The Effects of Solvation Enthalpy, Surface Tension, and Conductivity of Common Additives on Positive Electrospray Ionization in Selected Pharmaceuticals
Abstract
1. Introduction
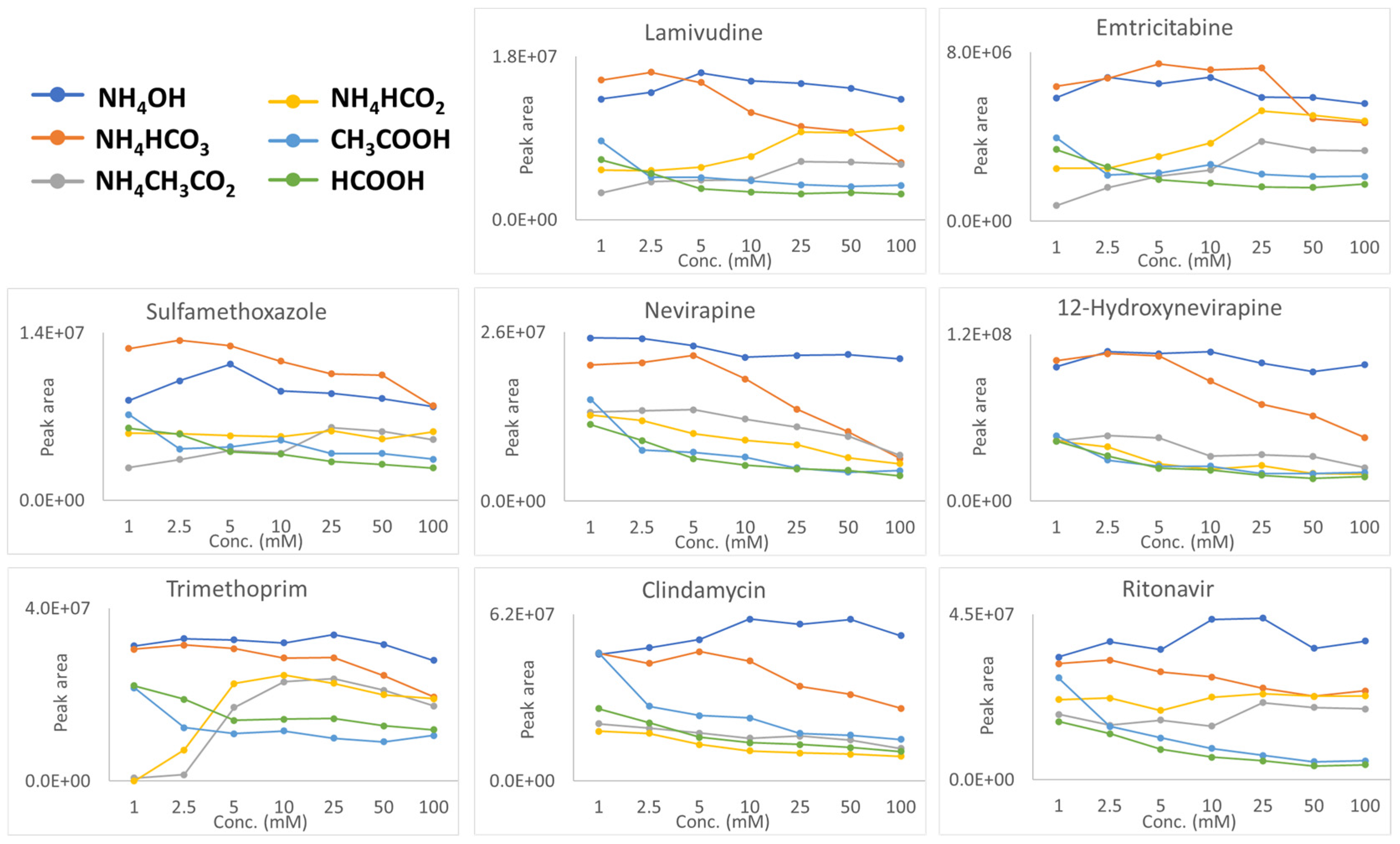
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Working Solution
3.3. Electrical Conductivity (EC) Measurements
3.4. Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry Analysis
3.5. Data Handling
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cech, N.B.; Enke, C.G. Practical implications of some recent studies in ESI fundamentals. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2001, 20, 362–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenn, J.B. Ion formation from charged droplets: Roles of geometry, energy, and time. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1993, 4, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, U.A.; Chait, B.T. Effects of Anions on the Positive Ion Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectra of Peptides and Proteins. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 2898–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Mo, J.; Lu, M.; Wang, H. Detection of Human Urinary 5—Hydroxymethylcytosine by Stable Isotope Dilution HPLC-MS/MS Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Accurate Quantification of Ten Methylated Purine Nucleosides by Highly Sensitive and Stable Isotope-Diluted UHPLC—MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 11366–11373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Liu, S.; Zhao, C.; Lu, M.; Tang, M.; Wang, H. An Ammonium Bicarbonate-Enhanced Stable Isotope Dilution UHPLC-MS/MS Method for Sensitive and Accurate Quanti fi cation of Acrolein—DNA Adducts in Human Leukocytes. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 3190–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Song, Y.; Wu, D.; Xu, T.; Lu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, H. Detection of 1,N2-propano-2′-deoxyguanosine adducts in genomic DNA by ultrahigh performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry in combination with stable isotope dilution. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1450, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Horiba, R.; Iwata, T.; Miki, Y.; Uno, B.; Sakai, T.; Kaneko, K.; Ishihama, Y.; Teshima, N.; Esaka, Y. Progress in a selective method for the determination of the acetaldehyde-derived DNA adducts by using HILIC-ESI-MS/MS. Talanta 2018, 177, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, J.; Vikse, K.L.; Janusson, E.; Taylor, N.; McIndoe, J.S. Solvent effects on surface activity of aggregate ions in electrospray ionization. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 373, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Omari, I.; Randhawa, P.; Randhawa, J.; Yu, J.; Mcindoe, J.S. Structure, Anion, and Solvent Effects on Cation Response in ESI-MS. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 30, 1750–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A.M.; Brown, P.R.; Munson, B. Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry of Tetracycline, Oxytetracycline, Chlorotetracycline, Minocycline, and Methacycline. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creydt, M.; Fischer, M. Plant Metabolomics: Maximizing Metabolome Coverage by Optimizing Mobile Phase Additives for Nontargeted Mass Spectrometry in Positive and Negative Electrospray Ionization Mode. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10474–10486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshraghi, J.; Chowdhury, S.K. Factors Affecting Electrospray Ionization of Effluents Containing Trifluoroacetic Acid for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 3528–3533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Mason, S.F.; Bartlett, M.G. The effect of organic modifiers on electrospray ionization charge-state distribution and desorption efficiency for oligonucleotides. