Abstract
Utilization of disease resistance components from wild potatoes is a promising and sustainable approach to control Phytophthora blight. Here, we combined avirulence (Avr) genes screen with RNA-seq analysis to discover the potential mechanism of resistance in Mexican wild potato species, Solanum pinnatisectum. Histological characterization displayed that hyphal expansion was significantly restricted in epidermal cells and mesophyll cell death was predominant, indicating that a typical defense response was initiated in S. pinnatisectum. Inoculation of S. pinnatisectum with diverse Phytophthora infestans isolates showed distinct resistance patterns, suggesting that S. pinnatisectum has complex genetic resistance to most of the prevalent races of P. infestans in northwestern China. Further analysis by Avr gene screens and comparative transcriptomic profiling revealed the presence and upregulation of multiple plant NBS-LRR genes corresponding to biotic stresses. Six NBS-LRR alleles of R1, R2, R3a, R3b, R4, and Rpi-smira2 were detected, and over 60% of the 112 detected NLR proteins were significantly induced in S. pinnatisectum. On the contrary, despite the expression of the Rpi-blb1, Rpi-vnt1, and Rpi-smira1 alleles, fewer NLR proteins were expressed in susceptible Solanum cardophyllum. Thus, the enriched NLR genes in S. pinnatisectum make it an ideal genetic resource for the discovery and deployment of resistance genes for potato breeding.
1. Introduction
Potatoes, one of the most important food crops, have been affected by late blight disease for nearly 180 years [1]. To decrease the yield losses caused by Phytophthora infestans, cultivars of Solanum tuberosum expressing diverse resistance (R) genes have been developed and extensively applied in potato growing areas worldwide. Many typical R genes, such as R1 to R11 from Solanum demissum, were initially demonstrated to be successful in improving disease-resistant commercial potatoes. However, the R-gene-insensitive strains of P. infestans frequently emerged after large-scale application of resistant cultivars harboring major R genes [2,3]. For instance, more aggressive P. infestans isolates escaping recognition by R1-R11 genes were reported worldwide [4,5]. However, the outstanding disease-free phenotypes and long-term stability of R genes remain valuable, stimulating numerous attempts to discover natural immune receptors from Solanum species for potato resistance breeding [6,7].
Over 1000 accessions of 216 wild Solanum spp. throughout North and South America were investigated as potential enriched genetic resources for molecular and genetic dissection of the resistance genes against P. infestans [8]. To date, less than 70 R genes or alleles conferring resistance to P. infestans (Rpi) have been identified, mapped, and cloned from several wild Solanum species, such as S. berthaultii, S. bulbocastanum, S. demissum, S. microdontum, S. mochiquense, S. stoloniferum, and S. venturii [8,9]. Most of the Rpi genes against potato late blight are members of the nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat (NLR) protein family [9,10]. Many Rpi genes have been defeated by fast-evolving P. infestans isolates, but both laboratory and field tests demonstrated that pyramiding several Rpi genes into a single potato cultivar was effective in preventing the R-gene destroyer P. infestans [11]. As a result, more efforts and research tools are still needed to facilitate the identification and rational deployment of resistant genes.
In addition to the techniques associated with high-throughput sequencing to discover resistance traits in plants, In planta screens of Phytophthora RxLR effectors is an alternative genomic approach for the detection of race-specific defense responses. These effector probes could accelerate R-gene identification, distinguish functional redundancy, detect recognition specificity, optimize R-gene utilization, and avoid sexual incompatibility in the traditional map-based genetic analysis [12]. A functional homolog of the RB/Rpi-blb1 gene from a non-crossable variety of S. bulbocastanum was mined by PVX (Potato Virus X) agroinfection with AVRblb1 in Nicotiana benthamiana [13]. The recognition between AVRblb1 and a RB functional allele in crossable S. stoloniferum enabled efficient introgression of Rpi-sto1 into cultivated potato-breeding materials [14]. Both qualitative Rpi genes (R3a, R3b, R4, and Rpi-Smira1) and a quantitative Rpi gene (Rpi-Smira2) in the potato cultivar ‘Sarpo Mira’ were identified via effectoromics as well [15].
To conquer fast-evolving P. infestans, a continuous influx of new Rpi genes with broad-spectrum resistance from genetically diverse wild germplasm are being pursued by potato breeders [12,16,17]. One wild Mexican diploid (2×) Solanum species S. pinnatisectum with an endosperm balance number of 1 (1EBN) has gained attention because it showed high-level resistance to late blight, and is crossable with another Mexican 2× (1EBN) Solanum species, S. cardiophyllum, which is susceptible to P. infestans [18,19,20]. So far, two Rpi genes, Rpi1 and Rpi2, have been characterized and mapped to chromosome 7 of S. pinnatisectum [20]. Analyses by Park et al. [21] indicated that gene clusters for late blight Rpi are prevalent on chromosomes 4 and 11 of S. pinnatisectum, In addition, Rpi1, a quantitative trait loci (QTL) on chromosome 7 for resistance to P. infestans (Pi_QTL), was recorded in the offspring of S. phureja and S. tuberosum [22]. Besides, the PiAvr2 recognition R gene was also detected via allele-mining [23]. Therefore, S. pinnatisectum was considered to be a valuable wild Solanum resource for the exploitation of Rpi genes.
In this research, based on the histological features of the resistant reaction, we combined a stripped-down version of the Avr gene screen with RNA-seq analysis to dissect the potential resistance machinery of S. pinnatisectum. The remarkable defense responses began at 6 h post-inoculation. Based on the RNA-seq samples together with the histological features, over 60% of 112 NLR protein candidates were responsible for P. infestans resistance, including the known Rpi genes R1, R2, R3a, R3b, R4, and Rpi-smira2. Compared to the NLR genes expressed in the susceptible cultivar S. cardiophyllum, a distinct group of NLR genes with higher expression levels were clustered in S. pinnatisectum. These results provide useful resources for guiding the identification and rational application of Rpi genes in the resistance breeding of potatoes.
