Searching for New Gold(I)-Based Complexes as Anticancer and/or Antiviral Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
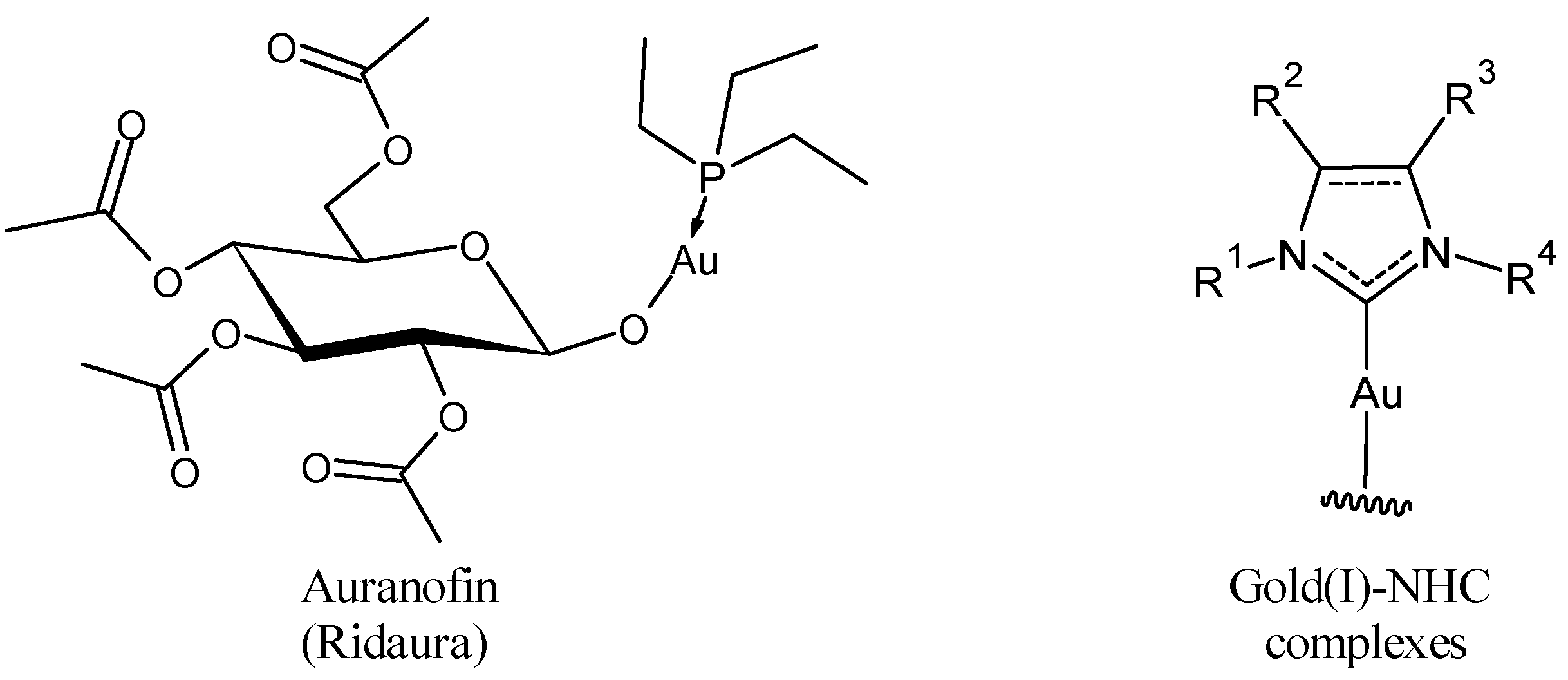
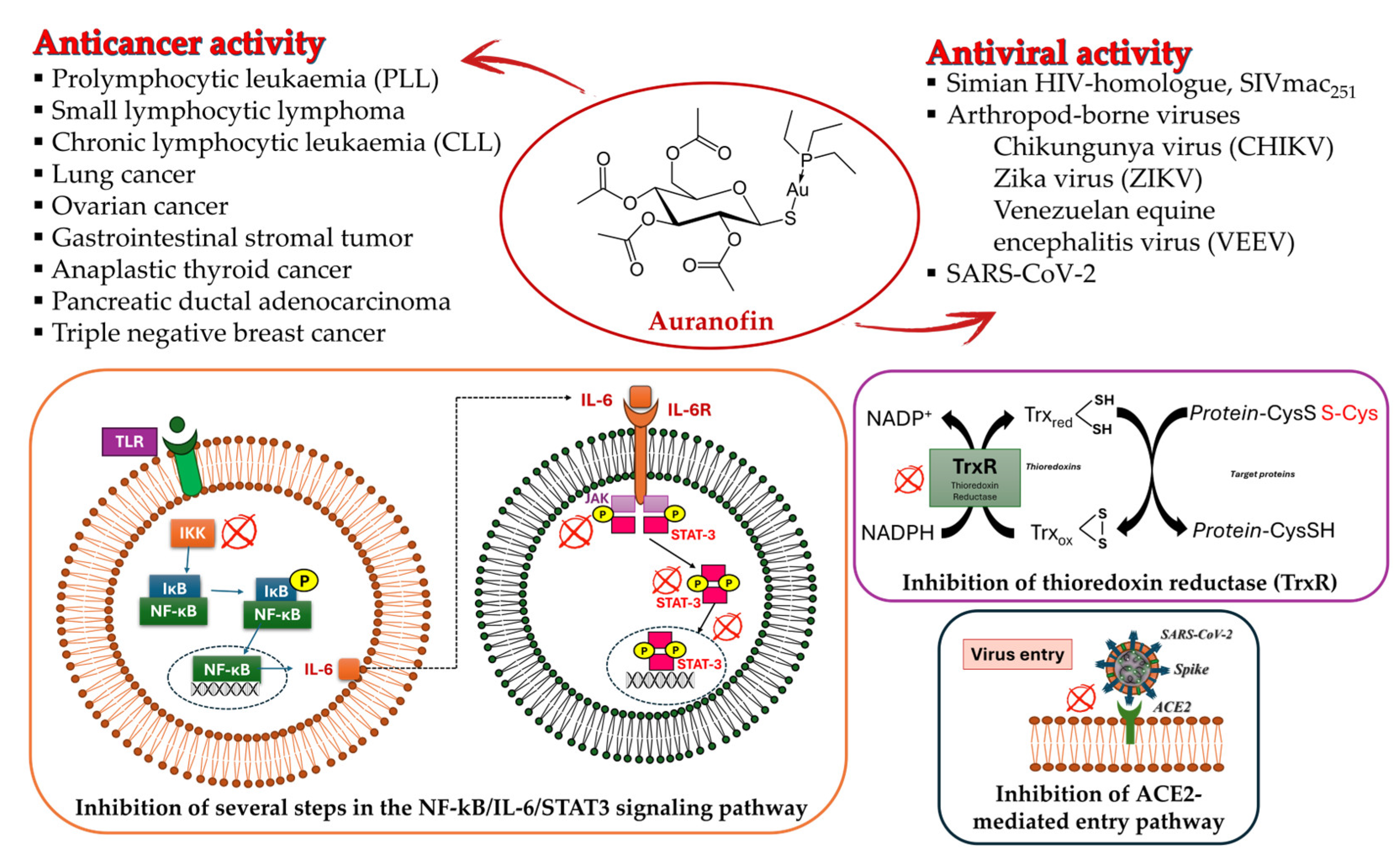
2. Auranofin: The First Gold Complex in Clinics
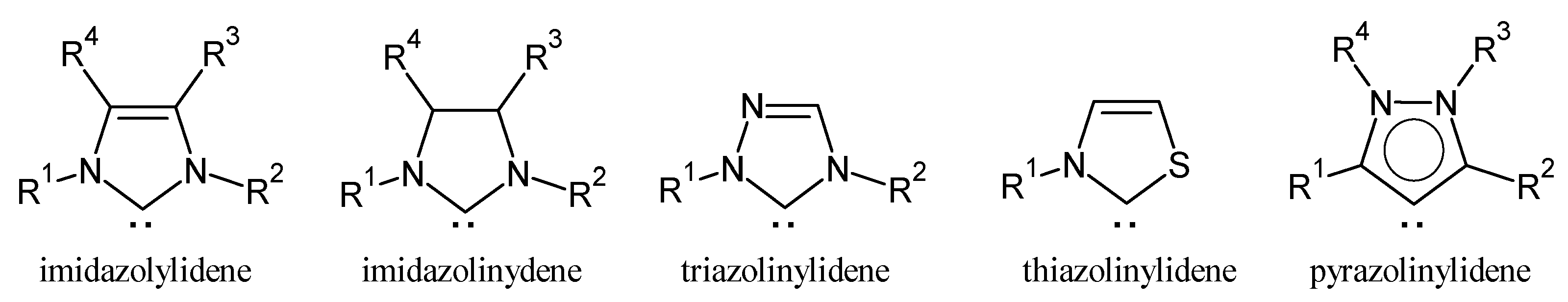
3. Gold(I)–NHC Complexes
3.1. Gold–NHC Complexes as Anticancer Agents
| Structure | Compound | Anticancer Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
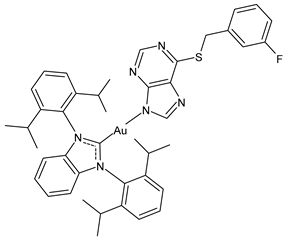 | 1 | IC50 = 3.4 ± 0.4 µM (A270) IC50 = 6.9 ± 1.7 µM (A270R) IC50 = 11.3 ± 0.1 µM (PC3) IC50 = 15.7 ± 1.1 µM (MCF-7) | [100] |
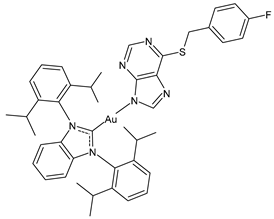 | 2 | IC50 = 3.5 ± 0.3 µM (A270) IC50 = 7.3 ± 2.1 µM (A270R) IC50 = 11.2 ± 0.6 µM (PC3) IC50 = 14.9 ± 1.2 µM (MCF-7) | [100] |
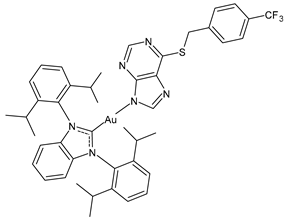 | 3 | IC50 = 6.2 ± 0.7 µM (A270) IC50 = 12.1 ± 0.7 µM (A270R) IC50 = 15.5 ± 2.3 µM (PC3) IC50 = 27.3 ± 1.2 µM (MCF-7) | [100] |
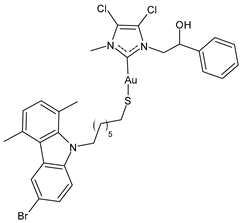 | 4 | IC50 = 3.6 ± 0.5 μM (MCF-7) IC50 = 6.4 ± 0.4 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [101] |
 | 5 | IC50 = 3.5 ± 0.2 μM (MCF-7) IC50 = 6.3 ± 0.7 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [101] |
 | 6 | IC50 = 2.7 ± 0.3 μM (MCF-7) IC50 = 6.1 ± 0.2 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [101] |
 | (R)-7 | IC50 = 2.2 ± 0.2 μM (MCF-7) IC50 = 1.2 ± 0.2 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [102] |
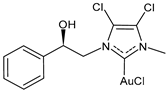 | (S)-7 | IC50 = 10.0 ± 0.5 μM (MCF-7) IC50 = 11.5± 0.4 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [102] |
 | (R)-8 | IC50 = 16.0 ± 0.8 μM (MCF-7) IC50 = 15.3 ± 4.5 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [102] |
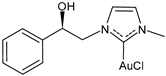 | (S)-8 | IC50 = 14.6 ± 1.0 μM (MCF-7) IC50 = 22.6 ± 0.4 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [102] |
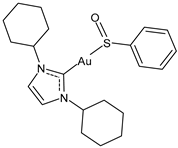 | 9 | IC50 = 2.7 ± 0.2 μM (OVCAR-8) | [103] |
 | 10 | IC50 = 2.9 ± 0.5 μM (OVCAR-8) | [103] |
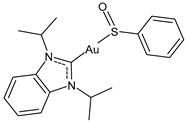 | 11 | IC50 = 2.9 ± 0.5 μM (OVCAR-8) | [103] |
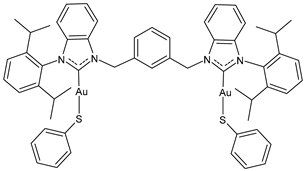 | 12 | IC50 = 0.4 ± 0.2 μM (A2780) IC50 = 2.4 ± 0.2 μM (A2780cis) IC50 = 4 ± 0.1 μM (HCT116) IC50 = 7.7 ± 0.1 μM (A549) IC50 = 4.5 ± 0.3 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [105] |
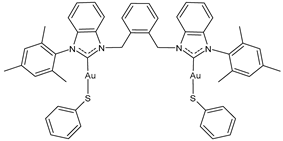 | 13 | IC50 = 0.3 ± 0.1 μM (A2780) IC50 = 1.0 ± 0.3 μM (A2780cis) IC50 = 4.4 ± 0.2 μM (HCT116) IC50 = 4.4 ± 0.2 μM (A549) IC50 = 4.4 ± 0.2 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [105] |
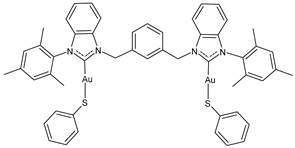 | 14 | IC50 = 0.12 ± 0.03 μM (A2780) IC50 = 0.11 ± 0.01 μM (A2780cis) IC50 = 1.0 ± 0.1 μM (HCT116) IC50 = 5.8 ± 0.2 μM (A549) IC50 = 1.2 ± 0.5 μM (MDA-MB-231) | [105] |
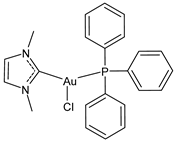 | 15 | IC50 = 11 μM (human NSCLC with KRAS mutations) IC50 = 3 μM (human NSCLC without KRAS mutations) | [106] |
 | 16 | IC50 = 14.7 ± 1.1 μM (MDA-MB-231) IC50 = 73.8 ± 1.1 μM (MCF-7) | [107] |
3.2. Gold–NHC Complexes as Antiviral Agents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdolmaleki, S.; Aliabadi, A.; Khaksar, S. Riding the Metal Wave: A Review of the Latest Developments in Metal-Based Anticancer Agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 501, 215579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, C.M.C.; Pérez de la Lastra, J.M.; Bustamante Munguira, E.; Andrés Juan, C.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Anticancer activity of Metallodrugs and Metallizing Host Defense Peptides—Current Developments in Structure-Activity Relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, S.; Nath, P.; Das, A.; Datta, A.; Baildya, N.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Pathak, S. A Review on Metal Complexes and Its Anti-Cancer Activities: Recent Updates from In Vivo Studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 171, 116211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Aodeng, G.; Ga, L.; Hai, W.; Ai, J. Research Progress of Metal Anticancer Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkova, D.D.; Marangozov, S.D.; Kostadinova, I.I. Pharmacological Activity of Metal-Based Organic Complexes Against Different Viral Diseases. Pharmacophore 2024, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, P.J.; Baker, M.V.; Berners-Price, S.J.; Day, D.A. Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Induced by Dinuclear Gold(I)-Carbene Complexes: Potential New Antimitochondrial Antitumour Agents. