Microglial Activation in the Retina of a Triple-Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model (3xTg-AD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
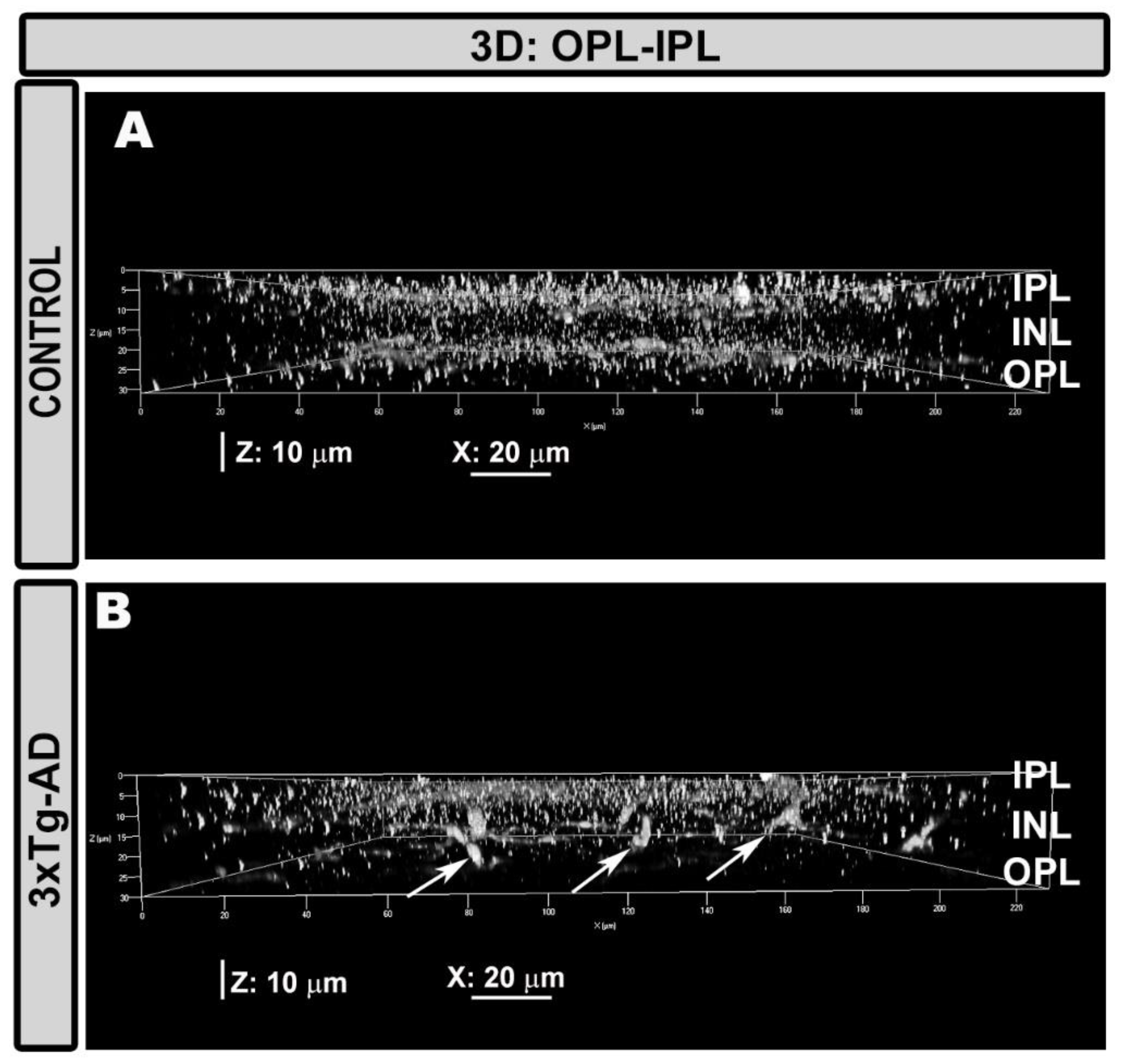
2.1. Qualitative Analysis of Iba-1+ Cells
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of Iba-1+ Cells
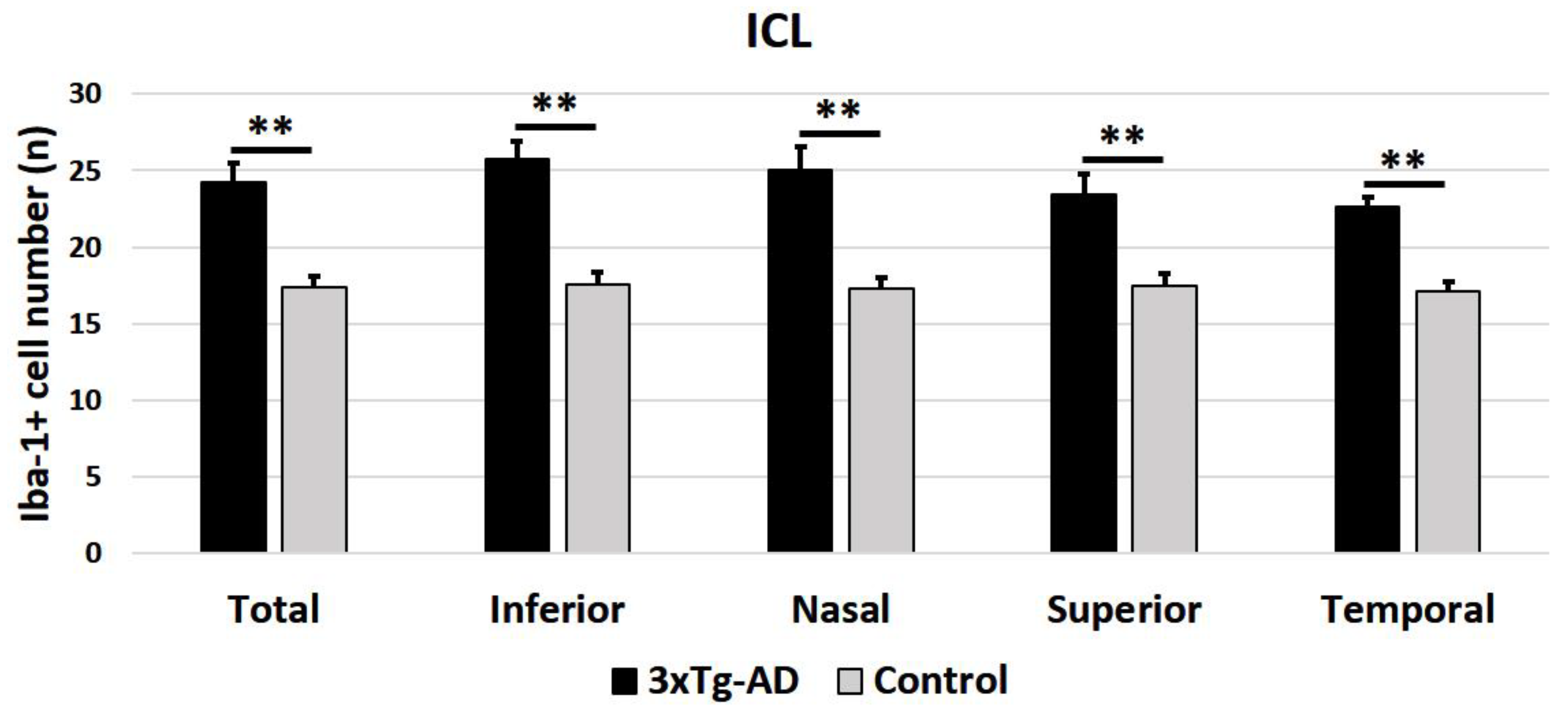
2.2.1. Number of Iba-1+ Cells in OPL and ILC
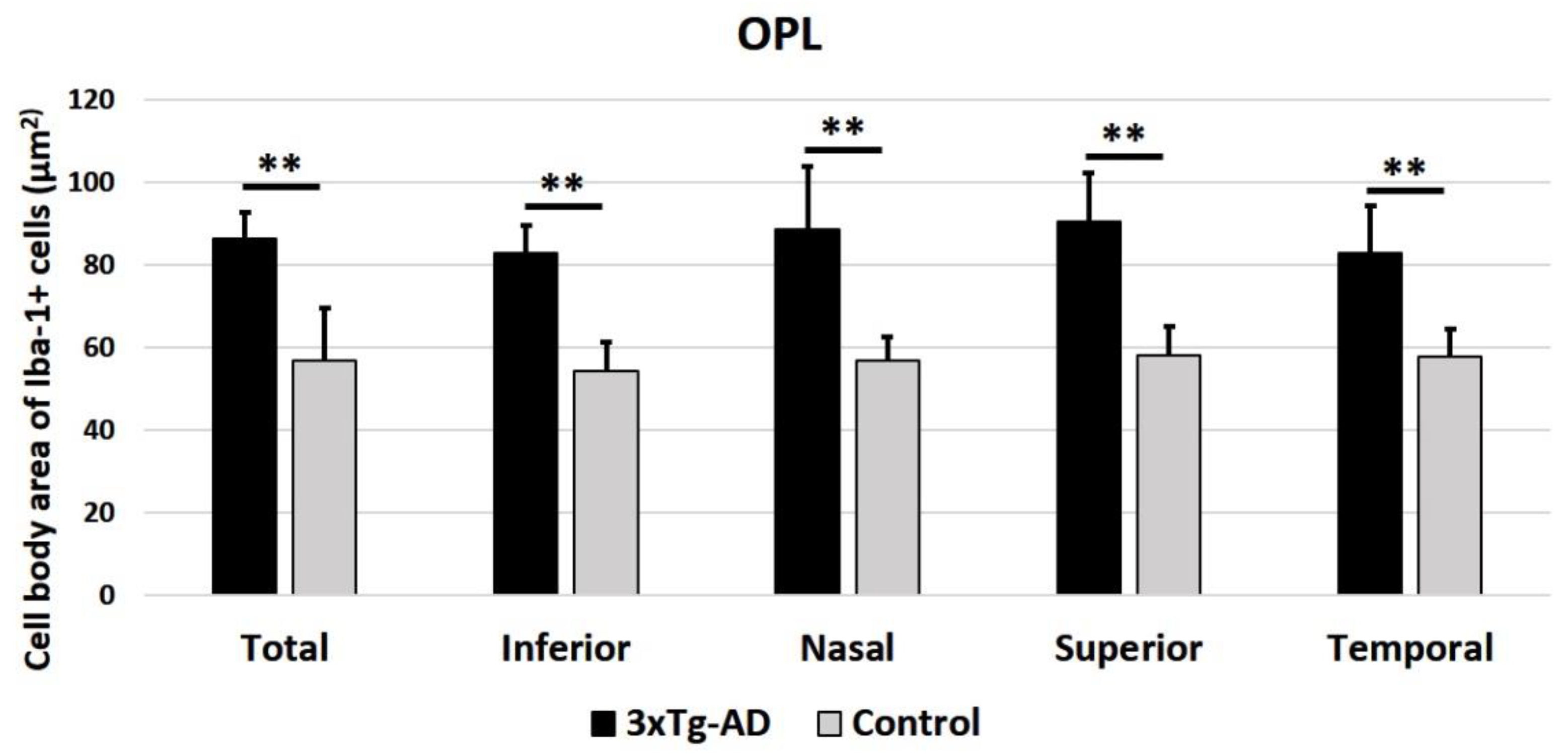
2.2.2. Cell Body Area of Iba-1+ Cells in the OPL and in the ILC
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Ethics
4.2. Experimental Groups
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Quantitative Retinal Analysis
4.5. Quantification of Iba-1+ Cells in the OPL and the ILC
4.6. Cell Body Area of Iba-1+ Cells in the OPL and ILC
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| GCL | Ganglion cell layer |
| IPL | Inner plexiform layer |
| ILC | Inner retinal layer complex |
| Iba-1 | Ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 |
| NFL | Nerve fiber layer |
| OCT | Optical Coherence Tomography |
| OPL | Outer plexiform layer |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| PNWs | Post-natal weeks |
| Aβ | Protein amyloid-β |
| RGCs | Retinal ganglion cells |
| WT | Wild type |
References
- De Lau, L.M.; Breteler, M.M. Epidemiology of Parkinson disease. Lancet Neurol. 2016, 5, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Singh, A.N. Exploring biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, KE01–KE06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghiso, J.A.; Doudevski, I.; Ritch, R.; Rostagno, A.A. Alzheimer’s disease and glaucoma: Mechanistic similarities and differences. J. Glaucoma 2013, 22, S36–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Ospina, G.; Jímenez-Del, M.R.; Lopera, F.; Vélez-Pardo, C. Neuronal DNA damage correlates with a positive detection of c-Jun, nuclear factor kB, p53 and Par-4 transcription factors in Alzheimer’s disease. Rev. Neurol. 2003, 36, 1004–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; Khoury, J.E.; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, M.H.; Boia, R.; Santos, P.F.; Ambrósio, A.F.; Santiago, A.R.; Ambrosio, A.F.; Santiago, A.R. Contribution of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation to retinal degenerative diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 673090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parpura, V.; Heneka, M.T.; Montana, V.; Oliet, S.H.R.; Schousboe, A.; Haydon, P.G.; Stout, R.F.; Spray, D.C.; Reichenbach, A.; Pannicke, T.; et al. Glial cells in (patho) physiology. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.D.; Zhu, Y.G.; Lin, N.