Abstract
There is a pandemic of obesity and associated chronic diseases. Dietary calcium and vitamin D have many extra-skeletal roles in human health. In this review we have summarized the current understanding of their influence on human energy balance by examining the epidemiological, clinical, animal, cellular and molecular evidence. We opine that while calcium and vitamin D are functional nutrients in the battle against obesity, there is a need for prospective human trials to tilt the balance of evidence in favour of these nutrients.
1. Introduction
Prevalence estimates of obesity are well over 50% in most WHO regions of the world, except South-East Asia. The observations that poor calcium intakes and inadequate vitamin D status are associated with chronic diseases like obesity, cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes (T2DM), hence become increasingly important [1–3]. Such relationships between nutrients and disease offer a potential public health strategy, if concerned agencies accept the available balance of evidence. Calcium and vitamin D have many biological effects and determining their requirements for health would depend on which endpoint is of greatest concern. Hence nutrient intake or nutrient status adequacy as judged against one biological endpoint may not be appropriate for other putative functions. Central to these issues is the precise cut off used to determine adequacy of nutrient status. In the case of vitamin D, while it is accepted that a value <25 nmol/L denotes deficiency, there is still disagreement whether >50 nmol/L signifies adequacy of function. There is the viewpoint that even for skeletal effects a value >75 nmol/L should be the norm [3–9]. Moreover given the dramatic increase in techniques for the determination of 25(OH)D standardisation of results between methods and laboratories is a problem [10,11]. So after a thorough review of the evidence available, a 2010 report by the Institute of Medicine advocated calcium and vitamin D only for bone health [12]. In this paper we summarize the evidence on their extra-skeletal benefits as they pertain to energy balance and obesity.
2. Calcium and Body Weight
An inverse relationship between calcium intake and body weight was first noted by McCarron et al. [13]. However interest in the area was sparked by observation that increasing the intake of calcium through yoghurt increased the loss of body fat particularly from the abdominal region [14]. Based primarily on studies with the agouti mouse model, Zemel et al. [14] proposed that intracellular calcium (iCa2+) was key to fat deposition and hence obesity. According to this early scheme increases in dietary calcium would, via PTH, chronically lower iCa2+ in the adipocyte. This would then act to reciprocally reduce lipid deposition while stimulating adipose tissue breakdown. We have updated this model to include several other potential pathways (Figure 1) that could influence both sides of the energy balance equation in humans [15,16]. A review of available randomised controlled trials (RCTs) led us to conclude that, ingested calcium could have two effects [16]: (1) An increase in whole body oxidation of fat. Carbohydrate and protein balances are readily achieved over the short term as fluctuations in intake are offset by reciprocal changes in substrate oxidation. In contrast an increase in fat oxidation will lag an increase in fat intake, leading to fat storage. It follows that any nutrient which acutely or chronically raises whole body fat oxidation would result in a less positive fat balance, all other things being equal. A meta-analysis by an independent group has confirmed that increasing calcium by ~800 mg/day would favour an 11% increase in fat oxidation [17]; (2) An increase in faecal fat excretion. Within the gastro intestinal tract unabsorbed calcium links with dietary fat to form insoluble calcium-fatty acid soaps that are excreted. This presents a pathway of faecal energy loss and a predisposition to a negative energy balance. Available data indicates for every ~1200 mg/day of calcium, one can predict an excretion of ~5 g/day of fat or 45 kcal/day [18]. Future studies based on dose response trials could determine the optimum intake for these two actions of calcium.
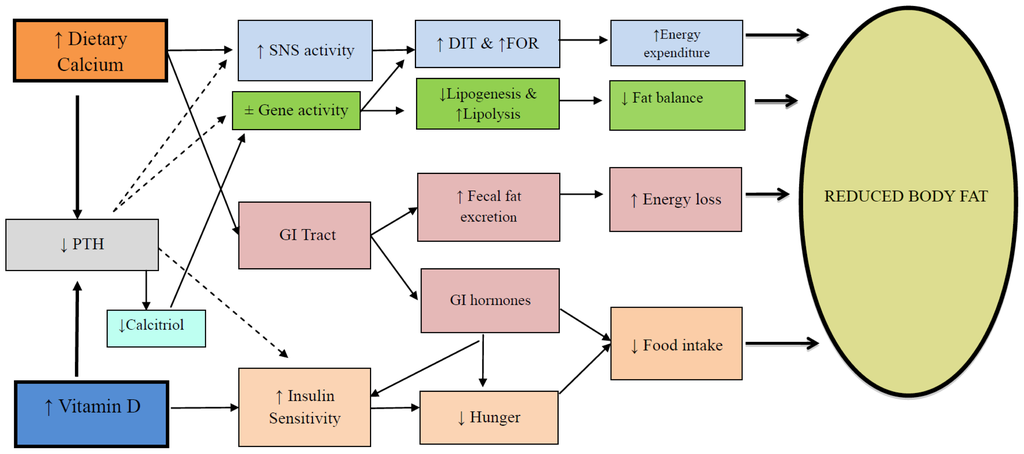
Figure 1.
