Discovery of Melittin as Triple-Action Agent: Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, and Potential Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Antimicrobial Activities of the Melittin In Vitro
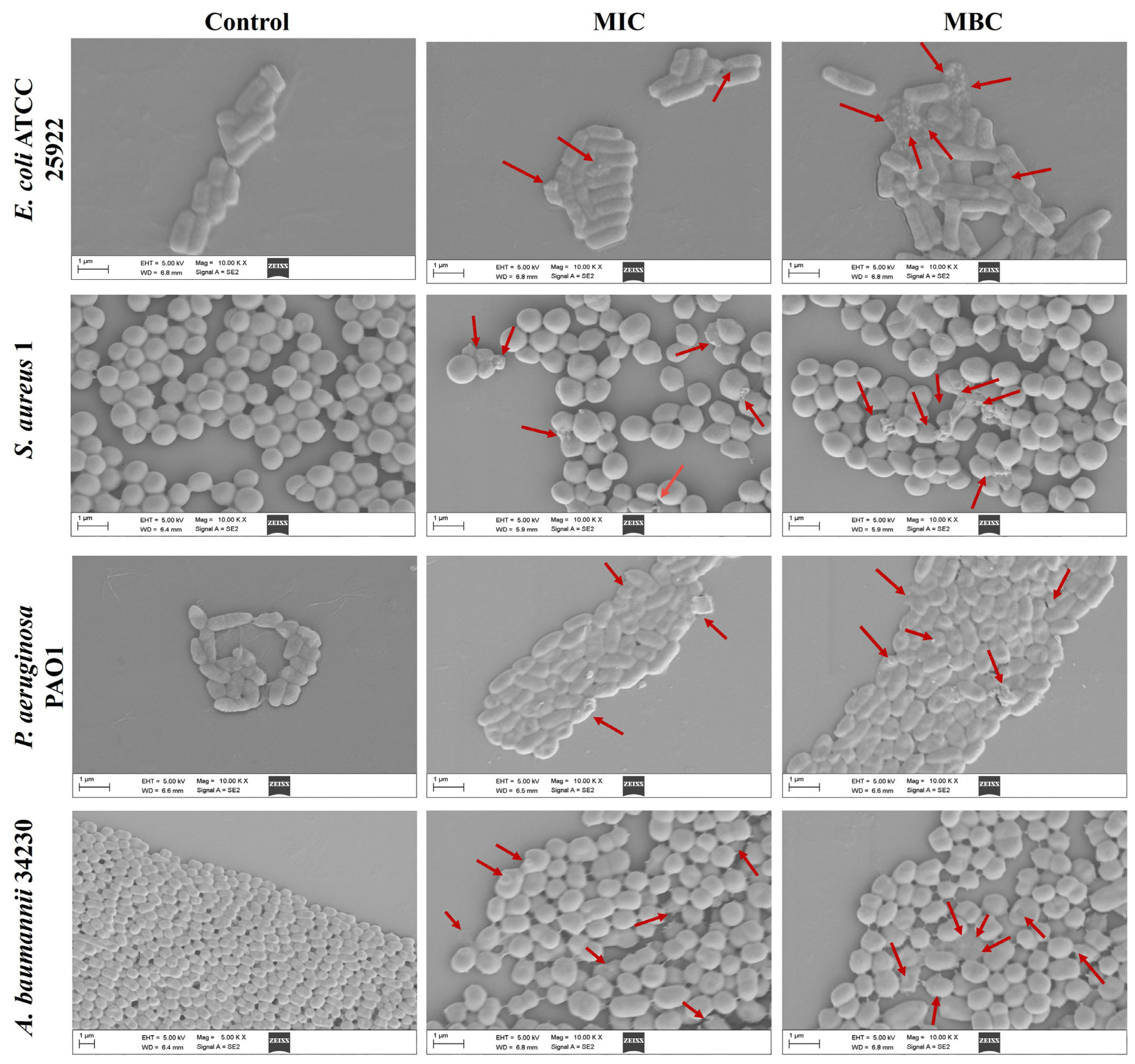
2.2. Effect of Melittin on Bacterial Cell Morphology
2.3. Melittin on Bacterial Cell Membrane Permeability and Cell Death
2.4. ROS Generation in Bacterial upon Exposure to Melittin
2.5. The Ability of Biofilm Formation
2.6. Inhibition and Eradication of Biofilm by Melittin
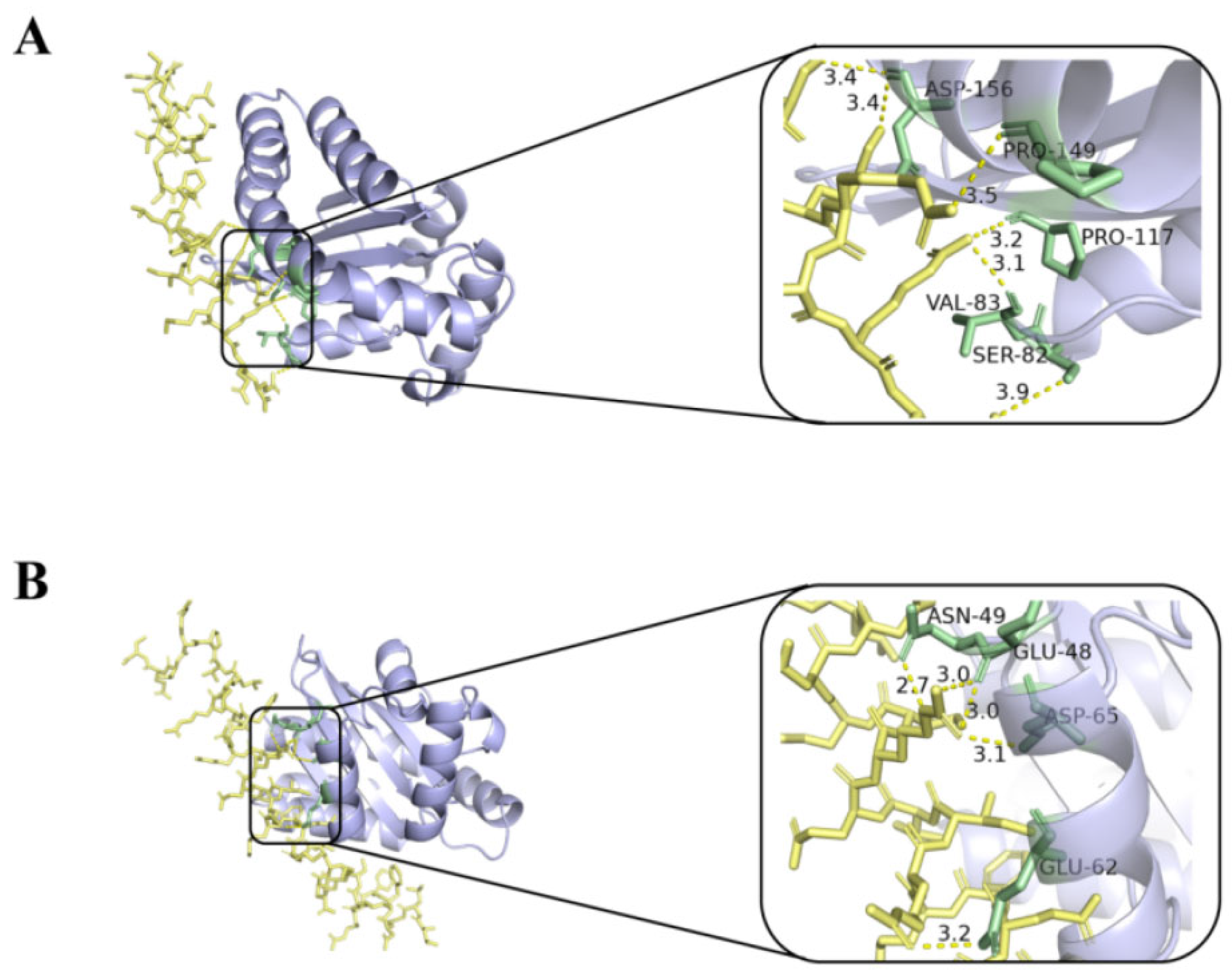
2.7. Molecular Docking and Dynamic Simulation
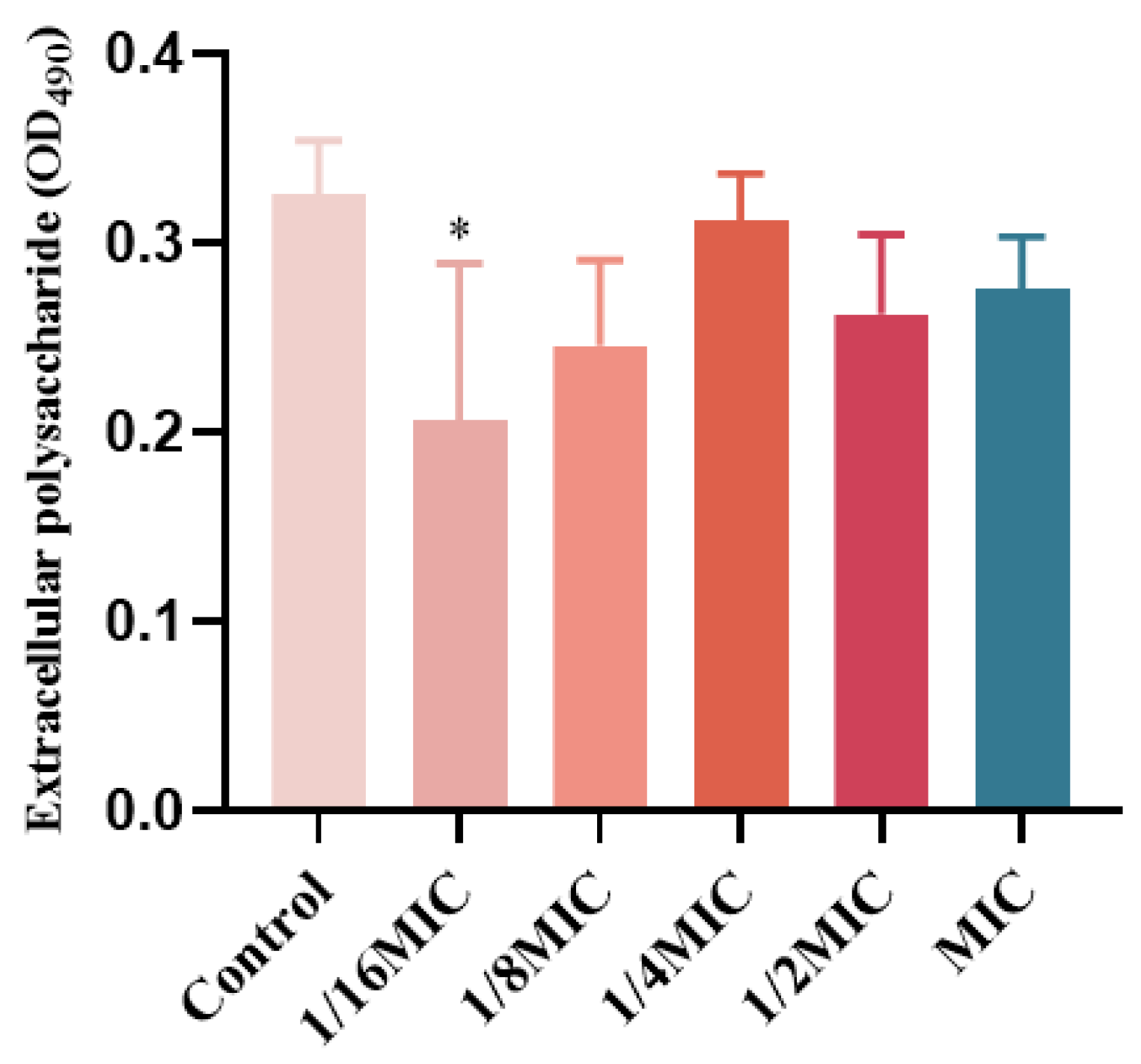
2.8. The Influence of EPS
2.9. Effect of Melittin on the Production of Virulence Factors
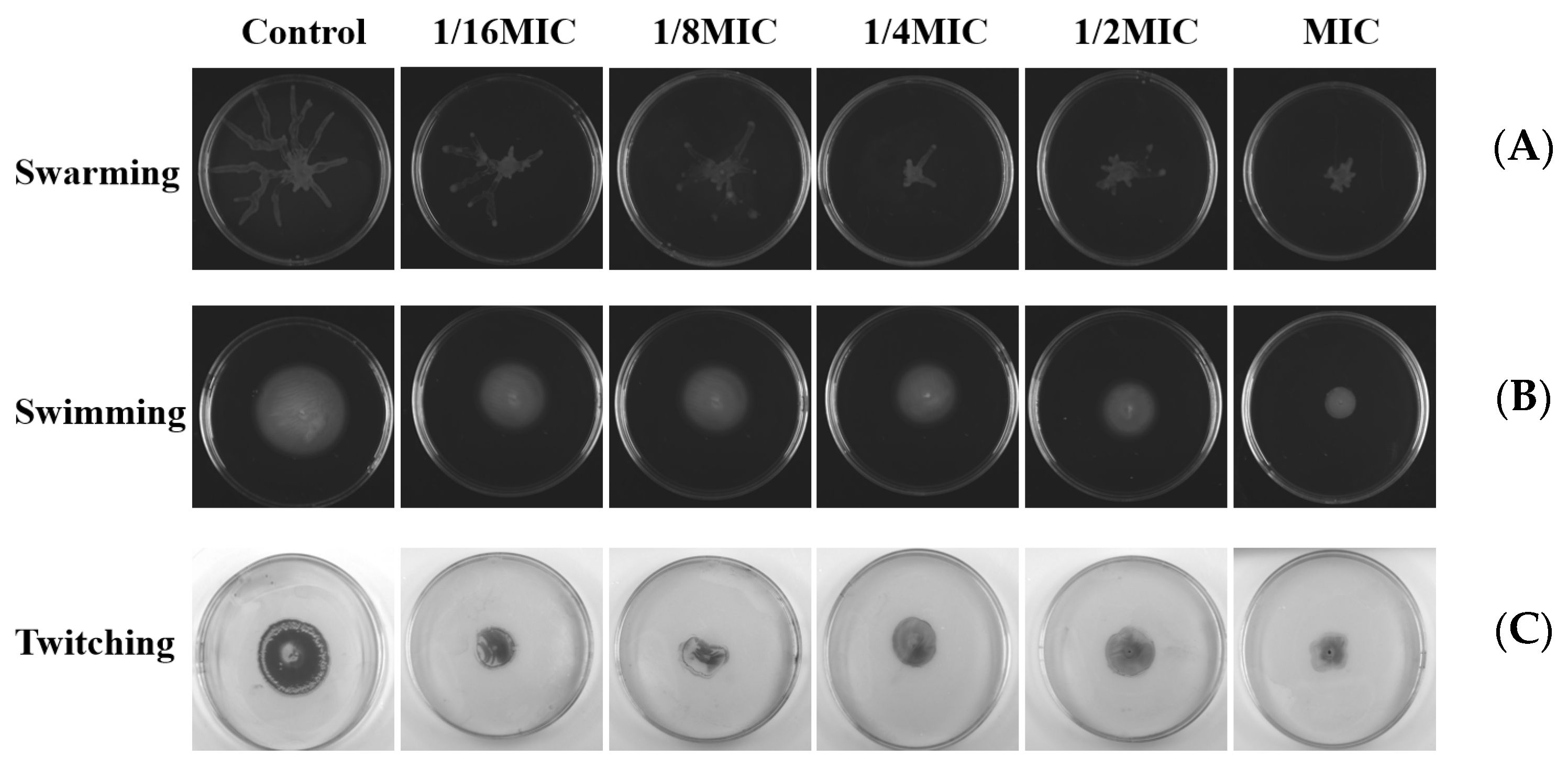
2.10. Effects on Swarming, Swimming, and Twitching Motility
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. The Source of Melittin
4.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
4.3. Antimicrobial Activity Assays
4.4. Growth Curve Assay
4.5. Effect of Melittin on Morphological Changes
4.6. Live and Dead Cell Staining
4.7. ROS Test
4.8. The Ability of Biofilm Formation
4.9. Effect of Melittin on Bacterial Strains Biofilm Inhibition and Eradication
4.10. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.11. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Analysis
4.12. EPS Assay
4.13. Pyocyanin Assay
4.14. Elastase Assay and Rhamnolipid Assay
4.15. Swarming, Swimming, and Twitching Motility Assay
4.16. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Rossolini, G.M.; Arena, F.; Pecile, P.; Pollini, S. Update on the antibiotic resistance crisis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvas, L.A.C. Bacterial resistance, a current crisis. Rev. Esp. Salud Publica 2023, 97, e202302013. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, I.; Rahman, S.; Jan, A.T.; Siddiqui, M.T.; Mondal, A.H.; Haq, Q.M.R. Antibiotics, Resistome and Resistance Mechanisms: A Bacterial Perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uruen, C.; Chopo-Escuin, G.; Tommassen, J.; Mainar-Jaime, R.C.; Arenas, J. Biofilms as Promoters of Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance and Tolerance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, A.L.; Sun, J.Z.; Liu, Y.P. Understanding bacterial biofilms: From definition to treatment strategies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1137947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, F.; Wynendaele, E.; Braet, S.; D’Hondt, M.; De Spiegeleer, B. Quality evaluation of synthetic quorum sensing peptides used in R&D. J. Pharm. Anal. Anal. 2015, 5, 169–181. [Google Scholar]
