Abstract
Neuroinflammation is a physiological response aimed at maintaining the homodynamic balance and providing the body with the fundamental resource of adaptation to endogenous and exogenous stimuli. Although the response is initiated with protective purposes, the effect may be detrimental when not regulated. The physiological control of neuroinflammation is mainly achieved via regulatory mechanisms performed by particular cells of the immune system intimately associated with or within the nervous system and named “non-neuronal cells.” In particular, mast cells (within the central nervous system and in the periphery) and microglia (at spinal and supraspinal level) are involved in this control, through a close functional relationship between them and neurons (either centrally, spinal, or peripherally located). Accordingly, neuroinflammation becomes a worsening factor in many disorders whenever the non-neuronal cell supervision is inadequate. It has been shown that the regulation of non-neuronal cells—and therefore the control of neuroinflammation—depends on the local “on demand” synthesis of the endogenous lipid amide Palmitoylethanolamide and related endocannabinoids. When the balance between synthesis and degradation of this bioactive lipid mediator is disrupted in favor of reduced synthesis and/or increased degradation, the behavior of non-neuronal cells may not be appropriately regulated and neuroinflammation exceeds the physiological boundaries. In these conditions, it has been demonstrated that the increase of endogenous Palmitoylethanolamide—either by decreasing its degradation or exogenous administration—is able to keep neuroinflammation within its physiological limits. In this review the large number of studies on the benefits derived from oral administration of micronized and highly bioavailable forms of Palmitoylethanolamide is discussed, with special reference to neuroinflammatory disorders.
1. Introduction
Modern neurosciences consider neuroinflammation as “any inflammatory process, both acute and chronic, that affects the central or peripheral nervous system” [1]. Neuroinflammation is a widely studied issue since it may be induced by—and associated with—certain pathological clinical conditions that may result in neurodegeneration [2]. Immune cells [3,4], like mast cells and microglia [5,6], as well as astrocytes (i.e., neuroglial cells that do not belong to the immune system [7]) are importantly involved in neuroinflammatory processes. These cells are collectively known as “non-neuronal cells” in relation to their lineage and location, since they are not neurons albeit they are associated with—or located within—the peripheral and central nervous system. Under physiological conditions, non-neuronal cells support the well-being and well-function of neurons through diverse functions, including neurotrophic factor secretion, and they are thus able to ensure the homodynamic balance of the nervous system, i.e., the dynamic homeostatic process aimed at coping with different challenges [8]. On the contrary, once hyper-activated they can profoundly affect neuronal responses, in particular pain signaling systems and neurodegenerative pathways [9,10]. Actually, it has emerged that hyper-activated non-neuronal cells mutually interact with each other through a cytokine-mediated cross-talk that can amplify or chronicize neuronal suffering [11,12]. If uncontrolled, non-neuronal cells are thus considered to play an important role in the induction and maintenance of peripheral and central sensitization, associated with inflammatory pain, chronic and neuropathic pain, and with many clinical conditions of dysmetabolic, traumatic, or degenerative nature [1,13,14]. Non-neuronal cells are actually recognized a crucial trait d’union between systemic inflammation and the brain [15,16,17]. Systemic increase of inflammatory mediators (e.g., cytokines) significantly contributes to neuroinflammatory reactions [18,19]. Damage to the blood brain barrier and increased entrance of proinflammatory mediators and immune cells into the brain are the main consequences and result in the activation of non-neuronal cell and hence neuroinflammation [17,18]. COVID-19 associated neurological disease (i.e., encephalitis) without evidence of central nervous system viral invasion is a current example of how systemic hyperinflammation (i.e., virus-induced strong systemic cytokine storm) can activate neuroinflammatory cascade at the central nervous system level [20,21].
On the basis of the aforementioned scientific knowledge, several research groups have focused their attention on the down-regulation of non-neuronal cells as a potential mean to control neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders, as extensively reviewed recently [22,23,24]. To this aim, the hypothesis of using Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) has been put forward, given its ability to physiologically regulate non-neuronal cells [25,26]. In mammalian species, PEA is produced “on demand” by different cell types [27,28,29] in response to actual or potential damage for protective purposes [30]. An ever-growing body of evidence indicates that PEA plays a key role in restoring homodynamic balance during disease conditions [31]. In particular, PEA is a promising lipid signaling molecule involved in the physiological program of resolution, i.e., the coordinated and dynamic control of inflammation aimed at averting the occurrence of non-resolving inflammation [32]. PEA has been detected in several tissues and body fluids, e.g., the brain and spinal cord [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], eye and cardiac tissues [41,42,43,44], liver and testicles [45,46,47], gastrointestinal system [48,49], skin, muscle [50,51,52,53] and blood [54,55,56,57]. In addition, PEA is normally present in the amniotic fluid, umbilical vein, and artery (i.e., the main sources of fetal nutrition), as well as human breast milk [47,58], and is thus considered a genuine early nutrient. Importantly, PEA was shown to be protective toward perinatal asphyxia [59] and critical for the healthy development of the fetal nervous system [60]. Furthermore, PEA occurs in several food sources, albeit at low levels (Table 1). In particular, it was originally detected in egg yolk [61,62], and subsequently in peas, tomato, beans, peanuts, soya lecithin [63,64], and in cow’s milk [65]. Recently, PEA has also been identified in coffee and their respective infusions [66]. Accordingly, it can be speculated that under physiological conditions appropriate levels of PEA can be obtained through breastfeeding in the newborns and a balanced diet in the adulthood, besides a suitable “on demand” body production. On the contrary, in diseased conditions associated with neuroinflammation, one might envision that PEA endogenous production is insufficient to fully exert its protective role [67]. This is the case of pathological settings characterized by microglial activation, like neuropathic pain, where spinal and/or supraspinal levels of PEA are severely decreased [39,68]. Conceivably, raising PEA levels may be a promising therapeutic strategy in the control of neuroinflammation [32]. In line with this view, inhibition of PEA catabolic enzyme in experimental systemic inflammation results in a significant elevation in the endogenous PEA levels in the brain and an associated decrease of brain inflammatory mediators [69]. Likewise, increasing the levels of PEA in LPS-challenged microglial cells through the inhibition of its hydrolysis significantly reduces microglial activation [70]. On the other hand, administration of PEA significantly relieves neuroinflammatory-associated disorders [32], and counteracts neuroinflammation at the cellular level, provided the compound is formulated in bioavailable forms [71].

Table 1.
PEA content in plant and animal derived foods. * 110 ± 32.3 lactation days; (§) on a dry weight basis.
The highly lipophilic nature of PEA, in fact, limits its dissolution and absorption as well as the bioavailability for achieving health benefits by oral route. Bioavailable formulations of PEA, i.e., micronized PEA (PEA-m) and ultra-micronized PEA (PEA-um) with a particle size distribution in the 2–10 μm and 0.8–6 μm range, respectively, have been developed accordingly [71,75]. After oral administration, PEA-m and PEA-um have repeatedly shown higher bioavailability and superior effects compared to naïve PEA [75,76]. PEA-um also penetrates into the central nervous system, as shown by the significant increase of PEA levels in the hippocampus, brain, and spinal cord after oral administration of PEA-um [76,77]. Finally, PEA-m and PEA-um have shown favorable safety profiles with no evidence of toxicity [78]. PEA-m and PEA-um are used in the formulation of products that are currently classified as Foods for Special Medical Purposes (FSMP) under the EU Regulation. The products are intended to meet part of the nutritional requirements of patients with specific diseases and clinical conditions sustained by neuroinflammation. In this review, we focus on the particular relevance of uncontrolled neuroinflammation in the onset of central and peripheral neurodegenerative disorders. The large number of studies on the beneficial effects of PEA-m and PEA-um in pre-clinical disease models as well as naturally occurring disorders are discussed from this perspective (Table 2 and Table 3). Moreover, given the role played by oxidative stress in neuroinflammation [79], we also focus on the advantage of combining PEA-um with polyphenolic antioxidant substances of vegetable origin [80], such as luteolin [81,82] and polydatin [83] (Table 2 and Table 3). However, inasmuch as it would be unmanageable to describe here all pathological conditions in which PEA-m and PEA-um (alone or in combination with luteolin or polydatin) have been administered, we place our attention only on some neurodegenerative and neurological disorders, as well as pain syndromes sustained by neuroinflammation.

Table 2.
Pre-clinical and clinical effects of PEA in micronized and co-micronized formulations on neuroinflammation associated with neurodegenerative and neurological disorders. Abbreviations: Aβ, beta amyloid; ALS, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; ASD, autism spectrum disorders; bid, twice a day; co-ultraPEA-Lut, PEA co-ultra-micronized with Luteolin; EAE, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis; FSMP, Foods for Special Medical Purposes; i.h., intra-hippocampal; i.p., intra-peritoneal; MCI, mild cognitive impairment; MG, myasthenia gravis; mos., months; MPTP, 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1 2 3 6-tetrahydropyridine; PEA, palmitoylethanolamide; PEA-m: micronized PEA; PEA-um: ultra-micronized PEA; PD, Parkinson’s disease; p.o.; oral; RoA, routes of administration; RR-MS, relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis; s.c., subcutaneous; SL, sublingual; tabs, tablets; tid, three times a day; TMEV-IDD, Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus-Induced Demyelinating Disease; wks, weeks; 3×Tg-AD, triple transgenic Alzheimer’s disease; 6-OHDA: 6-hydroxydopamine.

Table 3.
Pre-clinical and clinical effects of PEA in micronized and co-micronized formulations in pain syndromes sustained by neuroinflammation. Abbreviations: bid, twice a day; CCI, chronic constriction injury; FSMP, food for special medical purpose; i.p., intra-peritoneal; i.pl., intra-plantar; NP, neurophatic pain; p.o., oral. PEA-m, micronized PEA; PEA-um, ultra-micronized PEA; PEA, palmitoylethanolamide; s.c., subcutaneous; SNI, spared nerve injury.
