Targeted Delivery of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Loaded Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Spherical Neural Masses for Treating Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Determination of the Concentration of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Cell Labeling
2.2. Visualization of FIONs for Cell Labeling
2.3. Measurement of Targeted Delivery of SNMs via Detection of FIONs by Prussian Blue Staining
2.4. Targeted Delivery of SNMs Attenuated Swelling after ICH, but Not Hematoma
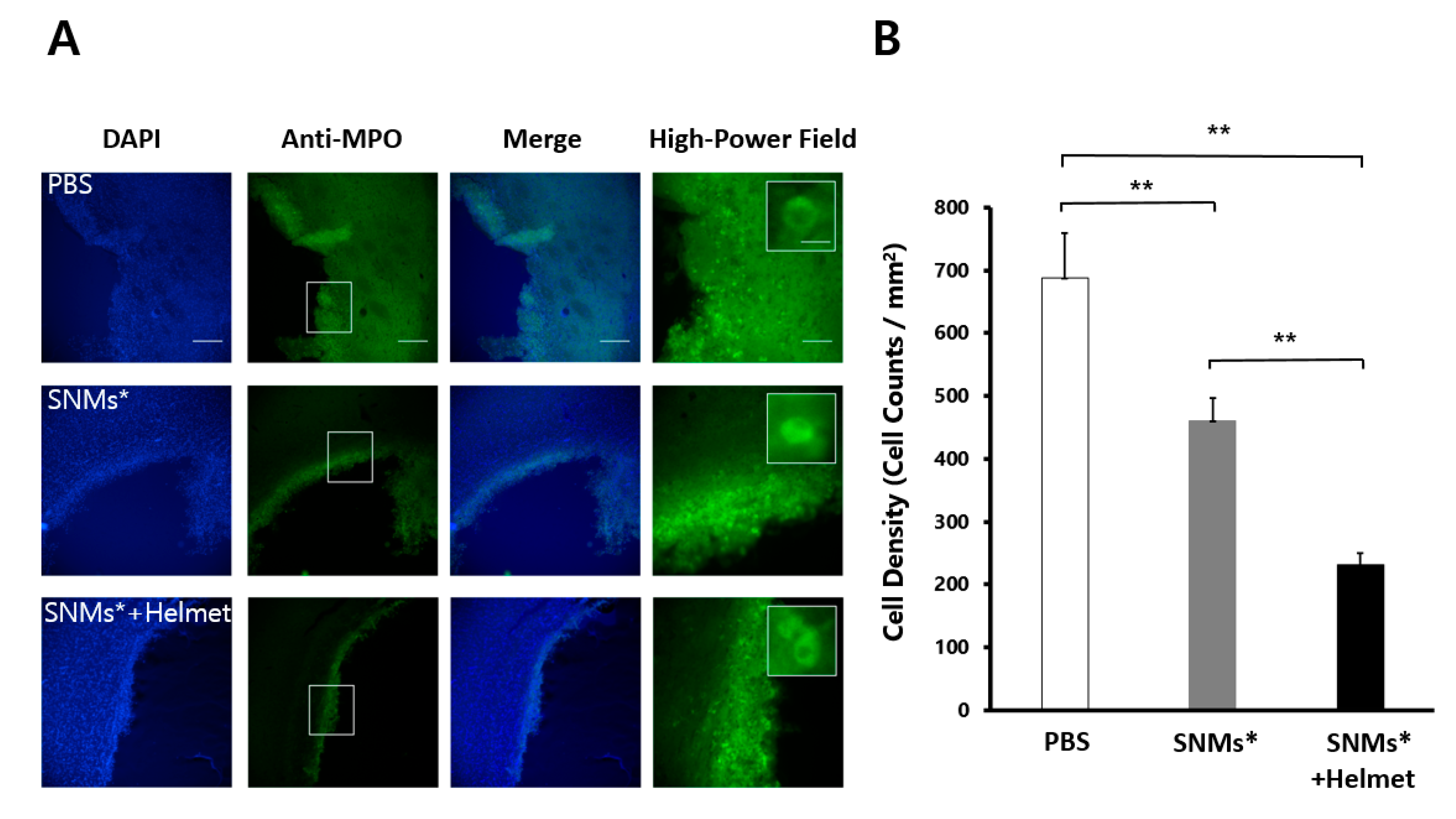
2.5. Targeted Delivery of SNMs Reduced Recruitment of Inflammatory Cells
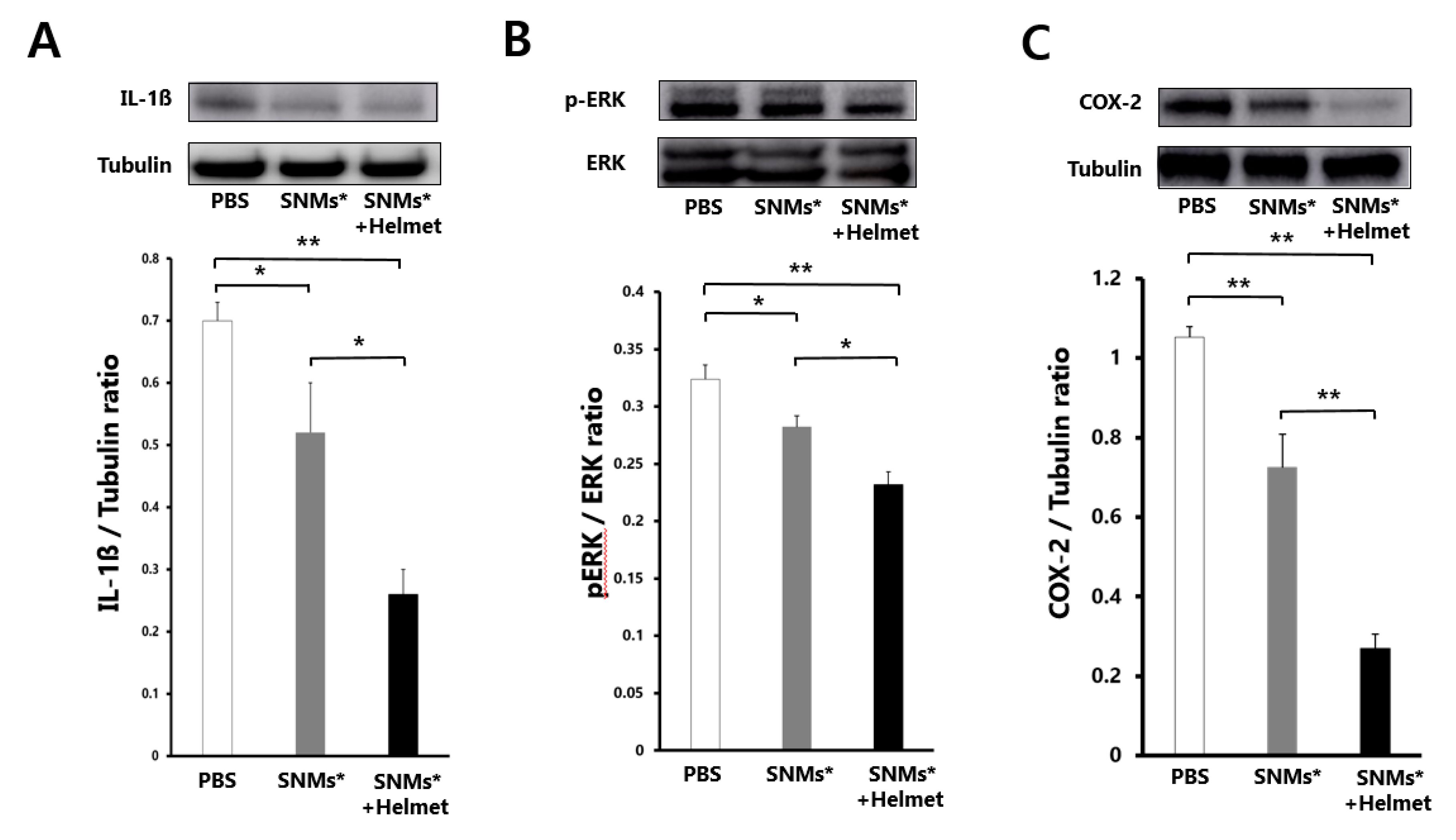
2.6. Targeted Delivery of SNMs Reduced COX-2 Mediated Inflammatory Response
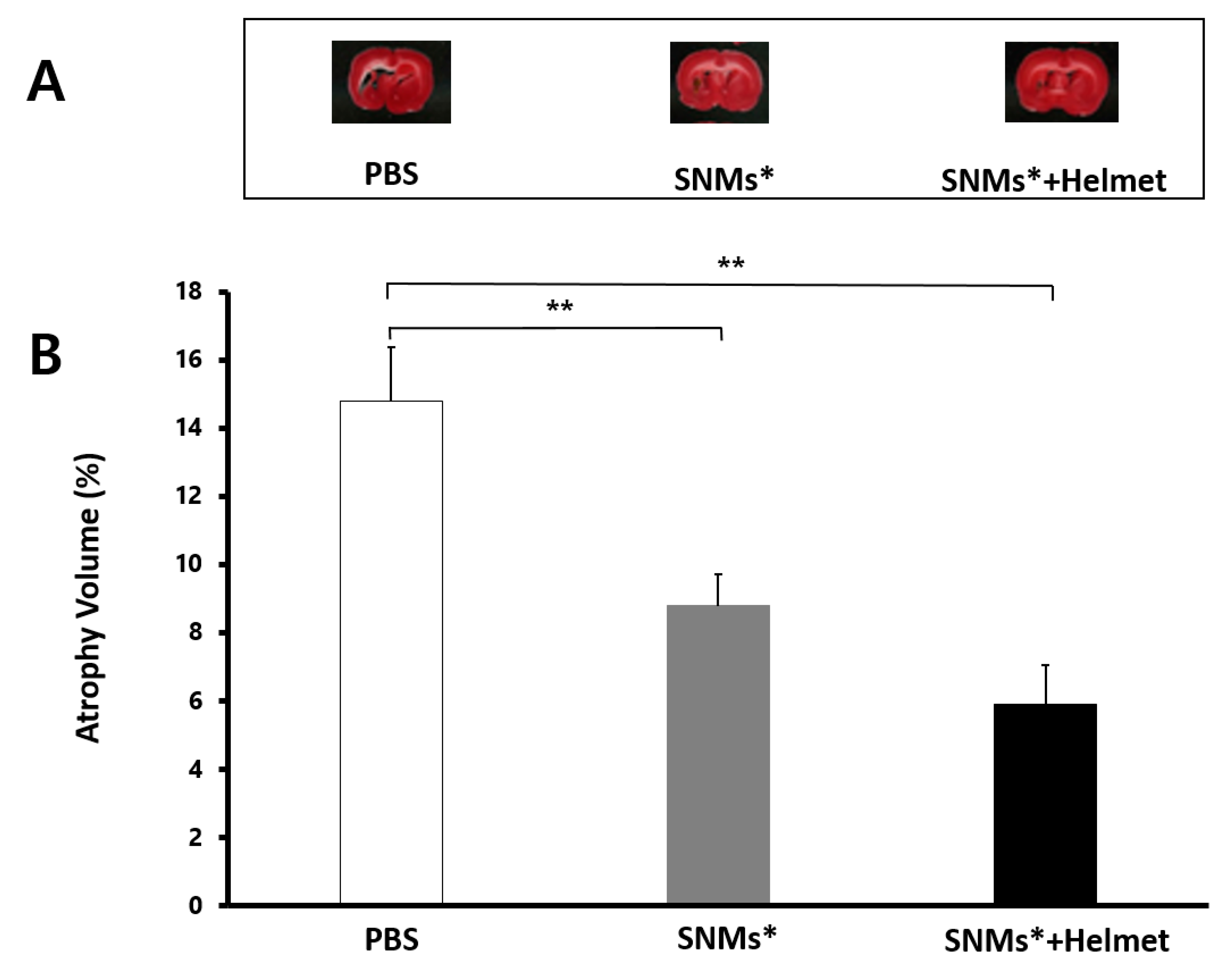
2.7. Measurement of Brain Atrophy Volume
2.8. Targeted Delivery of SNMs Enhanced the Neurological Function Recovery in the Early Stage
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Differentiation of SNMs from Human ESCs
4.2. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Cell Labeling
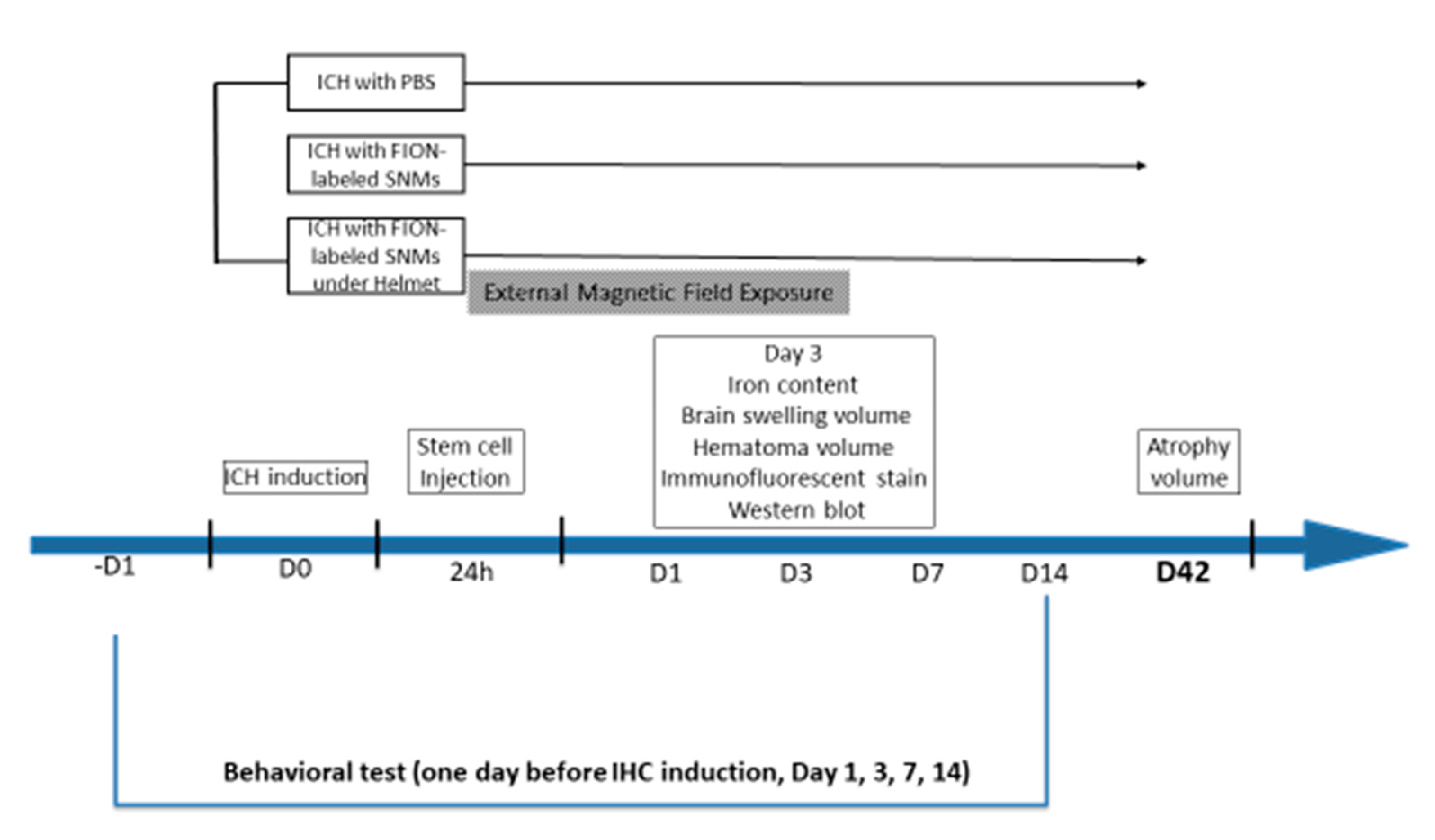
4.3. Induction of ICH, Intravenous Injection of FION-Labeled SNMs, and Application of a Magnet-Embedded Helmet for Targeted Delivery
4.4. Measurement of Iron Content, Hematoma Volume, and Swelling Volume
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining and Cell Quantification
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Measurement of Brain Atrophy Volume
4.8. Behavioral Testing
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESC | Embryonic Stem Cells |
| SNM | Spherical Neural Masses |
| ICH | Intracerebral Hemorrhage |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| FION | Magnetosome-like Ferrimagnetic Iron Oxide Nanocubes |
| NP | Neural Precursors |
| NSC | Neural Stem Cells |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| RITC | Rhodamine B Isothiocyanate |
| MPO | Myeloperoxidase |
| Ox-6 | MHC Class II RT1B |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 Beta |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase |
| p-ERK | Phosphorylated Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| MSC | Mesenchymal Stem Cells |