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 1642–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-F.; Yin, Y.-K.; Zhang, H.; Han, Y.-F. Metal N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes as Potential Metallodrugs in Antitumor Therapy. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 514, 215941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, S.; Haribabu, J.; Karvembu, R. From Concept to Cure: The Road Ahead for Ruthenium-Based Anticancer Drugs. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, S.; Zhao, Z.; He, W.; Song, M. Novel Insights into Anticancer Mechanisms of Elesclomol: More than a Prooxidant Drug. Redox Biol. 2023, 67, 102891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, S.P.; Pashinsky, Y.Y.; Gershon, D.; Winicov, I.; Srivilasa, C.; Kristic, K.J.; Asbell, P.A. Efficacy of Topical Cobalt Chelate CTC-96 against Adenovirus in a Cell Culture Model and against Adenovirus Keratoconjunctivitis in a Rabbit Model. BMC Opthalmol. 2006, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, C.; Thomson, M.J. Auranofin: Repurposing an Old Drug for a Golden New Age. Drugs RD 2015, 15, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappetta, G.; Gamberi, T.; Faienza, F.; Limaj, X.; Rizza, S.; Messori, L.; Filomeni, G.; Modesti, A.; Vinh, J. Redox Proteome Analysis of Auranofin Exposed Ovarian Cancer Cells (A2780). Redox Biol. 2022, 52, 102294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejman-Yarden, N.; Miyamoto, Y.; Leitsch, D.; Santini, J.; Debnath, A.; Gut, J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Reed, S.L.; Eckmann, L. A Reprofiled Drug, Auranofin, Is Effective against Metronidazole-Resistant Giardia lamblia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, M. Auranofin: Past to Present, and Repurposing. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarup, S.; Obukhov, A.G.; Raizada, S.; Atre, R.; Baig, M.S. Drug Repurposing in the Treatment of Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Fut. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yuan, S.; Wei, X.; Sun, H. Metal-Based Strategies for the Fight Against COVID-19. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 7466–7482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Hashmi, A.A.; Al-Bogami, A.S.; Wani, M.Y. Harnessing the Power of Gold: Advancements in Anticancer Gold Complexes and their Functionalized Nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 552–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanpour, M.; Soltani, B. An Updated Overview on Nitrogen-rich Azole-based Gold Coordination Complexes as Potent Anticancer Agents. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2025, 523, 216233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, B.; Casini, A. A Golden Future in Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry: The Promise of Anticancer Gold Organometallic Compounds. Dalton Transact. 2014, 43, 4209–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porchia, M.; Pellei, M.; Marinelli, M.; Tisato, F.; Del Bello, F.; Santini, C. New Insights in Au-NHCs Complexes as Anticancer Agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 709–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.; Gimeno, M.C.; Visbal, R. Recent Advances in Gold–NHC Complexes with Biological Properties. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominelli, B.; Correia, J.D.; Kuehn, F.E. Medicinal Applications of Gold(I/III)-based Complexes Bearing N-Heterocyclic Carbene and Phosphine Ligands. J. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 866, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Majid, A.M.; Yousuf, S.; Choudhary, M.I.; Nahra, F.; Nolan, S.P. Gold-NHC Complexes as Potent Bioactive Compounds. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Rosano, C.; Mariconda, A.; Pellegrino, M.; Sirignano, M.; Saturnino, C.; Catalano, A.; Aquaro, S.; Longo, P.; et al. N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Gold(I) Complexes Targeting Actin Polymerization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, M.; Granda, E. Au⋯H− X (X= N or C) Intramolecular Interactions in Gold(I)-NHC Carbene Complexes with Potential Anticancer Properties: A Quantum Mechanical Study with Two Basis Sets. ChemistryOpen 2024, 13, e202400140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceramella, J.; Catalano, A.; Mariconda, A.; D’Amato, A.; Aquila, S.; Saturnino, C.; Rosano, C.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Longo, P. Silver N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes as Antimicrobial and/or Anticancer Agents. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S. Computational Characterization of Benzimidazolium-Acridine-Based Gold N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes and Investigation of their Anti-tumor Properties. Polyhedron 2024, 261, 117105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolbatov, I.; Marrone, A.; Coletti, C.; Re, N. Computational Studies of Au(I) and Au(III) Anticancer Metallodrugs: A Survey. Molecules 2021, 26, 7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varchmin, A.; Muñoz-Castro, A.; Ott, I. Gold(I) Organometallics with Alkynyl and N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands and their Medicinal and Computational Chemistry Evaluation as Prospective Anticancer Drugs. J. Organometal. Chem. 2024, 1012, 123148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.C.; Barrionuevo, M.V.; San-Miguel, M.A.; Abbehausen, C. Unraveling Ligand Exchange Reactions in Linear Neutral Au(I) and Cu(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes for Biological Applications. New J. Chem. 2024, 48, 2040–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üstün, E.; Şahin, N. Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Benzimidazolium Type NHC Molecule and Its Silver Complex and Their Theoretical Analysis for Potential Anti-Cancer Activity. Karadeniz Fen Bilim. Derg. 2023, 13, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderizadeh, B.; Bayat, M. Chemical Bonding in Some Anticancer NHC Complexes [R′C ≡ C → ML](M = Cu (I), Ag (I), Au (I); R′ = C10H7 and C9NH12SO2; L = NHC (R) and P (R)3; and R= F, Cl, Br, H, CH3, SiH3, Ph). J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2024, 21, 2775–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Moles, M.; Türck, S.; Basu, U.; Pettenuzzo, A.; Bhattacharya, S.; Rajan, A.; Ma, X.; Büssing, R.; Wölker, J.; Burmeister, H.; et al. Metallodrug Profiling against SARS-CoV-2 Target Proteins Identifies Highly Potent Inhibitors of the S/ACE2 interaction and the Papain-like Protease PLpro. Chemistry 2021, 27, 17928–17940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Moles, M.; Basu, U.; Büssing, R.; Hoffmeister, H.; Türck, S.; Varchmin, A.; Ott, I. Gold Metallodrugs to Target Coronavirus Proteins: Inhibitory Effects on the Spike-ACE2 Interaction and on PLpro Protease Activity by Auranofin and Gold Organometallics. Chemistry 2020, 26, 15140–15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karges, J.; Cohen, S.M. Metal Complexes as Antiviral Agents for SARS-CoV-2. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 2600–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, T.; Cirri, D.; Gabbiani, C.; Gamberi, T.; Magherini, F.; Pratesi, A.; Guerri, A.; Biver, T.; Binacchi, F.; Stefanini, M.; et al. Auranofin, Et3PAuCl, and Et3PAuI Are Highly Cytotoxic on Colorectal Cancer Cells: A Chemical and Biological Study. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Joseph, J.P.; Jagdish, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; Ramteke, N.S.; Karhale, A.K.; Waturuocha, U.; Saini, D.K.; Nandi, D. High Throughput Screening Identifies Auranofin and Pentamidine as Potent Compounds that Lower IFN-γ-induced Nitric Oxide and Inflammatory Responses in Mice: DSS-induced Colitis and Salmonella typhimurium-induced Sepsis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 122, 110569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwangbo, H.; Ji, S.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.Y.; Choi, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory Effect of Auranofin on Palmitic Acid and LPS-induced Inflammatory Response by Modulating TLR4 and NOX4-mediated NF-κB Signaling Pathway in RAW264. 7 Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwangbo, H.; Kim, M.Y.; Ji, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Kim, G.Y.; Park, C.; Keum, Y.S.; Hong, S.H.; Cheong, J.; et al. Auranofin Attenuates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Suppressing Lipid Accumulation and NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Hepatic Inflammation In Vivo and In Vitro. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, J.M.; Gibson, D.L.; Kean, W.F.; Klegeris, A. The Biological Activity of Auranofin: Implications for Novel Treatment of Diseases. Inflammopharmacology 2012, 20, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coscione, F.; Zineddu, S.; Vitali, V.; Fondi, M.; Messori, L.; Perrin, E. The Many Lives of Auranofin: How an Old Anti-Rheumatic Agent May Become a Promising Antimicrobial Drug. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.M.; Koh, D.H.; Jun, D.W.; Roh, Y.J.; Kang, H.T.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, H.S. Auranofin Attenuates Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via NRF2 and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Kharashi, L.A.; Al-Harbi, N.O.; Ahmad, S.F.; Attia, S.M.; Algahtani, M.M.; Ibrahim, K.E.; Bakheet, S.A.; Alanazi, M.M.; Alqarni, S.A.; Alsanea, S.; et al. Auranofin Modulates Thioredoxin Reductase/Nrf2 Signaling in Peripheral Immune Cells and the CNS in a Mouse Model of Relapsing-Remitting EAE. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiskus, W.; Saba, N.; Shen, M.; Ghias, M.; Liu, J.; Gupta, S.D.; Chauhan, L.; Rao, R.; Gunewardena, S.; Schorno, K.; et al. Auranofin Induces Lethal Oxidative and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Exerts Potent Preclinical Activity against Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2520–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hu, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, L.; Cao, X.; Zhang, X.; Dai, B.; Cao, M.; Shao, R.; Zhang, R.; et al. Auranofin-mediated Inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis and Anticancer Activity in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 3548–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire Boullosa, L.; Van Loenhout, J.; Flieswasser, T.; De Waele, J.; Hermans, C.; Lambrechts, H.; Cuypers, B.; Laukens, K.; Bartholomeus, E.; Siozopoulou, V.; et al. Auranofin Reveals Therapeutic Anticancer Potential by Triggering Distinct Molecular Cell Death Mechanisms and Innate Immunity in Mutant p53 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.Y.; Park, S.H.; Park, W.H. Anti-Cancer Effects of Auranofin in Human Lung Cancer Cells by Increasing Intracellular ROS Levels and Depleting GSH Levels. Molecules 2022, 27, 5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Lee, J.; Berek, J.; Hu, M. Auranofin Displays Anticancer Activity against Ovarian Cancer Cells through FOXO3 Activation Independent of p53. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessetto, Z.Y.; Weir, S.J.; Sethi, G.; Broward, M.A.; Godwin, A.K. Drug Repurposing for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.C.; Jun, H.H.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, I.; Choi, S.; Yeo, H.; Lee, S.; An, H.J. Auranofin as a Novel Anticancer Drug for Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalbari, F.H.; Telleria, C.M. The Gold Complex Auranofin: New Perspectives for Cancer Therapy. Discov. Oncol. 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, T.; Momose, I.; Kawada, M. Potential Anticancer Activity of Auranofin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 67, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deben, C.; Boullosa, L.F.; Fortes, F.R.; De La Hoz, E.C.; Le Compte, M.; Seghers, S.; Peeters, M.; Vanlanduit, S.; Lin, A.; Dijkstra, K.K.; et al. Auranofin Repurposing for Lung and Pancreatic Cancer: Low CA12 Expression as a Marker of Sensitivity in Patient-Derived Organoids, with Potentiated Efficacy by AKT Inhibition. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, B.; Rullo, A.; Zhang, A.; Chang, K.; Petukhova, V.Z.; Aboagye, S.Y.; Angelucci, F.; Williams, D.L.; Kregel, S.; Petukhov, P.A.; et al. Pleiotropic Anti-Cancer Activities of Novel Non-Covalent Thioredoxin Reductase Inhibitors Against Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2024, 227, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nag, D.; Bhanja, P.; Riha, R.; Sanchez-Guerrero, G.; Kimler, B.F.; Tsue, T.T.; Lominska, C.; Saha, S. Auranofin Protects Intestine against Radiation Injury by Modulating p53/p21 Pathway and Radiosensitizes Human Colon Tumor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4791–4807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, H. Auranofin, an Anti-rheumatic Gold Drug, Aggravates the Radiation-Induced Acute Intestinal Injury in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, D.L.; Masci, J.R. Treatment of HIV Associated Psoriatic Arthritis with Oral Gold. J. Rheumatol. 