2. Endogenous PEA: Metabolic Pathways and Mechanisms of Action
The body production of PEA mainly depends on a membrane phospholipid precursor, namely C:16 N-acyl-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine (NAPE) or N-palmitoyl-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine, which is then hydrolyzed to generate PEA by the action of NAPE-selective phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) [134]. The degradation of PEA is instead catalyzed by the action of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) [135] and N-acylethanolamide hydrolyzing acid amidase (NAAA) [136], leading to the formation of palmitic acid and ethanolamine, which are fully reused by cells to synthesize the membrane phospholipids [137,138]. The mechanism through which PEA maintains the normal reactivity of mast cells and microglia/astrocytes in the peripheral and central nervous system respectively is historically known as autacoid local injury antagonism (ALIA) [139,140,141]. It is now acknowledged that ALIA depends on the ability of PEA to (i) indirectly interact with the type-1 (CB1) and type-2 (CB2) cannabinoid receptors [142,143], (ii) exert a positive allosteric modulation of the transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1 (TRPV1) [57,144,145,146,147], (iii) directly interact with the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α) [148] or with the orphan G-protein coupled receptor 55 (GPR55) [149,150]. The indirect interaction of PEA with specific receptors of the endocannabinoid and endovanilloid systems is well-known as the “entourage effect” [142,151]. By inhibiting the expression of the enzyme hydrolyzing the endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA) [142], or by stimulating the activity of the enzyme biosynthesizing the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) [143], PEA increases the endogenous levels of these lipid mediators and potentiates their actions at CB1, CB2, and TRPV1 receptors [57,142,143,145,146]. Nevertheless, it has also been demonstrated that PEA via direct interaction with PPAR-α receptors is capable to activate TRPV1 receptors [152,153], as well as to increase the expression of CB2 receptors [154]. These discoveries revealed interesting multiple and synergistic mechanisms of action of PEA, making it able to exert multiple effects and act on different cell types in both the central and the peripheral nervous system (Figure 1).
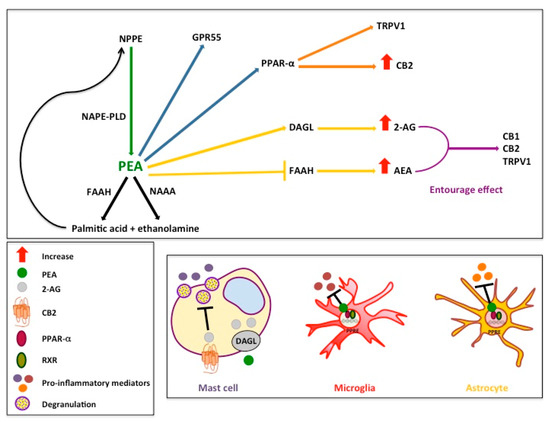
Figure 1.
Metabolic pathways and mechanisms of action of PEA. PEA is synthetized by NAPE-PLD (green arrow) and hydrolyzed to palmitic acid and ethanolamine by FAAH and NAAA (black arrows) [28]. PEA directly activates GPR55 [149] and PPAR-α receptors (blue arrows) [148]. PEA activates TRPV1 receptors [145,146] and increases the expression of CB2 receptors (orange arrows) via direct activation of PPAR-α receptors (blue arrow) [154]. PEA, through the stimulation of the activity of DAGL [143] or the inhibition of the expression of FAAH (yellow arrows) [142], increases the endogenous levels of 2-AG and AEA, respectively, which directly activate CB1, CB2, and TRPV1 receptors (“entourage effect”) (violet arrow) [57,142,143,145,146]. PEA, possibly through an allosteric modulation of TRPV1 receptors, potentiates the actions of AEA and 2-AG at TRPV1 receptors (“entourage effect”) [57,145,146]. PEA inhibits the activation of mast cells through an indirect CB2-mediated mechanism (i.e., increased 2-AG synthesis) [140,143]. PEA reduces the activation of microglia and astrocytes through a PPAR-α-mediated mechanism [155,156]. Abbreviations: 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; AEA, anandamide; CB1, type-1 cannabinoid receptors; CB2, type-2 cannabinoid receptors; DAGL, diacylglycerol lipase; FAAH, fatty acid amide hydrolase; GPR55, G-protein coupled receptor 55; NAAA, N-acylethanolamide hydrolyzing acid amidase; NAPE-PLD, N-acyl-phosphatidyl-ethanolamine-selective phospholipase D; PEA, palmitoylethanolamide; PPAR-α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α; TRPV1, transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1.
3. Pre-Clinical and Clinical Effects of PEA in Micronized and Co-Micronized Formulations on Neuroinflammation Associated with Neurodegenerative and Neurological Disorders
3.1. Parkinson’s Disease
Under physiological conditions, non-neuronal cells like microglia and astrocytes support the well-being and well-function of the brain through diverse functions, including neurotrophic factor secretion. On the contrary, in the course of Parkinson’s disease (PD) a shift from neuroprotective to neuroinflammatory phenotype occurs and the non-neuronal cells sustain disease onset and progression [157,158,159]. The efficacy of PEA in controlling neuroinflammation-associated neurodegeneration has been demonstrated in an animal model of PD induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1 2 3 6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Chronic treatment with PEA (10 mg/kg for 7 days) protected against MPTP-induced loss of tyrosine hydroxylase neurons, reduced MPTP-induced microglial activation and the number of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-positive astrocytes [84]. Moreover, PEA exerted a positive effect on the cognitive and motor deficits, which was shown to be mediated at least in part by PPAR-α receptor [84]. A formulation containing PEA co-ultra-micronized with luteolin (co-ultraPEA-Lut) has been investigated in the same animal model of PD. The administration of co-ultraPEA-Lut (for 7 days at 1 mg/kg dose) re-established the normal expression of the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase, and most importantly, reduced the increased expression of GFAP (a marker of astrocyte activation), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and pro-inflammatory cytokines in the brain [85]. In a further study performed on MPTP-induced PD in aged mice, chronic pre-treatment with PEA-m (10 mg/kg for 60 days) was found to counteract the behavioral deficits, the reduced expression of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine transporter, as well as the up-regulation of α-synuclein and β3-tubulin in the substantia nigra [80]. Importantly, PEA-m also reduced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and showed a pro-neurogenic effect in the hippocampus [80]. A different animal model of PD was also used to investigate the protective effect of PEA against PD-associated neuroinflammation. In particular, the disease was induced by 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) and PEA was administered at 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg for 28 days [86]. Results showed that PEA was able to (i) improve 6-OHDA-induced behavioral impairments, (ii) increase tyrosine hydroxylase expression, (iii) exert an anti-apoptotic effect and, most importantly, (iv) reduce oxidative stress and neuroinflammation (i.e., reduced iNOS and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression) [86]. The observed effects were PPAR-α receptor-mediated [86]. These pre-clinical studies suggest that PEA-m and PEA-um (alone or in association with Luteolin) are effective in improving PD motor function through mechanisms aimed at controlling neuroinflammation and protecting neurons. Accordingly, the clinical utility of FSMP containing PEA-m has been evaluated in a study conducted on 30 patients affected by PD [87]. Add-on oral administration of PEA-um (3 months at 600 mg/bid followed by 600 mg/die for 12 months) to PD patients receiving levodopa therapy produced a significant and progressive reduction in the total Movement Disorder Society/Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) score (parts I, II, III, and IV) [87]. In other words, oral supplementation with PEA-um slowed down the disease progression and disability scores, and proved to be a valuable add-on option in PD patients [87].
3.2. Alzheimer’s Disease
The efficacy of PEA in controlling neuroinflammation and the associated neurodegeneration has also been demonstrated in several pre-clinical models of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). In particular, in an animal model of AD, consisting of intracerebroventricular injection of beta amyloid (Aβ) 25–35 peptide, chronic treatment with PEA (10 or 30 mg/kg once a day for 1 or 2 weeks), starting 3 h after Aβ 25–35 peptide injection, reduced (10 mg/kg) or prevented (30 mg/kg) learning and memory deficits, lipid peroxidation, iNOS induction, and caspase3 activation induced by Aβ 25–35 peptide [88]. Again, the effects were PPAR-α receptor-mediated [88]. In a similar animal model of AD, consisting of intrahippocampal injection of Aβ 1–42 peptide, PEA (10 mg/kg once day for 7 days) was likewise shown to counteract the memory-impairing effect, amyloidogenesis, tau protein hyperphosphorylation, and reactive gliosis induced by Aβ 1–42 peptide, through the involvement of PPAR-α receptors [89]. In a different animal model of AD, namely in young (6-month-old) and adult (12-month-old) triple transgenic AD (3×Tg-AD) mice, the anti-neuroinflammatory effects of PEA-um have also been demonstrated [90]. Chronic treatment with PEA-um (10 mg/kg) for 3 months was able to normalize astrocyte function [90,91]. Improvement of learning and memory, decreased depressive and anhedonia-like behaviors, as well as reduced Aβ formation and tau protein phosphorylation were also observed [90,91]. Finally, PEA-um promoted neuronal survival in the CA1 sub-region of the hippocampus [90,91]. The observed effects (e.g., reduced reactive astrogliosis and restored neuronal trophic support) were superior in younger mice as compared to older mice, suggesting that PEA-um may be a promising strategy to slow AD progression in the early stages of the disease [90,91]. More recently, in the same 3×Tg-AD model, chronic oral administration of PEA-um (100 mg/kg/day for 3 months) also rescued cognitive deficit and decreased the hippocampal level of extracellular glutamate [77]. Again, a significant effect on neuroinflammation was observed, as shown by the almost complete inhibition of interleukin (IL)-6 increase in the hippocampus, and the reduced the production of ROS [77]. Evaluation of co-ultraPEA-Lut has also been reported in the early stage of AD. In particular, the animals received co-ultraPEA-Lut (5 mg/kg/day) for 2 weeks starting on the day of intrahippocampal Aβ 1–42 peptide injection [92]. Chronic administration of co-ultraPEA-Lut prevented the Aβ-induced astrogliosis and microgliosis and the upregulation of iNOS, COX-2, IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and IL-6 gene expressions [92]. Moreover, the treatment normalized the downregulated IL-10 mRNA levels, demonstrating clear anti-neuroinflammatory properties [92]. Although clinical studies on PEA formulations in AD patients are still missing, a case report of a 67-year-old woman affected by mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and administered co-ultraPEA-Lut (700 mg + 70 mg once daily) has recently been described [93]. MCI is the stage between the expected cognitive decline of normal aging and the more serious decline of dementia, hence recognized as a risk factor for AD. At baseline, the patient presented a mild memory impairment—as demonstrated by specific neuropsychological assessments—as well as a bilateral hypo-perfusion in different brain areas at single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) [93]. After 3-months supplementation a mild (although non-significant) cognitive amelioration was recorded, whereas 3 months later the neuropsychological evaluation was almost normal with a significant improvement of Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT), Attentive Matrices (AM), and Trail Making Test (TMT) compared to basal conditions [93]. Moreover, the brain SPECT was almost within the normal range [93]. These promising results suggest that dietary supplementation with co-ultraPEA-Lut might be a valuable option in the management of MCI-associated neuroinflammation and related neurodegenerative disorders.
