Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Adenylyl Cyclase Inhibition and Phosphoinositide Hydrolysis
3. Muscarinic Regulation of Ion Channel Activity
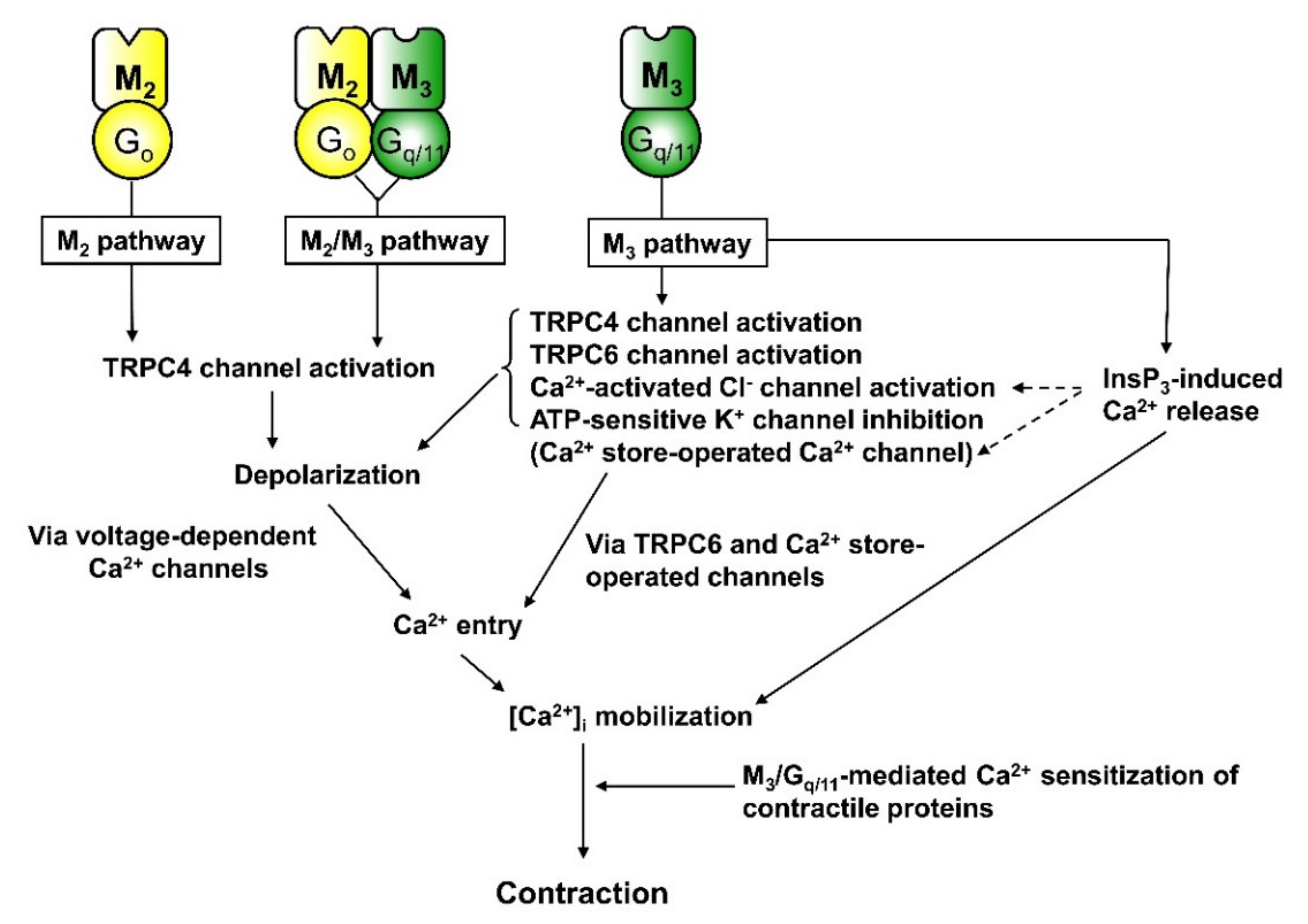
3.1. Activation of Non-Selective Cationic Channels
3.2. Regulation of K+ and Cl− Channels
3.3. Inhibition of Voltage-Dependent Ca2+ Channels
4. Depolarisation
5. Ca2+ Sensitisation of Contraction
6. Heterologous Desensitisation of Contraction
7. Smooth Muscle Contraction
7.1. Contraction Evoked by Applied Muscarinic Agonists
7.2. Cholinergic Nerve-Mediated Contraction
7.3. Indirect Contraction by Inhibiting Cyclic AMP-Dependent Relaxation
7.4. Muscarinic Contractile Mechanisms in Mouse Intestinal Smooth Muscle
8. In Vivo and In Vitro Gastrointestinal Motility
9. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACh | acetylcholine |
| BK channels | large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels |
| [Ca2+]i | intracellular Ca2+ concentration |
| cAMP | cyclic AMP |
| DAG | diacylglycerol |
| EC50 | 50% effective concentration |
| EFS | electrical field stimulation |
| EJP | excitatory junction potential |
| Emax | maximum response |
| G-proteins | GTP binding proteins |
| Ica | Ca2+ current |
| ICCs | interstitial cells of Cajal |
| InsP3 | inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate |
| KATP channels | ATP-sensitive K+ channels |
| KO | knockout |
| mIcat | mAChR-mediated cationic current |
| muscarinic acetylcholine receptors | mAChRs |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NPY | neuropeptide Y |
| pEC50 | negative logarithm of EC50 |
| PGF2α | prostaglandin F2α |
| PIP2 | phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PLC | phospholipase C |
| PTX | pertussis toxin |
| RASSL | Receptor Solely by Synthetic Ligand |
| STOCs | spontaneous transient outward currents |
| TRPC channels | Transient receptor potential canonical channels |
| VDCCs | voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels |
References
- Caulfield, M.P. Muscarinic receptors-characterization, coupling and function. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 58, 319–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, M.; Birdsall, N. International Union of Pharmacology. XVII. Classification of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1998, 50, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felder, C.C. Muscarinic acetylcholine-receptors-signal-transduction through multiple effectors. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wess, J. Molecular biology of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 1996, 10, 69–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jositsch, G.; Papadakis, T.; Haberberger, R.; Wolff, M.; Wess, J.; Kummer, W. Suitability of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antibodies for immunohistochemistry evaluated on tissue sections of receptor gene-deficient mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2009, 379, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wess, J.; Duttaroy, A.; Zhang, W.; Gomeza, J.; Cui, Y.; Miyakawa, T.; Bymaster, F.P.; McKinzie, L.; Felder, C.C.; Lamping, K.G.; et al. M-1-M-5 muscarinic receptor knockout mice as novel tools to study the physiological roles of the muscarinic cholinergic system. Recept. Channels 2003, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Yamada, S.; Oki, T.; Manabe, T.; Taketo, M.M.; Ehlert, F.J. Functional analysis of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors using knockout mice. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wess, J. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor knockout mice: Novel phenotypes and clinical implications. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2004, 44, 423–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eglen, R.M.; Hegde, S.S.; Watson, N. Muscarinic receptor subtypes and smooth muscle function. Pharmacol. Rev. 1996, 48, 531–565. [Google Scholar]
