Profile of Polyphenols, Fatty Acids, and Terpenes in Henola Hemp Seeds Depending on the Method of Fertilization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fatty Acids
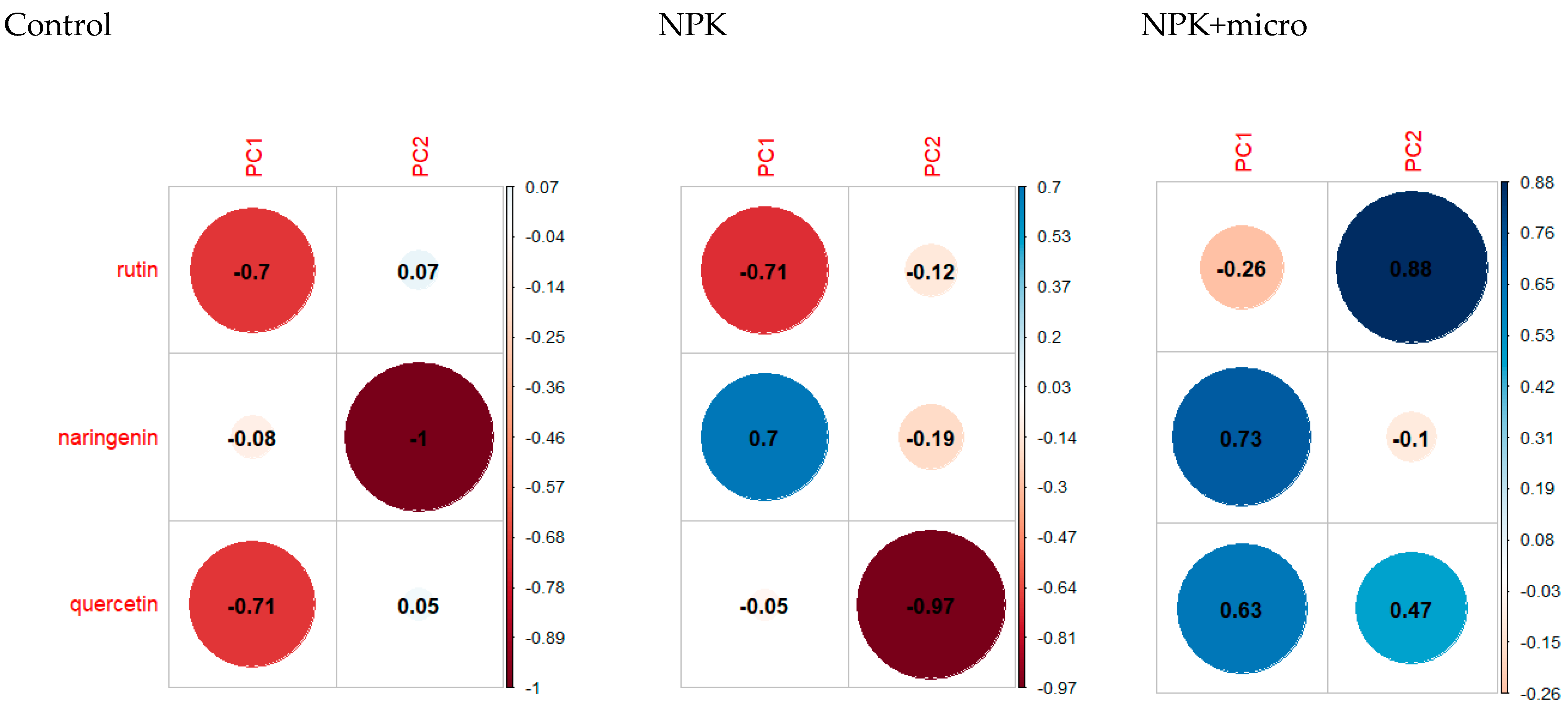
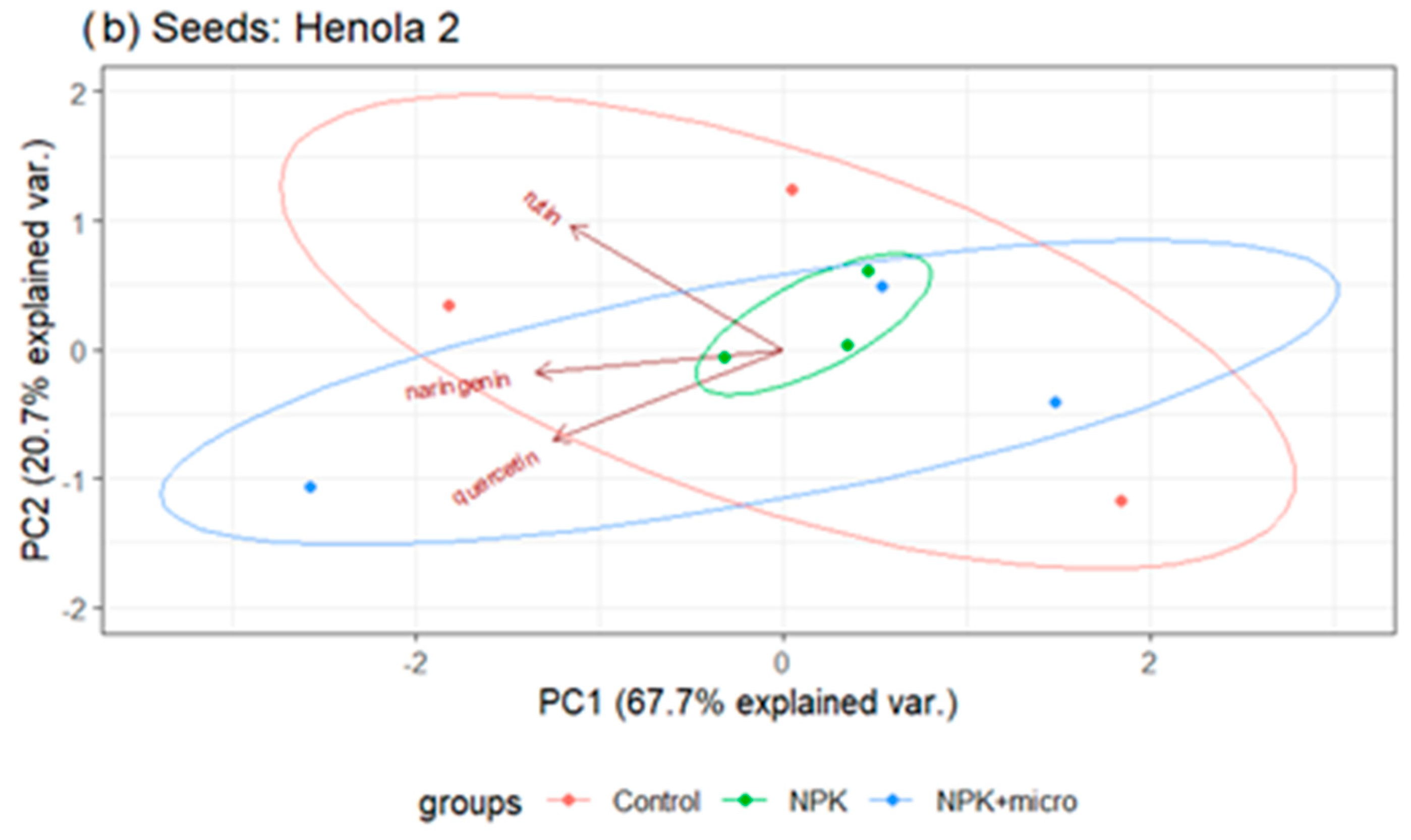
2.2. Profile of Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids
2.3. Terpenes Analysis
2.3.1. Volatile Organic Compounds—Monotermes and Sesquiterpenes
2.3.2. Triterpenes and Tetraterpenes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Methodology of Conducting the Experiment
- No mineral fertilization.