2. Results
2.1. Infection with P. infestans on S. pinnatisectum is Evident
In order to determine the susceptibility of the wild potato species S. pinnatisectum to infection by P. infestans, zoospore inoculation was performed with an aggressive isolate, Pi21366, which is virulent to all tested potato R-gene differentials (R1-R11). The detached leaves of the susceptible species S. cardiophyllum and resistant species S. pinnatisectum were inoculated with 103 zoospores. As shown in Figure 1a, only restricted water-soaked lesions developed at 72 h post inoculation (hpi) on S. pinnatisectum leaves. Well-expanded diseased areas with fluffy hyphae and a large number of sporangia were observed on the leaf surface of S. cardiophyllum (Figure 1a). The relative biomass of P. infestans measured at 72 hpi via qPCR was more than 2-fold greater in diseased tissue on S. cardiophyllum than that detected on leaves of S. pinnatisectum (Figure 1b). At the later stage of infection (108 hpi), the lesions expanded to the whole S. cardiophyllum leaves, but lesions on S. pinnatisectum were only slightly larger than at 72 hpi (Figure 1c).

Figure 1.
Infection of Solanum pinnatisectum and Solanum cardiophyllum by Phytophthora infestans. (a) The symptom on S. cardiophyllum and S. pinnatisectum 72 h post-inoculation (hpi). (b) The biomass of P. infestans detected in S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum 72 hpi. Each error bar represents the mean ± SD. (c) The lesion size on S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum measured at different times post inoculation. Sc: S. cardiophyllum, Sp: S. pinnatisectum. (Each error bar represents the mean ± SD, ** and *** indicate statistical significance where p < 0.05 and p < 0.001 using t test, respectively).
2.2. Histological Characteristics of S. pinnatisectum Infected by P. infestans
To investigate the histological characteristics of early interactions between P. infestans and S. pinnatisectum or S. cardiophyllum, detached leaves were drop inoculated with zoospores and collected at 3, 6, 9, and 12 hpi, respectively. Within 3 hpi, no significant difference was observed between S. pinnatisectum and the susceptible control S. cardiophyllum. More than 80% of the cysts germinated on the leaf surface of both species, and most of them produced an appressorium at the tips of the germ tubes (Table 1, Figure 2a,b; both Table 1 and Figure 2 were modified from Cao [24]). Invasive hyphae were observed as well, which were predominant at the anticlinal walls between the epidermal cells (Figure 2a,b). By 6 hpi, infection vesicles were observed beneath appressoria in the epidermal cells of both S. pinnatisectum and the susceptible control (Figure 2c,d). The intercellular hyphae were generated and extended intercellularly among spongy cells, although penetration into the spongy tissue of S. pinnatisectum was occasionally visible (Table 1). By this time point, the reaction of plant cells and cell wall deposition were universal in the epidermal cells of S. pinnatisectum in response to the infection of P. infestans (Figure 2d) but not in the epidermal cells of S. cardiophyllum (Figure 2c).

Table 1.
Comparison of infection process of Phytophthora infestans on excised leaves between Solanum pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum at different times post-inoculation.
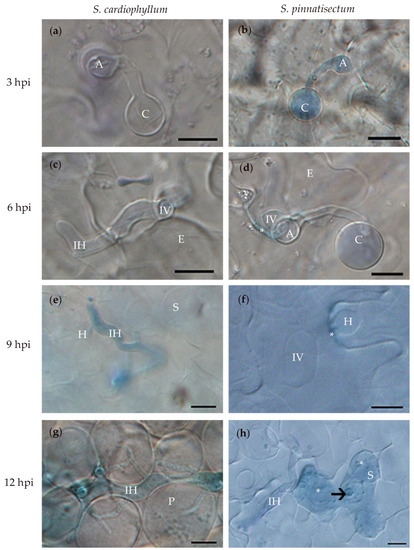
Figure 2.
Microscopic characterization of Solanum pinnatisectum and Solanum cardiophyllum interacted with Phytophthora infestans at different times post-inoculation. (a) and (b), the germinated cysts with appressorium at the tip on the leaf surface of S. cardiophyllum and S. pinnatisectum 3 h post-inoculation (hpi), respectively. (c) and (d), the pathogen penetrated into the epidermal cell of S. cardiophyllum and S. pinnatisectum 6 hpi, * in (d) indicates cell wall deposition at the infection site of epidermal cell on S. pinnatisectum. (e) Intercellular hyphae with haustoria invade spongy cells of S. cardiophyllum 9 hpi. (f) The pathogen extends underneath the cuticle as the infection vessel and forms haustoria in the epidermal cells of S. pinnatisectum 9 hpi. (g) Intercellular hyphae expand with multiple branches in the palisade cells of S. cardiophyllum 12 hpi. (h) Penetration of intercellular hyphae is stopped by the necrosis of mesophyll cells on S. pinnatisectum 12 hpi; the haustorium is pointed by the arrow; and the deeply blue-stained tissues indicate cell necrosis (indicate as *). A: appressorium, C: cyst, E: epidermal cell, H: haustorium, IH: intercellular hyphae, IV: infection vessel, P: palisade cell, S: sponge cell. Bar = 10 μm.
Phenotype differences between S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum became more evident at 9 hpi. In S. pinnatisectum, more than 90% of the infection hyphae were confined to the site of the initial penetration of the epidermal cell, while in S. cardiophyllum, the infection hyphae extended rapidly, with more than 40% of the hyphae reaching spongy tissue, and the haustoria were visible (Table 1, Figure 2e,f). In S. pinnatisectum, the infection was still restricted to the epidermal cells by 12 hpi, and some epidermal cells and mesophyll cells beneath the infection site were necrotic (Figure 2h). By this time point, nearly 60% of the hyphae spread into the spongy tissue of S. cardiophyllum, and about 25% of the hyphae had invaded into the palisade tissue but necrosis was rarely observed (Table 1, Figure 2g). These results provided preliminary evidence that a typical defense response rather than cell wall-associated penetration resistance was initiated in S. pinnatisectum upon P. infestans inoculation. Based on the above microscopic observations, we determined 3, 9, and 12 hpi as time points to investigate the transcriptional dynamics of S. pinnatisectum compared to S. cardiophyllum.
