Abstract
This study investigated the clinical outcomes of a 4-fraction stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) study using helical tomotherapy for brain metastases. Between August 2009 and June 2013, 54 patients with a total of 128 brain metastases underwent SRT using tomotherapy. A total dose of 28 or 28.8 Gy at 80% isodose was administered in 4 fractions for all tumors. The mean gross tumor volume (GTV) was 1.9 cc. Local control (LC) rates at 6, 12, and 18 months were 96%, 91%, and 88%, respectively. The 12-month LC rates for tumors with GTV ≤0.25, >0.25 and ≤1, and >1 cc were 98%, 82%, and 93%, respectively; the rates were 92% for tumors >3 cc and 100% for >10 cc. The 6-month rates for freedom from distant brain failure were 57%, 71%, and 55% for patients with 1, 2, and ≥3 brain metastases, respectively. No differences were significant. No major complications were observed. The 4-fraction SRT protocol provided excellent tumor control with minimal toxicity. Distant brain failure was not so frequent, even in patients with multiple tumors. The results of the current study warrant a prospective randomized study comparing single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) with SRT in this patient population.
1. Introduction
Patients with brain metastases have been traditionally treated by surgery, whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT), single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), or hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (SRT) [1–4]; in the past decade, the use of SRS has spread considerably. Recently published American Society for Radiation Oncology evidence-based guidelines on the management of newly diagnosed brain metastases state that patients presenting with multiple brain metastases (all less than 3–4 cm) have various treatment options, including SRS alone, WBRT with SRS boost, or WBRT alone, with no mention of SRT [5].
Many authors have reported the efficacy of SRS to obtain local tumor control [6–8]. However, hypofractionated SRT seems to become more appropriate than single-fraction SRS with the increase in tumor size, because fractionation provides a radiobiological advantage over single-fraction treatment [9]. As the tumor enlarges, the hypoxic fraction is considered to increase, so that the tumor becomes more radioresistant [10]. For tumors with a high hypoxic fraction, a single high radiation dose is not efficient enough. With fractionation, surviving hypoxic cells are expected to reoxygenate, so that they become more radiosensitive [11,12]. In addition, cell-cycle redistribution may also lead to increased radiosensitivity, although its contribution to radiosensitivity might be much less than that expected by reoxygenation [12]. Another biological advantage of fractionated SRT may derive from differences in the α/β ratio between normal tissues and tumors; it is usually assumed that the