Identification of Novel Compounds That Bind to the HGF β-Chain In Silico, Verification by Molecular Mechanics and Quantum Mechanics, and Validation of Their HGF Inhibitory Activity In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
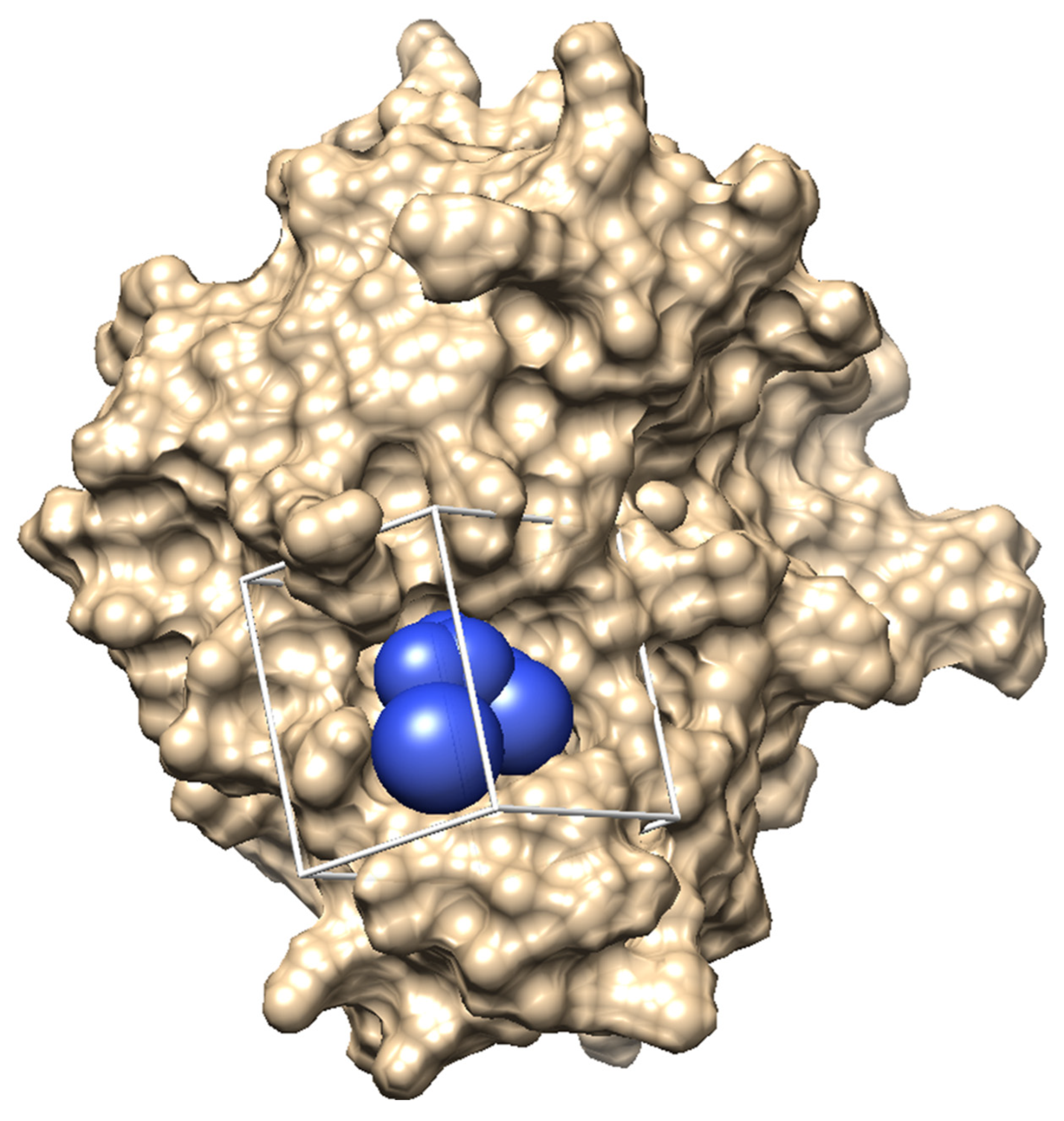
2.1. Interface Pocket in the HGF β-Chain That Binds to the Met Sema Domain
2.2. In Silico Exploration of the HGF β-Chain-Binding Compounds
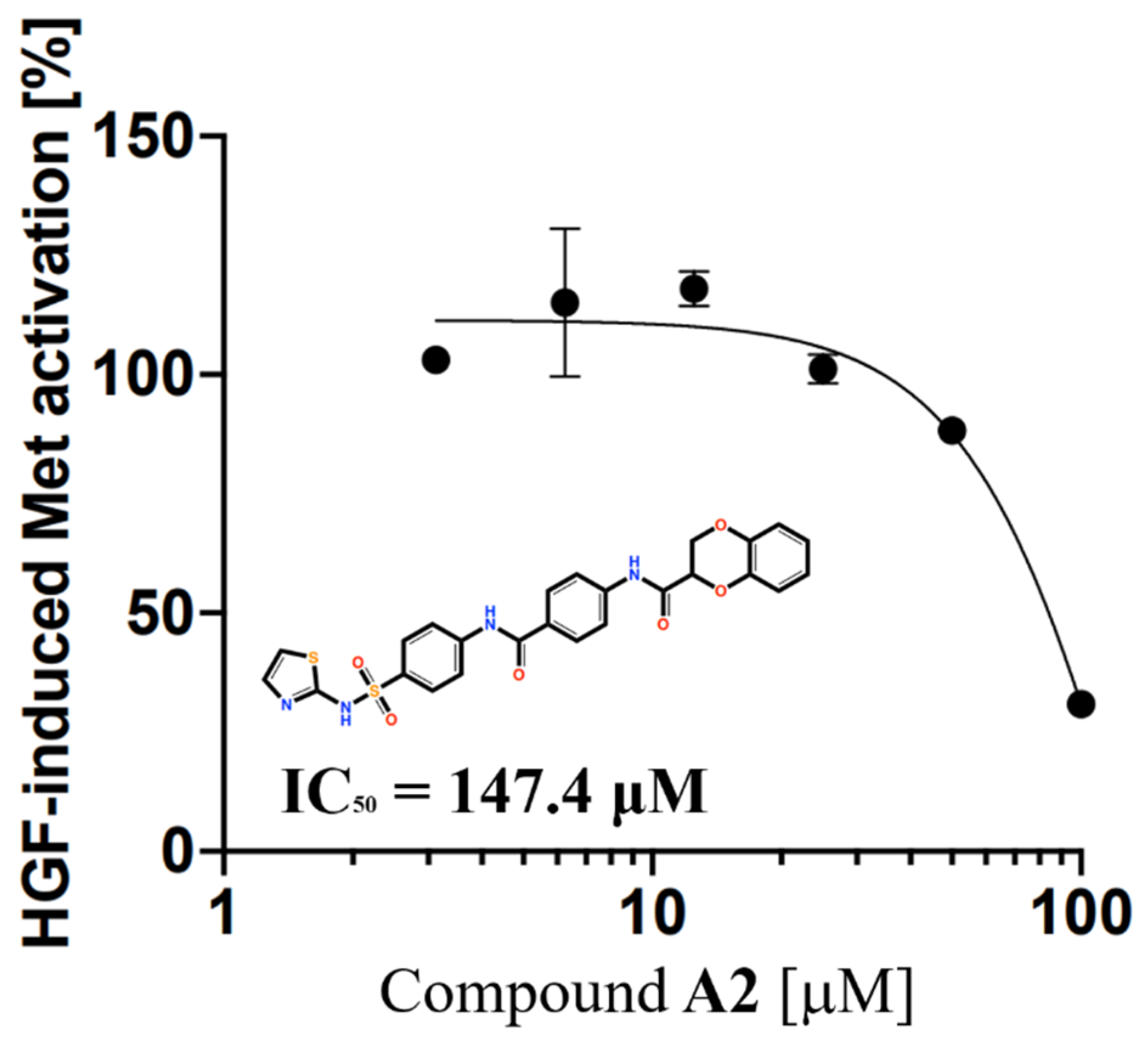
2.3. Experimental Validation of HGF Inhibition by Compounds Using pMet ELISA
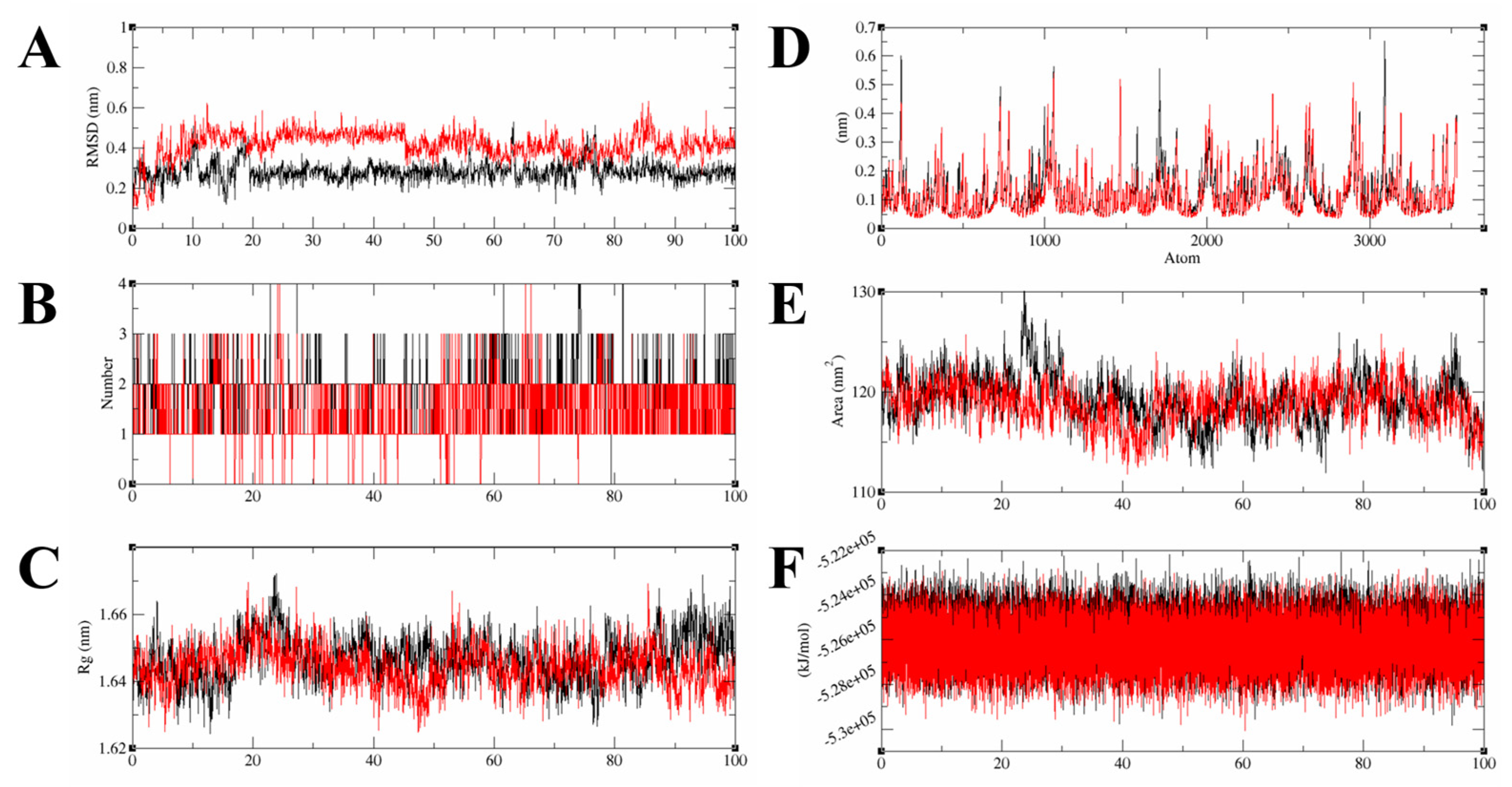
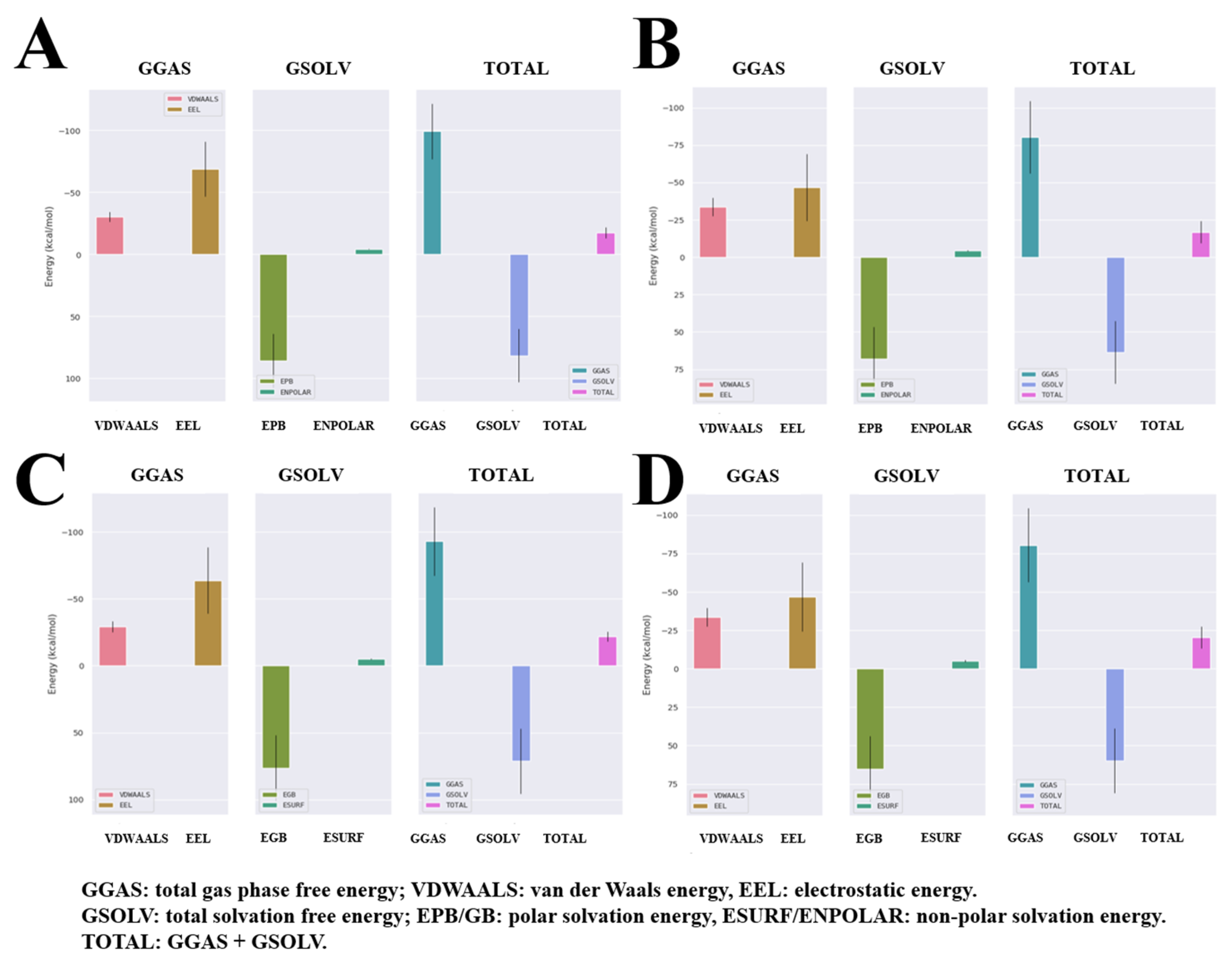
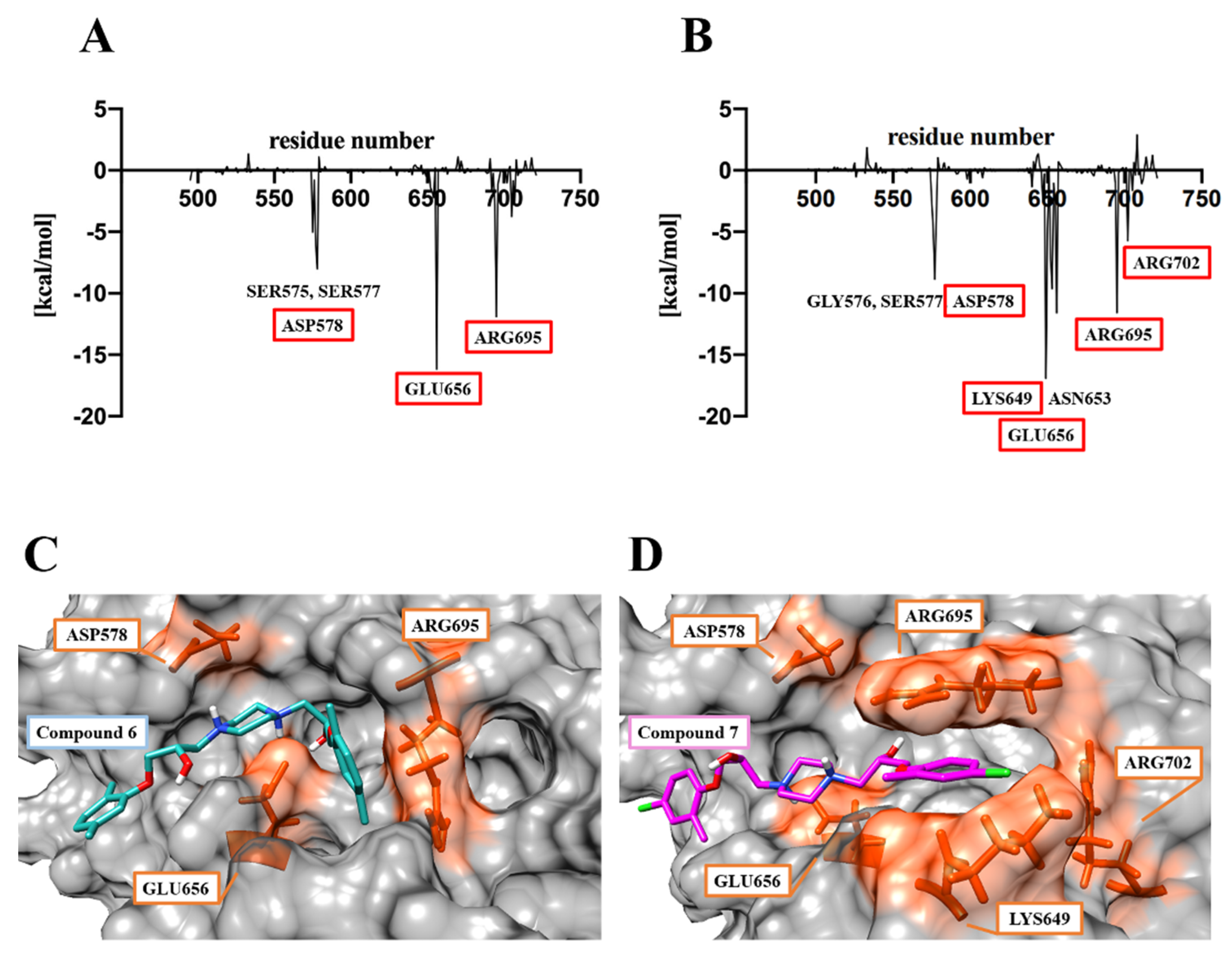
2.4. Molecular Dynamics Analysis for the Complex Structures of the HGF β-Chain and Compound 6/7
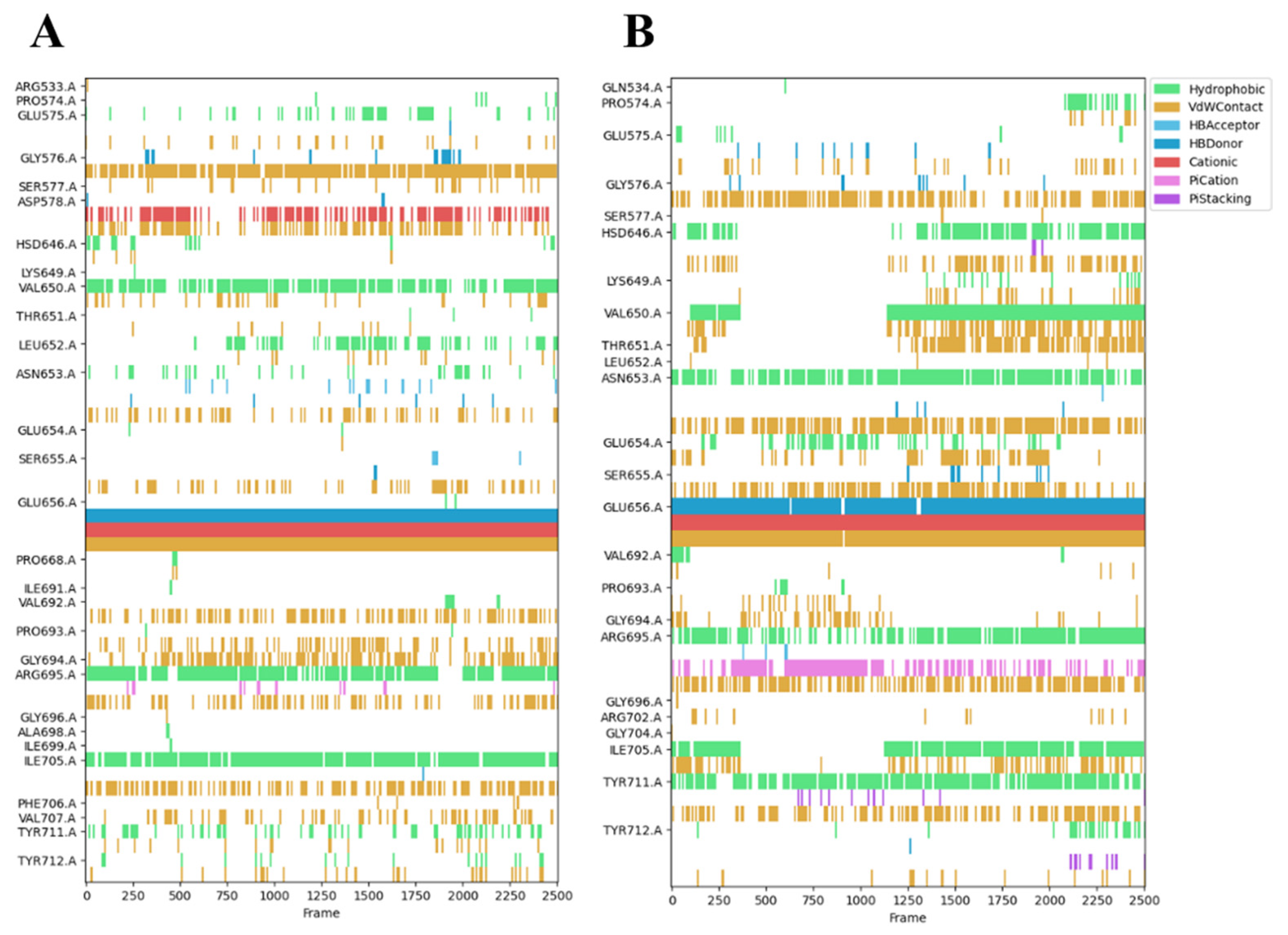
2.5. Analysis of the Binding Mode of Compound 6 and Compound 7 to the HGF β-Chains
2.6. ADME–Tox Predictions for Compound 6 and Compound 7