| SPION | Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles |
| EB | Embryoid Bodies |
| DAPI | 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| BSA | Bovine Serum Albumin |
References
- An, S.J.; Kim, T.J.; Yoon, B.W. Epidemiology, risk factors, and clinical features of intracerebral hemorrhage: An update. J. Stroke 2017, 19, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemphill, J.C., 3rd; Greenberg, S.M.; Anderson, C.S.; Becker, K.; Bendok, B.R.; Cushman, M.; Fung, G.L.; Goldstein, J.N.; Macdonald, R.L.; Mitchell, P.H.; et al. Guidelines for the Management of Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2015, 46, 2032–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.T.; Chu, K.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kang, K.M.; Hong, N.H.; Kim, J.H.; Ban, J.J.; Park, H.K.; et al. Anti-inflammatory mechanism of intravascular neural stem cell transplantation in haemorrhagic stroke. Brain 2008, 131, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.P.; Wang, Z.H.; Peng, D.Y.; Li, S.M.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.H. Therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage: Reduced apoptosis and enhanced neuroprotection. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Kim, K.S.; Park, I.H.; Kim, S.U. Human neural stem cells over-expressing VEGF provide neuroprotection, angiogenesis and functional recovery in mouse stroke model. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bacigaluppi, M.; Pluchino, S.; Martino, G.; Kilic, E.; Hermann, D.M. Neural stem/precursor cells for the treatment of ischemic stroke. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 265, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichterle, H.; Lieberam, I.; Porter, J.A.; Jessell, T.M. Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells into motor neurons. Cell 2002, 110, 385–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marei, H.E.; Hasan, A.; Rizzi, R.; Althani, A.; Afifi, N.; Cenciarelli, C.; Caceci, T.; Shuaib, A. Potential of Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Ischemic Stroke. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.S.; Lee, Y.