Effects of Polyphenols on the Structure, Interfacial Properties, and Emulsion Stability of Pea Protein: Different Polyphenol Structures and Concentrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fluorescence Quenching
2.2. Molecular Docking
2.3. MD Simulation
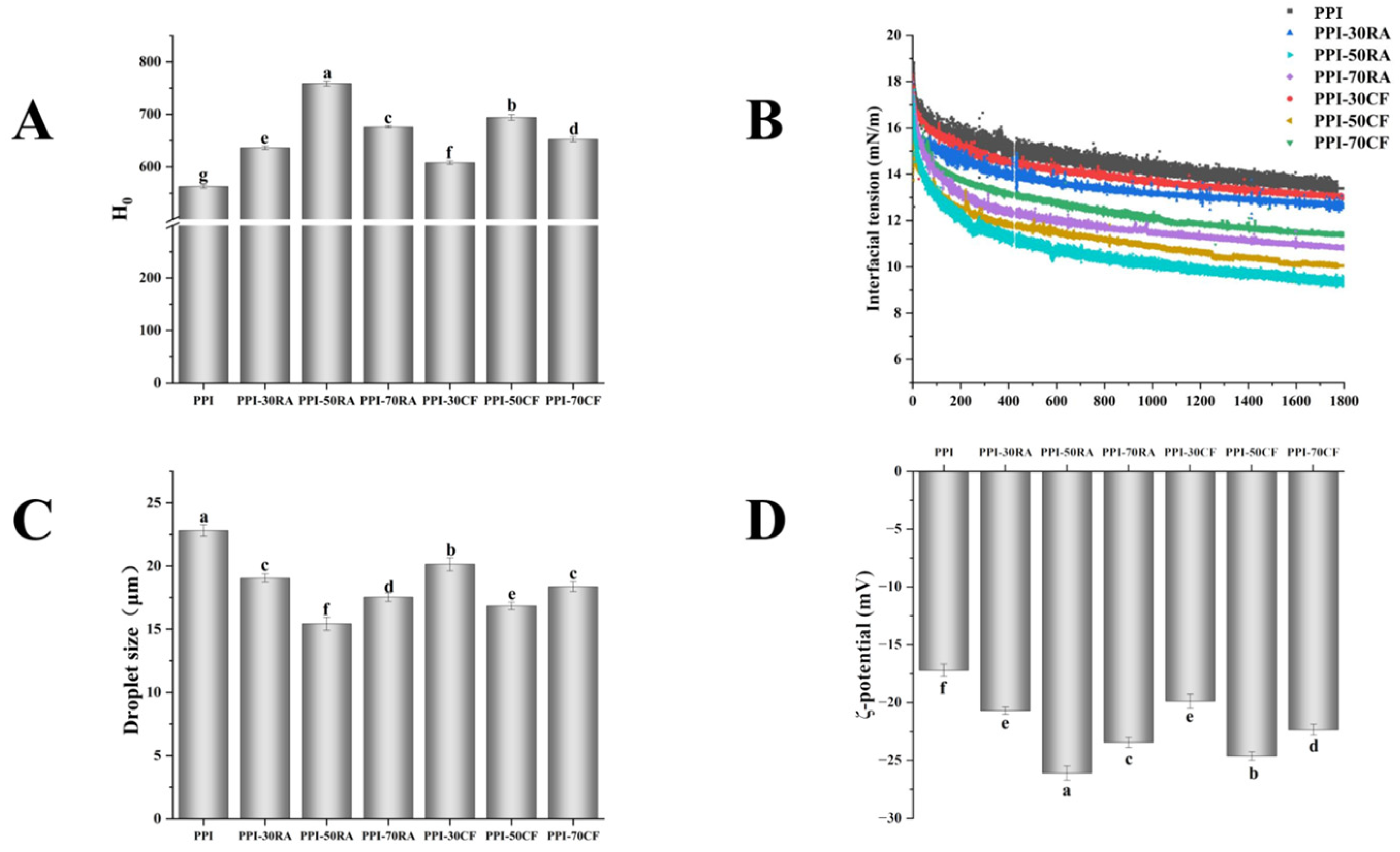
2.4. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
2.5. Emulsifying Properties
2.6. Interfacial Tension
2.7. Interfacial Protein Content (AP%) of Emulsion
2.8. Property of Emulsion Prepared by PPI-Polyphenol
2.8.1. Droplet Size and Zeta Potential
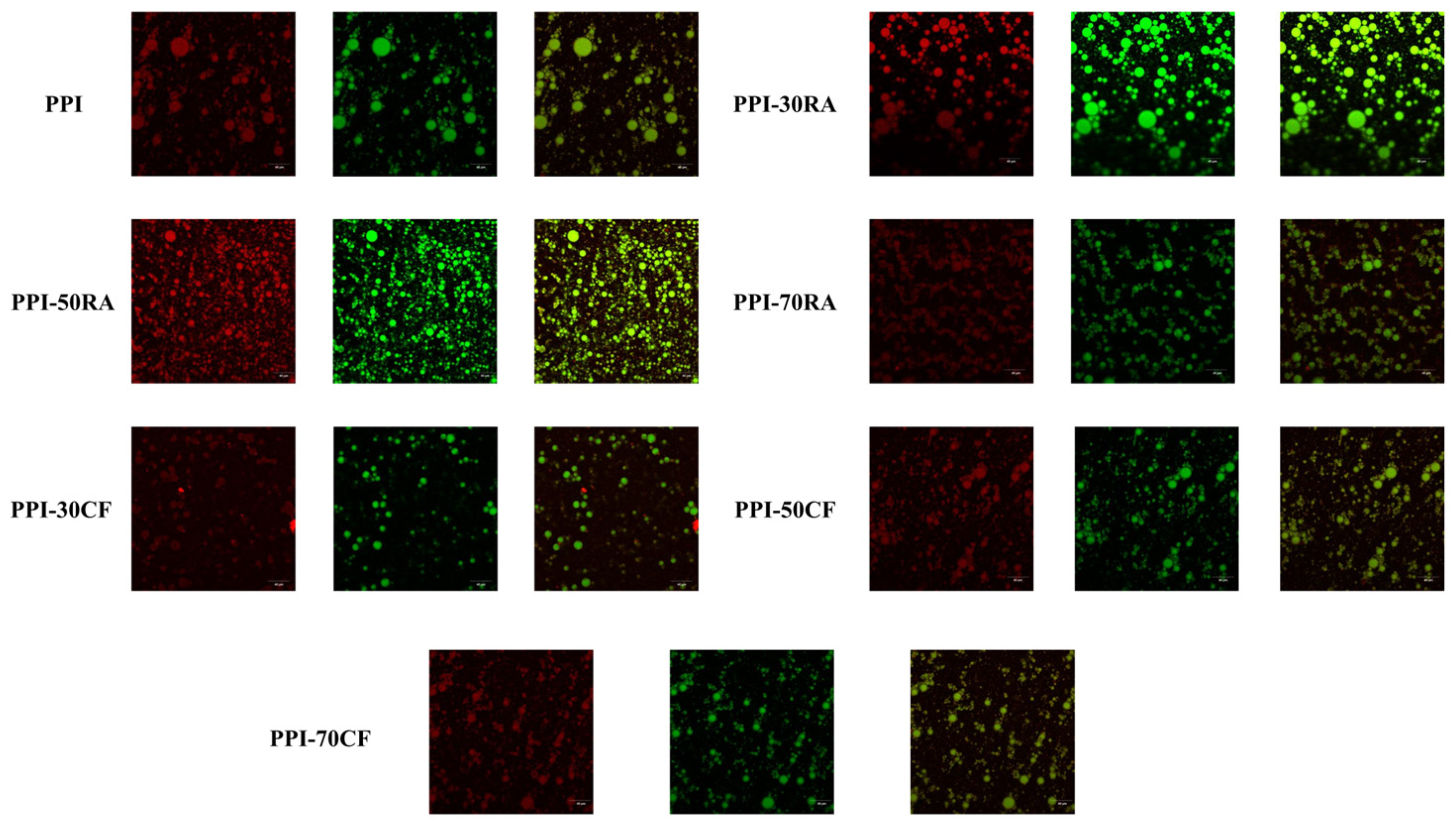
2.8.2. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM)
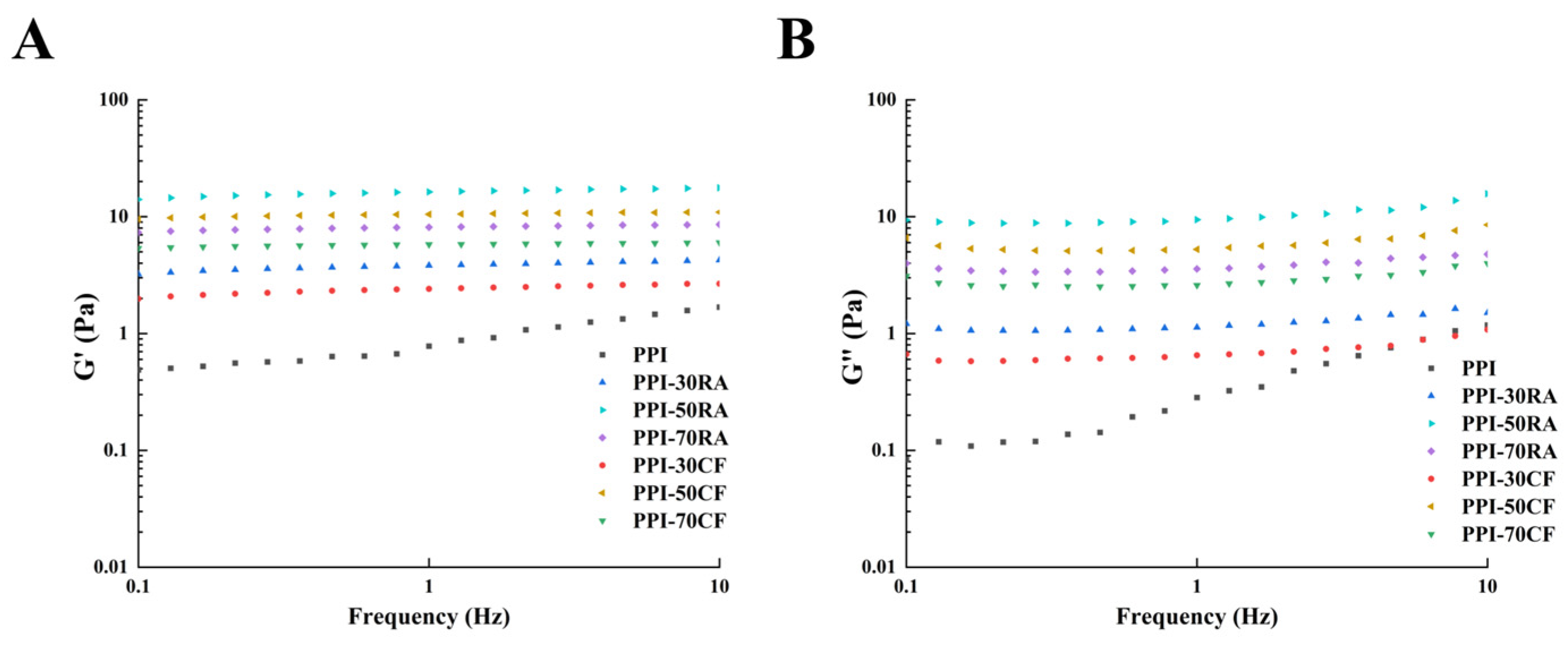
2.8.3. Rheological Behaviors
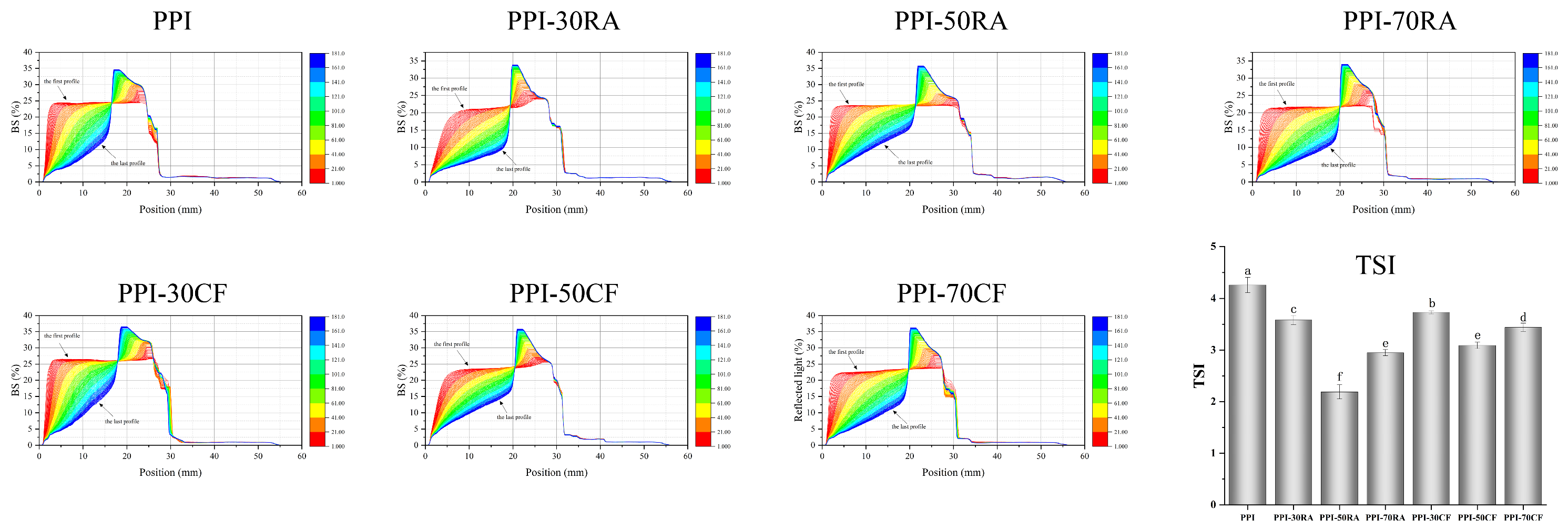
2.8.4. Stability of Emulsion
Emulsion Stability
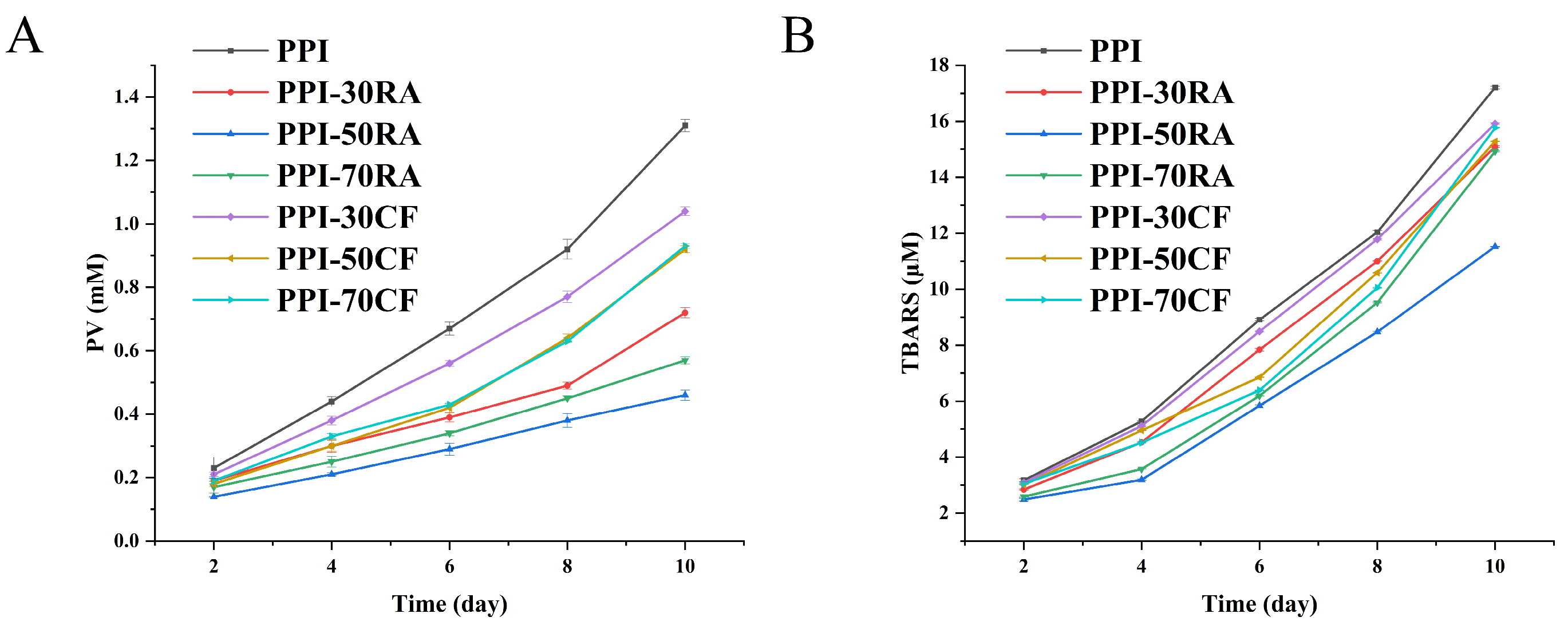
Emulsion Oxidative Stability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of PPI-Polyphenol Complexes
3.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.4. Thermodynamic Parameters
3.5. Molecular Docking
3.6. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
3.7. Surface Hydrophobicity (H0)
3.8. Emulsifying Properties
3.9. Interfacial Tension
3.10. Preparation of Emulsions
3.11. Interfacial Protein Content (AP%) of Emulsion
3.12. Droplet Size and Zeta Potential
3.13. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy (CLSM)
3.14. Rheological Properties
3.15. Stability of Emulsion Measurements
3.15.1. Emulsion Stability
3.15.2. Oxidative Stability