- Sol, I.; Yang, D.K.; Kim, H.J.; Min, K.W.; Kang, T.M.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, K.W.; Park, K.H.; Jeon, J.H.; Choi, K.H.; et al. Five subtypes of muscarinic receptors are expressed in gastric smooth muscles of guinea pig. Exp. Mol. Med. 2003, 35, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Bolton, T.B. Mechanisms of action of transmitters and other substances on smooth-muscle. Physiol. Rev. 1979, 59, 606–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beech, D.J. Actions of neurotransmitters and other messengers on Ca2+ channels and K+ channels in smooth muscle cells. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 73, 91–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlert, F.J.; Thomas, E.A. Functional-role of M(2) muscarinic receptors in the guinea-pig ileum. Life Sci. 1995, 56, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, T.B.; Prestwich, S.A.; Zholos, A.V.; Gordienko, D.V. Excitation-contraction coupling in gastrointestinal and other smooth muscles. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1999, 61, 85–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlert, F.J.; Ostrom, R.S.; Sawyer, G.W. Subtypes of the muscarinic receptor in smooth muscle. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, G.W.; Ehlert, F.J. Muscarinic M-3 receptor inactivation reveals a pertussis toxin-sensitive contractile response in the guinea pig colon: Evidence for M-2/M-3 receptor interactions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 464–476. [Google Scholar]
- Zholos, A.V.; Bolton, T.B. Muscarinic receptor subtypes controlling the cationic current in guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 122, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komori, S.; Unno, T.; Nakayama, T.; Ohashi, H. M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors couple, respectively, with activation of nonselective cationic channels and potassium channels in intestinal smooth muscle cells. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 76, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucovsky, V.; Zholos, A.V.; Bolton, T.B. Muscarinic cation current and suppression of Ca2+ current in guinea pig ileal smooth muscle cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 346, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Fujinami, K.; Goto, H.; Fujita, A.; Taketo, M.M.; Manabe, T.; Matsui, M.; Hata, F. Roles of M-2 and M-4 muscarinic receptors in regulating acetylcholine release from myenteric neurons of mouse ileum. J. Neurophysiol. 2005, 93, 2841–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, T.; Toyoshima, M.; Mukai, K.; Hagi, K.; Matsui, M.; Nakajima, H.; Azuma, Y.T.; Hata, F. Involvement of M-2 muscarinic receptors in relaxant response of circular muscle of mouse gastric antrum. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2006, 18, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, A.M.; Hutson, J.M.; Southwell, B.R. Cholinergic neurotransmission and muscarinic receptors in the enteric nervous system. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 2010, 44, 173–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Unno, T.; Kitazawa, T.; Taneike, T.