Occurrence and Ecological Risks of Neonicotinoids in Wheat, Corn and Rice Field Soils in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Occurrence of NEOs in Soil Samples
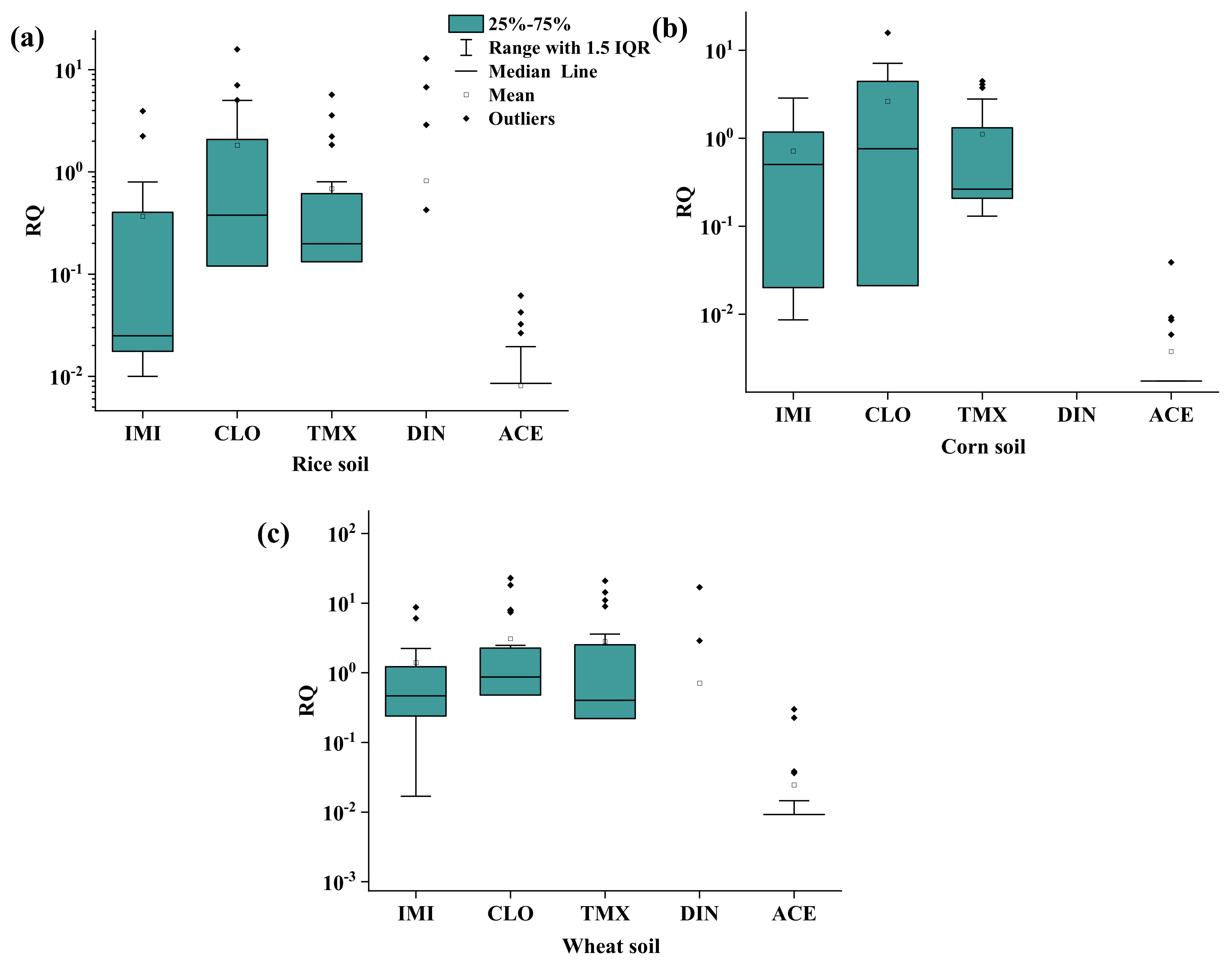
2.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
3. Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents
3.2. Sample Extraction and Analysis
3.3. Quality Assurance and Quality Control
3.4. Ecological Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R. Neonicotinoids—From zero to hero in insecticide chemistry. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsafran, M.; Rizwan, M.; Usman, K.; Saleem, M.H.; Al Jabri, H. Neonicotinoid insecticides in the environment: A critical review of their distribution, transport, fate, and toxic effects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Bayo, F. The trouble with neonicotinoids. Science 2014, 346, 806–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, M.J.; Capel, P.D.; Arnold, W.A. Neonicotinoid insecticides in surface water, groundwater, and wastewater across Land-Use gradients and potential effects. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 1017–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Jia, C.; Jing, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, P.; He, M.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhao, E. Occurrence and dietary risk assessment of 37 pesticides in wheat fields in the suburbs of Beijing, China. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 129245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hu, H.; Wu, R.; Ling, J.; Yue, R.; Yang, D.; Yu, W.; Du, W.; Shen, G. Neonicotinoid pollution in marine sediments of the East China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 842, 156658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehle, S.; Ovcharova, V.; Wolfram, J.; Bub, S.; Herrmann, L.Z.; Petschick, L.L.; Schulz, R. Neonicotinoid insecticides in global agricultural surface waters-Exposure, risks and regulatory challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 867, 161383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose Climent, M.; Herrero-Hernandez, E.; Jesus Sanchez-Martin, M.; Sonia Rodriguez-Cruz, M.; Pedreros, P.; Urrutia, R. Residues of pesticides and some metabolites in dissolved and particulate phase in surface stream water of Cachapoal River basin, central Chile. