Cholesterol-Rich Microdomains Contribute to PAR1 Signaling in Platelets Despite a Weak Localization of the Receptor in These Microdomains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
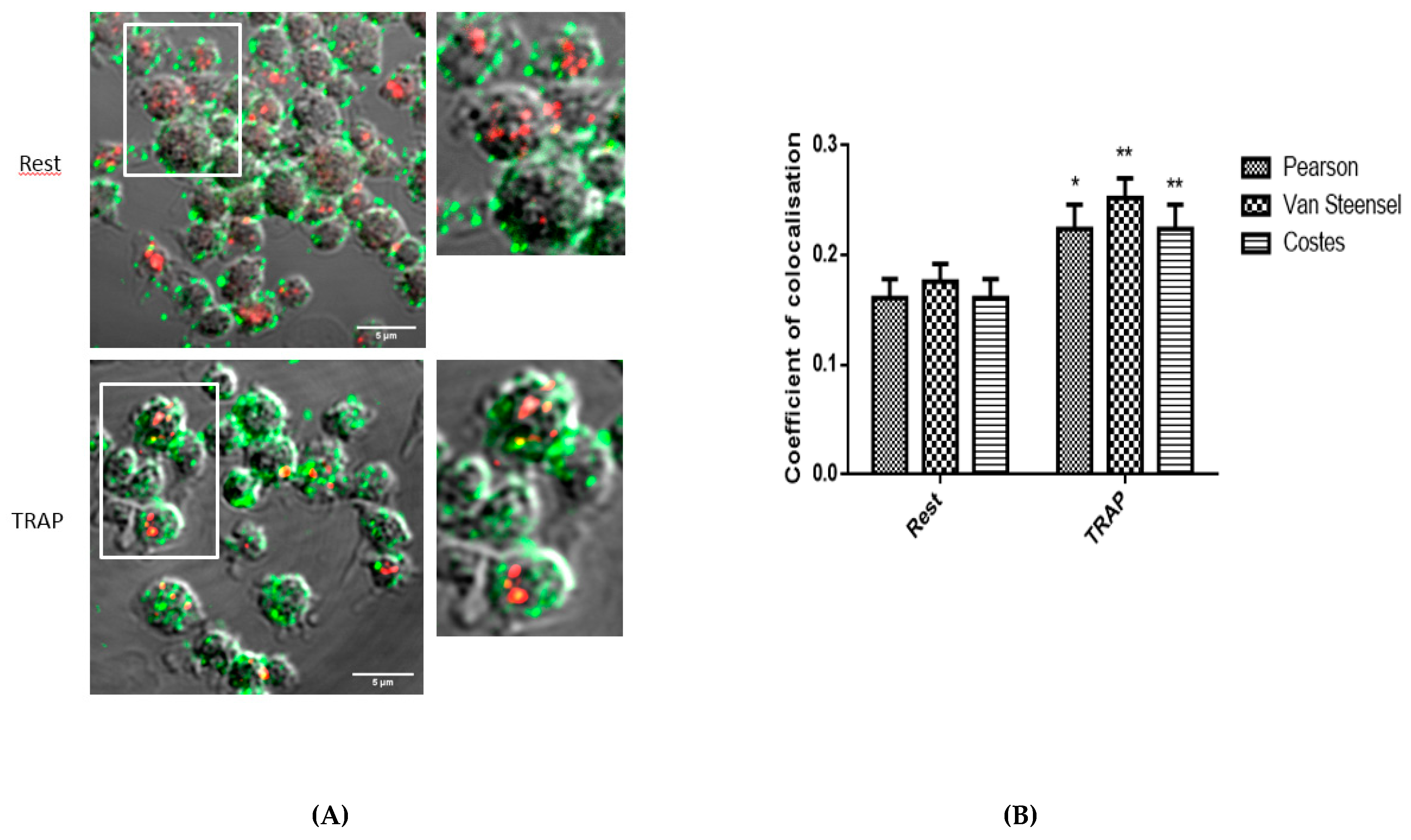
2.1. Analysis of the Colocalization of PAR1 and Cholesterol-Rich Microdomains
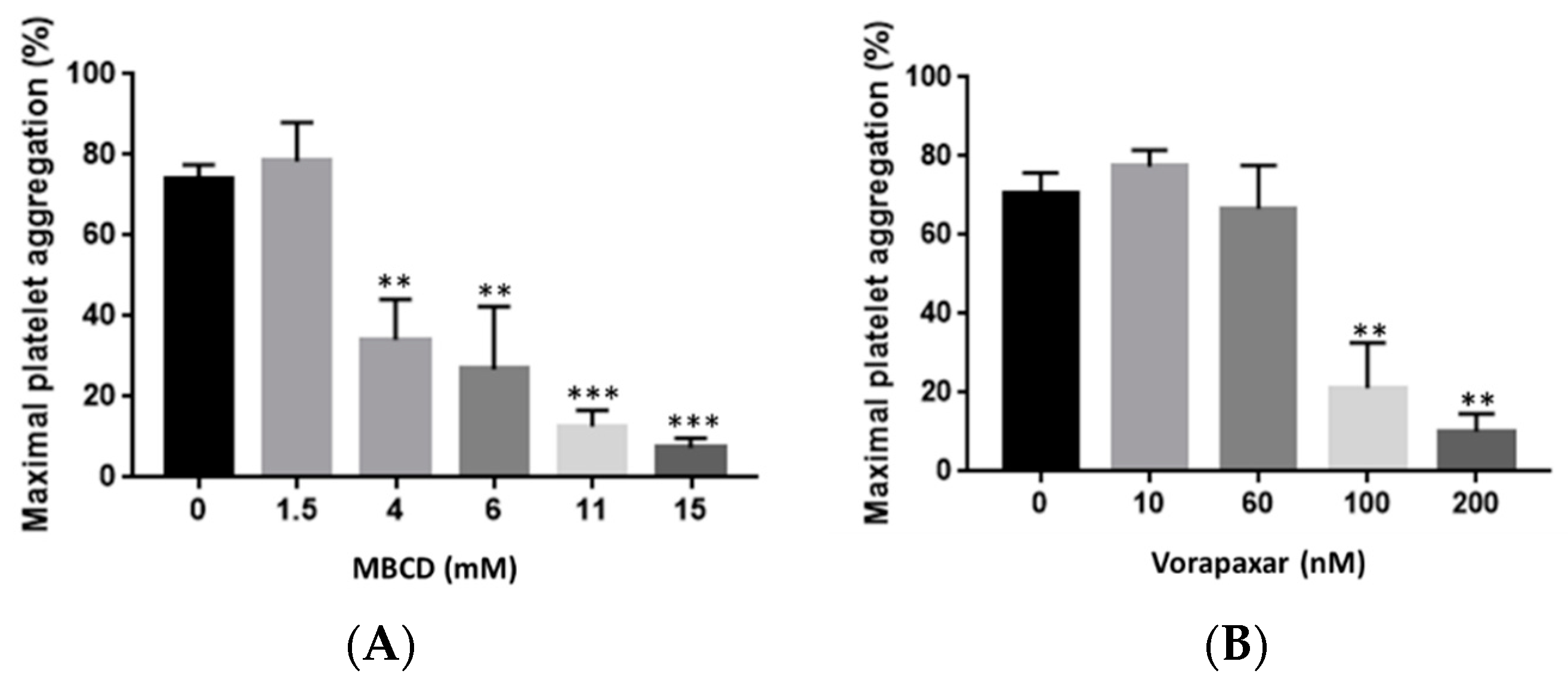
2.2. Impact of Cholesterol Depletion and Vorapaxar on Akt and p38 MAP Kinase Activation in TRAP-Stimulated Platelets
2.2.1. Flow Cytometry Analysis
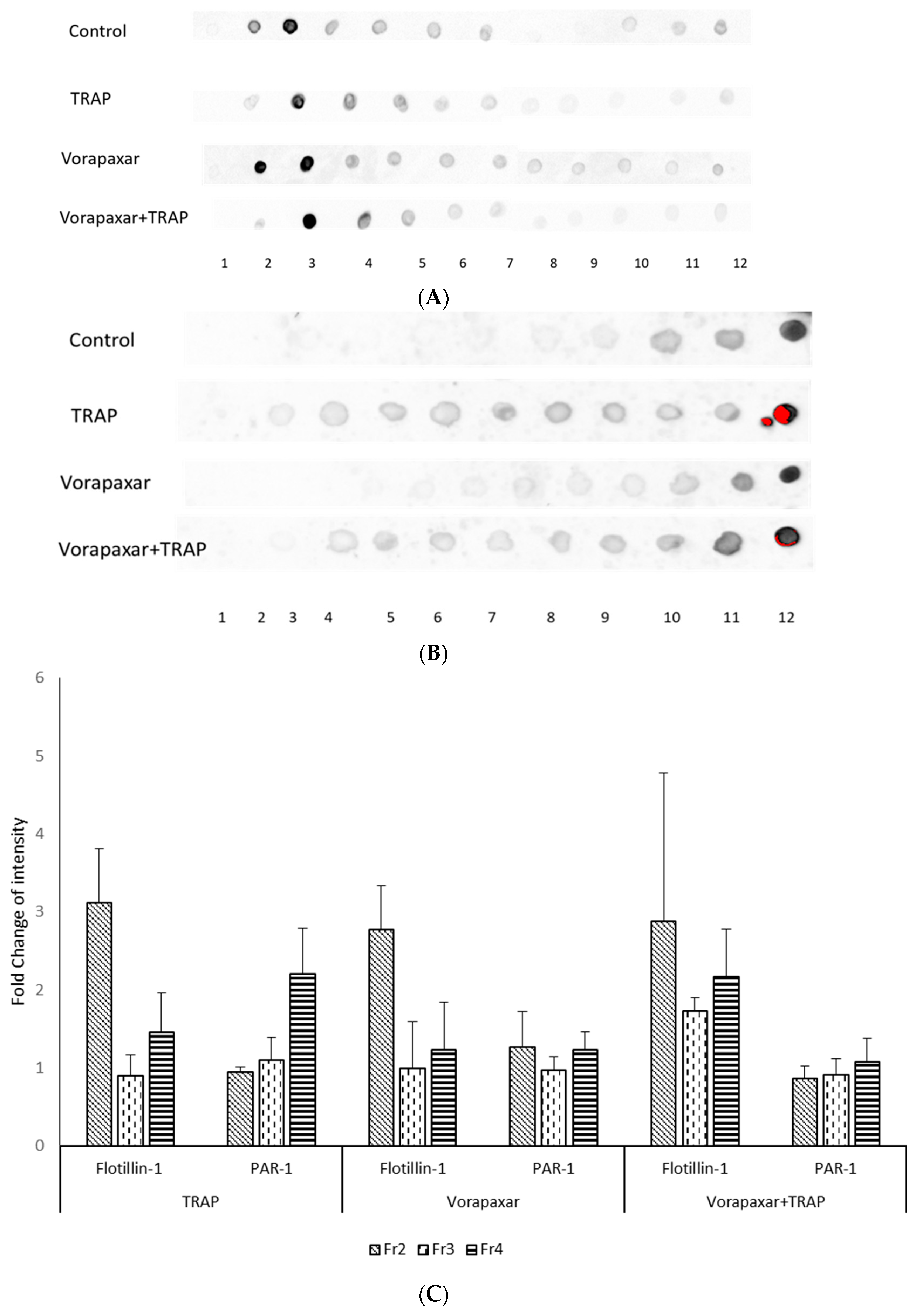
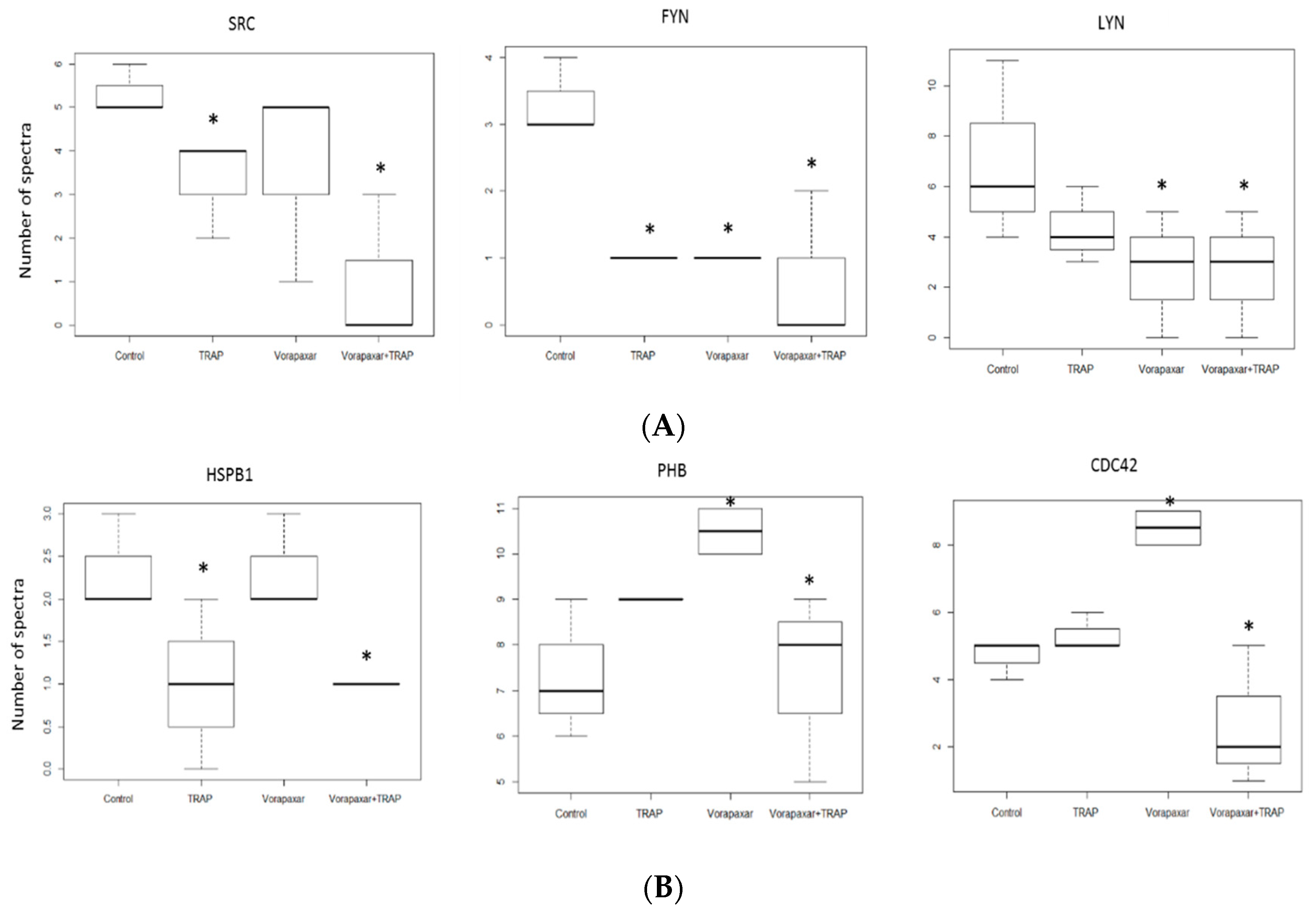
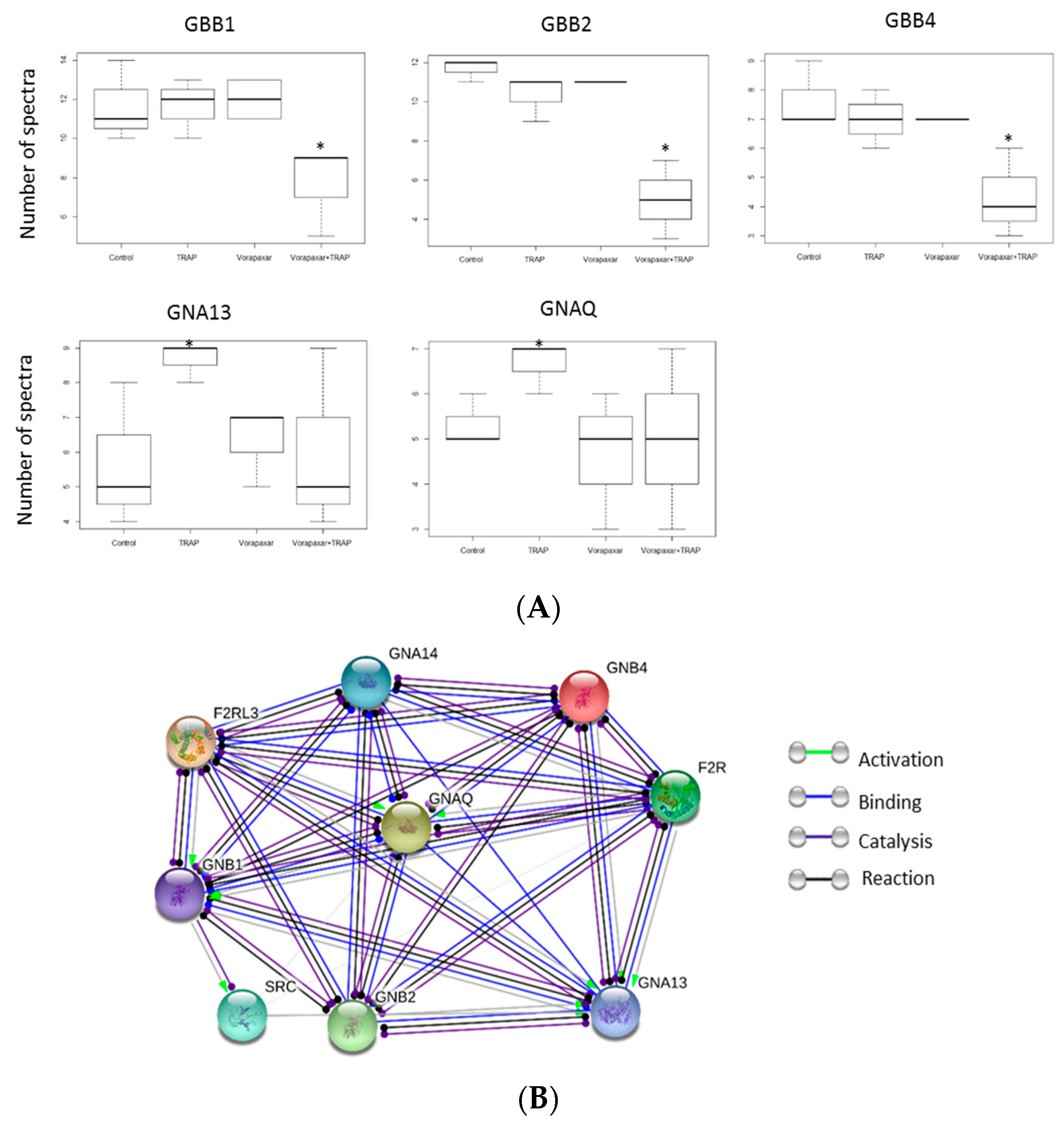
2.2.2. Proteomic Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Groups
4.2. Platelet Preparation
4.3. Platelet Aggregation
4.4. Analysis of Platelet Signaling Pathways by Flow Cytometry
4.5. Confocal Microscopy Analysis
4.6. Isolation of Membrane Cholesterol-Rich Microdomains
4.7. Immunoblot Analysis
4.8. Proteomics Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MBCD | Methyl β cyclodextrin |
| TRAP | Thrombin receptor-activating peptide |
| PAR1 | Protease-activated receptor 1 |
| GPCRs | G-protein coupled receptors |
References
- van den Eshof, B.L.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; Simpson, P.J.; van Alphen, F.P.J.; Zanivan, S.; Mertens, K.; Meijer, A.B.; van denBiggelaar, M. Paradigm of Biased PAR1 (Protease-Activated Receptor-1) Activation and Inhibition in Endothelial Cells Dissected by PhosphoproteomicsHighlights. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1891–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.-S.; Rezaie, A.R. Protease activated receptor 1 (PAR-1) activation by thrombin is protective in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells if endothelial protein C receptor is occupied by its natural ligand. