Borylated 5-Membered Ring Iminosugars: Detailed Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Characterisation, and Method for Analysis of Anomeric and Boron Equilibria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. 11B-NMR Data Analysis
2.1.1. Analysis and Comparison of Pinacol Boronates ortho 2, meta 2 and para 6 (Figure 1A)
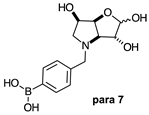
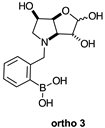
2.1.2. Analysis and Comparison of Lactols ortho 3, meta 3 and para 7 (Figure 1B)
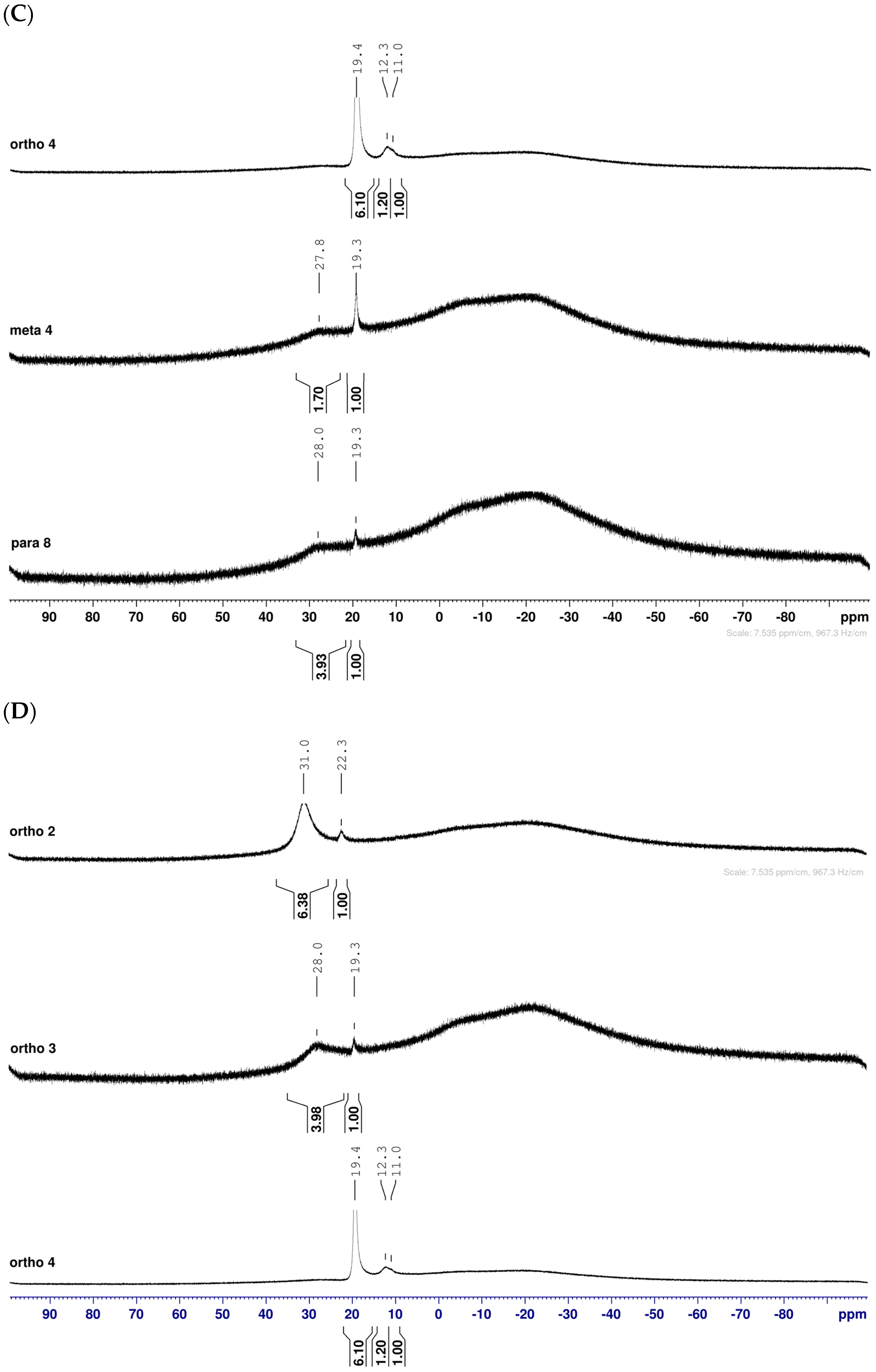
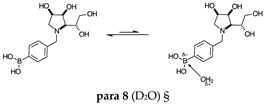
2.1.3. Analysis and Comparison of Final Iminosugars ortho 4, meta 4 and para 8 (Figure 1C)
2.1.4. Analysis of the Signal Integration Ratios
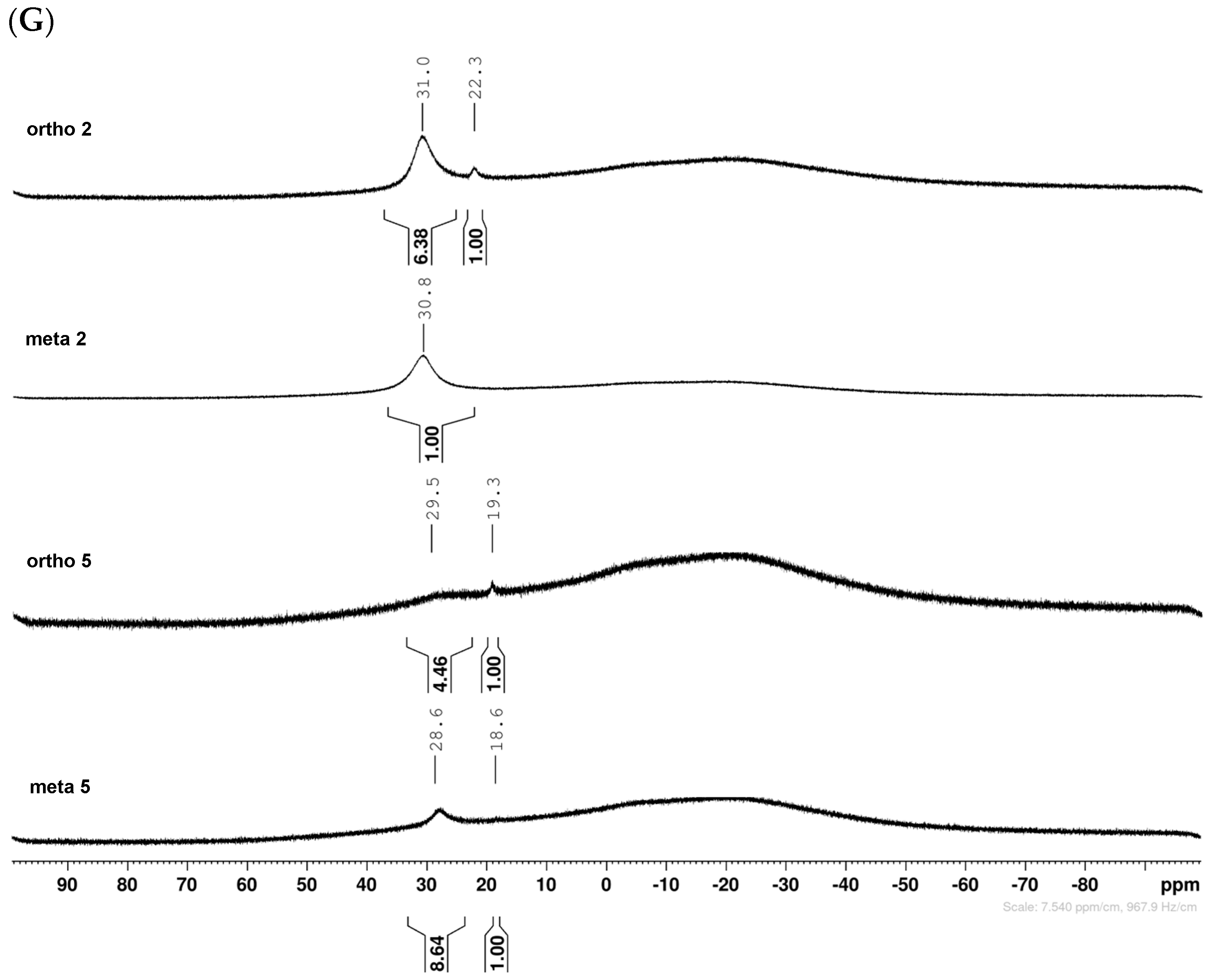
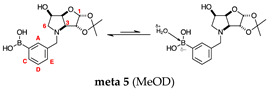
2.1.5. Boronic Acid Species ortho 5 and meta 5 (Figure 1G)
2.2. 1H-, 13C- and 2D NMR Data Analysis
2.2.1. N-(3-Methylphenyl boronic acid)-3,6-dideoxy-3,6-imino-d-gulofuranose meta 3 (Figures S2–S4)
2.2.2. N-(3-Methylphenyl boronic acid)-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-gulitol meta 4 (Figure S5)
2.2.3. N-(2-Methylphenyl boronic acid)-3,6-dideoxy-3,6-imino-d-gulofuranose ortho 3 (Figures S7–S9)
2.2.4. N-(2-Methylphenyl boronic acid)-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-gulitol ortho 4 (Figures S10–S12)
2.2.5. N-(3-Methylphenyl boronic acid)-3,6-dideoxy-3,6-imino-1,2-O-isopropylidene-α-d-glucofuranose meta 5 (Figures S13–S17)
2.2.6. N-(2-Methylphenyl boronic acid)-3,6-dideoxy-3,6-imino-1,2-O-isopropylidene-α-d-gulofuranose ortho 5 (Figures S18–S20)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Numbering System
3.2. General Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Experimental
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Campkin, D.M.; Shimadate, Y.; Bartholomew, B.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Nash, R.J.; Sakoff, J.A.; Kato, A.; Simone, M. Borylated 2,3,4,5-Tetrachlorophthalimide and Their 2,3,4,5-Tetrachlorobenzamide Analogues: Synthesis, Their Glycosidase Inhibition and Anticancer Properties in View to Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Molecules 2022, 27, 3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legge, W.J.; Shimadate, Y.; Sakoff, J.; Houston, T.A.; Kato, A.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Simone, M. Borylated methyl cinnamates: Green synthesis, characterization, crystallographic analysis and biological activities—In glycosidase inhibition and in cancer cells lines. Beilstein Arch. 2021, 20214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, M. Diastereoselective Synthesis of the Borylated d-Galactose Monosaccharide 3-Boronic-3-Deoxy-d-Galactose and Biological Evaluation in Glycosidase Inhibition and in Cancer for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT). Molecules 2023, 28, 4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, M. Borylated Monosaccharide 3-Boronic-3-deoxy-d-galactose: Detailed NMR Spectroscopic Characterisation, and Method for Spectroscopic Analysis of Anomeric and Boron Equilibria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Hosmane, N.S.; Zhu, Y. Nanostructured boron agents for boron neutron capture therapy: A review of recent patents. Med. Rev. 2023, 3, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Igawa, K.; Kasai, T.; Sadahira, T.; Wang, W.; Watanabe, T.; Bekku, K.; Katayama, S.; Iwata, T.; Hanafusa, T.; et al. The current status and novel advances of boron neutron capture therapy clinical trials. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2024, 14, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency. Advances in Boron Neutron Capture Therapy; International Atomic Energy Agency: Vienna, Austria, 2023; ISBN 978-92-0-132723-9/978-92-0-132623-2. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, L.; Li, Y. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Current Status and Challenges. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 788770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verlinden, B.; Hoecke, K.V.; Aerts, A.; Daems, N.; Dobney, A.; Janssens, K.; Cardinaels, T. Quantification of boron in cells for evaluation of drug agents used in boron neutron capture therapy. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2021, 36, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, C.; Rudhra, O.; Alothaim, A.S.; Alkhanani, M.; Singh, S.K. Structure and chemistry of enzymatic active sites that play a role in the switch and conformation mechanism. Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol. 2022, 130, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, N.; Nash, R.J.; Molyneux, R.J.; Fleet, G.W.J. Sugar-mimic glycosidase inhibitors: Natural occurrence, biological activity and prospects for therapeutic application. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2000, 11, 1645–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-K.; Hao, H.; Bian, Y.; Ge, Y.-X.; Lu, S.; Xie, H.-X.; Wang, K.-M.; Tao, H.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Discovery of New α-Glucosidase Inhibitors: Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Biological Evaluation. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 639279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Li, H.; Choi, J.; Boo, J.; Jo, H.; Hyun, J.Y.; Shin, I. Glycosidase-targeting small molecules for biological and therapeutic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 7036–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.