1996, 23, 1818–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.G.; DaFonseca, S.; Chomont, N.; Palamara, A.T.; Tardugno, M.; Mai, A.; Collins, M.; Wagner, W.L.; Yalley-Ogunro, J.; Greenhouse, J.; et al. Gold Drug Auranofin Restricts the Viral Reservoir in the Monkey AIDS Model and Induces Containment of Viral Load Following ART Suspension. AIDS 2011, 25, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, R.S.; Shytaj, I.L.; Giron, L.B.; Obermaier, B.; Della Libera, E.; Galinskas, J.; Dias, D.; Hunter, J.; Janini, M.; Gossen, G.; et al. Potential Impact of the Antirheumatic Agent Auranofin on Proviral HIV-1 DNA in Individuals under Intensified Antiretroviral Therapy: Results from a Randomised Clinical Trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 54, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarino, A.; Shytaj, I.L. Chloroquine and Beyond: Exploring Antirheumatic Drugs to Reduce Immune Hyperactivation in HIV/AIDS. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, M.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Salpini, R.; Svicher, V.; Marsico, S.; Aquaro, S.; Pellegrino, M. New Therapies and Strategies to Curb HIV Infections with a Focus on Macrophages and Reservoirs. Viruses 2024, 16, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langsjoen, R.M.; Auguste, A.J.; Rossi, S.L.; Roundy, C.M.; Penate, H.N.; Kastis, M.; Schnizlein, M.K.; Le, K.C.; Haller, S.L.; Chen, R.; et al. Host Oxidative Folding Pathways Offer Novel Anti-Chikungunya Virus Drug Targets with Broad Spectrum Potential. Antivir. Res. 2017, 143, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciotti, M.; Ciccozzi, M.; Terrinoni, A.; Jiang, W.C.; Wang, C.B.; Bernardini, S. The COVID-19 Pandemic. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 365–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, A. COVID-19: Could Irisin Become the Handyman Myokine of the 21st Century? Coronaviruses 2020, 1, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paiva, R.E.F.; Marçal Neto, A.; Santos, I.A.; Jardim, A.C.G.; Corbi, P.P.; Bergamini, F.R.G. What Is Holding Back the Development of Antiviral Metallodrugs? A Literature Overview and Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutics and Future Viral Outbreaks. Dalton Trans. 2020, 49, 16004–16033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonzogni-Desautels, K.; Ndao, M. Will Auranofin Become a Golden New Treatment Against COVID-19? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 683694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzo, T.; Messori, L. A Role for Metal-Based Drugs in Fighting COVID-19 Infection? The Case of Auranofin. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1067–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothan, H.A.; Stone, S.; Natekar, J.; Kumari, P.; Arora, K.; Kumar, M. The FDA-Approved Gold Drug Auranofin Inhibits Novel Coronavirus (SARS-COV-2) Replication and Attenuates Inflammation in Human Cells. Virology 2020, 547, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Saitoh, S.I.; Miyake, K.; Hwang, D.H. Auranofin, as an Anti-rheumatic Gold Compound, Suppresses LPS-Induced Homodimerization of TLR4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 350, 866–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, K.I.; Jeong, J.Y.; Jue, D.M. Thiol-Reactive Metal Compounds Inhibit NF-Kappa B Activation by Blocking I Kappa B Kinase. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.-H.; Lee, M.-Y.; Park, S.-J.; Choi, J.-S.; Oh, M.-K.; Kim, I.-S. Auranofin Blocks Interleukin-6 Signalling by Inhibiting Phosphorylation of JAK1 and STAT3 Nam-Hoon. Immunology 2007, 122, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Shen, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, F.; Min, J. Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications of the Gold Drug Auranofin. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 493, 215323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Selvaraju, K.; Saei, A.A.; D’Arcy, P.; Zubarev, R.A.; Arnér, E.S.; Linder, S. Repurposing of Auranofin: Thioredoxin Reductase Remains a Primary Target of the Drug. Biochimie 2019, 162, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Singh, A.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, A. Repurposing of Auranofin against Bacterial Infections: An in Silico and in Vitro Study. Curr. Comput. Aided. Drug Des. 2021, 17, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, I.J.; Cheng, Q.; Rengifo, E.M.; Nehzati, S.; Dolgova, N.V.; Kroll, T.; Sokaras, D.; George, G.N.; Arner, E.S.J. Direct Observation of Methylmercury and Auranofin Binding to Selenocysteine in Thioredoxin Reductase. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 2711–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checconi, P.; De Angelis, M.; Marcocci, M.E.; Fraternale, A.; Magnani, M.; Palamara, A.T.; Nencioni, L. Redox-Modulating Agents in the Treatment of Viral Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiser, K.; François, K.O.; Schols, D.; Bergman, T.; Jörnvall, H.; Balzarini, J.; Karlsson, A.; Lundberg, M. Thioredoxin-1 and Protein Disulfide Isomerase Catalyze the Reduction of Similar Disulfides in HIV gp120. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplantine, E.; Chable-Bessia, C.; Oudin, A.; Swain, J.; Soria, A.; Merida, P.; Gourdelier, M.; Mestiri, S.; Besseghe, I.; Bremaud, E.; et al. The FDA-Approved Drug Auranofin Has a Dual Inhibitory Effect on SARS-CoV-2 Entry and NF-κB Signaling. iScience 2022, 25, 105066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbehausen, C.; Peterson, E.J.; de Paiva, R.E.F.; Corbi, P.P.; Formiga, A.L.B.; Qu, Y.; Farrell, N.P. Gold(I)-phosphine-N-Heterocycles: Biological Activity and Specific (Ligand) Interactions on the C-terminal HIV-NCp7 Zinc Finger. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 11280–11287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Moles, M.; O’Beirne, C.; Esarev, I.V.; Lippmann, P.; Tacke, M.; Cinatl, J.; Bojkova, D.; Ott, I. Silver N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes are Potent Uncompetitive Inhibitors of the Papain-Like Protease with Antiviral Activity against SARS-CoV-2. RSC Med. Chem. 2023, 14, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varna, D.; Geromichalos, G.; Gioftsidou, D.K.; Tzimopoulos, D.; Hatzidimitriou, A.G.; Dalezis, P.; Papi, R.; Trafalis, D.; Angaridis, P.A. N-Heterocyclic-carbene vs Diphosphine Auxiliary Ligands in Thioamidato Cu(I) and Ag(I) Complexes towards the Development of Potent and Dual-Activity Antibacterial and Apoptosis-inducing Anticancer Agents. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2024, 252, 112472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Nasr, I.S.; Koko, W.S.; Khan, T.A.; Gurbuz, N.; Ozdemir, I.; Hamdi, N. Evaluation of Ruthenium(II) N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes as Enzymatic Inhibitory Agents with Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, Antiparasitical and Antiproliferative Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominique, N.L.; Jensen, I.M.; Kaur, G.; Kotseos, C.Q.; Boggess, W.C.; Jenkins, D.M.; Camden, J.P. Giving Gold Wings: Ultrabright and Fragmentation Free Mass Spectrometry Reporters for Barcoding, Bioconjugation Monitoring, and Data Storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202219182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplanai, E.; Tzouras, N.V.; Tsoureas, N.; Pozsoni, N.B.; Bhandary, S.; Van Hecke, K.; Nolan, S.P.; Vougioukalakis, G.C. Synthesis of N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC)-Au/Ag/Cu Benzotriazolyl Complexes and their Catalytic Activity in Propargylamide Cycloisomerization and Carbonyl Hydrosilylation Reactions. Dalton Transact. 2024, 53, 11001–11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scattolin, T.; Tonon, G.; Botter, E.; Guillet, S.G.; Tzouras, N.V.; Nolan, S.P. Gold(I)-N-Heterocyclic Carbene Synthons in Organometallic Synthesis. Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202301961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppanen, O.; Lenarda, A.; Nieger, M.; Helaja, J. In Situ Brønsted Acid Activated Cyclometalated N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Au(III)-Sulfonamide Complexes as Precatalysts for Alkyne Activation in Benzofuran Synthesis. Organometallics 2024, 43, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacopetta, D.; Rosano, C.; Sirignano, M.; Mariconda, A.; Ceramella, J.; Ponassi, M.; Saturnino, C.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Longo, P. Is the Way to Fight Cancer Paved with Gold? Metal-based Carbene Complexes with Multiple and Fascinating Biological Features. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.; Mandal, S.M.; Biswas, R.; Chakraborty, S.; Natarajan, R.; Isab, A.A.; Dinda, J. Design, Synthesis and Bioactivity Evaluation of Ag(I)-, Au(I)-and Au(III)-Quinoxaline-Wingtip N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes Against Antibiotic Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. ChemMedChem 2024, 19, e202400236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Carabineiro, S.A.; Aureliano, M.; Faleiro, L. Evaluation of Gold Complexes to Address Bacterial Resistance, Quorum Sensing, Biofilm Formation, and Their Antiviral Properties against Bacteriophages. Toxics 2023, 11, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, M.; Checconi, P.; Ceramella, J.; Prezioso, C.; Limongi, D.; Marra, M.; Mariconda, A.; Catalano, A.; De Angelis, M.; Nencioni, L.; et al. Antibacterial and Anti-Influenza Activities of N-Heterocyclic Carbene–Gold Complexes. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Mariconda, A.; Rosano, C.; Scumaci, D.; Saturnino, C.; Longo, P.; Sinicropi, M.S. New Achievements for the Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, J.C.; Wyllie, J.A.; Hamilton, A.; da Costa, T.P.S.; Barnard, P.J. Antibacterial Silver and Gold Complexes of Imidazole and 1,2,4-Triazole Derived N-Heterocyclic Carbenes. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 12056–12070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augello, G.; Azzolina, A.; Rossi, F.; Prencipe, F.; Mangiatordi, G.F.; Saviano, M.; Ronga, L.; Cervello, M.; Tesauro, D. New Insights into the Behavior of NHC-Gold Complexes in Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca, Ö.; Scalcon, V.; Meier-Menches, S.M.; Bonsignore, R.; Brouwer, J.M.J.L.; Tonolo, F.; Folda, A.; Rigobello, M.P.; Kühn, F.E.; Casini, A. Characterization of Hydrophilic Gold(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes as Potent TrxR Inhibitors Using Biochemical and Mass Spectrometric Approaches. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 14237–14250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaaslan, M.G.; Aktaş, A.; Gürses, C.; Gök, Y.; Ateş, B. Chemistry, Structure, and Biological Roles of Au-NHC Complexes as TrxR Inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 95, 103552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.; Albrecht, L.; Balasupramaniam, S.; Misgeld, R.; Karge, B.; Brönstrup, M.; Prokop, A.; Baumann, K.; Reichl, S.; Ott, I.A. A Gold(I) Biscarbene Complex with Improved Activity as a TrxR Inhibitor and Cytotoxic Drug: Comparative Studies with Different Gold Metallodrugs. Metallomics 2019, 11, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetzfried, S.; Kapitza, P.; Gallati, C.M.; Nindl, A.; Cziferszky, M.; Hermann, M.; Wurst, K.; Kircher, B.; Gust, R. Investigations on Reactivity, Stability and Biological Activity of Halido (NHC)gold(I) Complexes. Dalton Tranacts. 2022, 51, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, M.; Podolski-Renić, A.; Krasavin, M.; Pešić, M. The Role of the Thioredoxin Detoxification System in Cancer Progression and Resistance. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 883297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, D.; Karver, M.R.; Fiorillo, E.; Orrú, V.; Stanford, S.M.; Bottini, N.; Barrios, A.M. Gold(I)-Mediated Inhibition of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases: A Detailed in Vitro and Cellular Study. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4790–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trávníček, Z.; Vančo, J.; Čajan, M.; Belza, J.; Popa, I.; Hošek, J.; Lenobel, R.; Dvořák, Z. Gold(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Complexes Containing 6-Mercaptopurine Derivatives and Their In Vitro Anticancer and Anti-Inflammatory Effects. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2024, 38, e7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; Troiano, R.; Mariconda, A.; Catalano, A.; Marra, M.; Saturnino, C.; Rosano, C.; Sinicropi, M.S.; et al. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Multitarget Hybrid Molecules Containing NHC-Au(I) Complexes and Carbazole Moieties. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 277, 116757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marra, M.; Mariconda, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Ceramella, J.; D’Amato, A.; Rosano, C.; Tkachenko, K.; Pellegrino, M.; Aquaro, S.; Sinicropi, M.S.; et al. When Chirality Makes the Difference: The Case of Novel Enanntiopure N-Heterocyclic Carbene–Gold and–Silver Complexes. Molecules 2024, 29, 5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Buthabhak, H.S.; Falasca, V.; Yu, Y.; Sobolev, A.N.; Skelton, B.W.; Moggach, S.A.; Ferro, V.; Al-Salami, H.; Baker, M.V. Au-NHC Complexes with Thiocarboxylate Ligands: Synthesis, Structure, Stability, Thiol Exchange and In Vitro Anticancer Activity. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2024, 38, e6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, J.L.; Ruhayel, R.A.; Barnard, P.J.; Baker, M.V.; Berners-Price, S.J.; Filipovska, A. Mitochondria-Targeted Chemotherapeutics: The Rational Design of gold(I) N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes That Are Selectively Toxic to Cancer Cells and Target Protein Selenols in Preference to Thiols. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12570–12571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Caligiuri, I.; Rizzolio, F.; Pozsoni, N.B.; Van Hecke, K.; Scattolin, T.; Nolan, S.P. Dinuclear NHC–Gold (I)–Thiolato and –Alkynyl Complexes: Synthesis, Anticancer Activity, and Catalytic Activity in Lactonization Reactions. Dalton Transact. 2024, 53, 7939–7945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galassi, R.; Sargentoni, N.; Renzi, S.; Luciani, L.; Bartolacci, C.; Pattabhi, P.; Andreani, C.; Pucciarelli, S. Anticancer Activity of Imidazolyl Gold (I/III) Compounds in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cell Lines. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariconda, A.; Iacopetta, D.; Sirignano, M.; Ceramella, J.; D’Amato, A.; Marra, M.; Pellegrino, M.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Aquaro, S.; Longo, P. Silver and Gold Complexes with NHC-Ligands Derived from Caffeine: Catalytic and Pharmacological Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, R.L.; Santos, I.A.; Fontes, J.V.; Bergamini, F.R.G.; Jardim, A.C.G.; Abbehausen, C. Triphenylphosphine Gold (I) Derivatives Promote Antiviral Effects against the Chikungunya Virus. Metallomics 2022, 14, mfac056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, I.S.; Garcia, M.S.A.; Cassani, N.M.; Oliveira, A.L.C.; Freitas, L.C.F.; Bertolini, V.K.S.; Castro, J.; Clauss, G.; Honorato, J.; Gadelha, F.R.; et al. Exploring Antiviral and antiparasitic Activity of Gold N-Heterocyclic Carbenes with Thiolate Ligands. Dalton Trans. 2024, 53, 18963–18973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Case, J.B.; Rothlauf, P.W.; Chen, R.E.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Kim, A.S.; Bloyet, L.M.; Zeng, Q.; Tahan, S.; Droit, L.; et al. Neutralizing Antibody and Soluble ACE2 Inhibition of a Replication-Competent VSV-SARS-CoV-2 and a Clinical Isolate of SARS-CoV-2. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 475–485.e475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Structure | Compound | Antiviral Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
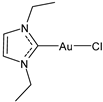 | 17 | IC50 = 6.3 ± 1.6 μM (SARS-CoV PLpro) IC50 = 1.04 ± 0.02 μM (SARS-CoV-2 PLpro) | [33] |
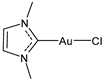 | 18 | IC50 = 0.35 ± 0.11 μM (SARS-CoV PLpro) IC50 = 1.46 ± 0.44 μM (SARS-CoV-2 PLpro) | [33] |
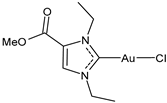 | 19 | IC50 = 0.33 ± 0.11 μM (SARS-CoV PLpro) IC50 = 1.10 ± 0.06 μM (SARS-CoV-2 PLpro) | [33] |
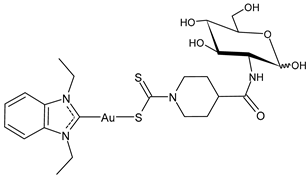 | 20 | IC50 = 0.71 ± 0.05 μM (SARS-CoV PLpro) IC50 = 0.41 ± 0.14 μM (SARS-CoV-2 PLpro) | [33] |
 | 21 | IC50 not given 48.5 (±17.8)% CHIKV inhibition at 10 uM 70% ZIKV inhibition at 10 uM 76.2% MAYV inhibition at 10 uM | [108,109] |
 | 22 | IC50 not given 50.7 (±15.2)% CHIKV inhibition at 10 uM | [108] |
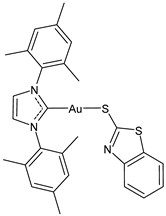 | 23 | IC50 not given 96% ZIKV inhibition at 2 uM 80–90% MAYV inhibition at 2 uM | [109] |
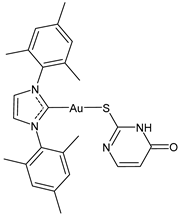 | 24 | IC50 not given 94% ZIKV inhibition at 2 uM 80–90% MAYV inhibition at 2 uM | [109] |
 | 25 | IC50 not given 88,3% ZIKV inhibition at 2 uM 80–90% MAYV inhibition at 2 uM | [109] |
 | 26 | IC50 not given 55% ZIKV inhibition at 2 uM 90% MAYV inhibition at 2 uM | [109] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Checconi, P.; Mariconda, A.; Catalano, A.; Ceramella, J.; Pellegrino, M.; Aquaro, S.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Longo, P. Searching for New Gold(I)-Based Complexes as Anticancer and/or Antiviral Agents. Molecules 2025, 30, 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081726
Checconi P, Mariconda A, Catalano A, Ceramella J, Pellegrino M, Aquaro S, Sinicropi MS, Longo P. Searching for New Gold(I)-Based Complexes as Anticancer and/or Antiviral Agents. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081726
Chicago/Turabian StyleChecconi, Paola, Annaluisa Mariconda, Alessia Catalano, Jessica Ceramella, Michele Pellegrino, Stefano Aquaro, Maria Stefania Sinicropi, and Pasquale Longo. 2025. "Searching for New Gold(I)-Based Complexes as Anticancer and/or Antiviral Agents" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081726
APA StyleChecconi, P., Mariconda, A., Catalano, A., Ceramella, J., Pellegrino, M., Aquaro, S., Sinicropi, M. S., & Longo, P. (2025). Searching for New Gold(I)-Based Complexes as Anticancer and/or Antiviral Agents. Molecules, 30(8), 1726. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081726