3.16. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.; Xu, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, R. Mechanism of structural interplay between rice proteins and soy protein isolates to design novel protein hydrocolloids. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 84, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, L. Proteins from land plants—Potential resources for human nutrition and food security. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 32, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y. Oleogel-based Pickering emulsions stabilized by pea protein isolate aggregates with different morphologies: Curcumin protection and microencapsulation. Food Chem. 2025, 473, 143108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, A.C.Y.; Can Karaca, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Nickerson, M.T. Pea protein isolates: Structure, extraction, and functionality. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiao, B.; Meng, S.; Fu, W.; Faisal, S.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Q. Edible mayonnaise-like Pickering emulsion stabilized by pea protein isolate microgels: Effect of food ingredients in commercial mayonnaise recipe. Food Chem. 2022, 376, 131866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Pei, J.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, W. Conjugation of coconut protein with ferulic acid promotes interfacial adsorption and mitigates lipid oxidation in O/W emulsion. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 156, 110371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Sarteshnizi, R.A.; Udenigwe, C.C. Recent advances in protein–polyphenol interactions focusing on structural properties related to antioxidant activities. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2022, 45, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yao, M.; Peng, S.; Fang, Y.; Wan, L.; Shang, W.; Xiang, D.; Zhang, W. Development of protein-polyphenol particles to stabilize high internal phase Pickering emulsions by polyphenols’ structure. Food Chem. 2023, 428, 136773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, T.; Song, Z.; Zhang, S.; Meng, Y.; Guo, Y. Young apple polyphenols confer excellent physical and oxidative stabilities to soy protein emulsions for effective β-carotene encapsulation and delivery. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 275, 133607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, R.; Xing, K.; Huang, Z.; Elfalleh, W.; Zhang, H.; Yu, D. Microfluidization of soybean protein isolate-tannic acid complex stabilized emulsions: Characterization of emulsion properties, stability and in vitro digestion properties. Food Chem. 2024, 430, 137065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fan, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, J. Migration of gallic acid from the aqueous phase to the oil–water interface using pea protein to improve the physicochemical stability of water–in–oil emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108179. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Ran, C.; Pan, L.; Jin, J.; Zhou, J.; Ye, Y.; Lu, S.; Dong, J.; Wang, Q. Bovine bone protein-quercetin conjugates for improved physical and oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions. LWT 2023, 188, 115448. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, C.; Das, K.P. Thermal unfolding and refolding of β-lactoglobulin: An intrinsic and extrinsic fluorescence study. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 3957–3964. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Jin, H.; Liu, G.; Yang, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sui, X. An insight into the changes in conformation and emulsifying properties of soy β-conglycinin and glycinin as affected by EGCG: Multi-spectral analysis. Food Chem. 2022, 394, 133484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Gong, Q.; Sun, F.; Cheng, T.; Fan, Z.