-T.; Shimadate, Y.; Cheng, B.; Kanekiyo, U.; Kato, A.; Wang, J.-Z.; Li, Y.-X.; Jia, Y.-M.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Yu, C.-Y. Synthesis and glycosidase inhibition of 5-C-alkyl-DNJ and 5-C-alkyl-l-ido-DNJ derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 224, 113716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Désiré, J.; Debbah, Z.; Gueyrard, D.; Marrot, J.; Blériot, Y.; Kato, A. Evaluation of non-natural l-iminosugar C,C-glycosides, a new class of C-branched iminosugars, as glycosidase inhibitors. Carbohydr. Res. 2023, 532, 108903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferjancic, Z.; Bihelovic, F.; Vulovic, B.; Matovic, R.; Trmcic, M.; Jankovic, A.; Pavlovic, M.; Djurkovic, F.; Prodanovic, R.; Djelmas, A.D.; et al. Development of iminosugar-based glycosidase inhibitors as drug candidates for SARS-CoV-2 virus via molecular modelling and in vitro studies. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2024, 39, 2289007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güzel, E.; Koçyiğit, Ü.M.; Taslimi, P.; Erkan, S.; Taskin, O.S. Biologically active phthalocyanine metal complexes: Preparation, evaluation of α-glycosidase and anticholinesterase enzyme inhibition activities, and molecular docking studies. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevimli, E.; Seyhan, G.; Akkaya, D.; Sarı, S.; Barut, B.; Köksoy, B. Effective α-glycosidase inhibitors based on polyphenolic benzothiazole heterocycles. Bioorg. Chem. 2024, 147, 107366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseynova, A.; Kaya, R.; Taslimi, P.; Farzaliyev, V.; Mammadyarova, X.; Sujayev, A.; Tüzün, B.; Kocyigit, U.M.; Alwasel, S.; Gulçin, İ. Design, synthesis, characterization, biological evaluation, and molecular docking studies of novel 1,2-aminopropanthiols substituted derivatives as selective carbonic anhydrase, acetylcholinesterase and α-glycosidase enzymes inhibitors. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 40, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenister, A.; Chen, C.K.J.; Renfrew, A.K.; Simone, M.; Hambley, T.W. Warburg Effect Targeting Cobalt(III) Cytotoxin Chaperone Complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 2678–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenister, A.; Simone, M.; Hambley, T.W. A Warburg effect targeting vector designed to increase the uptake of compounds by cancer cells demonstrates glucose and hypoxia dependent uptake. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.L.; Houston, T.A. A drug targeting motif for glycosidase inhibitors: An iminosugar–boronate shows unexpectedly selective β-galactosidase inhibition. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 8905–8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, P.M.; Ferrier, R.J. Monosaccharides: Their Chemistry and Their Roles in Natural Products; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1995; ISBN 978-0-471-95343-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ksenofontov, A.A.; Isaev, Y.I.; Lukanov, M.M.; Makarov, D.M.; Eventova, V.A.; Khodov, I.A.; Berezin, M.B. Accurate prediction of 11B NMR chemical shift of BODIPYs via machine learning. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2023, 25, 9472–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Cao, P.; Wang, Y.; Xie, F.; Ma, J.; Yu, M.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, J. A Review of Approaches for Predicting Drug–Drug Interactions Based on Machine Learning. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 814858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Zhang, K. A machine learning framework for predicting drug–drug interactions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.N.; Wang, X.G.; Xiong, G.L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Lu, A.P.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.; Hou, T.J.; Cao, D.S. Machine learning to predict metabolic drug interactions related to cytochrome P450 isozymes. J. Cheminform. 2022, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angyal, S.J. The composition of reducing sugars in solution. Adv. Carbohydr. Chem. Biochem. 1984, 42, 15–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imperio, D.; Panza, L. Sweet Boron: Boron-Containing Sugar Derivatives as Potential Agents for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy. Symmetry 2022, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, S.F.; Thompson, A.L.; Simone, M. Methyl 2-(5,5-dimethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborinan-2-yl)-4-nitrobenzoate. Acta Cryst. 2012, E68, o2699–o2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Király, P. Background-free solution boron NMR spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2012, 50, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöth, H. Chapter 7: 11B NMR of Tetracoordinate Boron. 7.1. Metal Tetrahydroborates. In Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy of Boron Compounds; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1978; pp. 74–101. ISBN 0387084568/3540084568. [Google Scholar]
- Wrackmeyer, B. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of boron compounds containing two-, three- and four-coordinate boron. Annu. Rep. NMR Spectrosc. 1988, 20, 61–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ColeResearchGroup. 11B NMR Chemical Shifts. Available online: https://www.chemistry.sdsu.edu/research/BNMR/ (accessed on 17 January 2025).