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Q.Y.; Huang, H.P.; Chen, X.C. Microglial phagocytosis induced by fibrillar β-amyloid is attenuated by oligomeric β-amyloid: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, T. The biphasic role of microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 2012, 737846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salobrar-Garcia, E.; De Hoz, R.; Rojas, B.; Ramirez, A.I.; Salazar, J.J.; Yubero, R.; Gil, P.; Triviño, A.; Ramirez, J.M. Ophthalmologic Psychophysical Tests Support OCT Findings in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 736949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jáñez-Escalada, L.; Jáñez-García, L.; Salobrar-García, E.; Santos-Mayo, A.; de Hoz, R.; Yubero, R.; Gil, P.; Ramírez, J.M. Spatial analysis of thickness changes in ten retinal layers of Alzheimer’s disease patients based on optical coherence tomography. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Hoyas, I.; Leal, M.; De Hoz, R.; Rojas, B.; Ramirez, A.I.I.; Salazar, J.J.J.; Yubero, R.; Gil, P.; Triviño, A.; et al. Analysis of Retinal Peripapillary Segmentation in Early Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 636548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandrov, P.N.; Pogue, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Lukiw, W.J. Retinal amyloid peptides and complement factor H in transgenic models of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroreport 2011, 22, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnayaka, J.A.; Serpell, L.C.; Lotery, A.J. Dementia of the eye: The role of amyloid beta in retinal degeneration. Eye 2015, 29, 1013–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, N.J.; Koronyo, Y.; Black, K.L.; Koronyo-Hamaoui, M. Ocular indicators of Alzheimer’s: Exploring disease in the retina. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 767–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Salazar, J.J.; Rojas, B.; Ajoy, D.; López-Cuenca, I.; Rojas, P.; Triviño, A.; Ramírez, J.M. The Role of Microglia in Retinal Neurodegeneration: Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson, and Glaucoma. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Albarral, J.A.; Salobrar-García, E.; Martínez-Páramo, R.; Ramírez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; Ramírez, J.M.; Salazar, J.J. Retinal glial changes in Alzheimer’s disease—A review. J. Optom. 2019, 12, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Morgia, C.; Ross-Cisneros, F.N.; Hannibal, J.; Montagna, P.; Sadun, A.A.; Carelli, V. Melanopsin-expressing retinal ganglion cells: Implications for human diseases. Vision Res. 2011, 51, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koronyo, Y.; Biggs, D.; Barron, E.; Boyer, D.S.; Pearlman, J.A.; Au, W.J.; Kile, S.J.; Blanco, A.; Fuchs, D.T.; Ashfaq, A.; et al. Retinal amyloid