- Basic mineral fertilization (in kg·ha−1): N—150; P2O5—40; K2O—80.
- Full mineral fertilization (in kg·ha−1): 800 kg·ha−1 of Azofoska fertilizer: N—108.8; P2O5—51.2 K2O—152.8; MgO—36.0; SO3—184.0; B—0.36; Cu—1.44; Fe—1.36; Mn—2.16; Mo—0.32; Zn—0.36.
3.2. Chemical Analyses
3.2.1. Fatty Acids Analysis
3.2.2. Terpenes Analysis
Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds Such as Monoterpenes and Sesquiterpenes
Analysis of Triterpenes-Phytosterols
Analysis of Tetraterpenes-Carotenoids
Analysis of Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids
3.2.3. Statistical Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clarke, R.A.; Merlin, M.D. Cannabis: Evolution and Ethnobotany; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Irakli, M.; Tsaliki, E.; Kalivas, A.; Kleisiaris, F.; Sarrou, E.; Cook, C. Effect οf genotype and growing year on the nutritional, phytochemical, and antioxidant properties of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Integrated Taxonomic Information System. Available online: http://www.itis.gov (accessed on 19 January 2024).
- Żuk-Gołaszewska, K.; Gołaszewski, J. Cannabis sativa L.—Cultivation and quality of raw material. J. Elem. 2018, 23, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Rahimi, R.; Abbasabadi, F.; Abdollahi, M. A systematic review of plant-derived natural compounds for anxiety disorders. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1924–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferber, S.G.; Namdar, D.; Hen-Shoval, D.; Eger, G.; Koltai, H.; Shoval, G.; Shbiro, L.; Weller, A. The Entourage Effect: Terpenes Coupled with Cannabinoids for the Treatment of Mood Disorders and Anxiety Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Izzo, L.; Pacifico, S.; Piccolella, S.; Castaldo, L.; Narváez, A.; Grosso, M.; Ritieni, A. Chemical Analysis of Minor Bioactive Components and Cannabidiolic Acid in Commercial Hemp Seed Oil. Molecules 2020, 25, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-Esteban, J.I.; González-Fernández, M.J.; Fabrikov, D.; de Cortes Sánchez-Mata, M.; Torija-Isasa, E.; Guil-Guerrero, J.L. Fatty acids and minor functional compounds of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds and other Cannabaceae species. J. Food Compost. Anal. 2023, 115, 104962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Martin, N.M.; Toscano, R.; Villanueva, A.; Pedroche, F.; Millan, J.; Montserrat-de la Paz , S.; Millan-Linares, M.C. Neuroprotective protein hydrolysates from hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6732–6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, J.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Graczyk, M.; Niedziela, G.; Sieracka, D.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. The Effect of Mineral Fertilization on the Content of Bioactive Compounds in Hemp Seeds and Oil. Molecules 2023, 28, 4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łochyńska, M.; Frankowski, J. Impact of silkworm excrement organic fertilizer on hemp biomass yield and composition. J. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 20, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankowski, J.; Wawro, A.; Batog, J.; Burczyk, H. New polish oilseed hemp cultivar Henola–Cultivation, properties and utilization for bioethanol production. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 7283–7295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górecki, T. Basics of Statistics with Examples in 2011, 1st ed.; BTC: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kiralan, M.; Gul, V.; Kara, S. Fatty acid composition of hempseed oils from different locations in Turkey. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 8, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, H. Nutritional indicators for assessing fatty acids: A mini—Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambuś, H.; Litwinek, D.; Sabat, R.; Wywrocka-Gurgul, A.; Szary-Sworst, K.; Baczyński, J. Chemical composition and health-promoting properties of hemp seeds, oil and flour (Cannabis sativa L.). In Żywność a Oczekiwania Współczesnego Konsumenta; Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Rolniczego im Hugona Kołłątaja w Krakowie: Kraków, Poland, 2020; pp. 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- House, J.D.; Neufeld, J.; Leson, G. Evaluating the quality of protein from hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) products through the use of the protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 11801–11807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, W.; Zhang, P.; Ying, D.; Xiong, Y.; Fang, Z. Extrusion improves the phenolic profile and biological activities of hempseed (Cannabis sativa L.) hull. Food Chem. 2021, 346, 128606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.G.; Song, Z.X.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Shu, G.F.; Lu, H.X.; Wang, S.K.; Sun, G.J. Low n-6/n-3 PUFA ratio improves lipid metabolism, inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial function in rats using plant oils as n-3 fatty acid source. Lipids 2016, 51, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaway, J.; Schwab, U.; Harvima, I. Efficacy of dietary hempseed oil in patients with atopic dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2005, 16, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The importance of the omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2002, 56, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowska, J.; Polak, E.; Drabent, A.; Żak, A. Cannabis sativa L.—Varieties, properties, applications. Żywność Nauka Technol. Jakość 2021, 127, 90–104. [Google Scholar]
- Audu, B.S.; Ofojekwu, P.C.; Ujah, A.; Ajima, M.N.O. Phytochemical, proximate composition, amino acid profile and characterization of Marijuana (Cannabis sativa L.). J. Phytopharm. 2014, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, G.; Skrajda, M. Lipid and protein fraction of hemp seeds (C. sativa L.) and its beneficial effect on human health. J. Educ. Health Sport 2016, 6, 357–366. [Google Scholar]
- Firenzuoli, F.; Epifani, F.; Loiacono, I. Hemp for everyone. In Other Medicinal Uses of Marijuana; Esteri: Wrocław, Poland, 2016; pp. 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Minkowski, K.; Zawada, K.; Ptasznik, S.; Kalinowski, A. The influence of phenolic compounds of seeds on the oxidative stability and antiradical activity of oils pressed from them rich in n-3 PUFA. Żywność Nauka Technol. Jakość 2013, 20, 118–132. [Google Scholar]
- Worobiej, E.; Mądrzak, J.; Piecyk, M. Content of selected nutrients and biologically active compounds in products from hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and edible chestnuts. (Castanea sativa Mill.). Bromat. Chem. Toksykol. 2015, 48, 573–577. [Google Scholar]
- Barčauskaitė, K.; Žydelis, R.; Ruzgas, R.; Bakšinskaitė, A.; Tilvikienė, V. The Seeds of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) a Source of Minerals and Biologically Active Compounds. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 13025–13039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, W.; Zhang, P.; Ying, D.; Fang, Z. Hempseed in food industry: Nutritional value, health benefits, and industrial applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 282–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, F.; Przybylski, R. Effect of solvents extraction on total phenolics and antioxidant activity ofextracts from flaxseed (Linum usitatissimum L.). Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2012, 11, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Czaplicki, S.; Zadernowski, R.; Nowak-Polakowska, H. Phenolic compounds of echium (Echium vulgare L.). Bromat. Chem. Toksykol. 2011, XLIV, 815–821. [Google Scholar]
- Terpinc, P.; Polak, T.; Makuc, D.; Poklar Ulrich, N.; Abramoviĉ, H. The occurrence and characterization of phenolic compounds in Camelina sativa seeds, cake and oil. Food Chem. 2011, 131, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horanin, A.; Bryndal, I. Hemp—Active Ingredients, Medicinal Properties and Using. Res. Pap. Wrocław Univ. Econ. 2017, 494, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniewski, R.; Pniewska, I.; Kubacki, A.; Strzelczyk, M.; Chudy, M.; Oleszak, G. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.)—A valuable useful and medicinal plant. Postępy Fitoter. 2017, 18, 139–144. [Google Scholar]
- Kaniewski, R.; Strzelczyk, M.; Rajewicz, Z.; Hołderna-Kędzia, E. Hemp essential oil Cannabis aetheroleum research. Adv. Phytother. 2021, 22, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Sommano, S.R.; Chittasupho, C.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Jantrawut, P. The Cannabis Terpenes. Molecules 2020, 25, 5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leizer, C.; Ribnicky, D.; Poulev, A.; Dushenkov, V.; Raskin, I. The Composition of Hemp Seed Oil and its potential as an important food source. J. Nutraceut. Funct. Med. Foods 2000, 2, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PN-EN ISO 11085:2015-10; Determination of Fat Content. ISO: Vernier, Switzerland, 2015.
- Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Frankowski, J.; Sieracka, D.; Sázavská, T.; Wacławek, S.; Raczak, B.K.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. The Content of Antioxidant Compounds and VOCs in Sorghum Grain Grown in Central and Eastern Europe. Agronomy 2024, 14, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchowilska, E.; Wiwart, M.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. The profile of bioactive compounds in the grain of various x Tritordeum genotypes. J. Cereal Sci. 2021, 102, 103352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurasiak-Popowska, D.; Graczyk, M.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Stuper-Szablewska, K.; Szwajkowska-Michałek, L. An Analysis of Variability in the Content of Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids in Camelina Seeds Depending on Weather Conditions, Functional Form, and Genotypes. Molecules 2022, 27, 3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Frankowski, J.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. The influence of weather conditions on bioactive compound content in sorghum grain. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, R.; Szczepanek, M.; Błaszczyk, K.; Kobus-Cisowska, J.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Stuper-Szablewska, K.; Pobereżny, J.; Hassanpouraghdam, M.B.; Rasouli, F. Impact of the Farming System and Amino-Acid Biostimulants on the Content of Carotenoids, Fatty Acids, and Polyphenols in Alternative and Common Barley Genotypes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, O.; Szwajkowska-Michałek, L.; Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Szablewski, T.; Cegielska-Radziejewska, R.; Świerk, D.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. New Insights into Bioactive Compounds of Wild-Growing Medicinal Plants. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



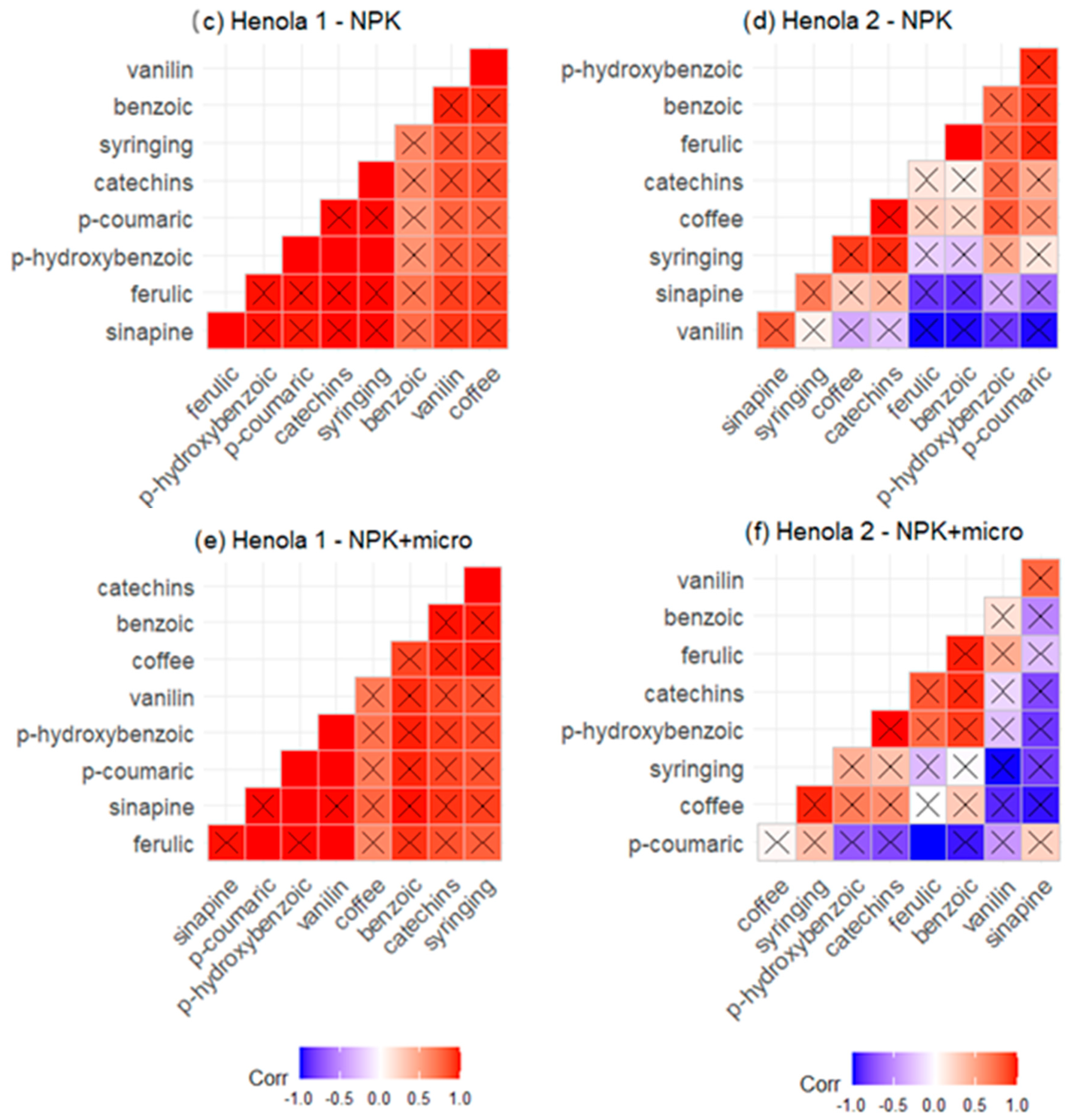
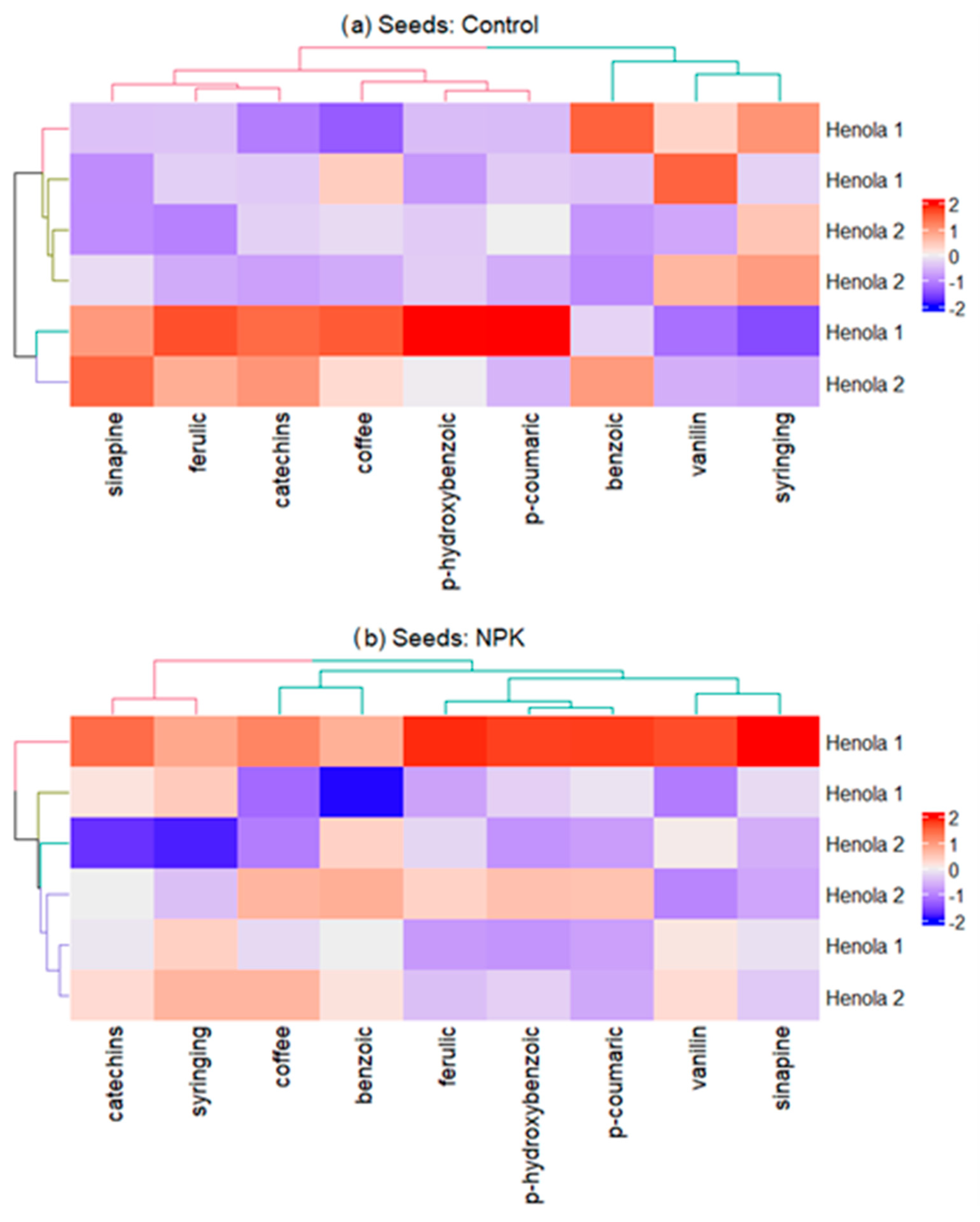
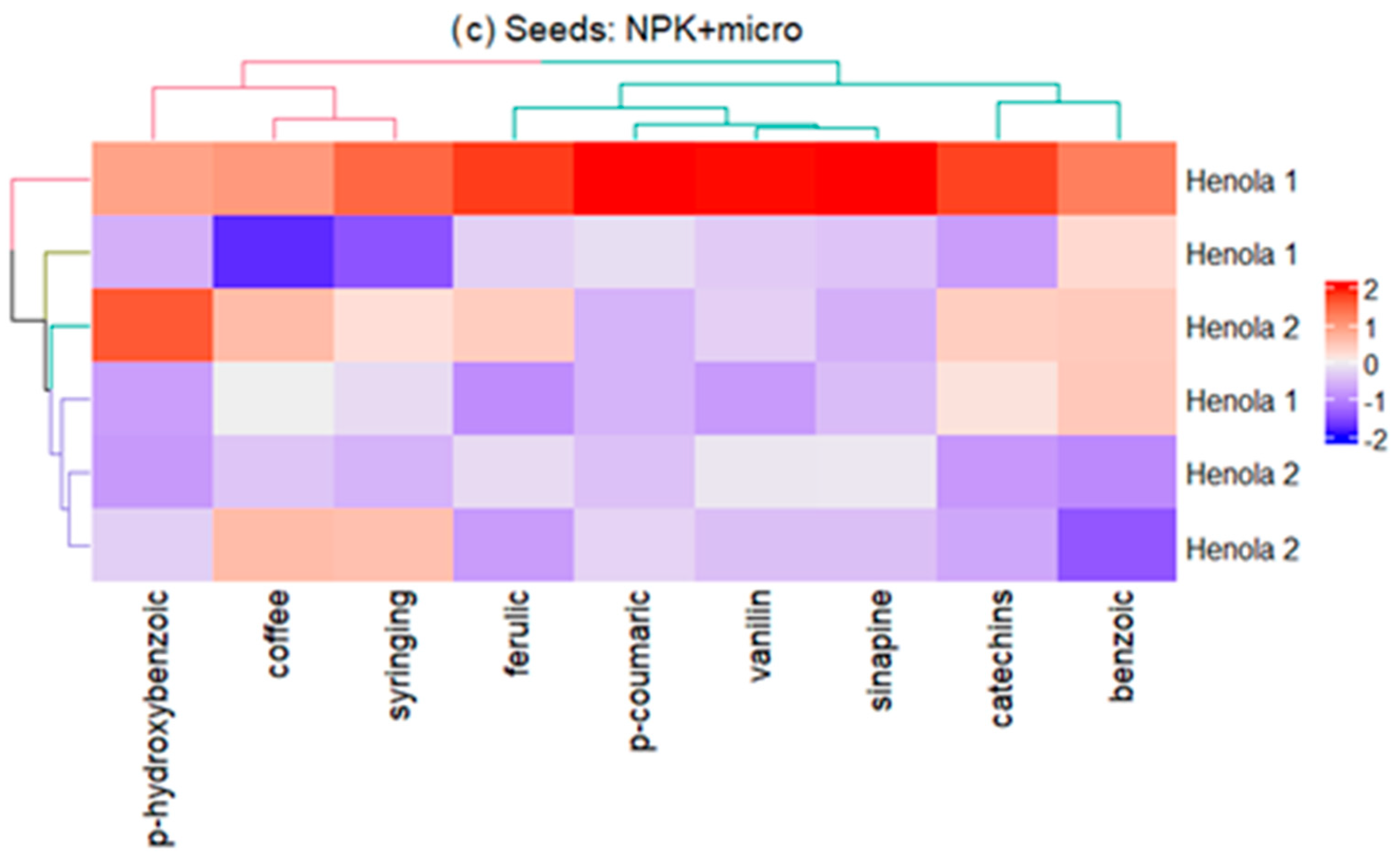

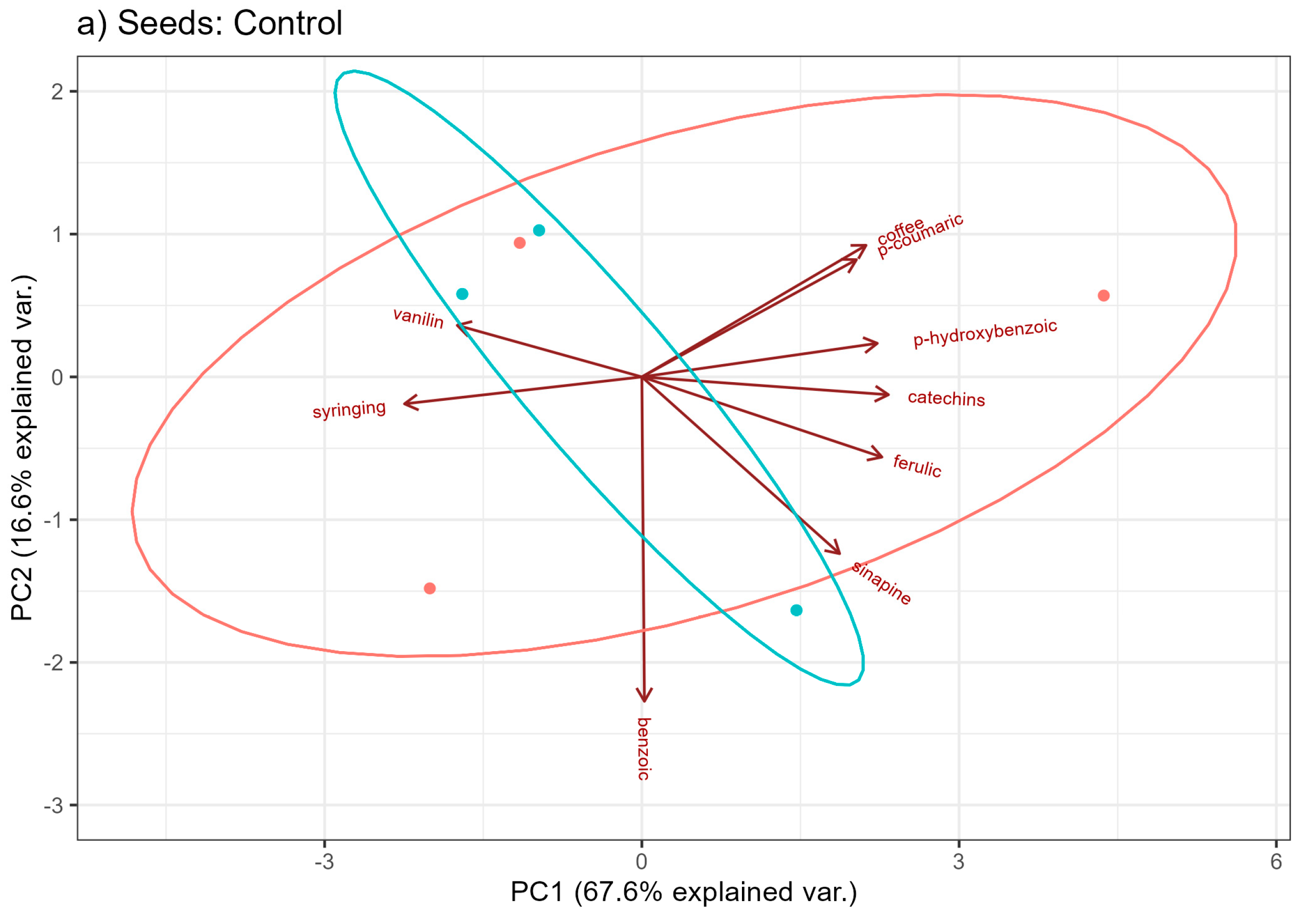
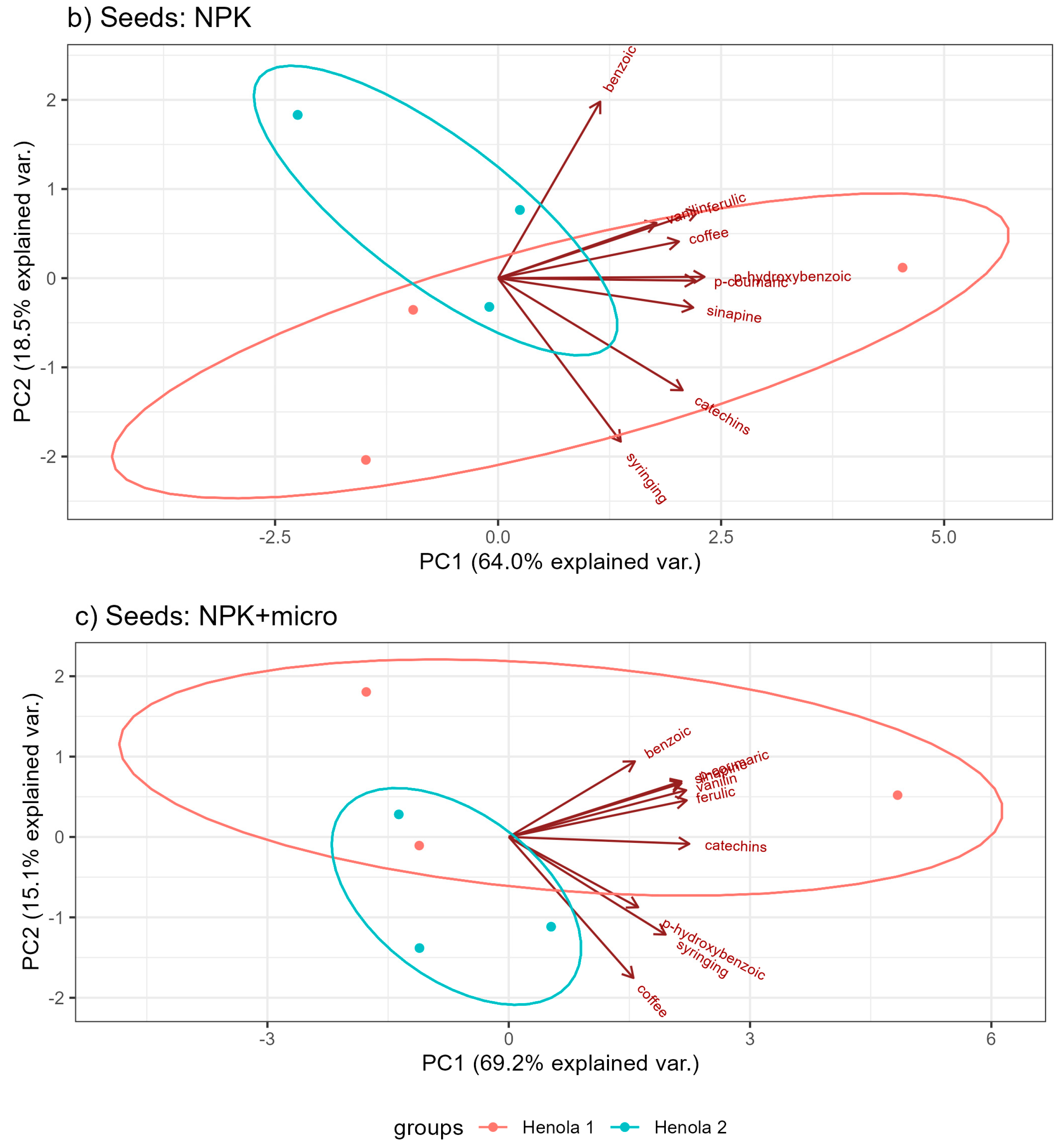

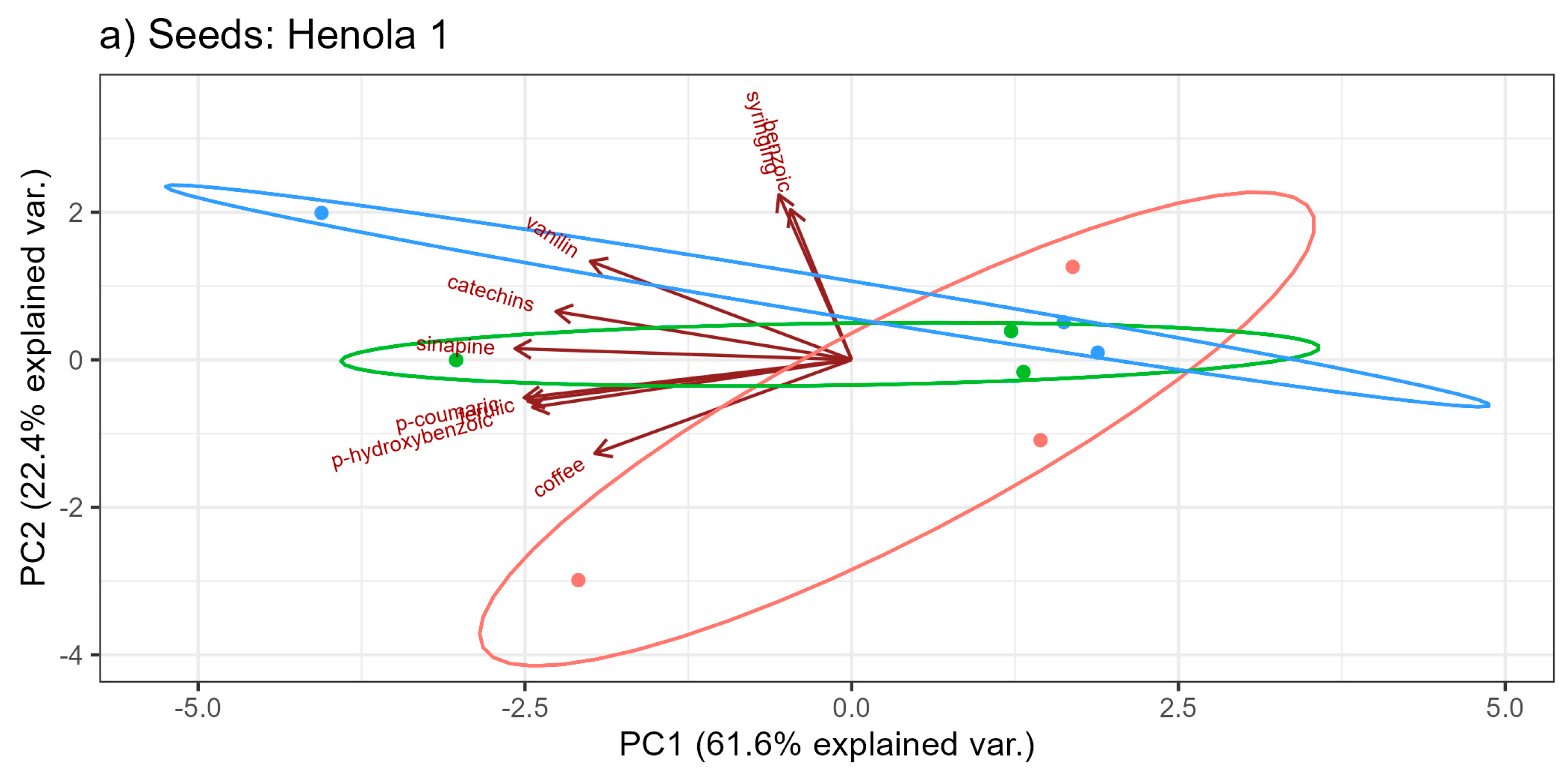


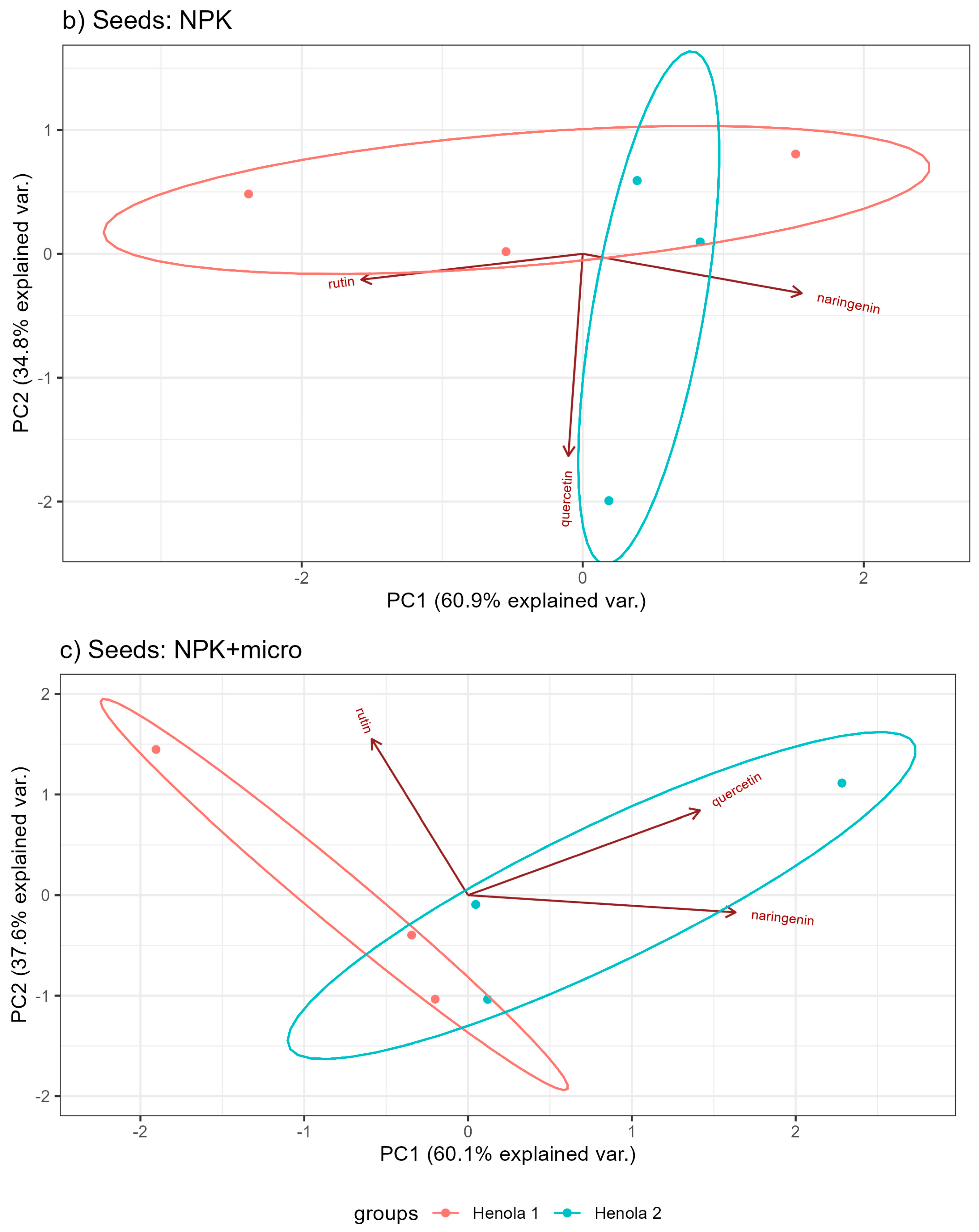


