Natural Products as Novel Therapeutic Agents for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Evidence, Mechanisms, Challenges, and Opportunities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Activity of Natural Products in Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
2.1. Terpenoids
2.1.1. Anti-Metastasis
2.1.2. Regulation of Cell Cycle
2.1.3. Modulation of Autophagy
| Natural Products | Structure | Sources | Concentration In Vitro | Dosage In Vivo | Biological Activities/Mechanisms | Potential Targets | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
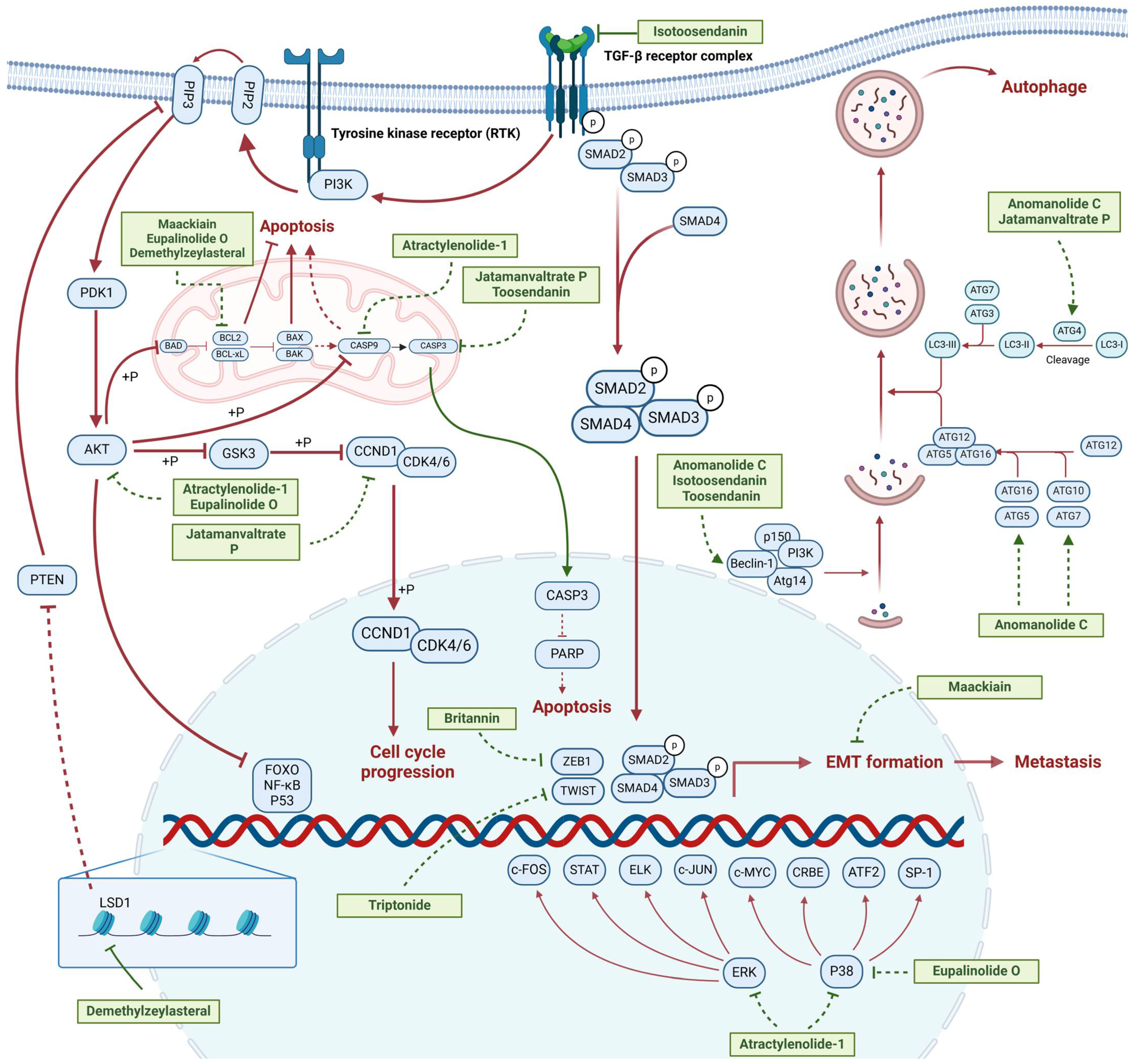
| Anomanolide C |  | Tubocapsicum anomalum (S. Vidal) M. J. Pires | 0.25, 1, 2 μM | 25, 50 mg/kg | Induces glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) ubiquitination to trigger autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in TNBC. | GPX4 | [38] |
| Atractylenolide-1 | 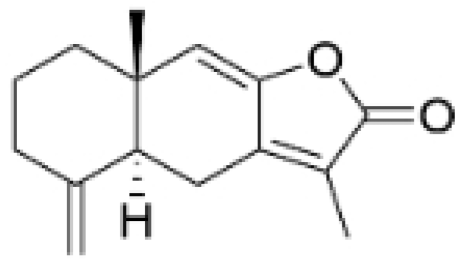 | Atractylodes lancea | 25, 50 μM | 20, 50 mg/kg | Inhibits phosphorylation of the Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) family; suppresses the expression of Triosephosphate Isomerase 1 (TPI1) and Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase GPI (GPI), thereby affecting the glycolytic/gluconeogenic pathway. | TPI1 and GPI | [21] |
| Britannin |  | Inula japonica Thunb | 5, 10, 20 μM | 5, 10 mg/kg | Induces Zinc finger e-box binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) degradation, inhibiting invasion and metastasis of TNBC cells. | ZEB1 | [40] |
| Demethylzeylasteral | 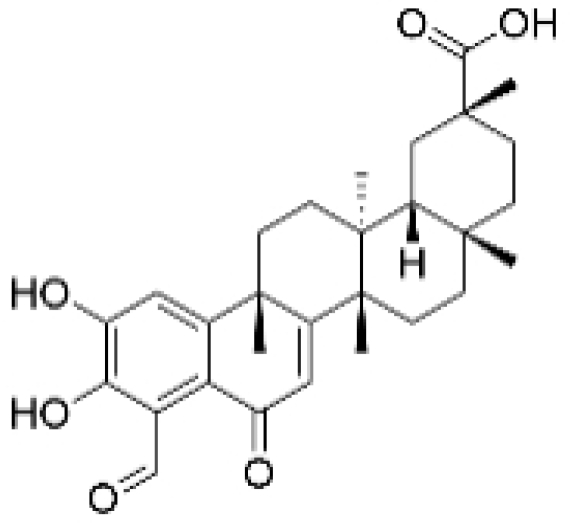 | Tripterygium wilfordii | 5, 10 μM | 4 mg/kg | Reduces the expression of LSD1 protein, enhances the expression of its target protein PTEN, and suppresses the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. | LSD1 | [25] |
| Isotoosendanin | 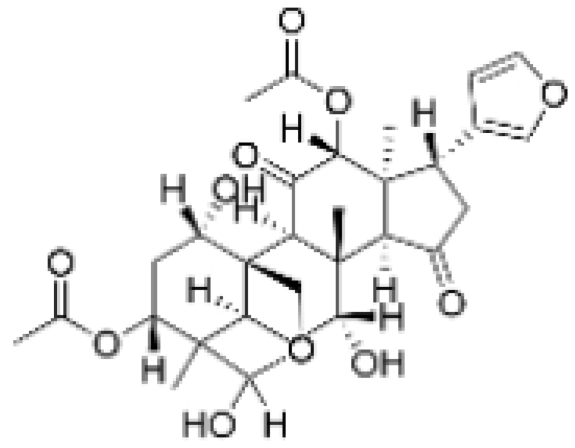 | Melia azedarach L. | 0.1, 0.3, 1 μM | 0.1, 1 mg/kg | Directly engages with the kinase domain of TGF-β receptor type-1 (TGFβR1), thereby abolishing TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) in the TNBC microenvironment. | TGFβR1 | [20,37] |
| Toosendanin | 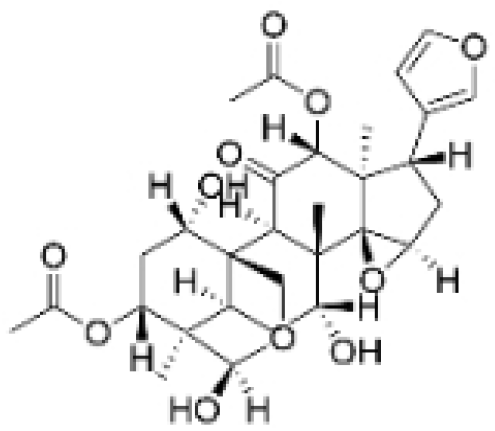 | Melia azedarach L. | 0.1, 1, 5 μM | / | Inhibits autophagy by alkalizing lysosomal pH. | / | [20,39] |
| Jatamanvaltrate P |  | Valeriana jatamansi A. DC. | 2.5, 5 μM | 15 mg/kg | Enhances PARP and caspase cleavage, indicating apoptosis induction, and reducing Cyclin B1, CCND1, and Cell division cycle 2 (Cdc-2) expression, which are crucial for cell cycle progression. | / | [24] |
| Maackiain |  | Spatholobus suberectus H. S. Lo | 1, 2, 2.5, 5 μM | 25, 50 mg/kg | Enhances the induction of GADD45α protein and mRNA through the inhibition of miR-374a. | / | [26] |
| Triptonide |  | Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. | 0.2 μM | 5 mg/kg | Suppresses the tumorigenesis and metastasis of TNBC via triggering the degradation of Twist1 and Notch1 oncoproteins. | / | [41,42] |
| Eupalinolide O |  | Eupatorium lindleyanum DC. | 5, 10 μM | 15, 30 mg/kg | Induces apoptosis, which is orchestrated through ROS generation and the AKT/p38 MAPK signaling pathway. | / | [23] |
2.2. Glycosides
2.2.1. Anti-Metastasis
2.2.2. Pro-Apoptosis
2.2.3. Other Anti-TNBC Effects
| Natural Products | Structure | Sources | Concentration In Vitro | Dosage In Vivo | Biological Activities/Mechanisms | Potential Targets | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
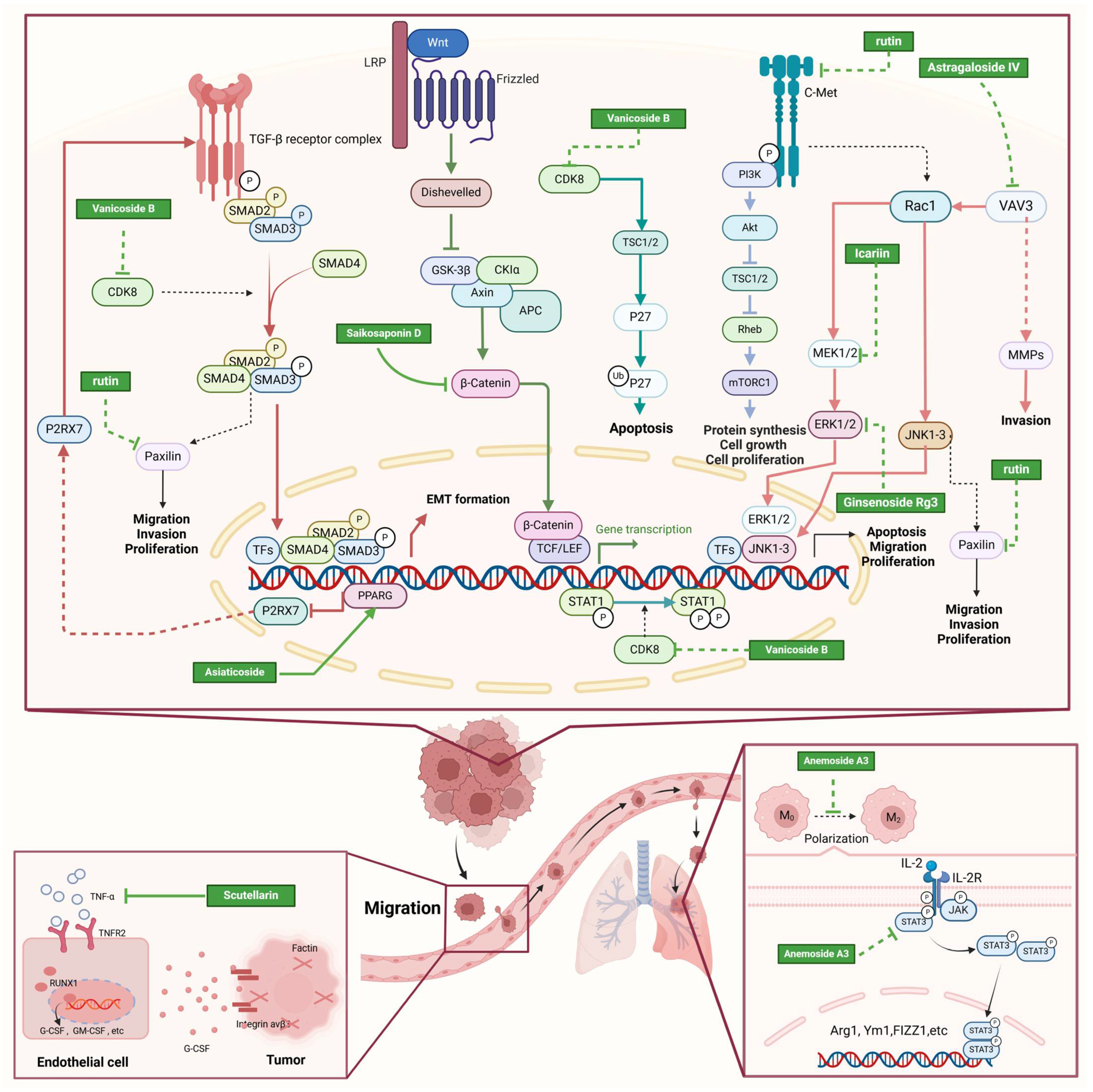
| Rutin | 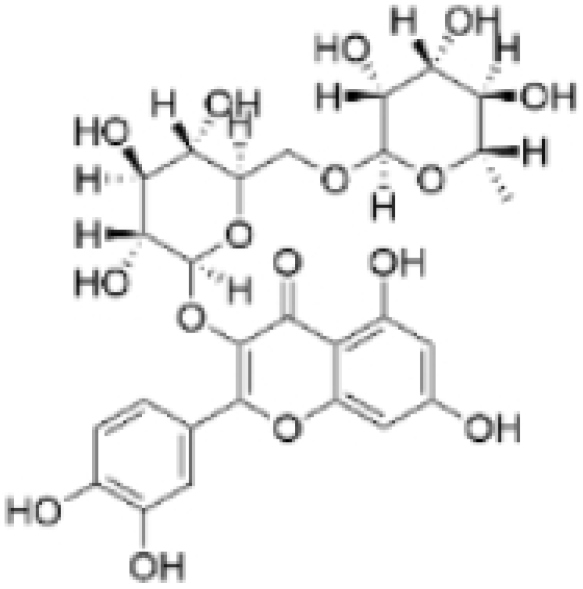 | Acacia erioloba E. Mey. | 150, 300 μM | 30 mg/kg | Rutin acts as an inhibitor of c-Met Kinase and effectively inhibits the proliferation of TNBC cells both in vitro and in vivo. | / | [56] |
| Icariin | 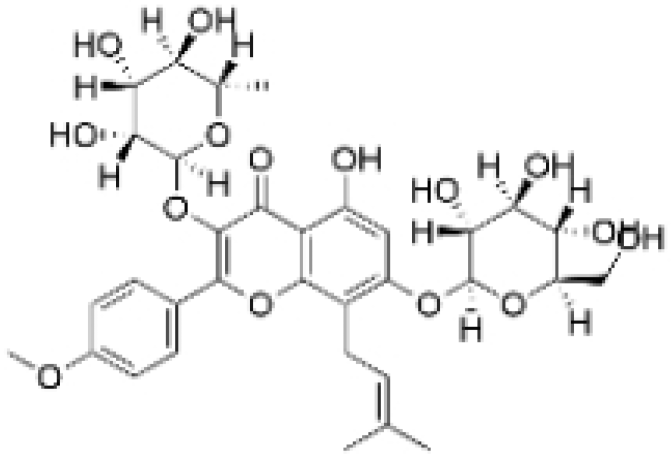 | Epimedium wushanense Maxim. | 5, 10, 20 μM | 20, 40 mg/kg | Induces apoptosis and suppresses the migration of TNBC cells through modulation of the Sirtuin (Sirt) 6 /NF-κB signaling pathway. | / | [47] |
| Vanicoside B |  | Persicaria dissitiflora H. Hara | 5, 10, 20 μM | 5, 10 mg/kg | The inhibition of CDK8-mediated signaling pathways leads to downregulation of EMT proteins and instigates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in TNBC cells. | / | [43] |
| Anemoside A3 | 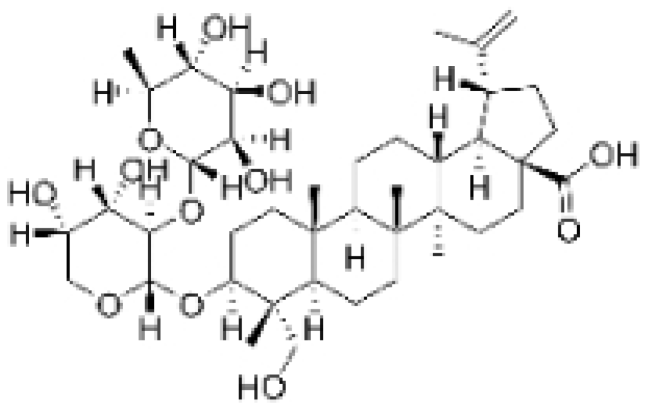 | Pulsatilla chinensis (Maxim.) Klob. | 50, 100 μg/mL | 10, 20 mg/kg | Promotes differentiation of M0 macrophages into the M1 phenotype, which hinges upon the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) /NF-κB/MAPK signaling cascade. | TLR4 | [68] |
| Asiaticoside | 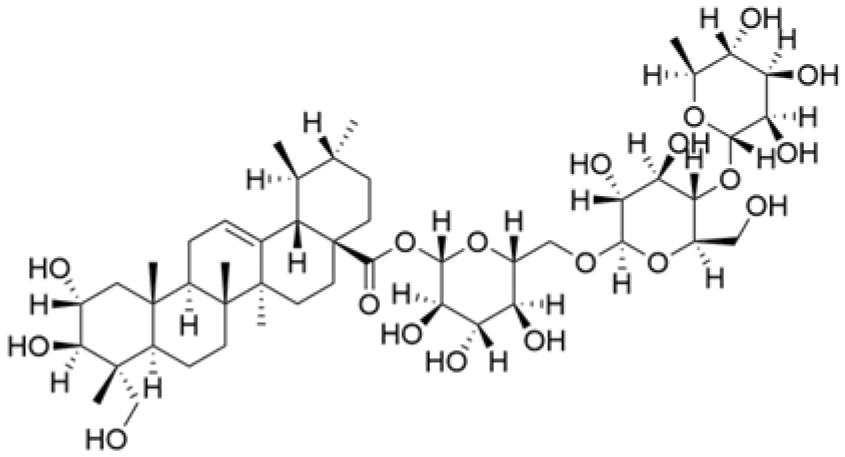 | Centella asiatica (L.) Urban | 0.25 μM | 1, 2, 3 mg/kg | Inhibits P2RX7-mediated TGF-β/SMAD signaling through upregulation of PPARγ expression, thus attenuating EMT in TNBC. | PPARγ | [44] |
| Astragaloside IV | 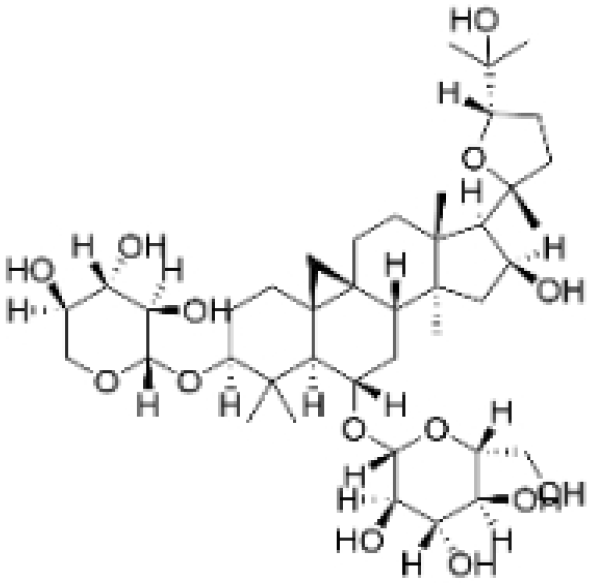 | Astragalus membranaceus Bunge | 20, 40 μg/mL | 20, 40 mg/kg | Reduces Vav3 expression. | / | [54] |
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | 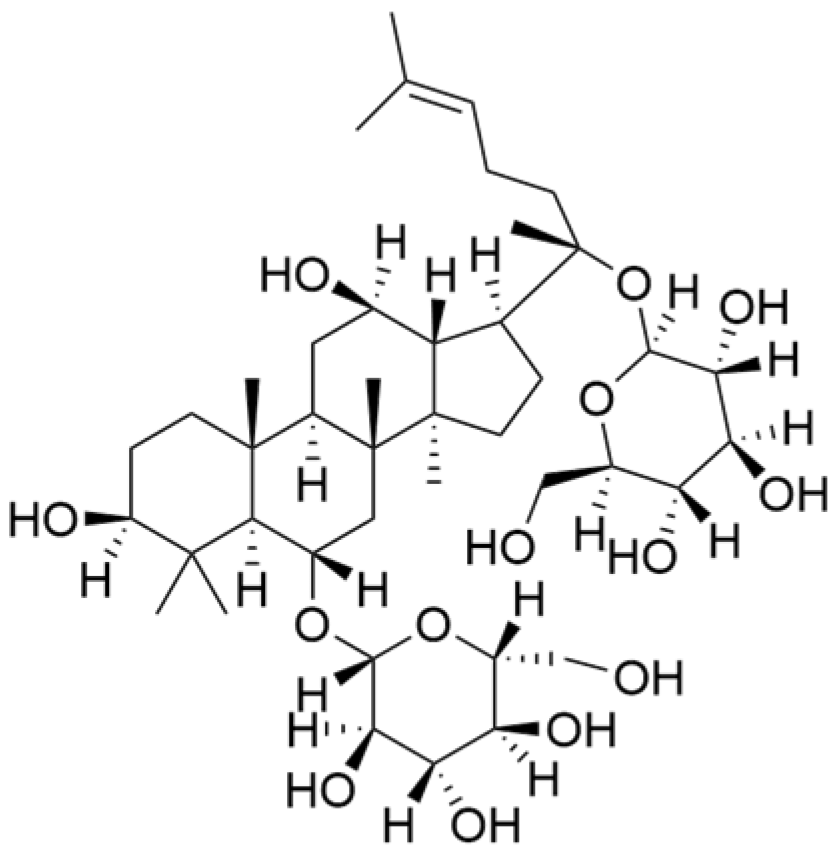 | Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. | 10 μM | / | Activates the DNA damage-response elements [Ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein kinase (ATM), H2A histone family member X (H2AX), Radiation-sensitive 51 (RAD51), X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1(XRCC1), apoptosis-related genes (P21, TP53, Apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 (APAF1), BAX, Caspase 3(CASP3), and Caspase 9(CASP9))] in MDA-MB-231 cells. | / | [66,69] |
| Ginsenosides Rg3 | 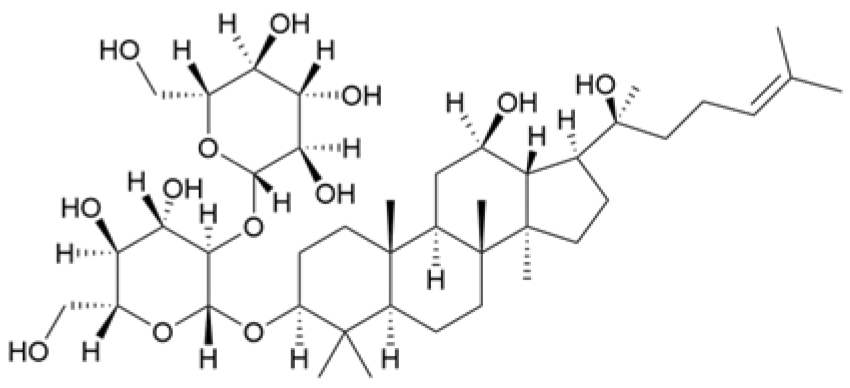 | Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. | 300 mg/mL | / | Increases the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio, causes mitochondrial membrane potential depolarization, leads to cytochrome c release, and induces caspase-3 and PARP cleavage. | / | [64,65] |
| Saikosaponin D | 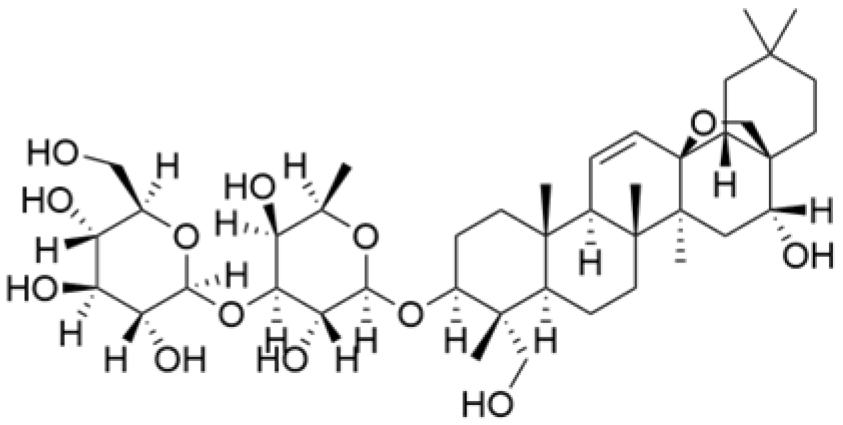 | Bupleurum rotundifolium L. | 10, 15, 30 μM | / | Suppresses the proliferation of TNBC cells through modulation of the β-catenin signaling cascade. | β-catenin | [70] |
| Scutellarin | 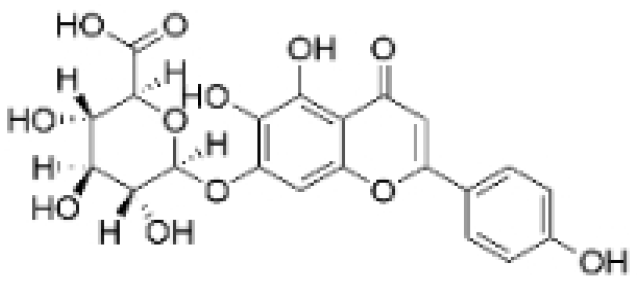 | Erigeron breviscapus (Vaniot) Hand. -Mazz. | 20 μM | 10 mg/kg | Reduces TNBC metastasis through the targeting of TNFα/TNFR2-initiated activation of RUNX1 and subsequent production of G-CSF in TNBC-associated endothelial cells. | TNFα/TNFR2 | [71] |
2.3. Phenolics
2.3.1. Anti-Metastasis
2.3.2. Anti-Angiogenesis
2.3.3. Other Anti-TNBC Effects
2.4. Alkaloids
| Natural Products | Structure | Sources | Concentration In Vitro | Dosage In Vivo | Biological Activities/Mechanisms | Potential Targets | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
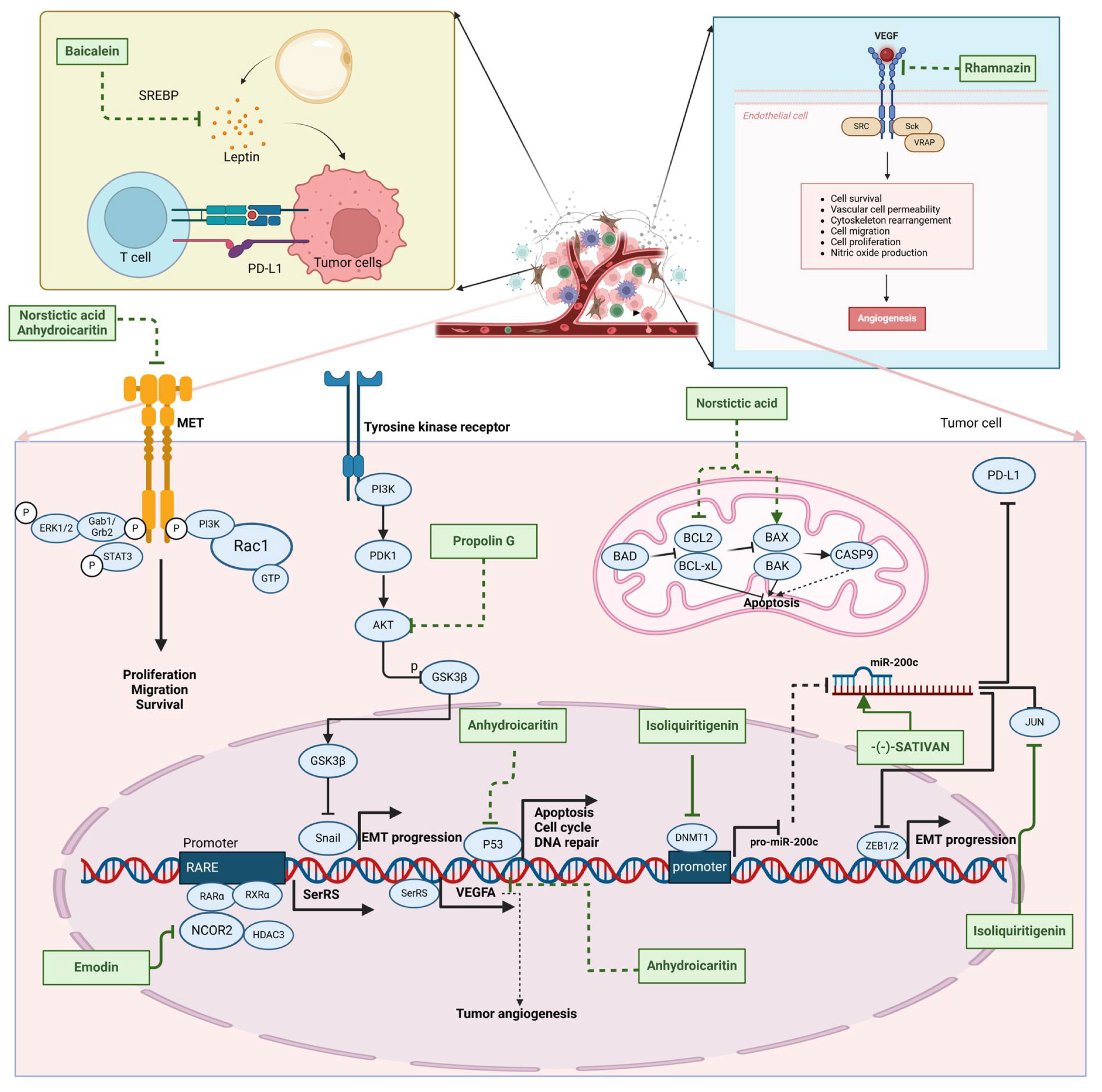
| (-)-Sativan(SA) | 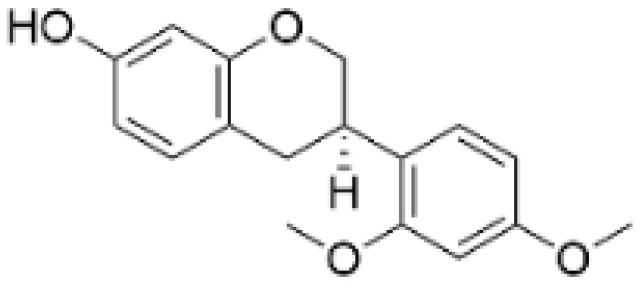 | Spatholobus suberectus Dunn | 5, 10, 20 μM | 25, 50 mg/kg | Upregulates miR-200c to suppress the process of EMT. | / | [76] |
| Anhydroicaritin | 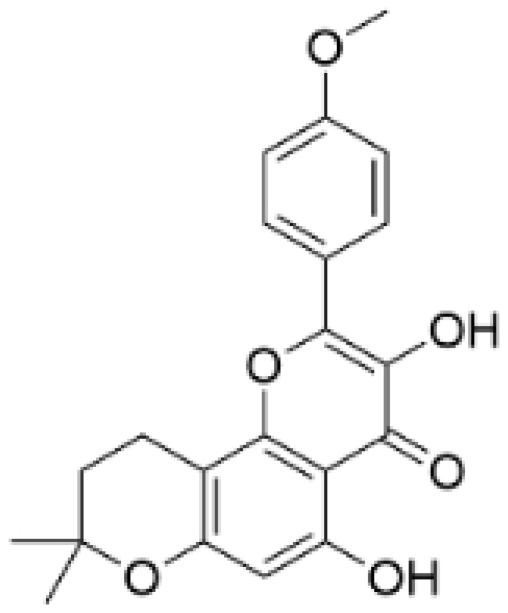 | Epimedium brevicornu Maxim. | 10, 20, 30 μM | 20 mg/kg | Inhibits the HIF-1α/VEGFA signaling pathway. | / | [86] |
| Emodin | 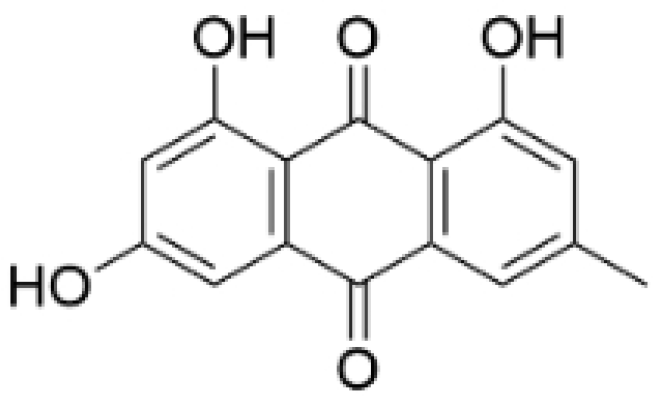 | Rheum palmatum L. | 0.25, 10, 25 μM | 40 mg/kg | Regulates the activity of NCOR2; inhibits SIK3; suppresses TGF-β1. | NCOR2 | [82] |
| Isoliquiritigenin | 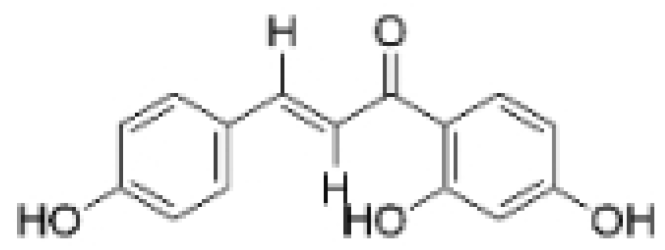 | Spatholobus suberectus Dunn | 10 μM | 20, 40 mg/kg | Reduces miR-374a expression; elevates BAX protein and mRNA levels by inhibiting miR-374a; enhances miR-200c expression. | / | [99,100] |
| Kaempferol | 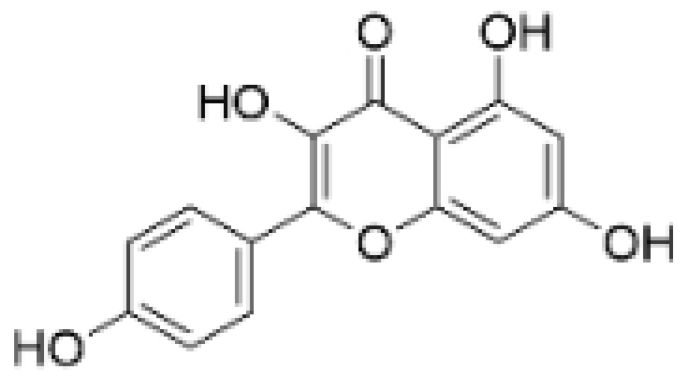 | Caragana frutex (L.) C. Koch | 12.5, 25 μg/mL, | / | Inhibits Sirt3 and Sirt6 proteins, inhibiting the PI3K/AKT pathway. | Sirts | [87] |
| Morin | 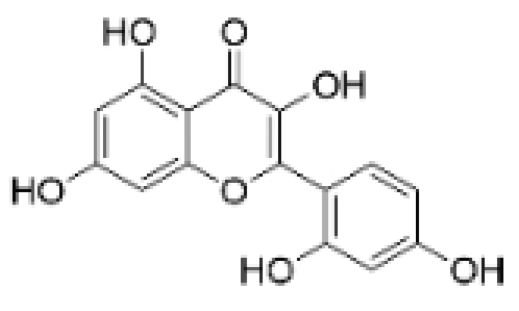 | Maclura pomifera (Raf.) C. K. Schneid., Petasites formosanus Kitam. | 10, 50, 100, 200 μM | 10 mg/kg | Inhibits the growth and invasion of the highly metastatic BC cell line MDA-MB-231, which is partly achieved through the suppression of the AKT pathway. | / | [100,101] |