The modulation of energy balance by calcium and vitamin D. ↑ = increased, ↓ = decreased, PTH = parathyroid hormone, Calcitriol = 1,25(OH2)D, SNS = sympathetic nervous system, ±Gene activity = decreased expression of genes controlling lipogenesis (usually sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, fatty acid synthase) or increased expression of genes for lipolysis (lipoprotein lipase or hormone sensitive lipase) and increased thermogenesis (uncoupling protein activity), GI = gastro intestinal, DIT = diet-induced thermogenesis, FOR = fat oxidation rate. (From Soares et al. 2012 [8] with permission).
A greater fat oxidation and increased faecal fat excretion through increased calcium intake will not result in an instant shedding of all excess body fat. So far reviews of RCTs show either no or a small augmentation of weight and fat loss (~0.7 to 0.9 kg) from calcium whether with or without vitamin D [19,20]. This will change as more prospective trials demonstrate their beneficial effect [21,22]. Interestingly, there is also evidence that despite no change in total fat, calcium may also increase the loss of visceral adipose tissue [21,23]. Overall, while such small decreases (<1 kg) in fat mass would be treated as clinically non-significant, they could have a dramatic effect on secular weight gain at the population level [24].
3. Vitamin D and Energy Regulation
Animal and cellular studies strongly indicate a role for the vitamin in energy metabolism. The active form of the vitamin, 1,25(OH)2D, acts through a nuclear vitamin D receptor (VDR). This receptor is expressed in many cells not directly involved in calcium metabolism [25]. VDR null mice demonstrate that the vitamin has a role in energy regulation, since these animals display a greater rate of energy expenditure, an increased β oxidation of fatty acids, up-regulation of uncoupling protein (UCP) and a leaner phenotype when compared to wild type mice [26,27]. In contrast to VDR null mice, however, the targeted expression of human VDR in adipocytes of transgenic mice resulted in a suppression of energy expenditure and fat oxidation leading to an obese phenotype [28]. The latter is also supported by a non-genomic action of the active metabolite, where 1,25(OH)2D stimulated enzymes controlling fat synthesis and reciprocally inhibited lipolysis in a human adipose tissue cell line [29]. The CYP27B1 gene is responsible for encoding the renal enzyme 1,α-hydroxylase, which in turn produces the active hormone from 25(OH)D. Mice lacking CYP27B1 also show lower body weights and reduced abdominal fat mass [25]. Based on the above one would conclude that a higher 1,25(OH)2D promoted adiposity [25,30].
However 1,25(OH)2D can regulate a spectrum of cellular processes, from proliferation, differentiation and development to apoptosis and secretion [31]. Sergeev [32] has documented that 1,25(OH)2D acted through intracellular increases in Ca2+ which in turn lead to increased apoptosis of adipocytes. As this was observed in mature adipocytes which are generally believed to be very stable, it has potential implications for human obesity. Follow up animal studies confirmed these findings, since supplementation of calcium and vitamin D reduced adiposity via increased adipocyte apoptosis [33]. Clearly this is a complex area and extrapolation from cellular and animal outcomes to the human condition is difficult. How does the rise in 25(OH)D from correcting vitamin D insufficiency in humans, affect obesity? Is its action through conversion to 1,25(OH)2D and hence downstream effects at the cellular level? Could it be acting through an improvement in calcium absorption? Or is the lowering of PTH central to these effects (Figure 1)? In a thought provoking paper, Heaney [3] has proposed that 25(OH)D has an endocrine action that subserves calcium metabolism, and also has a permissive autocrine role on intracellular 1,25(OH)2D. The key facet of the model is that without an optimal serum level of 25(OH)D the target cell is not enabled towards a proper functioning of its 1,25(OH)2D, and potential extra-skeletal effects [3]. If applied to human obesity this model would predict that supplementation with 1,25(OH)2D is unlikely to have an effect on adiposity, unless circulating 25(OH)D is at an optimal level. Deciding what is the optimal level of 25(OH)D for humans is then crucial. In reality, as is for bone health, there needs to be a close interplay between optimal calcium intake, optimal 25(OH)D, the suppression of PTH and action of 1,25(OH)2D [3].