- Lewinski, J.; Kubicki, D. NMR Spectroscopy, Heteronuclei, B, Al, Ga, In, Tl. In Encyclopedia of Spectroscopy and Spectrometry, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 318–329. ISBN 0128032251/9780128032251. [Google Scholar]
- Boron Molecular. A Fine Chemicals Manufacturer. Available online: https://www.boronmolecular.com (accessed on 20 January 2020).
- Sigma-Aldrich. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/AU/en/product/aldrich/dwk231700006?srsltid=AfmBOooBqu8eAIi5jtc28sWdih3PbRDScnsOaxbYMVB8PVNLSPe6lWxm (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Corning. Available online: https://ecatalog.corning.com/life-sciences/b2c/US/en/General-Labware/Tubes/Tubes-Storage/PYREX®-Tube%2C-NMR%2C-5-mm-Diameter/p/pyrexTubeNMR5mmDiameter (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Bruker. Available online: https://www.bruker.com/en/products-and-solutions/mr/nmr/nmr-probes.html (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Hoang, C.T.; Prokes, I.; Clarkson, G.J.; Rowland, M.J.; Tucker, J.H.R.; Shipman, M.; Walsh, T.R. Study of boron–nitrogen dative bonds using azetidine inversion dynamics. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2509–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonio, J.P.M.; Farias, G.D.V.; Santos, F.M.F.; Oliveira, R.; Cal, P.M.S.D.; Gois, P.M.P. Non-Covalent Interactions in the Synthesis and Design of New Compounds. Chapter 2. Boron-Nitrogen Bond. Non-Covalent Interactions in the Synthesis and Design of New Compounds; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 23–48. [Google Scholar]
- Murruzzu, C.; Riera, A. Enantioselective synthesis of hydroxylated pyrrolidines via Sharpless epoxidation and olefin metathesis. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2007, 18, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.G.; Foster, E.M.; Lee, J.A.; Roberts, P.M.; Thomson, J.E. Stereospecific Cyclization Strategies for α,ε-Dihydroxy-β-amino Esters: Asymmetric Syntheses of Imino and Amino Sugars. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 79, 9686–9698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, J.G.; Lumbard, K.W.; Sturgeon, R.J.; Thompson, D.K.; Wightman, R.H. Potential glycosidase inhibitors: Synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino derivatives of d-glucitol, d- and l-xylitol, d- and l-allitol, d- and l-talitol, and d-gulitol. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1 1990, 3, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, B.; Madhan, A.; Rao, B.V. Synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-derivatives of d-allitol, l-allitol and d-talitol: A stereoselective approach for azasugars. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 8746–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, G.W.J.; Son, J.C. Polyhydroxylated pyrrolidines from sugar lactomes: Synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-glucitol from d-galactonolactone and syntheses of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-allitol, 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-ribitol, and (2s,3r,4s)-3,4-dihydroxyproline from d-gulonolactone. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 2637–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundt, I.; Madsen, R. Deoxyiminoalditols from Aldonolactones; I. Preparation of 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-iminohexitols with d- and l-Allo and d- and l-Talo Configuration: Potential Glycosidase Inhibitors. Synthesis 1993, 1993, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bande, O.P.; Jadhav, V.H.; Puranik, V.G.; Dhavale, D.D.; Lombardo, M. Stereo-controlled approach to pyrrolidine iminosugar C-glycosides and 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-allitol using a d-mannose-derived cyclic nitrone. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 6906–6908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelis, M.D.; Primitivo, L.; Lucarini, C.; Agostinelli, S.; Sappino, C.; Ricellia, A.; Righi, G. Stereocontrolled total synthesis of iminosugar 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-iditol. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 492, 108028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, G.; Mandic, E.; Sappino, C.; Dema, E.; Bovicelli, P. Asymmetric routes toward polyhydroxylated pyrrolidines: Synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-galactitol and 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-glucitol. Carbohydr. Res. 2016, 435, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, M.; Fabbroni, S.; Trombini, C. Entropy-Controlled Selectivity in the Vinylation of a Cyclic Chiral Nitrone. An Efficient Route to Enantiopure Polyhydroxylated Pyrrolidines. J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 1264–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.E.; Smith, M.D.; Nash, R.J.; Griffiths, R.C.; McNeil, M.; Grewal, R.K.; Yan, W.; Besra, G.S.; Brennan, P.J.; Fleet, G.J.W. Inhibition of UDP-gal mutase and myco- bacterial galactan biosynthesis by pyrrolidine analogues of galactofuranose. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 6733–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Hou, L.; Meng, A.; Han, G.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, S. Design, synthesis and bioactivity evaluation of Galf mimics as antitubercular agents. Carbohydr. Res. 2016, 429, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernotas, R.C. A short, versatile approach to polyhydroxylated pyrrolidines utilizing a reductive elimination-reductive amination as a key step. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundt, I.; Madsen, R. Deoxyiminoalditols from Aldonolactones; II. Preparation of 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-iminohexitols with d- and l-Galacto and d- and l-Ido Configuration: Potential Glycosidase Inhibitors. Synthesis 1993, 1993, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, P.S.; Santhoshi, A.; Rao, V.J. Total Synthesis of Azasugar 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-galactitol. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2012, 33, 3554–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guazzelli, L.; D’Andrea, F.; Sartini, S.; Giorgelli, F.; Confini, G.; Quattrini, L.; Piano, I.; Gargini, C.; Motta, C.L. Synthesis and investigation of polyhydroxylated pyrrolidine derivatives as novel chemotypes showing dual activity as glucosidase and aldose reductase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 92, 103298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, T.; Génisson, Y.; Broussy, S.; Baltas, M.; Gorrichon, L. A Flexible Route Towards Five-Membered Ring Imino Sugars and Their Novel 2-Deoxy-2-fluoro Analogues. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 2003, 2903–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundt, I.; Madsen, R.; Daher, S.A.; Winchester, B. Deoxyiminoalditols from Aldonolactones. III. Preparation of 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-gulitol. Evaluation of 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-iminohexitols as Glycosidase Inhibitors. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 7513–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, G.N.; Baird, P.D.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Peach, J.M.; Smith, P.W.; Watkin, D.J. 3,6-Dideoxy-3,6-imino-1,2-O-isopropylidene-α-d-glucofuranose intermediate for the synthesis of hydroxylated pyrrolidines: Synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-gulitol, 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-lyxitol, 2S,3S,4R-3,4-dihydroxyproline and (1S,2R,8S,RaR)-1,2,8-trihydroxyoctahydroindolizine [8-epi-swainsonine]. X-ray crystal structure of (1S,2R,8S,8aR)-1,2,8-trihydroxy-5-oxo-octahydroindolizine. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 3095–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.-F.; Shimadate, Y.; Kato, A.; Li, Y.-X.; Jia, Y.-M.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Yu, C.-Y. Synthesis and glycosidase inhibition of N-substituted derivatives of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-mannitol (DIM). Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashyal, B.P.; Fleet, G.W.J.; Gough, M.J.; Smith, P.W. Synthesis of the α-mannosidase inhibitors swainsonine [(1S,2R,8R,8aR)-1,2,8-trihydroxyoctahydroindolizine] and 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-mannitol from mannose. Tetrahedron 1987, 43, 3083–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setoi, H.; Kayakiri, H.; Takeno, H.; Hashimoto, M. Synthesis of Some Polyhydroxylated Pyrrolidine Derivatives. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 3995–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkansson, A.E.; Ameijde, J.v.; Guglielmini, L.; Horne, G.; Nash, R.J.; Evinson, E.L.; Kato, A.; Fleet, G.W.J. Looking glass inhibitors: Synthesis of a potent naringinase inhibitor l-DIM [1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-mannitol], the enantiomer of DIM [1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-mannitol] a potent a-d-mannosidase inhibitor. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2007, 18, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleet, G.W.J.; Son, J.C.; Green, D.S.C.; Bello, I.C.d.; Wlnchester, B. Synthesis from d-mannose of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-ribitol and of the a-mannosidase inhibitor 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-talitol. Tetrahedron 1988, 44, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhan, A.; Rao, B.V. Stereoselective synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-allitol and formal synthesis of (2S,3R,4S)-3,4-dihydroxyproline. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 5641–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, S.A.; Fleet, G.; Namgoong, S.K.; Winchester, B. Change in specificity of glycosidase inhibition by N-alkylation of amino sugars. Biochem. J. 1989, 258, 613–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulsen, H.; Steinert, K.; Heyns, K. Monosaccharide mit stickstoffhaltigem Ring, XXVI. Darstellung freier 4-Amino-4-desoxy-d-glucose und 4-Amino-4-desoxy-d-galaktose. Dimerisierung zu Bis-Pyrrolidin-Zuckern. Chem. Berichte 1970, 103, 1599–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuszmann, J.; Kiss, L. Synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-glucitol, a glucosidase inhibitor. Carbohydr. Res. 1986, 153, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, N.M.; FIeet, G.W.J.; Bello, I.C.d.; Winchester, B.; Fellows, L.E.; Nash, R.J. Synthesis of the mannosidase inhibitors swainsonine and 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-mannitol and of the ring contracted swaisonines, (1S, 2R, 7R, 7aR)-1,2,7-trihydroxypyrrolizidine and (1S, 2R, 7S, 7aR)-12,7-trihydroxypyrrolizidine. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 7261–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badorrey, R.; Cativiela, C.; íaz-de-Villegas, M.D.D.; Díez, R.; Gálvez, J.A. Efficient stereodivergent synthesis of 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-iminohexitols from an (S)-glyceraldimine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.