2.7. Structure and Activity Relationships of Compound 6 and Compound 7 Analogs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. The HGF β Structure
3.2. 3D Chemical Structure Library for SBDS
3.3. Hierarchical In Silico SBDS
3.4. pMet ELISA
3.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.6. MDS Trajectory Data Analysis
3.7. Ab Initio FMO Calculations
3.8. Prediction of ADME–Tox
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakai, K.; Aoki, S.; Matsumoto, K. Hepatocyte growth factor and Met in drug discovery. J. Biochem. 2015, 157, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottaro, D.P.; Rubin, J.S.; Faletto, D.L.; Chan, A.M.-L.; Kmiecik, T.E.; Vande Woude, G.F.; Aaronson, S.A. Identification of the Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor As the c-met Proto-Oncogene Product. Science 1991, 251, 802–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrini, I. Biology of MET: A double life between normal tissue repair and tumor progression. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, O.; Pillozzi, S.; Deakin, J.A.; Carafoli, F.; Kemp, L.; Butler, P.J.G.; Lyon, M.; Gherardi, E. Insights into the Structure/Function of Hepatocyte Growth Factor/Scatter Factor from Studies with Individual Domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 367, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamos, J.; Lazarus, R.A.; Yao, X.; Kirchhofer, D.; Wiesmann, C. Crystal Structure of the HGF β-Chain in Complex with the Sema Domain of the Met Receptor. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2325–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kim, H. Progress of antibody-based inhibitors of the HGF–cMET axis in cancer therapy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, J.E.; Saba, N.F.; Roe, D.; Bauman, J.R.; Kaczmar, J.; Bhatia, A.; Muzaffar, J.; Julian, R.; Wang, S.; Bearelly, S.