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z. Interaction mechanism of pea proteins with selected pyrazine flavors: Differences in alkyl numbers and flavor concentration. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 147, 109314. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, W.N.; McClements, D.J.; Maqsood, S. Whey protein–polyphenol conjugates and complexes: Production, characterization, and applications. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130455. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Ning, M.J.L. Antioxidant activity stability and digestibility of protein from Se-enriched germinated brown rice. LWT 2021, 142, 111032. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhao, R.; Sun, Y.; Sun, B.; Cuina, W. pH-Dependent complexation between β-lactoglobulin and lycopene: Multi-spectroscopy, molecular docking and dynamic simulation study. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.; Ding, S.; Xie, W.; Zhu, X.; Hu, J.; Gao, J.; Li, B.; Chen, Y. Towards understanding the interaction of β-lactoglobulin with capsaicin: Multi-spectroscopic, thermodynamic, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation approaches. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 105, 105767. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, R.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Deciphering the non-covalent binding patterns of three whey proteins with rosmarinic acid by multi-spectroscopic, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation approaches. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, D.; Xing, K.; Han, X.; Gao, S.; Wang, T.; Yu, D.; Elfalleh, W. Ultrasonic treatment of rice bran protein-tannic acid stabilized oil-in-water emulsions: Focus on microstructure, rheological properties and emulsion stability. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2023, 99, 106577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Wu, N.; Wu, F.; Yu, D.; Elfalleh, W. Effects of (+)-catechin on a rice bran protein oil-in-water emulsion: Droplet size, zeta-potential, emulsifying properties, and rheological behavior. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105306. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.-D.; Lin, Y.-F.; Xu, X.; Meng, L.; Dong, M.-S. Effect of non-covalent and covalent complexation of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate with soybean protein isolate on protein structure and in vitro digestion characteristics. Food Chem. 2020, 309, 125718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, L.; Sun, Q.; McClements, D.J.; Xu, X. Effect of molecular weight on the interfacial and emulsifying characteristics of rice glutelin hydrolysates. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Liu, T.-X.; Tang, C.-H. Transforming monomeric globulins into pickering particles to stabilize nanoemulsions: Contribution of trehalose. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 141, 108687. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Meredith, J.C.; Behrens, S.H. Stabilization of liquid foams through the synergistic action of particles and an immiscible liquid. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 13603–13607. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Z.; Cao, S.