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 24, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, P.; van Onselen, R. Evaluating the “wrong-way-round” electrospray ionization of antiretroviral drugs for improved detection sensitivity. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantopoulos, T.L.; Jackson, G.S.; Enke, C.G. Effects of salt concentration on analyte response using electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 10, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebarle, P.; Tang, L. From Ions in Solution To Ions in the Gas Phase. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 972A–986A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. The Thermodynamics of Solvation of Ions. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1 1987, 83, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulyk, D.S.; Sahraeian, T.; Lee, S.; Badu-Tawiah, A.K. Microsampling with a Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridge: Storage and Online Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13632–13640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Cook, K.D. Protonation in electrospray mass spectrometry: Wrong-way-round or right-way-round? J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 11, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, K.; Murata, K.; Kudaka, I. Do the Electrospray Mass Spectra Reflect the Ion Concentrations in Sample Solution? J. Mass Spectrom. Soc. Jpn. 1995, 43, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurman, E.M.; Ferrer, I.; Barceló, D. Choosing between atmospheric pressure chemical ionization and electrospray ionization interfaces for the HPLC/MS analysis of pesticides. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5441–5449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, C.G.; Krajete, A. Analysis of nucleic acids by capillary ion-pair reversed-phase HPLC coupled to negative-ion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 3730–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, R.B.; Harrata, A.K. Solvent effect on analyte charge state, signal intensity, and stability in negative ion electrospray mass spectrometry; implications for the mechanism of negative ion formation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1993, 4, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apffel, A.; Fischer, S.; Goldberg, G.; Goodley, P.C.; Kuhlmann, F.E. Enhanced sensitivity for peptide mapping with electrospray liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in the presence of signal suppression due to trifluoroacetic acid-containing mobile phases. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 712, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostiainen, R.; Kauppila, T.J. Effect of eluent on the ionization process in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 685–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Venter, P. The Effects of Solvation Enthalpy, Surface Tension, and Conductivity of Common Additives on Positive Electrospray Ionization in Selected Pharmaceuticals. Molecules 2025, 30, 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091885
Venter P. The Effects of Solvation Enthalpy, Surface Tension, and Conductivity of Common Additives on Positive Electrospray Ionization in Selected Pharmaceuticals. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091885
Chicago/Turabian StyleVenter, Pieter. 2025. "The Effects of Solvation Enthalpy, Surface Tension, and Conductivity of Common Additives on Positive Electrospray Ionization in Selected Pharmaceuticals" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091885
APA StyleVenter, P. (2025). The Effects of Solvation Enthalpy, Surface Tension, and Conductivity of Common Additives on Positive Electrospray Ionization in Selected Pharmaceuticals. Molecules, 30(9), 1885. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091885