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 251, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaun, O.; Rodríguez, J.G.; Menchaca, I.; Lopez-Garcia, E.; Martínez, E.; Zonja, B.; Postigo, C.; Lopez de Alda, M.; Barcelo, D.; Borja, A.; et al. Contaminants of emerging concern in the Basque coast (N Spain): Occurrence and risk assessment for a better monitoring and management decisions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 765, 142765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, B.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wang, F.; Sui, Q.; Chen, Z.; Xu, D.; et al. Occurrence, source and ecotoxicological risk assessment of pesticides in surface water of Wujin District (northwest of Taihu Lake), China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 114953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satiroff, J.A.; Messer, T.L.; Mittelstet, A.R.; Snow, D.D. Pesticide occurrence and persistence entering recreational lakes in watersheds of varying land uses. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 273, 116399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonmatin, J.; Noome, D.A.; Moreno, H.; Mitchell, E.A.D.; Glauser, G.; Soumana, O.S.; van Lexmond, M.B.; Sanchez-Bayo, F. A survey and risk assessment of neonicotinoids in water, soil and sediments of Belize. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 249, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmatin, J.M.; Giorio, C.; Girolami, V.; Goulson, D.; Kreutzweiser, D.P.; Krupke, C.; Liess, M.; Long, E.; Marzaro, M.; Mitchell, E.A.D.; et al. Environmental fate and exposure; Neonicotinoids and fipronil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 35–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaafsma, A.; Limay-Rios, V.; Xue, Y.; Smith, J.; Baute, T. Field-scale examination of neonicotinoid insecticide persistence in soil as a result of seed treatment use in commercial maize (corn) fields in southwestern Ontario. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmatin, J.; Mitchell, E.A.D.; Glauser, G.; Lumawig-Heitzman, E.; Claveria, F.; van Lexmond, M.B.; Taira, K.; Sanchez-Bayo, F. Residues of neonicotinoids in soil, water and people’s hair: A case study from three agricultural regions of the Philippines. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 757, 143822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.; Harrington, P.; Turnbull, G. Neonicotinoid concentrations in arable soils after seed treatment applications in preceding years. Pest Manag. Sci. 2014, 70, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankyi, E.; Gordon, C.; Carboo, D.; Apalangya, V.A.; Fomsgaard, I.S. Sorption and degradation of neonicotinoid insecticides in tropical soils. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B-Pestic. Food Contam. Agric. Wastes 2018, 53, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, A.R.; Webb, E.B.; Goyne, K.W.; Mengel, D. Neonicotinoid insecticides negatively affect performance measures of non-target terrestrial arthropods: A meta-analysis. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, M.; Stara, A.; Aliko, V.; Faggio, C. Impact of Neonicotinoids to Aquatic Invertebrates-In Vitro Studies on Mytilus galloprovincialis: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Wen, R.; Zhang, H.; Wan, X.; Wang, X.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Ying, G.; et al. Inference of emission history of neonicotinoid pesticides from marine sediment cores impacted by riverine runoff of a developed agricultural region: The Pearl River Basin, China. Water Res. 2022, 218, 118475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, T.; Ning, M.; Liang, J.; Guan, S.; Fang, L.; Ding, R.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Dong, Z. Pollution characteristics and non-dietary human cumulative risk assessment of neonicotinoids in vegetable greenhouse soils: A case study in Shandong Province, China. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zhang, J.; Tang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, J. Persistence and vertical distribution of neonicotinoids in soils under different citrus orchards chrono sequences from southern China. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.; Yu, B.; Wang, D.; Zhao, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, J. Comparison of neonicotinoid residues in soils of different land use types. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 782, 146803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Zeng, E. The human and ecological risks of neonicotinoid insecticides in soils of an agricultural zone within the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 284, 117358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul, K.; Wu, C.; Man, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, F.; Zheng, Y. Residue behavior of imidacloprid FS formulation in peanut cultivation system in china and its dietary and ecological risk assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 47, 35. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.; He, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Meng, F.; Wang, L.; Xu, F. Residual concentrations and ecological risks of neonicotinoid insecticides in the soils of tomato and cucumber greenhouses in Shouguang, Shandong Province, East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 140248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Huang, X.; Guo, X.; Jia, C.; Li, B.; Zhao, E.; Wu, J. Efficient degradation of imidacloprid in soil by thermally activated persulfate process: Performance, kinetics, and mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 241, 113815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vryzas, Z.; Alexoudis, C.; Vassiliou, G.; Galanis, K.; Papadopoulou-Mourkidou, E. Determination and aquatic risk assessment of pesticide residues in riparian drainage canals in northeastern Greece. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2011, 74, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, D.J.; Okada, E.; Iturburu, F.G.; De Geronimo, E.; Canton, G.; Aparicio, V.C.; Costa, J.L.; Menone, M.L. Monensin occurrence in surface water and its impact on aquatic biota in a stream of the southeast Pampas, Argentina. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 8530–8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprague, J.B. Measurement of pollutant toxicity to fish—III: Sublethal effects and “safe” concentrations. Water Res. 1971, 5, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Bayo, F.; Baskaran, S.; Kennedy, I.R. Ecological relative risk (EcoRR): Another approach for risk assessment of pesticides in agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasickova, J.; Hvezdova, M.; Kosubova, P.; Hofman, J. Ecological risk assessment of pesticide residues in arable soils of the Czech Republic. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, W.J.; Sibley, P.K.; Prosser, R.S. Comparison of Established and Novel Insecticides on survival and reproduction of Folsomia candida. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2023, 42, 1516–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Yu, C.; Lin, R.; Hou, Y.; Li, M.; Liang, H.; Chen, L.; Gao, X.; Chen, S. Ecotoxicological effects of the neonicotinoid insecticide dinotefuran on springtails (Folsomia candida) at soil residual concentration. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2025, 209, 106345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akeju, T.O. Assessment of the Effects of the Neonicotinoids Thiacloprid and Acetamiprid on Soil Fauna. Master’s Thesis, Universidade de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Mao, L.; Jiang, H. Oxidative stress of imidaclothiz on earthworm Eisenia fetida. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 191, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Xiao, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yan, H.; Wu, R.; Xin, X.; Wang, D.; Yu, X. Sub-Lethal effects of six neonicotinoids on avoidance behavior and reproduction of earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xiong, K.; Chen, A.; Li, F. Toxicity of a novel neonicotinoid insecticide paichongding to earthworm Eisenia fetida. Soil Sediment Contam. 2016, 26, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Wang, D.; Zhu, L.; Teng, M.; Wang, C.; Xue, X.; Wu, L. Effects of a novel neonicotinoid insecticide cycloxaprid on earthworm, Eisenia fetida. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 14138–14147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
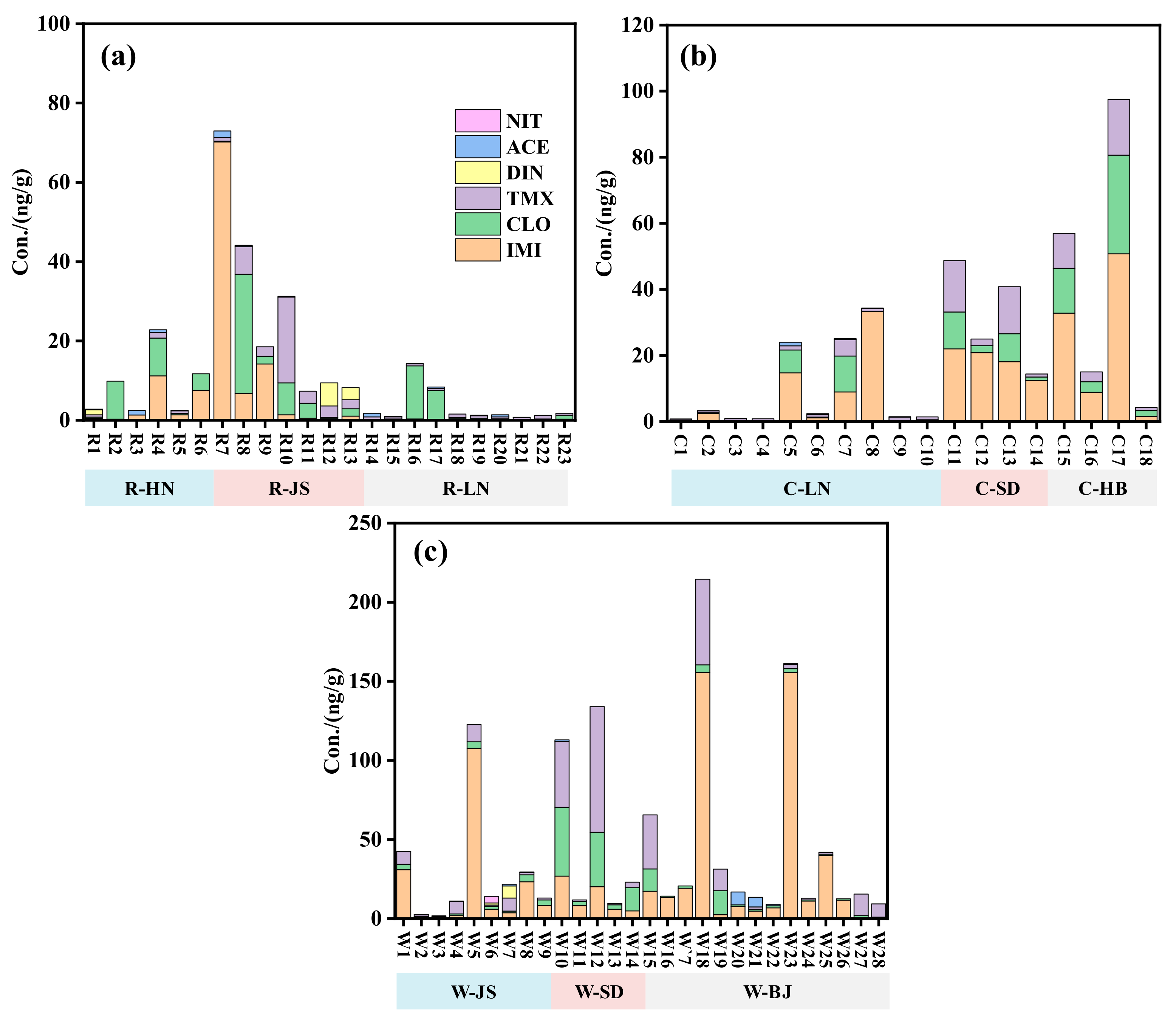

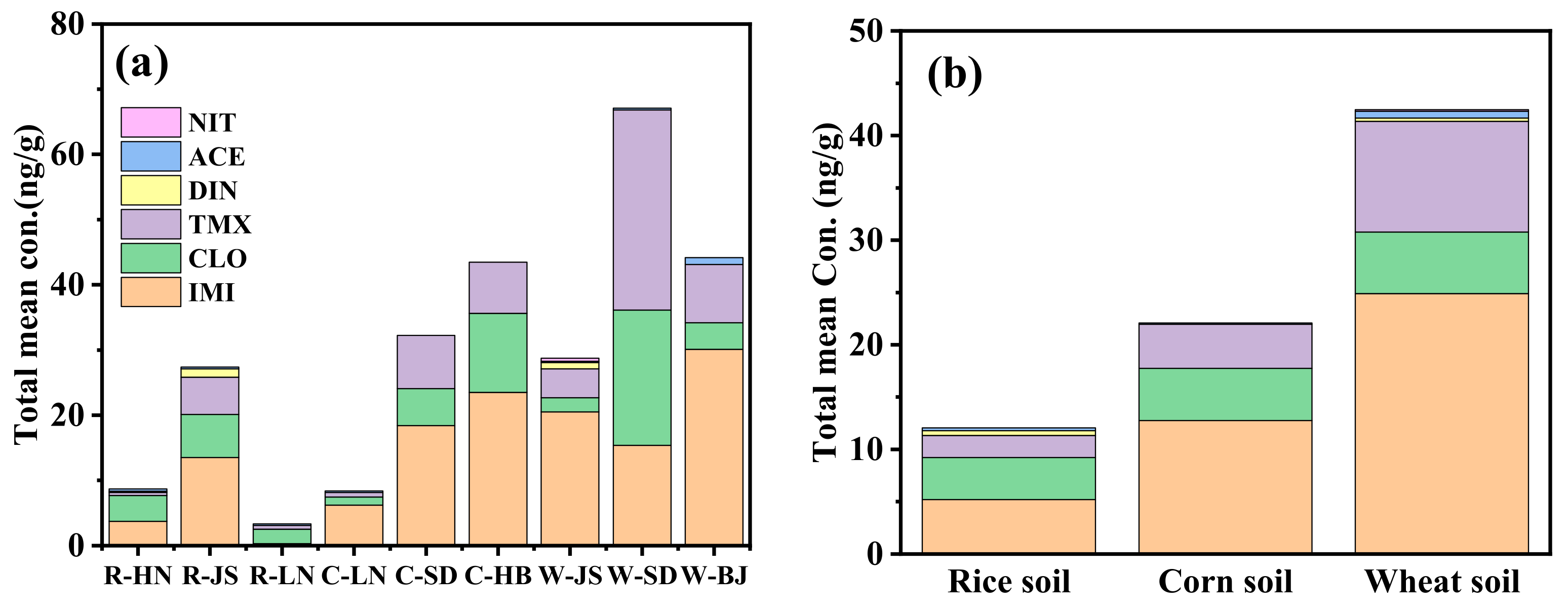

| Soil Type | IMI | CLO | TMX | DIN | ACE | NIT | IMTH | THIA | CYC | IPP | ΣNEOs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rice field | DF (%) | 100 | 78.3 | 87.0 | 13.0 | 56.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Maximum | 70.20 | 30.09 | 21.63 | 5.81 | 1.66 | 72.97 | ||||||
| Minimum | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.48 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 0.75 | ||||||
| Median | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.63 | <LOD | <LOQ | 7.35 | ||||||
| Mean | 5.21 | 4.02 | 2.12 | 0.44 | 0.26 | 12.05 | ||||||
| Corn field | DF (%) | 100 | 83.3 | 100 | 0 | 38.9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Maximum | 50.75 | 29.88 | 16.90 | 1.05 | 97.53 | |||||||
| Minimum | 0.15 | <LOQ | 1.00 | <LOD | 0.79 | |||||||
| Median | 8.94 | 1.44 | 4.23 | <LOD | 14.73 | |||||||
| Mean | 12.76 | 4.99 | 1.85 | 0.10 | 22.08 | |||||||
| Wheat field | DF (%) | 100 | 96.4 | 82.1 | 7.1 | 42.9 | 3.6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Maximum | 155.70 | 43.46 | 79.39 | 7.58 | 8.10 | 4.11 | 214.55 | |||||
| Minimum | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.48 | <LOQ | <LOQ | 4.11 | 1.77 | |||||
| Median | 8.32 | 1.65 | 1.52 | <LOD | <LOD | <LOD | 16.20 | |||||
| Mean | 109.61 | 5.86 | 10.60 | 0.30 | 0.66 | 0.15 | 42.47 |