ratio is 2 to 3 Gy for normal brain tissues and up to 10 Gy for malignant tumors. Therefore, the use of lower radiation doses per fraction would increase the therapeutic ratio in the treatment of brain metastases, and SRT is recommended for tumors that are not expected to be controlled by a single tolerable dose of SRS. In fact, the local control (LC) rate for large tumors treated with SRS has been reported to be relatively low [13,14], and the clinical advantage of fractionated treatment on sensitive structures in the brain has been reported [9].
Recently, several authors have reported that helical tomotherapy could provide both SRS and SRT. In most studies, the outcomes of SRS/SRT combined with WBRT have been reported [15–20]. Only two studies have reported on SRS alone for brain metastases with respect to dosimetric equivalency between helical tomotherapy and intensity-modulated radiosurgery or gammaknife [19,20]. In this article, we report the results of our 4-fraction SRT protocol study using tomotherapy for brain metastases.
2. Results
2.1. Treatment Plan Analysis
The mean gross tumor volume (GTV) was 1.9 cc (range, 0.01–18). The median GTV was 0.4 cc and the median cumulative GTV was 1.9 cc. The averages of maximum dose and minimum dose for the planning target volume (PTV) were 34 (range, 28–39) and 27 (23–33) Gy, respectively. The homogeneity index (HI) was 1.2 ± 0.1 (mean ± SD, Table 1).

Table 1.
Tumor characteristics.
2.2. Local Control
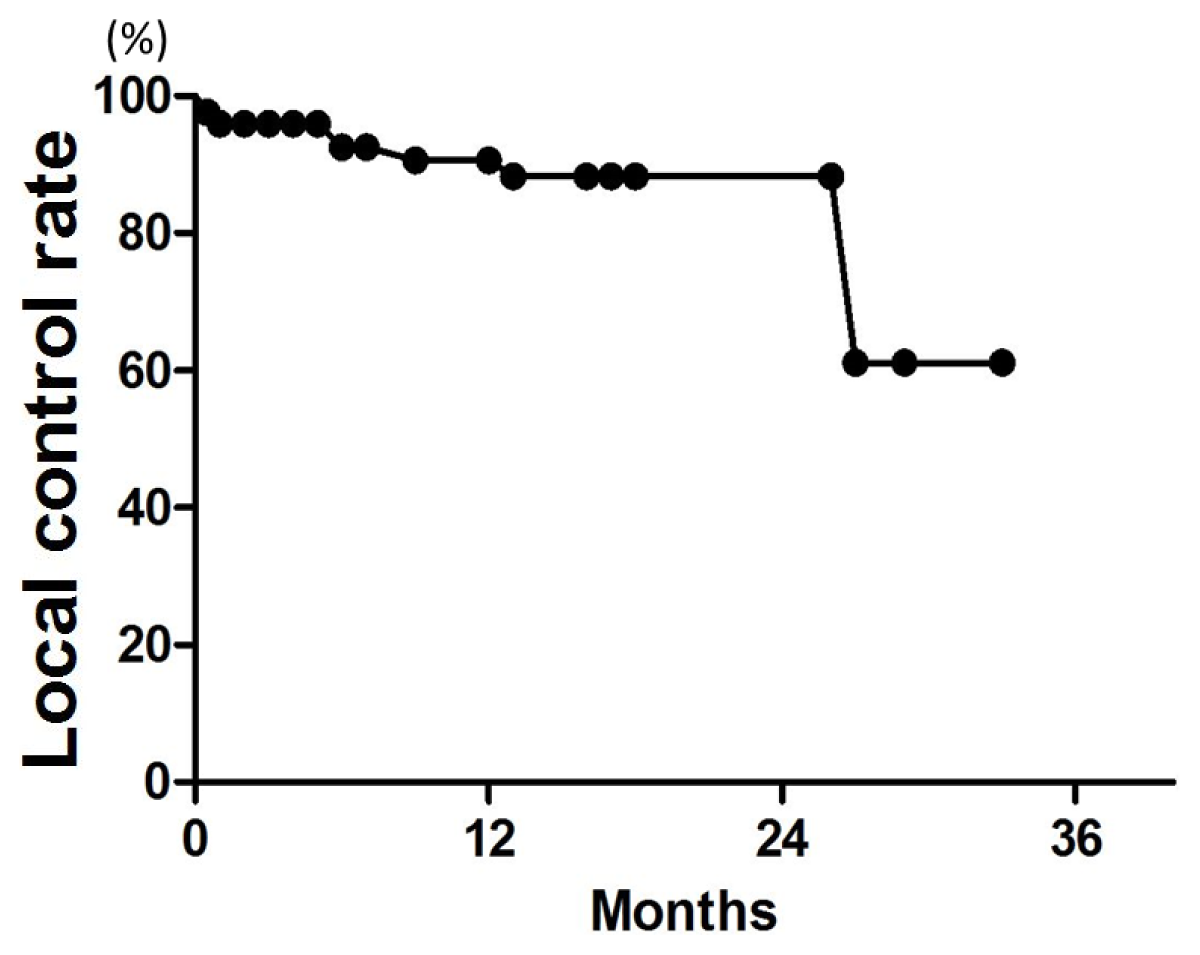
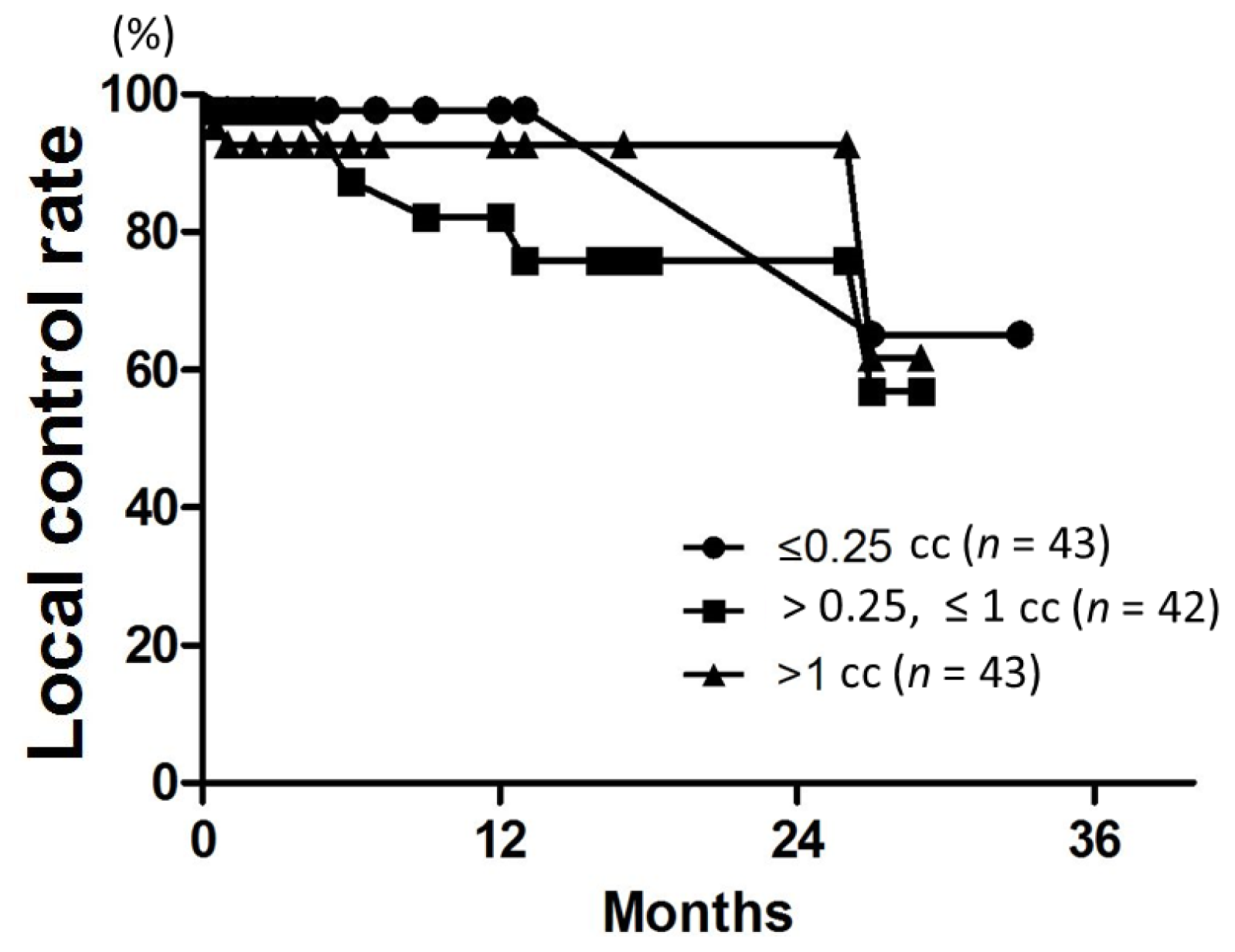
Patient characteristics are listed in Table 2. Patient age ranged from 38 to 89 years (median, 67 years). The median follow-up was 18 months for all patients (range, 3–34 months). LC rates at 6, 12, and 18 months were 96%, 91%, and 88%, respectively (Figure 1). On univariate analysis, the 12-month LC rate was 79% for patients with multiple metastases and 100% for those with single metastasis (p = 0.04) (Table 3). The 6-month LC rates for tumors with GTV ≤0.25, >0.25 and ≤1, and >1 cc were 98%, 87%, and 93%, respectively. One-year LC rates for GTV ≤0.25, >0.25 and ≤1, and >1 cc were 98%, 82%, and 93%, respectively, with no significant difference (Figure 2). The LC rate at 12 months was 92% for GTV >3 cc (n = 24), and 100% for GTV >10 cc (n = 6). On multivariate analysis, there was no significant factor in all subsets (Table 4). Table 5 shows the distribution of tumor size according to tumor histology. Most of the tumors >3 cc were moderately radiosensitive tumors like adenocarcinomas and squamous cell carcinomas.

Table 2.
Patient characteristics.
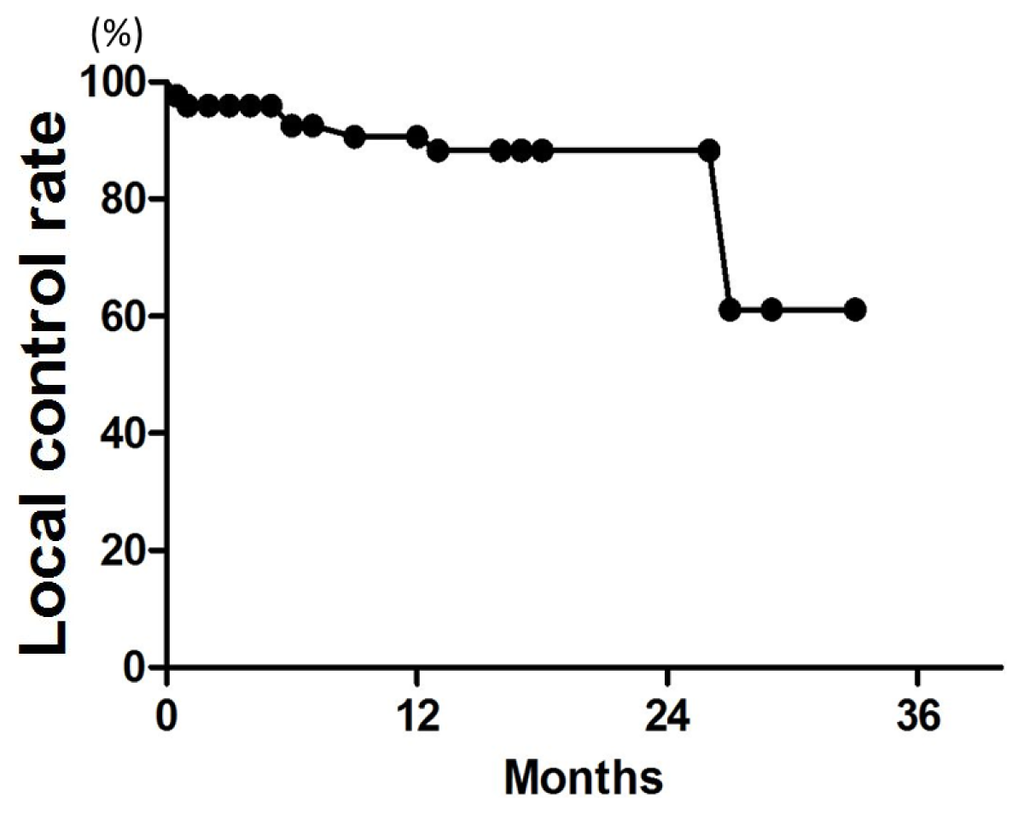
Figure 1.
Local control (LC) curve for all 128 brain metastases.

Table 3.
Univariate analysis of prognostic factors affecting local control (LC), overall survival (OS), and freedom from distant brain failure (FDBF).
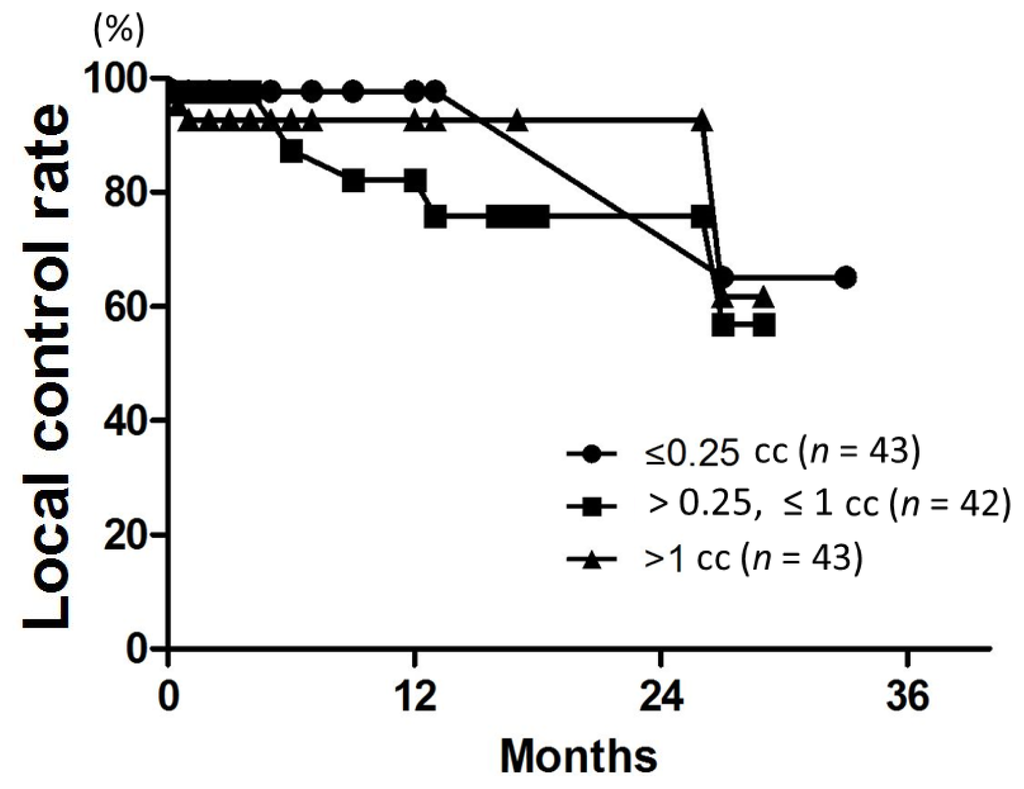
Figure 2.