-J.; Sardina, F.J. Enantiospecific and Stereoselective Synthesis of Polyhydroxylated Pyrrolidines and Indolizidines from trans-4-Hydroxy-l-proline. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 4748–4755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieß, F.-M.; Poggendorf, P.; Picasso, S.; Jäger, V. Synthesis of iminopolyols via Henry reaction: A short route to the a-manno- sidase inhibitor 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-mannitol and to amino analogues. Chem. Commun. 1998, 119–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNaught, A.D. IUPAC and IUBMB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature; Nomenclature of Carbohydrates. Pure Appl. Chem. 1996, 68, 1919–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruker. Available online: https://store.bruker.com/products/copy-of-archived-2021-06-99-5-acetic-acid-d4 (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Gottlieb, H.E.; Kotlyar, V.; Nudelman, A. NMR Chemical Shifts of Common Laboratory Solvents as Trace Impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Intermediates |  |  |  |
 |  |  | |
| Target Compounds | 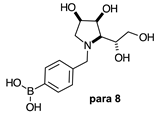 | 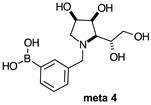 | 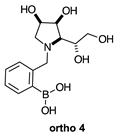 |
| Side-Products |  | 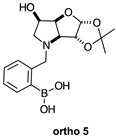 |
| Compound (Deuterated Solvent) | Chemical Shifts | Compound (Deuterated Solvent) | Chemical Shifts | Compound (Deuterated Solvent) | Chemical Shifts | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal Integration Ratio | Signal Integration Ratio | Signal Integration Ratio | |||||||
| Signal Shape | Signal Shape | Signal Shape | |||||||
| Geometry | Geometry | Geometry | |||||||
 | 30.6 | 22.3 | 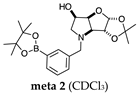 | 30.8 | 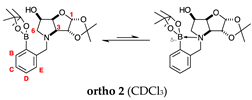 | 31.0 | 22.3 | ||
| 3.7 | 1.0 | NA | 6.4 | 1.0 | |||||
| broad | sharp | Broad | sharp | sharp | |||||
| Boronate ester (trigonal planar) | Boronate ester (partially tetrahedral) | Boronate ester (trigonal planar) | Boronate ester (trigonal planar) | Boronate ammonium (partially tetrahedral) | |||||
 | 28.7 | 19.4 | 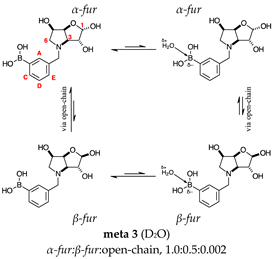 | 28.6 | 19.2 | 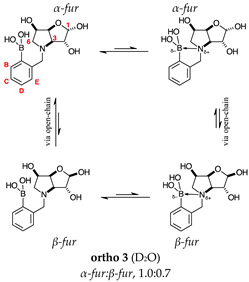 | 28.0 | 19.3 | |
| 9.3 | 1.0 | 6.5 | 1.0 | 4.0 | 1.0 | ||||
| broad | sharp | broad | sharp | broad | sharp | ||||
| Boronic acid (trigonal planar) | Boronate (partially tetrahedral) | Boronic acid (trigonal planar) | Boronate (partially tetrahedral) | Boronic acid (trigonal planar) | Boronate (partially tetrahedral) | ||||
 | 28.0 | 19.3 | 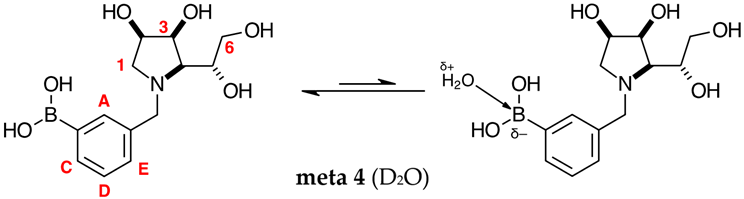 | 27.8 | 19.3 | 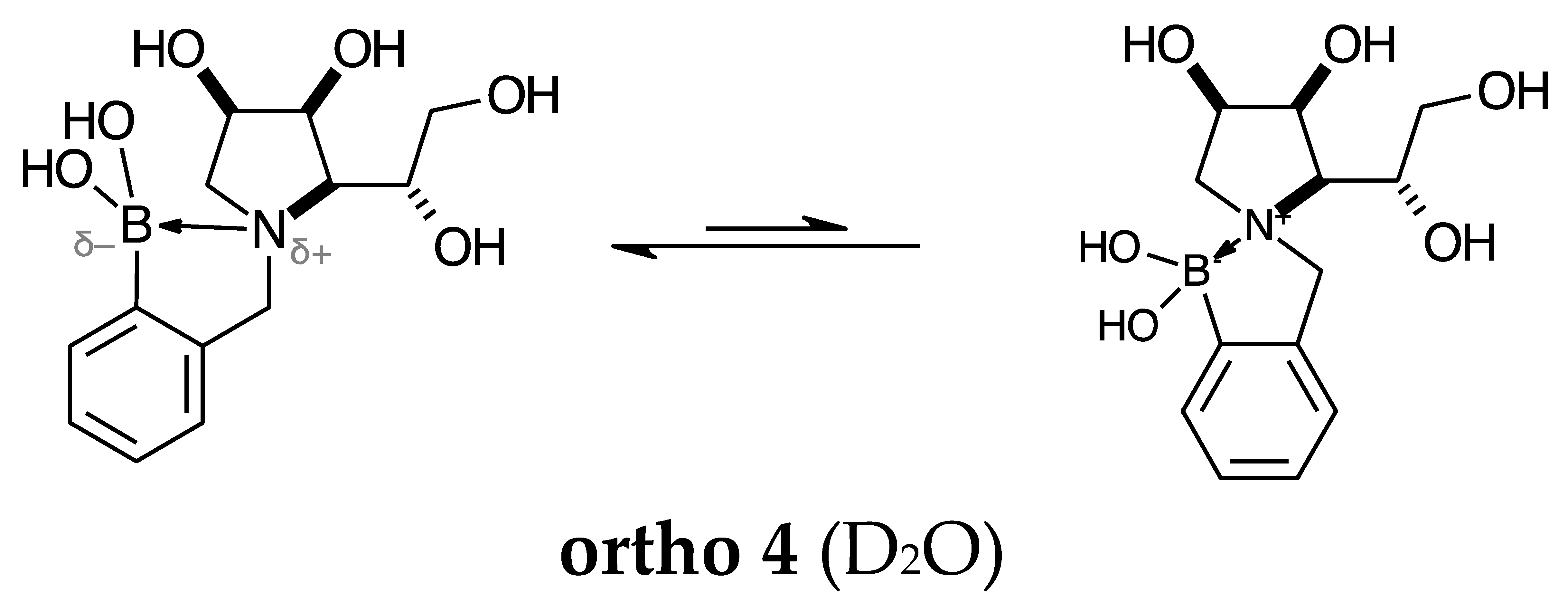 | 28.3 | 19.4 | 12.3, 11.0 |
| 3.9 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 1.0 | 1.1 | 6.1 | 1.2, 1.0 | |||
| broad | sharp | broad | sharp | broad | sharp | Sharp and merging | |||
| Boronic acid (trigonal planar) | Boronate (partially tetrahedral) | Boronic acid (trigonal planar) | Boronate (partially tetrahedral) | Boronic acid (trigonal planar) | Boronate ammonium (partially tetrahedral) | Boronate ammonium (tetrahedral) | |||
 | 28.6 | 18.6 | 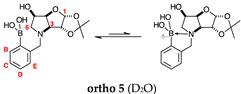 | 29.5 | 19.3 | ||||
| 8.6 | 1.0 | 4.5 | 1.0 | ||||||
| sharp | sharp | broad | sharp | ||||||
| Boronic acid (trigonal planar) | Boronate (partially tetrahedral) | Boronic acid (trigonal planar) | Boronate (partially tetrahedral) | ||||||
 | ||||||||
| Compound: 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-imino- | 1H-NMR Chemical Shifts (δ, ppm), Multiplicity, and Coupling Constants (J, Hz) for Nucleus: | |||||||
| H-1 | H-1′ | H-2 | H-3 | H-4 | H-5 | H-6 | H-6′ | |
| d-Allitol.HCl [42] # | δ 3.24, dd J 12.8, 1.6 | δ 3.33, dd J 12.8, 3.6 | δ 4.25, dd J 4.6, 2.4 | δ 4.29, dd J 2.4, 4.4 | δ 3.61, d J 4 | δ 4.01, dd J 5, 3.6 | δ 3.61, d J 4 | δ 3.55, dd J 8, 3.2 |
| [43] | δ 3.20, dd JH-1,H-1′ 12.6 JH-1,H-2 2.1 | δ 3.31, dd JH-1′,H-1 12.6 JH-1′,H-2 3.8 | δ 4.21–4.26, m | δ 4.28, dd JH-3,H-4 8.0 J 4.3 | δ 3.50, dd JH-4,H-3 8.0 J 3.6 | δ 4.00–3.96, m | δ 3.64, dd JH-6,H-6′ 11.8 JH-6,H-5 4.6 | δ 3.60, dd JH-6′,H-6 11.8 JH-6′,H-5 6.5 |
| [44] | δ 3.41, dd JH-1,H-1′ 12.8 JH-1,H-2 2.1 | δ 3.50, dd JH-1′,H-1 12.8 JH-1′,H-2 3.8 | δ 4.41, dt | δ 4.47, dd JH-3,H-2 4.2 | δ 3.73, dd JH-4,H-3 8.2 JH-4,H-5 3.5 | δ 4.18, m | δ 3.79, m, 2H | |
| [45] # | δ 3.30–3.50, m, 2H | δ 4.3–4.5, m, 2H | δ 3.60–3.80, m, 1H | δ 4.1–4.2, m, 1H | δ 3.60–3.80, m, 1H | |||
| [46] | δ 3.20, dd JH-1,H-1′ 12.8 JH-1,H-2 2.0 | δ 3.29, dd JH-1′,H-1 12.8 JH-1,H-2 3.7 | δ 4.20, dt JH-2,H-3 4.2 | δ 4.26, dd | δ 3.51, dd JH-4,H-3 8.2 JH-4,H-5 3.5 | δ 3.97, dt | δ 3.57, m, H-6, H-6′ | |
| [47] | Spectra as for enantiomer as synthesised in [47] | |||||||
| l-Allitol.HCl [48] # | δ 3.35, dd JH-1,H-1′ 12.9 JH-1,H-2 2.1 | δ 3.46, dd JH-1′,H-1 12.9 JH-1′,H-2 3.6 | δ 4.33–4.40, m | δ 4.42, dd J 8.1, 4.2 | δ 3.67, dd J 8.1, 3.3 | NA | δ 3.72–3.79, m | |
| [47] | δ 3.33, dd JH-1,H-1′ 13 JH-1,H-2 4.7 | δ 3.41, dd J H-1′,H-2 4 | δ 4.33, ddd JH-2,H-3 5 | δ 4.38, dd | δ 3.64, dd JH-4,H-3 8 JH-4,H-5 3 | δ 4.10, ddd JH-5,H-6 6 JH-5,H-6′ 5 | δ 3.69, d | δ 3.70, d |
| [44] | Spectra as for enantiomer | |||||||
| d-Altritol | NA | |||||||
| l-Altritol | NA | |||||||
| d-Galactitol.HCl [49] | δ 3.25, dd J 12.4, 3.2 | δ 3.49–3.43, m | δ 4.24, dt J 5.0, 3.2 | δ 4.08, br t J 3.5 | δ 3.49–3.43, m | δ 3.93–3.88, m | δ 3.69, dd J 12.2, 3.6 | δ 3.58, dd J 12.2, 4.9 |