| Location | Soil Samples | IMI | TMX | CLO | ACE | THIA | DIN | NIT | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Belize | Crop soil Fallow soil | 2.65 ± 2.42 0.118 ± 0.213 | 0.138 ± 0.309 0.035 ± 0.059 | 0.326 ± 0.728 0.199 ± 0.355 | 0.019 ± 0.042 0.004 ± 0.011 | [12] | |||
| Philippines | Sweet peas soil Rice soil, banana, citrus soil | 0.758 0.013 1.048 | 0.005 0.005 0.278 | 0.022 n.d. a 1.430 | 0.002 n.d. n.d. | [15] | |||
| Ontario, Canada | Maize soil, 2013 Maize soil, 2014 | Σ2 NEOs, 4.0 ± 1.1 Σ2 NEOs, 5.6 ± 0.9 | [14] | ||||||
| England | Arable soil | <0.09–10.7 | <0.02–1.50 | 0.02–13.6 | [16] | ||||
| Shandong, China | Celery soil Cucumber soil Pepper soil Tomato soil | 0.49–2.38 × 103 0.52–5.32 × 103 n.d.-2.80 × 103 0.41–2.62 × 103 | n.d.-1.21 × 103 1.03–8.56 × 103 n.d.-1.78 × 103 n.d.-1.82 × 103 | 0.24–2.36 × 103 n.d.-3.39 × 103 3.48–1.07 × 103 0.36–1.29 × 103 | n.d.-2.03 n.d.-15.6 0.13–81.7 n.d.-115 | n.d. n.d.-0.07 n.d.-0.07 n.d.-0.04 | n.d.-35.1 n.d.-1.09 × 103 n.d.-1.76 × 103 0.12–119 | n.d.-9.81 n.d.-1.28 × 103 n.d.-54.3 n.d.-12.8 | [21] |
| Southern China | Citrus orchards soil | Σ5NEOs, 0–25.76 | [22] | ||||||
| Tianjin, China | Land soil (spring) Land soil (fall) | 0.74–1.06 × 103 n.d.-2.61 × 103 | n.d.-1.56 × 103 n.d.-2.32 × 103 | n.d.-74.6 n.d.-1.32 × 103 | 0.19–4.40 × 103 0.19–31.9 | n.d.-18.2 n.d.-0.14 | n.d.-3.28 n.d.-1.35 | [23] | |
| Beijing, China | Wheat field soil | n.d.-5.33 × 103 | <1.0–1.22 × 103 | [5] | |||||
| Six provinces, China | Rice field soil Cron field soil Wheat field soil | 0.18–70.20 0.15–50.75 0.30–155.70 | 0.48–21.63 1.00–16.90 0.48–79.39 | 0.19–30.09 <0.08–29.88 0.30–43.46 | n.d.-1.66 n.d.-1.05 n.d.-8.10 | n.d. n.d. n.d. | n.d.-5.81 n.d.-7.58 n.d. | n.d. n.d. n.d.-4.11 | The present study |
| Pesticides | Abbr. | Formula | R.T. (min) | Ionization Mode | Precursor Ion (m/z) | C.V. (V) | Quantitative Ion (m/z) | C.E. (V) | Qualitative Ion (m/z) | C.E. (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Imidacloprid | IMI | C9H10ClN5O2 | 2.45 | ESI+ | 255.95 | 26 | 175.03 | 28 | 209.28 | 16 |
| Clothianidin | CLO | C6H8ClN5O2S | 2.36 | ESI+ | 249.97 | 18 | 168.92 | 16 | 131.93 | 22 |
| Thiamethoxam | TMX | C8H10ClN5O3S | 2.19 | ESI+ | 291.98 | 18 | 211.01 | 18 | 180.98 | 34 |
| Dinotefuran | DIN | C7H14N4O3 | 1.10 | ESI+ | 203.07 | 20 | 129.06 | 16 | 87.06 | 22 |
| Acetamiprid | ACE | C10H11ClN4 | 2.53 | ESI+ | 223.03 | 16 | 125.94 | 28 | 90.05 | 44 |
| Thiacloprid | THIA | C10H9ClN4S | 2.74 | ESI+ | 252.99 | 20 | 125.99 | 32 | 98.96 | 54 |
