A Comparison of Methods for Assessing the Antioxidant Expression in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
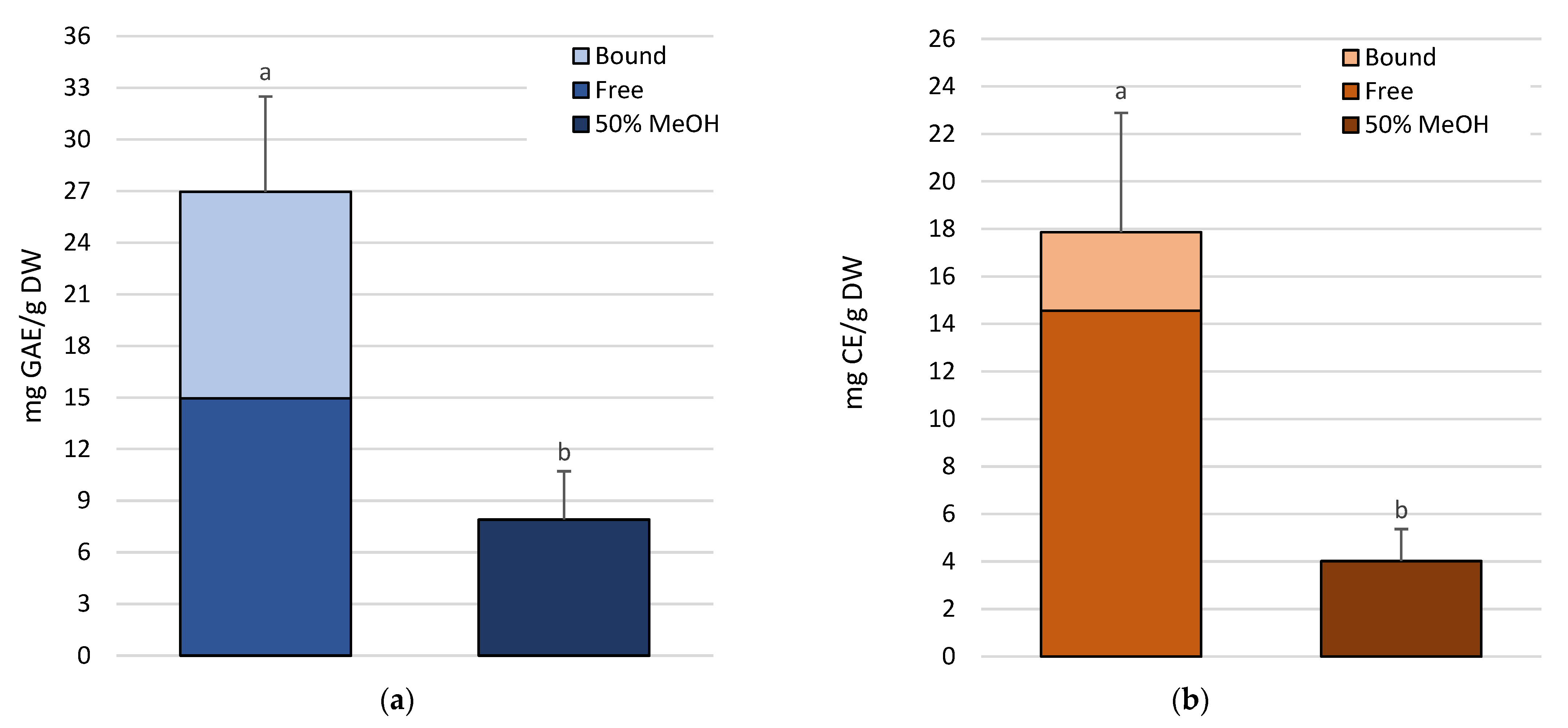
2.1. Polyphenols Extraction and Quantification
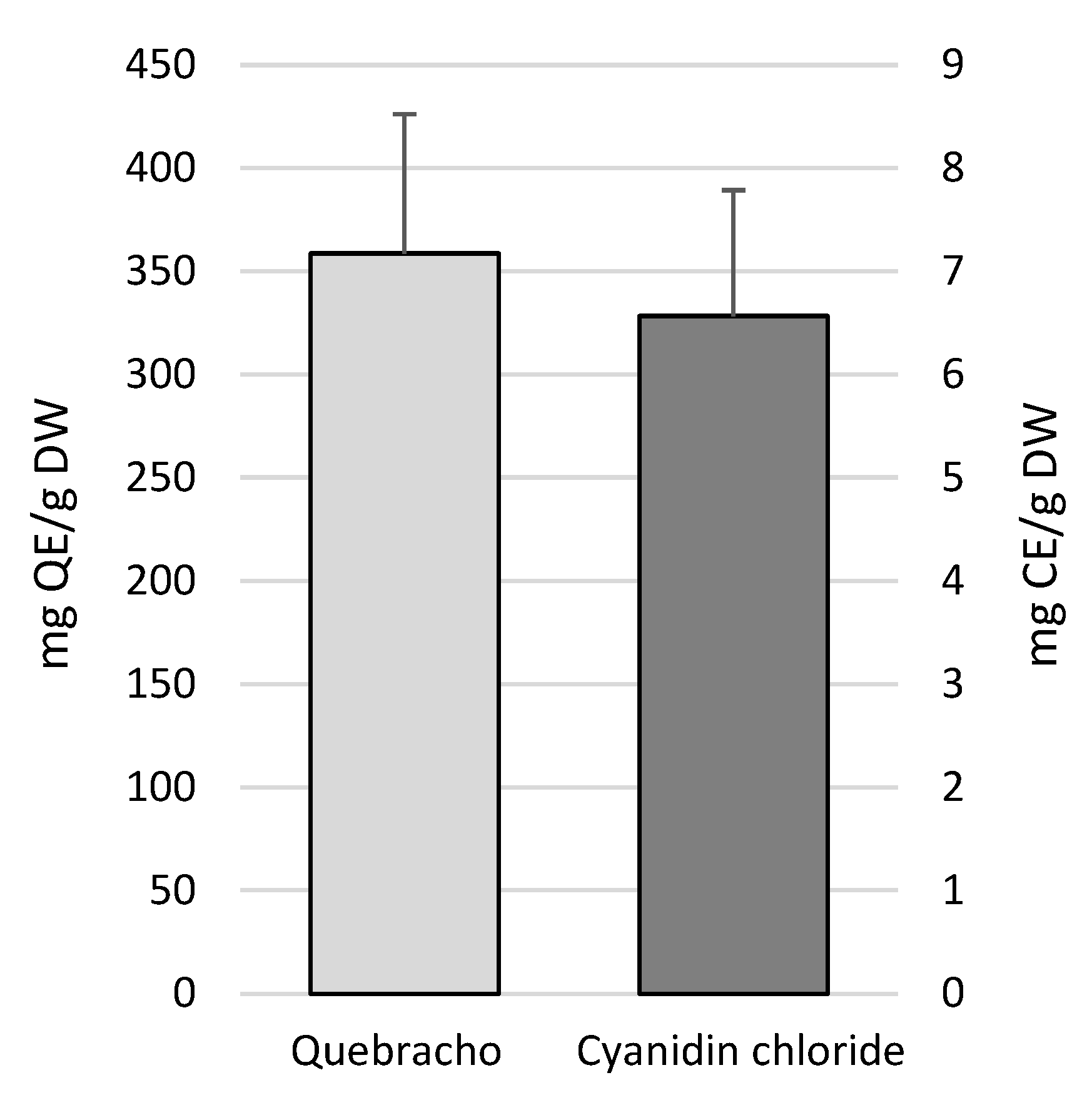
2.2. Condensed Tannins (Proanthocyanidins) Quantification
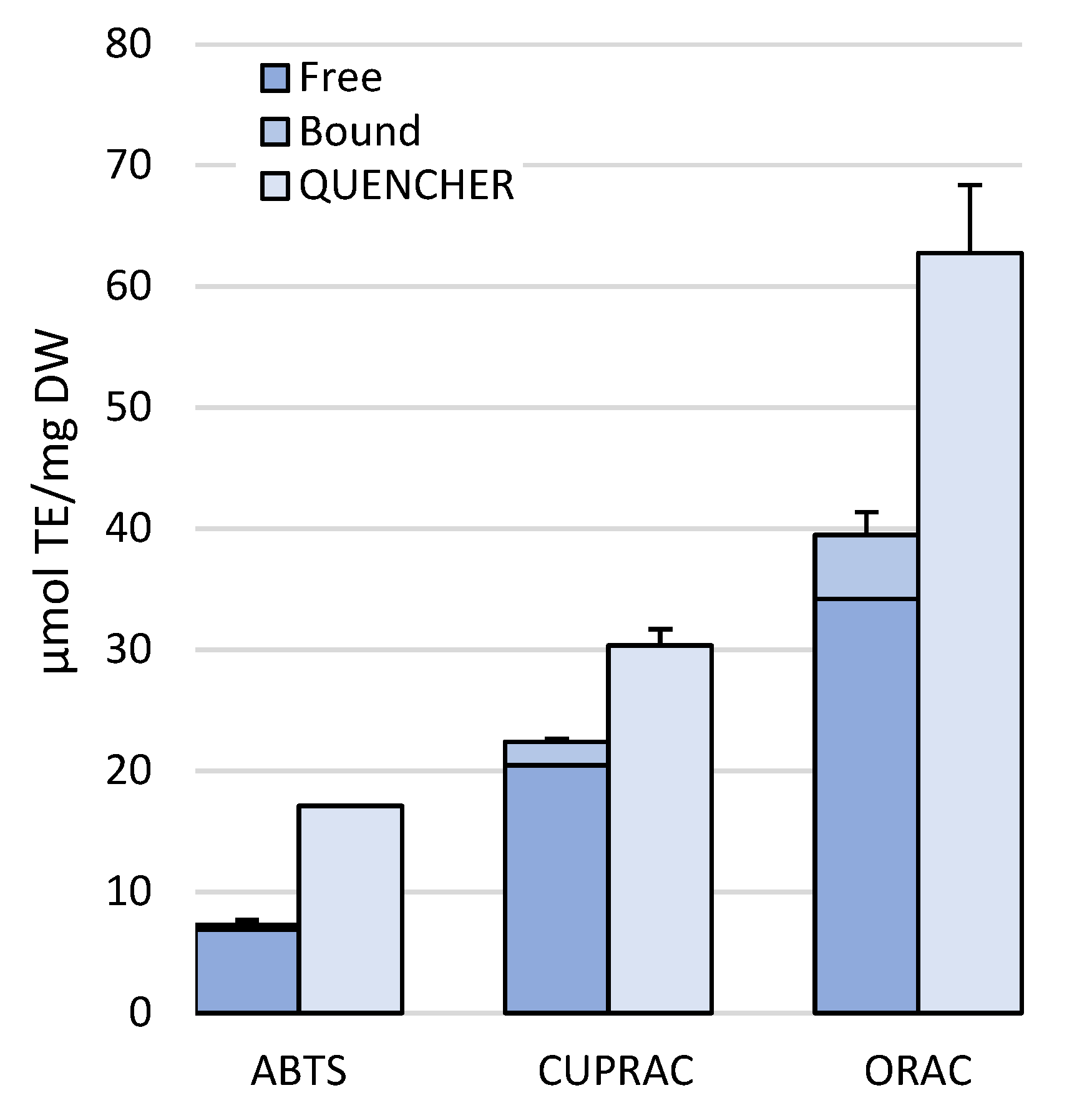
2.3. QUENCHER (QUick Easy New CHEap Reproducible) Method for Antioxidant Capacity Assays
2.4. “In-Solution” vs. QUENCHER Total Antioxidant Capacity Assays
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Site
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Phenolic Compounds Extraction
4.4. Phenol and Flavonoid Assays
4.5. Proanthocyanidins (Condensed Tannins) Quantification
4.6. Total Antioxidant Capacity—QUENCHER (QUick Easy New CHEap Reproducible) (Direct) Method
4.6.1. QUENCHER-ABTS
4.6.2. QUENCHER-CUPRAC
4.6.3. QUENCHER-ORAC
4.7. Total Antioxidant Capacity—“In-Solution” Method
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABTS | 2,2′-Azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) |
| CE | Catechin equivalent |
| CUPRAC | CUPric ion Reducing Antioxidant Capacity |
| FRAP | Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power |
| GAE | Gallic acid equivalent |
| HBAI | HCl-butanol-acetone-iron |
| ORAC | Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity |
| PA | Proanthocyanidin |
| QUENCHER | QUick Easy New CHEap Reproducible |
| TAC | Total antioxidant capacity |
| TE | Trolox equivalent |
References
- Gobert, S.; Cambridge, M.L.; Velimirov, B.; Pergent, G.; Lepoint, G.; Bouquegneau, J.-M.; Dauby, P.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Walker, D.I. Biology of Posidonia. In Seagrasses: Biology, Ecology and Conservation; Larkum, A.W.D., Orth, R.J., Duarte, C.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 387–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habitats Directive. Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora. Off. J. Eur. Union 1992, 206, 7–50. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Murillo, F.; Fernandez-Torquemada, Y.; Garrote-Moreno, A.; Sa′ez, C.A.; Sa′nchez-Lizaso, J.L. Posidonia oceanica L. (Delile) meadows regression: Long-term affection may be induced by multiple impacts. Mar. Environ. Res. 2002, 174, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadie, A.; Lejeune, P.; Pergent, G.; Gobert, S. From mechanical to chemical impact of anchoring in seagrasses: The premises of anthropogenic patch generation in Posidonia oceanica meadows. Mar. Pollut. Bull 2006, 109, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbà, N.; Arthur, R.; Alcoverro, T. Getting turfed: The population and habitat impacts of Lophocladia lallemandii invasions on endemic Posidonia oceanica meadows. Aquat. Bot. 2014, 116, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbà, N.; Díaz-Almela, E.; Duarte, C.M. Mediterranean seagrass (Posidonia oceanica) loss between 1842 and 2009. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 176, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Los Santos, C.B.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Alcoverro, T.; Marbà, N.; Duarte, C.M.; van Katwijk, M.M.; Pérez, M.; Romero, J.; Sánchez-Lizaso, J.L.; Roca, G. Recent trend reversal for declining European seagrass meadows. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazzaglia, J.; Santillán-Sarmiento, A.; Helber, S.B.; Ruocco, M.; Terlizzi, A.; Marín-Guirao, L.; Procaccini, G. Does warming enhance the effects of eutrophication in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica? Front. Mar. Sci. 2020, 7, 564805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, B.; Enríquez, S.; Duarte, C.M.; Sand-Jensen, K. Depth-acclimation of photosynthesis, morphology and demography of Posidonia oceanica and Cymodocea nodosa in the Spanish Mediterranean Sea. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 236, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dattolo, E.; Ruocco, M.; Brunet, C.; Lorenti, M.; Lauritano, C.; D’Esposito, D.; De Luca, P.; Sanges, R.; Mazzuca, S.; Procaccini, G. Response of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica to different light environments: Insights from a combined molecular and photo-physiological study. Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 101, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procaccini, G.; Ruocco, M.; Marín-Guirao, L.; Dattolo, E.; Brunet, C.; D’Esposito, D.; Lauritano, C.; Mazzuca, S.; Serra, I.A.; Bernardo, L. Depth-specific fluctuations of gene expression and protein abundance modulate the photophysiology in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, M.; Entrambasaguas, L.; Dattolo, E.; Milito, A.; Marín-Guirao, L.; Procaccini, G. A king and vassals’ tale: Molecular signatures of clonal integration in Posidonia oceanica under chronic light shortage. J. Ecol. 2021, 109, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, F.K.; Rivero, R.M.; Blumwald, E.; Mittler, R. Reactive oxygen species, abiotic stress and stress combination. Plant J. 2017, 90, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, R.; Dall’Osto, L. Dissipation of light energy absorbed in excess: The molecular mechanisms. Ann. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingvay, M.; Akhtar, P.; Sebők-Nagy, K.; Páli, T.; Lambrev, P.H. Photobleaching of chlorophyll in light-harvesting complex II increases in lipid environment. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice-Evans, C.; Miller, N.; Paganga, G. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds. Trends Plant Sci. 1997, 2, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A. Concept, mechanism, and applications of phenolic antioxidants in foods. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, S.; Desjobert, J.M.; Pergent, G. Distribution of phenolic compounds in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertini, L.; Focaracci, F.; Proietti, S.; Papetti, P.; Caruso, C. Physiological response of Posidonia oceanica to heavy metal pollution along the Tyrrhenian coast. Funct. Plant Biol. 2019, 46, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capó, X.; Tejada, S.; Ferriol, P.; Pinya, S.; Mateu-Vicens, G.; Montero-González, I.; Box, A.; Sureda, A. Hypersaline water from desalinization plants causes oxidative damage in Posidonia oceanica meadows. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.M.; Barrote, I.; Silva, J.; Olivé, I.; Alexandre, A.; Albano, S.; Santos, R. Epiphytes modulate Posidonia oceanica photosynthetic production, energetic balance, antioxidant mechanisms, and oxidative damage. Front. Mar. Sci. 2015, 2, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumay, O.; Costa, J.; Desjobert, J.M.; Pergent, G. Variations in the concentration of phenolic compounds in the seagrass Posidonia oceanica under conditions of competition. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Márquez, M.G.; Rodríguez-Castañeda, J.C.; Agawin, N.S. Sunscreen exposure interferes with physiological processes while inducing oxidative stress in seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannino, A.M.; Micheli, C. Ecological function of phenolic compounds from mediterranean fucoid algae and seagrasses: An overview on the genus Cystoseira sensu lato and Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaglioli, C.; Capocchi, A.; Fontanini, D.; Mori, G.; Nuccio, C.; Bulleri, F. Macro-grazer herbivory regulates seagrass response to pulse and press nutrient loading. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 136, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Márquez, M.G.; Fernández-Juárez, V.; Rodríguez-Castañeda, J.C.; Agawin, N.S. Response of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile and its associated N2 fixers to different combinations of temperature and light levels. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 757572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaglioli, C.; Marchi, L.D.; Anselmi, S.; Dattolo, E.; Fontanini, D.; Pretti, C.; Procaccini, G.; Rilov, G.; Renzi, M.; Silverman, J.; et al. Ocean acidification impairs seagrass performance under thermal stress in shallow and deep water. Environ. Res. 2024, 241, 117629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesraoui, O.; Marzouki, M.N.; Maugard, T.; Limam, F. In vitro evaluation of antioxidant activities of free and bound phenolic compounds from Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile leaves. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barletta, E.; Ramazzotti, M.; Fratianni, F.; Pessani, D.; Degl′Innocenti, D. Hydrophilic extract from Posidonia oceanica inhibits activity and expression of gelatinases and prevents HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cell line invasion. Cell Adh. Migr. 2015, 9, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leri, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Vasarri, M.; Peri, S.; Barletta, E.; Pretti, C.; Degl’Innocenti, D. Bioactive Compounds from Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile Impair Malignant Cell Migration through Autophagy Modulation. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornara, L.; Pastorino, G.; Borghesi, B.; Salis, A.; Clericuzio, M.; Marchetti, C.; Damonte, G.; Burlando, B. Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile Ethanolic Extract Modulates Cell Activities with Skin Health Applications. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasarri, M.; Leri, M.; Barletta, E.; Ramazzotti, M.; Marzocchini, R.; Degl′Innocenti, D. Anti-inflammatory properties of the marine plant Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 247, 112252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messina, C.M.; Arena, R.; Manuguerra, S.; Pericot, Y.; Curcuraci, E.; Kerninon, F.; Renda, G.; Hellio, C.; Santulli, A. Antioxidant Bioactivity of Extracts from Beach Cast Leaves of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Shahzad, B.; Rehman, A.; Bhardwaj, R.; Landi, M.; Zheng, B. Response of Phenylpropanoid Pathway and the Role of Polyphenols in Plants under Abiotic Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanian, Z.; Habibi, K.; Dehghanian, M.; Aliyar, S.; Asgari Lajayer, B.; Astatkie, T.; Minkina, T.; Keswani, C. Reinforcing the bulwark: Unravelling the efficient applications of plant phenolics and tannins against environmental stresses. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, R.H. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activity of common vegetables. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 6910–6916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krygier, K.; Sosulski, F.; Hogge, L. Free, esterified, and insoluble bound phenolic-acids. 1. Extraction and purification procedure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1982, 30, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astudillo-Pascual, M.; Domínguez, I.; Aguilera, P.A.; Garrido Frenich, A. New Phenolic Compounds in Posidonia oceanica Seagrass: A Comprehensive Array Using High Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Plants 2021, 10, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, D.; Santos, J.S.; Maciel, L.G.; Nunes, D.S. Chemical perspective and criticism on selected analytical methods used to estimate the total content of phenolic compounds in food matrices. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, M.; Dominguez-López, I.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. The Chemistry Behind the Folin-Ciocalteu Method for the Estimation of (Poly)phenol Content in Food: Total Phenolic Intake in a Mediterranean Dietary Pattern. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2023, 71, 17543–17553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignon-Dubois, M.; Rezzonico, B. Phenolic fingerprint of the seagrass Posidonia oceanica from four locations in the Mediterranean Sea: First evidence for the large predominance of chicoric acid. Bot. Mar. 2015, 58, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannac, M.; Ferrat, L.; Barboni, T.; Pergent, G.; Pasqualini, V. The influence of tissue handling on the flavonoid content of the aquatic plant Posidonia oceanica. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannac, M.; Ferrat, L.; Pergent-Martini, C.; Pergent, G.; Pasqualini, V. Effects of fish farming on flavonoids in Posidonia oceanica. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 370, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Cheng, C.-W.; Liang, J.-Y. Effect of esterification condensation on the Folin–Ciocalteu method for the quantitative measurement of total phenols. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shraim, A.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Hijji, Y.M. Determination of total flavonoid content by aluminum chloride assay: A critical evaluation. LWT 2021, 150, 111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, T.M.; Targett, N.M. Marine tannins: The importance of a mechanistic framework for predicting ecological roles. J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 1919–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boumaza, S.; Sengouga, A.; Gasmi, D.; Misraoui, A.; Pergent, G.; Semroud, R. Patterns of Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile tannin cells and leaf characteristics according to environmental conditions. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2022, 23, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabber, J.H.; Zeller, W.E. Direct versus Sequential Analysis of Procyanidin- and Prodelphinidin-Based Condensed Tannins by the HCl−Butanol−Acetone−Iron Assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 2906–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, P.E.; Trofymow, J.A.; Constabel, C.P. An improved butanol-HCl assay for quantification of water-soluble, acetone:methanol-soluble, and insoluble proanthocyanidins (condensed tannins). Plant Methods 2017, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, L.J.; Hrstich, L.N.; Chan, B.G. The Conversion of Procyanidins and Prodelphinidins to Cyanidin and Delphinidin. Phytochem. 