- Turan, N.B.; Chormey, D.S.; Buyukpinar, C.; Engin, G.O.; Bakirdere, S. Quorum sensing: Little talks for an effective bacterial coordination. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.F.F.; Magalhaes, R.P.P.; Simoes, M.; Sousa, S.F. Drug Repurposing Targeting Pseudomonas aeruginosa MvfR Using Docking, Virtual Screening, Molecular Dynamics, and Free-Energy Calculations. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Li, M.X.; Yi, G.J.; Liao, L.; Cheng, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, M. Screening strategies for quorum sensing inhibitors in combating bacterial infections. J. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Zeng, X.; Yen, G.G. Evolutionary Multi-Objective Optimization in Searching for Various Antimicrobial Peptides Feature. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2023, 18, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.; Wang, K.; Liang, Y.; Chai, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, X. The first Brevinin-1 antimicrobial peptide with LPS-neutralizing and anti-inflammatory activities in vitro and in vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1102576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.-Y.; Yan, Z.-B.; Meng, Y.-M.; Hong, X.-Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.-J.; Cheng, X.-R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.-Y. Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Military Med. Res. 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiss, A.S.; Henriques, S.T.; Lawrence, N. Antimicrobial peptides provide wider coverage for targeting drug-resistant bacterial pathogens. Pept. Sci. 2022, 114, e24246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahnsen, J.S.; Franzyk, H.; Sayers, E.J.; Jones, A.T.; Nielsen, H.M. Cell-Penetrating Antimicrobial Peptides—Prospectives for Targeting Intracellular Infections. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perekalin, D.S.; Novikov, V.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Ivanov, I.A.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Kopylov, A.N.; Volkov, D.S.; Seregina, I.F.; Bolshov, M.A.; Kudinov, A.R. Selective Ruthenium Labeling of the Tryptophan Residue in the Bee Venom Peptide Melittin. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 4923–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghuraman, H.; Chattopadhyay, A. Melittin: A membrane-active peptide with diverse functions. Biosci. Rep. 2007, 27, 189–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wu, J. Advance on the Main Compositions and the Functions of Honeybee Venom. GAB 2013, 32, 246–253. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, V.C.; Patel, S.K.S.; Lee, J.-K. Bacterial biofilm inhibitors: An overview. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Breslawec, A.P.; Liang, T.; Deng, Z.; Kuperman, L.L.; Yu, Q. Strategy to combat biofilms: A focus on biofilm dispersal enzymes. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2023, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Rao, S.; Bansal, A.; Dang, S.; Gupta, S.; Gabrani, R. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm: Potential therapeutic targets. Biologicals 2014, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Ma, L.Y.Z. Biofilm Matrix and Its Regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 20983–21005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, K.; Luecke, A.R.; Wakeman, C.A. Temperature-specific adaptations and genetic requirements in a biofilm formed by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1032520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harimawan, A.; Ting, Y.P. Investigation of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) properties of P. aeruginosa and B. subtillis and their role in bacterial adhesion. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brindhadevi, K.; LewisOscar, F.; Mylonakis, E.; Shanmugam, S.; Verma, T.N.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biofilm and Quorum sensing mediated pathogenicity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Process Biochem. 2020, 96, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiarasan, E.; Kottha, T.; Harish, B.N.; Gnanasambandam, V.; Sali, V.K.; John, J. Inhibition of quorum sensing-controlled biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by quorum-sensing inhibitors. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 111, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Hao, S.Q.; Zhao, L.; Shi, F.; Ye, G.; Zou, Y.F.; Song, X.; Li, L.X.; Yin, Z.Q.; He, X.L.; et al. Paeonol Attenuates Quorum-Sensing Regulated Virulence and Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 692474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ordonez, A.; Coughlan, L.M.; Briandet, R.; Cotter, P.D. Biofilms in Food Processing Environments: Challenges and Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, C.; Raheem, D.; Ramos, F.; Saraiva, A.; Raposo, A. Microbial