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 100, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaumenhaft, R. Protease-Activated Receptor-1 Signaling: The Big Picture. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1809–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.-S.; Yang, L.; Rezaie, A.R. Lipid raft localization regulates the cleavage specificity of protease activated receptor 1 in endothelial cells. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2008, 6, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, A.; Fujiwara, T.K.; Tsunoyama, T.A.; Kasai, R.S.; Liu, A.-A.; Hirosawa, K.M.; Kinoshita, M.; Matsumori, N.; Komura, N.; Ando, H.; et al. Defining raft domains in the plasma membrane. Traffic 2020, 21, 106–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaumenhaft, R.; De Ceunynck, K. Targeting PAR1: Now what? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 701–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Soh, U.J.K.; Paing, M.M.; Arora, P.; Trejo, J. Caveolae are required for protease-selective signaling by protease-activated receptor–1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6393–6397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodin, S.; Tronchère, H.; Payrastre, B. Lipid rafts are critical membrane domains in blood platelet activation processes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1610, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, K.; Kaneda, M.; Miki, T.; Iida, K.; Sekino-Suzuki, N.; Kawashima, I.; Suzuki, H.; Shimonaka, M.; Arai, M.; Ohno-Iwashita, Y.; et al. Clot retraction is mediated by factor XIII-dependent fibrin-αIIbβ3-myosin axis in platelet sphingomyelin-rich membrane rafts. Blood 2013, 122, 3340–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, P.; Zachayus, J.