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Chung, S.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, H.; Kim, M.H.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Highly efficient and large-scale generation of functional dopamine neurons from human embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3392–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, M.S.; Kim, S.J.; Ku, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Lee, H.; Yoo, D.H.; Park, U.C.; Song, S.A.; Choi, Y.M.; Yu, H.G. Generation of retinal pigment epithelial cells from human embryonic stem cell-derived spherical neural masses. Stem Cell Res. 2012, 9, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.U.; de Vellis, J. Stem cell-based cell therapy in neurological diseases: A review. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 2183–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, A.; Srivastava, M.; Bhatia, R.; Mohanty, S.; Kumaran, S.; Bose, S. Autologous intravenous mononuclear stem cell therapy in chronic ischemic stroke. J. Stem Cells Regen. Med. 2012, 8, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Roh, J.; Kim, E.C.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.U.; Yoon, B.W. Long-term effects of magnetically targeted ferumoxide-labeled human neural stem cells in focal cerebral ischemia. Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.K.; Kim, H.S.; Ahn, H.J.; Seol, H.W.; Kim, Y.Y.; Park, Y.B.; Yoon, C.J.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.H.; Moon, S.Y. Derivation and characterization of new human embryonic stem cell lines: SNUhES1, SNUhES2, and SNUhES3. Stem Cells 2005, 23, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.C.; Wernig, M.; Duncan, I.D.; Brustle, O.; Thomson, J.A. In vitro differentiation of transplantable neural precursors from human embryonic stem cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.S.; Hwang, D.Y.; Kim, D.W. Efficient derivation of functional dopaminergic neurons from human embryonic stem cells on a large scale. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1888–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Kim, H.; Choi, S.H.; Park, M.