2.3. S. pinnatisectum Reveals Complicated Pathotypes Based on Multiple R Genes
To dissect the genetic resistance of S. pinnatisectum, the detached leaves were subjected to inoculation with a panel of 12 P. infestans isolates displaying SSR-based genotype variations [5] and R-gene-dependent pathotype diversity (Table 2). The phenotypes of both S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum to each isolate were evaluated macroscopically and qualitatively based on a hypersensitive response (HR) or expanding sporulating lesions. As shown in Figure 3a, isolate 10, 11, and 12, and H2O control failed to generate any visible lesions, whereas isolate 1, 2, and 5 produced many tiny brown spots on S. pinnatisectum. Lesions caused by isolate 3, 4, and 6 were restricted to inoculation sites, but isolate 8 and 9 were more virulent on the inoculation sites of S. pinnatisectum (Figure 3a). Based on the pathotypes of isolate 8 and 9, functional homologs of R1, R2, R5, R8, R9, R10, and R11 may not be present in S. pinnatisectum or are not sufficient to trigger defense responses. On the contrary, only isolate 7 was avirulent on S. cardiophyllum (Figure 3d). Ten other isolates, except isolate 5, were more aggressive on the susceptible control S. cardiophyllum (Figure 3b–e). Interestingly, hypervirulent isolate 12, escaping the recognition of all 11 R genes S. demissum, and the isolate 6, which is avirulent on most of the R1–R11 differential hosts, produced similar pathotypes on S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum (Figure 3a,c). Moreover, we noticed that isolates 8 and 9, showing avirulence on R5, R8, and R9 differential hosts, were virulent on S. pinnatisectum. However, isolate 6, showing avirulence on R5, R8, and R9 differential host as well, was avirulent on S. pinnatisectum. Altogether, the distinct resistance patterns observed in the detached-leaf assay illustrate that the resistance machinery in S. pinnatisectum is complicated and no single R gene of R1–R11 determines the avirulence phenotype.

Table 2.
Solanum pinnatisectum and Solanum cardiophyllum show distinct patterns of the phenotype challenged by different isolates of Phytophthora infestans with a different ability to infect the differential set of potato carrying R1 to R11.
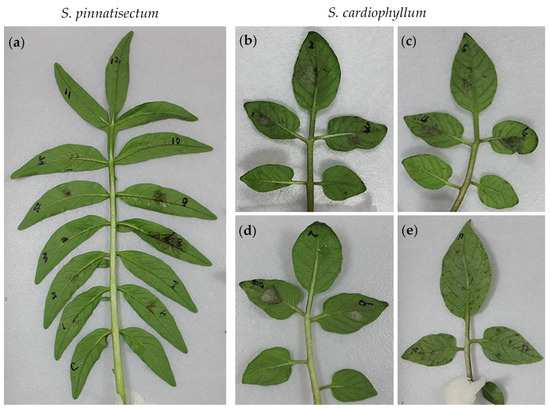

Figure 3.
Symptoms on Solanum pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum leaves inoculated with 12 isolates of Phytophthora infestans 4 days post-inoculation. (a) Symptoms on a leaflet of S. pinnatisectum inoculated with 12 isolates of P. infestans. (b) to (e) Symptoms on leaflets of S. cardiophyllum caused by 12 isolates of P. infestans. C: water control. The virulence spectrum of these 12 P. infestans isolates are described in Table 2.
2.4. RxLR Effector Screening Reveals Different R Protein Composition in S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum
Ten cloned notable RxLR effector genes (Avr genes) and two Avr-R gene pairs were delivered into S. pinnatisectum or S. cardiophyllum leaves by agroinfiltration. Based on the development of cell death symptoms, it is clear that S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum possess distinct recognition spectra of the Avr genes tested (Figure 4, Supplementary Table S1). Of the 10 tested Avr genes, 6 of them, Avr1, Avr2, Avr3aKI, Avr3b, Avr4, and Avrsmira2, triggered hypersensitive responses in S. pinnatisectum (Figure 4a,b), whereas in S. cardiophyllum, cell death was observed on leaves expressing Avrblb2, Avrsmira1, and Avrvnt1 (Figure 4c). The two potato species have distinct matching R genes, all of which belong to typical NBS-LRR resistance genes. The higher number of R genes in S. pinnatisectum may be responsible for its strong resistance to diverse isolates of P. infestans. Avr3aKI and Avr3a-R3a both triggered cell death in S. pinnatisectum, but functional R3a was absent in S. cardiophyllum. It is remarkable that neither Avrvnt1 nor the Avrvnt1/Rpivnt1 pair produced cell death in S. pinnatisectum, indicating that the presence of a specific interacting protein rather than a functional homolog of Rpi-vnt1 is needed for the initiation of HR.
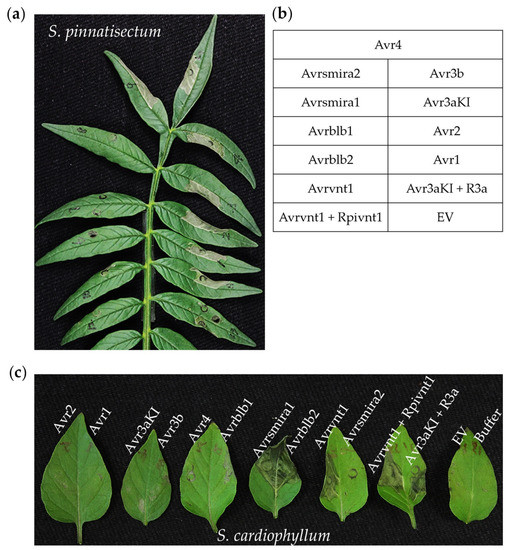
Figure 4.
Detection of cell death on Solanum pinnatisectum and Solanum cardiophyllum triggered by 10 cloned notable Avr genes and Avr-R gene pairs of Phytophthora infestans. Avrvnt1/Rpi-vnt1 and Avr3aKI/R3a were used as positive, buffer or empty vector (EV) was used as the negative control. Photographs were taken 3–4 days after agroinfiltration (a) Cell death on the leaflet of S. pinnatisectum caused by Avrsmira2, Avr4, Avr3b, Avr3aKI, Avr2, and Avr1. (b) Agroinfiltration sites with the matching Avr gene or Avr-R gene pair on each pinnately compound leaf. (c) Cell death on leaves of the susceptible cultivar S. cardiophyllum triggered by Avrsmira1, Avrblb2, and Avrvnt1.