| Seeds: Henola 2 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name of fatty acids | Fatty acid pattern | Control | Fertilizer: NPK | Fertilizer: NPK+micro | |||||||
| [%] | [%] | [%] | |||||||||
| Saturated fatty acids | Myristic acid | C14:0 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 20.0 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 22.2 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 50.0 |
| Palmitic acid | C16:0 | 6.15 | 0.49 | 8.0 | 6.49 | 0.21 | 3.2 | 6.64 | 0.17 | 2.6 | |
| Stearic acid | C18:0 | 2.48 | 0.21 | 8.5 | 2.20 | 0.10 | 4.5 | 2.38 | 0.17 | 7.1 | |
| Arachidic acid | C20:0 | 0.60 | 0.07 | 11.7 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 11.1 | 0.57 | 0.04 | 7.0 | |
| Behenic acid | C22:0 | 0.80 | 0.06 | 7.5 | 0.70 | 0.05 | 7.1 | 0.72 | 0.11 | 15.3 | |
| Lignoceric acid | C24:0 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 60.0 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 100.0 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 71.4 | |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | Palmitoleic acid | C16:1 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 28.6 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 14.3 | 0.16 | 0.01 | 6.3 |
| Oleic acid | C18:1 | 11.58 | 0.35 | 3.0 | 12.38 | 0.28 | 2.3 | 11.71 | 0.44 | 3.8 | |
| Gondolaic acid | C20:1 | 1.07 | 0.21 | 19.6 | 0.92 | 0.78 | 84.8 | 1.32 | 1.11 | 84.1 | |
| Erucic acid | C22:1 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 12.5 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 12.5 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 20.0 | |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | Linoleic acid | C18:2 n−6 | 54.90 | 1.63 | 3.0 | 56.79 | 0.94 | 1.7 | 54.63 | 1.19 | 2.2 |
| γ-linolenic acid GLA | C18:3 n−6 | 0.75 | 0.11 | 14.7 | 0.62 | 0.02 | 3.2 | 0.74 | 0.14 | 18.9 | |
| α-linolenic acid | C18:3 n−3 | 20.82 | 0.41 | 2.0 | 21.26 | 0.41 | 1.9 | 21.88 | 0.64 | 2.9 | |
| Stearidonic acid | C18:4 n−3 | 0.22 | 0.06 | 27.3 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 9.1 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 17.1 | |
| Eicosadienoic acid | C20:2 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 14.3 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 50.0 | 0.06 | 0.03 | 50.0 | |