LC curves according to the gross tumor volume (GTV). There was no difference among the three groups (p = 0.4).

Table 4.
Multivariate analysis for prognostic factors affecting LC, OS, and FDBF.

Table 5.
Histology and tumor size.
2.3. Overall Survival
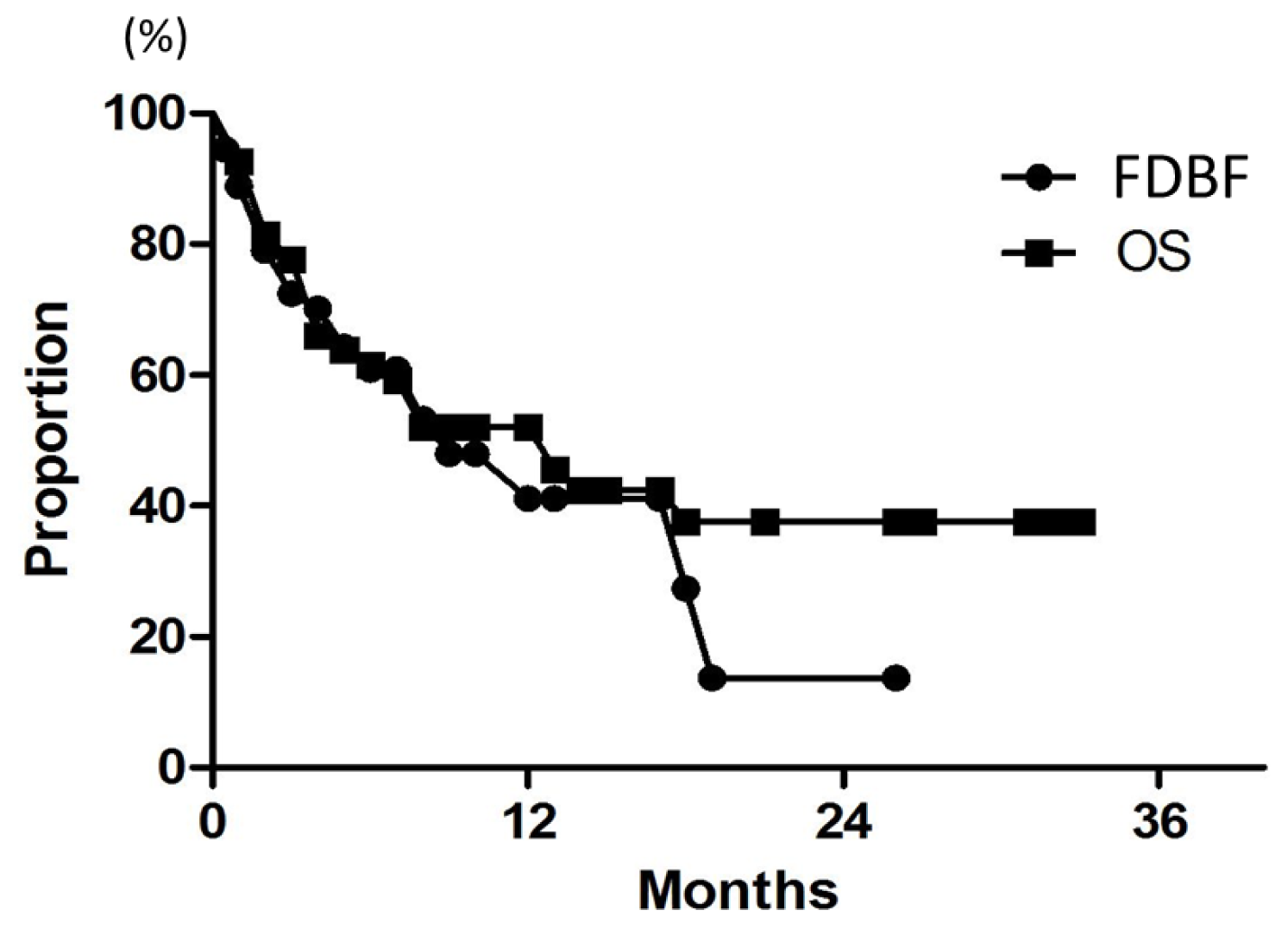
After SRT, 28 (52%) of the 54 patients eventually died of their disease. Median survival of all patients was 7 months. Overall survival (OS) rates at 6, 12, and 18 months were 61%, 52%, and 38%, respectively (Figure 3). The results of univariate analysis of relevant patient characteristics are shown in Table 3. Controlled extracranial disease was a significant predictor of OS when analyzed as a continuous variable (p = 0.0002). The 12-month OS was 31% for patients with total GTV >2 cc, but it was 72% for patients with smaller lesions (p < 0.0001). On multivariate analysis, only controlled extracranial disease was a significant predictor of OS, with a hazard ratio of 0.2 (p = 0.02) (Table 4).
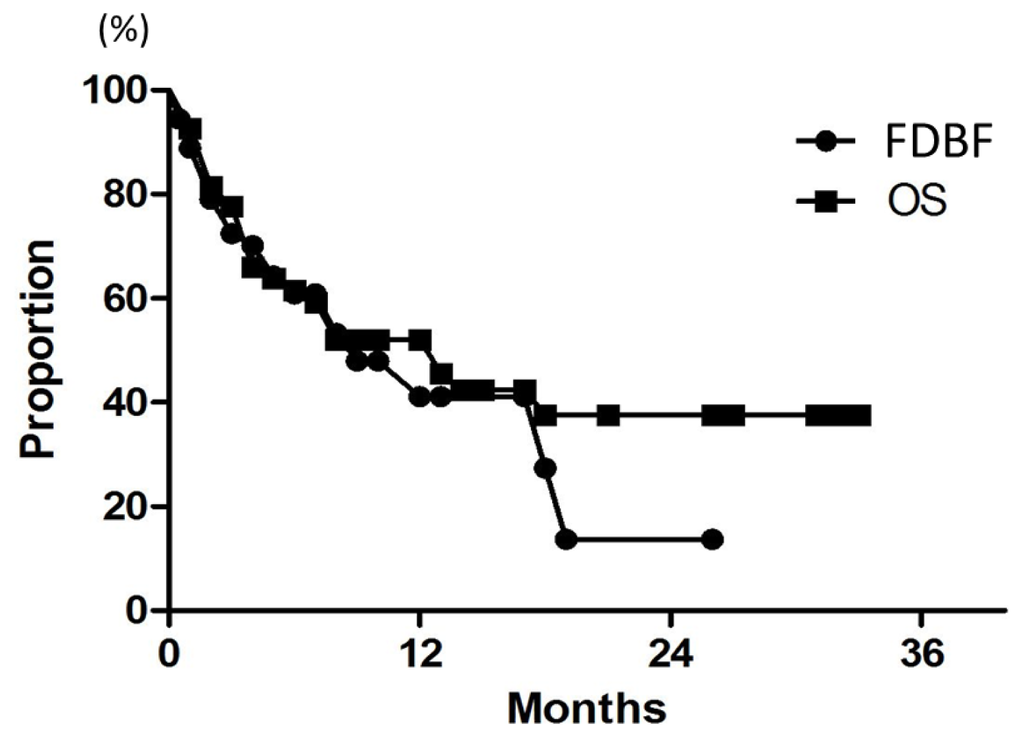
Figure 3.
Curves for FDBF and OS for all 54 patients.