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Ficlatuzumab with or Without Cetuximab in Pan-Refractory, Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3851–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taira, J.; Yamaguchi, M.; Tashiro, A.; Kida, A.; Suzuki, K.; Sakai, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Aoki, S. Computer-Assisted Identification of Inhibitor with Novel Pharmacophore Targeting First Kringle Domain of Hepatocyte Growth Factor. ChemistrySelect 2023, 8, e202301577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, M.; Ma, X.; Maun, H.R.; Zheng, Z.; Peng, J.; Romero, M.; Huang, A.; Yang, N.Y.; Nishimura, M.; Greve, J.; et al. Monovalent Antibody Design and Mechanism of Action of Onartuzumab, a MET Antagonist with Anti-Tumor Activity as a Therapeutic Agent. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, e2987–e2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, W.J.; Balius, T.E.; Mukherjee, S.; Brozell, S.R.; Moustakas, D.T.; Lang, P.T.; Case, D.A.; Kuntz, I.D.; Rizzo, R.C. DOCK 6: Impact of new features and current docking performance. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 1132–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol. 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, K.; Passioura, T.; Sato, H.; Ito, K.; Furuhashi, H.; Umitsu, M.; Takagi, J.; Kato, Y.; Mukai, H.; Warashina, S. Macrocyclic peptide-based inhibition and imaging of hepatocyte growth factor. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, B.R.; McGee, T.D.; Swails, J.M.; Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H.; Roitberg, A.E. MMPBSA.py: An efficient program for end-state free energy calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. Gmx_MMPBSA: A New Tool to Perform End-State Free Energy Calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouysset, C.; Fiorucci, S. ProLIF: A Library to Encode Molecular Interactions as Fingerprints. J. Cheminform. 