Biofilms in the Food Industry—A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharahi, J.Y.; Azimi, T.; Shariati, A.; Safari, H.; Tehrani, M.K.; Hashemi, A. Advanced strategies for combating bacterial biofilms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 14689–14708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, T. Microbial diversity in biofilms on water distribution pipes of different materials. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.C.M.; Ferreira, R.B.R. Biofilms and bacterial virulence. Rev. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 22, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshiro, K.G.N.; Rodrigues, G.; Monges, B.E.D.; Cardoso, M.H.; Franco, O.L. Bioactive Peptides Against Fungal Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alni, R.H.; Tavasoli, F.; Barati, A.; Badarbani, S.S.; Salimi, Z.; Babaeekhou, L. Synergistic activity of melittin with mupirocin: A study against methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) and methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA) isolates. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2580–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangel, K.; Lechuga, G.C.; Almeida Souza, A.L.; Rangel da Silva Carvalho, J.P.; Simoes Villas Boas, M.H.; De Simone, S.G. Pan-Drug Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii, but Not Other Strains, Are Resistant to the Bee Venom Peptide Melittin. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, R.; Singh, P.K.; Pearce, P.; Mok, R.; Song, B.; Diaz-Pascual, F.; Dunkel, J.; Drescher, K. Emergence of three-dimensional order and structure in growing biofilms. Nat. Phys. 2019, 15, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Zhang, L. The hierarchy quorum sensing network in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Protein Cell 2015, 6, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhao, L.; Wu, H.; Zhao, C.; Gong, Q.; Yu, W. Cladodionen Is a Potential Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, I.; Abbas, H.A.; Ashour, M.L.; Yasri, A.; El-Shazly, A.M.; Wink, M.; Sobeh, M. Polyphenols from Salix tetrasperma Impair Virulence and Inhibit Quorum Sensing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Molecules 2020, 25, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Byrd, M.S.; Sergeant, S.; Azad, A.K.; Parsek, M.R.; McPhail, L.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Wozniak, D.