Vortioxetine Subchronically Activates Serotonergic Transmission via Desensitization of Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptor with 5-HT3 Receptor Inhibition in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of the Interaction between the Local Administration of 5-HT3R Agents (Ondansetron and SR57227) into the mPFC and the Acute Systemic Administrations of Effective Doses of Antidepressants (Escitalopram and Vortioxetine) on the Extracellular Levels of 5-HT and GABA in the mPFC (Study-1)
2.1.1. Effects of the Interaction between the Local Administration of 5-HT3R Agents (Ondansetron and SR57227) into the mPFC and the Acute Systemic Administrations of Effective Doses of Antidepressants (Escitalopram and Vortioxetine) on the Extracellular 5-HT Level in the mPFC
2.1.2. Effects of the Interaction between the Local Administration of 5-HT3R Agents (Ondansetron and SR57227) into the mPFC and the Acute Systemic Administrations of Effective Doses of Antidepressants (Escitalopram and Vortioxetine) on the Extracellular GABA Level in the mPFC
2.2. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on the Functions of 5-HT1AR and 5-HT3R in the mPFC and on Extracellular Levels of 5-HT and GABA in the mPFC (Study-2)
2.2.1. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on the Functions of 5-HT1AR and 5-HT3R in the mPFC and on the Extracellular 5-HT Level in the mPFC
2.2.2. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on the Functions of 5-HT1AR and 5-HT3R in the mPFC and on the Extracellular GABA Level in the mPFC.
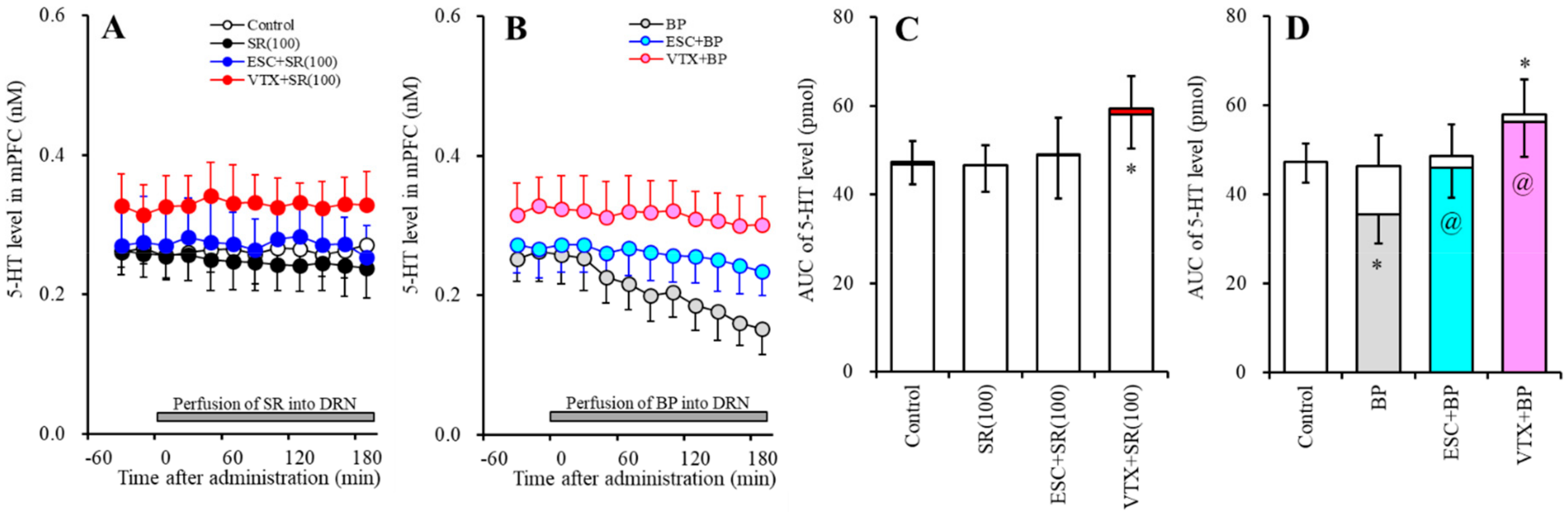
2.3. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on the Function of 5-HT1AR and 5-HT3R in the DRN and on Extracellular Levels of 5-HT and GABA in the mPFC (Study-3)
2.3.1. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on Functions of 5-HT1AR and 5-HT3R in the DRN on the Extracellular 5-HT Level in the mPFC
2.3.2. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on the Functions of 5-HT1AR and 5-HT3R in the DRN and on the Extracellular GABA Level in the mPFC
2.4. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on Releases of 5-HT and GABA in the mPFC Induced by Local MK801 Administration into the DRN and RTN (Study-4)
2.4.1. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on 5-HT Release in the mPFC Induced by Local MK801 Administration into the DRN
2.4.2. Effects of Subchronic Systemic Administrations of Escitalopram and Vortioxetine on GABA Release in the mPFC Induced by Local MK801 Administration into the DRN
3. Discussion
3.1. Regulation Mechanisms Asociated with 5-HT1AR in the Mesocortical Serotonergic Pathway
3.2. Regulation Mechanisms Associated with 5-HT3R in the Mesocortical Serotonergic Pathway
3.3. Effects of Vortioxetine on Activated Transmission Induced by NMDA-R Attenuation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical Agents
4.2. Preparation of the Microdialysis System
4.3. Determination of Extracellular Levels of GABA and 5-HT
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-HT | serotonin |
| 5-HT1AR | serotonin 5-HT1A receptor |
| 5-HT3R | serotonin 5-HT3 receptor |
| 5-HT7R | serotonin 5-HT7 receptor |
| DRN | dorsal raphe nucleus |
| MDTN | mediodorsal thalamic nucleus |
| mPFC | medial prefrontal cortex |
| MRS | modified Ringer’s solution |
| NMDA | N-methyl-d-aspartate |
| NMDA-R | glutamate/N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA)/glutamate receptor |
| OND | ondansetron |
| RTN | reticular thalamic nucleus |
| SET | serotonin transporter |
| UHPLC | ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography |
References
- FDA (Federal Drug Administration). Brintillex Prescribing Information (Highlights). Available online: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2013/204447s000lbl.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2019).
- EMA (European Medicines Agency). Brintillex (Vortixetine). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/smop-initial/chmp-summary-positive-opinion-brintellix_en.pdf (accessed on 3 December 2019).