2.4. Freedom from Distant Brain Failure
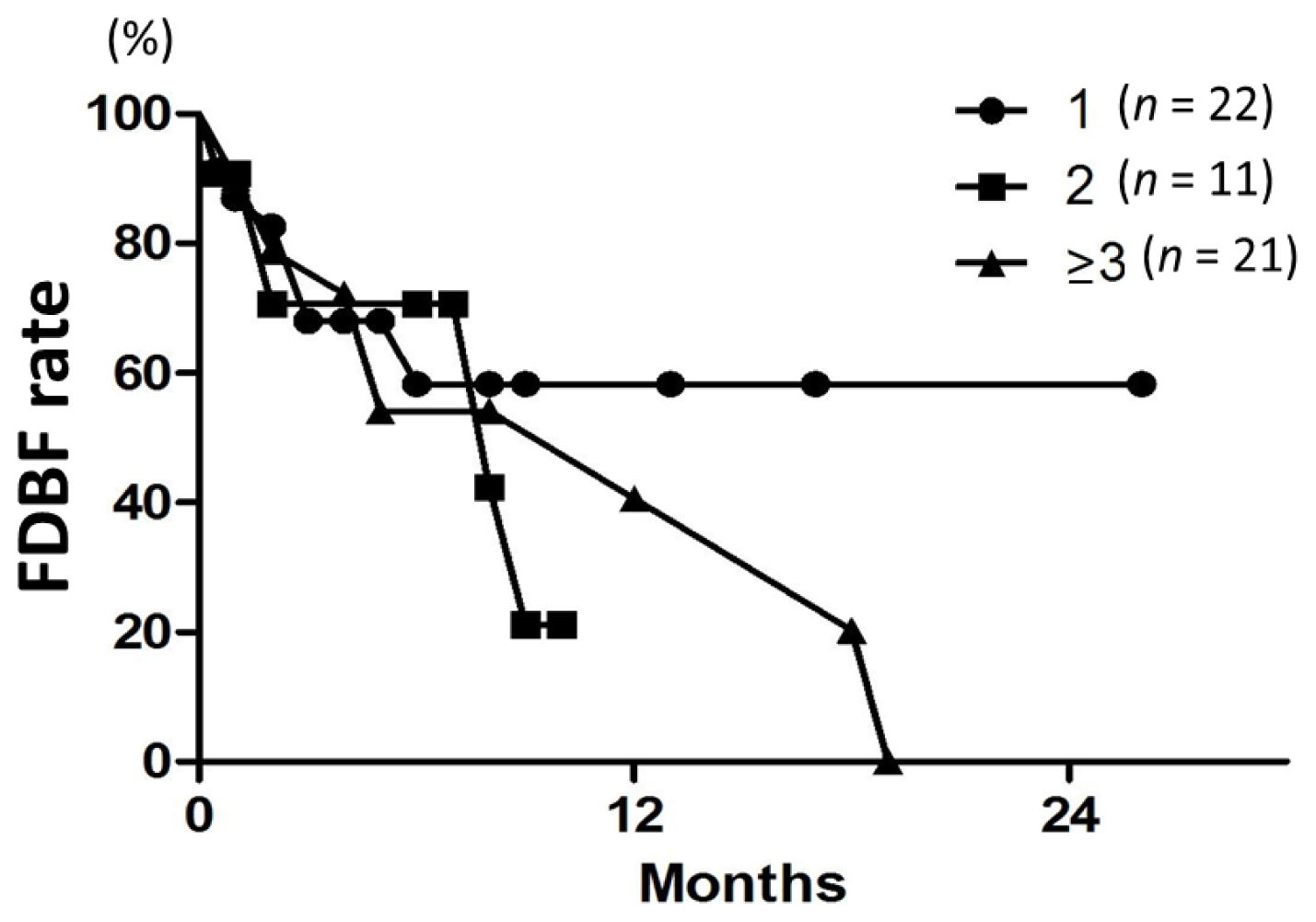
Median time to distant brain failure was 5 months. Freedom from distant brain failure (FDBF) rates at 6, 12, and 18 months were 61%, 41%, and 27%, respectively (Figure 3). The most common modalities for salvage were additional SRS (28%) and WBRT (9.3%). On univariate and multivariate analyses, there was no significant factor in all subsets (Tables 3 and 4). FDBF rates at 6 months for the number of brain metastases of 1, 2, and ≥3 were 57%, 71%, and 55%, respectively (Figure 4, p = 0.7).
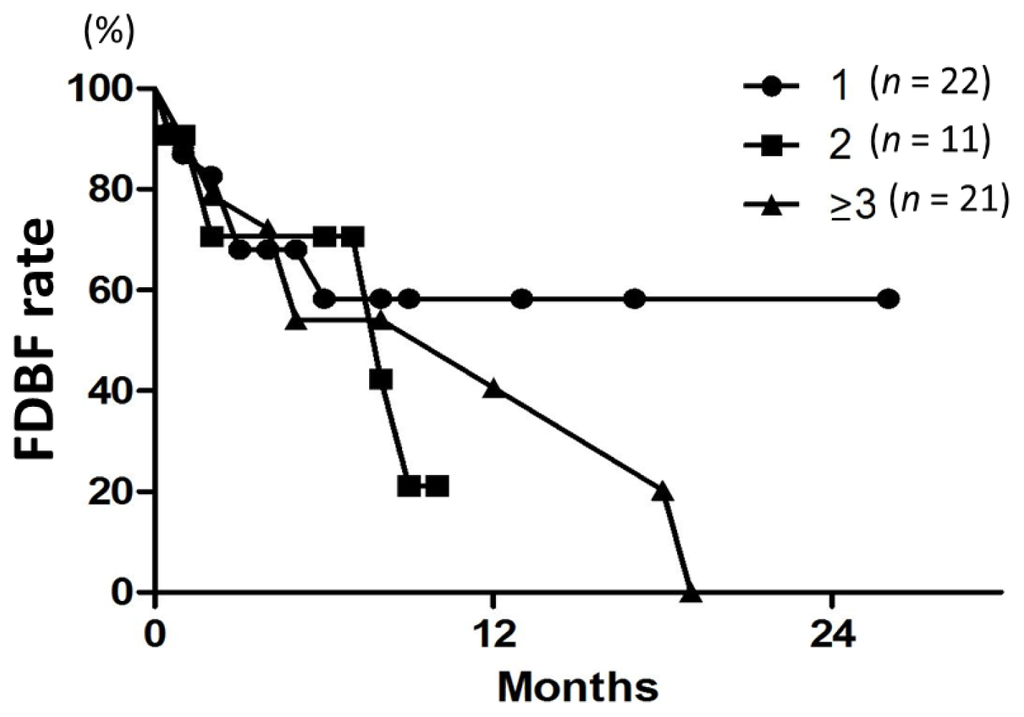
Figure 4.
FDBF curves according to the tumor number (1, 2, or ≥3) in all 54 patients. There was no difference among the three groups (p = 0.7).
2.5. Toxicity
There were no acute adverse events of grade 3 or higher. Only one patient had grade 2 nausea during treatment and one had grade 2 motor neuropathy. The late adverse events were grade 2 neurologic dysfunction observed in 2 patients (4%) and there was no radiation necrosis.
3. Discussion
In previous studies, single-fraction SRS for brain metastases yielded 12-month LC rates of about 80% [13,21]. A recent study reported the rate of 92%, but severe neurological complications (Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) grade 3 and 4) occurred in 5.8% of the patients [22]. Data on cyberknife, with either SRS or SRT, suggested a 6-month LC of 80%–90% [23]. In our study using SRT alone, LC rates at 6 and 12 months were 96% and 91%, respectively. Thus, our fractionated SRT data compare favorably with the SRS and cyberknife data. In an SRS study, the LC rate decreased with increase in the tumor volume; for tumors >3 cc, the LC rate was approximately 60%, but for tumors >10 cc, it was only 25% [9]. In contrast, 12-month LC rates for GTV >3 and >10 cc were 92% and 100%, respectively, in the present study. The high LC rates for GTV >3 and >10 cc may in part be due to the small number of lesions (n = 24 and 6, respectively), but our study would suggest that LC rates of such tumors may be improved by using hypofractionated SRT. Tomotherapy has another advantage. Brain metastases often cause brain edema and bleeding, which result in dislocation of brain metastases. Megavoltage computed tomography (MVCT) images taken before each treatment session can detect the dislocation of a tumor, so it is possible to adjust the patient position for the precise delivery of irradiation to the tumor, which cannot be accomplished with cyberknife and older versions of linac-based SRT machines.
Previous studies on SRT are shown in Table 6. Narayana et al. [24] reported on cyberknife SRT with a dose of 30 Gy in 5 fractions to the 100% isodose line. The LC rate was 70% at 12 months. Inoue et al. [25] reported SRT with 27 Gy in 3 fractions to the 60% isodose line; LC was obtained in 137 of 143 metastases (95.8%) during a median follow-up of 7 months. Fahrig et al. [26] used three different dose concepts for SRT: 5 × (6–7) Gy (A), 10 × 4 Gy (B), and 7 × 5 Gy (C). LC rates with A, B, and C regimens were 96%, 87%, and 85%, respectively. However, complications occurred significantly more often with A (22%) and C (7%) than with B (without complication). Therefore, they concluded that 10 × 4 Gy was well tolerated without severe adverse events. Martens et al. [27] analyzed clinical data using various dose concepts including reirradiation cases, and concluded that the equivalent dose in 2 Gy fractions of ≥35 Gy, which corresponds to the biological effective dose assuming an α/β ratio of 10 Gy (BED10) of ≥42 Gy, seemed to be most effective in patients with primary or recurrent limited brain metastases. The BED10 was 51.3 Gy for the 27 Gy/3 fr schedule and 56 Gy for the 40 Gy/10 fr schedule. Although the BED must be cautiously used in these dose-fractionation ranges [28,29], it was recommended that an appropriate BED10 range was 42 to 56 Gy. Therefore, we started with a prescription dose of 28 Gy delivered in 4 fractions, with a BED of 47.6 Gy. Furthermore, we intended to give higher maximum doses for the PTV than in the usual intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) [30]; the HI was 1.2 ± 0.1 in our study (Figure 5). Reported mean HI for coplanar IMRT radiosurgery, non-coplanar IMRT radiosurgery, and tomotherapy were 1.15 ± 0.05, 1.13 ± 0.04, and 1.18 ± 0.06, respectively, being lower than the HI in our study. The central part of tumors should contain hypoxic cells, so higher doses are necessary to kill such cells [31,32]. We assumed that the LC rates would improve by giving higher doses to the central parts. Moreover, rapid dose fall off outside the PTV was seen even in multiple brain metastases that existed close to each other (Figure 6). Since no severe acute and late complications were seen, still higher doses may be investigated in future studies, but the LC rates obtained in this study might be satisfactory for palliative purposes.

