TULP1 and TUB Are Required for Specific Localization of PRCD to Photoreceptor Outer Segments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
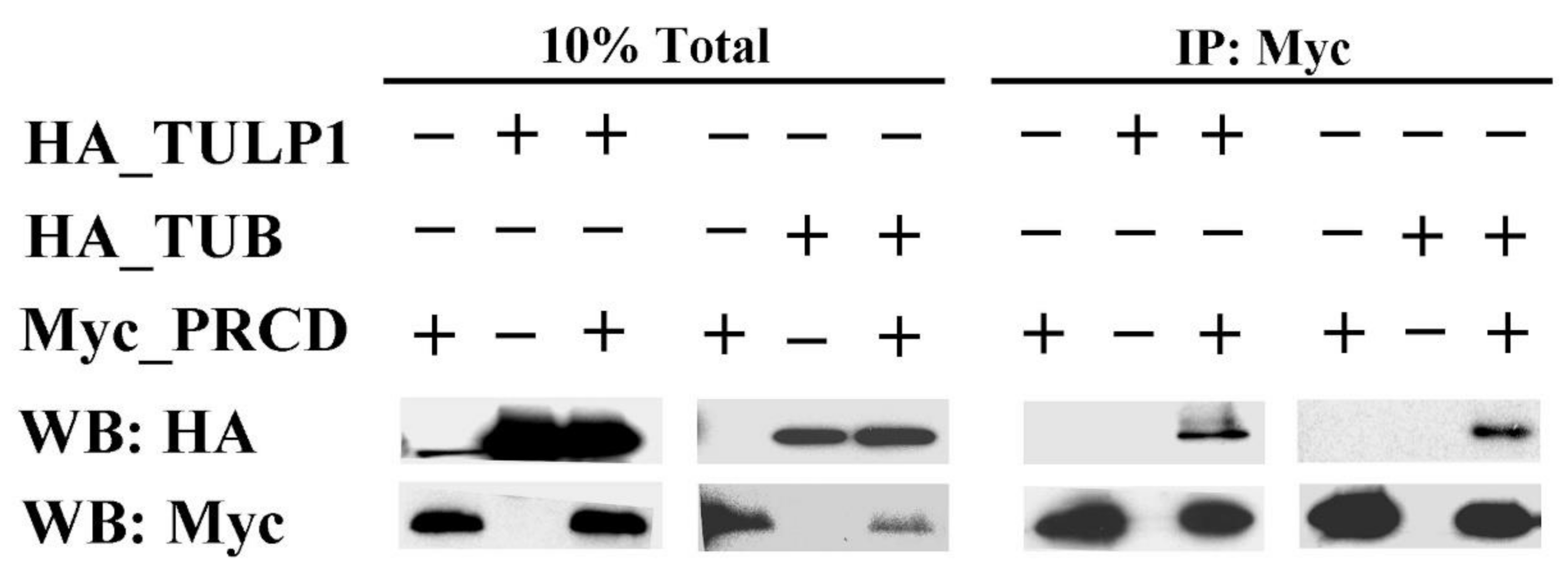
2.1. PRCD Interacts with Both TULP1 and TUB
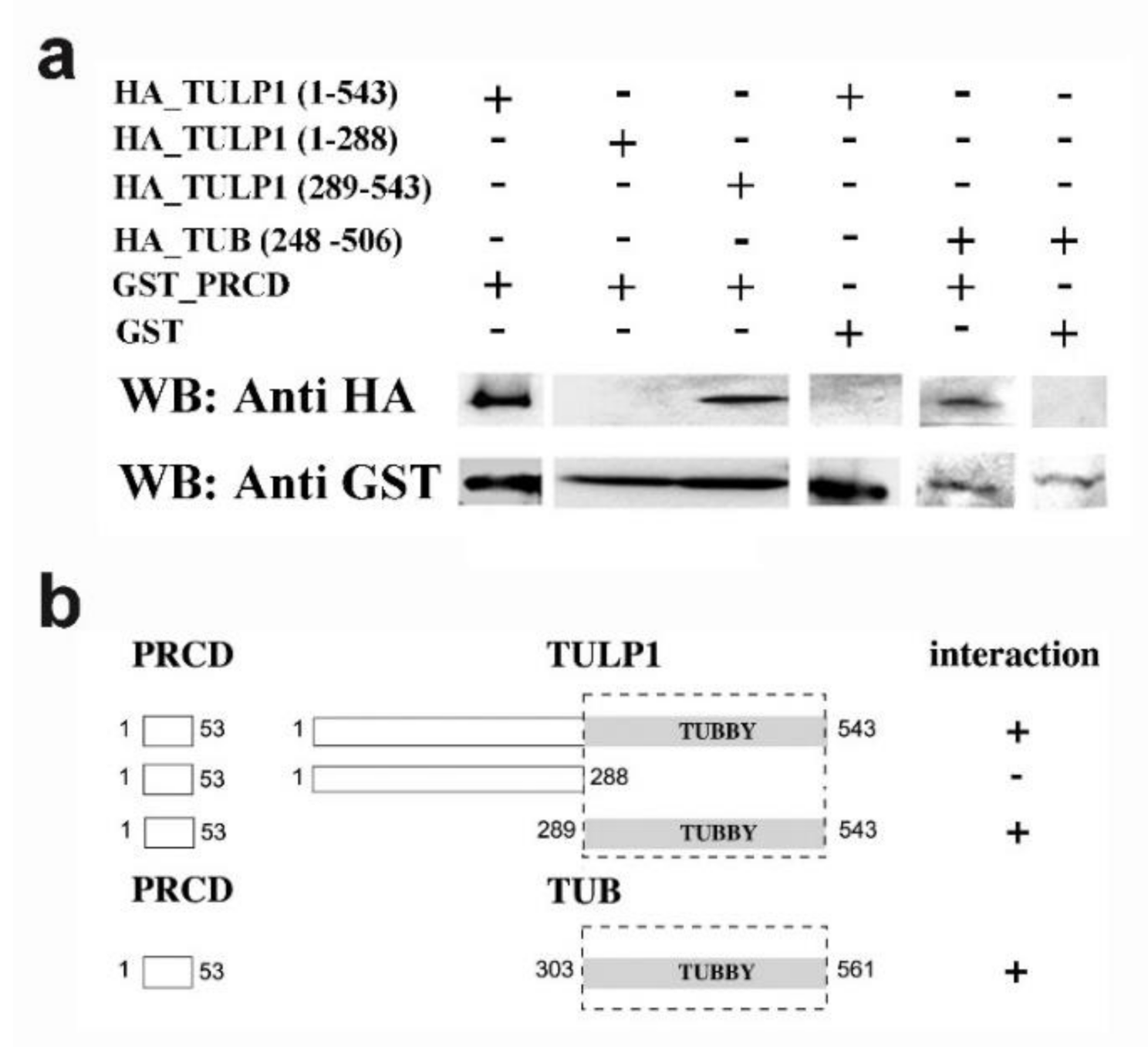
2.2. PRCD’s Interaction with TULP1 and TUB Is Mediated by the Highly Conserved Tubby Domain
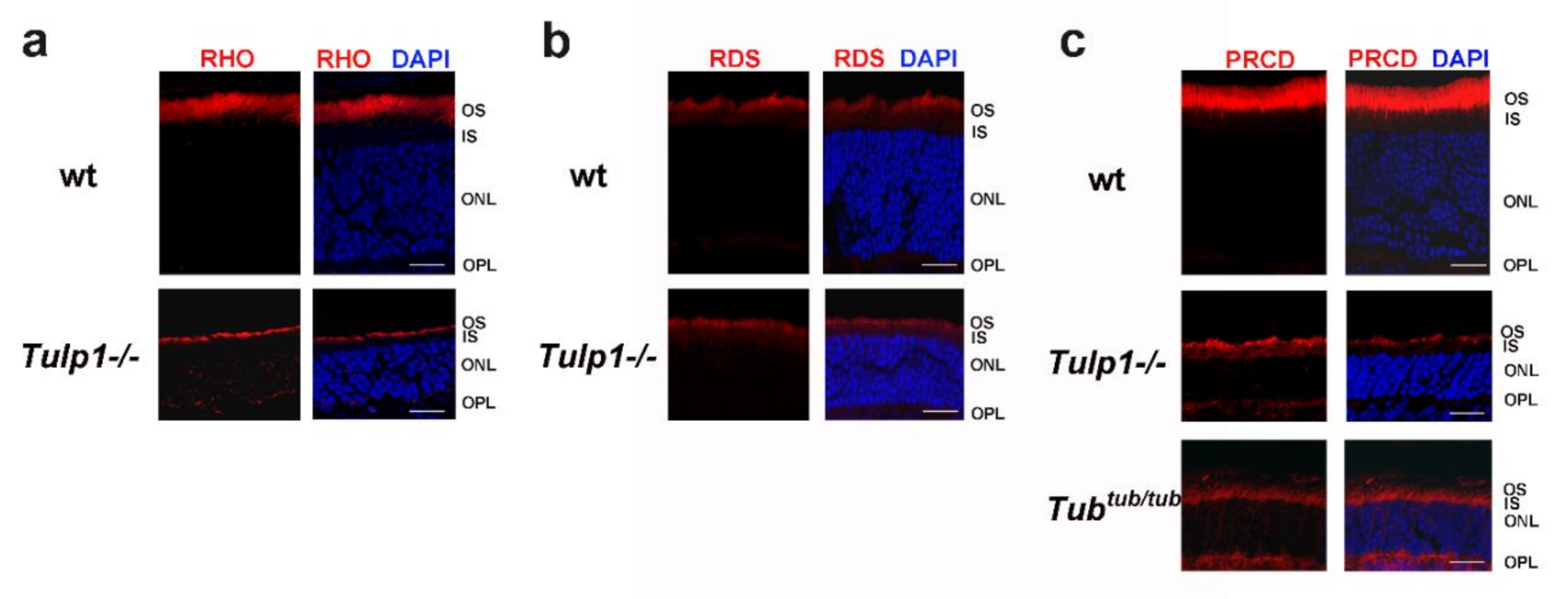
2.3. PRCD Is Mislocalized in Photoreceptors of TULP1- and TUB-Deficient Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ras-Recruitment System (RRS)
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Co-Immunoprecipitation (co-IP)
4.4. Pull-Down Assays
4.5. Animal Experiments
4.6. Immunofluorescence
4.7. Antibodies
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Co-IP | co-immunoprecipitation |
| GC1 | guanylate cyclase 1 |
| GCAP1 | guanylate cyclase activating protein |
| IS | inner segment |
| ONL | outer nuclear layer |
| OPL | outer plexiform layer |
| OS | outer segment |
| PRCD | Photoreceptor Disc Component |
| RP | Retinitis pigmentosa |
| RRS | Ras-Recruitment System |
| TULP1 | Tubby-like protein 1 |
References
- May-Simera, H.; Nagel-Wolfrum, K.; Wolfrum, U. Cilia—The sensory antennae in the eye. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 60, 144–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kevany, B.M.; Palczewski, K. Phagocytosis of retinal rod and cone photoreceptors. Physiology 2010, 25, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, R.Y.; Pearring, J.N.; Ding, J.D.; Spencer, W.J.; Hao, Y.; Arshavsky, V.Y. Photoreceptor discs form through peripherin-dependent suppression of ciliary ectosome release. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skiba, N.A.; Spencer, W.J.; Salinas, R.Y.; Lieu, E.C.; Thompson, J.W.; Arshavsky, V.Y. Proteomic identification of unique photoreceptor disc components reveals the presence of PRCD, a protein linked to retinal degeneration. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 3010–3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allon, G.; Mann, I.; Remez, L.; Sehn, E.; Rizel, L.; Nevet, M.J.; Perlman, I.; Wolfrum, U.; Ben-Yosef, T. PRCD is concentrated at the base of photoreceptor outer segments and is involved in outer segment disc formation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 4078–4088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Kolandaivelu, S. Palmitoylation of Progressive Rod-Cone Degeneration (PRCD) Regulates Protein Stability and Localization. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 23036–23046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, W.J.; Pearring, J.N.; Salinas, R.Y.; Loiselle, D.R.; Skiba, N.P.; Arshavsky, V.Y. Progressive Rod-Cone Degeneration (PRCD) Protein Requires N-Terminal S-Acylation and Rhodopsin Binding for Photoreceptor Outer Segment Localization and Maintaining Intracellular Stability. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5028–5037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, W.J.; Ding, J.D.; Lewis, T.R.; Yu, C.; Phan, S.; Pearring, J.N.; Kim, K.Y.; Thor, A.; Mathew, R.; Kalnitsky, J.; et al. PRCD is essential for high-fidelity photoreceptor disc formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 13087–13096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangerl, B.; Goldstein, O.; Philp, A.R.; Lindauer, S.J.; Pearce-Kelling, S.E.; Mullins, R.F.; Graphodatsky, A.S.; Ripoll, D.; Felix, J.S.; Stone, E.M.; et al. Identical mutation in a novel retinal gene causes progressive rod-cone degeneration in dogs and retinitis pigmentosa in humans. Genomics 2006, 88, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevet, M.J.; Shalev, S.A.; Zlotogora, J.; Mazzawi, N.; Ben-Yosef, T. The identification of a prevalent founder mutation in an Israeli Muslim Arab village confirms the role of PRCD in the etiology of retinitis pigmentosa in humans. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 47, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronheim, A. The Ras Recruitment System (RRS) for the Identification and Characterization of Protein-Protein Interactions. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1794, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Xu, Z.; Kong, Y. The tubby-like proteins kingdom in animals and plants. Gene 2018, 642, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.; Kleyn, P.W.; Knowles, J.A.; Lewis, C.A.; Ross, B.M.; Parano, E.; Kovats, S.G.; Lee, J.J.; Penchaszadeh, G.K.; Ott, J.; et al. TULP1 mutation in two extended Dominican kindreds with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borman, A.D.; Pearce, L.R.; Mackay, D.S.; Nagel-Wolfrum, K.; Davidson, A.E.; Henderson, R.; Garg, S.; Waseem, N.H.; Webster, A.R.; Plagnol, V.; et al. A homozygous mutation in the TUB gene associated with retinal dystrophy and obesity. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagstrom, S.A.; Duyao, M.; North, M.A.; Li, T. Retinal degeneration in tulp1-/- mice: Vesicular accumulation in the interphotoreceptor matrix. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1999, 40, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar]
- Hagstrom, S.A.; North, M.A.; Nishina, P.L.; Berson, E.L.; Dryja, T.P. Recessive mutations in the gene encoding the tubby-like protein TULP1 in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Nat. Genet. 1998, 18, 174–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, S.; Shiva, N.; Ikeda, A.; Smith, R.S.; Nusinowitz, S.; Yan, G.; Lin, T.R.; Chu, S.; Heckenlively, J.R.; North, M.A.; et al. Retinal degeneration but not obesity is observed in null mutants of the tubby-like protein 1 gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, G.H.; Watson, R.F.; Pauer, G.J.; Bollinger, K.; Hagstrom, S.A. Immunocytochemical evidence of Tulp1-dependent outer segment protein transport pathways in photoreceptor cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagstrom, S.A.; Adamian, M.; Scimeca, M.; Pawlyk, B.S.; Yue, G.; Li, T. A role for the Tubby-like protein 1 in rhodopsin transport. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2001, 42, 1955–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Haley, J.; Bulgakov, O.V.; Cai, X.; McGinnis, J.; Li, T. Tubby is required for trafficking G protein-coupled receptors to neuronal cilia. Cilia 2012, 1, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Aronheim, A.; Broder, Y.C.; Cohen, A.; Fritsch, A.; Belisle, B.; Abo, A. Chp, a homologue of the GTPase Cdc42Hs, activates the JNK pathway and is implicated in reorganizing the actin cytoskeleton. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 1125–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remez, L.; Zobor, D.; Kohl, S.; Ben-Yosef, T. The progressive rod-cone degeneration (PRCD) protein is secreted through the conventional ER/Golgi-dependent pathway. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 125, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Lennon, A.; Li, Y.; Lorenz, B.; Fossarello, M.; North, M.; Gal, A.; Wright, A. Tubby-like protein-1 mutations in autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Lancet 1998, 351, 1103–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanein, S.; Perrault, I.; Gerber, S.; Tanguy, G.; Barbet, F.; Ducroq, D.; Calvas, P.; Dollfus, H.; Hamel, C.; Lopponen, T.; et al. Leber congenital amaurosis: Comprehensive survey of the genetic heterogeneity, refinement of the clinical definition, and genotype-phenotype correlations as a strategy for molecular diagnosis. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 23, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebrard, M.; Manes, G.; Bocquet, B.; Meunier, I.; Coustes-Chazalette, D.; Herald, E.; Senechal, A.; Bolland-Auge, A.; Zelenika, D.; Hamel, C.P. Combining gene mapping and phenotype assessment for fast mutation finding in non-consanguineous autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa families. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 19, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannabiran, C.; Singh, H.; Sahini, N.; Jalali, S.; Mohan, G. Mutations in TULP1, NR2E3, and MFRP genes in Indian families with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Mol. Vis. 2012, 18, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Qin, M.; Mizota, A.; Kondo, M.; Hayashi, H.; Hayashi, K.; Oshima, K.; Tahira, T.; Hayashi, K. A homozygosity-based search for mutations in patients with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa, using microsatellite markers. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 4433–4439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loktev, A.V.; Jackson, P.K. Neuropeptide Y family receptors traffic via the Bardet-Biedl syndrome pathway to signal in neuronal primary cilia. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caberoy, N.B. Synergistic interaction of tubby and tubby-like protein 1 (Tulp1). Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 801, 503–509. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, J.L.; Hill, C.R.; Cole, K.D. Authentication of African green monkey cell lines using human short tandem repeat markers. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roth, M.B.; Zahler, A.M.; Stolk, J.A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 115, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, D.L.; Eicher, E.M. Fat (fat) and tubby (tub): Two autosomal recessive mutations causing obesity syndromes in the mouse. J. Hered. 1990, 81, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Remez, L.; Cohen, B.; Nevet, M.J.; Rizel, L.; Ben-Yosef, T. TULP1 and TUB Are Required for Specific Localization of PRCD to Photoreceptor Outer Segments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228677
Remez L, Cohen B, Nevet MJ, Rizel L, Ben-Yosef T. TULP1 and TUB Are Required for Specific Localization of PRCD to Photoreceptor Outer Segments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(22):8677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228677
Chicago/Turabian StyleRemez, Lital, Ben Cohen, Mariela J. Nevet, Leah Rizel, and Tamar Ben-Yosef. 2020. "TULP1 and TUB Are Required for Specific Localization of PRCD to Photoreceptor Outer Segments" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 22: 8677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228677
APA StyleRemez, L., Cohen, B., Nevet, M. J., Rizel, L., & Ben-Yosef, T. (2020). TULP1 and TUB Are Required for Specific Localization of PRCD to Photoreceptor Outer Segments. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), 8677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228677