-L.; Delesque-Touchard, N.; Labouret, C.; Hervé, C.; Uzabiaga, M.-F.; Pereillo, J.-M.; Culouscou, J.-M.; Bono, F.; Ferrara, P.; et al. The active metabolite of Clopidogrel disrupts P2Y12 receptor oligomers and partitions them out of lipid rafts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11069–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, Á.; Senis, Y.A. (Eds.) Frontmatter. In Platelet Proteomics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. i–xx. ISBN 978-0-470-94029-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zinzalla, G.; Thurston, D.E. Targeting protein-protein interactions for therapeutic intervention: A challenge for the future. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 65–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, S.K.; Guixa-Gonzalez, R.; Dainese, E.; Pastor, M.; De Fabritiis, G.; Selent, J. Molecular modeling and simulation of membrane lipid-mediated effects on GPCRs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryka, R.J.; Buckley, L.F.; Anderson, S.M. Vorapaxar: The Current Role and Future Directions of a Novel Protease-Activated Receptor Antagonist for Risk Reduction in Atherosclerotic Disease. Drugs RD 2017, 17, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aisiku, O.; Peters, C.G.; De Ceunynck, K.; Ghosh, C.C.; Dilks, J.R.; Fustolo-Gunnink, S.F.; Huang, M.; Dockendorff, C.; Parikh, S.M.; Flaumenhaft, R. Parmodulins inhibit thrombus formation without inducing endothelial injury caused by vorapaxar. Blood 2015, 125, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, J.Y.; Franchi, F.; Rollini, F.; Angiolillo, D.J. Role for Thrombin Receptor Antagonism with Vorapaxar in Secondary Prevention of Atherothrombotic Events: From Bench to Bedside. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 23, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judge, H.M.; Jennings, L.K.; Moliterno, D.J.; Hord, E.; Ecob, R.; Tricoci, P.; Rorick, T.; Kotha, J.; Storey, R.F. PAR1 antagonists inhibit thrombin-induced platelet activation whilst leaving the PAR4-mediated response intact. Platelets 2015, 26, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesco, G.G.; Mauro, T. Canobbio Ilaria Focal Adhesion Kinases in Platelet Function and Thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, E.; Brown, D.A. Insolubility of lipids in Triton X-100: Physical origin and relationship to sphingolipid/cholesterol membrane domains (rafts). Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Biomembr. 2000, 1508, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shogomori, H.; Brown, D.A. Use of Detergents to Study Membrane Rafts: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Masilamani, M.; Rajendran, L.; Bastmeyer, M.; Stuermer, C.A.O.; Illges, H. The Lipid Raft Microdomain-Associated Protein Reggie-1/ Flotillin-2 is Expressed in Human B Cells and Localized at the Plasma Membrane and Centrosome in PBMCs. Immunobiology 2002, 205, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Bouck, E.G.; Zunica, E.R.; Arachiche, A.; Nieman, M.T. 13—Protease-Activated Receptors. In Platelets, 4th ed.; Michelson, A.D., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 243–257. ISBN 978-0-12-813456-6. [Google Scholar]