More interestingly, this effector-based avirulence pattern does not perfectly match the inoculation pathotypes. For instance, R1 and R2 functional alleles were detected via the effector infiltration assay in S. pinnatisectum, and some Avr1- or Avr2-expressing isolates still caused infection whereas some Avr1- and/or Avr2-expressing isolates did not (Figure 4a, Table 2). Similarly, even though Rpi-blb2, Rpi-smira1, and Rpi-vnt1 are expressed in S. cardiophyllum (Figure 4c) and the expression of some cognate Avr genes was validated in several tested isolates [25], 11 out of the 12 tested P. infestans isolates were more aggressive on this wild potato species (Table 2). These results raise the possibility that pathogens deliver multiple effectors to suppress effector-triggered immunity (ETI) and induce potato susceptibility.
2.5. Transcriptome Dynamics of NLR Genes in Susceptible and Resistant Potatoes against P. infestans
According to the previous histological observations in susceptible and resistant cultivars upon P. infestans challenge, four key time points were established at the early stage of infection. Inoculated leaves of S. cardiophyllum or S. pinnatisectum were collected at 6, 9, and 12 hpi, and samples at 0 hpi were used as the control, respectively. Illumina sequencing was conducted to generate transcriptome profiles of both the pathogen and potato over the infection time course. A summary of the number of potato reads after sequence filtering to remove short-length and low-quality sequences is shown in Supplementary Table S2. Approximately 31–70% of the sequences from each sample were mapped to the S. tuberosum genome.
To characterize the molecular basis of the defense mechanism induced after pathogen infection, we identified the NLR genes (see the materials and methods) from the potato genome and investigated their expression. A total of 123 NLR genes were annotated. Of these, 112 have at least one read in at least one sample. Clustering of the expression profiling of the NLR genes revealed that they could be divided into two groups related to the resistant (Sp) and susceptible (Sc) potato cultivar, respectively (Figure 5). Previous studies showed that Rpi1 and Rpi2 have been mapped to chromosome 7 of S. pinnatisectum [20]. However, according to our RNAseq data, only two NLRs, PGSC0003DMG401030700 and PGSC0003DMG400017317, were dramatically upregulated in the chromosome 7 region of S. pinnatisectum and S. cardophyllum, respectively. In general, over 60% of NLRs were induced and exhibited higher expression levels in S. pinnatisectum but not in S. cardiophyllum after P. infestans infection. In particular, R1 homologue (PGSC0003DMG402004578), R2 homolgue (PGSC0003DMG400025259), and R3a-like genes (PGSC0003DMG400009455, PGSC0003DMG400018570, and PGSC0003DMG400027377) were identified in the upregulated NLRs of the Sp group. Thus, the massive expression of NLR genes in S. pinnatisectum is probably responsible for the resistant phenotype of S. pinnatisectum. While most of the NLR genes coinciding with S. pinnatisectum resistance are highly expressed at 12 hpi, some of them are expressed immediately upon infection (Figure 5), indicating that S. pinnatisectum may recruit different NLRs at different stages to deal with the pathogen attack.
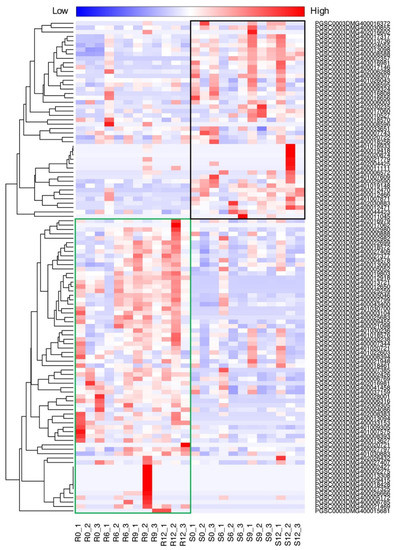
Figure 5.
Expression profile of putative nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat (NLR) orthologous genes in infected S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum at 0, 6, 9, and 12 hpi. The heatmap indicates the sum of counts per million (CPM) values for genes in subclasses; the data are in Supplementary Material file S1. The green rectangle frame harbors most upregulated NLR genes in S. pinnatisectum. The black rectangle frame includes the most upregulated NLR genes in S. cardiophyllum. Each time point contains three replicates. R, refers to S. pinnatisectum; S, refers to S. cardiophyllum.
3. Discussion
Compared to other wild potato species, very few novel R genes or functional homologues have been identified from S. pinnatisectum in the last two decades, but this Mexican wild potato species has been proposed to contain potential qualitative and quantitative resistance against P. infestans. Kuhl et al. [18] characterized 13 accessions of S. pinnatisectum by means of P. infestans zoospore inoculation, and more than 10 of them showed resistance, including accession PI275233. A large proportion of 44 S. pinnatisectum accessions were reported to be resistant to P. infestans in laboratory assays and in field sprays [8]. In agreement with the above results, our studies verified that S. pinnatisectum displayed considerable resistance against multiple P. infestans isolates, which are characterized by different SSR genotypes and diverse pathotypes [5]. Especially, those predominant isolates, which are virulent to the R1–R11 potato differential set, failed to infect this wild potato species. On the contrary, these supervirulent isolates induced rapidly expanding water-soaked lesions on susceptible cultivars of S. cardiophyllum. Remarkable resistance or tolerance against P. infestans was observed from 3 to 72 hpi, and much lower amounts of inoculum proliferated in the diseased tissue of S. pinnatisectum.