| Seeds: Henola 1 | |||||||||||
| Name of fatty acids | Fatty acid pattern | Control | Fertilizer: NPK | Fertilizer:NPK+micro | |||||||
| x | ±SD | [%] | x | ±SD | [%] | [%] | |||||
| Saturated fatty acids | Myristic acid | C14:0 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 40.0 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 57.1 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 42.9 |
| Palmitic acid | C16:0 | 6.36 | 0.07 | 1.1 | 6.32 | 0.20 | 3.2 | 6.51 | 0.22 | 3.4 | |
| Stearic acid | C18:0 | 2.38 | 0.18 | 7.6 | 2.38 | 0.02 | 0.8 | 2.41 | 0.14 | 5.8 | |
| Arachidic acid | C20:0 | 0.65 | 0.04 | 6.2 | 0.52 | 0.08 | 15.4 | 0.58 | 0.12 | 20.7 | |
| Behenic acid | C22:0 | 0.73 | 0.11 | 15.1 | 0.69 | 0.06 | 8.7 | 0.67 | 0.09 | 13.4 | |
| Lignoceric acid | C24:0 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 66.7 | 0.12 | 0.03 | 25.0 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 50.0 | |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | Palmitoleic acid | C16:1 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 6.7 | 0.14 | 0.01 | 7.1 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 21.4 |
| Oleic acid | C18:1 | 11.45 | 0.35 | 3.1 | 11.53 | 0.22 | 1.9 | 11.47 | 0.28 | 2.4 | |
| Gondolaic acid | C20:1 | 1.84 | 0.89 | 48.4 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 116.7 | 2.93 | 0.96 | 32.8 | |
| Erucic acid | C22:1 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 15.8 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 14.3 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 13.3 | |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | Linoleic acid | C18:2 n−6 | 55.35 | 0.67 | 1.2 | 55.83 | 0.38 | 0.7 | 54.97 | 0.63 | 1.1 |
| γ-linolenic acid GLA | C18:3 n−6 | 0.57 | 0.13 | 22.8 | 0.73 | 0.15 | 20.5 | 0.76 | 0.06 | 7.9 | |
| α-linolenic acid | C18:3 n−3 | 20.41 | 0.32 | 1.6 | 20.31 | 0.28 | 1.4 | 21.44 | 0.58 | 2.7 | |
| Stearidonic acid | C18:4 n−3 | 0.37 | 0.06 | 16.2 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 23.5 | 0.42 | 0.04 | 9.5 | |
| Eicosadienoic acid | C20:2 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 33.3 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 16.7 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 20.0 | |