| Propolin G |  | Taiwanese propolis | 5, 10, 15, 20 μM | / | Inhibits the stabilization of vimentin protein, mediated by GSK-3β-Snail, and interferes with HDAC6, thereby impeding the suppression of cell migration and invasion in TNBC. | GSK-3β, HDAC6 | [78] |
| Rhamnazin | 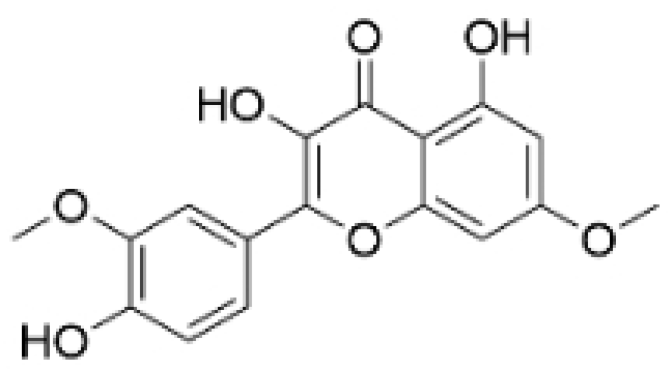 | Callicarpa kwangtungensis chun, Alocnemum strobilaceum | 10, 15, 20 μM | 200 mg/kg | Suppresses VEGF-induced phosphorylation of VEGFR2 and its downstream signaling mediators in HUVECs. | VEGFR2 | [84] |
| Baicalein | 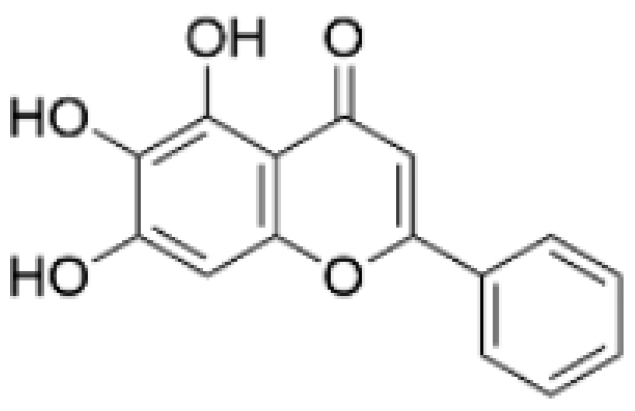 | Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi | 50, 100 ng/ml | 50 mg/kg | Reverses the expression of IFIT2. | / | [89,102] |
| Norstictic acid |  | Dimelaena oreina, Umbilicaria virginis | 15, 30 μM | 15 mg/kg | Inhibits the proliferation, migration, and invasion of TNBC MDA-MB-231 cells. | / | [80] |
Anti-Proliferation
| Natural Products | Structure | Sources | Concentration In Vitro | Dosage In Vivo | Biological Activities/Mechanisms | Potential Targets | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
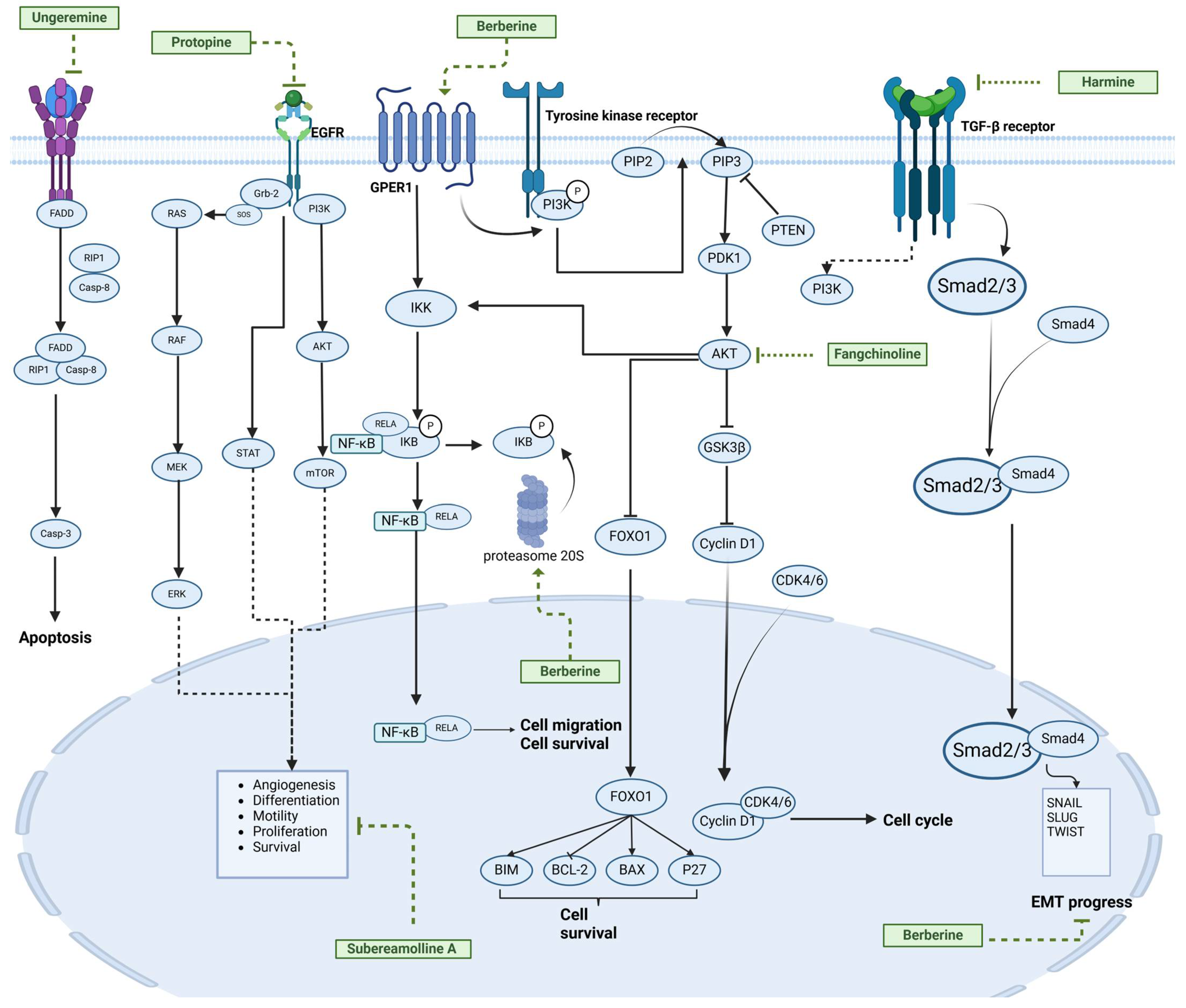
| Fangchinoline | 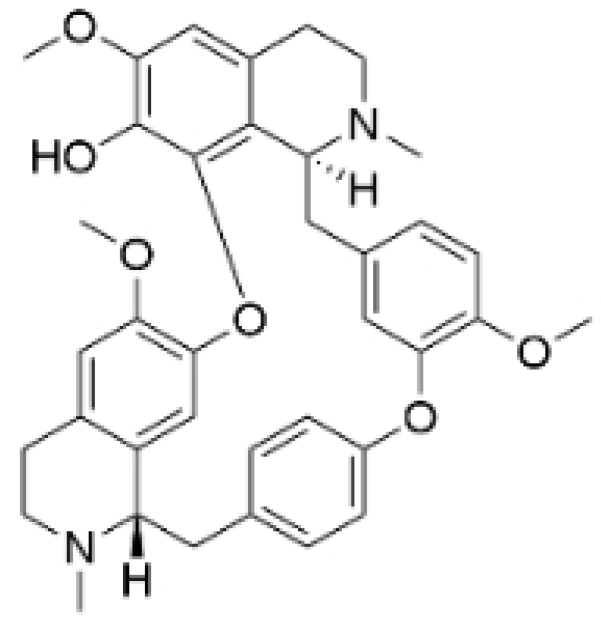 | Stephania tetrandra (Radix) | 6, 12, 24 μM5, 10, 30 μM | / | Inhibits the AKT/Gsk 3β/CCND1 signaling pathway; blocks cell cycle progression at the G1 phase; induces apoptosis. | / | [94,95] |
| Dragmacidin D | 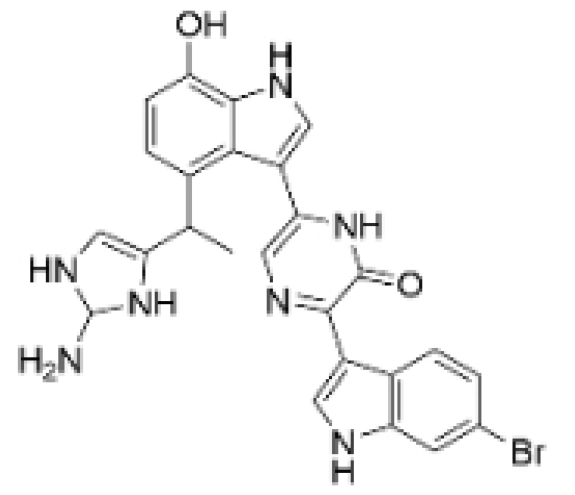 | Genus Spongosorites | 3.8, 7.6 μM | / | Induces apoptosis in TNBC spheroids. | / | [98] |
| Protopine | 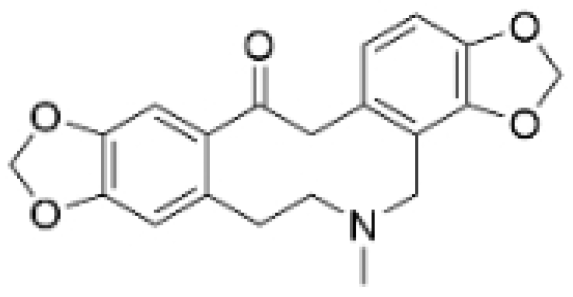 | Corydalis yanhusuo | 1, 10, 100 μM | / | Specifically inhibits the cell adhesion ability of MDA-MB-231. | / | [108] |
| Subereamolline A | 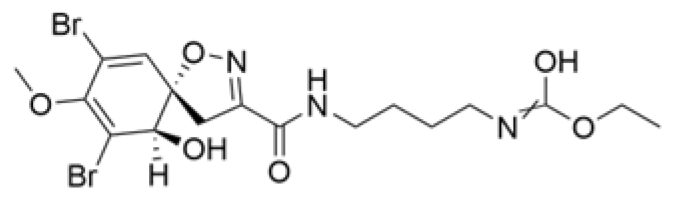 | Pseudoceratina arabica | 2 μM | / | Inhibits the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells. | / | [109] |
| Harmine |  | Peganum harmala | 10 μM | / | Inhibits the process of EMT, associated with the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. | / | [110] |
| Ungeremine | 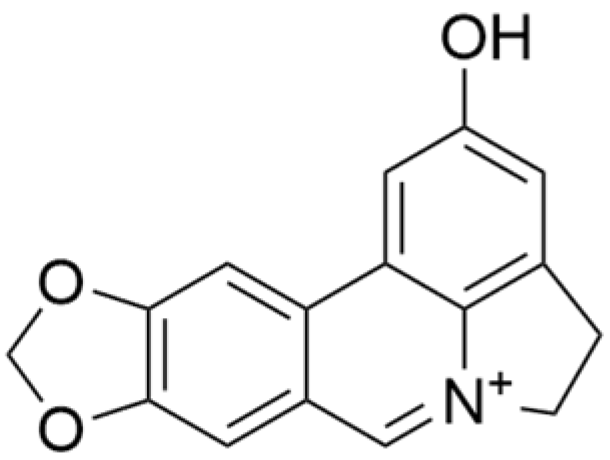 | Crinum zeylanicum | 3.67 μM | / | Induces ferroptosis, necroptosis, and autophagy, as well as apoptosis, mediated by caspase activation, MMP alteration, and increase ROS production. | / | [106] |
| Berberine |  | Coptis chinensis | 1.25, 2.5, 5 μM | 15, 30 mg/mL | Reduces IL-6 secretion and LH2 expression; modulates the GPER1/NF-κB pathway; inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway. | LH2 | [107,111] |
| Matrine | 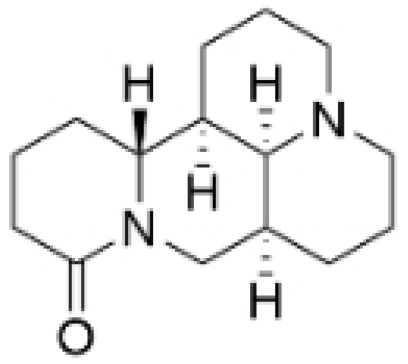 | Sophora flavescens | 2, 4 μM | / | Inhibits the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; suppresses HN1 expression. | / | [93,97] |
3. Natural Products: Mechanisms of Inhibiting TNBC
3.1. TGF-β Signaling Pathway
3.2. VEGFA Signaling Pathway
3.3. PI3K Signaling Pathway
3.4. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
3.5. MAPK Signaling Pathway
4. Challenges and Opportunities
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| NPs | Natural products |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth receptor 2 |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| TCMs | Traditional Chinese medicines |
| HMs | Herbal medicines |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| AT-1 | Atractylenolide-1 |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| AS | Asiaticoside |
| ITSN | Isotoosendanin |
| GPX4 | Glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| T-96 | Demethylzeylasteral |
| AC | Anomanolide C |
| TPI1 | Triosephosphate Isomerase 1 |
| GPI | Glucose-6-phosphate isomerase |
| EO | Eupalinolide O |
| LSD1 | Lysine-specific demethylase 1 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| MA | Maackiain |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 |
| PARP | Poly adenosinediphosphate-ribose polymerase |
| BRCA | Breast cancer gene |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide3kinase |
| AKT | Protein kinase B |
| Wnt | Wingless/Int-1 |
| AS- IV | Astragaloside IV |
| SC | Scutellarin |
| PD | Platycodin D |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TNFR2 | Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 |
| TGFβR1 | TGF-β receptor type-1 |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| Rho GTPase | Rho family GTPases |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| Bcl2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| c-Myc | Cellular myelocytomatosis oncogene |
| ZEB1 | Zinc finger e-box binding homeobox 1 |
| Cdc-2 | Cell division cycle 2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PTP1B | Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B |
| CDK8 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 8 |
| Vav3 | Vav Family Member 3 |
| RUNX1 | Runt-related transcription factor 1 |
| G-CSF | Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor |
| MMP-9 | Matrix metalloproteinase-9 |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| NTSR1 | Neurotensin receptor 1 |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like epichlorohydrin-associated protein 1 |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| Sirt | Sirtuin |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| ATM | Ataxia telangiectasia mutated protein kinase |
| H2AX | H2A histone family member X |
| RAD51 | Radiation-sensitive 51 |
| XRCC1 | X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 1 |
| APAF1 | Apoptotic peptidase activating factor 1 |
| CASP3 | Caspase 3 |
| CASP9 | Caspase 9 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| miR | microRNA |
| GSK-3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3β |
| HDAC6 | Histone deacetylase 6 |
| IFIT2 | Interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 2 |
| NCOR2 | Nuclear receptor corepressor 2 |
| SerRS | Seryl-tRNA synthetase |
| HUVECs | Human umbilical vascular endothelial cells |
| TSN | Toosendanin |
| MET | Methionine |
| VEGFR2 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prat, A.; Adamo, B.; Cheang, M.C.U.; Anders, C.K.; Carey, L.A.; Perou, C.M. Molecular Characterization of Basal-Like and Non-Basal-Like Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2013, 18, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Lin, N.U.; Polyak, K. Insights into molecular classifications of triple-negative breast cancer: Improving patient selection for treatment. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 176–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, J.C.; Serrels, A.; Stupack, D.G.; Schlaepfer, D.D.; Frame, M.C. Targeting FAK in anticancer combination therapies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Xu, Q.; Ji, W.; Tian, R.; Niu, R. Elevated STAT3 signaling-mediated upregulation of MMP-2/9 confers enhanced invasion ability in multidrug-resistant breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24772–24790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koudelka, Š.; Turánek, J. Liposomal paclitaxel formulations. J. Control. Release 2012, 163, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaan, T.M.A.; Samec, M.; Liskova, A.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D. Paclitaxel’s mechanistic and clinical effects on breast cancer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, P.; Scatena, C.; Ghilli, M.; Bargagna, I.; Lorenzini, G.; Nicolini, A. Molecular Mechanisms, Biomarkers and Emerging Therapies for Chemotherapy Resistant TNBC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Merkher, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, N.; Leonov, S.; Chen, Y. Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for triple-negative breast cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, T.E.; Tolaney, S.M. Role of immunotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wu, N.; Chen, Y.C.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, J. PARP inhibitor resistance: The underlying mechanisms and clinical implications. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.Y.; Wei, W.C.; Jian, F.Y.; Yang, N.S. Therapeutic applications of herbal medicines for cancer patients. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 302426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.-Y.; Litscher, G.; Gao, S.-H.; Zhou, S.-F.; Yu, Z.-L.; Chen, H.-Q.; Zhang, S.-F.; Tang, M.-K.; Sun, J.-N.; Ko, K.-M. Historical perspective of traditional indigenous medical practices: The current renaissance and conservation of herbal resources. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 525340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tholl, D. Biosynthesis and biological functions of terpenoids in plants. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2015, 148, 63–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baba, C.; Baassiri, A.; Kiriako, G.; Dia, B.; Fadlallah, S.; Moodad, S.; Darwiche, N. Terpenoids’ anti-cancer effects: Focus on autophagy. Apoptosis 2021, 26, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Tang, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhao, Z.; Cui, H. Meroterpenoids produced by fungi: Occurrence, structural diversity, biological activities, and their molecular targets. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 209, 112860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, T.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; He, W.; Tang, X.; Xie, L.; Wu, R. Exploring Chemical and Biological Space of Terpenoids. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 59, 3667–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Mei, X.; Yang, R.; Lu, B.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L. Isotoosendanin inhibits triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by reducing mitochondrial fission and lamellipodia formation regulated by the Smad2/3-GOT2-MYH9 signaling axis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 2672–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, L.; Qu, L.; Tu, J.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, K. Atractylenolide-1 affects glycolysis/gluconeogenesis by downregulating the expression of TPI1 and GPI to inhibit the proliferation and invasion of human triple-negative breast cancer cells. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ji, Y.; Fan, J.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Wu, M.; Cheng, H.; Xu, C. Demethylzeylasteral (T-96) inhibits triple-negative breast cancer invasion by blocking the canonical and non-canonical TGF-β signaling pathways. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Fu, L.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Tian, C.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, R. Eupalinolide O Induces Apoptosis in Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via Modulating ROS Generation and Akt/p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 8802453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Zhu, R.; Tian, S.; Wang, Y.; Lou, S.; Zhao, H. Jatamanvaltrate P induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis and autophagy in human breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Gu, Y.; Jiang, R.; Qian, H.; Li, S.; Xu, L.; Gu, W.; Zuo, Y. Antitumor Effect of Demethylzeylasteral (T-96) on Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via LSD1-Mediate Epigenetic Mechanisms. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2022, 2022, 2522597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Wang, L.; Xiong, L.; Tang, H.; Du, J.; Peng, C. Maackiain Modulates miR-374a/GADD45A Axis to Inhibit Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Initiation and Progression. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 806869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.K.; Ali, A.Y.; Hayward, O.A.; Turnham, D.; Jackson, T.; Bowen, I.D.; Clarkson, R. β-Bisabolene, a Sesquiterpene from the Essential Oil Extract of Opoponax (Commiphora guidottii), Exhibits Cytotoxicity in Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Germacrone alleviates breast cancer-associated osteolysis by inhibiting osteoclastogenesis via inhibition of MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 2860–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahrestanaki, M.K.; Mirjani, A.; Ghanadian, M.; Aghaei, M. Cycloartane triterpenoid from Euphorbia macrostegia modulates ER stress signaling pathways to induce apoptosis in MDA-MB231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 1749–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.-J.; Jin, H.-Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, S.-D.; Shan, L.; Voruganti, S.; Nag, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, W.-D.; Zhang, R. Selective cytotoxicity, inhibition of cell cycle progression, and induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells by sesquiterpenoids from Inula lineariifolia Turcz. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 68, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, M.; Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Lu, C. Diselenium-linked dimeric prodrug nanomedicine breaking the intracellular redox balance for triple-negative breast cancer targeted therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 193, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; Chen, X.; Tan, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhou, K.; Wu, T.; Cui, L.; Wang, Y. Germacrone inhibits the proliferation of breast cancer cell lines by inducing cell cycle arrest and promoting apoptosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 667, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duangmano, S.; Sae-lim, P.; Suksamrarn, A.; Domann, F.E.; Patmasiriwat, P. Cucurbitacin B inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation through disruption of microtubule polymerization and nucleophosmin/B23 translocation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 12, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.W.; Zhao, W.W.; Lu, J.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Chen, X.P. Cucurbitacin B suppresses metastasis mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) via focal adhesion kinase (FAK) in breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 16, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, R.; PriyaDharshini, L.C.; Sakthivel, K.M.; Rasmi, R.R. Role and regulation of autophagy in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.W.; Jeon, J.; Go, G.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. The dual role of autophagy in cancer development and a therapeutic strategy for cancer by targeting autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-N.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Z.-L.; Guo, Q.; Wu, Z.-Q.; Ke, C.; Lu, B.; Wang, Z.-T.; Ji, L.-L. Isotoosendanin exerts inhibition on triple-negative breast cancer through abrogating TGF-β-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition via directly targeting TGFβR1. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2990–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.-H.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Wang, Z.-W.; Sun, D.-J.; Li, H.; Liu, B.; Chen, L.-X. Anomanolide C suppresses tumor progression and metastasis by ubiquitinating GPX4-driven autophagy-dependent ferroptosis in triple negative breast cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 2531–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, Y.; Chen, X.; Tan, C.S.H.; Li, M.; Miao, K.; Lu, J.-H. Toosendanin, a late-stage autophagy inhibitor, sensitizes triple-negative breast cancer to irinotecan chemotherapy. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, B.; Hong, M. Study on inhibition of Britannin on triple-negative breast carcinoma through degrading ZEB1 proteins. Phytomedicine 2022, 104, 154291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Meng, M.; Liu, Y.; Qi, J.; Zhao, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, P.; et al. Triptonide effectively inhibits triple-negative breast cancer metastasis through concurrent degradation of Twist1 and Notch1 oncoproteins. Breast Cancer Res. 2021, 23, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Chen, J.; Han, B.