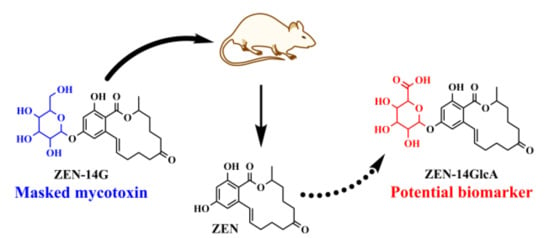
Metabolic Profile, Bioavailability and Toxicokinetics of Zearalenone-14-Glucoside in Rats after Oral and Intravenous Administration by Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Metabolic Profile of ZEN-14G in Rat Plasma Using Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS)
2.2. Method Validation
2.3. Toxicokinetic Characterization
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Animals and Experimental Protocol
3.3. Plasma Sample Preparation
3.4. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
3.5. LC-MS/MS Method and Validation
3.6. Toxicokinetic Analysis Using WinNonlin 6.3
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ZEN-14G | zearalenone |
| LC-MS/MS | liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry |
| AUC | area under the plasma concentration–time curve |
| VZ | apparent volume of distribution |
| CL | total body clearance |
| DON | deoxynivalenol |
| LOQ | limit of quantitation |
| GlcA | glucuronic acid |
| LC-HRMS | liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry |
References
- Minervini, F.; Dell’Aquila, M.E. Zearalenone and reproductive function in farm animals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2570–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Kim, W.; Park, J.H.; Kim, D.; Kim, C.R.; Chung, S.; Lee, C. The Occurrence of Zearalenone in South Korean Feedstuffs between 2009 and 2016. Toxins (Basel) 2017, 9, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain. Scientific Opinion on the risks for public health related to the presence of zearalenone in food. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, L.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Modified mycotoxins: An updated review on their formation, detection, occurrence, and toxic effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellafiora, L.; Galaverna, G.; Righi, F.; Cozzini, P.; Dall’Asta, C. Assessing the hydrolytic fate of the masked mycotoxin zearalenone-14-glucoside - A warning light for the need to look at the "maskedome". Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 99, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, J.; Borzekowski, A.; Haase, H.; Menzel, R.; Ruess, L.; Koch, M. Toxicity Assay for Citrinin, Zearalenone and Zearalenone-14-Sulfate Using the Nematode Caenorhabditis elegans as Model Organism. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knutsen, H.K.; Alexander, J.; Barregård, L.; Bignami, M.; Brüschweiler, B.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cottrill, B.; Dinovi, M.; Edler, L.; Grasl-Kraupp, B. Risks for animal health related to the presence of zearalenone and its modified forms in feed. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04851. [Google Scholar]
- Broekaert, N.; Devreese, M.; de Baere, S.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Modified Fusarium mycotoxins unmasked: From occurrence in cereals to animal and human excretion. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015, 80, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirlini, M.; Barilli, A.; Galaverna, G.; Michlmayr, H.; Adam, G.; Berthiller, F.; Dall’Asta, C. Study on the uptake and deglycosylation of the masked forms of zearalenone in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 98, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, L.; Atanasova-Penichon, V.; Chereau, S.; Richard-Forget, F. Metabolomics to Decipher the Chemical Defense of Cereals against Fusarium graminearum and Deoxynivalenol Accumulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 24839–24872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; He, X.; Matsuo, Y.; Singh, P.K.; Kushiro, M. Analysis of the Masked Metabolite of Deoxynivalenol and Fusarium Resistance in CIMMYT Wheat Germplasm. Toxins (Basel) 2017, 9, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagl, V.; Woechtl, B.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Hennig-Pauka, I.; Moll, W.D.; Adam, G.; Berthiller, F. Metabolism of the masked mycotoxin deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside in pigs. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broekaert, N.; Devreese, M.; van Bergen, T.; Schauvliege, S.; De Boevre, M.; De Saeger, S.; Vanhaecke, L.; Berthiller, F.; Michlmayr, H.; Malachova, A.; et al. In vivo contribution of deoxynivalenol-3-beta-D-glucoside to deoxynivalenol exposure in broiler chickens and pigs: Oral bioavailability, hydrolysis and toxicokinetics. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlig, S.; Stanic, A.; Hofgaard, I.S.; Kluger, B.; Schuhmacher, R.; Miles, C.O. Glutathione-Conjugates of Deoxynivalenol in Naturally Contaminated Grain Are Primarily Linked via the Epoxide Group. Toxins (Basel) 2016, 8, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binder, S.B.; Schwartz-Zimmermann, H.E.; Varga, E.; Bichl, G.; Michlmayr, H.; Adam, G.; Berthiller, F. Metabolism of Zearalenone and Its Major Modified Forms in Pigs. Toxins (Basel) 2017, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, R.E.; Reese, R.E.; Brouwer, E.A. Metabolism of [14C]zearalenone in laying hens. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1980, 28, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleck, S.C.; Churchwell, M.I.; Doerge, D.R. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of zearalenone following oral and intravenous administration in juvenile female pigs. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiessling, K.H.; Pettersson, H. Metabolism of zearalenone in rat liver. Acta Pharm. Toxicol. (Copenh.) 1978, 4, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, F.; De Ruyck, K.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; de Saeger, S.; et al. Metabolic Profile of Zearalenone in Liver Microsomes from Different Species and Its in Vivo Metabolism in Rats and Chickens Using Ultra High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 11292–11303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devreese, M.; Antonissen, G.; Broekaert, N.; De Baere, S.; Vanhaecke, L.; De Backer, P.; Croubels, S. Comparative Toxicokinetics, Absolute Oral Bioavailability, and Biotransformation of Zearalenone in Different Poultry Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 5092–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.; Kersten, S.; Meyer, U.; Engelhardt, U.; Daenicke, S. Residues of zearalenone (ZEN), deoxynivalenol (DON) and their metabolites in plasma of dairy cows fed Fusarium contaminated maize and their relationships to performance parameters. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, B.S.; Hong, S.H.; Bulitta, J.B.; Hwang, S.W.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.B.; Yang, S.D.; Kim, J.E.; Yoon, H.S.; Kim, D.J.; et al. Disposition, oral bioavailability, and tissue distribution of zearalenone in rats at various dose levels. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2009, 72, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, K.; Habrowska-Gorczynska, D.E.; Dominska, K.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. The dose-dependent effect of zearalenone on mitochondrial metabolism, plasma membrane permeabilization and cell cycle in human prostate cancer cell lines. Chemosphere 2017, 180, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dall’Erta, A.; Cirlini, M.; Dall’Asta, M.; Del Rio, D.; Galaverna, G.; Dall’Asta, C. Masked mycotoxins are efficiently hydrolyzed by human colonic microbiota releasing their aglycones. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2013, 26, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, S.; De Saeger, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, F.; et al. Deglucosylation of zearalenone-14-glucoside in animals and human liver leads to underestimation of exposure to zearalenone in humans. Arch. Toxicol. 2018, 92, 2779–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, S.W.; Dinesh, R.; Yoshinari, T.; Holtrop, G.; Richardson, A.J.; Duncan, G.; MacDonald, S.; Lloyd, A.; Tarbin, J. Masked trichothecene and zearalenone mycotoxins withstand digestion and absorption in the upper GI tract but are efficiently hydrolyzed by human gut microbiota in vitro. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1600680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareis, M.; Bauer, J.; Thiem, J.; Plank, G.; Grabley, S.; Gedek, B. Cleavage of Zearalenone-Glycoside, a Masked Mycotoxin, during Digestion in Swine. J. Vet. Med. B 1990, 37, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellafiora, L.; Perotti, A.; Galaverna, G.; Buschini, A.; Dall’Asta, C. On the masked mycotoxin zearalenone-14-glucoside. Does the mask truly hide? Toxicon 2016, 111, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehl, M.L.; Prelusky, D.B.; Koritz, G.D.; Hartin, K.E.; Buck, W.B.; Trenholm, H.L. Biliary excretion and enterohepatic cycling of zearalenone in immature pigs. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1993, 121, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danicke, S.; Swiech, E.; Buraczewska, L.; Ueberschar, K.H. Kinetics and metabolism of zearalenone in young female pigs. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. (Berl.) 2005, 89, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Deng, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Gong, Y.Y.; Wu, Y. High-throughput and sensitive determination of urinary zearalenone and metabolites by UPLC-MS/MS and its application to a human exposure study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5301–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadzala-Kopciuch, R.; Cendrowski, K.; Cesarz, A.; Kielbasa, P.; Buszewski, B. Determination of zearalenone and its metabolites in endometrial cancer by coupled separation techniques. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 401, 2069–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, D.G.; Bolton, V.E.; Guilford, F.T.; Straus, D.C. Mycotoxin detection in human samples from patients exposed to environmental molds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; De Boevre, M.; De Saeger, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, F. Toxicokinetics of α-zearalenol and its masked form in rats and the comparative biotransformation in liver microsomes from different livestock and humans. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameters | Unit | p.o. | i.v. |
|---|---|---|---|
| λZ | h−1 | 0.72 ± 0.08 | 3.18 ± 0.47 |
| Elimination t1/2 | h | 0.96 ± 0.07 | 0.22 ± 0.03 |
| Cmax | ng·mL−1 | 0.2 ± 0.03 | - |
| tmax | h | 0.083 ± 0.01 | - |
| AUClast | h·ng·mL−1 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 1.79 ± 0.03 |
| AUC0-infinity | h·ng·mL−1 | 0.16 ± 0.02 | 1.80 ± 0.02 |
| VZ | L·kg−1 | 6.24 ± 0.73 | 7.25 ± 1.23 |
| CL | L·h−1·kg−1 | 4.50 ± 0.65 | 5.02 ± 0.62 |
| MRT | h | 0.60 ± 0.05 | 0.20 ± 0.03 |
| F | % | 8.89% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, F.; Tan, H.; Li, Y.; De Boevre, M.; De Saeger, S.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Rao, Z.; Yang, S.; Zhang, H. Metabolic Profile, Bioavailability and Toxicokinetics of Zearalenone-14-Glucoside in Rats after Oral and Intravenous Administration by Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215473
Sun F, Tan H, Li Y, De Boevre M, De Saeger S, Zhou J, Li Y, Rao Z, Yang S, Zhang H. Metabolic Profile, Bioavailability and Toxicokinetics of Zearalenone-14-Glucoside in Rats after Oral and Intravenous Administration by Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(21):5473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215473
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Feifei, Haiguang Tan, Yanshen Li, Marthe De Boevre, Sarah De Saeger, Jinhui Zhou, Yi Li, Zhenghua Rao, Shupeng Yang, and Huiyan Zhang. 2019. "Metabolic Profile, Bioavailability and Toxicokinetics of Zearalenone-14-Glucoside in Rats after Oral and Intravenous Administration by Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 21: 5473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215473
APA StyleSun, F., Tan, H., Li, Y., De Boevre, M., De Saeger, S., Zhou, J., Li, Y., Rao, Z., Yang, S., & Zhang, H. (2019). Metabolic Profile, Bioavailability and Toxicokinetics of Zearalenone-14-Glucoside in Rats after Oral and Intravenous Administration by Liquid Chromatography High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(21), 5473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215473