| Seeds: Henola 2 | ||||||
| Control | Fertilizer: NPK | Fertilizer:NPK+micro | ||||
| Phenolic acids | ||||||
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | 6.27 | 0.43 | 6.65 | 1.98 | 7.95 | 4.13 |
| vanillic | 1.39 | 0.08 | 1.47 | 0.20 | 1.52 | 0.15 |
| caffeic | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.04 |
| p-coumaric | 1.46 | 0.31 | 1.56 | 0.51 | 1.37 | 0.18 |
| sinapic | 4.29 | 1.47 | 3.64 | 0.32 | 3.25 | 0.28 |
| ferulic | 1.62 | 0.81 | 1.68 | 0.29 | 1.64 | 0.52 |
| catechins (sum) | 647.62 | 27.02 | 668.64 | 43.74 | 649.00 | 49.85 |
| syringic | 69.01 | 6.61 | 69.69 | 6.21 | 74.37 | 3.77 |
| benzoic | 28.65 | 5.69 | 34.59 | 0.73 | 35.18 | 3.76 |
| Seeds: Henola 1 | ||||||
| Control | Fertilizer: NPK | Fertilizer:NPK+micro | ||||
| Phenolic acids | ||||||
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | 7.32 | 3.71 | 7.87 | 3.86 | 6.23 | 2.13 |
| vanillic | 1.41 | 0.15 | 1.63 | 0.42 | 1.56 | 1.15 |
| caffeic | 0.17 | 0.10 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
| p-coumaric | 2.29 | 1.35 | 1.91 | 0.91 | 2.24 | 1.41 |
| sinapic | 3.74 | 1.17 | 4.68 | 1.65 | 4.43 | 1.64 |
| ferulic | 2.13 | 0.89 | 1.77 | 0.94 | 1.98 | 1.09 |
| catechins (sum) | 649.63 | 38.98 | 707.32 | 34.31 | 703.37 | 53.55 |
| syringic | 64.68 | 10.74 | 75.14 | 1.36 | 71.07 | 8.92 |
| benzoic | 33.57 | 5.89 | 32.53 | 3.35 | 39.19 | 2.035 |
| Seeds: Henola 2 | ||||||
| Control | Fertilizer: NPK | Fertilizer:NPK+micro | ||||
| Flavonoids | ||||||
| rutin | 0.77 | 0.52 | 0.82 | 0.09 | 0.73 | 0.32 |
| naringenin | 863.63 | 60.14 | 842.35 | 8.40 | 867.00 | 45.45 |
| quercetin | 17.16 | 2.48 | 18.59 | 3.90 | 20.34 | 10.83 |
| Seeds: Henola 1 | ||||||
| Control | Fertilizer: NPK | Fertilizer:NPK+micro | ||||
| Flavonoids | ||||||
| rutin | 0.85 | 0.25 | 0.99 | 0.46 | 0.86 | 0.47 |
| naringenin | 765.60 | 97.62 | 778.37 | 71.40 | 783.50 | 44.84 |
| quercetin | 18.21 | 1.01 | 16.92 | 0.92 | 12.12 | 0.59 |
| Retention Time | Retention Index/Literary | Retention Index Actual | Odour Characteristic | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MONOTERPENE | α-Pinene | 6.95 | 936 | 942 | Terpeny, Fruity, Sweet, Green, Woody, Pine, Citrus, Lime, Camphor |