3.3. Multiple Sclerosis
Uncontrolled neuroinflammation is a widely recognized hallmark of Multiple sclerosis (MS) [160,161]. In an animal model of MS, i.e., the Theiler’s Murine Encephalomyelitis Virus-Induced Demyelinating Disease (TMEV-IDD), the administration of PEA (5 mg/kg daily for 10 days, started 60 days post-infection) counteracted the motor deficits associated with the disease, and exerted an anti-neuroinflammatory effect by reducing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and decreasing microglial activation [94]. In a different animal model of MS, the Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) based on active immunization with a fragment of Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein (MOG35–55), the administration of co-ultraPEA-Lut (5 mg/kg from 11 to 27 post-immunization days) also produced beneficial effects by reducing the development of clinical signs and the expression of pro-inflammatory proteins [95]. In a clinical study conducted on 29 patients with Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RR-MS), oral supplementation with PEA-um (600 mg/day for 12 months, added to subcutaneous Interferon (IFN)-β1a), beside relieving pain at IFN-β1a injection site, significantly reduced the plasma concentration of inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-17, TNF-α) [96]. The quality of life of supplemented patients was also improved compared to the placebo-treated group, as assessed with MSQoL-54—Multiple Sclerosis Quality of Life 54 questionnaire [96].
3.4. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a deadly neurodegenerative disease characterized by the ongoing degeneration of motor neurons, which leads to progressive paralysis of skeletal muscle and death in 3–5 years after diagnosis. Neuroinflammation is currently considered a highly important driving force [162,163]. In a clinical case of a patient affected by sporadic ALS, oral supplementation with PEA-um improved the respiratory and motor functions, accompanied by the appearance of muscle tone, plausibly because of the control of neuroinflammation [97]. More recently, a broad clinical study performed on 64 patients suffering from ALS has shown that dietary administration of PEA-um (600 mg twice daily for 6 months) added to standard therapy (i.e., riluzole) significantly slowed down the decline in pulmonary function as measured by forced vital capacity (FVC), and lowered the severity of ALS symptoms, compared to patients treated with riluzole alone [98]. It is also noteworthy that a short-term add-on dietary PEA-um (600 mg twice daily for 1 week) proved to reduce the level of disability and improve muscular response to fatigue in 22 patients with myasthenia gravis (MG), as assessed by Repetitive Nerve Stimulation and Quantitative MG score [99].
3.5. Autism Spectrum Disorders
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are a range of heterogeneous neurodevelopmental conditions defined by repetitive behaviors as well as deficits in socialization and communication. The affected patients frequently present altered levels of cytokines, including an increase of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IFN-γ, eotaxin, and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1) [164], confirming the role of neuroinflammation in the etiology of autism [165]. The first case report on PEA-um in ASD dealt with two children (aged 13 and 15) [102]. Both patients had severe comprehension problems and difficulty expressing themselves, and suffered from behavioral disorders [102]. The add-on administration of PEA-um (600 mg twice daily for 3 months) to the standard therapy led to a clear improvement in the expressive, relational, and cognitive-behavioral abilities, in both patients [102]. Moreover, in a translational study it was found that co-ultraPEA-Lut (1 mg/kg for 2 weeks or 3 months) ameliorated social and nonsocial behaviors in a murine model of valproic acid-induced autistic behaviors, and benefited a male child aged 10 affected by ASD (700 mg + 70 mg bid) [100]. In particular, after one-year supplementation, the child experienced reduced ASD-associated behavioral problems, especially in the area of social skills and anxiety [100]. In the BTBR mouse model of idiopathic autism, dietary supplementation with PEA-um (30 mg/kg for 10 days) was recently shown to revert the altered behavioral phenotype through the activation of PPAR-α and reduce the inflammatory state in the hippocampus [101]. In addition, improvement of the epithelial barrier integrity and microbiota composition in the gut was also detected, suggesting an involvement of microbiota-gut-brain axis [101].
4. Pre-Clinical and Clinical Effects of PEA in Micronized and Co-Micronized Formulations in Pain Syndromes Sustained by Neuroinflammation
4.1. Acute and Chronic Pain
Accumulating evidence suggests that neuroinflammation—accompanied by non-neuronal cell activation and pro-inflammatory factor release—is a major contributor to pain states [7,166,167]. Several studies report the protective effects of PEA in different murine models of neuropathic pain (NP). In particular, in mice with chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the sciatic nerve, PEA relieved thermal hyperalgesia as well as mechanical allodynia, and reduced sensitizing factors (such as nerve growth factor, NGF) [103,104,105]. Moreover, the administration of this lipid amide prevented the reduction of myelin sheet thickness and axonal diameter, and reduced edema and macrophage infiltration [103,104,105]. The anti-nociceptive functions exerted by PEA depended, at least in part, on the down-regulation of non-neuronal cells, as shown by the delayed mast cell recruitment and decreased mast cell degranulation in the sciatic nerve, as well as reduced microglia activation at the spinal level [104]. Interestingly, the control of microglia activation was also shown to mediate the effect of PEA in formalin-induced neuropathic pain [106]. Moreover, PEA improved pain-related behaviors in the spared nerve injury (SNI) model of NP [107] and oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy [108]. One of the mechanisms sustaining the anti-nociceptive function of PEA, at least in models of acute and persistent inflammatory pain (i.e., formalin test and carrageenan-induced paw edema) is thought to be a PPAR-α receptor-mediated increase of neurosteroidogenesis [109]. Micronized and ultramicronized formulations of PEA, PEA-m, and PEA-um respectively, and their effect on acute and neuropathic pain were also investigated. In this regard, interesting results came from a study in which PEA-m was administered to rats (30 mg/kg for 11 days) concurrently treated with morphine [110]. The results demonstrated that PEA-m attenuated the development of tolerance to morphine, doubling the number of days morphine was effective, and preventing morphine-induced hyperplasia of microglia and astrocytes, thus suggesting the usefulness of adding PEA-m to opioid-based therapies [110]. The efficacy of PEA-um formulation was also demonstrated in the SNI model [111]. In particular, PEA-um (10 mg/kg once a day, started 15 days after the sham or SNI surgery and lasted for 15 days) was able to relieve thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia [111]. In addition, it improved cognitive impairments and neurogenesis, and restored the level of glutamate as well as the expression of phosphorylated metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (GluR1) subunits [111]. In a mice model of tibia fracture derived pain, which resembles the clinical features of acute complex regional pain syndrome type 1 (CRPS-I), a new formulation of PEA-m together with PEA-um (300 mg/kg + 600 mg/kg for 28 days) improved the fracture regeneration and reduced the thermal nociception and mechanical hyperalgesia [112]. The effect was found to partly depend on the control of mast cell density and the decrease of NGF and cytokines expression [112]. Moreover, a recent study investigated the synergistic effect of PEA-um with paracetamol on neuroinflammation and neuropathic pain in a rat model of sciatic nerve injury [113]. Combining PEA-um to paracetamol at ineffective or, at most, marginally effective doses (5 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg, respectively) for a 14-day regimen after sciatic nerve injury induction relieved hyperalgesia, protected nerve fibers against histological damage and cell apoptosis, down-modulated endoneural mast cells, and reduced NGF expression and serum cytokine levels [113]. Recently, PEA-m has been shown to relieve one of the most common form of acute pain, i.e., post-operative pain [114]. In particular, oral administration of PEA-m (10 mg/kg) at different time points, either before and after a surgical paw incision in rats proved to significantly reduce hyperalgesia [114]. Control of surgery-induced mast cell hyperplasia at the paw level and NGF increase at the spinal level were also shown, together with the return to nearly normal levels of microglia and astrocyte markers respectively [114]. On the clinical side, several observational studies have been conducted on patients with chronic pain of different etiologies. In particular, a pilot study has been performed on 610 patients with chronic pain associated to different pathological conditions, whose pain was not adequately controlled by standard analgesic therapies [115]. Dietary administration of PEA-um (600 mg twice daily for 3 weeks followed by single daily administration for 4 weeks, in addition to standard analgesic drugs or as a single intervention) showed a significant decrease of pain severity assessed by the Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) [115]. All patients administered PEA-um completed the study without reporting adverse effects [115]. The effect of PEA-um-based FSMP has also been evaluated in 30 patients with diabetic or traumatic chronic neuropathic pain [116]. Patients given PEA-um (1200 mg/die for 40 days) showed a significant improvement of pain and paraesthesia/dysesthesia scores, assessed by Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory (NPSI), respectively. In addition, PEA-um-administered patients experienced a better quality of life, as evaluated by means of the Five-Dimensional Health Questionnaire (EQ-5D) [116]. A further study has recently been performed on 155 patients with lower back pain related to nonsurgical lumbar radiculopathy. They were given acetaminophen/codeine (500 mg + 30 mg/die) for 7 days, and then changed to PEA-um (1200 mg/die) for 30 days. The treatment regimen relieved pain in all patients with mild pain (VAS from 3–4 to 1) and 75% of those with moderate pain (VAS from 5–6 to 2) [117]. Patients who did not experience pain or disability improvement had a second cycle with PEA-um (600 mg/die for 30 days) followed by acetaminophen/codeine for 30 days, which was found to relieve symptoms in all patients with moderate pain [117]. Given together with tapentadol a FSMP based on PEA-um (600 mg twice daily for 6 months) provided a superior effect on pain relief compared to tapentadol only in 55 patients with low back pain [118]. Moreover, patients in the combined treatment group recorded a lower analgesic dose requirement and lesser disability compared to patients in the tapentadol only group [118]. A further investigation has been carried out on 35 patients affected by failed back surgery syndrome, who were orally administered a FSMP based on PEA-um (1200 mg/die for the first month followed by 600 mg/die for the second month) as an add-on dietary intervention to tapentadol and pregabalin [119]. A significant adjunctive effect was observed in pain relief (pain intensity was measured by VAS) with no serious side effects being recorded in this as well as the previously described studies [117,118,119]. Recently, the benefit of combining a PEA-um based FSMP with rehabilitative therapy has also been studied in patients with chronic low back pain [120]. The study enrolled 120 patients who suffered from lumbosciatica (95) and lumbocruralgia (25) pain caused by multiple herniated discs in the lumbar spine [120]. PEA-um (600 mg twice a day for 40 days) was added to a standard analgesic regimen and combined with a 20-day session of daily functional rehabilitation and decontracting massage [120]. During the study period, patients experienced a significant reduction of pain severity (scored using the Numeric Rating Scale) accompanied by improvements in the physical and mental components of quality of life (evaluated with the SF-36 questionnaire), as well as in disability for low back pain (assessed by Oswestry Disability Questionnaire) [120]. Oral supplementation with PEA-um (600 mg twice daily) has also been evaluated in an open controlled study on 42 patients waiting for carpal tunnel syndrome surgery and suffering from sleep disorders and painful symptoms [121]. During the pre-surgery period a significant improvement of the sleep quality with an increase of continuous time sleep (measured by Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index), and mitigation of the painful stimuli (assessed by NRS), were recorded in PEA-um group compared to untreated patients [121]. It is finally worth noting that a post-hoc analysis of a controlled study on over 600 patients with lower back pain (i.e., a mixed pain condition) has recently demonstrated that the higher the probability of suffering from neuropathic pain, the better the treatment outcome following PEA-m oral administration [168]. The analysis yielded a Number Needed to Treat (NNT) value of 1.7 for PEA-m 600 mg daily, which is considerably better than that of first-line drugs, with tricyclic antidepressants yielding a score of 3.5, serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors of 6.4, gabapentin of 7.2, and pregabalin of 7.7 [168].