Table 6.
Studies on stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases.
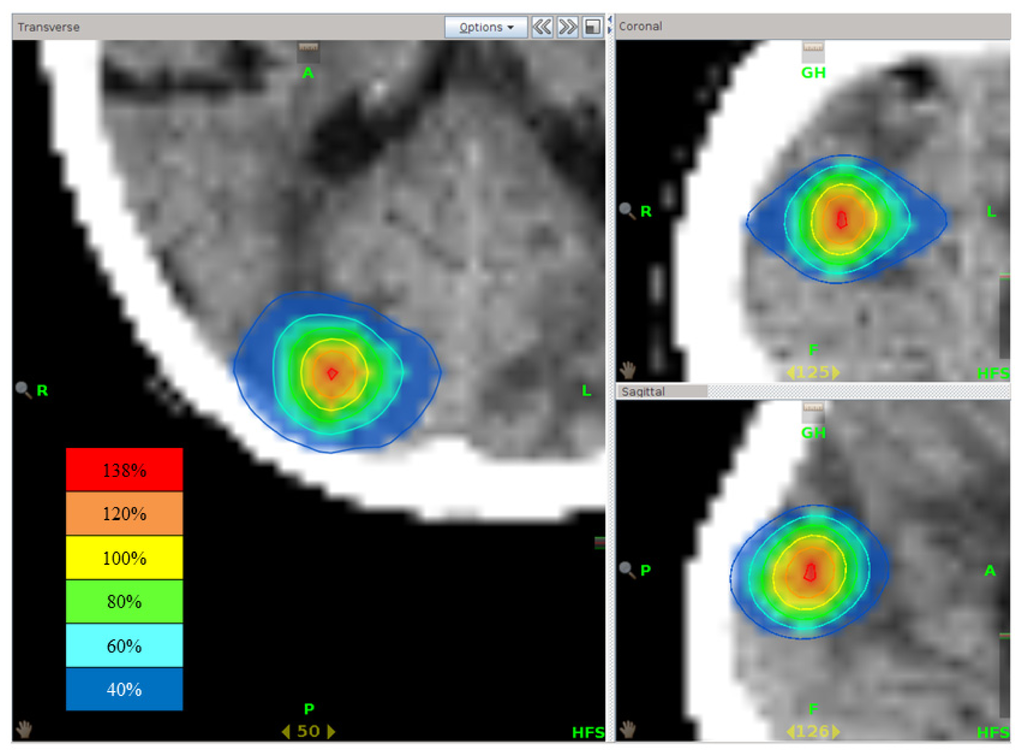
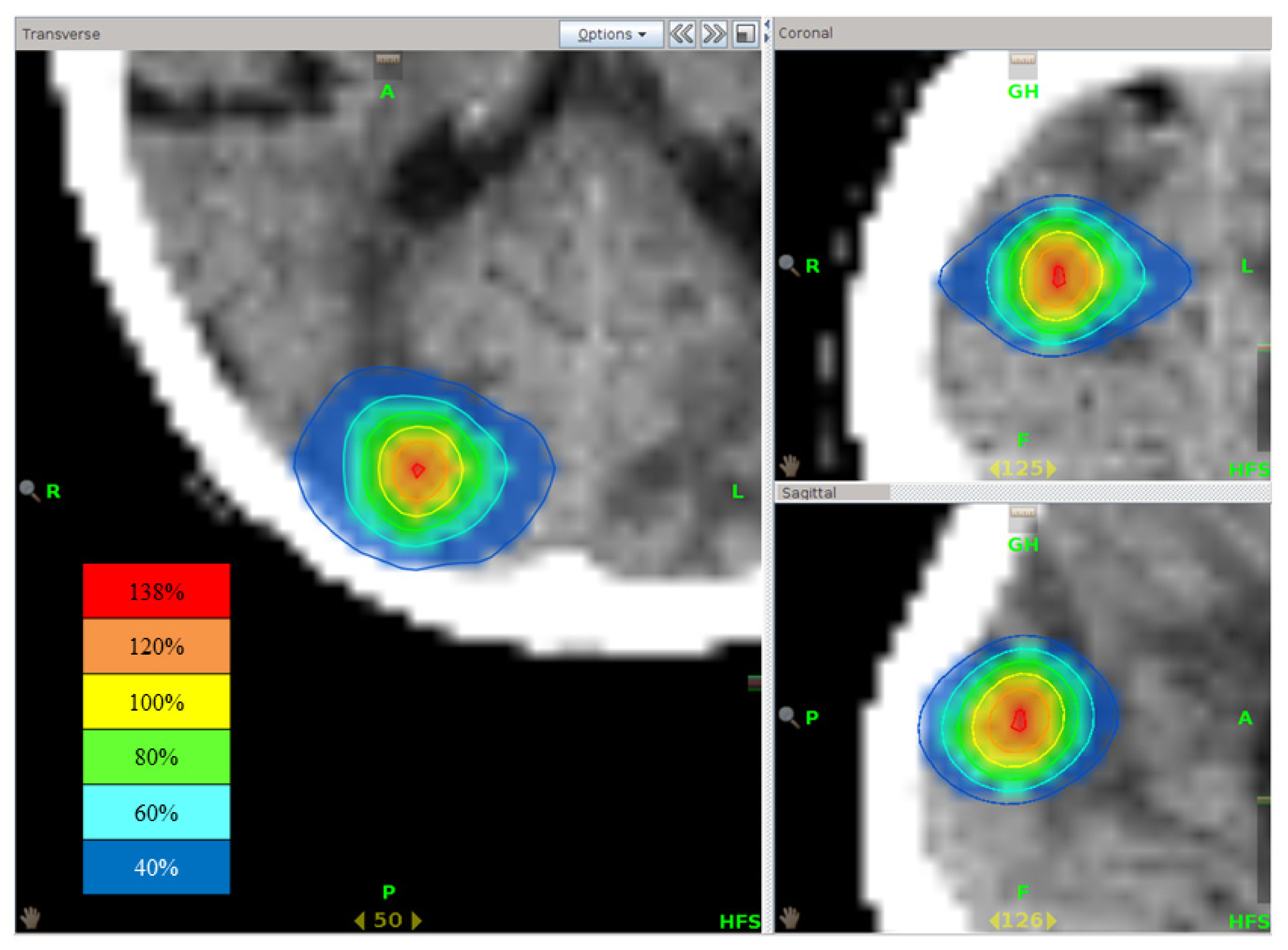
Figure 5.
Isodose distribution of stereotactic radiotherapy using tomotherapy. The highest dose point is present at the central part of the brain metastasis.