- Guilloux, J.P.; Mendez-David, I.; Pehrson, A.; Guiard, B.P.; Reperant, C.; Orvoen, S.; Gardier, A.M.; Hen, R.; Ebert, B.; Miller, S.; et al. Antidepressant and anxiolytic potential of the multimodal antidepressant vortioxetine (Lu AA21004) assessed by behavioural and neurogenesis outcomes in mice. Neuropharmacology 2013, 73, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zohar, J.; Nutt, D.J.; Kupfer, D.J.; Moller, H.J.; Yamawaki, S.; Spedding, M.; Stahl, S.M. A proposal for an updated neuropsychopharmacological nomenclature. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mork, A.; Pehrson, A.; Brennum, L.T.; Nielsen, S.M.; Zhong, H.; Lassen, A.B.; Miller, S.; Westrich, L.; Boyle, N.J.; Sanchez, C.; et al. Pharmacological effects of Lu AA21004: A novel multimodal compound for the treatment of major depressive disorder. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 340, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, J.B.; du Jardin, K.G.; Song, D.; Budac, D.; Smagin, G.; Sanchez, C.; Pehrson, A.L. Vortioxetine, but not escitalopram or duloxetine, reverses memory impairment induced by central 5-HT depletion in rats: Evidence for direct 5-HT receptor modulation. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 148–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Jardin, K.G.; Jensen, J.B.; Sanchez, C.; Pehrson, A.L. Vortioxetine dose-dependently reverses 5-HT depletion-induced deficits in spatial working and object recognition memory: A potential role for 5-HT1A receptor agonism and 5-HT3 receptor antagonism. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pehrson, A.L.; Cremers, T.; Betry, C.; van der Hart, M.G.; Jorgensen, L.; Madsen, M.; Haddjeri, N.; Ebert, B.; Sanchez, C. Lu AA21004, a novel multimodal antidepressant, produces regionally selective increases of multiple neurotransmitters—A rat microdialysis and electrophysiology study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 23, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelliny, M.; Croarkin, P.E.; Moore, K.M.; Bobo, W.V. Profile of vortioxetine in the treatment of major depressive disorder: An overview of the primary and secondary literature. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 1193–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Svob Strac, D.; Pivac, N.; Muck-Seler, D. The serotonergic system and cognitive function. Transl. Neurosci. 2016, 7, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bang-Andersen, B.; Ruhland, T.; Jorgensen, M.; Smith, G.; Frederiksen, K.; Jensen, K.G.; Zhong, H.; Nielsen, S.M.; Hogg, S.; Mork, A.; et al. Discovery of 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl]piperazine (Lu AA21004): A novel multimodal compound for the treatment of major depressive disorder. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3206–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mork, A.; Montezinho, L.P.; Miller, S.; Trippodi-Murphy, C.; Plath, N.; Li, Y.; Gulinello, M.; Sanchez, C. Vortioxetine (Lu AA21004), a novel multimodal antidepressant, enhances memory in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 105, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leiser, S.C.; Li, Y.; Pehrson, A.L.; Dale, E.; Smagin, G.; Sanchez, C. Serotonergic Regulation of Prefrontal Cortical Circuitries Involved in Cognitive Processing: A Review of Individual 5-HT Receptor Mechanisms and Concerted Effects of 5-HT Receptors Exemplified by the Multimodal Antidepressant Vortioxetine. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 970–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamura, S.; Abe, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Ochi, S.; Ueno, S.; Okada, M. Different actions for acute and chronic administration of mirtazapine on serotonergic transmission associated with raphe nuclei and their innervation cortical regions. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuyama, K.; Tanahashi, S.; Hamaguchi, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Shiroyama, T.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Differential mechanisms underlie the regulation of serotonergic transmission in the dorsal and median raphe nuclei by mirtazapine: A dual probe microdialysis study. Psychopharmacology 2013, 229, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmudzka, E.; Salaciak, K.; Sapa, J.; Pytka, K. Serotonin receptors in depression and anxiety: Insights from animal studies. Life Sci. 2018, 210, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkumar, R.; Mahesh, R. The auspicious role of the 5-HT3 receptor in depression: A probable neuronal target? J. Psychopharmacol. 2010, 24, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpatrick, G.J.; Jones, B.J.; Tyers, M.B. Identification and distribution of 5-HT3 receptors in rat brain using radioligand binding. Nature 1987, 330, 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.; Riffaud, A.; Marday, T.; Brouillard, C.; Franc, B.; Tassin, J.P.; Sevoz-Couche, C.; Mongeau, R.; Lanfumey, L. Response of Htr3a knockout mice to antidepressant treatment and chronic stress. Br. J. Pharm. 