| [50] | δ 3.52–3.37, m, 1H | δ 3.23, dd J 12.4, 2.6 | δ 4.27–4.19, br t J 2.8 | δ 4.06, br t J 3.5 | δ 3.52–3.37, m, 1H | δ 3.98–3.82, m | δ 3.68, dd J 12.1, 3.7 | δ 3.56, dd J 12.2, 4.9 |
| [51] # | δ 3.42, dd J 12.0, 6.9 | δ 3.56, dd J 12.0, 3.6 | δ 3.91–3.94, m | δ 3.60–3.65, m | δ 2.82, br d J 6.0, 5.1 | δ 3.98, dt J 5.1, 3.0 | δ 2.97, dd J 12.6, 5.1 | δ 2.77, dd J 12.6, 3.0 |
| [52] (MeOD) # | δ 3.43, dd JH-1,H-1’ 11.9 JH-1,H-2 4.6 | δ 3.23, dd JH-1’,H-1 11.9 JH-1’,H-2 2.5 | δ 4.18, ddd JH-2,H-1’ 4.5 JH-2,H-1 2.6 JH-2,H-3 2.6 | δ 4.11, dd JH-3,H-4 3.2 JH-3,H-2 2.9 | δ 3.47, dd JH-4,H-5 7.0 JH-4,H-3 3.6 | δ 3.92, ddd JH-5,H-4 7.1 JH-5,H-6 4.3 JH-5,H-6’ 4.2 | δ 3.72, dd JH-6,H-6’ 11.6 JH-6,H-5 4.1 | δ 3.65, dd JH-6’,H-6 11.6 JH-6’,H-5 4.4 |
| [53] | δ 2.99, dd J 12.4, 4.9 | δ 2.79, dd J 12.5, 2.8 | δ 3.93–3.96, m | δ 4.01, dt | δ 2.85–2.83, m | δ 3.62–3.66, m | δ 3.58, dd J 11.8, 3.5 Hz | δ 3.45, dd, J 12.0, 6.6 Hz |
| [54] # | δ 3.35, dd J 12.7, 3.0 | δ 3.60–3.53, m, 1H | δ 4.35, m | δ 4.18, t J 3.8 | δ 4.01, m | δ 3.60–3.53, m, 1H | 3.80, dd J 12.2, 3.6 | δ 3.68, dd J 12.0, 5.0 |
| [55] | Spectra as for enantiomer as synthesised in [55] | |||||||
| d-Galactitol [56] # | δ 3.06, dd J 12.0, 5.6 | δ 2.72, m | δ 4.05–3.99, m | δ 3.79, dd J 6.2, 3.9 | δ 2.80, d J 8.4 | δ 3.71–3.62, m | δ 3.51–3.45, m | δ 3.40–3.33, m |
| [52] | δ 3.00, dd JH-1,H-1’ 12.2 JH-1,H-2 5.7 | δ 2.78, dd JH-1’,H-1 12.2 JH-1’,H-2 3.9 | δ 4.02, ddd JH-2,H-1 5.7 JH-2,H-1’ 3.8 JH-2,H-3 3.7 | δ 3.82, dd JH-3,H-4 6.0 JH-3,H-2 3.7 | δ 2.81, dd JH-4,H-3 5.8 JH-4,H-5 5.6 | δ 3.73, ddd JH-5,H-6’ 7.4 JH-5,H-4 5.1 JH-5,H-6 4.0 | δ 3.58, dd JH-6,H-6’ 11.8 JH-6,H-5 3.9 Hz | δ 3.47, dd, JH-6’,H-6 11.8 JH-6’,H-5 7.4 Hz |
| [54] # | δ 2.87–2.81, m, 1H | δ 3.04, dd J 12.3, 5.1 | δ 4.11, m | δ 4.04, m | δ 2.87–2.81, m, 1H | δ 3.77–3.70, m, 2H | δ 3.57, dd J 12.4, 7.9 | |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-galactitol [57] | δ 2.86, m | δ 2.71, dd JH-1’,H-1 10.7 JH-1’,H-2 4.4 | δ 3.95–3.84, m | δ 4.09, m | δ 2.91, dd JH-4,H-5 4.6 JH-4,H-3 2.7 | δ 3.95–3.84, m | δ 3.72, dd JH-6,H-6’ 11.1 JH-6,H-5 5.6 | δ 3.68, dd JH-6’,H-6 11.1 JH-6,H-5 6.2 |
| l-Galactitol.HCl [55] | δ 3.31, dd JH-1,H-1’ 13 JH-1,H-2 3 | δ 3.52, dd JH-1’,H-2 5 | δ 4.30, dt | δ 4.13, dd JH-3,H-2 3 | δ 3.51, dd JH-4,H-3 4 JH-4,H-5 7 | δ 3.96, m | δ 3.64, dd JH-6,H-6′ 12 JH-6,H-5 5 Hz | δ 3.75, dd, JH-6′,H-5 4 Hz |
| l-Galactitol [CD3OD/D2O] [58] | δ 3.04, AB of ABX [∆δa-δb 72.0] JH-1,H-1′ 12.0 JH-1′,H-2 4.4 JH-1,H-2 2.4 | δ 4.08–4.05, m | δ 4.10, ddd JH-3,H-4 4.5 Hz JH-3,H-2 4.5 Hz JH-3,H-1 0.8 Hz | δ 3.02, t JH-4,H-5/H-3 4.8 | δ 3.80–3.76, m | δ 3.44, AB of ABX [∆δa-δb 22.8] JH-6,H-6′ 11.2 JH-6,H-5 4.4 JH-6′,H-5 6.4 | ||
| d-Glucitol.HCl [44] | δ 3.37, dd JH-1,H-1′ 13.1 JH-1,H-2 0.7 | δ 3.80, m, 1H | δ 4.45, m | δ 3.80, m, 1H | δ 4.18, dt J 8.8, 5.0 | δ 3.80, m, 2H | ||
| [46] | δ 3.14, d JH-1,H-1′ 13.1 | δ 3.59, m, 1H | δ 4.21, m, 2H | δ 3.59, m, 1H | 3.96, m | δ 3.59, m, 2H | ||
| [CDCl3] [50] | δ 3.40, dd J 12.4, 2.7 | δ 3.60, dd J 12.4, 4.5 | δ 4.41–4.34, m | δ 3.63, dd J 10.1, 5.5 | δ 4.09, ddd J = J = J 5.5 | δ 3.75, dd J 11.9, 5.7 | δ 3.79, dd J 11.9, 5.3 | |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-glucitol.HCl [46] | δ 3.27, d JH-1,H-1′ 13.2 | δ 3.71, dd JH-1′,H-1 13.2 JH-1′,H-2 4.2 | δ 4.31, m | δ 4.16, d | δ 3.60, br s, 1H | δ 3.79, m | δ 3.60, br s, 2H | |
| d-Glucitol [46] | δ 2.69, d JH-1,H-1′ 12.8 | δ 3.20, dd JH-1’,H-1 12.8 JH-1’,H-2 4.9 | δ 4.03, m | δ 3.14, dd J 9.5, 3.6 | δ 3.70, m | δ 3.43, dd JH-6,H-6 12.0 JH-6,H-5 6.5 Hz | δ 3.59, dd JH-6’,H-6 12.0 JH-6’,H-5 3.2 | |
| l-Glucitol | NA | |||||||
| d-Gulitol.HCl [44] | δ 3.22, dd JH-1,H-1’ 12.0 JH-1,H-2 8.4 | δ 3.60, dd JH-1’,H-1 12.0 JH-1’,H-2 8.1 | δ 4.55, dt | δ 4.34, t JH-3,H-2=H-3,H-4 3.7 | δ 3.69, m | δ 4.18, ddd JH-5,H-4 8.6 | δ 3.68, dd JH-6,H-6’ 12.2 JH-6,H-5 5.1 | δ 3.81, dd JH-6’,H-6 12.2 JH-6’,H-5 3.2 |
| l-Gulitol.HCl [59] | δ 3.13 | δ 3.52 JH-1’,H-1 12 | δ 4.47 JH-2,H-1’ 8 JH-2,H-1 8 JH-2,H-3 4 | δ 4.25 JH-3,H-4 4 | δ 3.60 | δ 4.10 JH-5,H-4 9 JH-5,H-6 5 JH-5,H-6’ 3 | δ 3.60 | δ 3.73 JH-6’,H-6 12 |
| [60] | δ 3.01, dd JH-1,H-1’ 12.0 | δ 3.45, m, 1H | δ 4.35, dt JH-2,H-1 8.3 JH-2,H-3 4.0 | δ 4.13, t | δ 3.45, m, 1H | δ 3.98, m | δ 3.62, dd JH-6,H-6’ 12.2 | δ 3.45, m, 1H |
| § | δ 3.02, dd JH-1,H-1’ 11.5 JH-1,H-2 8.4 | δ 3.43, m, 1H | δ 4.35, dt JH-2,H-1 8.1 JH-2,H-3 3.9 | δ 4.14, t J 3.6 | δ 3.43, m, 1H | δ 3.98, m | δ 3.62, dd JH-6,H-6′ 12.2 JH-6,H-5 3.1 | δ 3.43, m, 1H |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-gulitol[CDCl3] § | δ 3.28, dd JH-1′,H-1 12.1 JH-1′,H-2 9.1 | δ 3.59, dd JH-1,H-1′ 12.0 JH-1,H-2 7.0 | δ 4.55, dddd JH-2,H-1′ 9.3 JH-2,H-1/H-3 6.9 J 3.6 | δ 4.42, ddd JH-3,H-2 7.1 JH-3,H-4 4.2 J 3.0 | δ 3.84, dd JH-4,H-5 9.3 JH-4,H-3 4.0 | δ 4.38, ddd JH-5,H-4 8.5 JH-5,H-6′ 4.7 JH-5,H-6 3.2 | δ 3.85, dd JH-6,H-6′ 12.6 JH-6,H-5 3.2 | δ 3.70, dd JH-6′,H-6 12.8 JH-6′,H-5 4.8 |
| d-Iditol.HCl [CDCl3] [49] # | δ 3.19, bd J 13.1 | δ 3.58–3.55, m, 1H | δ 4.31, bd J 3.9 | δ 4.20, bd J 2.5 | δ 3.75–3.66, m, 1H | δ 4.04, ddd, J 8.5, 4.8, 3.3 | δ 3.75–3.66, m, 1H | δ 3.58–3.55, m, 1H |
| [55] | δ 3.24, dd JH-1′,H-1 13 JH-1′,H-2 0 | δ 3.62, dd JH-1,H-2 4 | δ 4.36, bd | δ 4.24, dd JH-3,H-2 1 | δ 3.77, dd JH-4,H-5 9 JH-4,H-3 3 | δ 4.08, ddd | δ 3.74, dd JH-6′,H-5 3 | δ 3.62, dd JH-6′,H-6 12 JH-6′,H-5 5 |
| l-Iditol | NA | |||||||
| d-Mannitol.HCl # | δ 3.03, dd JH-1,H-1′ 11.9 JH-1,H-2 8.9 | δ 3.45, dd, 1H JH-1′,H-1 11.8 JH-1′,H-2 8.9 | δ 4.35, dt JH-2,H-1/H-1′ 8.9 J 3.9 | δ 4.23, t J 2.6 | δ 3.45, 1H | δ 3.96, m | δ 3.55, m | |