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Giuliano, A.E.; Cui, Y.; Cui, X. Identification of triptonide as a therapeutic agent for triple negative breast cancer treatment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Wang, C.Y.; Hu, R.; Lee, J.Y.; Luu, T.-T.-T.; Park, H.-J.; Lee, S.K. Antitumor Activity of Vanicoside B Isolated from Persicaria dissitiflora by Targeting CDK8 in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3140–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Jia, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Yu, X.; Xia, J. Asiaticoside hampers epithelial–mesenchymal transition by promoting PPARG expression and suppressing P2RX7-mediated TGF-β/Smad signaling in triple-negative breast cancer. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 1771–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wei, L.; Mao, D.; Che, X.; Ye, X.; Liu, Y. Combination of oxymatrine (Om) and astragaloside IV (As) enhances the infiltration and function of TILs in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 125, 111026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, M.; Obata, Y.; Takahashi, D.; Hase, K. Fine-tuning of the mucosal barrier and metabolic systems using the diet-microbial metabolite axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 37, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Ji, F.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Han, X.; Wu, H.; Yin, Y.; et al. Icariin Induces Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis and Suppresses Invasion by Inhibiting the JNK/c-Jun Signaling Pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.-H.; Li, T.; Gao, H.-W.; Sun, W.; Chen, X.-P.; Wang, Y.-T.; Lu, J.-J. Platycodin D from Platycodonis Radix enhances the anti-proliferative effects of doxorubicin on breast cancer MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. Chin. Med. 2014, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Kim, Y.S. Platycodin D inhibits migration, invasion, and growth of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells via suppression of EGFR-mediated Akt and MAPK pathways. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2013, 205, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.-A.; Lee, S.K.; Park, J.; Jung, M.J.; An, S.-E.; Yang, H.J.; Son, S.H.; Kim, K.R.; Park, K.-K.; Chung, W.-Y. Platycodin D Inhibits Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Induced Angiogenesis by Blocking the Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases and the Production of Interleukin-8. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 1645–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimehdipoor, H.; Tahmasvand, Z.; Nejad, F.G.; Maresca, M.; Rajabi, S. Rutin Promotes Proliferation and Orchestrates Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Angiogenesis in MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.; Ouyang, H.; Zhang, H.; Jia, W.; Lu, B.; Zhang, J.; Ji, L. Scutellarin suppresses the metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer via targeting TNFα/TNFR2-RUNX1-triggered G-CSF expression in endothelial cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 217, 115808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.-N.; Jia, W.-Y.; Lu, B.; Wang, M.-N.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Ji, L.-L. Scutellarin suppresses triple-negative breast cancer metastasis by inhibiting TNFα-induced vascular endothelial barrier breakdown. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 2666–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Lu, Q.; Li, Q.; Ji, Y.; Chen, W.; Xue, X. Astragaloside IV inhibits breast cancer cell invasion by suppressing Vav3 mediated Rac1/MAPK signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 42, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, Y. Ophiopogonin D suppresses TGF-β1-mediated metastatic behavior of MDA-MB-231 breast carcinoma cells via regulating ITGB1/FAK/Src/AKT/β-catenin/MMP-9 signaling axis. Toxicol. Vitr. 2020, 69, 104973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsayed, H.E.; Ebrahim, H.Y.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Siddique, A.B.; Kamal, A.M.; Haggag, E.G.; El Sayed, K.A. Rutin as A Novel c-Met Inhibitory Lead for The Control of Triple Negative Breast Malignancies. Nutr. Cancer 2017, 69, 1256–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, A.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, M.; Ma, S.; Hong, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, D.; et al. Targeting therapy and tumor microenvironment remodeling of triple-negative breast cancer by ginsenoside Rg3 based liposomes. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhjavani, M.; Palethorpe, H.M.; Tomita, Y.; Smith, E.; Price, T.J.; Yool, A.J.; Pei, J.V. Stereoselective anti-cancer activities of ginsenoside rg3 on triple negative breast cancer cell models. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Chang, N.W.; Chung, J.G.; Chen, K.C. Saikosaponin-A induces apoptotic mechanism in human breast MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cancer cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2003, 31, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zang, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, T.; Zhan, H.; Lu, M.; Zhuge, H. Neohesperidin induces cellular apoptosis in human breast adenocarcinoma MDA-MB-231 cells via activating the Bcl-2/Bax-mediated signaling pathway. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2012, 7, 1475–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandrasasmita, O.M.; Lee, J.S.; Baek, S.H.; Tjandrawinata, R.R. Induction of cellular apoptosis in human breast cancer by DLBS1425, a Phaleria macrocarpa compound extract, via downregulation of PI3-kinase/AKT pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wei, G.; Luo, L.; Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Tan, X.; Wang, S.; Chang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Ginsenoside Rg3 nanoparticles with permeation enhancing based chitosan derivatives were encapsulated with doxorubicin by thermosensitive hydrogel and anti-cancer evaluation of peritumoral hydrogel injection combined with PD-L1 antibody. Biomater. Res. 2022, 26, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kwak, J.H.; Pyo, S. Different anticancer effects of Saxifragifolin A on estrogen receptor-positive and estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Na, H.-K.; Surh, Y.-J. Ginsenoside Rg 3 Induces Apoptosis of Human Breast Cancer (MDA-MB-231) Cells. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 18, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.-M.; Kim, D.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Surh, Y.-J.; Na, H.-K. Ginsenoside Rg3 Inhibits Constitutive Activation of NF-κB Signaling in Human Breast Cancer (MDA-MB-231) Cells: ERK and Akt as Potential Upstream Targets. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 19, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Gao, F.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, R. Ginsenoside RG1 augments doxorubicin-induced apoptotic cell death in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell lines. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e22945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chu, S.; Shao, Q.; Zhang, M.; Xia, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lou, Y.; Huang, H.; Chen, N. Antioxidant activities of ginsenoside Rg1 against cisplatin-induced hepatic injury through Nrf2 signaling pathway in mice. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Fan, Z.; Luo, Y.; Cui, Y. Anemoside A3 Inhibits Macrophage M2-Like Polarization to Prevent Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Metastasis. Molecules 2023, 28, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, R.Y.K.; Chen, W.F.; Dong, A.; Guo, D.; Wong, M.S. Estrogen-like activity of ginsenoside Rg1 derived from Panax notoginseng. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3691–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Ming, Y.; Li, Z.; Xing, H.; Chen, J. Saikosaponin D inhibits autophagosome-lysosome fusion and induces autophagy-independent apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yue, G.G.; Lee, J.K.-M.; Gao, S.; Yuen, K.-K.; Cheng, W.; Li, X.; Lau, C.B. Scutellarin, a flavonoid compound from Scutellaria barbata, suppresses growth of breast cancer stem cells in vitro and in tumor-bearing mice. Phytomedicine 2024, 128, 155418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foss, K.; Przybyłowicz, K.E.; Sawicki, T. Antioxidant Activity and Profile of Phenolic Compounds in Selected Herbal Plants. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2022, 77, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; Subbiah, V.; Suleria, H.A.R. Extraction and characterization of phenolic compounds and their potential antioxidant activities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 81112–81129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Singh, J.P.; Kaur, A.; Singh, N. Phenolic composition, antioxidant potential and health benefits of citrus peel. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Everson, R.J.C.; Joshi, B.; Bulsara, P.A.; Upasani, R.; Clarke, M.J. Structure-function relationship of phenolic antioxidants in topical skin health products. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2017, 39, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xiong, L.; Peng, C. (-)-Sativan Inhibits Tumor Development and Regulates miR-200c/PD-L1 in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Tang, H.; Du, J.; Chen, J.; Peng, C. Isoliquiritigenin Suppresses EMT-Induced Metastasis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer through miR-200c/C-JUN/β-Catenin. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 505–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, J.T.; Chen, X.H.; Leu, Y.L.; Weng, M.S. Propolin G-Suppressed Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells via Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β-Mediated Snail and HDAC6-Regulated Vimentin Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, S.Y.; Moon, J.Y.; Unno, T.; Cho, S.K. Baicalein suppresses stem cell-like characteristics in radio-and chemoresistant MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells through up-regulation of IFIT2. Nutrients 2019, 11, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, H.Y.; Elsayed, H.E.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; Akl, M.R.; Bhattacharjee, J.; Egbert, S.; El Sayed, K.A. Norstictic Acid Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and In Vivo Invasive Growth Through Targeting C-Met. Phytother. Res. 2016, 30, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, Z.; Su, Z.; Song, J.; Zhou, L.; Sun, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Gigantol inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling and exhibits anticancer activity in breast cancer cells. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2018, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Xie, T.; Zhao, J.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Ye, H.; Jiao, S.; et al. Herb-sourced emodin inhibits angiogenesis of breast cancer by targeting VEGFA transcription. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6839–6853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdellatef, A.A.; Fathy, M.; Mohammed, A.E.-S.I.; Bakr, M.S.A.; Ahmed, A.H.; Abbass, H.S.; El-Desoky, A.H.; Morita, H.; Nikaido, T.; Hayakawa, Y. Inhibition of cell-intrinsic NF-κB activity and metastatic abilities of breast cancer by aloe-emodin and emodic-acid isolated from Asphodelus microcarpus. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 840–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Cai, W.; Pei, C.G.; Shao, Y. Rhamnazin, a novel inhibitor of VEGFR2 signaling with potent antiangiogenic activity and antitumor efficacy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeon Park, J.; Young Kim, H.; Shibamoto, T.; Su Jang, T.; Cheon Lee, S.; Suk Shim, J.; Hahm, D.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Lee, S.; Sung Kang, K. Beneficial effects of a medicinal herb, Cirsium japonicum var. maackii, extract and its major component, cirsimaritin on breast cancer metastasis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3968–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, C.; Yang, J.; Zheng, J.; Chen, L.; Wei, Z.; Yue, H.; et al. Identifying the anti-metastasis effect of Anhydroicaritin on breast cancer: Coupling network pharmacology with experimental validation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 293, 115326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, T.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; An, H. The Protective Effect of Kaempferol Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Through Activating SIRT3 to Inhibit Oxidative Stress. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2022, 37, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, S.; Lee, M.G.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Nam, K.S. Morin Sensitizes MDA-MB-231 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to Doxorubicin Cytotoxicity by Suppressing FOXM1 and Attenuating EGFR/STAT3 Signaling Pathways. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, F.; Xiao, Y.-Y.; Qu, X.-H.; Li, S.-S.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, C.; He, J.-L.; Zhu, Y.; Wan, Y.-Y.; Jiang, L.-P.; et al. Baicalein sensitizes triple negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells to doxorubicin via autophagy-mediated down-regulation of CDK1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2023, 478, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Pu, G.; Zhang, F.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. Co-delivery of baicalein and doxorubicin by hyaluronic acid decorated nanostructured lipid carriers for breast cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1364–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Gutiérrez, L.; Ferrara, N. Biology and therapeutic targeting of vascular endothelial growth factor A. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 816–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Shibuya, M. The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)/VEGF receptor system and its role under physiological and pathological conditions. Clin. Sci. 2005, 109, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Khan, M.; Fang, N.; Ma, F.; Du, H.; Tan, Z.; Wang, H.; Yin, S.; Wei, X. Berberine Attenuates Cell Motility via Inhibiting Inflammation-Mediated Lysyl Hydroxylase-2 and Glycolysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 856777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Pang, D. Fangchinoline induces g1 arrest in breast cancer cells through cell-cycle regulation. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 1790–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-D.; Yuan, C.-F.; Bu, Y.-Q.; Wu, X.-M.; Wan, J.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, N.; Liu, X.-J.; Zu, Y.; Liu, G.-L.; et al. Fangchinoline inhibits cell proliferation via Akt/GSK-3beta/cyclin D1 signaling and induces apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhuang, J. MAT as a promising therapeutic strategy against triple-negative breast cancer via inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yu, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhou, S.; Lv, X. Matrine exerts an anti-tumor effect via regulating HN1 in triple breast cancer both in vitro and in vivo. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2023, 102, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, E.A.; Peterson, T.A.; Wright, A.E. The Marine Natural Compound Dragmacidin D Selectively Induces Apoptosis in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Spheroids. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Xiong, L.; Xie, X.; Tang, H.; Huang, R.; Peng, C. Isoliquiritigenin Derivative Regulates miR-374a/BAX Axis to Suppress Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Tumorigenesis and Development. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, S.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, M.G.; Lee, K.S.; Nam, K.S. Cell cycle arrest-mediated cell death by morin in MDA-MB-231 triple-negative breast cancer cells. Pharmacol. Rep. 2021, 73, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Lee, W.S.; Eun, S.Y.; Jung, J.H.; Park, H.-S.; Kim, G.; Choi, Y.H.; Ryu, C.H.; Jung, J.M.; Hong, S.C.; et al. Morin, a flavonoid from Moraceae, suppresses growth and invasion of the highly metastatic breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 partly through suppression of the Akt pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Ma, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S. Baicalein induces apoptosis and autophagy of breast cancer cells via inhibiting PI3K/AKT pathway in vivo and vitro. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2018, 12, 3961–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, P.; Yao, P.; Ku, X.; Yang, J. Harmine suppresses the malignant phenotypes and PI3K activity in breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs 2023, 34, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sayed, E.; Ke, T.-Y.; Hwang, T.-L.; Chen, S.-R.; Korinek, M.; Chen, S.-L.; Cheng, Y.-B. Cytotoxic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Lignans and Diterpenes from Cupressus Macrocarpa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommareddy, A.; Knapp, K.; Nemeth, A.; Steigerwalt, J.; Landis, T.; Vanwert, A.L.; Gorijavolu, H.P.; Dwivedi, C. Alpha-Santalol, a Component of Sandalwood Oil Inhibits Migration of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting the β-Catenin Pathway. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 4475–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaveng, A.T.; Bitchagno, G.T.M.; Kuete, V.; Tane, P.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity of ungeremine towards multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cells and induction of apoptosis, ferroptosis, necroptosis and autophagy. Phytomedicine 2019, 60, 152832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, R.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Design, synthesis and in vitro evaluation of fangchinoline derivatives as potential anticancer agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 94, 103431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Gao, J.L. Protopine inhibits heterotypic cell adhesion in MDA-MB-231 cells through down-regulation of multi-adhesive factors. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. AJTCAM/Afr. Netw. Ethnomed. 2014, 11, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaala, L.A.; Youssef, D.T.A.; Sulaiman, M.; Behery, F.A.; Foudah, A.I.; El Sayed, K.A. Subereamolline A as a potent breast cancer migration, invasion and proliferation inhibitor and bioactive dibrominated alkaloids from the red sea sponge Pseudoceratina arabica. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2492–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Mi, D.; Ling, J.; Li, H.; He, P.; Liu, N.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L. Discovery of YH677 as a cancer stemness inhibitor that suppresses triple-negative breast cancer growth and metastasis by regulating the TGFβ signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2023, 560, 216142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, J.; Xiang, J. Berberine inhibits mda-mb-231 cells as an agonist of g protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabeta, P.; Steenkamp, V. The VEGF/VEGFR Axis Revisited: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Zhao, H.; Ren, X.B. Relationship of VEGF/VEGFR with immune and cancer cells: Staggering or forward? Cancer Biol. Med. 2016, 13, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakowicz, D.; Zajkowska, M.; Mroczko, B. Relationship between VEGF Family Members, Their Receptors and Cell Death in the Neoplastic Transformation of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Regulation of VEGF-A expression and VEGF-A-targeted therapy in malignant tumors. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elebiyo, T.C.; Rotimi, D.; Evbuomwan, I.O.; Maimako, R.F.; Iyobhebhe, M.; Ojo, O.A.; Oluba, O.M.; Adeyemi, O.S. Reassessing vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in anti-angiogenic cancer therapy. Cancer Treat. Res. Commun. 2022, 32, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Zhang, H.; Yin, M.; Kong, D.; Kang, L.; Teng, X.; Wang, J.; Chu, Z.; Sun, Y.; Long, P.; et al. Combined Inhibition of PI3K and STAT3 signaling effectively inhibits bladder cancer growth. Oncogenesis 2024, 13, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaviano, A.; Foo, A.S.C.; Lam, H.Y.; Yap, K.C.H.; Jacot, W.; Jones, R.H.; Eng, H.; Nair, M.G.; Makvan-di, P.; Geoerger, B.; et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Liu, G.; Li, C.; Song, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, Y. PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sun, M.M.; Zhang, G.G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.S.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.A. The role of the PI3K-AKT pathway in melanoma. Cancer J. 2012, 18, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, J.; Niu, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Shu, G.; Yin, G. Wnt/β-catenin signalling: Function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, L. Wnt/β-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and Function of the MAPKs and Their Substrates, the MAPK-Activated Protein Kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovida, E.; Tusa, I. Targeting MAPK in Cancer 2.0. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, M.; Sinha, S.; Sudarshan, K.; Aidhen, I.S.; Doble, M. Inhibition of the Enzymes in the Leukotriene and Prostaglandin Pathways in Inflammation by 3-Aryl Isocoumarins. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarshan, K.; Boda, A.K.; Dogra, S.; Bose, I.; Yadav, P.N.; Aidhen, I.S. Discovery of an Isocoumarin Analogue That Modulates Neuronal Functions via Neurotrophin Receptor TrkB. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.S.; Vikas, P.; Costa, R.L.B.; Jahan, N.; Taye, A.; Stringer-Reasor, E.M. Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Journey: Beginning, End, and Everything in Between. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2023, 43, e390464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusztai, L.; Yau, C.; Wolf, D.M.; Han, H.S.; Du, L.; Wallace, A.M.; String-Reasor, E.; Boughey, J.C.; Chien, A.J.; Elias, A.D.; et al. Durvalumab with Olaparib and Paclitaxel for High-Risk HER2-Negative Stage II/III Breast Cancer: Results from the Adaptively Randomized I-SPY2 Trial. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 989–998.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaFargue, C.J.; Dal Molin, G.Z.; Sood, A.K.; Coleman, R.L. Exploring and Comparing Adverse Events between PARP Inhibitors. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, e15–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L. Quercetin Attenuates Toosendanin-Induced Hepatotoxicity through Inducing the Nrf2/GCL/GSH Antioxidant Signaling Pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ji, C.; Tong, W.; Lian, X.; Wu, Y.; Fan, X.; Gao, Y. Integrated Analysis of microRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles Highlights the Complex and Dynamic Behavior of Toosendanin-Induced Liver Injury in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thant, M.T.; Bhummaphan, N.; Wuttiin, J.; Puttipanyalears, C.; Chaichompoo, W.; Rojsitthisak, P.; Punpreuk, Y.; Böttcher, C.; Likhitwitayawuid, K.; Sritularak, B. New Phenolic Glycosides from Coelogyne fuscescens Lindl. Var. brunnea and Their Cytotoxicity against Human Breast Cancer Cells. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7679–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarti, B.; Maurya, R.