| β-Pinene | 7.72 | 964 | 987 | Musty, Green, Sweet, Pine, Resin, Turpentine, Woody | |
| β-Myrcene | 7.8 | 991 | 992 | Metallic, Musty, Geranium, Sweet, Fruity, Ethereal, Soapy, Lemon, Spicy, Woody | |
| p-cymene | 8.14 | 1025 | 1013 | Lemon, Fruity, Fuel-Like, Sweet, Herbal, Spicy | |
| Limonene | 8.55 | 1036 | 1040 | Licorice, Green, Citrus, Ethereal, Fruity | |
| Eucalyptol | 8.61 | 1024 | 1043 | Camphor, Minty, Sweet, Liquorices, Mentholic, Pine | |
| β-Ocimene | 8.74 | 1050 | 1052 | Herbal, Mild, Citrus, Sweet, Orange, Lemon | |
| SESQUITERPENE | α-trans-bergamotene | 14.16 | 1435 | 1424 | Warm, Tea leaf |
| Caryophyllene | 14.38 | 1419 | 1442 | Musty, Green, Spicy, Woody, Terpeny, Fruity, Sweet | |
| α-humulene | 14.57 | 1458 | 1457 | earthy, musky | |
| E-β-Farnesene | 14.84 | 1456 | 1478 | Oily, Fruity, Citrus, Woody | |
| Z-β-farnesene | 14.9 | 1443 | 1483 | Woody, Green | |
| α-Farnesene | 15.26 | 1508 | 1514 | Woody | |
| Selina-3,7(11)-diene | 15.77 | 1550 | 1569 | Woody | |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 16.14 | 1589 | 1613 | Sweet, Fruity, Sawdust, Fruity, Herbal | |
| Humulene-1,2-epoxide | 16.34 | 1607 | 1644 | Creamy, Fatty, Buttery |
| Henola 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Fertilizer: NPK | Fertilizer: NPK + micro | |||||
| Triterpens—sterols (mg/100 g) | Campesterol | 52.61 | 1.03 | 53.99 | 0.23 | 55.80 | 1.14 |
| Stigmasterol | 9.74 | 0.32 | 8.71 | 0.60 | 7.66 | 0.44 | |
| β-sitosterol | 174.00 | 16.72 | 178.67 | 0.78 | 179.57 | 9.68 | |
| Δ5 avenasterol | 15.80 | 1.88 | 15.41 | 0.61 | 17.92 | 1.79 | |
| Tetraterpens—carotenoids (mg/100 g) | Lutein | 8.26 | 0.44 | 7.79 | 0.40 | 8.68 | 0.72 |
| Zeaxanthin | 4.67 | 0.52 | 5.56 | 1.44 | 4.89 | 1.42 | |
| β–carotene | 45.52 | 9.49 | 46.84 | 10.17 | 58.96 | 10.35 | |
| Henola 1 | |||||||
| Control | Fertilizer: NPK | Fertilizer: NPK + micro | |||||
| Triterpens—sterols (mg/100 g) | Campesterol | 52.10 | 3.33 | 47.82 | 7.12 | 49.55 | 4.05 |
| Stigmasterol | 7.37 | 0.79 | 8.86 | 1.52 | 8.74 | 3.96 | |
| β-sitosterol | 158.87 | 12.19 | 162.05 | 15.50 | 179.55 | 8.62 | |
| Δ5 avenasterol | 14.32 | 1.05 | 16.11 | 2.45 | 17.72 | 0.25 | |
| Tetraterpens—carotenoids (mg/100 g) | Lutein | 6.30 | 3.55 | 8.07 | 0.32 | 7.82 | 0.58 |