pathology and proof-of-concept imaging trial in Alzheimer’s disease. JCI Insight 2017, 2, e93621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surguchov, A.; McMahan, B.; Masliah, E.; Surgucheva, I. Synucleins in ocular tissues. J. Neurosci. Res. 2001, 65, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surgucheva, I.; Weisman, A.D.; Goldberg, J.L.; Shnyra, A.; Surguchov, A. Gamma-synuclein as a marker of retinal ganglion cells. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, A.; Irizarry, M.C.; Duff, K.; Saido, T.C.; Hsiao Ashe, K.; Hasegawa, M.; Mann, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Iwatsubo, T. Age-related amyloid beta deposition in transgenic mice overexpressing both Alzheimer mutant presenilin 1 and amyloid beta precursor protein Swedish mutant is not associated with global neuronal loss. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, S.; Caccamo, A.; Shepherd, J.D.; Murphy, M.P.; Golde, T.E.; Kayed, R.; Metherate, R.; Mattson, M.P.; Akbari, Y.; LaFerla, F.M. Triple-Transgenic Model of Alzheimer’s Disease with Plaques and Tangles: Intracellular Aβ and Synaptic Dysfunction. Neuron 2003, 39, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, H.; Cole, S.L.; Logan, S.; Maus, E.; Shao, P.; Craft, J.; Guillozet-Bongaarts, A.; Ohno, M.; Disterhoft, J.; Van Eldik, L.; et al. Intraneuronal β-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: Potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10129–10140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipson, O.; Lord, A.; Gumucio, A.; O’Callaghan, P.; Lannfelt, L.; Nilsson, L.N.G. Animal models of amyloid-β-related pathologies in Alzheimer’s disease. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 1389–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koronyo-Hamaoui, M.; Koronyo, Y.; Ljubimov, A.V.; Miller, C.A.; Ko, M.K.H.K.; Black, K.L.; Schwartz, M.; Farkas, D.L. Identification of amyloid plaques in retinas from Alzheimer’s patients and noninvasive in vivo optical imaging of retinal plaques in a mouse model. Neuroimage 2011, 54, S204–S217. [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi, A.; Brighi, C.; Peruzzi, G.; Ragozzino, D.; Bonanni, V.; Limatola, C.; Ruocco, G.; Di Angelantonio, S. Inflammation, neurodegeneration and protein aggregation in the retina as ocular biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease in the 3xTg-AD mouse model. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, A.; Cui, J.; To, E.; Ashe, K.H.; Matsubara, J. Amyloid-β Deposits Lead to Retinal Degeneration in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer Disease. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 5136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrekar-Colucci, S.; Landreth, G.E. Microglia and inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2010, 9, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.I.; Rojas, B.; de Hoz, R.; Salazar, J.J.; Gallego, B.I.; Triviño, A.; Ramírez, J.M. Microglia, inflammation, and glaucoma. In Glaucoma; SM Group Open Access eBooks: Dover, DE, USA, 2015; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.C.; Vilalta, A. How microglia kill neurons. Brain Res. 2015, 1628, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnell, M.; Guo, L.; Abdi, M.; Cordeiro, M.F. Ocular manifestations of Alzheimer’s disease in animal models. Int. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 2012, 786494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, S.E.; Lumayag, S.; Kovacs, B.; Mufson, E.J.; Xu, S. β-Amyloid Deposition and Functional Impairment in the Retina of the APPswe/PS1ΔE9 Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Rasool, S.; Yang, Z.; Glabe, C.G.; Schreiber, S.S.; Ge, J.; Tan, Z. Amyloid-peptide vaccinations reduce β-amyloid plaques but exacerbate vascular deposition and inflammation in the retina of Alzheimer’s transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madeira, M.H.; Ambrósio, A.F.; Santiago, A.R.; Ambrosio, A.F.; Santiago, A.R. Glia-Mediated Retinal Neuroinflammation as a Biomarker in Alzheimer’s Disease. Ophthalmic Res. 2015, 54, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, A.; Kirchhoff, F.; Helmchen, F. Resting microglial cells are highly dynamic surveillants of brain parenchyma in vivo. Science 2005, 308, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biber, K.; Neumann, H.; Inoue, K.; Boddeke, H.W.G.M. Neuronal “On” and “Off” signals control microglia. Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambuyzer, B.R.; Ponsaerts, P.; Nouwen, E.J. Microglia: Gatekeepers of central nervous system immunology. J. Leukoc. Biol 2009, 85, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beynon, S.B.; Walker, F.R. Microglial activation in the injured and healthy brain: What are we really talking about? Practical and theoretical issues associated with the measurement of changes in microglial morphology. Neuroscience 2012, 225, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-J.; Chung, W.-S. Phagocytic Roles of Glial Cells in Healthy and Diseased Brains. Biomol. Ther. 2018, 26, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlus, H.; Heneka, M.T. Microglia in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3240–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Lu, B.; Ljubimov, A.V.; Girman, S.; Ross-Cisneros, F.N.; Sadun, A.A.; Svendsen, C.N.; Cohen, R.M.; Wang, S. Ocular Changes in TgF344-AD Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palop, J.J.; Mucke, L. Amyloid-Β-induced neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: From synapses toward neural networks. Nat. Neurosci. 