Enhanced Solubility of Ibuprofen by Complexation with β-Cyclodextrin and Citric Acid
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Theoretical Modelling
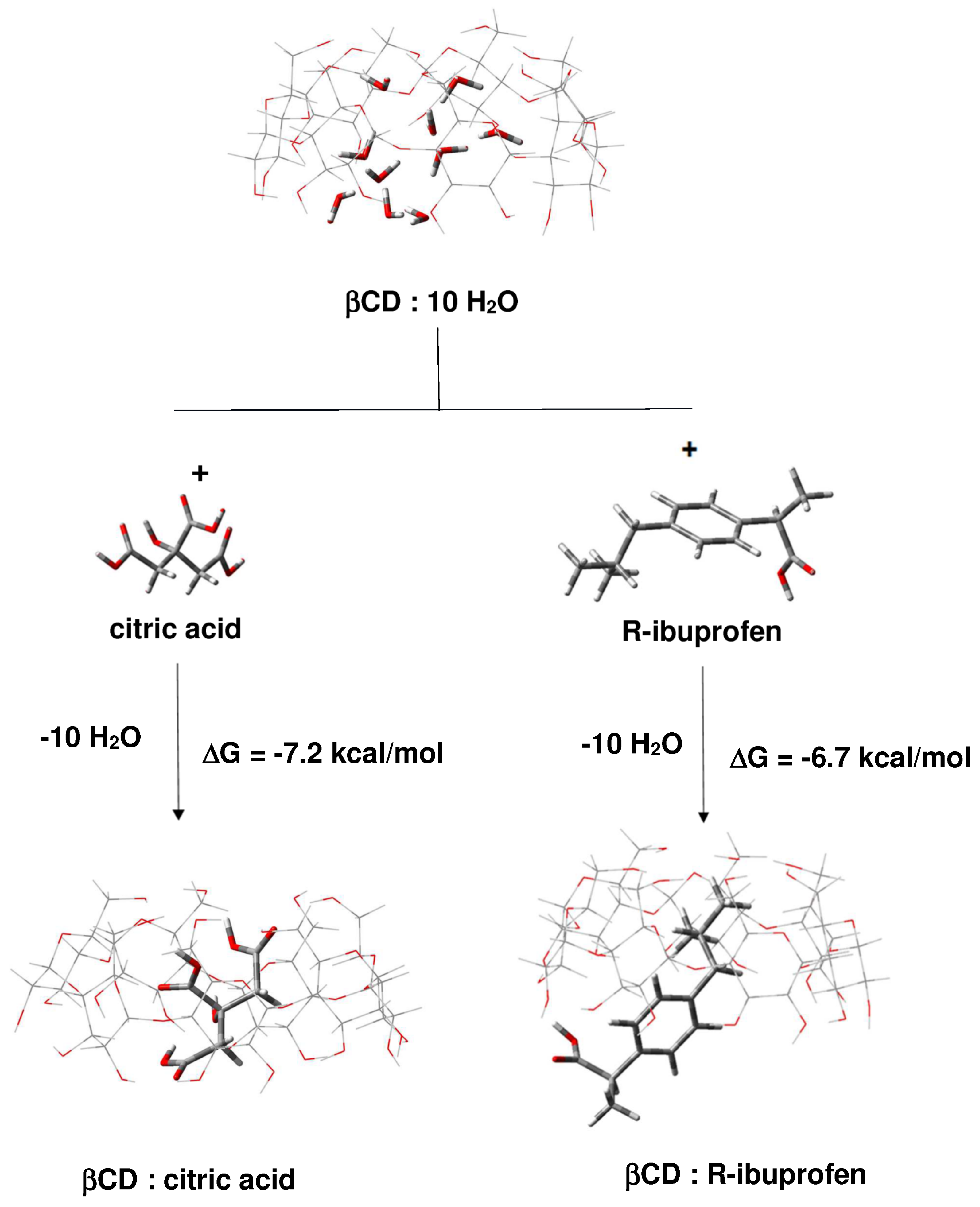
2.1.1. Binding of Citric Acid and Ibuprofen to β-CD in Forming 1:1 Binary Complexes
2.1.2. Formation of β-CD/CA/IBU Ternary Complexes
2.1.3. Formation of β-CD/IBU/CA Ternary Complexes
2.2. Experimental Evidence for the Formation of Ternary Complexes
Thermal, Spectral, and Microstructural Characteristics of β-CD/IBU and β-CD/IBU/CA Complexes
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarafska, T.; Ivanova, S.; Dudev, T.; Petrov, V.; Spassov, T. Beta-cyclodextrin—Citric acid complexation by ball milling and annealing. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1295, 136701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdal, D.; Bednarz, S.; Kasprzyk, W. Sorption properties of β-cyclodextrin-citric acid derivatives. In Proceedings of the 14th International Electronic Conference on Synthetic Organic Chemistry, Krakow, Poland, 30 October 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, V.; Monflier, E. Cyclodextrins and Their Complexes: Chemistry, Analytical Methods, Applications; Dodziuk, H., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2006; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, C.; Huang, W.; Hu, J.-L. Water-insoluble β-cyclodextrin polymer crosslinked by citric acid: Synthesis and adsorption properties toward phenol and methylene blue. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2009, 63, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, B.; Morcellet, M.; Ruffin, D.; Vinet, F.; Weltrowski, M. Capture and Controlled Release of Fragrances by CD Finished Textiles. J. Incl. Phenom. 2002, 44, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednarz, S.; Lukasiewicz, M.; Mazela, W.; Pajda, M.; Kasprzyk, W. Chemical Structure of Poly(b-cyclodextrin-co-citric acid). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 119, 3511–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, P.; Bilal, M.; de Brauer, C. Beta-cyclodextrin/citric acid complexation equilibrium: Thermodynamic study. Apparent solubility of beta-CD in aqueous solutions of citric acid. Thermochim. Acta 1995, 259, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaz, I.; Isasi, J.R.; Sanchez, M.; Uzqueda, M.; Ponchel, G. Structural characteristics of some soluble and insoluble b-cyclodextrin polymers. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 57, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaoka, M.; Hayashi, K. Adsorption of bisphenol A by crosslinked b-cyclodextrin polymer. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 44, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, B.; Morcellet, M.; Ruffin, D.; Ducoroy, L.; Weltrowski, M. Finishing of polyester fabrics with cyclodextrins and polycarboxylic acids as crosslinking agents. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 44, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treshkova, I.V.; Kulikov, O.V.; Kumeev, R.; Nikiforov, M.Y. 1H NMR study of Complexation of alfa and beta-cyclodextrins with some Biologically active acid. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2005, 31, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, C.; Núñez, I.; Torrado, J.J.; Gordon, J.; Potthast, H.; García-Arieta, A. Investigation on the possibility of biowaivers for Ibuprofen. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 2343–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheirsilp, B.; Rakmai, J. Inclusion complex formation of cyclodextrin with its guest and their applications. Biol. Eng. Med. 2017, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, S.B.; Costa Duarte, F.Í.; Heimfarth, L.; Siqueira Quintans, J.S.