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Psl polysaccharide reduces neutrophil phagocytosis and the oxidative response by limiting complement-mediated opsonization. Cell. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picoli, T.; Peter, C.M.; Zani, J.L.; Waller, S.B.; Lopes, M.G.; Boesche, K.N.; Vargas, G.D.Á.; Hübner, S.d.O.; Fischer, G. Melittin and its potential in the destruction and inhibition of the biofilm formation by Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from bovine milk. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafale, N.A.; Semwal, U.P.; Rajput, R.K.; Singh, G.N. Selection of appropriate analytical tools to determine the potency and bioactivity of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance. J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satlin, M.J.; Lewis, J.S., II; Weinstein, M.P.; Patel, J.; Humphries, R.M.; Kahlmeter, G.; Giske, C.G.; Turnidge, J. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute and European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Position Statements on Polymyxin B and Colistin Clinical Breakpoints. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, E523–E529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, R.; Bohlouli, S.; Dizaj, S.M.; Shahi, S.; Memar, M.Y.; Salatin, S. The Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Effects of Hypericum perforatum Oil on Common Pathogens of Periodontitis: An In Vitro Study. Clin. Pract. 2022, 12, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, R.; Ghaleh, H.E.G.; Ranjbar, R. Antibiofilm effect of melittin alone and in combination with conventional antibiotics toward strong biofilm of MDR-MRSA and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1030401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, J.Y.; Jing, Q.; Chen, Z.; Ullah, A.; Jiang, L.G.; Zheng, K.; Yuan, C.; Huang, M.D. Development of a Potent Antimicrobial Peptide with Photodynamic Activity. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 624465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.; Lu, D.; Wang, J.; Xie, Q.; Guo, J. Comparison of pharmacological activity and safety of different stereochemical configurations of borneol: L-borneol, D-borneol, and synthetic borneol. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.; Lai, Z.H.; Jian, Q.; Shao, C.X.; Zhu, Y.J.; Li, G.Y.; Shan, A.S. Design of Heptad Repeat Amphiphiles Based on Database Filtering and Structure-Function Relationships to Combat Drug-Resistant Fungi and Biofilms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 2129–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starr, C.G.; Ghimire, J.; Guha, S.; Hoffmann, J.P.; Wang, Y.H.; Sun, L.S.; Landreneau, B.N.; Kolansky, Z.D.; Kilanowski-Doroh, I.M.; Sammarco, M.C.; et al. Synthetic molecular evolution of host cell-compatible, antimicrobial peptides effective against drug-resistant, biofilm-forming bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8437–8448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilaka, E.; Rajapaksha, D.C.; Nikapitiya, C.; De Zoysa, M.; Whang, I. Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Peptide Octominin for Controlling Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Deng, Z.F.; Li, Y.M.; Xu, K.Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, S.T.; Wang, J.F. Antibiofilm property and multiple action of peptide PEW300 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 963292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardbari, A.M.; Arabestani, M.R.; Karami, M.; Keramat, F.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Bagheri, K.P. Correlation between ability of biofilm formation with their responsible genes and MDR pattetns in clinical and environmental Acinetobacter baumannii isolates. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 108, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, A.A.; Kim, M.; Shin, M.K.; Sung, J.S. Supermagnetic halloysite nanotubes surface-tuned with aminosilane for protease immobilization and applied for eradication of bacterial biofilm. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 593, 153469. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, R.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Arciola, C.R.; Sedighi, I.; Yousefimashouf, R.; Bagheri, K.P. Prevention, inhibition, and degradation effects of melittin alone and in combination with vancomycin and rifampin against strong biofilm producer strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopal, R.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Chae, J.D.; Son, B.K.; Seo, C.H.; Park, Y. Synergistic Effects and Antibiofilm Properties of Chimeric Peptides against Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardbari, A.M.; Arabestani, M.R.; Karami, M.; Keramat, F.; Aghazadeh, H.; Alikhani, M.Y.; Bagheri, K.P. Highly synergistic activity of melittin with imipenem and colistin in biofilm inhibition against multidrug-resistant strong biofilm producer strains of Acinetobacter baumannii. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, P.; Devadatha, B.; Sarma, V.V.; Ranganathan, S.; Ampasala, D.R.; Siddhardha, B. Anti-quorum sensing and antibiofilm activities of Blastobotrys parvus PPR3 against Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 138, 103811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaieb, K.; Kouidhi, B.; Hosawi, S.B.; Baothman, O.A.S.; Zamzami, M.A.; Altayeb, H.N. Computational screening of natural compounds as putative quorum sensing inhibitors targeting drug resistance bacteria: Molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 145, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Tao, H.; He, J.; Huang, S.-Y. The HDOCK server for integrated protein-protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 1829–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Altayb, H.N.; Firoz, A.; Bayoumi, A.A.M.; El Omri, A.; Chaieb, K. Inhibitory activity of marine sponge metabolites on SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent polymerase: Virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 10191–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, A.; Huq, M.A.; Rahman, M.S. Bioinformatics approaches identified dasatinib and bortezomib inhibit the activity of MCM7 protein as a potential treatment against human cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, M.S.; Thangam, R.; Sakthidhasan, P.; Arun, S.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Thirumurugan, R. Combined effect of a natural flavonoid rutin from Citrus sinensis and conventional antibiotic gentamicin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Food Control 2018, 90, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-F.; Su, Y.-L.; Liu, W.-L.; Chen, H.-G.; Zeng, S.-G.; Zhou, H.-B.; Chen, W.-M.; Zheng, J.-X.; Sun, P.-H. Design and synthesis of caffeic acid derivatives and evaluation of their inhibitory activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Med. Chem. Res. 2022, 31, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forezi, L.D.M.; Froes, T.Q.; Cardoso, M.F.C.; Maciel, C.A.D.; Nicastro, G.G.; Baldini, R.L.; Costa, D.C.S.; Ferreira, V.F.; Castilho, M.S.; da Silva, F.D. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Coumarins Derivatives as Potential Inhibitors of the Production of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence Factor pyocyanin. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filik, N.; Kubilay, A. Detection of Quorum Sensing System (Cell to Cell Communication) Using Marker Strains in Vibrio alginolyticus Strains and Determine Virulence under Master of this System. J. Hell. Vet. Med. Soc. 2022, 73, 4945–4956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Tian, J.; Weng, L.X.; Wang, L.H. A new quorum-sensing inhibitor attenuates virulence and decreases antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, J.