| Imidaclothiz | IMTH | C7H8ClN5O2S | 2.52 | ESI+ | 261.98 | 26 | 180.94 | 14 | 122.17 | 28 |
| Nitenpyram | NIT | C11H15ClN4O2 | 1.08 | ESI+ | 270.99 | 26 | 224.99 | 12 | 98.90 | 14 |
| Cycloxaprid | CYC | C14H15ClN4O3 | 2.13 | ESI+ | 323.05 | 30 | 276.99 | 14 | 151.01 | 24 |
| Paichongding | IPP | C17H23CIN4O3 | 2.68 | ESI+ | 367.11 | 32 | 137.04 | 26 | 321.05 | 12 |
| Compound | Eisenia fetida (mg kg−1) | Folsomia candida (mg kg−1) | Hypoaspis aculeifer (mg kg−1) | CC (mg kg−1) | AF | PNEC (mg kg−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMI | ≥0.178 | 1.25 | >2.67 | 0.178 | 10 | 0.0178 | PPDB |
| CLO | 2.5 | 0.19 (EC50) | n.d.a | 0.19 | 100 | 0.0019 | PPDB, [33] |
| TMX | 5.34 | 0.38 (EC50) | n.d.a | 0.38 | 100 | 0.0038 | PPDB, [33] |
| DIN | 0.2 | 0.045 (EC50) | n.d.a | 0.045 | 100 | 0.00045 | PPDB, [34] |
| ACE | 1.26 | 0.27 | 454 | 0.27 | 10 | 0.027 | PPDB, [35] |
| THIA | 0.185 | 10 | 1600 | 0.185 | 10 | 0.0185 | PPDB, [35] |
| IMTH | 1.41 (LC50) | n.d.a | n.d.a | 1.41 (LC50) | 1000 | 0.00141 | [36] |
| NIT | 1.32 (EC50) | n.d.a | n.d.a | 1.32 (EC50) | 1000 | 0.00132 | [37] |
| CYC | 10.21 (LC50) | n.d.a | n.d.a | 10.21 (LC50) | 1000 | 0.01021 | [38] |
| PCD | 541.07 (LC50) | n.d.a | n.d.a | 541.07 (LC50) | 1000 | 0.54107 | [39] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, J.; Yu, P.; Zou, Z.; Zhao, E.; Jing, J.; Zhang, J.; Tao, Y.; Ren, L.; He, M.; Chen, L.; et al. Occurrence and Ecological Risks of Neonicotinoids in Wheat, Corn and Rice Field Soils in China. Molecules 2025, 30, 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081803
Wu J, Yu P, Zou Z, Zhao E, Jing J, Zhang J, Tao Y, Ren L, He M, Chen L, et al. Occurrence and Ecological Risks of Neonicotinoids in Wheat, Corn and Rice Field Soils in China. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081803
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Junxue, Pingzhong Yu, Ziyu Zou, Ercheng Zhao, Junjie Jing, Jinwei Zhang, Yan Tao, Lirui Ren, Min He, Li Chen, and et al. 2025. "Occurrence and Ecological Risks of Neonicotinoids in Wheat, Corn and Rice Field Soils in China" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081803
APA StyleWu, J., Yu, P., Zou, Z., Zhao, E., Jing, J., Zhang, J., Tao, Y., Ren, L., He, M., Chen, L., & Han, P. (2025). Occurrence and Ecological Risks of Neonicotinoids in Wheat, Corn and Rice Field Soils in China. Molecules, 30(8), 1803. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081803






