TRAV7-2*02 Expressing CD8+ T Cells Are Responsible for Palladium Allergy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Activated T Cells Accumulate in Regional Lymph Nodes during Pd Allergy
2.2. The Pathogenic TCR Repertoire in Pd Allergic Mice
2.3. MHC I and Activated CD8+ T Cells Are Critical for Pd Allergy
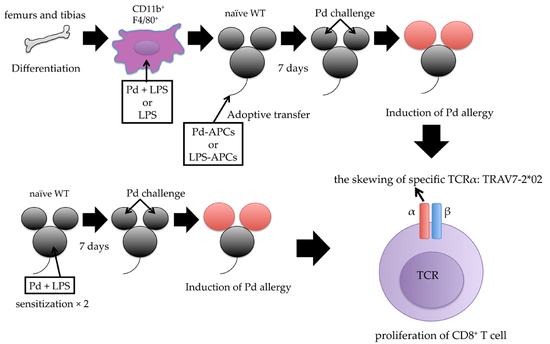
2.4. Adoptive Transfer of In Vitro Prepared Pd-Treated APCs Induces Pd Allergy
2.5. MHC I-Dependent CD8+ T Cell Activation Is Essential for the Onset of Pd Allergy
2.6. Identification of CDR3 Amino Acid Sequences in Pd Allergy
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Mice
4.3. Antibodies and Reagents
4.4. Induction of Pd Allergy
4.5. Histological Analysis
4.6. Adoptive Transfer of Bone Marrow-Derived Antigen-Presenting Cells
4.7. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Cell Populations
4.8. T Cell Repertoire Sequence Analysis Using a Next-Generation Sequencer
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Pd | Palladium |
| DTH | Delayed-type hypersensitivity |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| TRAV | TCRα variable |
| APCs | Antigen presenting cells |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| TRAJ | TCRα junction |
| WT | Wild-type |
| SLN | Submandibular lymph node |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TRBV | TCRβ variable |
| B2m | β2m-Microgloblin |
| B2m−/− mice | C57BL/6 deficient β2m-microgloblin mice |
| I-Ab−/− mice | C57BL/6 deficient MHC II H2-Ab1 (I-Ab) mice |
| mM-CSF | Mouse macrophage colony stimulating factor |
| mAbs | Monoclonal antibodies |
| PMA | Phorbol myristate acetate |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
References
- Raap, U.; Stiesch, M.; Reh, H.; Kapp, A.; Werfel, T. Investigation of contact allergy to dental metals in 206 patients. Contact Dermat. 2009, 60, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faurschou, A.; Menne, T.; Johansen, J.D.; Thyssen, J.P. Metal allergen of the 21st century—A review on exposure, epidemiology and clinical manifestations of palladium allergy. Contact Dermat. 2011, 64, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, D.H.; Igyarto, B.Z.; Gaspari, A.A. Early immune events in the induction of allergic contact dermatitis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Goebeler, M. Immunology of metal allergies. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2015, 13, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muris, J.; Feilzer, A.J.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Rustemeyer, T.; van Hoogstraten, I.M.; Scheper, R.J.; von Blomberg, B.M. Palladium-induced Th2 cytokine responses reflect skin test reactivity. Allergy 2012, 67, 1605–1608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawano, M.; Nakayama, M.; Aoshima, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Ono, M.; Nishiya, T.; Nakamura, S.; Takeda, Y.; Dobashi, A.; Takahashi, A.; et al. NKG2D+ IFN-γ+ CD8+ T cells are responsible for palladium allergy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.T.; Wherry, E.J.; Goldrath, A.W. Molecular regulation of effector and memory T cell differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, K.; Yoshinaga, S.K.; Lanier, L.L. Inducible costimulator costimulates cytotoxic activity and IFN-gamma production in activated murine NK cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3676–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossjohn, J.; Gras, S.; Miles, J.J.; Turner, S.J.; Godfrey, D.I.; McCluskey, J. T cell antigen receptor recognition of antigen-presenting molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, C.D.; Luoma, A.M.; Adams, E.J. Coevolution of T-cell receptors with MHC and non-MHC ligands. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 267, 30–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashizume, H.; Seo, N.; Ito, T.; Takigawa, M.; Yagi, H. Promiscuous interaction between gold-specific T cells and APCs in gold allergy. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8096–8102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennecke, J.; Wiley, D.C. T cell receptor-MHC interactions up close. Cell 2001, 104, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, K.C.; Adams, E.J. How the T cell receptor sees antigen—A structural view. Cell 2005, 122, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honda, T.; Egawa, G.; Grabbe, S.; Kabashima, K. Update of immune events in the murine contact hypersensitivity model: Toward the understanding of allergic contact dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Kinbara, M.; Kuroishi, T.; Kimura, K.; Iwakura, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Sugawara, S.; Endo, Y. Lipopolysaccharide promotes and augments metal allergies in mice, dependent on innate immunity and histidine decarboxylase. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, H.; Kumagai, K.; Eguchi, T.; Shigematsu, H.; Kitaura, K.; Kawano, M.; Horikawa, T.; Suzuki, S.; Matsutani, T.; Ogasawara, K.; et al. Characterization of T cell receptors of Th1 cells infiltrating inflamed skin of a novel murine model of palladium-induced metal allergy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muris, J.; Kleverlaan, C.J.; Feilzer, A.J.; Rustemeyer, T. Sodium tetrachloropalladate (Na2[PdCl4]) as an improved test salt for palladium allergy patch testing. Contact Dermat. 2008, 58, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Raghavan, B.; Muller, V.; Vogl, T.; Fejer, G.; Tchaptchet, S.; Keck, S.; Kalis, C.; Nielsen, P.J.; Galanos, C.; et al. Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toivonen, R.; Arstila, T.P.; Hanninen, A. Islet-associated T-cell receptor-beta CDR sequence repertoire in prediabetic NOD mice reveals antigen-driven T-cell expansion and shared usage of VbetaJbeta TCR chains. Mol. Immunol. 2015, 64, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haqqi, T.M.; Anderson, G.D.; Banerjee, S.; David, C.S. Restricted heterogeneity in T-cell antigen receptor V β gene usage in the lymph nodes and arthritic joints of mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1253–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Vollmer, J.; Moulon, C.; Weltzien, H.U.; Marrack, P.; Kappler, J. Components of the ligand for a Ni++ reactive human T cell clone. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamerdinger, K.; Moulon, C.; Karp, D.R.; Van Bergen, J.; Koning, F.; Wild, D.; Pflugfelder, U.; Weltzien, H.U. A new type of metal recognition by human T cells: Contact residues for peptide-independent bridging of T cell receptor and major histocompatibility complex by nickel. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; Kumagai, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Eguchi, T.; Kitaura, K.; Suzuki, S.; Horikawa, T.; Matsutani, T.; Ogasawara, K.; Hamada, Y.; et al. Accumulation of metal-specific T cells in inflamed skin in a novel murine model of chromium-induced allergic contact dermatitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinbara, M.; Nagai, Y.; Takano-Yamamoto, T.; Sugawara, S.; Endo, Y. Cross-reactivity among some metals in a murine metal allergy model. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, S.; Kaji, K.; Kudo, A. Identification and characterization of the new osteoclast progenitor with macrophage phenotypes being able to differentiate into mature osteoclasts. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2000, 15, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiya, T.; DeFranco, A.L. Ligand-regulated chimeric receptor approach reveals distinctive subcellular localization and signaling properties of the Toll-like receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19008–190017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennino, D.; Eyerich, K.; Scarponi, C.; Carbone, T.; Eyerich, S.; Nasorri, F.; Garcovich, S.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Albanesi, C.; Cavani, A. IL-17 amplifies human contact hypersensitivity by licensing hapten nonspecific Th1 cells to kill autologous keratinocytes. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 4880–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| TRAV7-2*02 Bearing TRAJ | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| TRAJ6*01 | 6.8 |
| TRAJ15*01 | 10.6 |
| TRAJ22*01 | 25.5 |
| TRAJ26*01 | 4.6 |
| TRAJ27*01 | 4.8 |
| TRAJ31*01 | 4.6 |
| TRAJ37*01 | 7.1 |
| TRAV | CDR3 | TRAJ | Frequency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3′ V-Region | N | 5′ J-Region | ||||
| Mouse 1 | TRAV7-2*02 | CAAR | G | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 22.1 |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | T | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 20.1 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AGA | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 20.1 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | I | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 14.9 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AA | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 14.9 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CA | ARA | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 7.8 | |
| Mouse 2 | TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | SHA | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 39.3 |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AR | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 39.3 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | IA | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 21.4 | |
| Mouse 3 | TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AR | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 69.0 |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | KIP | GSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 31.0 | |
| Mouse 4 | TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AA | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 33.3 |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | L | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 42.8 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | P | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 23.9 | |
| TRAV | CDR3 | TRAJ | Frequency (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3′ V-Region | N | 5′ J-Region | ||||
| Mouse 1 | TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | T | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 30.8 |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | S | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 23.1 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | PA | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 15.4 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | R | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 15.4 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AR | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 15.4 | |
| Mouse 2 | TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AA | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 30.8 |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | A | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 23.1 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | R | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 15.4 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AR | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 15.4 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CA | AQ | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 15.4 | |
| Mouse 3 | TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | I | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 50.0 |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | I | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 50.0 | |
| Mouse 4 | TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | T | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 25.9 |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | MA | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 25.9 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAAS | I | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 18.5 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | GS | SSGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 14.8 | |
| TRAV7-2*02 | CAA | SP | SGSWQLIF | TRAJ22*01 | 14.8 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takeda, Y.; Suto, Y.; Ito, K.; Hashimoto, W.; Nishiya, T.; Ueda, K.; Narushima, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ogasawara, K. TRAV7-2*02 Expressing CD8+ T Cells Are Responsible for Palladium Allergy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061162
Takeda Y, Suto Y, Ito K, Hashimoto W, Nishiya T, Ueda K, Narushima T, Takahashi T, Ogasawara K. TRAV7-2*02 Expressing CD8+ T Cells Are Responsible for Palladium Allergy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061162
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakeda, Yuri, Yoshiko Suto, Koyu Ito, Wataru Hashimoto, Tadashi Nishiya, Kyosuke Ueda, Takayuki Narushima, Tetsu Takahashi, and Kouetsu Ogasawara. 2017. "TRAV7-2*02 Expressing CD8+ T Cells Are Responsible for Palladium Allergy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061162
APA StyleTakeda, Y., Suto, Y., Ito, K., Hashimoto, W., Nishiya, T., Ueda, K., Narushima, T., Takahashi, T., & Ogasawara, K. (2017). TRAV7-2*02 Expressing CD8+ T Cells Are Responsible for Palladium Allergy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061162