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.C.; Choi, Y.; Lin, S.; Kim, B.H.; Jung, H.S.; et al. Magnetosome-like ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanocubes for highly sensitive MRI of single cells and transplanted pancreatic islets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2662–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, W.; Song, L.; Li, X.M.; Wang, D.; Guo, X.J.; Xu, W.G. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate airway inflammation and emphysema in COPD through down-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 via p38 and ERK MAPK pathways. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nucci, L.P.; Silva, H.R.; Giampaoli, V.; Mamani, J.B.; Nucci, M.P.; Gamarra, L.F. Stem cells labeled with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in a preclinical model of cerebral ischemia: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riegler, J.; Liew, A.; Hynes, S.O.; Ortega, D.; O’Brien, T.; Day, R.M.; Richards, T.; Sharif, F.; Pankhurst, Q.A.; Lythgoe, M.F. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle targeting of MSCs in vascular injury. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1987–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Lai, H.; Wang, C. Nanoparticles-assisted stem cell therapy for ischemic heart disease. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 1384658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourrinet, P.; Bengele, H.H.; Bonnemain, B.; Dencausse, A.; Idee, J.M.; Jacobs, P.M.; Lewis, J.M. Preclinical safety and pharmacokinetic profile of ferumoxtran-10, an ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide magnetic resonance contrast agent. Investig. Radiol. 2006, 41, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Shi, C.; Hu, B.; Gong, J.; Zhong, X.; Lin, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Xu, H. External magnetic field promotes homing of magnetized stem cells following subcutaneous injection. BMC Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschoe, C.; Bushnell, C.D.; Duncan, P.W.; Alexander-Miller, M.A.; Wolfe, S.Q. Neuroinflammation after Intracerebral Hemorrhage and Potential