There is a burgeoning literature on the potential role of vitamin D per se in the etio-pathogenesis of human obesity as well as other chronic diseases. Numerous cross-sectional studies have shown an inverse association between vitamin D and total body fat or visceral adiposity [34]. The predominant view is that being fat soluble, the vitamin is sequestered in the expanded adipose tissue mass and so results in an apparently lower level. Some confirmation comes from studies that report an improvement in vitamin status with weight loss [35,36], though the precise pathway for re-entry into the circulation needs investigation. There are very few RCTs that have examined the effect of vitamin D supplementation on a reduction in adiposity, so overall a consistent effect was not obtained [37]. More recently Vimaleswaran et al. [38] conducted a bi-directional Mendelian analysis in a very large number of individuals to ascertain causality between the vitamin D-body mass index (BMI) nexus. They concluded that obesity leads to a low vitamin D status but that any effect of a low status predisposing to a greater BMI was likely to be small. The corollary was also proven in a meta-analysis of studies on vitamin D supplementation and BMI [39]. Recently we questioned whether vitamin D supplementation had an effect on indices of body fatness in the absence of planned weight loss [40]. Our meta-analysis of high quality RCTs did not show any effect on percent fat or fat mass, though a marginal trend (p = 0.092) for BMI to decrease with increasing vitamin D status was noted. A potential decrease in BMI without a change in fat mass is intriguing when viewed in the absence of imposed caloric restriction. It could suggest a role for vitamin D in the mobilization of glycogen stores [40]. Overall, from the studies available to date, there is no consistent indication that improving vitamin D status caused a decrease in fat mass. Uncovering an effect of the vitamin on adiposity may require targeting a value of 25(OH)D well above current guidelines, and maintaining that value for a defined period.
4. Conclusions
The role of calcium and vitamin D in the regulation of energy balance has entered an exciting phase of research. The area receives inputs from epidemiology and clinical nutrition, as well as cellular and molecular research. A majority of the human evidence to date was designed with bone health in mind, and the optimal cut-off to determine vitamin D adequacy is still in discussion. It is our view that both calcium and vitamin D are functional nutrients in the battle against obesity. The drive to tilt the balance of evidence needs to continue, so expert committees acknowledge the extra skeletal effects of these nutrients.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the reviewers for their insightful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
- Author ContributionsMario J Soares generated the idea and wrote the first draft, Kaveri Pathak and Emily K Calton reviewed the literature and co-wrote the manuscript.
References
- Holick, M.; Chen, T.C. Vitamin D deficiency: A worldwide problem with health consequences. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1080S–1086S. [Google Scholar]
- Peterlik, M.; Cross, H. Vitamin D and calcium insufficiency-related chronic diseases: Molecular and cellular pathophysiology. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 6, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar]
- Heaney, R.P. Vitamin D in health and disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 3, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson-Hughes, B.; Heaney, R.P.; Holick, M.F.; Lips, P.; Meunier, P.J.; Vieth, R. Estimates of optimal vitamin D status. Osteoporos. Int 2005, 16, 713–716. [Google Scholar]
- Vieth, R. What is the optimal vitamin D status for health? Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol 2006, 92, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Vieth, R.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.; Boucher, B.J.; Dawson-Hughes, B.; Garland, C.F.; Heaney, R.P.; Hollis, M.F.; Hollis, B.W.; Lamberg-Allardt, C.; McGrath, J.J.; et al. The urgent need to recommend an intake of vitamin D that is effective. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 649–650. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, B.J. The 2010 recommendations of the American Institute of Medicine for daily intakes of vitamin D (Letter to the Editor). Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 740. [Google Scholar]
- Giovannucci, E. Vitamin D how much is enough and how much is too much? (Letter to the Editor). Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 740–741. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, A.W. Vitamin D nutrition is at a crossroads (Letter to the Editor). Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 744–745. [Google Scholar]
- Binkley, N.; Wiebe, D. Clinical controversies in vitamin D: 25(OH)D measurement target concentration and supplementation. J. Clin. Densitom. 2013, 16, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Thacker, T.D.; Clarke, B.L. Vitamin D insufficiency. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 50–60. [Google Scholar]
- IOM (Institute of Medicine), Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- McCarron, D.; Morris, C.D.; Henry, H.J.; Stanton, J.L. Blood pressure and nutrient intake in the United States. Science 1984, 224, 11392–11398. [Google Scholar]