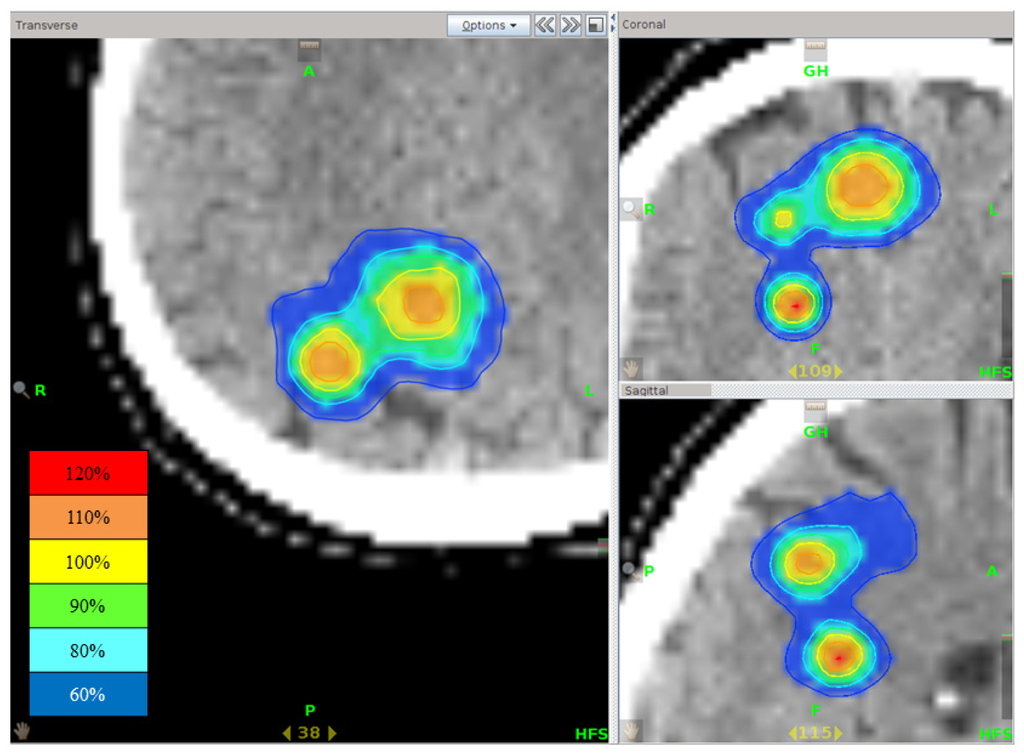
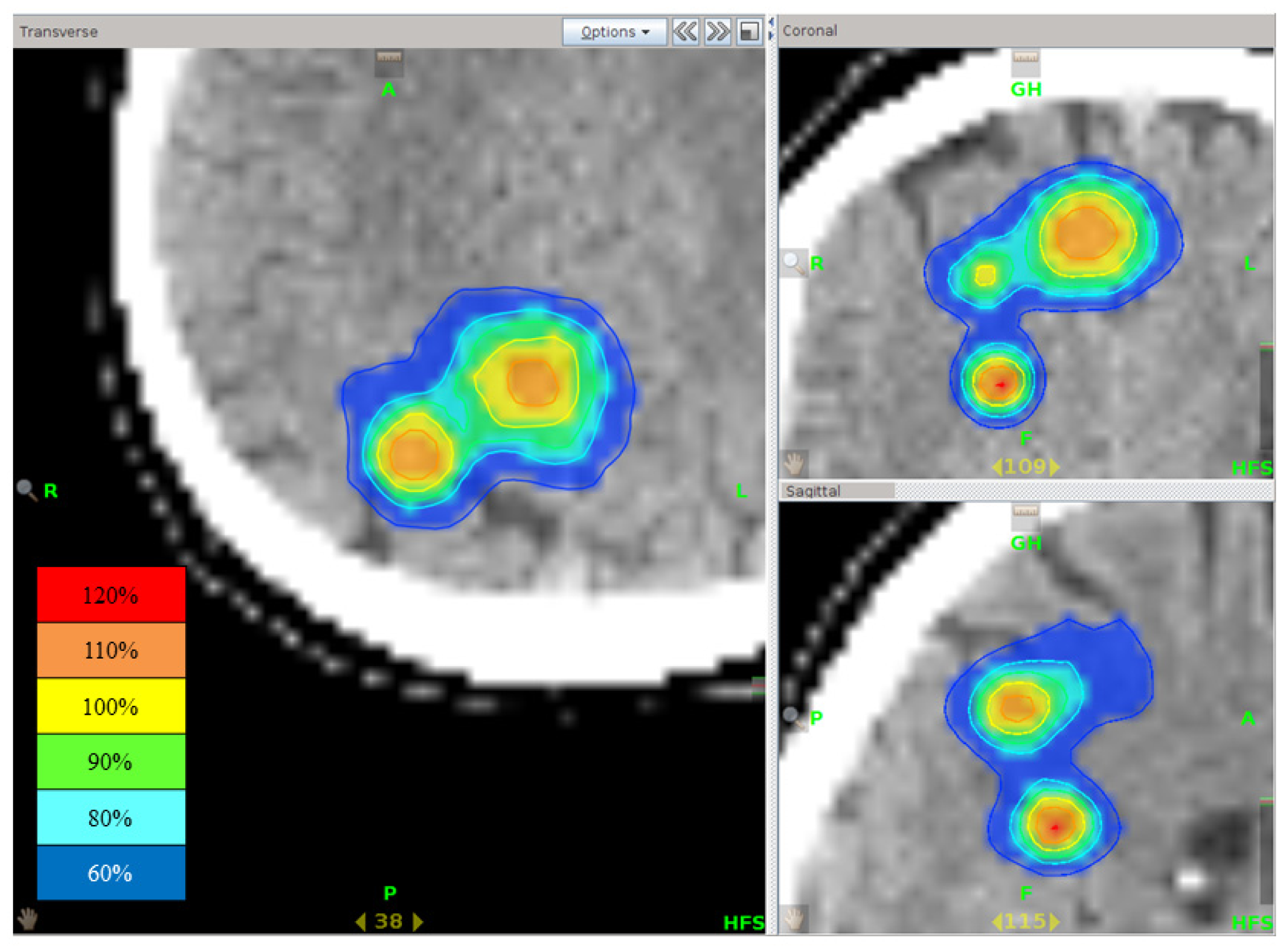
Figure 6.
Isodose distribution of stereotactic radiotherapy using tomotherapy for multiple brain metastases. Although three tumors existed close to each other, rapid dose fall outside the PTV was seen.
According to Likhacheva et al. [33], four factors were predictors of OS: (1) presence of extracranial disease at SRS; (2) total tumor volume of >2 cm3; (3) age > 60 years; and (4) baseline diagnosis-specific graded prognostic assessment (GPA). Antoni et al. [34] reported the following factors for better prognosis: (1) age under 60 years; (2) high Karnofsky performance status (KPS); (3) primary tumor control; (4) low number of extracranial metastases and brain metastases; and (5) triple negative subtype in breast cancer. In the current study, total GTV of >2 cc and the presence of extracranial disease were related to poor OS. Brain metastases are a heterogeneous population. The purpose of the GPA was to identify significant diagnosis-specific prognostic factors in a more recent era (1985–2007) compared with the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis (1979–1993). The original GPA was based on 4 criteria: age, KPS, number of brain metastases, and presence or absence of extracranial metastases [35]. In the current study, only the presence of extracranial disease was related to poor OS in multivariate analysis.
A Japanese multi-institutional prospective study (JLGK0901) [36] and Likhacheva et al. [33] reported a lack of prognostic significance of the number of brain metastases. In this study, treatment volume was more important than lesion number for predicting outcomes. In the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) 22952–26001 study, WBRT reduced the 2-year relapse at the initial site of surgery from 59% to 27% (p < 0.001), and at new sites from 42% to 23% (p = 0.008) [37]. Aoyama et al. [6] reported that the 12-month actuarial rates of developing new brain metastases were 42% (95% CI, 24%–59%) in the WBRT + SRS group and 64% (95% CI, 49%–78%) in the SRS-alone group (p = 0.003). In the current study, the 12-month distant brain control rate was 41%. Our result compares unfavorably with those results obtained with the addition of WBRT. However, in the current study, the 6-month FDBF rates for the number of brain metastases of 1, 2, and ≥3 were 57%, 71%, and 55%, respectively, with no difference among the three groups. Therefore, the role of adding WBRT was unclear. Possibly, the spread of low-dose regions in the surrounding brain when treated with tomotherapy might contribute to the prevention of new lesion development. Although the percentage of the normal brain receiving 12 Gy (3 Gy × 4 fractions) was up to 12.4% (mean: 3.8%) in the present study, this percentage apparently increased in patients with multiple targets and a large tumor. According to the previous study [38], the maximum dose delivered to the brain is about 6.6 cGy in 4 fractions, so the influence of the MVCT dose appears to be little.
EORTC showed that the health-related quality of life (physical and role activities, and cognitive functioning at 8 weeks) of the patients who received adjuvant WBRT after surgery or SRS of a limited number of brain metastases was worse than that of patients in the observation-only group [39]. In addition, WBRT can cause brain atrophy [40]. Therefore, fractionated SRT using tomotherapy may be a suitable option in the treatment of single or multiple brain metastases. However, caution must be taken in planning the treatment. At frame-fixed, 2.4 mm thin-slice magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for gammaknife surgery planning, an increased number of metastases were found in about one-third of the patients compared with the number on MRI at diagnosis [41]. Thus, thin-slice, preferably 1 mm slice, MRI is recommended before tomotherapy planning.