Therapeutic Targets. J. Stroke 2020, 22, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- You, S.; Zheng, D.; Delcourt, C.; Sato, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Lindley, R.I.; Robinson, T.; et al. Determinants of early versus delayed neurological deterioration in intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2019, 50, 1409–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, J.K.; Zhu, X.; Schlichter, L.C. Evolution of the inflammatory response in the brain following intracerebral hemorrhage and effects of delayed minocycline treatment. Brain Res. 2007, 1180, 140–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincon, F.; Mayer, S.A. Novel therapies for intracerebral hemorrhage. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2004, 10, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, C.; Grabel, L. Directing the differentiation of embryonic stem cells to neural stem cells. Dev. Dyn. 2007, 236, 3255–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.B.; Parmar, M. Strengths and limitations of the neurosphere culture system. Mol. Neurobiol. 2006, 34, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.J.; Kong, T.H.; Choi, J.S.; Yun, W.S.; Key, J.; Seo, Y.J. Strategies to enhance efficacy of SPION-labeled stem cell homing by magnetic attraction: A systemic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 4849–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, M.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Roh, J.; Kim, S.U.; Yoon, B.W. Using a neodymium magnet to target delivery of ferumoxide-labeled human neural stem cells in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Hum. Gene Ther. 2010, 21, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maredziak, M.; Tomaszewski, K.; Polinceusz, P.; Lewandowski, D.; Marycz, K. Static magnetic field enhances the viability and proliferation rate of adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells potentially through activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt (PI3K/Akt) pathway. Electromagn. Biol. Med. 2017, 36, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Zhang, X.; Miao, Y.; Li, J.; Gan, Y. Lipid-coated iron