-S.; Li, Y.-B.; Miao, Z.-Y.; Sun, P.-H.; Lin, J.; Chen, W.-M. Novel 2-Substituted 3-Hydroxy-1,6-dimethylpyridin-4(1H)-ones as Dual-Acting Biofilm Inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 10921–10945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Strain | MIC (μg/mL) | MBC (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | 8 | 16 |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | 8 | 16 |
| S. aureus 1 | 4 | 8 |
| S. aureus 3 | 8 | 16 |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | 16 | 32 |
| A. baumannii 34230 | 4 | 8 |
| A. baumannii 57190 | 4 | 8 |
| K. pneumoniae 53735 | 64 | 128 |
| Strain | Biofilm Formation |
|---|---|
| E. coli ATCC 25922 | Moderate |
| S. aureus ATCC 25923 | Strong |
| S. aureus 1 | Strong |
| S. aureus 3 | Moderate |
| P. aeruginosa PAO1 | Strong |
| A. baumannii 3423 | Moderate |
| A. baumannii 57190 | Moderate |
| K. pneumoniae 53735 | Strong |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.; Ma, R.; Chen, J.; Xie, Q.; Luo, W.; Sun, P.; Liu, Z.; Guo, J. Discovery of Melittin as Triple-Action Agent: Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, and Potential Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities. Molecules 2024, 29, 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030558
Yang H, Ma R, Chen J, Xie Q, Luo W, Sun P, Liu Z, Guo J. Discovery of Melittin as Triple-Action Agent: Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, and Potential Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities. Molecules. 2024; 29(3):558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030558
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Hongyan, Rong Ma, Jiarou Chen, Qian Xie, Wenhui Luo, Pinghua Sun, Zheng Liu, and Jialiang Guo. 2024. "Discovery of Melittin as Triple-Action Agent: Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, and Potential Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities" Molecules 29, no. 3: 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030558
APA StyleYang, H., Ma, R., Chen, J., Xie, Q., Luo, W., Sun, P., Liu, Z., & Guo, J. (2024). Discovery of Melittin as Triple-Action Agent: Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial, Anti-Biofilm, and Potential Anti-Quorum Sensing Activities. Molecules, 29(3), 558. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29030558