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Bid, H.K.; Rajendran, S.M.; Yadav, P.P.; Konwar, R. In Vitro Anti-Breast Cancer Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Wrightia Tomentosa: Role of pro-Apoptotic Effects of Oleanolic Acid and Urosolic Acid. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 142, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.-L.; Ma, G.-X.; Yang, E.-L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Sun, Z.-C.; Liang, H.-Q.; Xu, X.-D.; Wei, J.-H. Cadinane-Type Sesquiterpenoid Dimeric Diastereomers Hibisceusones A-C from Infected Stems of Hibiscus Tiliaceus with Cytotoxic Activity against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 127, 105982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Xia, T.-S.; Shi, L.; Xu, L.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, Q. D Rhamnose β-Hederin Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Human Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231. Biochem. Biophys. Res. 2018, 495, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.; Li, R.-J.; Cheng, M.-S.; Kim, Y.S. Alantolactone Selectively Suppresses STAT3 Activation and Exhibits Potent Anticancer Activity in MDA-MB-231 Cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 357, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.; Song, K.; Kim, Y.S. Sesquiterpene Lactones-enriched Fraction of Inula helenium L. Induces Apoptosis through Inhibition of Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription 3 Signaling Pathway in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2501–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güney Eskiler, G.; Deveci Özkan, A.; Kaleli, S.; Bilir, C. Inhibition of TLR4/TRIF/IRF3 Signaling Pathway by Curcumin in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 22, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.; Ooko, E.; Efferth, T. Collateral Sensitivity of Parthenolide via NF-κB and HIF-α Inhibition and Epigenetic Changes in Drug-Resistant Cancer Cell Lines. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; Yue, G.G.-L.; Lee, J.K.-M.; Puno, P.T.; Lau, C.B.-S. Natural Product Eriocalyxin B Suppressed Triple Negative Breast Cancer Metastasis Both in Vitro and in Vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 210, 115491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Ko, H.; Song, K.; Kim, Y. A Sesquiterpenoid from Farfarae Flos Induces Apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells through Inhibition of JAK–STAT3 Signaling. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.-Y.; Yan, Z.; Kang, J.; Chen, R.-Y.; Yu, D.-Q. Three New Triterpenoids from Ganoderma theaecolum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 19, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Yoon, J.; Park, B. Pomolic Acid Suppresses HIF1α/VEGF-Mediated Angiogenesis by Targeting P38-MAPK and mTOR Signaling Cascades. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, A.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Wang, C.; He, X. A Novel Triterpenoid Isolated from Apple Functions as an Anti-Mammary Tumor Agent via a Mitochondrial and Caspase-Independent Apoptosis Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, S.; Sudhagar, S.; Vidhya Priya, M.; Bharathi Raja, R.; Muthusamy, V.S.; Niranjali Devaraj, S.; Lakshmi, B.S. 3β-Hydroxylup-20(29)-Ene-27,28-Dioic Acid Dimethyl Ester, a Novel Natural Product from Plumbago Zeylanica Inhibits the Proliferation and Migration of MDA-MB-231 Cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2010, 188, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Lee, B.-M.; Kim, O.; Tran, H.N.K.; Lee, S.; Hwangbo, C.; Min, B.-S.; Lee, J.-H. Triterpenoids from Ziziphus jujuba Induce Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Cancer Cells through Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species Production. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3895–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-C.; Yen, J.-H.; Sung, Y.-W.; Tung, S.-L.; Chen, P.-M.; Chu, P.-Y.; Shih, Y.-C.; Chi, H.-C.; Huang, Y.-C.; Huang, S.-J.; et al. Novel Function of THEMIS2 in the Enhancement of Cancer Stemness and Chemoresistance by Releasing PTP1B from MET. Oncogene 2022, 41, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.-H.; Huang, W.-C.; Lin, S.-C.; Huang, Y.-W.; Chio, W.-T.; Tsay, G.J.; Hung, M.-C.; Huang, S.-T. Metabolic Remodeling in Tumor-Associated Macrophages Contributing to Antitumor Activity of Cryptotanshinone by Regulating TRAF6-ASK1 Axis. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2022, 26, 158–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Min, L.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Li, Z. Suppression of Migration and Invasion by Taraxerol in the Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231 via the ERK/Slug Axis. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0291693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, A.; Umar, S.; Dev J R, A.; Prasad, C. Dihydrotanshinone-I Modulates Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Thereby Impairing Migration and Clonogenicity of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumsuwan, P.; Khan, S.I.; Khan, I.A.; Ali, Z.; Avula, B.; Walker, L.A.; Shariat-Madar, Z.; Helferich, W.G.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Dasmahapatra, A.K. The Anticancer Potential of Steroidal Saponin, Dioscin, Isolated from Wild Yam (Dioscorea villosa) Root Extract in Invasive Human Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231 In Vitro. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 591, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christodoulou, P.; Boutsikos, P.; Neophytou, C.M.; Kyriakou, T.-C.; Christodoulou, M.-I.; Papageorgis, P.; Stephanou, A.; Patrikios, I. Amygdalin as a Chemoprotective Agent in Co-Treatment with Cisplatin. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1013692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, G.; Zhu, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J. Diosgenin Inhibits the Migration of Human Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells by Suppressing Vav2 Activity. Phytomedicine 2014, 21, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.V.; Hoang, H.N.T.; Vo, H.Q.; Nguyen, K.V.; Pham, T.V.; Le, A.T.; Van Phan, K.; Nguyen, H.M.; Morita, H.; Nguyen, H.T. Three New Steroidal Saponins from Aspidistra letreae Plants and Their Cytotoxic Activities. J. Nat. Med. 2020, 74, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, D.; Kwak, J.Y.; Park, E.H.; Kim, K.H.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, H.Y.; Jang, H.J.; Ham, J.; et al. Inhibitory Effects of Ginseng sapogenins on the Proliferation of Triple Negative Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5409–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, P.J.; Cai, S.; Carver, C.; Powell, D.R.; Risinger, A.L.; Grkovic, T.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Mooberry, S.L.; Cichewicz, R.H. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Exhibit Differential Sensitivity to Cardenolides from Calotropis gigantea. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2269–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Y.; Han, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, J.; Ma, W.; Zhou, D.; Li, X.; et al. Anti-Breast-Cancer Activity Exerted by β-Sitosterol-d-Glucoside from Sweet Potato via Upregulation of MicroRNA-10a and via the PI3K–Akt Signaling Pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9704–9718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, D.; Lin, D. Plantamajoside, a Potential Anti-Tumor Herbal Medicine Inhibits Breast Cancer Growth and Pulmonary Metastasis by Decreasing the Activity of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and -2. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Li, M.; Han, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X. Gypensapogenin I Suppresses Cell Proliferation in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Via Triggering the Closure of AKT/GSK3β/β-Catenin and Notch-1 Signaling Pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 5438–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fu, X.; Guan, Y.; Gong, M.; He, K.; Huang, B. 1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid Targeting 14-3-3 Tau Suppresses Human Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis through IL6/JAK2/PI3K Pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 172, 113752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Su, J.-C.; Lei, X.-P.; Huang, X.-J.; Zhang, D.-M.; Ye, W.-C.; Wang, Y. Acylphloroglucinol Derivatives from the Leaves of Syzygium samarangense and Their Cytotoxic Activities. Fitoterapia 2018, 129, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunilkumar, D.; Drishya, G.; Chandrasekharan, A.; Shaji, S.K.; Bose, C.; Jossart, J.; Perry, J.J.P.; Mishra, N.; Kumar, G.B.; Nair, B.G. Oxyresveratrol Drives Caspase-Independent Apoptosis-like Cell Death in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells through the Induction of ROS. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 173, 113724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.-P.; Chen, A.-L.; Hung, H.-C.; Chien, Y.-H.; Huang, J.-S.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-W.; Chen, C.-N. Chrysin: A Histone Deacetylase 8 Inhibitor with Anticancer Activity and a Suitable Candidate for the Standardization of Chinese Propolis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11748–11758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.H.; Sharma, G.; Dao, T.T.; Uddin, M.N.; Kang, K.W.; Ndinteh, D.T.; Mbafor, J.T.; Oh, W.K. New Prenylated Isoflavonoids as Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) Inhibitors from Erythrina addisoniae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2012, 20, 6459–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Lu, W.-J.; Li, N.-P.; Liu, J.-W.; He, J.; Ye, W.-C.; Wang, L. Four New Cinnamoyl-Phloroglucinols from the Leaves of Xanthostemon chrysanthus. Fitoterapia 2018, 128, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-F.; Pan, M.-H.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Cheng, A.-C.; Huang, H. Resveratrol Modulates MED28 (Magicin/EG-1) Expression and Inhibits Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-Induced Migration in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11853–11861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Hong, S.; Yoo, S.-H.; Kim, G.-W. Cyanidin-3-O-Sambubioside from Acanthopanax Sessiliflorus Fruit Inhibits Metastasis by Downregulating MMP-9 in Breast Cancer Cells MDA-MB-231. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Combinational Proanthocyanidins and Resveratrol Synergistically Inhibit Human Breast Cancer Cells and Impact Epigenetic–Mediating Machinery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gaafary, M.; Saber, F.R.; Mahrous, E.A.; Ashour, R.M.; Okba, M.M.; Jin, L.; Lang, S.J.; Schmiech, M.; Simmet, T.; Syrovets, T. The Phloroglucinol Calcitrinone A, a Novel Mitochondria-Targeting Agent, Induces Cell Death in Breast Cancer Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 162, 112896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Alam, M.B.; Quan, K.T.; Choi, H.-J.; An, H.; Ju, M.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Huh, Y.S.; Han, Y.-K.; Na, M. Cytotoxic Properties of the Anthraquinone Derivatives Isolated from the Roots of Rubia philippinensis. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunasree, K.M. Anti-Proliferative Effects of Carvacrol on a Human Metastatic Breast Cancer Cell Line, MDA-MB 231. Phytomedicine 2010, 17, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, I.; Smimmo, M.; d’Emmanuele Di Villa Bianca, R.; Bucci, M.; Cirino, G.; Panza, E.; Brancaleone, V. Erucin, an H2S-Releasing Isothiocyanate, Exerts Anticancer Effects in Human Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells Triggering Autophagy-Dependent Apoptotic Cell Death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.-R.; Yen, C.-T.; El-Shazly, M.; Yu, C.-Y.; Yen, M.-H.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Chen, S.-L.; Wu, Y.-C. Spirostanoids with 1,4-Dien-3-One or 3β,7α-Diol-5,6-Ene Moieties from Solanum violaceum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2738–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Ding, Y.; Du, W.W.; Sdiri, M.; Yang, B.B. Ergosterol Purified from Medicinal Mushroom Amauroderma rude Inhibits Cancer Growth in vitro and in vivo by up-Regulating Multiple Tumor Suppressors. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17832–17846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.-J.; Shiau, J.-P.; Tang, J.-Y.; Farooqi, A.A.; Cheng, Y.-B.; Hou, M.-F.; Yen, C.-H.; Chang, H.-W. Physapruin A Exerts Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress to Trigger Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis via Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-C.; Hu, H.-H.; Chang, F.-R.; Tsai, J.-Y.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-C. Different Effects of 4β-Hydroxywithanolide E and Withaferin A, Two Withanolides from Solanaceae Plants, on the Akt Signaling Pathway in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Phytomedicine 2019, 53, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, K.; Li, C.; Li, M.-X.; Song, Z.-R.; Ma, X.-X.; Sun, D.-J.; Li, H.; Chen, L.-X. Withanolides Isolated from Tubocapsicum Anomalum and Their Antiproliferative Activity. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 110, 104809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, K.; De, S.; Das, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Sengupta Bandyopadhyay, S. Withaferin A Induces ROS-Mediated Paraptosis in Human Breast Cancer Cell-Lines MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.E.; Mizuno, N.K.; Schuster, T.; Cleary, M.P. Punicic Acid Is an Omega-5 Fatty Acid Capable of Inhibiting Breast Cancer Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 36, 421–426. [Google Scholar]
- Guzmán, E.A.; Pitts, T.P.; Winder, P.L.; Wright, A.E. The Marine Natural Product Furospinulosin 1 Induces Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cell Spheroids, But Not in Cells Grown Traditionally with Longer Treatment. Mar Drugs. 2021, 19, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaw-on, P.; Pompimon, W.; Banjerdpongchai, R. Goniothalamin Induces Necroptosis and Anoikis in Human Invasive Breast Cancer MDA-MB-231 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, C.; Ma, J.; Wang, K.S.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.Y.; Li, J.B.; Li, X.; Piao, L.X.; Xu, G.H.; Jin, X. Amorfrutin A Inhibits TNF-α Induced JAK/STAT Signaling, Cell Survival and Proliferation of Human Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 39, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Ye, Z.; Wang, G.; Chen, Y.; Deng, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y. Natural Products as Novel Therapeutic Agents for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Evidence, Mechanisms, Challenges, and Opportunities. Molecules 2025, 30, 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061201
Li Q, Ye Z, Wang G, Chen Y, Deng J, Wang D, Wang Y. Natural Products as Novel Therapeutic Agents for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Evidence, Mechanisms, Challenges, and Opportunities. Molecules. 2025; 30(6):1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061201
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qingzhou, Zhen Ye, Guilin Wang, Yuhui Chen, Jinghong Deng, Dong Wang, and Yumei Wang. 2025. "Natural Products as Novel Therapeutic Agents for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Evidence, Mechanisms, Challenges, and Opportunities" Molecules 30, no. 6: 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061201
APA StyleLi, Q., Ye, Z., Wang, G., Chen, Y., Deng, J., Wang, D., & Wang, Y. (2025). Natural Products as Novel Therapeutic Agents for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Current Evidence, Mechanisms, Challenges, and Opportunities. Molecules, 30(6), 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061201