4.2. Chronic Pelvic Pain
When not appropriately regulated, neuroinflammation importantly contributes to the pathogenesis of endometriosis, a chronic estrogen-dependent gynecological disorder that often causes dysmenorrhea and pelvic pain [169].
A study in a rat model of endometriosis has recently shown that PEA-um (10 mg/kg for 25 days) reduced the number and duration of pain crises and cyst diameter [122]. Moreover, the number of mast cells and vessels as well as the expression of NGF in cysts and dorsal root ganglia were also significantly reduced [122]. These results suggested a potential clinical utility of PEA-um for the control of chronic pelvic pain associated with endometriosis [122]. Accordingly, in a preliminary observational study 4 patients with endometriosis-related pain were administered a FSMP containing PEA-m and polydatin (400 mg + 40 mg twice daily) for 90 days [123]. All patients showed pain relief (measured by VAS) as early as 1 month after starting the supplement and a reduction in the use of analgesic drugs that were previously employed for pain control [123]. Likewise, 24 women with symptoms of severe pelvic pain and suspected endometriosis experienced significant pain relief (assessed by VAS) after 90-day supplementation with a FSMP containing PEA-m and polydatin (400 mg + 40 mg twice daily) [124]. Quality of life was also improved and the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) decreased during the study [124]. Similar results were observed after the 3-month administration of the same FSMP (same dose) in 61 subjects with chronic pelvic pain related to endometriosis after laparoscopic conservative surgery [125]. A significant reduction in dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and pelvic pain (measured by VAS) was recorded, the effect being nearly equal to that exerted by celecoxib (a NSAIDS drug) [125]. Moreover, the studied FSMP proved to be safe, thus suggesting it could be a valuable alternative in those patients who cannot take analgesic drugs [125]. The same combination of PEA-m and polydatin has also been used in another clinical study performed on 47 women with chronic pelvic pain due to endometriosis, who were divided in two groups based on the endometriosis site: recto-vaginal septum or ovary [126]. In both groups the dietary supplementation showed a significant reduction in chronic pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, dyspareunia, and dyschezia (evaluated by VAS) already after 30 days [126]. A further study evaluated the effect of a 10-day regimen with FSMP containing PEA-m and polydatin (400 mg + 40 mg once a day, taken from the 24th day of cycle) compared to placebo. Two groups of 110 young patients each (age 16–24 years) with primary dysmenorrhea were included [127]. Pain relief was shown to be superior in the FSMP group compared to the placebo group [127]. Finally, an interesting finding comes from a recently published study performed on 30 women with the diagnosis of endometriosis and pregnancy desire, administered PEA-um twice daily for 10 days followed by PEA-m/polydatin twice daily for 80 days [128]. The severity of chronic pelvic pain, dyspareunia, dysmenorrhea, dyschezia, and dysuria was evaluated using VAS, while the quality of life and women’s psychological well-being were evaluated with 36-Item Short Form Health Survey Questionnaire and Symptom Check list-90 Questionnaire, respectively [128]. At the end of the study, all patients showed a significant improvement in painful symptoms, quality of life and psychological well-being, and did not record any grave side effect, proving that the study FSMP is particularly suitable for women with pregnancy desire and without other infertility factors [128].
4.3. Migraine Pain
Mast cells involved in neuroinflammation in the brain are considered key players in migraine pathophysiology [14].
The effect of a PEA-um based FSMP in the dietary management of migraine has been initially evaluated in a clinical case of nummular migraine [129]. The patient, a 57-year-old woman suffering from superficial cranial pain since the last 10 years was administered PEA-um (600 mg/day) after a one-month treatment with topiramate (50 mg × 2/day tablet), had lead only a minor improvement on pain scales (6 on VAS, 6 on NRS, and severe pain on VRS) [129]. Two months later, a clear decrease of pain was recorded (2 on VAS, 3 on NRS, and moderate-to-mild pain on VRS) and a progressing scaling of topiramate up to 25% of the original dose was decided. At the last follow-up (4 months after PEA-um was initiated) pain was importantly relieved (1 on VAS, 1 on NRS, and no or mild pain on VRS), with no adverse effects being recorded [129]. A single blind study was then conducted to evaluate both the safety and the efficacy of PEA-um (1200 mg/day) in 40 patients suffering of migraine with aura treated with NSAIDs (ibuprofen, diclofenac sodium, or nimesuilde) [130].
At the end of the study (3 months later) a significant pain relief (evaluated either as VAS score and number of attacks/month) was found in the group of patients taking PEA-um and NSAIDs, which was superior to that recorded in patients managed with NSAIDs only [130]. Moreover, unlike the control group, patients treated with PEA-um reduced the NSAIDs consumption throughout the study [130]. Finally, an open-label study has recently been conducted on 70 pediatric patients (with mean age of 10.3 ± 2.7, 24.5% male and 75.5% female) with a diagnosis of migraine without aura [131]. The patients received PEA-um (at the dose of 600 mg/day) for three months, and the headache attack frequency (AF) and attack intensity (AI) were measured at baseline and at the end of the study [131]. After three months, 63.9% of patients recorded a reduction of the headache AF by >50%; the number of monthly attacks, headache AI, percentage of patients with severe attacks and monthly assumption of drugs for the attack were significantly reduced [131]. In this study, only 1 patient recorded mild side effect consisting of nausea and vomiting [131].
4.4. Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia (FM) is a particularly disabling musculoskeletal disease characterized by widespread chronic pain, muscle stiffness and fatigue, often refractory to common analgesic drugs. There is considerable evidence of the involvement of neuroinflammation in FM pathogenesis [170,171,172]. In a observational study conducted on 80 patients with FM, 30-day administration of a FSMP containing PEA-um (600 mg/bid) followed by two-month supplementation with PEA-m (300 mg/bid) in addition to the standard therapy (duloxetine and pregabalin) showed a significant and greater improvement in pain intensity (assessed by VAS) and positive tender points, compared to the control group treated with duloxetine and pregabalin only [132]. None of the patients enrolled in this study recorded adverse side effects [132]. Similar results have been reported in another retrospective observational study recently performed on 407 patients with the diagnosis of FM, who received PEA-um (600 mg/day) regardless of the concurrent pharmacological therapy (add-on intervention) [133]. The results showed that 359 patients recorded an improvement in the pain score (measured by VAS) and quality of life (assessed by Fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire, FIQ), with only 36 patients reporting adverse events principally of gastrointestinal type (diarrhea, dyspepsia, bloating, constipation, and vomiting) [133].