The interaction between Avr and R protein triggered immediate and strong hypersensitive responses (HRs) in plant cells, which led to lesion-free phenotypes or could be visible as localized cell death [26]. The responses of plants to pathogen stress were more obvious and pervasive in mesophyll cells within 9 to 12 hpi but were rare in the susceptible control, S. cardiophyllum. Necrosis was visible in the infected mesophyll cells of S. pinnatisectum at 12 hpi and later, indicating that the HR was induced upon infection. As a result, expansion of P. infestans was restricted to the epidermis, consistent with other resistant germplasm of potato [27]. Significant variations of histological characteristics in the infection processes between S. pinnatisectum and the susceptible control S. cardiophyllum also illustrates that defense responses are different from penetration resistance as cysts normally geminated and penetrated into epidermal cells before 6 hpi. Thus, the R gene-mediated ETI probably plays a key role in disease resistance and tolerance under P. infestans challenge. The RNA-seq data verified this hypothesis by revealing an upregulation of many ETI components.
To sketch the genetic resistance of S. pinnatisectum, we first revaluated the late blight resistance of S. pinnatisectum by using different P. infestans isolates with distinct pathotypes. Surprisingly, only two isolates (No. 8 and 9) could readily infect S. pinnatisectum, indicating that the expression of Avr1 and Avr2 did not affect the infection. Supervirulent dominant isolates (No. 12) rarely infected this resistant cultivar but displayed high aggressiveness on S. cardiophyllum. Pathotype association analysis suggests that multiple genes govern the resistance. The use of P. infestans strains could be challenging, because multiple R genes in resistant cultivars can mask recognition specificities. Many resistance breeding studies have employed Phytophthora RxLR effectors rather than diverse P. infestans isolates as markers to mine novel R genes or dissect functional R gene alleles [28]. To better discriminate the specific R gene activities, in this research, we also took advantage of the RxLR effector screen and RNA-seq analysis and discovered a distinct group of NLR genes that are responsible for the remarkable resistance of S. pinnatisectum.
The functional homologues of qualitative R genes R1, R2, R3a, R3b, and R4 and quantitative R gene Rpi-smira2 could be accurately detected using Avr1, Avr2, Avr3aKI, Avr3b, Avr4, and Avrsmira2 in S. pinnatisectum. The pathogenic variations of different Avr1- and Avr2-expressing isolates suggest that other potential Avr genes are involved in R gene recognition or ETI suppression. Such a special case is that the loss of resistance of Rpi-blb1 (RB) is caused by ETI suppressing the variant of Avrblb1 [29]. Thus, the detection of mutations in cloned Avr probe genes may not be sufficient for a virulent profile prediction of filed isolates. This is different from the scenario of P. sojae, in which the presence of functional Avr genes in selected isolates is highly consistent with their avirulent phenotype [30]. Moreover, co-expression of Avrvnt1 and Rpi-vnt1 or single Avrvnt1 failed to induce HR in S. pinnatisectum, suggesting that specific interacting proteins are needed for Avrvnt1-Rpi-vnt1 recognition. As Gao C et al. pointed out [31], glycerate 3-kinase (GLYK) is involved in activation of of Rpi-vnt1. Similarly, Avrblb1 and Rpi-blb1 only triggered typical HR in N. benthamiana but not in Arabidopsis thaliana, indicating that species-specific interactors are involved in cell death induction [32]. According to the guard model and the decoy model, the Avr-R protein recognition specificity would depend on secondary molecules. For example, BSL1 was initially identified as a key chaperone for PiAvr2 and R2 interaction, and then was predicted to regulate multiple R gene-mediated immunity responses [33]. As a result, future studies should not only seek identification of novel genes conferring resistance but also patterns of defense genes activated in ETI.
None of those six R genes exist in S. cardiophyllum, but three other R genes (Rpi-blb2, Rpi-vnt1, and Rpi-smira1) were detected in this susceptible control by transient expression of cognate Avr genes. These R genes did not provide adequate resistance for this cultivar and resulted in high susceptibility. Currently, for late-blight management, breeders prefer to pyramid multiple R genes in one cultivar to avoid the rapid defeat of R genes [11]. Here, we have an opposite example, as although Rpi-blb2 and Rpi-vnt1 were documented as a broad-spectrum resistance gene from S. bulbocastanum and S. venturi [34,35], the natural combination of Rpi-blb2, Rpi-vnt1, and Rpi-smira1 in S. cardiophyllum changed its susceptibility against most isolates used in our detached-leaf inoculation assay. Moreover, the mutation or silencing of cognate RXLR effectors may not be responsible for the loss of resistance, since the transcripts of conserved Avrvnt1, Avrblb2, and Avrsmira1 were detected in at least one of isolate 1, 6, or 12 [25]. Thus, more effort is necessary for the construction of desired long-term stable resistant cultivars.
Despite only part of the known Avr genes being employed in the screening, the results suggest that more active R genes were clustered in S. pinnatisectum. It is also reported that even defeated R genes in wild potatoes may lead to a delay in infection. Considering that all tested local isolates of P. infestans contain truncated Avr4 [25], our findings suggest that the remarkable resistance of S. pinnatisectum is probably due to pyramiding of R1, R2, R3a, R3b, and Rpi-smira2. Of course, genetic validations are required to test whether the desired resistance can be attributed to these functional alleles. Then, the major genes for late blight resistance can be cis-transformed into potato cultivars. In addition, the degree of resistance is dependent on the genotype of the P. infestans population, and monitoring for virulence to specific R genes in the local P. infestans population can assist the deployment of R genes [36]. Once the transgenic techniques are broadly accepted, it could accelerate genetic modifications with R genes.
The RNA-seq data revealed that a massive number of immune-associated NLR genes, including a distinct NLR gene group, were dramatically upregulated in S. pinnatisectum. Despite the low similarity between different orthologs and some species-specific NLR genes being absent in our mapping process, the RNA profile analysis validated the previous effector screen and demonstrated the expression of multiple NLR genes. Considering that most of the known resistant genes belong to the NBS-LRR superfamily with a 3-kb average length [17], we mapped RNAseq reads to 123 full-length NLR genes with an entire NB-ARC and LRR domain. Similarly, Andolfo et al. employed cDNA RENseq to identify 124 and 221 full-length NB-LRR in two tomatoes [37]. Furthermore, taking advantage of the RENseq technique to enrich pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) [38], NLR and other ETI components could provide a better understanding of the broad and durable resistance mechanisms in S. pinnatisectum.