1986, 25, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.M.; Latona, R.J.; Taylor, M.M.; Gehring, A.G. Powdered hide model for vegetable tanning. J. Am. Leather Chem. Assoc. 2014, 109, 8–13. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, P.B.; Sisa, M.; van der Merwe, M.J.; Bonnet, S.L.; van der Westhuizen, J.H. Analysis of commercial proanthocyanidins. Part 1: The chemical composition of quebracho (Schinopsis lorentzii and Schinopsis balansae) heartwood extract. Phytochemistry 2012, 73, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Trombley, J.D.; Schmidt, M.A.; Hagerman, A.E. Preparation of an acid butanol standard from fresh apples. J. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 36, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbatinejad, N.M.; Annison, G.; Rutherfurd-Markwick, K.; Sabine, J.R. Structural Constituents of the Seagrass Posidonia australis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4021–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, E.E.; Cömert, E.D.; Gökmen, V. The power of the QUENCHER method in measuring total antioxidant capacity of foods: Importance of interactions between different forms of antioxidants. Talanta 2024, 269, 125474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gökmen, V.; Serpen, A.; Fogliano, V. Direct measurement of the total antioxidant capacity of foods: The ‘QUENCHER’ approach. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 20, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apak, R.; Özyürek, M.; Güçlü, K.; Çapanoğlu, E. Antioxidant Activity/Capacity Measurement. 1. Classification, Physicochemical Principles, Mechanisms, and Electron Transfer (ET)-Based Assays. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2016, 64, 997–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Rossi, J.A., Jr. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic phosphotungstic acid reagents. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1965, 16, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanto, V.; Wu, X.; Adom, K.K.; Liu, R.H. Thermal processing enhances the nutritional value of tomatoes by increasing total antioxidant activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3010–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, R.; Pellegrini, N.; Proteggente, A.; Pannala, A.; Yang, M.; Rice-Evans, C. Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radical Biol. Med. 1999, 26, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino, M.S.M.; Alves, R.E.; de Brito, E.S.; de Morais, S.M.; de Goes Sampaio, C.; Pérez-Jiménez, J.; Saura-Calixto, F.; Mancini-Filho, J. Metodologia Cientifica: Determinacao da Atividade Antioxidanta Total em Frutas pela Captura do Radical Livre ABTS+. Comun. Tec. 2007, 128, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tufan, A.N.; Celik, S.E.; Ozyurek, M.; Guclu, K.; Apak, R. Direct measurement of total antioxidant capacity of cereals: QUENCHER-CUPRAC method. Talanta 2013, 108, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apak, R.; Güçlü, K.; Özyürek, M.; Karademir, S.E. Novel total antioxidant capacity index for dietary polyphenols and vitamins C and E, using their cupric ion reducing capability in the presence of neocuproine: CUPRAC method. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7970–7981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Hampsch-Woodill, M.; Flanagan, J.A.; Prior, R.L. High-Throughput Assay of Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) Using a Multichannel Liquid Handling System Coupled with a Microplate Fluorescence Reader in 96-Well Format. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4437–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigo-Benavent, M.; del Castillo, M.D.; Fogliano, V. Are the major antioxidants derived from soy protein and fructo-oligosaccharides model systems colored aqueous soluble or insoluble compounds? Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2010, 231, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, B.; Chang, T.; Huang, D.; Prior, R.L. Determination of Total Antioxidant Capacity by Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capacity (ORAC) Using Fluorescein as the Fluorescence Probe: First Action 2012.23. J. AOAC Int. 2013, 6, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fontanini, D.; Bulleri, F.; Ravaglioli, C.; Capocchi, A. A Comparison of Methods for Assessing the Antioxidant Expression in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Molecules 2025, 30, 1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081828
Fontanini D, Bulleri F, Ravaglioli C, Capocchi A. A Comparison of Methods for Assessing the Antioxidant Expression in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081828
Chicago/Turabian StyleFontanini, Debora, Fabio Bulleri, Chiara Ravaglioli, and Antonella Capocchi. 2025. "A Comparison of Methods for Assessing the Antioxidant Expression in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081828
APA StyleFontanini, D., Bulleri, F., Ravaglioli, C., & Capocchi, A. (2025). A Comparison of Methods for Assessing the Antioxidant Expression in Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile. Molecules, 30(8), 1828. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081828