| Zeaxanthin | 4.89 | 1.35 | 5.41 | 0.39 | 5.02 | 1.02 | |
| β–carotene | 46.74 | 7.15 | 57.69 | 9.91 | 63.48 | 10.74 | |
| p = 0.05 | |||||||
| Seeds: Phenolic Acids | Seeds: Flawonoids | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-hydroxybenzoic | vanillic | coffee | p-coumaric | sinapic | ferulic | catechins | syringing | benzoic | rutin | naringenin | quercetin | |
| Control | 0.7 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.99 | 1 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| NPK | 0.82 | 1 | 1 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.7 |
| NPK+micro | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.2 | 1 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Przybylska-Balcerek, A.; Frankowski, J.; Graczyk, M.; Niedziela, G.; Sieracka, D.; Wacławek, S.; Sázavská, T.H.; Buśko, M.; Szwajkowska-Michałek, L.; Stuper-Szablewska, K. Profile of Polyphenols, Fatty Acids, and Terpenes in Henola Hemp Seeds Depending on the Method of Fertilization. Molecules 2024, 29, 4178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174178
Przybylska-Balcerek A, Frankowski J, Graczyk M, Niedziela G, Sieracka D, Wacławek S, Sázavská TH, Buśko M, Szwajkowska-Michałek L, Stuper-Szablewska K. Profile of Polyphenols, Fatty Acids, and Terpenes in Henola Hemp Seeds Depending on the Method of Fertilization. Molecules. 2024; 29(17):4178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174178
Chicago/Turabian StylePrzybylska-Balcerek, Anna, Jakub Frankowski, Małgorzata Graczyk, Grażyna Niedziela, Dominika Sieracka, Stanisław Wacławek, Tereza Hulswit Sázavská, Maciej Buśko, Lidia Szwajkowska-Michałek, and Kinga Stuper-Szablewska. 2024. "Profile of Polyphenols, Fatty Acids, and Terpenes in Henola Hemp Seeds Depending on the Method of Fertilization" Molecules 29, no. 17: 4178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174178
APA StylePrzybylska-Balcerek, A., Frankowski, J., Graczyk, M., Niedziela, G., Sieracka, D., Wacławek, S., Sázavská, T. H., Buśko, M., Szwajkowska-Michałek, L., & Stuper-Szablewska, K. (2024). Profile of Polyphenols, Fatty Acids, and Terpenes in Henola Hemp Seeds Depending on the Method of Fertilization. Molecules, 29(17), 4178. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29174178