Our preliminary investigation of the resistance mechanisms in S. pinnatisectum provides an opportunity to explore potential novel ETI components and the effective combination of R genes for late-blight resistance breeding. Indeed, the employment of genetic engineering into late-blight resistance breeding programs should speed up the race against P. infestans. However, rational deployment of effective R genes and gene pyramiding can extend the durability of such resistance and offers potato growers an environmentally friendly alternative for late-blight management.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant and Pathogen Materials
The diploid potato species, S. pinnatisectum (Accession PI275233) and S. cardiophyllum (Accession PI186548), which are resistant or susceptible to P. infestans, respectively, were used in this study. Both species were propagated in vitro in sterile jars containing Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented with sucrose and grown for about 6 weeks after transplanting into nutrient soil at 20–25 °C under a 14 h:10 h day/night photoperiod.
All P. infestans isolates were previously described [5,25] and were routinely maintained on RSA (rye sucrose agar) medium. The numerous sporangia collected from 7- to 10-day cultures were chilled with cold sterilized water at 4 °C for about 1 h to release zoospores. The zoospores were filtered through one layer of Miracloth and the concentration was adjusted to 1 × 105 zoospores/mL. A highly aggressive isolate of P. infestans Pi21336, which overcomes the R1–R11 genes of potato, was used for inoculation of S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum in the histological and transcriptomic analyses. Additionally, 12 other isolates with complex virulence spectra (Table 2) were also used for detecting the genetic resistance of S. pinnatisectum. The pathogenicity of the 12 P. infestans isolates on S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum was evaluated 3–4 days post-inoculation (dpi). The inoculation site for the 12 isolates on each leaflet was randomized. Three leaflets of S. pinnatisectum and 12 leaflets of S. cardiophyllum were used for each repetition and the experiment was repeated twice.
4.2. Lesion Measurement and Biomass Analysis
Pictures of diseased leaves were taken at 4 dpi, and the relative lesion sizes were measured with ImageJ software. For the qPCR analyses, samples (20 μL) were prepared by mixing 1 μL (5 ng) of gDNA and 19 μL of 2 × SYBR Green mix (Bimake, Houston, TX, USA) with the appropriate primers (Table S3) added to a final concentration of 5 μM each and water. PCRs were performed in triplicate for each biological sample, using the default relative quantification program of CFX connect Real-Time PCR System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Ct values were determined with the included Bio-Rad software. The detection of real-time PCR products, calculations, and statistical analysis were performed as previously described [39].
4.3. Microscopic Characterization of S. pinnatisectum Infected by P. infestans
Detached-leaf inoculations were conducted as previously described [25] with some modifications. Leaflets were detached from robust growing plants in the greenhouse, placed on water-saturated filter paper in a tray, and inoculated on the abaxial side of both S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum with 10-μL droplets containing approximately 103 zoospores. The inoculated leaves were kept in moisture trays sealed with plastic wrap at 18 °C in the dark for the first 12 h, and then the trays were incubated at 18 °C under a photoperiod of 16 h light and 8 h darkness. For microscopic observations, samples were obtained at 3, 6, 9, 12, and 72 hpi. Samples were stained with trypan blue staining following the protocol described by Wang et al. [40]. The experiment was repeated at least three times.
4.4. In planta Transient Expression of Known Avr Genes of P. infestans
To detect the Rpi genes known for Solanum spp. in S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum, 10 notable RxLR effector genes of P. infestans, Avr1, Avr2, Avr3aKI, Avr3b, Avr4, Avrsmira1, Avrsmira2, Avrblb1, Avrblb2, and Avrvnt1 were cloned into pDonr201, and subcloned into pmAEV using LR clonase (Invitrogen, USA) and then transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 by heat shock treatment. The coding sequences of two resistance genes, R3a and Rpi-vnt1, were directly synthesized (Genscript Inc.,Nanjing, China) and inserted into a pmAEV vector.
Agroinfiltration was performed as previously described [25]. Briefly, A. tumefaciens strains were grown to an optical density at 600 nm of 0.2, and leaf panels of 6- to 8-week-old potato plants were infiltrated with the A. tumefaciens suspensions. The position for infiltration was randomized. Cell death was monitored from 4 to 6 days post-infiltration. The experiment was repeated three times. Analysis of each Avr gene consisted of five or three infiltrated leaves of S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum, respectively.
4.5. RNA-seq and Profiling of the Expression of NLR Genes
RNA was obtained by grinding tissue in liquid nitrogen, followed by extraction using the RNeasy Plant Mini Kit from Qiagen. The quality and integrity of purified RNA were verified with the Qubit® RNA Assay Kit in a Qubit® 2.0 Flurometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and the RNA Nano 6000 Assay Kit of the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), respectively. A total of 1.5 µg of RNA per sample were used for the generation of sequencing libraries using the NEBNext® Ultra™ RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® (NEB, Ipswich, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The PCR products were purified (AMPure XP system) and library quality was assessed on the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2100 system. The clustering of the index-coded samples was conducted on a cBot Cluster Generation System using the TruSeq PE Cluster Kit v3-cBot-HS (Illumina) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Finally, the library preparations were sequenced on an Illumina Hiseq platform and paired-end reads were generated. RNA sequencing data was deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (BioProject: PRJNA616420).
Reads passing the quality filter were aligned with the Solanum tuberosum reference genome using hisat2 2.1.0 [41] with default parameters. The number of mapped reads of each gene were counted by using featureCounts [42]. The TPM values (transcripts per million) of the genes in each library were calculated with in-house Perl script. To identify the NLR genes in potato, total potato proteins [43] were scanned for the NBS domain and LRR clans with hmmscan in the HMMER 3.1b2 package [44], with trusted cutoff parameters enabled (i.e., --cut_tc). Sequences containing both the NBS domain and LRR repeat were regarded as NLR candidates. The RNA-seq data were used to profile the expression of these NLR genes.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary Material can be found at https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/9/3211/s1. File S1: the CPM values for mapped genes in potato genome; Table S1: Agroinfiltration of 10 Avr genes in S. pinnatisectum and S. cardiophyllum; Table S2: Summary of high-quality reads and matching to Solanum tuberosum genome; Table S3: Primers used in this study.