2010, 13, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, F.R.; Beynon, S.B.; Jones, K.A.; Zhao, Z.; Kongsui, R.; Cairns, M.; Nilsson, M. Dynamic structural remodelling of microglia in health and disease: A review of the models, the signals and the mechanisms. Brain. Behav. Immun. 2014, 37, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, R.A.; Yuan, T.F.; Liang, Y.X.; Jonas, J.B.; Tay, D.K.C.; Ellis-Behnke, R.G. The spider effect: Morphological and orienting classification of microglia in response to stimuli in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salobrar-García, E.; de Hoz, R.; Ramírez, A.I.; López-Cuenca, I.; Rojas, P.; Vazirani, R.; Amarante, C.; Yubero, R.; Gil, P.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; et al. Changes in visual function and retinal structure in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Hoz, R.; Ramírez, A.I.; González-Martín, R.; Ajoy, D.; Rojas, B.; Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Avilés-Trigueros, M.; Villegas-Pérez, M.P.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; et al. Bilateral early activation of retinal microglial cells in a mouse model of unilateral laser-induced experimental ocular hypertension. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 171, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camandola, S.; Mattson, M.P. Brain metabolism in health, aging, and neurodegeneration. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1474–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordone, M.P.; Salman, M.M.; Titus, H.E.; Amini, E.; Andersen, J.V.; Chakraborti, B.; Diuba, A.V.; Dubouskaya, T.G.; Ehrke, E.; Espindola de Freitas, A.; et al. The energetic brain—A review from students to students. J. Neurochem. 2019, 151, 139–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Sancheti, H.; Patil, I.; Cadenas, E. Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016, 100, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldana, B.I. Microglia-Specific Metabolic Changes in Neurodegeneration. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 1830–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S.E.; Sena, L.A.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondria in the regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Immunity 2015, 42, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschopp, J.; Schroder, K. NLRP3 inflammasome activation: The convergence of multiple signalling pathways on ROS production? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, J.M.; Trivino, A.; Ramirez, A.I.; Salazar, J.J.; Garcia-Sanchez, J. Immunohistochemical study of human retinal astroglia. Vis. Res. 1994, 34, 1935–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.A.; Perez, Z.D.; Foresti, M.L.; Arisi, G.M.; Ribak, C.E. Morphological and ultrastructural features of Iba1-immunolabeled microglial cells in the hippocampal dentate gyrus. Brain Res. 2009, 1266, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapuscinski, J. DAPI: A DMA-Specific fluorescent probe. Biotech. Histochem. 1995, 70, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Albarral, J.A.; Ramírez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; López-Villarín, N.; Salobrar-García, E.; López-Cuenca, I.; Licastro, E.; Inarejos-García, A.M.; Almodóvar, P.; Pinazo-Durán, M.D.; et al. Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Hydrophilic Saffron Extract in a Model of Glaucoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, B.; Gallego, B.I.; Ramírez, A.I.; Salazar, J.J.; de Hoz, R.; Valiente-Soriano, F.J.; Avilés-Trigueros, M.; Villegas-Perez, M.P.; Vidal-Sanz, M.; Triviño, A.; et al. Microglia in mouse retina contralateral to experimental glaucoma exhibit multiple signs of activation in all retinal layers. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salobrar-García, E.; Rodrigues-Neves, A.C.; Ramírez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; Fernández-Albarral, J.A.; López-Cuenca, I.; Ramírez, J.M.; Ambrósio, A.F.; Salazar, J.J. Microglial Activation in the Retina of a Triple-Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model (3xTg-AD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030816
Salobrar-García E, Rodrigues-Neves AC, Ramírez AI, de Hoz R, Fernández-Albarral JA, López-Cuenca I, Ramírez JM, Ambrósio AF, Salazar JJ. Microglial Activation in the Retina of a Triple-Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model (3xTg-AD). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(3):816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030816
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalobrar-García, Elena, Ana C. Rodrigues-Neves, Ana I. Ramírez, Rosa de Hoz, José A. Fernández-Albarral, Inés López-Cuenca, José M. Ramírez, António F. Ambrósio, and Juan J. Salazar. 2020. "Microglial Activation in the Retina of a Triple-Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model (3xTg-AD)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 3: 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030816
APA StyleSalobrar-García, E., Rodrigues-Neves, A. C., Ramírez, A. I., de Hoz, R., Fernández-Albarral, J. A., López-Cuenca, I., Ramírez, J. M., Ambrósio, A. F., & Salazar, J. J. (2020). Microglial Activation in the Retina of a Triple-Transgenic Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model (3xTg-AD). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(3), 816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21030816











