J.; Yamane, N.; Kozone, I.; Horimoto, K.; Shin-ya, K.; Asai, K.; et al. MIDDAS-M: Motif-Independent De Novo Detection of Secondary Metabolite Gene Clusters through the Integration of Genome Sequencing and Transcriptome Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, T.; Shelest, V.; Nath, N.; Shelest, E. CASSIS and SMIPS: Promoter-Based Prediction of Secondary Metabolite Gene Clusters in Eukaryotic Genomes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1138–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, G.; Sze, S.H.; Thon, M.R. Identifying Clusters of Functionally Related Genes in Genomes. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1053–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural Products: A Continuing Source of Novel Drug Leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 3670–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the 30 Years from 1981 to 2010. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 311–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemert, N.; Alanjary, M.; Weber, T. The Evolution of Genome Mining in Microbes—A Review. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Chevrette, M.G.; Lu, X.; Schwalen, C.J.; Kautsar, S.A.; Suarez Duran, H.G.; De Los Santos, E.L.; Kim, H.U.; Nave, M.; Dickschat, J.S. antiSMASH 4.0—Improvements in Chemistry Prediction and Gene Cluster Boundary Identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W36–W41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Pascal Andreu, V.; De Los Santos, E.L.; Del Carratore, F.; Lee, S.Y.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. The antiSMASH Database Version 2: A Comprehensive Resource on Secondary Metabolite Biosynthetic Gene Clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D625–D630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Medema, M.H.; Kottmann, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Weber, T. The antiSMASH Database, a Comprehensive Database of Microbial Secondary Metabolite Biosynthetic Gene Clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 23, gkw960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Steinke, K.; Villebro, R.; Ziemert, N.; Lee, S.Y.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. antiSMASH 5.0: Updates to the Secondary Metabolite Genome Mining Pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W81–W87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villebro, R.; Shaw, S.; Blin, K.; Weber, T. Sequence-Based Classification of Type II Polyketide Synthase Biosynthetic Gene Clusters for antiSMASH. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, J.S.; Ghequire, M.G.; Nett, M.; Josten, M.; Sahl, H.G.; De Mot, R.; Gross, H. Biosynthetic Origin of the Antibiotic Pseudopyronines A and B in Pseudomonas putida BW11M1. Chem. Bio Chem. 2015, 16, 2491–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Shi, C.; Zhao, H. Computational Tools for Discovering and Engineering Natural Product Biosynthetic Pathways. iScience 2020, 23, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, T.; Blin, K.; Duddela, S.; Krug, D.; Kim, H.U.; Bruccoleri, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; Müller, R.; Wohlleben, W.; et al. antiSMASH 3.0—A Comprehensive Resource for the Genome Mining of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W237–W243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, B.; Akhgari, A.; Metsä-Ketelä, M. Activation of Microbial Secondary Metabolic Pathways: Avenues and Challenges. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2018, 3, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, M.K.; Meena, M.; Aamir, M.; Zehra, A.; Upadhyay, R.S. Regulation and Role of Metal Ions in Secondary Metabolite Production by Microorganisms. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Gupta, V.K., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 259–277. [Google Scholar]
- Bibb, M.J. Regulation of Secondary Metabolism in Streptomycetes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stutzman-Engwall, K.J.; Otten, S.L.; Hutchinson, C.R. Regulation of Secondary Metabolism in Streptomyces spp. and Overproduction of Daunorubicin in Streptomyces peucetius. J. Bacteriol. Res. 1992, 174, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, K.; Okamoto, S.; Tozawa, Y.; Inaoka, T.; Hosaka, T.; Xu, J.; Kurosawa, K. Ribosome Engineering and Secondary Metabolite Production. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 56, 155–179. [Google Scholar]
- Ashby, M.; Valley, M.; Shoemaker, D.D. Targeted Methods of Drug Screening Using Co-Culture Methods. U.S. Patent 6518035, 11 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Malpartida, F.; Hopwood, D.A. Molecular Cloning of the Whole Biosynthetic Pathway of a Streptomyces Antibiotic and Its Expression in a Heterologous Host. Nature 1984, 309, 462–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tao, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Long, Q.; Deng, Z.; Tao, M. Iteratively Improving Natamycin Production in Streptomyces gilvosporeus by a Large Operon-Reporter Based Strategy. Metab. Eng. 2016, 38, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potharla, V.Y.; Wang, C.; Cheng, Y.Q. Identification and Characterization of the Spiruchostatin Biosynthetic Gene Cluster Enable Yield Improvement by Overexpressing a Transcriptional Activator. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltz, R.H. Gifted Microbes for Genome Mining and Natural Product Discovery. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, B.K.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. Antibiotic Dialogues: Induction of Silent Biosynthetic Gene Clusters by Exogenous Small Molecules. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nah, H.J.; Pyeon, H.R.; Kang, S.H.; Choi, S.S.; Kim, E.S. Cloning and Heterologous Expression of a Large-Sized Natural Product Biosynthetic Gene Cluster in Streptomyces Species. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopatniuk, M.; Myronovskyi, M.; Nottebrock, A.; Busche, T.; Kalinowski, J.; Ostash, B.; Fedorenko, V.; Luzhetskyy, A. Effect of “Ribosome Engineering” on the Transcription Level and Production of S. albus Indigenous Secondary Metabolites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 7097–7110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, S.; Onaka, H.; Abe, I. Activation of Silent Biosynthetic Pathways and Discovery of Novel Secondary Metabolites in Actinomycetes by Co-Culture with Mycolic Acid-Containing Bacteria. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wright, G.D. Heterologous Expression-Facilitated Natural Products’ Discovery in Actinomycetes. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomm, H.A.; Ucciferri, L.; Ross, A.C. Advances in Microbial Culturing Conditions to Activate Silent Biosynthetic Gene Clusters for Novel Metabolite Production. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 1381–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammit, G.; Zammit, M.G.; Buttigieg, K.G. Emerging Technologies for the Discovery of Novel Diversity in Cyanobacteria and Algae and the Elucidation of Their Valuable Metabolites. Diversity 2023, 15, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, B.C.; McLean, J.A.; Bachmann, B.O. Comparative Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics Strategies for the Investigation of Microbial Secondary Metabolites. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, V. New Methods for the Discovery of Natural Products from Understudied and Uncultivated Bacterial Phyla. Ph.D. Dissertation, Open Access Te Herenga Waka-Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Craney, A.; Ozimok, C.; Pimentel-Elardo, S.M.; Capretta, A.; Nodwell, J.R. Chemical Perturbation of Secondary Metabolism Demonstrates Important Links to Primary Metabolism. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Davis, K.M.; Moon, K.; Bushin, L.B.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. A Genetics-Free Method for High-Throughput Discovery of Cryptic Microbial Metabolites. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.C.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. Though Much Is Taken, Much Abides: Finding New Antibiotics Using Old Ones. Biochemistry 2017, 56, 4925–4926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spraker, J.E.; Luu, G.T.; Sanchez, L.M. Imaging Mass Spectrometry for Natural Products Discovery: A Review of Ionization Methods. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemes, P.; Vertes, A. Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization for Atmospheric Pressure, In Vivo, and Imaging Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8098–8106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Balan, P.; Vertes, A. Molecular Imaging of Growth, Metabolism, and Antibiotic Inhibition in Bacterial Colonies by Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 15259–15263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fincher, J.A.; Korte, A.R.; Reschke, B.; Morris, N.J.; Powell, M.J.; Vertes, A. Enhanced Sensitivity and Metabolite Coverage with Remote Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry Aided by Coaxial Plume and Gas Dynamics. Analyst 2017, 142, 3157–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Vertes, A. Solvent Gradient Electrospray for Laser Ablation Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Analyst 2017, 142, 2921–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etalo, D.W.; De Vos, R.C.; Joosten, M.H.; Hall, R.D. Spatially Resolved Plant Metabolomics: Some Potentials and Limitations of Laser-Ablation Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry Metabolite Imaging. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stopka, S.A.; Agtuca, B.J.; Koppenaal, D.W.; Paša-Tolić, L.; Stacey, G.; Vertes, A.; Anderton, C.R. Laser-Ablation Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry with Ion Mobility Separation Reveals Metabolites in the Symbiotic Interactions of Soybean Roots and Rhizobia. Plant J. 2017, 91, 340–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poksay, K.S.; Sheffler, D.J.; Spilman, P.; Campagna, J.; Jagodzinska, B.; Descamps, O.; Gorostiza, O.; Matalis, A.; Mullenix, M.; Bredesen, D.E.; et al. Screening for Small Molecule Inhibitors of Statin-Induced APP C-Terminal Toxic Fragment Production. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, T.; Hester, Z.; Klinkert, I.; Both, J.P.; Heeren, R.M.; Brunelle, A.; Laprévote, O.; Desbenoit, N.; Robbe, M.F.; Stoeckli, M.; et al. imzML—A Common Data Format for the Flexible Exchange and Processing of Mass Spectrometry Imaging Data. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 5106–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, Y.; Kiyota, T.; Draghici, C.; Gao, J.M.; Yeboah, F.; Acoca, S.; Jarussophon, S.; Purisima, E. Molecular Formula Analysis by an MS/MS/MS Technique to Expedite Dereplication of Natural Products. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1187–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, P.M.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Wolfender, J.L. Deep Metabolome Annotation in Natural Products Research: Towards a Virtuous Cycle in Metabolite Identification. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 36, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kind, T.; Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Ma, Y.; Lai, Z.; Mehta, S.S.; Wohlgemuth, G.; Barupal, D.K.; Showalter, M.R.; Arita, M.; et al. Identification of Small Molecules Using Accurate Mass MS/MS Search. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohimani, H.; Gurevich, A.; Shlemov, A.; Mikheenko, A.; Korobeynikov, A.; Cao, L.; Shcherbin, E.; Nothias, L.F.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Pevzner, P.A. Dereplication of Microbial Metabolites through Database Search of Mass Spectra. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kildgaard, S.; Subko, K.; Phillips, E.; Goidts, V.; De la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Andersen, B.; Frisvad, J.C.; Nielsen, K.F.; et al. A Dereplication and Bioguided Discovery Approach to Reveal New Compounds from a Marine-Derived Fungus Stilbella fimetaria. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, C.L.; Carroll, A.R. Database for Rapid Dereplication of Known Natural Products Using Data from MS and Fast NMR Experiments. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudêncio, S.P.; Pereira, F. Dereplication: Racing to Speed up the Natural Products Discovery Process. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 779–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, J.; Nuzillard, J.M.; Renault, J.H. Dereplication Strategies in Natural Product Research: How Many Tools and Methodologies Behind the Same Concept? Phytochem. Rev. 2017, 16, 55–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, A.E.; Evanno, L.; Poupon, E.; Champy, P.; Beniddir, M.A. Natural Products Targeting Strategies Involving Molecular Networking: Different Manners, One Goal. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 960–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivon, F.; Allard, P.M.; Koval, A.; Righi, D.; Genta-Jouve, G.; Neyts, J.; Apel, C.; Pannecouque, C.; Nothias, L.F.; Cachet, X.; et al. Bioactive Natural Products Prioritization Using Massive Multi-Informational Molecular Networks. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.C.; Petras, D.; Quinn, R.A.; Protsyuk, I.; Archer, F.I.; Ransome, E.; Williams, G.J.; Bailey, B.A.; Vermeij, M.J.; Alexandrov, T.; et al. Meta-Mass Shift Chemical Profiling of Metabolomes from Coral Reefs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11685–11690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watrous, J.; Roach, P.; Alexandrov, T.; Heath, B.S.; Yang, J.Y.; Kersten, R.D.; van der Voort, M.; Pogliano, K.; Gross, H.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; et al. Mass Spectral Molecular Networking of Living Microbial Colonies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1743–E1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Sanchez, L.M.; Rath, C.M.; Liu, X.; Boudreau, P.D.; Bruns, N.; Glukhov, E.; Wodtke, A.; De Felicio, R.; Fenner, A.; et al. Molecular Networking as a Dereplication Strategy. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar]

| Number | % | Drugs | Success% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synthetic compounds | 8–10 M | 93–94% | 2000–2500 | 0.005% |
| All natural compounds (plants + animals + microbes) | ≈500,000 | 4.7–5.8% | 1200–1300 | 0.6% |
| Microbial compounds | ≈70,000 | 0.66–0.82% | 450–500 | 1.6% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meena, S.N.; Wajs-Bonikowska, A.; Girawale, S.; Imran, M.; Poduval, P.; Kodam, K.M. High-Throughput Mining of Novel Compounds from Known Microbes: A Boost to Natural Product Screening. Molecules 2024, 29, 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133237
Meena SN, Wajs-Bonikowska A, Girawale S, Imran M, Poduval P, Kodam KM. High-Throughput Mining of Novel Compounds from Known Microbes: A Boost to Natural Product Screening. Molecules. 2024; 29(13):3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133237
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeena, Surya Nandan, Anna Wajs-Bonikowska, Savita Girawale, Md Imran, Preethi Poduval, and Kisan M. Kodam. 2024. "High-Throughput Mining of Novel Compounds from Known Microbes: A Boost to Natural Product Screening" Molecules 29, no. 13: 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133237
APA StyleMeena, S. N., Wajs-Bonikowska, A., Girawale, S., Imran, M., Poduval, P., & Kodam, K. M. (2024). High-Throughput Mining of Novel Compounds from Known Microbes: A Boost to Natural Product Screening. Molecules, 29(13), 3237. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29133237