Author Contributions
B.G. and H.Z. conceived the research; H.Z., X.C., Z.C., X.Z., and W.L. performed the experiment; B.G. and Q.W. performed RNA-seq data analysis; Q.C. supplied the plant material for all the experiments; B.G., H.Z., Q.W. and Q.C. wrote the paper with contributions from all authors. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2018JM3030), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M582716), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31301644).
Acknowledgments
We appreciate Weixing Shan (Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China) for kindly providing P. infestans strains; Brett M. Tyler (Oregon State University, Corvallis, USA) for pleasant collaborations on the effector set. We thank Xili Liu and Jianqiang Miao (Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China) for critical reading of the manuscript and useful discussions. Xiaoli Cao’s research work for her master thesis [24] is partially included in the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Abbreviations
| Avr gene | Avirulence gene |
| EBN | Endosperm Balance Number |
| ETI | Effector Triggered Immunity |
| hpi | hours post inoculation |
| HR | Hypersensitive Response |
| NLR | NBS-LRR (nucleotide-binding site and leucine-rich repeat) |
| PRR | Pattern Recognition Receptor |
| PVX | Potato Virus X |
| QTL | Quantitative Trait Loci |
| RENseq | Resistance Gene Enrichment and Sequencing Method |
| R gene | Resistance gene |
| Rpi | Resistance (R) genes to P. infestans |
| RSA | Rye Sucrose Agar |
References
- Savary, S.; Willocquet, L.; Pethybridge, S.J.; Esker, P.; McRoberts, N.; Nelson, A. The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, W. Phytophthora infestans: The plant (and R gene) destroyer. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2008, 9, 385–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, W.E.; Birch, P.R.J.; Judelson, H.S.; Grunwald, N.J.; Danies, G.; Everts, K.L.; Gevens, A.J.; Gugino, B.K.; Johnson, D.A.; Johnson, S.B.; et al. Five reasons to consider Phytophthora infestans a reemerging pathogen. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 966–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooke, D.E.; Cano, L.M.; Raffaele, S.; Bain, R.A.; Cooke, L.R.; Etherington, G.J.; Deahl, K.L.; Farrer, R.A.; Gilroy, E.M.; Goss, E.M.; et al. Genome analyses of an aggressive and invasive lineage of the Irish potato famine pathogen. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Yin, J.L.; Sun, J.P.; Ma, H.M.; Ma, Y.F.; Quan, J.L.; Shan, W.X. Population structure of the late blight pathogen Phytophthora infestans in a potato germplasm nursery in two consecutive years. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 771–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicki, M.; Foolad, M.R.; Nowakowska, M.; Kozik, E.U. Potato and tomato late blight caused by Phytophthora infestans: An overview of pathology and resistance breeding. Plant. Dis. 2012, 96, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A. New strategies towards durable late blight resistance in potato. In The Potato Genome; Kumar Chakrabarti, S., Xie, C., Kumar Tiwari, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A.; Finkers, R.; Budding, D.; Visser, M.; Jacobs, M.M.J.; van Berloo, R.; Pel, M.; Champouret, N.; Bakker, E.; Krenek, P.; et al. SolRgene: An online database to explore disease resistance genes in tuber-bearing Solanum species. BMC Plant. Biol. 2011, 11, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodewald, J.; Trognitz, B. Solanum resistance genes against Phytophthora infestans and their corresponding avirulence genes. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2013, 14, 740–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marla, S.S. Structural analysis of resistance (R) genes in potato (Solanum species) genome. In The Potato Genome; Kumar Chakrabarti, S., Xie, C., Kumar Tiwari, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.X.; Li, Y.; Vossen, J.H.; Visser, R.G.F.; Jacobsen, E. Functional stacking of three resistance genes against Phytophthora infestans in potato. Transgenic Res. 2012, 21, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleeshouwers, V.G.; Oliver, R.P. Effectors as tools in disease resistance breeding against biotrophic, hemibiotrophic, and necrotrophic plant pathogens. Mol. Plant. Microbe Interact. 2014, 27, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.K.; Young, C.; Lee, M.; Oliva, R.; Bozkurt, T.O.; Cano, L.M.; Win, J.; Bos, J.I.B.; Liu, H.Y.; van Damme, M.; et al. In planta expression screens of Phytophthora infestans RXLR effectors reveal diverse phenotypes, including activation of the Solanum bulbocastanum disease resistance protein Rpi-blb2. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2928–2947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A.; Rietman, H.; Krenek, P.; Champouret, N.; Young, C.; Oh, S.K.; Wang, M.Q.; Bouwmeester, K.; Vosman, B.; Visser, R.G.F.; et al. Effector genomics accelerates discovery and functional profiling of potato disease resistance and Phytophthora infestans avirulence genes. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietman, H.; Bijsterbosch, G.; Cano, L.M.; Lee, H.R.; Vossen, J.H.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G.F.; Kamoun, S.; Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A. Qualitative and quantitative late blight resistance in the potato cultivar Sarpo Mira is determined by the perception of five distinct RXLR effectors. Mol. Plant. Microbe 2012, 25, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokossou, A.A.; Rietman, H.; Wang, M.Q.; Krenek, P.; van der Schoot, H.; Henken, B.; Hoekstra, R.; Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A.; van der Vossen, E.A.G.; Visser, R.G.F.; et al. Diversity, distribution, and evolution of Solanum bulbocastanum late blight resistance genes. Mol. Plant. Microbe 2010, 23, 1206–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupe, F.; Pritchard, L.; Etherington, G.J.; Mackenzie, K.; Cock, P.J.; Wright, F.; Sharma, S.K.; Bolser, D.; Bryan, G.J.; Jones, J.D.; et al. Identification and localisation of the NB-LRR gene family within the potato genome. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, J.C.; Hanneman, R.E.; Havey, M.J. Characterization and mapping of Rpi1, a late-blight resistance locus from diploid (1EBN) Mexican Solanum pinnatisectum. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2001, 265, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Kawchuk, L.M.; Lynch, D.R.; Goettel, M.S.; Fujimoto, D.K. Identification of late blight, Colorado potato beetle, and blackleg resistance in three Mexican and two south American wild 2x (1EBN) Solanum species. Am. J. Potato Res. 2003, 80, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, D.D.