5. Conclusions
In the light of increasing evidence for a key role of uncontrolled neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of common and disabling disorders, targeting non-neuronal cells is emerging as a promising therapeutic strategy. PEA is an endogenous fatty acid amide with protective functions mainly exerted through the down-regulation of non-neuronal cells (such as mast cells, microglia and astrocytes) at both central and peripheral level. The shift toward a homeodynamic phenotype exerted by the prophylactic administration of PEA confirms its protective role, i.e., the ability to prepare cells to successfully cope with incoming perturbations [173,174,175]. The data reviewed in the present paper highlight the effectiveness and safety of PEA in controlling neuroinflammation, once it has been administered in formulations with adequate bioavailability, i.e., micronized or ultra-micronized forms [57,76]. Moreover, the endogenous nature, the occurrence in common food sources [72,73,74] (Table 1) and the physiological functions described so far sustain the value of supplementing PEA to meet the increased requirements in the course of clinical conditions sustained by neuroinflammation. In the words of the Nobel Prize winner Rita Levi-Montalcini, “The observed effects of Palmitoylethanolamide appear to reflect the consequences of supplying the tissue with a sufficient quantity of its physiological regulator of cellular homeostasis” [141]. Particular FSMPs containing PEA-m and PEA-um (alone or in combination with compounds endowed with important antioxidant properties, such as Luteolin and polydatin) have been developed in recent years [29]. As discussed in the present review paper, they have been repeatedly evaluated in clinical trials and collectively resulted safe and effective in patients with neurodegenerative and neurological disorders, and pain syndromes sustained by neuroinflammation, especially if utilized in the context of a multimodal pharmacotherapy. This is particularly relevant for frail patients (i.e., with declined physiological reserve and vulnerability to adverse outcomes) given that PEA-m and PEA-um based FSMPs resulted to synergize conventional therapies and decrease the effective dose of drugs that are usually associated with frequent or even serious adverse effects [87,118,123,124,130]. All that said, PEA-based FSMPs may be deservedly considered part of a new and promising nutritional approach to disorders sustained be neuroinflammation. The recent FDA approval for the adjunct use of PEA-um in patients affected by one the most severe forms of neuroinflammation, i.e., COVID-19, provides a further proof-of-concept in this respect [https://www.biospace.com/article/releases/fsd-pharma-begins-phase-2-clinical-trial-to-evaluate-fsd201-for-the-treatment-of-hospitalized-covid-19-patients/].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.P.; formal analysis, S.P. and A.S.M.; resources, S.P. and A.S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, S.P. and A.S.M.; writing—review and editing, S.P. and A.S.M.; visualization, S.P. and A.S.M.; supervision, S.P.; project administration, S.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
S.P. and A.S.M. are employees of Epitech Group SpA. Stefania Petrosino is a co-inventor on patent EP2965765A1 that is wholly unrelated to the present study.
References
- Boche, D.; Perry, V.H.; Nicoll, J.A.R. Review: Activation patterns of microglia and their identification in the human brain. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2013, 39, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordon, Y. Neuroinflammation: Inflammatory brain drain. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Interactions between the immune and nervous systems in pain. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1267–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sominsky, L.; Walker, A.K.; Hodgson, D.M. Editorial: Neuroinflammation and behavior. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, S.; Lemmens, E.; Geurts, N.; Kramer, P.; Maurer, M.; Hendriks, J.; Hendrix, S. The role of mast cells in neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Y. Mast cells and neuroinflammation. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2014, 20, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.-R.; Xu, Z.-Z.; Gao, Y.-J. Emerging targets in neuroinflammation-driven chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, D.; Aon, M.A.; Cortassa, S. Why Homeodynamics, Not Homeostasis? Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 918917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, F.; Perretti, M.; McMahon, S.B. Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.; Bernardino, L. Dual role of microglia in health and disease: Pushing the balance toward repair. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Giusti, P. Neuroinflammation, microglia and mast cells in the pathophysiology of neurocognitive disorders: A review. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 1654–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.M.; Pires, J.; Esteves, M.; Graça, B.; Bernardino, L. Histamine: A new immunomodulatory player in the neuron-glia crosstalk. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, C.; Oliveira, A.F.; Cunha, C.; Vaz, A.R.; Falcão, A.S.; Fernandes, A.; Brites, D. Microglia change from a reactive to an age-like phenotype with the time in culture. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, E.; van Bergeijk, D.; Oosting, R.S.; Redegeld, F.A. Mast cells in neuroinflammation and brain disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 79, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C. Microglia and neurodegeneration: The role of systemic inflammation. Glia 2013, 61, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Giusti, P.; Facci, L. Microglia and mast cells: Two tracks on the road to neuroinflammation. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 3103–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Zusso, M.; Giusti, P. Neuroinflammation, Mast Cells, and Glia: Dangerous Liaisons. Neuroscientist 2017, 23, 478–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Thangavel, R.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Zaheer, S.; Ahmed, M.E.; Raikwar, S.P.; Zahoor, H.; Saeed, D.; Natteru, P.A.; Iyer, S.; et al. Brain and Peripheral Atypical Inflammatory Mediators Potentiate Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabrera-Pastor, A.; Llansola, M.; Montoliu, C.; Malaguarnera, M.; Balzano, T.; Taoro-Gonzalez, L.; García-García, R.; Mangas-Losada, A.; Izquierdo-Altarejos, P.; Arenas, Y.M.; et al. Peripheral inflammation induces neuroinflammation that alters neurotransmission and cognitive and motor function in hepatic encephalopathy: Underlying mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Acta Physiol. (Oxf.) 2019, 226, e13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzini, A.; Padovani, A. Lifting the mask on neurological manifestations of COVID-19. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadian, S.; Glick, L.R.; Vogels, C.B.F.; Thomas, J.; Chiarella, J.; Casanovas-Massana, A.; Zhou, J.; Odio, C.; Vijayakumar, P.; Geng, B.; et al. Acute encephalopathy with elevated CSF inflammatory markers as the initial presentation of COVID-19. BMC Neurol. 2020, 20, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, R.-R.; Chamessian, A.; Zhang, Y.-Q. Pain Regulation by Non-neuronal Cells and Inflammation. Science 2016, 354, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refolo, V.; Stefanova, N. Neuroinflammation and Glial Phenotypic Changes in Alpha-Synucleinopathies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Zusso, M.; Giusti, P. An Inflammation-Centric View of Neurological Disease: Beyond the Neuron. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L. Mast cell-glia axis in neuroinflammation and therapeutic potential of the anandamide congener palmitoylethanolamide. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 3312–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Giusti, P. Glia and mast cells as targets for palmitoylethanolamide, an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective lipid mediator. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachur, N.R.; Masek, K.; Melmon, K.L.; Udenfriend, S. Fatty acid amides of ethanolamine in mammalian tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1965, 240, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar]
- Iannotti, F.A.; Di Marzo, V.; Petrosino, S. Endocannabinoids and endocannabinoid-related mediators: Targets, metabolism and role in neurological disorders. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 62, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrosino, S.; Di Marzo, V. The pharmacology of palmitoylethanolamide and first data on the therapeutic efficacy of some of its new formulations. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 1349–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Giusti, P. Mast cells, glia and neuroinflammation: Partners in crime? Immunology 2014, 141, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piomelli, D.; Sasso, O. Peripheral gating of pain signals by endogenous lipid mediators. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Barbierato, M.; Zusso, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Giusti, P. N-Palmitoylethanolamine and Neuroinflammation: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy of Resolution. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, P.C.; Krebsbach, R.J.; Perry, S.R.; Dettmer, T.M.; Maasson, J.L.; Schmid, H.H. Occurrence and postmortem generation of anandamide and other long-chain N-acylethanolamines in mammalian brain. FEBS Lett. 1995, 375, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, A.; Parmentier-Batteur, S.; Walter, L.; Greenberg, D.A.; Stella, N. Palmitoylethanolamide increases after focal cerebral ischemia and potentiates microglial cell motility. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7767–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, N.; Piomelli, D. Receptor-dependent formation of endogenous cannabinoids in cortical neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 425, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, L.; Franklin, A.; Witting, A.; Moller, T.; Stella, N. Astrocytes in culture produce anandamide and other acylethanolamides. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20869–20876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muccioli, G.G.; Stella, N. Microglia produce and hydrolyze palmitoylethanolamide. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.; Pryce, G.; Croxford, J.L.; Brown, P.; Pertwee, R.G.; Makriyannis, A.; Khanolkar, A.; Layward, L.; Fezza, F.; Bisogno, T.; et al. Endocannabinoids control spasticity in a multiple sclerosis model. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, S.; Palazzo, E.; de Novellis, V.; Bisogno, T.; Rossi, F.; Maione, S.; Di Marzo, V. Changes in spinal and supraspinal endocannabinoid levels in neuropathic rats. Neuropharmacology 2007, 52, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, T.; Martire, A.; Petrosino, S.; Popoli, P.; Di Marzo, V. Symptom-related changes of endocannabinoid and palmitoylethanolamide levels in brain areas of R6/2 mice, a transgenic model of Huntington’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, T.; Delton-Vandenbroucke, I.; Milone, A.; Lagarde, M.; Di Marzo, V. Biosynthesis and inactivation of N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide) and N-docosahexaenoylethanolamine in bovine retina. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1999, 370, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Matias, I.; Dinh, T.; Lu, T.; Venezia, S.; Nieves, A.; Woodward, D.F.; Di Marzo, V. Finding of endocannabinoids in human eye tissues: Implications for glaucoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 330, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, I.; Wang, J.W.; Moriello, A.S.; Nieves, A.; Woodward, D.F.; Di Marzo, V. Changes in endocannabinoid and palmitoylethanolamide levels in eye tissues of patients with diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2006, 75, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epps, D.E.; Schmid, P.C.; Natarajan, V.; Schmid, H.H. N-Acylethanolamine accumulation in infarcted myocardium. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1979, 90, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Sugiura, T.; Kodaka, T.; Kudo, N.; Waku, K.; Tokumura, A. Accumulation of various N-acylethanolamines including N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide) in cadmium chloride-administered rat testis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1998, 354, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraceni, P.; Viola, A.; Piscitelli, F.; Giannone, F.; Berzigotti, A.; Cescon, M.; Domenicali, M.; Petrosino, S.; Giampalma, E.; Riili, A.; et al. Circulating and hepatic endocannabinoids and endocannabinoid-related molecules in patients with cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuel, H.; Burkman, L.J.; Lippes, J.; Crickard, K.; Forester, E.; Piomelli, D.; Giuffrida, A. N-Acylethanolamines in human reproductive fluids. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2002, 121, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, R.; Izzo, A.A.; Fezza, F.; Pinto, A.; Capasso, F.; Mascolo, N.; Di Marzo, V. Inhibitory effect of palmitoylethanolamide on gastrointestinal motility in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmani, N.A.; Izzo, A.A.; Degenhardt, B.; Valenti, M.; Scaglione, G.; Capasso, R.; Sorrentini, I.; Di Marzo, V. Involvement of the cannabimimetic compound, N-palmitoyl-ethanolamine, in inflammatory and neuropathic conditions: Review of the available pre-clinical data, and first human studies. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdyshev, E.V.; Schmid, P.C.; Dong, Z.; Schmid, H.H. Stress-induced generation of N-acylethanolamines in mouse epidermal JB6 P+ cells. Biochem. J. 2000, 346, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, S.; Cristino, L.; Karsak, M.; Gaffal, E.; Ueda, N.; Tüting, T.; Bisogno, T.; De Filippis, D.; D’Amico, A.; Saturnino, C.; et al. Protective role of palmitoylethanolamide in contact allergic dermatitis. Allergy 2010, 65, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri, N.; Ghafouri, B.; Larsson, B.; Turkina, M.V.; Karlsson, L.; Fowler, C.J.; Gerdle, B. High levels of N-palmitoylethanolamide and N-stearoylethanolamide in microdialysate samples from myalgic trapezius muscle in women. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri, N.; Ghafouri, B.; Larsson, B.; Stensson, N.; Fowler, C.J.; Gerdle, B. Palmitoylethanolamide and stearoylethanolamide levels in the interstitium of the trapezius muscle of women with chronic widespread pain and chronic neck-shoulder pain correlate with pain intensity and sensitivity. Pain 2013, 154, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuffrida, A.; Piomelli, D. Isotope dilution GC/MS determination of anandamide and other fatty acylethanolamides in rat blood plasma. FEBS Lett. 1998, 422, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, D.; Harlfinger, S.; Nolden, B.M.; Gerth, C.W.; Jaehde, U.; Schömig, E.; Klosterkötter, J.; Giuffrida, A.; Astarita, G.; Piomelli, D.; et al. Determination of anandamide and other fatty acyl ethanolamides in human serum by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 361, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvers, M.G.J.; Verhoeckx, K.C.M.; Witkamp, R.F. Development and validation of a quantitative method for the determination of 12 endocannabinoids and related compounds in human plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, S.; Schiano Moriello, A.; Cerrato, S.; Fusco, M.; Puigdemont, A.; De Petrocellis, L.; Di Marzo, V. The anti-inflammatory mediator palmitoylethanolamide enhances the levels of 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol and potentiates its actions at TRPV1 cation channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, P.M.W.; Marczylo, T.H.; Konje, J.C. Simultaneous measurement of three N-acylethanolamides in human bio-matrices using ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 2089–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.I.; Udovin, L.D.; Toro-Urrego, N.; Kusnier, C.F.; Luaces, J.P.; Capani, F. Palmitoylethanolamide Ameliorates Hippocampal Damage and Behavioral Dysfunction After Perinatal Asphyxia in the Immature Rat Brain. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagberg, H.; Mallard, C.; Ferriero, D.M.; Vannucci, S.J.; Levison, S.W.; Vexler, Z.S.; Gressens, P. The role of inflammation in perinatal brain injury. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2015, 11, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coburn, A.F.; Graham, C.E.; Haninger, J. The effect of egg yolk in diets on anaphylactic arthritis (passive Arthus phenomenon) in the guinea pig. J. Exp. Med. 1954, 100, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehl, F.A.; Jacob, T.A.; Ganley, O.H.; Ormond, R.E.; Meisinger, M.A.P. The identification of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-palmitamide as a naturally occurring anti-inflammatory agent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1957, 79, 5577–5578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilaru, A.; Blancaflor, E.B.; Venables, B.J.; Tripathy, S.; Mysore, K.S.; Chapman, K.D. The N-acylethanolamine-mediated regulatory pathway in plants. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 1933–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, B.J.; Waggoner, C.A.; Chapman, K.D. N-acylethanolamines in seeds of selected legumes. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia-Figueira, S.; Nording, M.L. Development and validation of a sensitive UPLC-ESI-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of 15 endocannabinoids and related compounds in milk and other biofluids. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 1186–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Bruschetta, G.; Crupi, R.; Pascali, J.; Alfonsi, D.; Marcolongo, G.; Cuzzocrea, S. 2-pentadecyl-2-oxazoline: Identification in coffee, synthesis and activity in a rat model of carrageenan-induced hindpaw inflammation. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 108, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Di Marzo, V. Endocannabinoids in nervous system health and disease: The big picture in a nutshell. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2012, 367, 3193–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasti, L.; Richardson, D.; Jhaveri, M.; Eldeeb, K.; Barrett, D.; Elphick, M.R.; Alexander, S.P.H.; Kendall, D.; Michael, G.J.; Chapman, V. Minocycline treatment inhibits microglial activation and alters spinal levels of endocannabinoids in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, R.J.; Kerr, D.M.; Flannery, L.E.; Killilea, M.; Hughes, E.M.; Corcoran, L.; Finn, D.P.; Roche, M. Pharmacological inhibition of FAAH modulates TLR-induced neuroinflammation, but not sickness behaviour: An effect partially mediated by central TRPV1. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 62, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ji, C.; Li, Y.; Hu, F.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Ren, J.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, Y. Natural Potent NAAA Inhibitor Atractylodin Counteracts LPS-Induced Microglial Activation. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skaper, S.D.; Facci, L.; Fusco, M.; Della Valle, M.F.; Zusso, M.; Costa, B.; Giusti, P. Palmitoylethanolamide, a naturally occurring disease-modifying agent in neuropathic pain. Inflammopharmacology 2014, 22, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordaro, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Crupi, R. An Update of Palmitoylethanolamide and Luteolin Effects in Preclinical and Clinical Studies of Neuroinflammatory Events. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, L.; Ferracane, R.; Vitaglione, P. Food database of N-acyl-phosphatidylethanolamines, N-acylethanolamines and endocannabinoids and daily intake from a Western, a Mediterranean and a vegetarian diet. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepe, N.; De Petrocellis, L.; Montanaro, F.; Cimino, G.; Di Marzo, V. Bioactive long chain N-acylethanolamines in five species of edible bivalve molluscs. Possible implications for mollusc physiology and sea food industry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1389, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impellizzeri, D.; Bruschetta, G.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Siracusa, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Micronized/ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide displays superior oral efficacy compared to nonmicronized palmitoylethanolamide in a rat model of inflammatory pain. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, S.; Cordaro, M.; Verde, R.; Schiano Moriello, A.; Marcolongo, G.; Schievano, C.; Siracusa, R.; Piscitelli, F.; Peritore, A.F.; Crupi, R.; et al. Oral Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide: Plasma and Tissue Levels and Spinal Anti-hyperalgesic Effect. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggiato, S.; Tomasini, M.C.; Cassano, T.; Ferraro, L. Chronic Oral Palmitoylethanolamide Administration Rescues Cognitive Deficit and Reduces Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Glutamate Levels in A Transgenic Murine Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestmann, E.R. Safety of micronized palmitoylethanolamide (microPEA): Lack of toxicity and genotoxic potential. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 5, 292–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.M.; Main, B.S.; Crack, P.J. Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress: Co-conspirators in the pathology of Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 62, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Casili, G.; Evangelista, M.; Cuzzocrea, S. N-palmitoylethanolamide Prevents Parkinsonian Phenotypes in Aged Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8455–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafeiadou, K.; Vauzour, D.; Spencer, J.P.E. Neuroinflammation and its modulation by flavonoids. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2007, 7, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Gortzi, O.; Sobarzo-Sanchez, E.; Daglia, M.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Nabavi, S.M. Luteolin as an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agent: A brief review. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 119, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.-H.; Peng, C.; Zhang, H. Polydatin: A review of pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 1347–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, E.; Impellizzeri, D.; Mazzon, E.; Paterniti, I.; Cuzzocrea, S. Neuroprotective activities of palmitoylethanolamide in an animal model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, R.; Paterniti, I.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Navarra, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E. The Association of Palmitoylethanolamide with Luteolin Decreases Neuroinflammation and Stimulates Autophagy in Parkinson’s Disease Model. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2015, 14, 1350–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avagliano, C.; Russo, R.; De Caro, C.; Cristiano, C.; La Rana, G.; Piegari, G.; Paciello, O.; Citraro, R.; Russo, E.; De Sarro, G.; et al. Palmitoylethanolamide protects mice against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity and endoplasmic reticulum stress: In vivo and in vitro evidence. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 113, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brotini, S.; Schievano, C.; Guidi, L. Ultra-micronized Palmitoylethanolamide: An Efficacious Adjuvant Therapy for Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2017, 16, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Agostino, G.; Russo, R.; Avagliano, C.; Cristiano, C.; Meli, R.; Calignano, A. Palmitoylethanolamide protects against the amyloid-β25-35-induced learning and memory impairment in mice, an experimental model of Alzheimer disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, C.; Stecca, C.; Valenza, M.; Ratano, P.; Bronzuoli, M.R.; Bartoli, S.; Steardo, L.; Pompili, E.; Fumagalli, L.; Campolongo, P.; et al. Palmitoylethanolamide controls reactive gliosis and exerts neuroprotective functions in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuderi, C.; Bronzuoli, M.R.; Facchinetti, R.; Pace, L.; Ferraro, L.; Broad, K.D.; Serviddio, G.; Bellanti, F.; Palombelli, G.; Carpinelli, G.; et al. Ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide rescues learning and memory impairments in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease by exerting anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronzuoli, M.R.; Facchinetti, R.; Steardo, L.; Romano, A.; Stecca, C.; Passarella, S.; Steardo, L.; Cassano, T.; Scuderi, C. Palmitoylethanolamide Dampens Reactive Astrogliosis and Improves Neuronal Trophic Support in a Triple Transgenic Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 4720532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinetti, R.; Valenza, M.; Bronzuoli, M.R.; Menegoni, G.; Ratano, P.; Steardo, L.; Campolongo, P.; Scuderi, C. Looking for a Treatment for the Early Stage of Alzheimer’s Disease: Preclinical Evidence with Co-Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Luteolin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrò, R.S.; Naro, A.; De Luca, R.; Leonardi, S.; Russo, M.; Marra, A.; Bramanti, P. PEALut efficacy in mild cognitive impairment: Evidence from a SPECT case study! Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 28, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loría, F.; Petrosino, S.; Mestre, L.; Spagnolo, A.; Correa, F.; Hernangómez, M.; Guaza, C.; Di Marzo, V.; Docagne, F. Study of the regulation of the endocannabinoid system in a virus model of multiple sclerosis reveals a therapeutic effect of palmitoylethanolamide. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contarini, G.; Franceschini, D.; Facci, L.; Barbierato, M.; Giusti, P.; Zusso, M. A Co-Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide/Luteolin Composite Mitigates Clinical Score and Disease-Relevant Molecular Markers in a Mouse Model of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orefice, N.S.; Alhouayek, M.; Carotenuto, A.; Montella, S.; Barbato, F.; Comelli, A.; Calignano, A.; Muccioli, G.G.; Orefice, G. Oral Palmitoylethanolamide Treatment Is Associated with Reduced Cutaneous Adverse Effects of Interferon-β1a and Circulating Proinflammatory Cytokines in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, S. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis treatment with ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide: A case report. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2012, 11, 933–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, E.; Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Lopergolo, D.; Roseti, C.; Bertollini, C.; Ruffolo, G.; Cifelli, P.; Onesti, E.; Limatola, C.; Miledi, R.; et al. Acetylcholine receptors from human muscle as pharmacological targets for ALS therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3060–3065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onesti, E.; Frasca, V.; Ceccanti, M.; Tartaglia, G.; Gori, M.C.; Cambieri, C.; Libonati, L.; Palma, E.; Inghilleri, M. Short-Term Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide Therapy in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis: A Pilot Study to Possible Future Implications of Treatment. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 18, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, B.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Bruschetta, G.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Beneficial Effects of Co-Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide/Luteolin in a Mouse Model of Autism and in a Case Report of Autism. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, C.; Pirozzi, C.; Coretti, L.; Cavaliere, G.; Lama, A.; Russo, R.; Lembo, F.; Mollica, M.P.; Meli, R.; Calignano, A.; et al. Palmitoylethanolamide counteracts autistic-like behaviours in BTBR T+tf/J mice: Contribution of central and peripheral mechanisms. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 74, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonucci, N.; Cirillo, A.; Siniscalco, D. Beneficial Effects of Palmitoylethanolamide on Expressive Language, Cognition, and Behaviors in Autism: A Report of Two Cases. Case Rep. Psychiatry 2015, 2015, 325061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, B.; Comelli, F.; Bettoni, I.; Colleoni, M.; Giagnoni, G. The endogenous fatty acid amide, palmitoylethanolamide, has anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects in a murine model of neuropathic pain: Involvement of CB(1), TRPV1 and PPARgamma receptors and neurotrophic factors. Pain 2008, 139, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettoni, I.; Comelli, F.; Colombo, A.; Bonfanti, P.; Costa, B. Non-neuronal cell modulation relieves neuropathic pain: Efficacy of the endogenous lipid palmitoylethanolamide. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; D’Agostino, G.; Pacini, A.; Russo, R.; Zanardelli, M.; Ghelardini, C.; Calignano, A. Palmitoylethanolamide is a disease-modifying agent in peripheral neuropathy: Pain relief and neuroprotection share a PPAR-alpha-mediated mechanism. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 328797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luongo, L.; Guida, F.; Boccella, S.; Bellini, G.; Gatta, L.; Rossi, F.; de Novellis, V.; Maione, S. Palmitoylethanolamide reduces formalin-induced neuropathic-like behaviour through spinal glial/microglial phenotypical changes in mice. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 12, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guida, F.; Luongo, L.; Marmo, F.; Romano, R.; Iannotta, M.; Napolitano, F.; Belardo, C.; Marabese, I.; D’Aniello, A.; De Gregorio, D.; et al. Palmitoylethanolamide reduces pain-related behaviors and restores glutamatergic synapses homeostasis in the medial prefrontal cortex of neuropathic mice. Mol. Brain 2015, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Pacini, A.; Corti, F.; Boccella, S.; Luongo, L.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Maione, S.; Calignano, A.; Ghelardini, C. Antineuropathic profile of N-palmitoylethanolamine in a rat model of oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, O.; Russo, R.; Vitiello, S.; Raso, G.M.; D’Agostino, G.; Iacono, A.; Rana, G.L.; Vallée, M.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Piazza, P.V.; et al. Implication of allopregnanolone in the antinociceptive effect of N-palmitoylethanolamide in acute or persistent pain. Pain 2012, 153, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Corti, F.; Micheli, L.; Zanardelli, M.; Ghelardini, C. Delay of morphine tolerance by palmitoylethanolamide. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 894732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccella, S.; Cristiano, C.; Romano, R.; Iannotta, M.; Belardo, C.; Farina, A.; Guida, F.; Piscitelli, F.; Palazzo, E.; Mazzitelli, M.; et al. Ultra-micronized palmitoylethanolamide rescues the cognitive decline-associated loss of neural plasticity in the neuropathic mouse entorhinal cortex-dentate gyrus pathway. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 121, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Campolo, M.; Evangelista, M.; Di Paola, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Effect of a new formulation of micronized and ultramicronized N-palmitoylethanolamine in a tibia fracture mouse model of complex regional pain syndrome. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peritore, A.F.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Impellizzeri, D.; Cuzzocrea, S.; et al. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide and Paracetamol, a New Association to Relieve Hyperalgesia and Pain in a Sciatic Nerve Injury Model in Rat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Cordaro, M.; Peritore, A.F.; D’Amico, R.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Genovese, T.; Evangelista, M.; Di Paola, R.; et al. The Protective Effects of Pre- and Post-Administration of Micronized Palmitoylethanolamide Formulation on Postoperative Pain in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, A.; Lazzari, M.; Gianfelice, V.; Di Paolo, A.; Sabato, E.; Sabato, A.F. Palmitoylethanolamide in the treatment of chronic pain caused by different etiopathogenesis. Pain Med. 2012, 13, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocito, D.; Peci, E.; Ciaramitaro, P.; Merola, A.; Lopiano, L. Short-term efficacy of ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide in peripheral neuropathic pain. Pain Res. Treat. 2014, 2014, 854560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirchiglia, D.; Paventi, S.; Seminara, P.; Cione, E.; Gallelli, L. N-Palmitoyl Ethanol Amide Pharmacological Treatment in Patients with Nonsurgical Lumbar Radiculopathy. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 58, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passavanti, M.B.; Fiore, M.; Sansone, P.; Aurilio, C.; Pota, V.; Barbarisi, M.; Fierro, D.; Pace, M.C. The beneficial use of ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide as add-on therapy to Tapentadol in the treatment of low back pain: A pilot study comparing prospective and retrospective observational arms. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017, 17, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, A.; Varrassi, G.; Bentivegna, G.; Carletti, S.; Piroli, A.; Coaccioli, S. Palmitoylethanolamide in the Treatment of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome. Pain Res. Treat. 2017, 2017, 1486010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaturro, D.; Asaro, C.; Lauricella, L.; Tomasello, S.; Varrassi, G.; Letizia Mauro, G. Combination of Rehabilitative Therapy with Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide for Chronic Low Back Pain: An Observational Study. Pain Ther. 2020, 9, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, M.; Cilli, V.; De Vitis, R.; Militerno, A.; Fanfani, F. Ultra-micronized Palmitoylethanolamide Effects on Sleep-wake Rhythm and Neuropathic Pain Phenotypes in Patients with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: An Open-label, Randomized Controlled Study. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 17, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuvone, T.; Affaitati, G.; De Filippis, D.; Lopopolo, M.; Grassia, G.; Lapenna, D.; Negro, L.; Costantini, R.; Vaia, M.; Cipollone, F.; et al. Ultramicronized palmitoylethanolamide reduces viscerovisceral hyperalgesia in a rat model of endometriosis plus ureteral calculosis: Role of mast cells. Pain 2016, 157, 80–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indraccolo, U.; Barbieri, F. Effect of palmitoylethanolamide-polydatin combination on chronic pelvic pain associated with endometriosis: Preliminary observations. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2010, 150, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Monte, G.; Soave, I.; Marci, R. Administration of micronized palmitoylethanolamide (PEA)-transpolydatin in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain in women affected by endometriosis: Preliminary results. Minerva Ginecol. 2013, 65, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cobellis, L.; Castaldi, M.A.; Giordano, V.; Trabucco, E.; De Franciscis, P.; Torella, M.; Colacurci, N. Effectiveness of the association micronized N-Palmitoylethanolamine (PEA)-transpolydatin in the treatment of chronic pelvic pain related to endometriosis after laparoscopic assessment: A pilot study. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2011, 158, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giugliano, E.; Cagnazzo, E.; Soave, I.; Lo Monte, G.; Wenger, J.M.; Marci, R. The adjuvant use of N-palmitoylethanolamine and transpolydatin in the treatment of endometriotic pain. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2013, 168, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, E.; Armentano, M.; Giugliano, B.; Sena, T.; Giuliano, P.; Loffredo, C.; Mastrantonio, P. Effectiveness of the Association N-Palmitoylethanolamine and Transpolydatin in the Treatment of Primary Dysmenorrhea. J. Pediatric Adolesc. Gynecol. 