- Nieman, M.T. Protease-activated receptors in hemostasis. Blood 2016, 128, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitley, M.J.; Henke, D.M.; Ghazi, A.; Nieman, M.; Stoller, M.; Simon, L.M.; Chen, E.; Vesci, J.; Holinstat, M.; McKenzie, S.E.; et al. The protease-activated receptor 4 Ala120Thr variant alters platelet responsiveness to low-dose thrombin and protease-activated receptor 4 desensitization, and is blocked by non-competitive P2Y12 inhibition. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 2501–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reséndiz, J.C.; Kroll, M.H.; Lassila, R. Protease-activated receptor-induced Akt activation—Regulation and possible function. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2007, 5, 2484–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, K.; Enomoto, Y.; Onuma, T.; Tsujimoto, M.; Doi, T.; Matsushima-Nishiwaki, R.; Tokuda, H.; Ogura, S.; Iida, H.; Kozawa, O.; et al. Rac Regulates the TRAP-Induced Release of Phosphorylated-HSP27 from Human Platelets via p38 MAP Kinase but Not JNK. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 1523–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzieciatkowska, M.; D’Alessandro, A.; Burke, T.A.; Kelher, M.R.; Moore, E.E.; Banerjee, A.; Silliman, C.C.; West, B.F.; Hansen, K.C. Proteomics of apheresis platelet supernatants during routine storage: Gender-related differences. J. Proteomics 2015, 112, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senis, Y.A.; Mazharian, A.; Mori, J. Src family kinases: At the forefront of platelet activation. Blood 2014, 124, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieswandt, B.; Varga-Szabo, D.; Elvers, M. Integrins in platelet activation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7 (Suppl. S1), 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Séverin, S.; Nash, C.A.; Mori, J.; Zhao, Y.; Abram, C.; Lowell, C.A.; Senis, Y.A.; Watson, S.P. Distinct