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, L.; Cao, X.L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q. A new resistance gene against potato late blight originating from Solanum pinnatisectum located on potato chromosome 7. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.H.; Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A.; Jacobsen, E.; van der Vossen, E.; Visser, R.G.F. Molecular breeding for resistance to Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bary in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.): A perspective of cisgenesis. Plant Breed 2009, 128, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghislain, M.; Trognitz, B.; Herrera, M.D.; Solis, J.; Casallo, G.; Vasquez, C.; Hurtado, O.; Castillo, R.; Portal, L.; Orrillo, M. Genetic loci associated with field resistance to late blight in offspring of Solanum phureja and S. tuberosum grown under short-day conditions. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokossou, A.A.; Park, T.H.; van Arkel, G.; Arens, M.; Ruyter-Spira, C.; Morales, J.; Whisson, S.C.; Birch, P.R.J.; Visser, R.G.F.; Jacobsen, E.; et al. Exploiting knowledge of R/Avr genes to rapidly clone a new LZ-NBS-LRR family of late blight resistance genes from potato linkage group IV. Mol. Plant. Microbe 2009, 22, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.L. Research on Late Blight Resistance and Amino Acid Transporter Genes in Potato. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, China, June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, J.L.; Gu, B.; Huang, G.Y.; Tian, Y.; Quan, J.L.; Lindqvist-Kreuze, H.; Shan, W.X. Conserved RXLR effector genes of Phytophthora infestans expressed at the early stage of potato infection are suppressive to host defense. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplan, J.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. Recognition and signal transduction associated with R gene-mediated resistance. In Natural Resistance Mechanisms of Plants to Viruses; Loebenstein, G., Carr, J.P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Switzerland, 2006; pp. 73–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.M.; Thieme, R.; Gao, X.N.; Kang, Z.S.; Huang, L.L. Investigation of host responses of different potato genotypes at tissue, cellular and subcellular levels after infection with Phytophthora infestans. Am. J. Potato Res. 2013, 90, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenman, M.; Ali, A.; Muhlenbock, P.; Carlson-Nilsson, U.; Liljeroth, E.; Champouret, N.; Vleeshouwers, V.G.; Andreasson, E. Effector-driven marker development and cloning of resistance genes against Phytophthora infestans in potato breeding clone SW93-1015. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Halterman, D.A. Molecular determinants of resistance activation and suppression by Phytophthora infestans effector IPI-O. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dussault-Benoit, C.; Arsenault-Labrecque, G.; Sonah, H.; Belzile, F.; Belanger, R.R. Discriminant haplotypes of avirulence genes of Phytophthora sojae lead to a molecular assay to predict phenotypes. Mol Plant. Pathol. 2020, 21, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Xu, H.; Huang, J.; Sun, B.; Zhang, F.; Savage, Z.; Duggan, C.; Yan, T.; Wu, C.H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Pathogen manipulation of chloroplast function triggers a light-dependent immune recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9613–9620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shao, G.D.; Gao, W.X.; Gu, B. Double-barreled particle bombardment mediated transient gene expression in Arabidopsis. Chin. Bull. Bot. 2020, 55. Available online: http://www.chinbullbotany.com/CN/10.11983/CBB19169 (accessed on 28 November 2019). [CrossRef]
- Saunders, D.G.O.; Breen, S.; Win, J.; Schornack, S.; Hein, I.; Bozkurt, T.O.; Champouret, N.; Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A.; Birch, P.R.J.; Gilroy, E.M.; et al. Host protein BSL1 associates with Phytophthora infestans RXLR effector AVR2 and the Solanum demissum immune receptor R2 to mediate disease resistance. Plant. Cell 2012, 24, 3420–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbegozo, J.; Roman, M.L.; Rivera, C.; Gamboa, S.; Tovar, J.C.; Forbes, G.A.; Lindqvist-Kreuze, H.; Kreuze, J.F.; Ghislain, M. Rpi-blb2 gene from Solanum bulbocastanum confers extreme resistance to late blight disease in potato. Plant. Cell Tiss. Org. 2016, 125, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.R.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, T.Y.; Bergervoet, M.; Jongsma, M.A.; Visser, R.G.; Jacobsen, E.; Vossen, J.H. Development of late blight resistant potatoes by cisgene stacking. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vleeshouwers, V.G.A.A.; Raffaele, S.; Vossen, J.H.; Champouret, N.; Oliva, R.; Segretin, M.E.; Rietman, H.; Cano, L.M.; Lokossou, A.; Kessel, G.; et al. Understanding and exploiting late blight resistance in the age of effectors. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 507–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andolfo, G.; Jupe, F.; Witek, K.; Etherington, G.J.; Ercolano, M.R.; Jones, J.D.G. Defining the full tomato NB-LRR resistance gene repertoire using genomic and cDNA RenSeq. BMC Plant. Biol. 2014, 14, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witek, K.; Jupe, F.; Witek, A.I.; Baker, D.; Clark, M.D.; Jones, J.D.G. Accelerated cloning of a potato late blight-resistance gene using RenSeq and SMRT sequencing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.G.; McDowell, J.M. A PCR assay for the quantification of growth of the oomycete pathogen Hyaloperonospora arabidopsidis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, Y.L.; Zhang, M.; Tong, X.M.; Wang, Q.H.; Sun, Y.Y.; Quan, J.L.; Govers, F.; Shan, W.X. Infection of Arabidopsis thaliana by Phytophthora parasitica and identification of variation in host specificity. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2011, 12, 187–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Landmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pan, S.K.; Cheng, S.F.; Zhang, B.; Mu, D.S.; Ni, P.X.; Zhang, G.Y.; Yang, S.; Li, R.Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 2011, 475, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Finn, R.D.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A.; Punta, M. Challenges in homology search: HMMER3 and convergent evolution of coiled-coil regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).