2017, 174, 2471–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Kurhe, Y. Ondansetron, a 5HT3 receptor antagonist reverses depression and anxiety-like behavior in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice: Possible implication of serotonergic system. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 744, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food; Drug Administration. FDA approves new nasal spray medication for treatment-resistant depression; available only at a certified doctor’s office or clinic. In FDA News Release; 3 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Aan Het Rot, M.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Charney, D.S.; Mathew, S.J. Ketamine for depression: Where do we go from here? Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 72, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Javitt, D.C. Negative schizophrenic symptomatology and the PCP (phencyclidine) model of schizophrenia. Hillside J. Clin. Psychiatry 1987, 9, 12–35. [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra, A.K.; Pinals, D.A.; Weingartner, H.; Sirocco, K.; Missar, C.D.; Pickar, D.; Breier, A. NMDA receptor function and human cognition: The effects of ketamine in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 1996, 14, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuyama, K.; Kato, R.; Murata, M.; Shiroyama, T.; Okada, M. Clozapine Normalizes a Glutamatergic Transmission Abnormality Induced by an Impaired NMDA Receptor in the Thalamocortical Pathway via the Activation of a Group III Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Ueda, Y. Lurasidone inhibits NMDA/glutamate antagonist-induced functional abnormality of thalamocortical glutamatergic transmission via 5-HT7 receptor blockade. Br. J. Pharm. 2019, 176, 4002–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Kawano, Y.; Shiroyama, T.; Suzuki, D.; Ueda, Y. Effects of acute and sub-chronic administrations of guanfacine on catecholaminergic transmissions in the orbitofrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2019, 156, 107547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Nakano, T.; Ueda, Y. Pharmacological Discrimination of Effects of MK801 on Thalamocortical, Mesothalamic, and Mesocortical Transmissions. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Pastor, B.; Ortega, J.E.; Grandoso, L.; Castro, E.; Ugedo, L.; Pazos, A.; Meana, J.J. Chronic citalopram administration desensitizes prefrontal cortex but not somatodendritic alpha2-adrenoceptors in rat brain. Neuropharmacology 2017, 114, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Palomar, B.; Mollinedo-Gajate, I.; Berrocoso, E.; Meana, J.J.; Ortega, J.E. Serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonism potentiates the antidepressant activity of citalopram. Neuropharmacology 2018, 133, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, E.; Grunnet, M.; Pehrson, A.L.; Frederiksen, K.; Larsen, P.H.; Nielsen, J.; Stensbol, T.B.; Ebert, B.; Yin, H.; Lu, D.; et al. The multimodal antidepressant vortioxetine may facilitate pyramidal cell firing by inhibition of 5-HT3 receptor expressing interneurons: An in vitro study in rat hippocampus slices. Brain Res. 2018, 1689, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.; Asin, K.E.; Artigas, F. Vortioxetine, a novel antidepressant with multimodal activity: Review of preclinical and clinical data. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 145, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, S.; Yamamura, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors mediate the actions of aripiprazole in mesocortical and mesoaccumbens transmission. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Okubo, R.; Shiroyama, T.; Ueda, Y. Lurasidone sub-chronically activates serotonergic transmission via desensitization of 5-HT1A and 5-HT7 receptors in dorsal raphe nucleus. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albert, P.R.; Le Francois, B.; Millar, A.M. Transcriptional dysregulation of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in mental illness. Mol. Brain 2011, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gocho, Y.; Sakai, A.; Yanagawa, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Saitow, F. Electrophysiological and pharmacological properties of GABAergic cells in the dorsal raphe nucleus. J. Physiol. Sci. 2013, 63, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohoyama, K.; Yamamura, S.; Hamaguchi, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Motomura, E.; Shiroyama, T.; Tanii, H.; Okada, M. Effect of novel atypical antipsychotic, blonanserin, on extracellular neurotransmitter level in rat prefrontal cortex. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 653, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamura, S.; Ohoyama, K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Kashimoto, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Kanehara, S.; Suzuki, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Motomura, E.; Shiroyama, T.; et al. Effects of quetiapine on monoamine, GABA, and glutamate release in rat prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 2009, 206, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, S.; Ueda, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Yamamura, S.; Nagase, H.; Okada, M. Novel delta1-receptor agonist KNT-127 increases the release of dopamine and L-glutamate in the striatum, nucleus accumbens and median pre-frontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Ohoyama, K.; Hamaguchi, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Suzuki, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Motomura, E.; Tanii, H.; Shiroyama, T.; Okada, M. Effects of zotepine on extracellular levels of monoamine, GABA and glutamate in rat prefrontal cortex. Br. J. Pharm. 2009, 157, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celada, P.; Puig, M.V.; Casanovas, J.M.; Guillazo, G.; Artigas, F. Control of dorsal raphe serotonergic neurons by the medial prefrontal cortex: Involvement of serotonin-1A, GABA(A), and glutamate receptors. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 9917–9929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casanovas, J.M.; Vilaro, M.T.; Mengod, G.; Artigas, F. Differential regulation of somatodendritic serotonin 5-HT1A receptors by 2-week treatments with the selective agonists alnespirone (S-20499) and 8-hydroxy-2-(Di-n-propylamino)tetralin: Microdialysis and autoradiographic studies in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.; Jonas, P. A supercritical density of Na(+) channels ensures fast signaling in GABAergic interneuron axons. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hothersall, J.D.; Alexander, A.; Samson, A.J.; Moffat, C.; Bollan, K.A.; Connolly, C.N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) cellular sequestration during chronic exposure delays 5-HT3 receptor resensitization due to its subsequent release. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 32020–32029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Kurhe, Y. 5HT3 receptor antagonist (ondansetron) reverses depressive behavior evoked by chronic unpredictable stress in mice: Modulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical and brain serotonergic system. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Aghajanian, G.K.; Sanacora, G.; Krystal, J.H. Synaptic plasticity and depression: New insights from stress and rapid-acting antidepressants. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, K. Rapid-acting antidepressant ketamine, its metabolites and other candidates: A historical overview and future perspective. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 613–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, S.; Yamamura, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Clozapine, but not haloperidol, enhances glial D-serine and L-glutamate release in rat frontal cortex and primary cultured astrocytes. Br. J. Pharm. 2012, 165, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, M.; Fukuyama, K.; Kawano, Y.; Shiroyama, T.; Ueda, Y. Memantine protects thalamocortical hyper-glutamatergic transmission induced by NMDA receptor antagonism via activation of system xc−. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2019, 7, e00457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukuyama, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Okada, M. Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter and Aripiprazole Compensate NMDA Antagonist-Induced Dysfunction of Thalamocortical L-Glutamatergic Transmission. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakano, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Suzuki, D.