oxide nanoparticles for dual-modal imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 2033–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nethercott, H.E.; Brick, D.J.; Schwartz, P.H. Immunocytochemical analysis of human pluripotent stem cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 767, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Sun, J.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Ko, S.B.; Kim, C.K.; Jia, X.; Yoon, B.W. Pretreatment with low-dose fimasartan ameliorates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation and brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage. Exp. Neurol. 2018, 310, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Ma, L.; Shaligram, S.; Walker, E.J.; Yang, S.T.; Tang, C.; Zhu, W.; Zhan, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; et al. Effect of elevation of vascular endothelial growth factor level on exacerbation of hemorrhage in mouse brain arteriovenous malformation. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, K.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Roh, J.N.; Nam, J.M.; Kim, P.Y.; Ryu, W.S.; Lee, S.H.; Yoon, B.W. Lithium pretreatment reduces brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Neurol. Res. 2012, 34, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.C.; Chu, K.; Jeong, S.W.; Jung, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.; Yoon, B.W. Hyperglycemia exacerbates brain edema and perihematomal cell death after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2003, 34, 2215–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, B.Y.; Kim, O.J.; Min, S.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Suh, S.W.; Chung, T.N. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce mortality and hematoma size in a rat intracerebral hemorrhage model in an acute phase. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 1658195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, W.T.; Park, K.A.; Lee, J.E. Agmatine attenuates brain edema and apoptotic cell death after traumatic brain injury. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, C.K.; Ryu, W.S.; Choi, I.Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Rim, D.; Kim, B.J.; Jang, H.; Yoon, B.W.; Lee, S.H. Detrimental effects of leptin on intracerebral hemorrhage via the STAT3 signal pathway. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Markowitz, G.J.; Kadam, S.D.; Smith, D.R.; Johnston, M.V.; Comi, A.M. Different effects of high- and low-dose phenobarbital on post-stroke seizure suppression and recovery in immature CD1 mice. Epilepsy Res. 2011, 94, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.K.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kang, L.; Kim, J.; Lee, N.; Hyeon, T.; Lim, M.-s.; Mo, H.J.; Shin, J.H.; et al. Targeted Delivery of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Loaded Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Spherical Neural Masses for Treating Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103658
Kang MK, Kim TJ, Kim Y-J, Kang L, Kim J, Lee N, Hyeon T, Lim M-s, Mo HJ, Shin JH, et al. Targeted Delivery of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Loaded Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Spherical Neural Masses for Treating Intracerebral Hemorrhage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(10):3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103658
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Min Kyoung, Tae Jung Kim, Young-Ju Kim, Lamie Kang, Jonghoon Kim, Nohyun Lee, Taeghwan Hyeon, Mi-sun Lim, Hee Jung Mo, Jung Hwan Shin, and et al. 2020. "Targeted Delivery of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Loaded Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Spherical Neural Masses for Treating Intracerebral Hemorrhage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 10: 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103658
APA StyleKang, M. K., Kim, T. J., Kim, Y.-J., Kang, L., Kim, J., Lee, N., Hyeon, T., Lim, M.-s., Mo, H. J., Shin, J. H., Ko, S.-B., & Yoon, B.-W. (2020). Targeted Delivery of Iron Oxide Nanoparticle-Loaded Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Spherical Neural Masses for Treating Intracerebral Hemorrhage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(10), 3658. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103658