2021, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaura, K.; Ikeo, E.; Asada, T.; Nakano, T.; Uebayasi, M. Fragment Molecular Orbital Method: An Approximate Computational Method for Large Molecules. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1999, 313, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phusi, N.; Hashimoto, Y.; Otsubo, N.; Imai, K.; Thongdee, P.; Sukchit, D.; Kamsri, P.; Punkvang, A.; Suttisintong, K.; Pungpo, P.; et al. Structure-Based Drug Design of Novel M. Tuberculosis InhA Inhibitors Based on Fragment Molecular Orbital Calculations. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 152, 106434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A Free Web Tool to Evaluate Pharmacokinetics, Drug-Likeness and Medicinal Chemistry Friendliness of Small Molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Eckert, A.O.; Schrey, A.K.; Preissner, R. ProTox-II: A Webserver for the Prediction of Toxicity of Chemicals. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W257–W263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, S.; Cozza, G.; Moro, S. Medicinal chemistry and the molecular operating environment (MOE): Application of QSAR and molecular docking to drug discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1555–1572. Available online: https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ben/ctmc/2008/00000008/00000018/art00002 (accessed on 6 February 2025). [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Shah, S. Structure-based virtual screening. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1558, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, D.K.; Kuntz, I.D. Surface Solid Angle-Based Site Points for Molecular Docking. 1998. Available online: http://psb.stanford.edu/psb-online/proceedings/psb98/hendrix.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2025).