and overlapping functional roles of Src family kinases in mouse platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 1631–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, J.E.; McCarty, O.J.T. Rho GTPases in Platelet Function. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanowska-Grabowska, R.; Gear, A.R. Heat-shock proteins and platelet function. Platelets 2000, 11, 6–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigg, R.A.; Healy, L.D.; Nowak, M.S.; Mallet, J.; Thierheimer, M.L.D.; Pang, J.; McCarty, O.J.T.; Aslan, J.E. Heat shock protein 70 regulates platelet integrin activation, granule secretion and aggregation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2016, 310, C568–C575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Lee, W.; Zhang, Y. Prohibitins are involved in protease-activated receptor 1-mediated platelet aggregation. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jin, J.; Kunapuli, S.P. Akt Activation in Platelets Depends on Gi Signaling Pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4186–4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, A.J.; Jacques, S.L.; Badar, J.; Kaneider, N.C.; Derian, C.K.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Blocking the protease-activated receptor 1-4 heterodimer in platelet-mediated thrombosis. Circulation 2006, 113, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimsey, N.J.; Trejo, J. Integration of Endothelial Protease-activated Receptor-1 Inflammatory Signaling by Ubiquitin. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2016, 23, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolte, S.; Cordelières, F.P. A guided tour into subcellular colocalization analysis in light microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 224, 213–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabani, V.; Davani, S.; Gambert-Nicot, S.; Meneveau, N.; Montange, D. Comparative lipidomics and proteomics analysis of platelet lipid rafts using different detergents. Platelets 2016, 27, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langella, O.; Valot, B.; Balliau, T.; Blein-Nicolas, M.; Bonhomme, L.; Zivy, M. X!TandemPipeline: A Tool to Manage Sequence Redundancy for Protein Inference and Phosphosite Identification. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, T.U. UniProt: A hub for protein information. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, L.J.; Kuhn, M.; Stark, M.; Chaffron, S.; Creevey, C.; Muller, J.; Doerks, T.; Julien, P.; Roth, A.; Simonovic, M.; et al. STRING 8—A global view on proteins and their functional interactions in 630 organisms. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2009, 37, D412–D416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Snel, B.; Hooper, S.D.; Krupp, M.; Foglierini, M.; Jouffre, N.; Huynen, M.A.; Bork, P. STRING: Known and predicted protein-protein associations, integrated and transferred across organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, D433–D437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, J. VENNY: An Interactive Tool for Comparing Listes with Venn Diagrams. Available online: https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index2.0.2.html (accessed on 29 October 2020).