2015, 28, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stochino Loi, E.; Pontis, A.; Cofelice, V.; Pirarba, S.; Fais, M.F.; Daniilidis, A.; Melis, I.; Paoletti, A.M.; Angioni, S. Effect of ultramicronized-palmitoylethanolamide and co-micronized palmitoylethanolamide/polydatin on chronic pelvic pain and quality of life in endometriosis patients: An open-label pilot study. Int. J. Women’s Health 2019, 11, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirchiglia, D.; Della Torre, A.; Signorelli, F.; Volpentesta, G.; Guzzi, G.; Stroscio, C.A.; Deodato, F.; Gabriele, D.; Lavano, A. Administration of palmitoylethanolamide in combination with topiramate in the preventive treatment of nummular headache. Int. Med. Case Rep. J. 2016, 9, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirchiglia, D.; Cione, E.; Caroleo, M.C.; Wang, M.; Di Mizio, G.; Faedda, N.; Giacolini, T.; Siviglia, S.; Guidetti, V.; Gallelli, L. Effects of Add-On Ultramicronized N-Palmitol Ethanol Amide in Patients Suffering of Migraine with Aura: A Pilot Study. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papetti, L.; Sforza, G.; Tullo, G.; Alaimo di Loro, P.; Moavero, R.; Ursitti, F.; Ferilli, M.A.N.; Tarantino, S.; Vigevano, F.; Valeriani, M. Tolerability of Palmitoylethanolamide in a Pediatric Population Suffering from Migraine: A Pilot Study. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 3938640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Giorno, R.; Skaper, S.; Paladini, A.; Varrassi, G.; Coaccioli, S. Palmitoylethanolamide in Fibromyalgia: Results from Prospective and Retrospective Observational Studies. Pain Ther. 2015, 4, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweiger, V.; Martini, A.; Bellamoli, P.; Donadello, K.; Schievano, C.; Del Balzo, G.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Parolini, M.; Polati, E. Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide (um-PEA) as add-on Treatment in Fibromyalgia Syndrome (FMS): Retrospective Observational Study on 407 Patients. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 18, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Morishita, J.; Tsuboi, K.; Tonai, T.; Ueda, N. Molecular characterization of a phospholipase D generating anandamide and its congeners. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5298–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravatt, B.F.; Giang, D.K.; Mayfield, S.P.; Boger, D.L.; Lerner, R.A.; Gilula, N.B. Molecular characterization of an enzyme that degrades neuromodulatory fatty-acid amides. Nature 1996, 384, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, N.; Yamanaka, K.; Yamamoto, S. Purification and characterization of an acid amidase selective for N-palmitoylethanolamine, a putative endogenous anti-inflammatory substance. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35552–35557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, H.S.; Diep, T.A. N-acylethanolamines, anandamide and food intake. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleberg, K.; Hassing, H.A.; Hansen, H.S. Classical endocannabinoid-like compounds and their regulation by nutrients. Biofactors 2014, 40, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloe, L.; Leon, A.; Levi-Montalcini, R. A proposed autacoid mechanism controlling mastocyte behaviour. Agents Actions 1993, 39, C145–C147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facci, L.; Dal Toso, R.; Romanello, S.; Buriani, A.; Skaper, S.D.; Leon, A. Mast cells express a peripheral cannabinoid receptor with differential sensitivity to anandamide and palmitoylethanolamide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3376–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levi-Montalcini, R.; Skaper, S.D.; Dal Toso, R.; Petrelli, L.; Leon, A. Nerve growth factor: From neurotrophin to neurokine. Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; Melck, D.; Orlando, P.; Bisogno, T.; Zagoory, O.; Bifulco, M.; Vogel, Z.; De Petrocellis, L. Palmitoylethanolamide inhibits the expression of fatty acid amide hydrolase and enhances the anti-proliferative effect of anandamide in human breast cancer cells. Biochem. J. 2001, 358, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrosino, S.; Schiano Moriello, A.; Verde, R.; Allarà, M.; Imperatore, R.; Ligresti, A.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Peritore, A.F.; Iannotti, F.A.; Di Marzo, V. Palmitoylethanolamide counteracts substance P-induced mast cell activation in vitro by stimulating diacylglycerol lipase activity. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygmunt, P.M.; Petersson, J.; Andersson, D.A.; Chuang, H.; Sørgård, M.; Di Marzo, V.; Julius, D.; Högestätt, E.D. Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature 1999, 400, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Davis, J.B.; Di Marzo, V. Palmitoylethanolamide enhances anandamide stimulation of human vanilloid VR1 receptors. FEBS Lett. 2001, 506, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.-S.V.; Barrett, D.A.; Randall, M.D. “Entourage” effects of N-palmitoylethanolamide and N-oleoylethanolamide on vasorelaxation to anandamide occur through TRPV1 receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zygmunt, P.M.; Ermund, A.; Movahed, P.; Andersson, D.A.; Simonsen, C.; Jönsson, B.A.G.; Blomgren, A.; Birnir, B.; Bevan, S.; Eschalier, A.; et al. Monoacylglycerols activate TRPV1—A link between phospholipase C and TRPV1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Verme, J.; Fu, J.; Astarita, G.; La Rana, G.; Russo, R.; Calignano, A.; Piomelli, D. The nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha mediates the anti-inflammatory actions of palmitoylethanolamide. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryberg, E.; Larsson, N.; Sjögren, S.; Hjorth, S.; Hermansson, N.-O.; Leonova, J.; Elebring, T.; Nilsson, K.; Drmota, T.; Greasley, P.J. The orphan receptor GPR55 is a novel cannabinoid receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 152, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musella, A.; Fresegna, D.; Rizzo, F.R.; Gentile, A.; Bullitta, S.; De Vito, F.; Guadalupi, L.; Centonze, D.; Mandolesi, G. A novel crosstalk within the endocannabinoid system controls GABA transmission in the striatum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shabat, S.; Fride, E.; Sheskin, T.; Tamiri, T.; Rhee, M.H.; Vogel, Z.; Bisogno, T.; De Petrocellis, L.; Di Marzo, V.; Mechoulam, R. An entourage effect: Inactive endogenous fatty acid glycerol esters enhance 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol cannabinoid activity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 353, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosino, P.; Soldovieri, M.V.; Russo, C.; Taglialatela, M. Activation and desensitization of TRPV1 channels in sensory neurons by the PPARα agonist palmitoylethanolamide. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 168, 1430–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosino, P.; Soldovieri, M.V.; De Maria, M.; Russo, C.; Taglialatela, M. Functional and biochemical interaction between PPARα receptors and TRPV1 channels: Potential role in PPARα agonists-mediated analgesia. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 87, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, F.; Luongo, L.; Boccella, S.; Giordano, M.E.; Romano, R.; Bellini, G.; Manzo, I.; Furiano, A.; Rizzo, A.; Imperatore, R.; et al. Palmitoylethanolamide induces microglia changes associated with increased migration and phagocytic activity: Involvement of the CB2 receptor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuderi, C.; Esposito, G.; Blasio, A.; Valenza, M.; Arietti, P.; Steardo, L.; Carnuccio, R.; De Filippis, D.; Petrosino, S.; Iuvone, T.; et al. Palmitoylethanolamide counteracts reactive astrogliosis induced by β-amyloid peptide. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 2664–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scuderi, C.; Valenza, M.; Stecca, C.; Esposito, G.; Carratù, M.R.; Steardo, L. Palmitoylethanolamide exerts neuroprotective effects in mixed neuroglial cultures and organotypic hippocampal slices via peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troncoso-Escudero, P.; Parra, A.; Nassif, M.; Vidal, R.L. Outside in: Unraveling the Role of Neuroinflammation in the Progression of Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease and its potential as therapeutic target. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, M.G.; Goldberg, M.S. Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guevara, C.; Ortiz, F.C. Glial-derived transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1): A key factor in multiple sclerosis neuroinflammation. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 510–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwardt, E.; Zipp, F. Molecular mechanisms linking neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in MS. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 262 Pt A, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.-S.; Vijayalakshmi, K.; Nalini, A.; Sathyaprabha, T.N.; Kramer, B.W.; Alladi, P.A.; Raju, T.R. Etiogenic factors present in the cerebrospinal fluid from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients induce predominantly pro-inflammatory responses in microglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckl, P.; Weydt, P.; Steinacker, P.; Anderl-Straub, S.; Nordin, F.; Volk, A.E.; Diehl-Schmid, J.; Andersen, P.M.; Kornhuber, J.; Danek, A.; et al. Different neuroinflammatory profile in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia is linked to the clinical phase. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, A.; Quintana, D.S.; Glozier, N.; Lloyd, A.R.; Hickie, I.B.; Guastella, A.J. Cytokine aberrations in autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ansary, A.; Al-Ayadhi, L. Neuroinflammation in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrado-Carvajal, A.; Toschi, N.; Albrecht, D.S.; Chang, K.; Akeju, O.; Kim, M.; Edwards, R.R.; Zhang, Y.; Hooker, J.M.; Duggento, A.; et al. Thalamic neuroinflammation as a reproducible and discriminating signature for chronic low back pain. Pain 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Huh, Y.; Ji, R.-R. Roles of Inflammation, Neurogenic inflammation, and Neuroinflammation in Pain. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruccu, G.; Stefano, G.D.; Marchettini, P.; Truini, A. Micronized Palmitoylethanolamide: A Post Hoc Analysis of a Controlled Study in Patients with Low Back Pain—Sciatica. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2019, 18, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xie, H.; Yao, S.; Liang, Y. Macrophage and nerve interaction in endometriosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Tsilioni, I.; Bawazeer, M. Mast Cells, Neuroinflammation and Pain in Fibromyalgia Syndrome. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabkova, V.A.; Churilov, L.P.; Shoenfeld, Y. Neuroimmunology: What Role for Autoimmunity, Neuroinflammation, and Small Fiber Neuropathy in Fibromyalgia, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, and Adverse Events after Human Papillomavirus Vaccination? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Littlejohn, G. Neurogenic neuroinflammation in fibromyalgia and complex regional pain syndrome. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, S.C.; Djukic, M.; Gossner, J.; Eiffert, H.; Brück, W.; Nau, R. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy and septic encephalitis: An update. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heide, E.C.; Bindila, L.; Post, J.M.; Malzahn, D.; Lutz, B.; Seele, J.; Nau, R.; Ribes, S. Prophylactic Palmitoylethanolamide Prolongs Survival and Decreases Detrimental Inflammation in Aged Mice with Bacterial Meningitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, R.; Pascual Cuadrado, D.; Post, J.M.; Lutz, B.; Bindila, L. Broad Lipidomic and Transcriptional Changes of Prophylactic PEA Administration in Adult Mice. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).