| [61] # | δ 3.21, dd J 11.9, 8.6 | δ 3.78–3.68, m, 1H | δ 4.14, dt J 8.5, 4.9 | δ 3.78–3.68, m, 1H | δ 4.41, t J 3.4 | δ 4.55–4.50, m | δ 3.66–3.60, m, 2H | |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-mannitol.HCl [61] # | δ 3.89–3.78, m, 2H | δ 4.54–4.47, m | δ 3.89–3.78, m, 1H | δ 3.96, q J 5.0 | δ 3.64, dd J 12.0, 7.2 | δ 3.38, dd J 12.0, 7.2 | ||
| d-Mannitol [62] | δ 2.58, dd | δ 2.97, dd JH-1′,H-1 11.3 | δ 4.13, dt JH-2,H-1 8.1 JH-2,H-3 5.0 | δ 4.02, t JH-3,H-4 5.0 | δ 2.92, dd JH-4,H-5 10.0 | δ 3.66, ddd | δ 3.37, dd JH-5,H-6 6.3 | δ 3.56, dd JH-6′,H-6 11.3 JH-6′,H-5 3.8 |
| [63] # | 2.75, dd J 12, 7 | 3.15, dd J 11.5, 8 | 4.32, dt J 8, 4 | 4.20, t J 4 | 3.09, dd J 10, 4 | 3.85, ddd J 10, 7, 3.5 | 3.55, dd J 12, 7 | 3.75, dd J 12, 3.5 |
| l-Mannitol [64] | δ 2.72, dd JH-1,H-1′ 11.2 JH-1,H-2 3.5 | δ 3.12, dd JH-1′,H-1 11.2 JH-1′,H-2 8.1 | δ 4.29, dt JH-1,H-1′ 8.3 JH-2,H-3 4.1 | δ 4.16, app t J 3.9 | δ 3.07, dd JH-4,H-5 9.4 JH-4,H-3 3.5 | δ 3.81, ddd JH-5,H-4 9.4 JH-5,H-6′ 6.4 JH-5,H-6 2.8 | δ 3.71, dd JH-6,H-6′ 12.0 JH-6,H-5 2.8 | δ 3.51, dd JH-6’,H-6 12.0 JH-6’,H-5 6.4 |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-mannitol [64] | δ 2.76, dd JH-1,H-1’ 11.4 JH-1’,H-2 6.6 | δ 2.83, dd JH-1’,H-1 11.4 JH-1’,H-2 6.6 | δ 4.13, dt JH-2,H-1 6.6 JH-2,H-3 4.6 | δ 4.34–4.29, m | δ 3.01–2.97, m | δ 3.93, dt JH-5,H-6 6.3 JH-5,H-6’ 3.7 | δ 3.79, dd JH-6,H-6’ 11.8 JH-6,H-5 3.7 | δ 3.72, dd JH-6’,H-6 11.8 JH-6’,H-5 6.3 |
| d-Talitol.HCl [44] | δ 3.32, dd JH-1,H-1’ 13.0 JH-1,H-2 1.7 | δ 3.45, dd JH-1’,H-1 13.0 JH-1’,H-2 3.7 | δ 4.33, dt | δ 4.24, dd JH-3,H-2 3.9 | δ 3.54, dd JH-4,H-3 8.8 JH-4,H-5 4.4 | δ 3.98, m | δ 3.62, dd JH-6,H-6′ 12.1 JH-6,H-5 5.0 | δ 3.75, dd JH-6′,H-6 12.1 JH-6′,H-5 3.7 |
| [45] # | δ 3.31, dd J 12.7, 1.3 | δ 3.42, dd J 14, 3.8 | δ 4.3, dt J 3.8, 1.3 | δ 4.2, dd J 8.9, 3.8 | δ 3.52, dd J 8.9, 3.8 | δ 3.95, m | δ 3.6, dd J 11.4, 5.1 | δ 3.73, dd J 11.4, 3.8 |
| [65] | δ 3.19, dd JH-1,H-1′ 13.0 JH-1,H-2 1.6 | δ 3.30, dd JH-1′,H-1 13.0 JH-1′,H-2 3.8 | δ 4.20, dt JH-2,H-1′=H-2,H-3 4.0 JH-2,H-1 1.6 | δ 4.10, dd JH-3,H-4 8.9 JH-3,H-2 4.1 | δ 3.41, dd JH-4,H-3 8.9 JH-4,H-5 4.3 | δ 3.84, q | δ 3.50, dd JH-6,H-6′ 12.1 JH-6,H-5 4.9 | δ 3.61, dd JH-6′,H-6 12.1 JH-6′,H-5 3.7 |
| [47] | δ 3.33, dd JH-1,H-1′ 13 JH-1,H-2 2 | δ 3.43, dd JH-1′,H-2 4 | δ 4.33, ddd | δ 4.23, dd JH-3,H-2 4 | δ 3.54, dd JH-4,H-3 9 JH-4,H-5 4 | δ 3.97, dt | δ 3.63, dd JH-6,H-6′ 12 JH-6,H-5 5 | δ 3.74, dd JH-6′,H-5 4 |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-talitol.HCl [65] | δ 3.20, dd JH-1,H-1′ 12.9 JH-1,H-2 4.2 | δ 3.28, dd JH-1′,H-1 12.9 JH-1′,H-2 3.9 | δ 4.21, q | δ 4.11, dd JH-3,H-4 6.3 JH-3,H-2 4.2 | δ 3.53, m | δ 3.80, m | δ 3.44, dd JH-6,H-6′ 12.3 JH-6,H-5 4.9 | δ 3.53, m |
| d-Talitol [65] | δ 2.62, dd JH-1,H-1′ 12.5 JH-1,H-2 3.4 | δ 3.02, dd JH-1′,H-1 12.5 JH-1’,H-2 5.1 | δ 3.95, dt JH-2,H-1’/H-3 5.2 JH-2,H-1 3.4 | δ 3.78, dd JH-3,H-4 7.9 JH-3,H-2 5.2 | δ 2.78, dd JH-4,H-3 7.9 JH-4,H-5 4.2 | δ 3.62, m | δ 3.40, dd JH-6,H-6’ 11.8 JH-6,H-5 7.7 | δ 3.51, dd JH-6’,H-6 11.8 JH-6’,H-5 4.1 |
| [63] # | δ 2.80, dd JH-1,H-1’ 12 JH-1,H-2 3.5 | δ 3.21, dd JH-1’,H-1 12 JH-1’,H-2 5 | δ 3.97, dd J 8, 5 | δ 2.96, dd J 7.5, 4 | δ 3.82, dd J 8, 4 | δ 3.60, dd JH-6,H-6’ 12 JH-6,H-5 8 | δ 3.71, dd JH-6’,H-6 12 JH-6’,H-5 4 | |
| l-Talitol.HCl [47] | Spectra as for enantiomer as synthesised in [47] | |||||||
| Compound: 1,4-Dideoxy-1,4-imino- | 13C-NMR Chemical Shifts (δ, ppm) (in D2O Unless Stated Otherwise) for Nucleus: | Melting Points (°C) | Optical Rotation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-1 | C-2 | C-3 | C-4 | C-5 | C-6 | ||||
| Temp (°C) | [α]D (°) | ||||||||
| d-Allitol.HCl [42] # | 50.1 | 70.3 | 69.9 | 61.9 | 68.6 | 62.5 | 110–111 [42] | NA | +28.4 (c 0.6, H2O) [42] |
| [45] | 50.9 | 71.1 | 70.8 | 62.9 | 69.4 | 63.3 | 109–110 [45] | 25 | +25.6 (c 0.9, H2O) [45] |
| [46] | 50.9, t | 71.1, d | 70.9, d | 62.8, d | 69.4, d | 63.3, t | 110–111 [46] | 20 | +29.4 (c 0.53, H2O) [46] |
| [43] | NA | NA | 25 | +24.4 (c 1.0, H2O) [43] | |||||
| [44] | NA | 112–113 [44] | 25 | +25.6 (c 0.9, H2O) [44] | |||||
| [66] | NA | NA | 25 | +25.0 (c 1, H2O) [66] | |||||
| [47] | Spectra as for enantiomer as synthesised in [47] | 110–111 [47] | 20 | +28 (c 4, H2O) [47] | |||||
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-allitol.HCl [46] # | 58.4, t | 70.7, d | 71.4, d | 70.3, d | 69.1, d | 63.0, t | NA | 20 | +23.1 (c 0.72, H2O) [46] |
| l-Allitol.HCl [44] | Spectra as for enantiomer | 110–112 [44] | NA | −24.0 (c 2.1, H2O) [44] | |||||
| [48] # | 50.0 | 70.3 | 70.0 | 61.8 | 68.6 | 62.4 | 110–112 [48] | 20 | −26.0 (c 1.0, H2O) [48] |
| [67] | NA | 112–113 [67] | 20 | −24.6 (c 1.12, H2O) [67] | |||||
| [47] | 50.8 | 70.6 | 70.9 | 62.5 | 69.2 | 63.1 | 110–111 [47] | 20 | −28 (c 4, H2O) [47] |
| [46] | NA | 110–111 [46] | 25 | −29.4 (c 0.53, H2O) [46] | |||||
| l-Allitol | NA | ||||||||
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-allitol [67] | 110–111 [67] | 20 | −25.5 (c 1.07, H2O) [67] | ||||||
| d-Altritol | NA | ||||||||
| l-Altritol | NA | ||||||||
| d-Galactitol.HCl [49] # | 49.9 | 76.5 | 74.5 | 66.7 | 69.1 | 63.3 | 100–103 [49] | NA | −23 (c 1.5, H2O) [49] |
| [54] # | 52.3 | 78.9 | 77.0 | 71.5 | 69.1 | 65.7 | 103–104 [54] | 20 | −20.4 (c 1.0, H2O) [54] |
| (MeOD) [52] # | 51.5 | 78.1 | 76.1 | 70.3 | 69.2 | 65.0 | 102 [52] | 22 | −25.3 (c 1.0, MeOH) [52] |
| [50] # | 49.6 | 76.2 | 74.2 | 66.4 | 68.7 | 62.9 | 100–102 [50] | NA | −22 (c 1.5, H2O) [50] |
| [57] | NA | 98–101 [57] | NA | −24.1 (c 0.8, MeOH) [57] | |||||
| [55] | Spectra as for enantiomer as synthesised in [55] | 99–101 [55] | 20 | −23 (c 2, H2O) [55] | |||||