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; Veiga Júnior, V.F.D.; Neves de Lima, Á.A. Cyclodextrin-Drug Inclusion Complexes: In Vivo and In Vitro Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shohin, I.E.; Kulinich, J.I.; Ramenskaya, G.V.; Abrahamsson, B.; Kopp, S.; Langguth, P.; Polli, J.E.; Shah, V.P.; Groot, D.W.; Barends, D.M.; et al. Biowaiver monographs for immediate-release solid oral dosage forms: Ketoprofen. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3593–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvine, J.; Afrose, A.; Islam, N. Formulation and delivery strategies of ibuprofen: Challenges and opportunities. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levis, K.A.; Lane, M.E.; Corrigan, O.I. Effect of buffer media composition on the solubility and effective permeability coefficient of ibuprofen. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 253, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klueglich, M.; Ring, A.; Scheuerer, S.; Trommeshauser, D.; Schuijt, C.; Liepold, B.; Berndl, G. Ibuprofen extrudate, a novel, rapidly dissolving ibuprofen formulation: Relative bioavailability compared to ibuprofen lysinate and regular ibuprofen, and food effect on all formulations. J. Clin. Pharm. 2005, 45, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeal, C.J.; Meininger, C.J.; Wilborn, C.D.; Tekwe, C.D.; Wu, G. Safety of dietary supplementation with arginine in adult humans. Amino. Acids 2018, 50, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayamizu, K.; Oshima, I.; Nakano, M. Comprehensive Safety Assessment of ʟ-Lysine Supplementation from Clinical Studies: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2561S–2569S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiguchi, K.; Obi, N. Studies on Absorption of Eutectic Mixture. I. A Comparison of the Behavior of Eutectic Mixture of Sulfathiazole and that of Ordinary Sulfathiazole in Man. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1961, 9, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wei, X.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y. A deep eutectic solvent modified magnetic β-cyclodextrin particle for solid-phase extraction of trypsin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1137, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janus, E.; Ossowicz, P.; Klebeko, J.; Nowak, A.; Duchnik, W.; Kucharski, L.; Klimowicz, A. Enhancement of Ibuprofen solubility and skin permeation by conjugation with l-valine alkyl esters. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 7570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, Y.; Chen, S.; Hanawa, T. Solubility Enhancement of Ibuprofen by Adsorption onto Spherical Porous Calcium Silicate. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoyanova, K.; Vinarov, Z.; Tcholakova, S. Improving Ibuprofen solubility by surfactant-facilitated self-assembly into mixed micelles. J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, W.J.; Hedges, A.R. Properties and applications of cyclodextrins. J. Macromol. Sci. A Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 33, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.R.; Tong, W.; D’Souza, W.T. Self assembly in custom designed cyclodextrins. Supramol. Chem. 1994, 4, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifune, A.; Shima, A. Cyclodextrins and their application. J. Synth. Org. Chem. 1977, 35, 116–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Khan, S.; Parab, I. Cyclodextrin and its Derivative in Drug Delivery System. Asian J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 13, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Bhowmick, M.; Zhang, P.; Ling, C.C. Cyanoethylation of cyclodextrin derivatives. Can. J. Chem. 2016, 94, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delattre, F.; Woisel, P.; Surpateanu, G.; Bria, M.; Cazier, F.; Decock, P. 1, 3-Dipolar cycloaddition reaction of bipyridinium ylides with the propynamido-β-cyclodextrin. A regiospecific synthesis of a new class of fluorescent β-cyclodextrins. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 1557–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereva, S.; Nikolova, V.; Sarafska, T.; Angelova, S.; Spassov, T.; Dudev, T. Inclusion complexes of Ibuprofen and β-cyclodextrin: Supramolecular structure and stability. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1205, 127575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereva, S.; Nikolova, V.; Angelova, S.; Spassov, T.; Dudev, T. Water inside β-cyclodextrin cavity: Amount, stability and mechanism of binding. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 1592–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaussian, Inc. Gaussian 09, Version D.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolova, V.; Velinova, A.; Dobrev, S.; Kircheva, N.; Angelova, S.; Dudev, T. Host−Guest Complexation of Cucurbituril and Cucurbituril with the Antineoplastic and Multiple Sclerosis Agent Mitoxantrone (Novantrone). J. Phys. Chem. A 2021, 125, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EMA/CHMP/ICH/645469/2008. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/ich-guideline-q4b-annex-7-r2-note-evaluation-recommendation-pharmacopoeial-texts-use-ich-regions_en.pdf (accessed on 2 March 2024).
- FDA. Dissolution Testing and Acceptance Criteria for Immediate-Release Solid Oral Dosage Form Drug Products Containing High Solubility Drug Substances. Guidance for Industry. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/dissolution-testing-and-acceptance-criteria-immediate-release-solid-oral-dosage-form-drug-products/ (accessed on 2 March 2024).
- Sathe, P.; Tsong, Y.; Shah, P. In vitro dissolution profile comparison: Statistics and analysis, model-dependent approach. Pharm. Res. 1996, 13, 1799–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitag, G. Guidelines on dissolution profile comparison. Drug Inform. J. 2001, 35, 865–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use. Guideline on the Investigation of Bioequivalence CPMP/EWP/QWP/1401/98 Rev.1/Corr**; European Medicines Agency: London, UK, 2010.
- FDA. Guidance for Industry. Dissolution Testing of Immediate-Release Solid Dosage Forms; FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1997.
- Siepmann, J.; Siepmann, F. Mathematical modeling of drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 328–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Zero Order | First Order | Higuchi Model | Hixson-Crowell Model | Korsmeyer–Peppas | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 β-CD/IBU | 0.9438 | 0.9157 | 0.9795 | 0.863 | 0.9898 |
| R2 β-CD/IBU/CA | 0.9540 | 0.9157 | 0.9859 | 0.7842 | 0.9938 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarafska, T.; Ivanova, S.; Dudev, T.; Tzachev, C.; Petrov, V.; Spassov, T. Enhanced Solubility of Ibuprofen by Complexation with β-Cyclodextrin and Citric Acid. Molecules 2024, 29, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071650
Sarafska T, Ivanova S, Dudev T, Tzachev C, Petrov V, Spassov T. Enhanced Solubility of Ibuprofen by Complexation with β-Cyclodextrin and Citric Acid. Molecules. 2024; 29(7):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071650
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarafska, Tsveta, Stanislava Ivanova, Todor Dudev, Christo Tzachev, Vesselin Petrov, and Tony Spassov. 2024. "Enhanced Solubility of Ibuprofen by Complexation with β-Cyclodextrin and Citric Acid" Molecules 29, no. 7: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071650
APA StyleSarafska, T., Ivanova, S., Dudev, T., Tzachev, C., Petrov, V., & Spassov, T. (2024). Enhanced Solubility of Ibuprofen by Complexation with β-Cyclodextrin and Citric Acid. Molecules, 29(7), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29071650