- Zemel, M.; Shi, H.; Greer, B.; Dirienzo, D.B.; Zemel, P.C. Regulation of adiposity by dietary calcium. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M.; Chan She-Ping-Delfos, W.L. Postprandial energy metabolism in the regulation of body weight: Is there a mechanistic role for dietary calcium? Nutrients 2010, 2, 586–598. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M.; Murhadi, L.L.; Kurpad, A.V.; She-Ping-Delfos, W.L.C.; Piers, L.S. Mechanistic roles for calcium and vitamin D in the regulation of body weight. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 592–605. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, J.; Rumbold, P.L.S.; Stevenson, E.J. Effect of calcium intake on fat oxidation in adults: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 848–857. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, R.; Lorenzen, J.K.; Svith, C.R.; Bartels, E.M.; Melanson, E.L.; Saris, W.H.; Tremblay, A.; Astrup, A. Effect of calcium from dairy and dietary supplements on faecal fat excretion: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2009, 10, 475–486. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M.; Chan She Ping-Delfos, W.; Ghanbari, M.H. Calcium and vitamin D for obesity: A review of randomized controlled trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 994–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Onakpoya, I.; Perry, R.; Zhang, J.; Ernst, E. Efficacy of calcium supplementation for management of overweight and obesity: Systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 335–343. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Cai, D.; Wang, Y.; Lin, N.; Hu, Q.; Qi, Y.; Ma, S.; Amarasekara, S. Calcium plus vitamin D3 supplementation facilitated fat loss in overweight and obese college students with very-low calcium consumption: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, J.; Castro, V.M.; Moore, C.E.; Kaplan, L.M. Calcium and vitamin D supplementation is associated with decreased abdominal visceral adipose tissue in overweight and obese adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 101–108. [Google Scholar]
- Cummings, N. The Potential Role of Calcium in Obesity. Ph.D. Thesis, Curtin University of Technology, Perth, Western Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Heaney, R. Calcium and obesity: effect size and clinical relevance. Nutr. Rev. 2011, 69, 333–334. [Google Scholar]
- Bouillon, R.; Carmeliet, G.; Lieben, L.; Watanabe, M.; Perino, A.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Verstuyf, A. Vitamin D and energy homeostasis—Of mice and men. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.; Szeto, F.L.; Zhang, W.; Ye, H.; Kong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Li, Y. Involvement of the vitamin D receptor in energy metabolism: Regulation of uncoupling proteins. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 296, E820–E828. [Google Scholar]
- Narvaez, C.; Matthews, D.; Broun, E.; Chan, M.; Welsh, J. Lean phenotype and resistance to diet-induced obesity in vitamin D receptor knockout mice correlates with induction of uncoupling protein-1 in white adipose tissue. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 651–661. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.; Kong, J.; Zhang, W.; Szeto, F.L.; Ye, H.; Deb, D.K.; Brady, M.J.; Li, Y.C. Targeted expression of Human Vitamin D receptor in adipocytes decreases energy expenditure and induces obesity in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 33804–33810. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Norman, A.W.; Okamura, W.H.; Sen, A.; Zemel, M.B. 1α25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 modulates human adipocyte metabolism via nongenomic action. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2751–2753. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.; Hewison, M. Update in vitamin D. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 471–478. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Sergeev, I.N. Calcium and vitamin D in obesity. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2012, 25, 130–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeev, I. 125-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 induces Ca2+-mediated apoptosis in adipocytes via activation of calpain and caspase-12. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 384, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sergeev, I.N.; Song, Q. High vitamin D and calcium intakes reduce diet-induced obesity in mice by increasing adipose tissue apoptosis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.; Chan She Ping-Delfos, W.; Sherriff, J.L.; Nezhad, D.H.; Cummings, N.K.; Zhao, Y. Vitamin D and parathyroid hormone in insulin resistance of abdominal obesity: Cause or effect? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Mason, C.; Xiao, L.; Imayama, I.; Duggan, C.R.; Bain, C.; Foster-Schubert, K.E.; Kong, A.; Campbell, K.L.; Wang, C.T.; Neuhouser, M.L.; et al. Effects of weight loss on serum vitamin D in postmenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 94, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Rock, C.; Emond, J.A.; Flatt, S.W.; Heath, D.D.; Karanja, N.; Pakiz, B.; Sherwood, N.E.; Thomson, C.A. Weight loss is associated with increased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D in overweight or obese women. Obesity 2012, 20, 2296–2301. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, M.J.; Pathak, K. Vitamin D supplementation and weight loss: Potential mechanisms of action and an update of randomized controlled trials. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimaleswaran, K.; Berry, D.J.; Lu, C.; Tikkanen, E.; Pilz, S.; Hiraki, L.T.; Cooper, J.D.; Dastani, Z.; Li, R.; Houston, D.K.; et al. Causal relationship between obesity and vitamin D status: Bi-directional Mendelian randomization analysis of multiple cohorts. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001383. [Google Scholar]
- Mora, N.; Rieke, K.; Plitcha, J.; Segura, A.J.; Leehey, D.; DeShong, K.; Kramer, H.; Durazo, R. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D supplementation and BMI change: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Weight Loss Ther. 2013, 3, 181. [Google Scholar]
- Pathak, K.; Soares, M.J.; Calton, E.K.; Zhao, Y.; Hallett, J. Vitamin D supplementation and body weight status: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).