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X. Double network emulsion gel prepared with different polyphenol modified egg white protein: A promising fat substitute for oral processing and fatty taste supplement. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 142082. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, F.; Youssef, M.; Li, J.; Li, B. Beyond particle stabilization of emulsions and foams: Proteins in liquid-liquid and liquid-gas interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 308, 102743. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Xu, C.; Liu, F.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y.J. Native and thermally modified protein–polyphenol coassemblies: Lactoferrin-based nanoparticles and submicrometer particles as protective vehicles for (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10816–10827. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Xu, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhong, J. Protein nanoparticles for Pickering emulsions: A comprehensive review on their shapes, preparation methods, and modification methods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 113, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Shabbir, M.; Pei, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, X. Coalescence behavior of eco-friendly Pickering-MIPES and HIPEs stabilized by using bacterial cellulose nanofibrils. Food Chem. 2021, 349, 129163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julio, L.M.; Ixtaina, V.Y.; Fernández, M.; Torres Sanchez, R.M.; Nolasco, S.M.; Tomás, M.C.J. Development and characterization of functional O/W emulsions with chia seed (Salvia hispanica L.) by-products. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 3206–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Chatterton, D.E. Strategies to improve the physical stability of sodium caseinate stabilized emulsions: A literature review. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 119, 106853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Li, L.; Xiao, N.; Li, M.; Xie, X.; Physicochemical, S.A.; Aspects, E. Physical properties of oil-in-water nanoemulsions stabilized by OSA-modified starch for the encapsulation of lycopene. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 552, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zuo, Z.; Yu, P.; Li, T.; Guang, M.; Wang, L. Rice peptide nanoparticle as a bifunctional food-grade Pickering stabilizer prepared by ultrasonication: Structural characteristics, antioxidant activity, and emulsifying properties. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Cai, H.; Wang, H.; Li, C.; Liu, S. Improved oxidative stability of fish oil emulsion by grafted ovalbumin-catechin conjugates. Food Chem. 2018, 241, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Xu, L.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Role of polyphenols conjugation to glycated myofibrillar protein in manipulating the emulsifying behaviors of flaxseed oil emulsion. LWT 2024, 201, 116284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
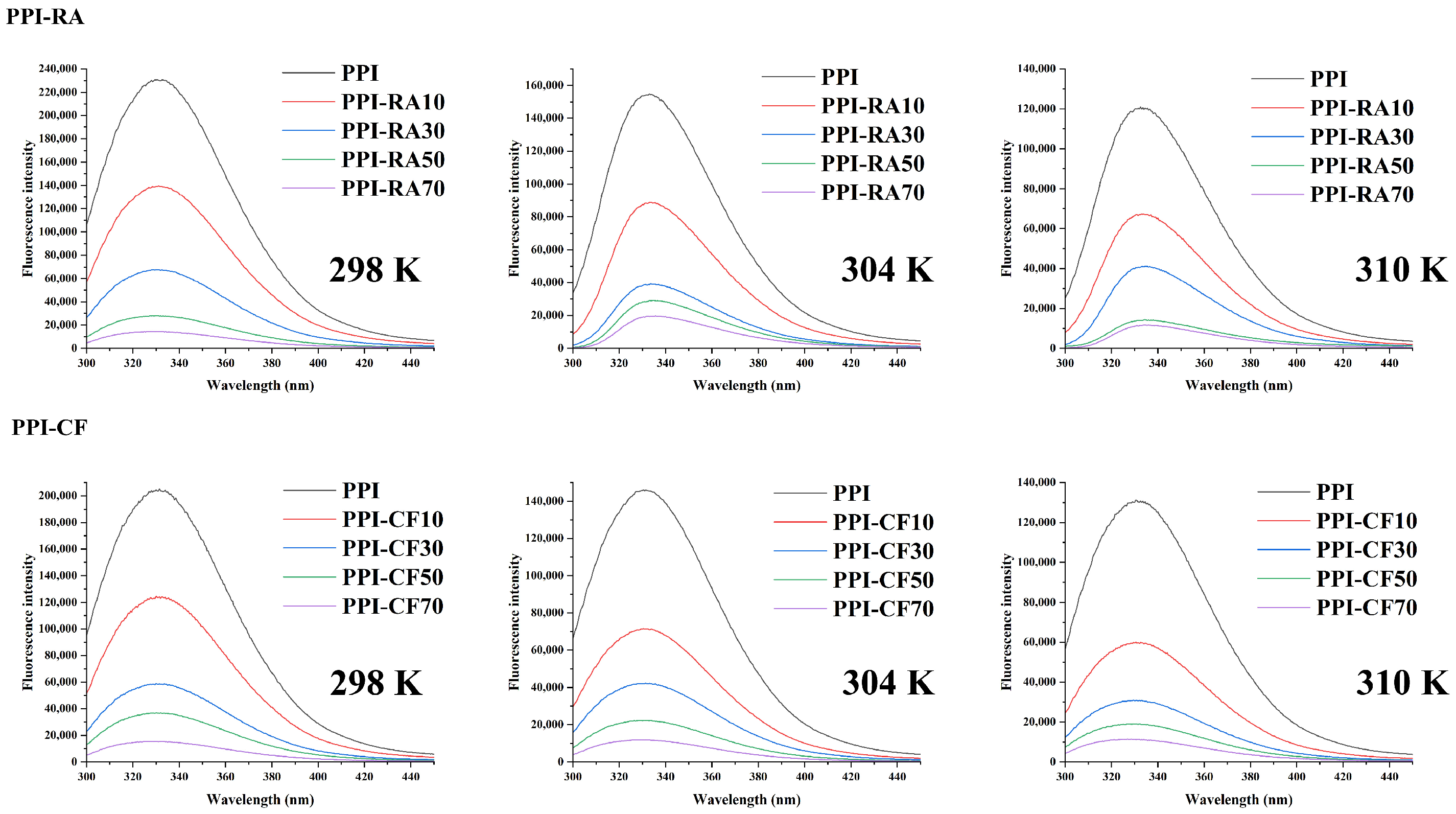
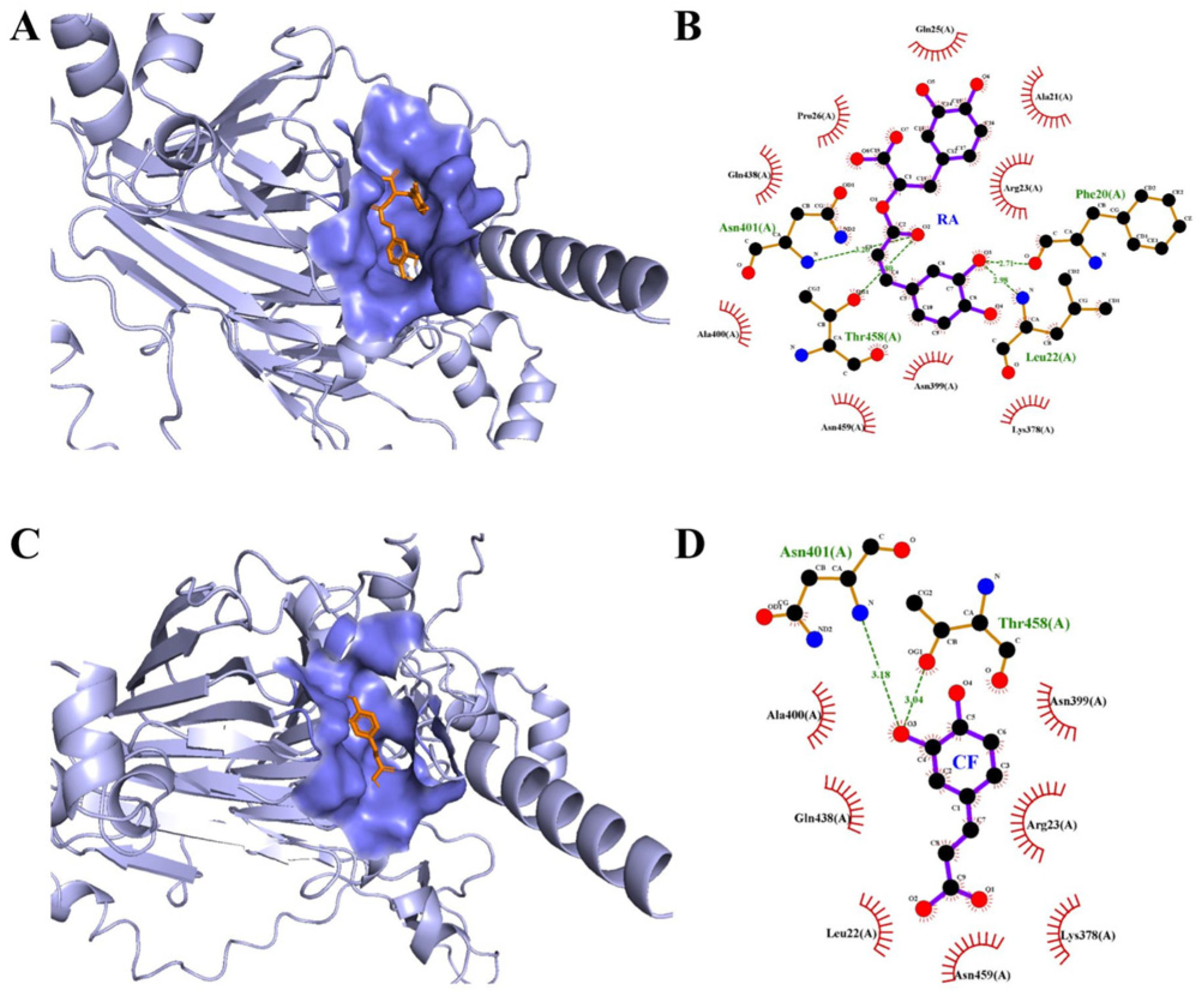

| Sample | Structure | T (K) | Ksv (106 M−1) | Ka (106 M−1) | n | ΔH/ (kJ⋅mol−1) | ΔS/ (kJ⋅mol−1) | ΔG/ (kJ⋅mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPI-RA |  | 298 | 0.046 | 1.58 | 1.11 | 69.73 | 0.35 | −35.17 |
| 304 | 0.041 | 2.15 | 1.18 | / | / | −37.27 | ||
| 310 | 0.033 | 3.64 | 1.25 | / | / | −39.39 | ||
| PPI-CF | 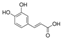 | 298 | 0.035 | 0.92 | 1.02 | 53.32 | 0.29 | −33.91 |