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Study Design and Eligibility Criteria
This was a prospective protocol-based study approved by an institutional review board. Informed consent was obtained from all patients. The eligibility criteria were as follows: (1) brain metastases diagnosed with contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MRI; (2) maximum tumor diameter ≤3 cm; (3) tumor number ≤ 10; (4) no cerebrospinal fluid dissemination; (5) imaging findings and clinical presentation consistent with brain metastases; (6) no concurrent chemotherapy; and (7) no previous WBRT, SRS, or SRT to the target volume to be treated. Since the incidence of radiation necrosis is considered to increase with enlargement of the irradiated brain volume [25], we applied the 4-fraction regimen to tumors with a diameter ≤3 cm. We also treated larger lesions with more fractions, but they were not the subject of this study. The primary endpoint of the study was LC at 6, 12, and 18 months. Secondary endpoints were OS and FDBF at 6, 12, and 18 months, and the incidence of acute and late toxicities. For evaluation of these endpoints, at least 50 patients were scheduled to be accrued.
4.2. Patient Characteristics
All patients were treated at Fukui Saiseikai Hospital using helical tomotherapy (HT, Tomotherapy®, Accuray, Madison, WI, USA). Between August 2009 and June 2013, a total of 54 patients with 128 brain metastases matched the inclusion criteria.
4.3. Treatment Methods
All patients were immobilized in a supine position with a custom head-and-neck thermoplastic shell (Uni-frame, CIVCO Medical Solutions, Kalona, IA, USA), and a customized Head & Neck Vac-Lok Cushion (Med-Tec, Orange City, IA, USA) bag constructed for simulation and treatment. Planning computed tomography (CT) (Toshiba Medical Systems Corporation, Tochigi, Japan) images through the whole head and upper neck were obtained with a 2 mm slice thickness. Next, MRI was performed using a T1 3D FFE (Fast Field Echo) with gadolinium and 3D reconstruction of the axial, sagittal, and coronal planes with 1 mm slice thickness (thin-slice MRI). After scanning, the CT images were fused with MRI for delineation of the target and organs at risk. All target volumes and normal structures were contoured on the Pinnacle3 workstation (Philips Medical Systems, Madison, WI, USA). The GTV was equal to the clinical target volume (CTV). According to a previous single-fraction study [42], the localization error of tomotherapy using volumetric localization was 0.45 ± 0.17 mm, indicating a localization precision of 0.3 mm within a 95% confidence interval. In a multi-fraction study [43], the total systematic (and random) deviations reached 1.6 mm (0.9 mm), 1.7 mm (1.1 mm), and 1.1 mm (0.8 mm) for brain cancer patients in the medial-lateral, cranial-caudal, and anterior-posterior directions, respectively. Therefore, a 2 mm isotropic margin was used in principle for CTV for planning target volume (PTV) expansion in the present study, although the use of 2 mm margins is controversial [44]. The dose was 28 Gy at 80% isodose in 4 fractions delivered on consecutive weekdays. This dose was determined after trial and error based on the concept described in the Discussion. After confirming the safety of the dose, the daily dose was increased in July 2012 from 7.0 to 7.2 Gy.
Treatment plans were optimized in the tomotherapy planning software version 1, 2, 3, 4 (Accuray, Madison, WI, USA), with a convolution/superposition dose calculation algorithm. The planning parameters used for the HT plans were as follows: a field width of 1.0 cm, a pitch of 0.287, a modulation factor of 1.1–2.0, and a fine calculation grid (1.96 mm × 1.96 mm × slice thickness). All plans were verified in-phantom on the HT unit before treatment began. The HI was defined as the ratio of the maximum dose in the PTV (Dmax) and the prescription dose in the PTV (Drx):
The patients were treated using the thermoplastic immobilization mask used for simulation, with positioning determined by coregistration of a MVCT scan acquired on the HT unit immediately before treatment. The initial automated MVCT co-registration using the bone and soft tissue setting on the HT unit was used with manual refinements by the therapists before treatment. An attending radiation oncologist verified all MVCT co-registrations.
4.4. Evaluation
Acute adverse reactions were monitored on the first and last days of treatment. Patients were followed at 1- to 3-month intervals after SRT and were evaluated by a physical examination and contrast-enhanced thin-slice MRI. The tumor response was evaluated by comparing follow-up MRI with pretreatment MRI and classified according to the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors. Adverse reactions were evaluated using the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events version 4.0.
4.5. Statistical Methods
LC, OS, and FDBF rates were calculated using the Kaplan-Meier method from the start of SRT. Univariate log-rank tests were used to assess the significance of prognostic factors affecting LC, OS, and FDBF. A two-sided p value of 0.05 or less was considered to reflect statistical significance. These univariate analyses were carried out using Prism (Graph Pad Institute Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). The Cox proportional hazard model was used for multivariate analysis to assess the effects of patient, tumor, and other factors on the endpoints. The forced entry test was used to assess the role of covariates in the model. These multivariate analyses were carried out using SPSS statistical software version 17.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
5. Conclusions
The 4-fraction SRT protocol with a total dose of 28 or 28.8 Gy provided excellent tumor control with minimal toxicity. Distant brain failure was not so frequent, even in patients with multiple tumors, possibly justifying the use of tomotherapy SRT in patients with multiple brain metastases. The results of the current study would warrant a prospective randomized study comparing single-fraction SRS with SRT in this patient population.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Yoshimasa Mori and Koji Inoda for their valuable help in this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
- Author ContributionsA.N. designed the study, contributed to the data acquisition, performed the statistical analysis, and prepared the manuscript. Y.S. designed the study and prepared the manuscript. M.Y. designed the study and contributed to the data acquisition. K.W. and Y.K. contributed to the data acquisition. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
References
- Soffietti, R.; Costanza, A.; Laguzzi, E.; Nobile, M.; Rudà, R. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy of brain metastases. J. Neurooncol 2005, 75, 31–42. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, C.M.; Khuntia, D.; Mehta, M.P. Therapeutic management of metastatic brain tumors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol 2007, 61, 70–78. [Google Scholar]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Sugie, C.; Iwata, H. Radiotherapy for metastatic brain tumors. Int. J. Clin. Oncol 2009, 14, 281–288. [Google Scholar]
- Caffo, M.; Barresi, V.; Caruso, G.; Cutugno, M.; la Fata, G.; Venza, M.; Alafaci, C.; Tomasello, F. Innovative therapeutic strategies in the treatment of brain metastases. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2013, 14, 2135–2174. [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, M.N.; Rades, D.; Wirth, A.; Lo, S.S.; Danielson, B.L.; Gaspar, L.E.; Sperduto, P.W.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Radawski, J.D.; Wang, J.Z.; et al. Radiotherapeutic and surgical management for newly diagnosed brain metastasis (es): An American society for radiation oncology evidence-based guideline. Pract. Radiat. Oncol 2012, 2, 210–225. [Google Scholar]
- Aoyama, H.; Shirato, H.; Tago, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Toyoda, T.; Hatano, K.; Kenjyo, M.; Oya, N.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases. JAMA 2006, 295, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar]
- Mehta, M.P.; Tsao, M.N.; Whelan, T.J.; Morris, D.E.; Hayman, J.A.; Flickinger, J.C.; Mills, M.; Rogers, C.L.; Souhami, L. The American society for therapeutic radiology and oncology (ASTRO) evidence-based review of the role of radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2005, 63, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Sanghavi, S.N.; Miranpuri, S.S.; Chappell, R.; Buatti, J.M.; Sneed, P.K.; Suh, J.H.; Regine, W.F.; Weltman, E.; King, V.J.; Goetsch, S.J.; et al. Radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases: Multi-institutional analysis, stratified by the RTOG recursive partitioning analysis method. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2001, 51, 426–434. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, E.J.; Brenner, D.J. The radiobiology of radiosurgery: Rationale for different treatment regimes for AVMs and malignancies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 1993, 25, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Yukawa, Y.; Tsutsui, K.; Takahashi, M.; Abe, M. Variation in the hypoxic fraction among mouse tumors of different types, sizes, and sites. Jpn. J. Cancer Res 1986, 77, 908–915. [Google Scholar]
- Tomita, N.; Shibamoto, Y.; Ito, M.; Ogino, H.; Sugie, C.; Ayakawa, S.; Iwata, H. Biological effect of intermittent radiation exposure in vivo: Recovery from sublethal damage versus reoxygenation. Radiother. Oncol 2008, 86, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Hashizume, C.; Baba, F.; Ayakawa, S.; Manabe, Y.; Nagai, A.; Miyakawa, A.; Murai, T.; Iwata, H.; Mori, Y.; et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy using a radiobiology-based regimen for stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer 2012, 118, 2078–2084. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.C.; Petrovich, Z.; O’Day, S.; Morton, D.; Essner, R.; Giannotta, S.L.; Yu, C.; Apuzzo, M.L. Stereotactic radiosurgery in the treatment of metastatic disease to the brain. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 268–279. [Google Scholar]