| d-Galactitol [56] # | 50.9 | 79.4 | 77.2 | 66.4 | 71.3 | 64.4 | NA | 25 | +2.9 (c 1.0, H2O) [56] |
| [51] # | 51.4 | 78.8 | 77.7 | 66.4 | 72.2 | 64.1 | 134–136 [51] | 20 | +3.0 (c 2.4, H2O) [51] |
| [52] # | 51.3, t | 77.8, d | 79.7, d | 66.1, d | 71.8, d | 64.3, t | NA | 22 | +3.0 (c 1.0, H2O) [52] |
| [53] | 60.9 | 75.6 | 76.8 | 61.8 | 69.4 | 68.3 | NA | 20 | +2.7 (c 1.8, H2O) [53] |
| [54] # | 53.6 | 81.7 | 80.5 | 75.1 | 68.4 | 66.3 | 134–135 [54] | 20 | −1.4, (c 2.4, H2O) [54] |
| [68] | NA | NA | NA | −0.8 (c 2.0, H2O) [68] | |||||
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-galactitol [57] | 58.9 | 75.7 | 79.2 | 73.3 | 71.2 | 63.7 | 133–135 [57] | NA | −25.5 (c 1.0, CHCl3) [57] |
| l-Galactitol.HCl [55] | 50.5 | 75.1 | 77.1 | 67.3 | 69.6 | 63.9 | 99–101 [55] | 20 | +24 (c 2, H2O) [55] |
| l-Galactitol[CD3OD/D2O] [58] | 52.0 | 78.0 | 78.2 | 67.8 | 71.6 | 64.5 | NA | 25 | −2.4 (c 3.8, H2O) [58] |
| d-Glucitol.HCl[CDCl3] [50] # | 50.4 | 75.3 | 74.8 | 66.4 | 68.7 | 62.9 | 138–140 [50] | NA | −26 (c 2, H2O) [50] |
| [46] # | 52.5, t | 75.5, d | 74.6, d | 63.3, d | 67.8, d | 64.3, t | 143–144 [46] | 20 | −28.1 (c 0.42, H2O) [46] |
| [44] | NA | 142–144 [44] | NA | −25.0 (c 0.34, H2O) [44] | |||||
| [69] | NA | 140–142 [69] | 20 | −27 (H2O) [69] | |||||
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-glucitol.HCl [46] # | 59.9, t | 74.8, d | 76.9, d | 70.0, d | 68.8, d | 63.6, t | NA | 20 | −31.9 (c 0.68, H2O) [46] |
| d-Glucitol [46] # | 52.5, t | 77.6, d | 77.7, d | 71.1, d | 61.9, d | 65.3, t | 194–196 [46] | 20 | −10.1 (c 0.43, H2O) [46] |
| [68] | NA | 200–203 [68] | 20 | −10.5 (c 1, H2O) [68] | |||||
| [69] | NA | 200–202 [69] | 20 | −11 (H2O) [69] | |||||
| l-Glucitol | NA | ||||||||
| d-Gulitol.HCl [44] | 46.3 | 70.1 | 69.5 | 62.7 | 67.8 | 62.7 | 180–182 [44] | NA | −4.9 (c 1.0, H2O) [44] |
| l-Gulitol.HCl [59] | 47.2 | 71.2 | 70.5 | 63.8 | 69.0 | 63.8 | 182–183 [59] | 20 | +6.0 (c 4, H2O) [59] |
| § | 47.6 | 71.5 | 70.9 | 64.2 | 69.3 | 64.2 | 168–170 § | NA | NA |
| [60] | 47.5, t | 69.1, d | 70.7, d | 64.0, d | 71.3, d | 64.0, t | 170–173 [60] | 20 | +7.1 (c 0.48, H2O) [60] |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-gulitol § | 53.1 | 68.9 | 70.2 | 70.1 | 68.6 | 63.1 | NA | 25 | −0.04 (c 0.08, MeOH) § |
| d-Iditol.HCl[CDCl3] [49] # | 50.5 | 75.0 | 74.4 | 68.3 | 63.5 | 63.3 | 154–156 [49] | NA | +3.2 (c 1.5, H2O) [49] |
| [55] | 51.1 | 75.6 | 75.0 | 68.8 | 64.1 | 63.8 | 157–158 [55] 161–162 [55] | 20 | +3.7 (c 3, H2O) [55] |
| d-Iditol | NA | ||||||||
| l-Iditol.HCl [55] | Spectra as for enantiomer as synthesised in [55] | 152–155 [55] 157–158 [55] | 20 | −3.8 (c 3.1, H2O) [55] | |||||
| l-Iditol | NA | ||||||||
| d-Mannitol.HCl [62] # | 48.4, t | 66.2, d | 70.8, d | 63.3, d | 71.0, d | 63.9, t | 148–149 [62] | 25 | −16.3 (c 1, H2O) [62] |
| [61] # | 47.2 | 67.1 | 69.8 | 62.2 | 69.9 | 62.8 | 147–148 [61] | 29 | −25.7 (c 0.94, MeOH) [61] |
| [70,71] | NA | 149–151 [70] | 25 | −15.7 (c 1, H2O) [71] | |||||
| [61] # | 55.2 | 68.4 | 68.5 | 67.7 | 70.9 | 62.6 | NA | 26 | −25.2 (c 0.27, MeOH) [61] |
| [72] # | 48.4 | 68.4 | 71.0 | 64.1 | 71.2 | 63.4 | 146–148 § | NA | NA |
| [73] | NA | 147–148 [73] | 20 | −15.8 (c 0.97, H2O) [73] | |||||
| d-Mannitol [62] | 48.5, t | 70.3, d | 71.4, d | 60.7, d | 72.1, d | 63.6, t | 137 [62] | 20 | −10.4 (c 0.12, H2O) [62] |
| [63] | NA | 125–128 [63] | 25 | −12.4 (c 0.7, H2O) [63] | |||||
| l-Mannitol [64] | 48.8 | 71.8 | 72.5 | 61.0 | 70.7 | 64.0 | NA | 21 | +10.3 (c 1.20, H2O) [64] |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-l-mannitol [64] | 55.8 | 70.0 | 72.8 | 66.3 | 71.2 | 63.7 | 108–109 [64] | 21 | +37.7 (c 1.20, H2O) [64] |
| d-Talitol.HCl [44] | 49.7 | 71.9 | 69.0 | 61.7 | 67.6 | 63.2 | 152–154 [44] | NA | −50.5 (c 1.01, H2O) [44] |
| [45] # | 49.9 | 72.2 | 67.8 | 61.9 | 69.3 | 63.1 | 150–152 [45] | 32 | −50.0 (c 0.5, H2O) [45] |
| [65] # | 50.9, t | 73.2, d | 68.8, d | 62.8, d | 70.3, d | 64.4, t | 144–145 [65] | 20 | −56.3 (c 0.41, H2O) [65] |
| [47] | 50.8 | 73.0 | 70.2 | 62.7 | 68.7 | 64.3 | 146–150 [47] 151–152 [47] | 20 | −54 (c 2, H2O) [47] |
| N-Benzyl-1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-talitol.HCl [65] # | 56.0, t | 73.4, d | 70.6, d | NA | 70.7, d | 63.6, t | NA | 20 | −10.1 (c 0.94, H2O) [65] |
| l-Talitol.HCl [44] | Spectra as the enantiomer | 148–152 [44] | NA | +46.7 (c 1.05, H2O) [44] | |||||
| [47] | Spectra as for enantiomer as synthesised in [47] | 151–152 [47] | 20 | +54 (c 2, H2O) [47] | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Simone, M. Borylated 5-Membered Ring Iminosugars: Detailed Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Characterisation, and Method for Analysis of Anomeric and Boron Equilibria. Molecules 2025, 30, 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071402
Simone M. Borylated 5-Membered Ring Iminosugars: Detailed Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Characterisation, and Method for Analysis of Anomeric and Boron Equilibria. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071402
Chicago/Turabian StyleSimone, Michela. 2025. "Borylated 5-Membered Ring Iminosugars: Detailed Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Characterisation, and Method for Analysis of Anomeric and Boron Equilibria" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071402
APA StyleSimone, M. (2025). Borylated 5-Membered Ring Iminosugars: Detailed Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Characterisation, and Method for Analysis of Anomeric and Boron Equilibria. Molecules, 30(7), 1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071402