| 304 | 0.026 | 1.39 | 1.12 | / | / | −35.45 | ||
| 310 | 0.022 | 2.74 | 1.22 | / | / | −37.20 |
| Sample | EAI (m2/g) | ESI (min) | AP (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPI | 83.95 ± 1.67 e | 68.58 ± 1.88 d | 39.52 ± 1.02 e |
| PPI-30RA | 95.47 ± 1.67 d | 89.59 ± 1.29 b | 49.67 ± 1.32 c |
| PPI-50RA | 105.54 ± 2.58 a | 94.68 ± 1.34 a | 56.31 ± 1.09 a |
| PPI-70RA | 101.68 ± 1.14 b | 90.35 ± 1.64 b | 52.22 ± 1.62 b |
| PPI-30CF | 92.64 ± 1.57 d | 82.11 ± 1.34 c | 42.69 ± 1.49 d |
| PPI-50CF | 98.67 ± 1.31c | 90.73 ± 2.31 b | 54.28 ± 1.01 b |
| PPI-70CF | 95.64 ± 2.56 d | 85.64 ± 2.67 c | 48.36 ± 1.64 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, C. Effects of Polyphenols on the Structure, Interfacial Properties, and Emulsion Stability of Pea Protein: Different Polyphenol Structures and Concentrations. Molecules 2025, 30, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081674
Tang S, Yang X, Wang C, Wang C. Effects of Polyphenols on the Structure, Interfacial Properties, and Emulsion Stability of Pea Protein: Different Polyphenol Structures and Concentrations. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081674
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Shiyao, Xiyuan Yang, Chang Wang, and Changyuan Wang. 2025. "Effects of Polyphenols on the Structure, Interfacial Properties, and Emulsion Stability of Pea Protein: Different Polyphenol Structures and Concentrations" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081674
APA StyleTang, S., Yang, X., Wang, C., & Wang, C. (2025). Effects of Polyphenols on the Structure, Interfacial Properties, and Emulsion Stability of Pea Protein: Different Polyphenol Structures and Concentrations. Molecules, 30(8), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081674