- Shiau, C.Y.; Sneed, P.K.; Shu, H.K.; Lamborn, K.R.; McDermott, M.W.; Chang, S.; Nowak, P.; Petti, P.L.; Smith, V.; Verhey, L.J.; et al. Radiosurgery for brain metastases: Relationship of dose and pattern of enhancement to local control. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 1997, 37, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Tomita, N.; Kodaira, T.; Tachibana, H.; Nakamura, T.; Nakahara, R.; Inokuchi, H.; Shibamoto, Y. Helical tomotherapy for brain metastases: Dosimetric evaluation of treatment plans and early clinical results. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat 2008, 7, 417–424. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, G.; Yartsev, S.; Yaremko, B.; Perera, F.; Dar, A.R.; Hammond, A.; Lock, M.; Yu, E.; Ash, R.; Caudrelier, J.M.; et al. Phase I trial of simultaneous in-field boost with helical tomotherapy for patients with one to three brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2011, 80, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Kirova, Y.M.; Chargari, C.; Zefkili, S.; Campana, F. Could helical tomotherapy do whole brain radiotherapy and radiosurgery? World J. Radiol 2010, 2, 148–150. [Google Scholar]
- Levegrün, S.; Pöttgen, C.; Wittig, A.; Lübcke, W.; Abu Jawad, J.; Stuschke, M. Helical tomotherapy for whole-brain irradiation with integrated boost to multiple brain metastases: Evaluation of dose distribution characteristics and comparison with alternative techniques. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2013, 86, 734–742. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderspek, L.; Bauman, G.; Wang, J.Z.; Yartsev, S.; Ménard, C.; Cho, Y.B.; Mundt, A.J.; Lawson, J.D.; Murphy, K.T. Dosimetric comparison of intensity-modulated radiosurgery and helical tomotherapy for the treatment of multiple intracranial metastases. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat 2009, 8, 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Peñagarícano, J.A.; Yan, Y.; Shi, C.; Linskey, M.E.; Ratanatharathorn, V. Dosimetric comparison of helical tomotherapy and gamma knife stereotactic radiosurgery for single brain metastasis. Radiat. Oncol 2006, 1, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa, T.; Kondziolka, D.; Flickinger, J.C.; Germanwala, A.; Lunsford, L.D. Brain metastases treated with radiosurgery alone: An alternative to whole brain radiotherapy? Neurosurgery 2003, 52, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar]
- Minniti, G.; Clarke, E.; Lanzetta, G.; Osti, M.F.; Trasimeni, G.; Bozzao, A.; Romano, A.; Enrici, R.M. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: Analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. Radiat. Oncol 2011, 6, 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nishizaki, T.; Saito, K.; Jimi, Y.; Harada, N.; Kajiwara, K.; Nomura, S.; Ishihara, H.; Yoshikawa, K.; Yoneda, H.; Suzuki, M.; et al. The role of cyberknife radiosurgery/radiotherapy for brain metastases of multiple or large-size tumors. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg 2006, 49, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Narayana, A.; Chang, J.; Yenice, K.; Chan, K.; Lymberis, S.; Brennan, C.; Gutin, P.H. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using intensity-modulated radiotherapy in patients with one or two brain metastases. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg 2007, 85, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, H.K.; Seto, K.; Nozaki, A.; Torikai, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, J.; Noda, S.E.; Nakano, T. Three-fraction cyberknife radiotherapy for brain metastases in critical areas: Referring to the risk evaluating radiation necrosis and the surrounding brain volumes circumscribed with a single dose equivalence of 14 Gy (V14). J. Radiat. Res 2013, 54, 727–735. [Google Scholar]
- Fahrig, A.; Ganslandt, O.; Lambrecht, U.; Grabenbauer, G.; Kleinert, G.; Sauer, R.; Hamm, K. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for brain metastases—Results from three different dose concepts. Strahlenther. Onkol 2007, 183, 625–630. [Google Scholar]
- Märtens, B.; Janssen, S.; Werner, M.; Frühauf, J.; Christiansen, H.; Bremer, M.; Steinmann, D. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy of limited brain metastases: A single-centre individualized treatment approach. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 497. [Google Scholar]
- Iwata, H.; Shibamoto, Y.; Murata, R.; Tomita, N.; Ayakawa, S.; Ogino, H.; Ito, M. Estimation of errors associated with use of linear-quadratic formalism for evaluation of biologic equivalence between single and hypofractionated radiation doses: An in vitro study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2009, 75, 482–488. [Google Scholar]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Otsuka, S.; Iwata, H.; Sugie, C.; Ogino, H.; Tomita, N. Radiobiological evaluation of the radiation dose as used in high-precision radiotherapy: Effect of prolonged delivery time and applicability of the linear-quadratic model. J. Radiat. Res 2012, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Han, C.; Liu, A.; Schultheiss, T.E.; Pezner, R.D.; Chen, Y.J.; Wong, J.Y. Dosimetric comparisons of helical tomotherapy treatment plans and step-and-shoot intensity-modulated radiosurgery treatment plans in intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2006, 65, 608–616. [Google Scholar]
- Tannock, I.F. The relation between cell proliferation and the vascular system in a transplanted mouse mammary tumour. Br. J. Cancer 1968, 22, 258–273. [Google Scholar]
- Thomlinson, R.H.; Gray, L.H. The histological structure of some human lung cancers and the possible implications for radiotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 1955, 9, 539–549. [Google Scholar]
- Likhacheva, A.; Pinnix, C.C.; Parikh, N.R.; Allen, P.K.; McAleer, M.F.; Chiu, M.S.; Sulman, E.P.; Mahajan, A.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; Prabhu, S.S. Predictors of survival in contemporary practice after initial radiosurgery for brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2013, 85, 656–661. [Google Scholar]
- Antoni, D.; Clavier, J.B.; Pop, M.; Benoît, C.; Lefebvre, F.; Noël, G. An institutional retrospective analysis of 93 patients with brain metastases from breast cancer: Treatment outcomes, diagnosis-specific prognostic factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2012, 13, 16489–16499. [Google Scholar]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Berkey, B.; Gaspar, L.E.; Mehta, M.; Curran, W. A new prognostic index and comparison to three other indices for patients with brain metastases: An analysis of 1960 patients in the RTOG database. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2008, 70, 510–514. [Google Scholar]
- Serizawa, T.; Hirai, T.; Nagano, O.; Higuchi, Y.; Matsuda, S.; Ono, J.; Saeki, N. Gamma knife surgery for 1–10 brain metastases without prophylactic whole-brain radiation therapy: Analysis of cases meeting the Japanese prospective multi-institute study (JLGK0901) inclusion criteria. J. Neurooncol 2010, 98, 163–167. [Google Scholar]
- Kocher, M.; Soffietti, R.; Abacioglu, U.; Villà, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.D.; Carrie, C.; et al. Adjuvant whole brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of 1–3 cerebral metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952–26001 study. J. Clin. Oncol 2011, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, A.P.; Langen, K.M.; Ruchala, K.J.; Cox, A.; Kupelian, P.A.; Meeks, S.L. Patient dose from megavoltage computed tomography imaging. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2008, 70, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Soffietti, R.; Kocher, M.; Abacioglu, U.M.; Villa, S.; Fauchon, F.; Baumert, B.G.; Fariselli, L.; Tzuk-Shina, T.; Kortmann, R.D.; Carrie, C.; et al. A european organisation for research and treatment of cancer phase III trial of adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation in patients with one to three brain metastases from solid tumors after surgical resection or radiosurgery: Quality-of-life results. J. Clin. Oncol 2013, 31, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Shibamoto, Y.; Baba, F.; Oda, K.; Hayashi, S.; Kokubo, M.; Ishihara, S.; Itoh, Y.; Ogino, H.; Koizumi, M. Incidence of brain atrophy and decline in mini-mental state examination score after whole-brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: A prospective study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2008, 72, 1168–1173. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, A.; Shibamoto, Y.; Mori, Y.; Hashizume, C.; Hagiwara, M.; Kobayashi, T. Increases in the number of brain metastases detected at frame-fixed, thin-slice MRI for gammaknife surgery planning. J. Neurooncol 2010, 12, 1187–1192. [Google Scholar]
- Soisson, E.T.; Hardcastle, N.; Tomé, W.A. Quality assurance of an image guided intracranial stereotactic positioning system for radiosurgery treatment with helical tomotherapy. J. Neurooncol 2010, 2, 277–285. [Google Scholar]
- Vaandering, A.; Lee, J.A.; Renard, L.; Grégoire, V. Evaluation of MVCT protocols for brain and head and neck tumor patients treated with helical tomotherapy. Radiother. Oncol 2009, 1, 50–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nataf, F.; Schlienger, M.; Liu, Z.; Foulquier, J.N.; Grès, B.; Orthuon, A.; Vannetzel, J.M.; Escudier, B.; Meder, J.F.; Roux, F.X.; et al. Radiosuegery with or without a 2-mm margin for 93 single brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys 2008, 70, 766–772. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).