- Kawamoto, S.; Hori, C.; Taniguchi, H.; Okubo, S.; Aoki, S. Identification of novel antimicrobial compounds targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis shikimate kinase using in silico hierarchical structure-based drug screening. Tuberculosis 2023, 141, 102362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J.C. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1–2, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, B.R.; Brooks, C.L., III; MacKerell, A.D., Jr.; Nilsson, L.; Petrella, R.J.; Roux, B.; Won, Y.; Archontis, G.; Bartels, C.; Boresch, S.; et al. CHARMM: The biomolecular simulation program. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 1545–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI input generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM simulations using the CHARMM36 additive force field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Rauscher, S.; Nawrocki, G.; Ran, T.; Feig, M.; de Groot, B.L.; Grubmüller, H.; MacKerell, A.D. CHARMM36m: An Improved Force Field for Folded and Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, B.; Bekker, H.; Berendsen, H.J.C.; Fraaije, J.G.E.M. LINCS: A Linear Constraint Solver for Molecular Simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 1997, 18, 1463–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darden, T.; York, D.; Pedersen, L. Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅log(N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 98, 10089–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Greene, D.; Xiao, L.; Qi, R.; Luo, R. Recent Developments and Applications of the MMPBSA Method. Front Mol Biosci. 2018, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Mochizuki, Y.; Komeiji, Y.; Okiyama, Y.; Fukuzawa, K. Electron-correlated fragment-molecular-orbital calculations for biomolecular and nano systems. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 10310–10344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Fukuzawa, K.; Mochizuki, Y.; Amari, S.; Nakano, T. BioStation Viewer: Analysis and Visualization for Interactions of Bio-Macromolecules. J. Vis. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 26, 124–129_1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suzuki, K.; Inoue, K.; Namiguchi, R.; Morita, S.; Hayakawa, S.; Yokota, M.; Sakai, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Aoki, S. Identification of Novel Compounds That Bind to the HGF β-Chain In Silico, Verification by Molecular Mechanics and Quantum Mechanics, and Validation of Their HGF Inhibitory Activity In Vitro. Molecules 2025, 30, 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081801
Suzuki K, Inoue K, Namiguchi R, Morita S, Hayakawa S, Yokota M, Sakai K, Matsumoto K, Aoki S. Identification of Novel Compounds That Bind to the HGF β-Chain In Silico, Verification by Molecular Mechanics and Quantum Mechanics, and Validation of Their HGF Inhibitory Activity In Vitro. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081801
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuzuki, Ko, Keitaro Inoue, Ryota Namiguchi, Seiya Morita, Suzuho Hayakawa, Mikuri Yokota, Katsuya Sakai, Kunio Matsumoto, and Shunsuke Aoki. 2025. "Identification of Novel Compounds That Bind to the HGF β-Chain In Silico, Verification by Molecular Mechanics and Quantum Mechanics, and Validation of Their HGF Inhibitory Activity In Vitro" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081801
APA StyleSuzuki, K., Inoue, K., Namiguchi, R., Morita, S., Hayakawa, S., Yokota, M., Sakai, K., Matsumoto, K., & Aoki, S. (2025). Identification of Novel Compounds That Bind to the HGF β-Chain In Silico, Verification by Molecular Mechanics and Quantum Mechanics, and Validation of Their HGF Inhibitory Activity In Vitro. Molecules, 30(8), 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081801





