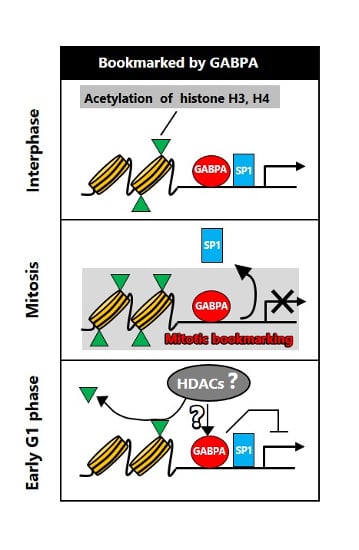
Identification of GA-Binding Protein Transcription Factor Alpha Subunit (GABPA) as a Novel Bookmarking Factor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
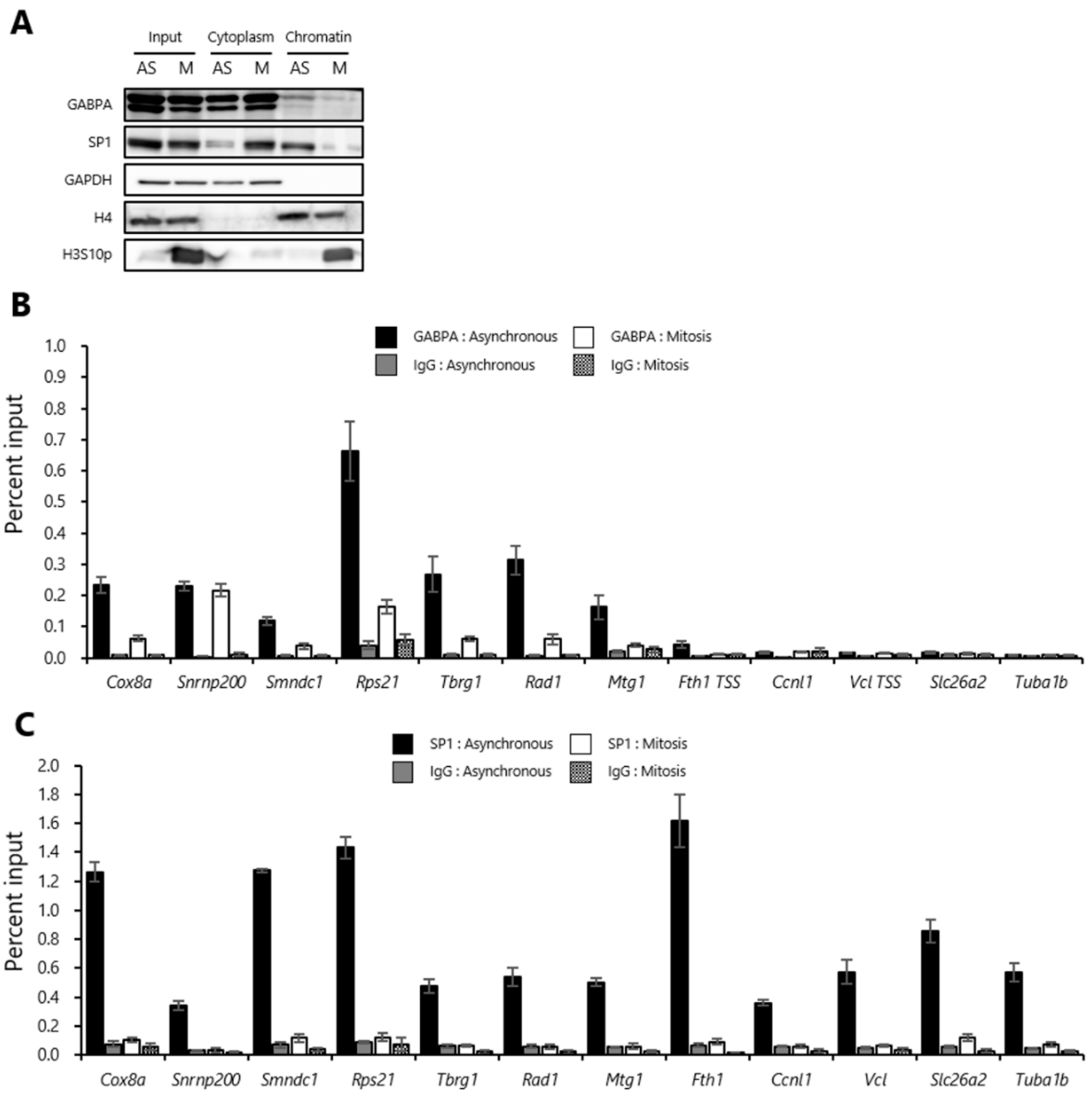
2.1. A Fraction of GABPA and SP1 Binds to Mitotic Chromatin
2.2. GABPA, but Not SP1, Binds to Upstream Regions of the Various Genes Reactivated during the M/G1 Transition in Mitotic-Arrested tsFT210 Cells
2.3. Histones at the Sites Bookmarked by GABPA are Highly Acetylated in Mitosis
2.4. Histones at the Sites Bookmarked by GABPA are Deacetylated during the M/G1 Transition
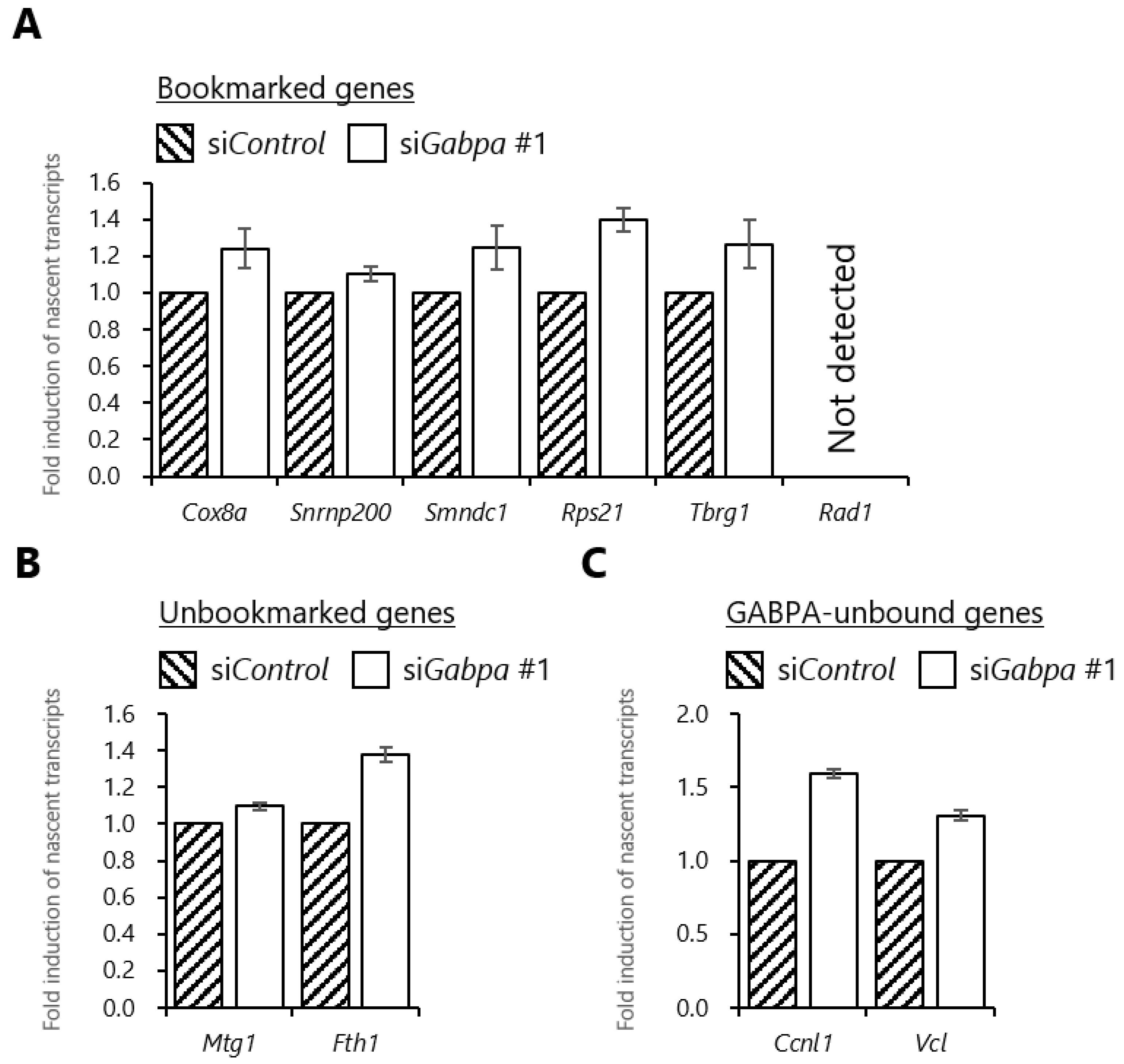
2.5. Gabpa Knockdown Increases Histone Acetylation Levels at Several Genes Reactivated during the M/G1 Transition
2.6. Gabpa Knockdown Increases Transcriptional Induction in the Early G1 Phase
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Synchronization of tsFT210 Cells
4.2. Immunofluorescence
4.3. Cell Fractionation
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Transfection of siRNA into tsFT210 Cells Via Electroporation
4.6. Cell Cycle Analysis by Staining with Propidium Iodide
4.7. Cell Cycle Analysis by Staining with Propidium Iodide and Phospho-H3 Antibody
4.8. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
4.9. ChIP-Quantitative PCR and Quantitative RT-PCR
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Egli, D.; Birkhoff, G.; Eggan, K. Mediators of reprogramming: Transcription factors and transitions through mitosis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Balbás, M.A.; Dey, A.; Rabindran, S.K.; Ozato, K.; Wu, C. Displacement of sequence-specific transcription factors from mitotic chromatin. Cell 1995, 83, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanth, K.V.; Sacco-Bubulya, P.A.; Prasanth, S.G.; Spector, D.L. Sequential entry of components of the gene expression machinery into daughter nuclei. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 1043–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadauke, S.; Blobel, G.A. Mitotic bookmarking by transcription factors. Epigenetics Chromatin 2013, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, H.; Vanderford, N.L.; Sarge, K.D. The TBP–PP2A mitotic complex bookmarks genes by preventing condensin action. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blobel, G.A.; Kadauke, S.; Wang, E.; Lau, A.W.; Zuber, J.; Chou, M.M.; Vakoc, C.R. A reconfigured pattern of MLL occupancy within mitotic chromatin promotes rapid transcriptional reactivation following mitotic exit. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 970–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Nishiyama, A.; Karpova, T.; McNally, J.; Ozato, K. Brd4 Marks Select Genes on Mitotic Chromatin and Directs Postmitotic Transcription. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 4899–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Nakamura, T.; Fu, Y.; Lazar, Z.; Spector, D.L. Gene bookmarking accelerates the kinetics of post-mitotic transcriptional re-activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, M.; Zhang, J.; Heine, G.F.; Ozer, G.; Liu, H.W.; Huang, K.; Parvin, J.D. Promoters active in interphase are bookmarked during mitosis by ubiquitination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10187–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadauke, S.; Udugama, M.I.; Pawlicki, J.M.; Achtman, J.C.; Jain, D.P.; Cheng, Y.; Hardison, R.C.; Blobel, G.A. Tissue-specific mitotic bookmarking by hematopoietic transcription factor GATA1. Cell 2012, 150, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arampatzi, P.; Gialitakis, M.; Makatounakis, T.; Papamatheakis, J. Gene-specific factors determine mitotic expression and bookmarking via alternate regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 2202–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caravaca, J.M.; Donahue, G.; Becker, J.S.; He, X.; Vinson, C.; Zaret, K.S. Bookmarking by specific and nonspecific binding of FoxA1 pioneer factor to mitotic chromosomes. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, R.J.; Tsai, P.F.; Choi, I.; Won, K.J.; Fan, H.Y. RBPJ, the major transcriptional effector of notch signaling, remains associated with chromatin throughout mitosis, suggesting a role in mitotic bookmarking. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodhi, N.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Tulin, A.V. Bookmarking promoters in mitotic chromatin: Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 as an epigenetic mark. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7028–7038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.M.; Byun, J.S.; Sacta, M.; Jin, Q.; Baek, S.J.; Gardner, K. Promoter-bound p300 complexes facilitate post-mitotic transmission of transcriptional memory. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, M.; Packard, C.Z.; Banerjee, T.; Parvin, J.D. RING1A and BMI1 bookmark active genes via ubiquitination of chromatin-associated proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, 2136–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, J.; Bagattin, A.; Verdeguer, F.; Makinistoglu, M.P.; Garbay, S.; Felix, T.; Heidet, L.; Pontoglio, M. Human mutations affect the epigenetic/bookmarking function of HNF1B. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 8097–8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deluz, C.; Friman, E.T.; Strebinger, D.; Benke, A.; Raccaud, M.; Callegari, A.; Leleu, M.; Manley, S.; Suter, D.M. A role for mitotic bookmarking of SOX2 in pluripotency and differentiation. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 2538–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festuccia, N.; Dubois, A.; Vandormael-Pournin, S.; Gallego Tejeda, E.; Mouren, A.; Bessonnard, S.; Mueller, F.; Proux, C.; Cohen-Tannoudji, M.; Navarro, P. Mitotic binding of Esrrb marks key regulatory regions of the pluripotency network. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Pelham-Webb, B.; Di Giammartino, D.C.; Li, J.; Kim, D.; Kita, K.; Saiz, N.; Garg, V.; Doane, A.; Giannakakou, P.; et al. Widespread mitotic bookmarking by histone marks and transcription factors in pluripotent stem cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palozola, K.C.; Donahue, G.; Liu, H.; Grant, G.R.; Becker, J.S.; Cote, A.; Yu, H.; Raj, A.; Zaret, K.S. Mitotic transcription and waves of gene reactivation during mitotic exit. Science 2017, 358, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiung, C.C.S.; Bartman, C.R.; Huang, P.; Ginart, P.; Stonestrom, A.J.; Keller, C.A.; Face, C.; Jahn, K.S.; Evans, P.; Sankaranarayanan, L.; et al. A hyperactive transcriptional state marks genome reactivation at the mitosis-G1 transition. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1423–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuoka, M.; Uehara, A.; Niki, K.; Goto, S.; Kato, D.; Utsugi, T.; Ohtsu, M.; Murakami, Y. Identification of preferentially reactivated genes during early G1 phase using nascent mRNA as an index of transcriptional activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ristevski, S.; O’Leary, D.A.; Thornell, A.P.; Owen, M.J.; Kola, I.; Hertzog, P.J. The ETS transcription factor GABPa is essential for early embryogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 5844–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manukjan, G.; Ripperger, T.; Venturini, L.; Stadler, M.; Göhring, G.; Schambach, A.; Schlegelberger, B.; Steinemann, D. GABP is necessary for stem/progenitor cell maintenance and myeloid differentiation in human hematopoiesis and chronic myeloid leukemia. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 16, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Cui, K.; Jothi, R.; Zhao, D.M.; Jing, X.; Zhao, K.; Xue, H.H. GABP controls a critical transcription regulatory module that is essential for maintenance and differentiation of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Blood 2011, 117, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.F.; Mott, S.; Rosmarin, A.G. The Ets transcription factor GABP is required for cell-cycle progression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.F.; Drumea, K.; Mott, S.; Wang, J.; Rosmarin, A.G. GABP transcription factor (nuclear respiratory factor 2) is required for mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2014, 34, 3194–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, L.; Gilmour, J.; Bonifer, C. The role of the ubiquitously expressed transcription factor Sp1 in tissue-specific transcriptional regulation and in disease. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2016, 89, 513–525. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chuang, J.Y.; Wang, S.A.; Yang, W.B.; Yang, H.C.; Hung, C.Y.; Su, T.P.; Chang, W.C.; Hung, J.J. Sp1 phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent kinase 1/cyclin B1 represses its DNA-binding activity during mitosis in cancer cells. Oncogene 2012, 31, 4946–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segil, N.; Roberts, S.B.; Heintz, N. Mitotic phosphorylation of the Oct-1 homeodomain and regulation of Oct-1 DNA binding activity. Science 1991, 254, 1814–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.B.; Segil, N.; Heintz, N. Differential phosphorylation of the transcription factor Octl during the cell cycle. Science 1991, 253, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dovat, S.; Ronni, T.; Russell, D.; Ferrini, R.; Cobb, B.S.; Smale, S.T. A common mechanism for mitotic inactivation of C2H2 zinc finger DNA-binding domains. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2985–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizkallah, R.; Alexander, K.E.; Hurt, M.M. Global mitotic phosphorylation of C2H2zinc finger protein linker peptides. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3327–3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Róna, G.; Borsos, M.; Ellis, J.J.; Mehdi, A.M.; Christie, M.; Környei, Z.; Neubrandt, M.; Tóth, J.; Bozóky, Z.; Buday, L.; et al. Dynamics of re-constitution of the human nuclear proteome after cell division is regulated by NLS-adjacent phosphorylation. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3551–3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizkallah, R.; Batsomboon, P.; Dudley, G.B.; Hurt, M.M. Identification of the oncogenic kinase TOPK/PBK as a master mitotic regulator of C2H2 zinc finger proteins. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1446–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, T.; Murano, K.; Kato, K.; Kawaguchi, A.; Nagata, K. Mitotic phosphorylation of CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) reduces its DNA binding activity. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raccaud, M.; Suter, D.M. Transcription factor retention on mitotic chromosomes: Regulatory mechanisms and impact on cell fate decisions. FEBS Lett. 2017, 592, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvagni, F.; Capo, S.; Oliviero, S. Sp1 and Sp3 physically interact and co-operate with GABP for the activation of the utrophin promoter. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 306, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudge, T.L.; Johnson, L.F. Synergistic activation of the TATA-less mouse thymidylate synthase promoter by the Ets transcription factor GABP and Sp1. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 274, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruhlak, M.J.; Hendzel, M.J.; Fischle, W.; Bertos, N.R.; Hameed, S.; Yang, X.J.; Verdin, E.; Bazett-Jones, D.P. Regulation of global acetylation in mitosis through loss of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases from chromatin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38307–38319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valis, E.; Sánchez-Molina, S.; Martínez-Balbás, M.A. Role of histone modifications in marking and activating genes through mitosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 42592–42600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, D.W.; Hassan, M.Q.; Pratap, J.; Galindo, M.; Zaidi, S.K.; Lee, S.; Yang, X.; Xie, R.; Javed, A.; Underwood, J.M.; et al. Mitotic occupancy and lineage-specific transcriptional control of rRNA genes by Runx2. Nature 2007, 445, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, D.W.; Hassan, M.Q.; Yang, X.Q.; Galindo, M.; Javed, A.; Zaidi, S.K.; Furcinitti, P.; Lapointe, D.; Montecino, M.; Lian, J.B.; et al. Mitotic retention of gene expression patterns by the cell fate-determining transcription factor Runx2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3189–3194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.A.; Zaidi, S.K.; Dobson, J.R.; Shakoori, A.R.; Lian, J.B.; Stein, J.L.; van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, G.S. Transcriptional corepressor TLE1 functions with Runx2 in epigenetic repression of ribosomal RNA genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4165–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Festuccia, N.; Owens, N.; Papadopoulou, T.; Gonzalez, I.; Tachtsidi, A.; Vandoermel-Pournin, S.; Gallego, E.; Gutierrez, N.; Dubois, A.; Cohen-Tannoudji, M.; et al. Transcription factor activity and nucleosome organisation in mitosis. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akıncılar, S.C.; Khattar, E.; Boon, P.L.; Unal, B.; Fullwood, M.J.; Tergaonkar, V. Long-range chromatin interactions drive mutant TERT promoter activation. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1276–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Jones, R.S.; Zhang, Y. Role of histone H3 lysine 27 methylation in polycomb-group silencing. Science 2002, 298, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tie, F.; Banerjee, R.; Saiakhova, A.R.; Howard, B.; Monteith, K.E.; Scacheri, P.C.; Cosgrove, M.S.; Harte, P.J. Trithorax monomethylates histone H3K4 and interacts directly with CBP to promote H3K27 acetylation and antagonize Polycomb silencing. Development 2014, 141, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitges, F.W.; Prusty, A.B.; Faty, M.; Stützer, A.; Lingaraju, G.M.; Aiwazian, J.; Sack, R.; Hess, D.; Li, L.; Zhou, S.; et al. Histone methylation by PRC2 is inhibited by active chromatin marks. Mol. Cell 2011, 42, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffen, P.A.; Fonseca, J.P.; Gänger, C.; Dworschak, E.; Kockmann, T.; Beisel, C.; Ringrose, L. Quantitative in vivo analysis of chromatin binding of Polycomb and Trithorax group proteins reveals retention of ASH1 on mitotic chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 5235–5250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tuzova, M.; Xiao, Z.X.; Cruikshank, W.W.; Center, D.M. Pro-IL-16 recruits histone deacetylase 3 to the Skp2 core promoter through interaction with transcription factor GABP. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravel-Chapuis, A.; Vandromme, M.; Thomas, J.L.; Schaeffer, L. Postsynaptic chromatin is under neural control at the neuromuscular junction. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goto, S.; Takahashi, M.; Yasutsune, N.; Inayama, S.; Kato, D.; Fukuoka, M.; Kashiwaba, S.-i.; Murakami, Y. Identification of GA-Binding Protein Transcription Factor Alpha Subunit (GABPA) as a Novel Bookmarking Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051093
Goto S, Takahashi M, Yasutsune N, Inayama S, Kato D, Fukuoka M, Kashiwaba S-i, Murakami Y. Identification of GA-Binding Protein Transcription Factor Alpha Subunit (GABPA) as a Novel Bookmarking Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051093
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoto, Shunya, Masashi Takahashi, Narumi Yasutsune, Sumiki Inayama, Dai Kato, Masashi Fukuoka, Shu-ichiro Kashiwaba, and Yasufumi Murakami. 2019. "Identification of GA-Binding Protein Transcription Factor Alpha Subunit (GABPA) as a Novel Bookmarking Factor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051093
APA StyleGoto, S., Takahashi, M., Yasutsune, N., Inayama, S., Kato, D., Fukuoka, M., Kashiwaba, S.-i., & Murakami, Y. (2019). Identification of GA-Binding Protein Transcription Factor Alpha Subunit (GABPA) as a Novel Bookmarking Factor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1093. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051093