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Amantadine Combines Astroglial System Xc(-) Activation with Glutamate/NMDA Receptor Inhibition. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vertes, R.P.; Linley, S.B.; Hoover, W.B. Limbic circuitry of the midline thalamus. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2015, 54, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, M.; Wada, K.; Kiryu, K.; Kawata, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Kondo, T.; Tasaki, H.; Kaneko, S. Effects of Ca2+ channel antagonists on striatal dopamine and DOPA release, studied by in vivo microdialysis. Br. J. Pharm. 1998, 123, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McGrath, J.C.; Drummond, G.B.; McLachlan, E.M.; Kilkenny, C.; Wainwright, C.L. Guidelines for reporting experiments involving animals: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharm. 2010, 160, 1573–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamura, S.; Ohoyama, K.; Nagase, H.; Okada, M. Zonisamide enhances delta receptor-associated neurotransmitter release in striato-pallidal pathway. Neuropharmacology 2009, 57, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, S.; Yamamura, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Motomura, E.; Okada, M. Effect of lamotrigine and carbamazepine on corticotropin-releasing factor-associated serotonergic transmission in rat dorsal raphe nucleus. Psychopharmacology 2012, 220, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Saito, H.; Suzuki, N.; Kashimoto, S.; Hamaguchi, T.; Ohoyama, K.; Suzuki, D.; Kanehara, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Shiroyama, T.; et al. Effects of zonisamide on neurotransmitter release associated with inositol triphosphate receptors. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 454, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Hirano, T.; Kawata, Y.; Murakami, T.; Wada, K.; Mizuno, K.; Kondo, T.; Kaneko, S. Biphasic effects of zonisamide on serotonergic system in rat hippocampus. Epilepsy Res. 1999, 34, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Yoshida, S.; Zhu, G.; Hirose, S.; Kaneko, S. Biphasic actions of topiramate on monoamine exocytosis associated with both soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptors and Ca(2+)-induced Ca(2+)-releasing systems. Neuroscience 2005, 134, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Hirano, T.; Mizuno, K.; Kawata, Y.; Wada, K.; Murakami, T.; Tasaki, H.; Kaneko, S. Effects of carbamazepine on hippocampal serotonergic system. Epilepsy Res. 1998, 31, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawata, Y.; Okada, M.; Murakami, T.; Kamata, A.; Zhu, G.; Kaneko, S. Pharmacological discrimination between effects of carbamazepine on hippocampal basal, Ca(2+)- and K(+)-evoked serotonin release. Br. J. Pharm. 2001, 133, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curtis, M.J.; Alexander, S.; Cirino, G.; Docherty, J.R.; George, C.H.; Giembycz, M.A.; Hoyer, D.; Insel, P.A.; Izzo, A.A.; Ji, Y.; et al. Experimental design and analysis and their reporting II: Updated and simplified guidance for authors and peer reviewers. Br. J. Pharm. 2018, 175, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okada, M.; Okubo, R.; Fukuyama, K. Vortioxetine Subchronically Activates Serotonergic Transmission via Desensitization of Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptor with 5-HT3 Receptor Inhibition in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246235
Okada M, Okubo R, Fukuyama K. Vortioxetine Subchronically Activates Serotonergic Transmission via Desensitization of Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptor with 5-HT3 Receptor Inhibition in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(24):6235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246235
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkada, Motohiro, Ruri Okubo, and Kouji Fukuyama. 2019. "Vortioxetine Subchronically Activates Serotonergic Transmission via Desensitization of Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptor with 5-HT3 Receptor Inhibition in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 24: 6235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246235
APA StyleOkada, M., Okubo, R., & Fukuyama, K. (2019). Vortioxetine Subchronically Activates Serotonergic Transmission via Desensitization of Serotonin 5-HT1A Receptor with 5-HT3 Receptor Inhibition in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(24), 6235. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20246235