- Fabregat, A.; Jupe, S.; Matthews, L.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Gillespie, M.; Garapati, P.; Haw, R.; Jassal, B.; Korninger, F.; May, B.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2018, 46, D649–D655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulumello, D.V.; Deber, C.M. Efficiency of detergents at maintaining membrane protein structures in their biologically relevant forms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R. A language and environment for statistical computing. Computing 2006, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rabani, V.; Lagoutte-Renosi, J.; Series, J.; Valot, B.; Xuereb, J.-M.; Davani, S. Cholesterol-Rich Microdomains Contribute to PAR1 Signaling in Platelets Despite a Weak Localization of the Receptor in These Microdomains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218065
Rabani V, Lagoutte-Renosi J, Series J, Valot B, Xuereb J-M, Davani S. Cholesterol-Rich Microdomains Contribute to PAR1 Signaling in Platelets Despite a Weak Localization of the Receptor in These Microdomains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(21):8065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218065
Chicago/Turabian StyleRabani, Vahideh, Jennifer Lagoutte-Renosi, Jennifer Series, Benoit Valot, Jean-Marie Xuereb, and Siamak Davani. 2020. "Cholesterol-Rich Microdomains Contribute to PAR1 Signaling in Platelets Despite a Weak Localization of the Receptor in These Microdomains" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 21: 8065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218065
APA StyleRabani, V., Lagoutte-Renosi, J., Series, J., Valot, B., Xuereb, J.-M., & Davani, S. (2020). Cholesterol-Rich Microdomains Contribute to PAR1 Signaling in Platelets Despite a Weak Localization of the Receptor in These Microdomains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(21), 8065. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218065