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Nishimura, M.; Komori, S. Three distinct muscarinic signalling pathways for cationic channel activation in mouse gut smooth muscle cells. J. Physiol. Lond. 2007, 582, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murthy, K.S.; Makhlouf, G.M. Differential coupling of muscarinic m(2) and m(3) receptors to adenylyl cyclases V/VI in smooth muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 21317–21324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tran, J.A.; Matsui, M.; Ehlert, F.J. Differential coupling of muscarinic M-1, M-2, and M-3 receptors to phosphoinositide hydrolysis in urinary bladder and longitudinal muscle of the ileum of the mouse. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noronhablob, L.; Lowe, V.; Patton, A.; Canning, B.; Costello, D.; Kinnier, W.J. Muscarinic receptors-relationships among phosphoinositide breakdown, adenylate-cyclase inhibition, in vitro detrusor muscle contractions and invivo cystometrogram studies in guinea-pig bladder. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1989, 249, 843–851. [Google Scholar]
- Candell, L.M.; Yun, S.H.; Tran, L.L.P.; Ehlert, F.J. Differential coupling of subtypes of the muscarinic receptor to adenylate-cyclase and phosphoinositide hydrolysis in the longitudinal muscle of the rat ileum. Mol. Pharmacol. 1990, 38, 689–697. [Google Scholar]
- Murthy, K.S.; Zhou, H.P.; Grider, J.R.; Brautigan, D.L.; Eto, M.; Makhlouf, G.M. Differential signalling by muscarinic receptors in smooth muscle: m2-mediated inactivation of myosin light chain kinase via G(i3), Cdc42/Rac1 and p21-activated kinase 1 pathway, and m3-mediated MLC20 (20 kDa regulatory light chain of myosin II) phosphorylation via Rho-associated kinase/myosin phosphatase targeting subunit 1 and protein kinase C/CPI-17 pathway. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carl, A.; Lee, H.K.; Sanders, K.M. Regulation of ion channels in smooth muscles by calcium. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1996, 271, C9–C34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholos, A.V. Muscarinic effects on ion channels in smooth muscle cells. Neurophysiology 1999, 31, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Tanahashi, Y.; Yan, H.D.; Komori, S. Muscarinic cationic current in gastrointestinal smooth muscles: Signal transduction and role in contraction. Auton. Autacoid Pharm. 2006, 26, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, R.; Isenberg, G. Acetylcholine activates nonselective cation channels in guinea-pig ileum through a g-protein. Am. J. Physiol. 1990, 258, C1173–C1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacaud, P.; Bolton, T.B. Relation between muscarinic receptor cationic current and internal calcium in guinea-pig jejunal smooth-muscle cells. J. Physiol. Lond. 1991, 441, 477–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komori, S.; Kawai, M.; Takewaki, T.; Ohashi, H. Gtp-binding protein involvement in membrane currents evoked by carbachol and histamine in guinea-pig ileal muscle. J. Physiol. Lond. 1992, 450, 105–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.D.; Okamoto, H.; Unno, T.; Tsytsyura, Y.D.; Prestwich, S.A.; Komori, S.; Zholos, A.V.; Bolton, T.B. Effects of G-protein-specific antibodies and G beta gamma subunits on the muscarinic receptor-operated cation current in guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zholos, A.V.; Tsytsyura, Y.D.; Gordienko, D.V.; Tsvilovskyy, V.V.; Bolton, T.B. Phospholipase C, but not InsP(3) or DAG, -dependent activation of the muscarinic receptor-operated cation current in guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 141, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, H.; Unno, T.; Arima, D.; Suzuki, M.; Yan, H.D.; Matsuyama, H.; Nishimura, M.; Komori, S. Phospholipase C involvement in activation of the muscarinic receptor-operated cationic current in guinea pig ileal smooth muscle cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 95, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takasaki, J.; Saito, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Kawasaki, T.; Moritani, Y.; Hayashi, K.; Kobori, M. A novel G alpha(q/11)-selective inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 47438–47445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanahashi, Y.; Katsurada, T.; Inasaki, N.; Uchiyama, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsuyama, H.; Komori, S.; Unno, T. Further characterization of the synergistic activation mechanism of cationic channels by M-2 and M-3 muscarinic receptors in mouse intestinal smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C514–C523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, T.; Unno, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Uchiyama, M.; Hattori, M.; Nishimura, M.; Komori, S. Characterization of muscarinic receptor-mediated cationic currents in longitudinal smooth muscle cells of mouse small intestine. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 100, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beech, D.J.; Muraki, K.; Flemming, R. Non-selective cationic channels of smooth muscle and the mammalian homologues of Drosophila TRP (vol 559, pg 685, 2004). J. Physiol. Lond. 2004, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvilovskyy, V.V.; Zholos, A.V.; Aberle, T.; Philipp, S.E.; Dietrich, A.; Zhu, M.X.; Birnbaumer, L.; Freichel, M.; Flockerzi, V. Deletion of TRPC4 and TRPC6 in mice impairs smooth muscle contraction and intestinal motility in vivo. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.P.; Jun, J.Y.; Chang, I.Y.; Suh, S.H.; So, I.S.; Kim, K.W. TRPC4 is an essential component of the nonselective cation channel activated by muscarinic stimulation in mouse visceral smooth muscle cells. Mol. Cells 2005, 20, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Tanahashi, Y.; Kitazawa, T.; Taneike, T.; Komori, S.; Unno, T. A non-selective cationic channel activated by diacylglycerol in mouse intestinal myocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 599, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuguro, K.I.; Tang, J.S.; Tang, Y.F.; Xiao, R.; Freichel, M.; Tsvilovskyy, V.; Ito, S.; Flockerzi, V.; Zhu, M.X.; Zholos, A.V. Isoform-specific inhibition of TRPC4 channel by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 10026–10036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dresviannikov, A.V.; Bolton, T.B.; Zholos, A.V. Muscarinic receptor-activated cationic channels in murine ileal myocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamoto, H.; Prestwich, S.A.; Asai, S.; Unno, T.; Bolton, T.B.; Komori, S. Muscarinic agonist potencies at three different effector systems linked to the M-2 or M-3 receptor in longitudinal smooth muscle of guinea-pig small intestine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 1765–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misra, S.; Mahavadi, S.; Grider, J.R.; Murthy, K.S. Differential expression of Y receptors and signaling pathways in intestinal circular and longitudinal smooth muscle. Regul. Pept. 2005, 125, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, Y.; Unno, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Ishii, T.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Komori, S. Multiple muscarinic pathways mediate the suppression of voltage-gated Ca2+channels in mouse intestinal smooth muscle cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 158, 1874–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aslanoglou, D.; Alvarez-Curto, E.; Marsango, S.; Milligan, G. Distinct agonist regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine M-2-M-3 heteromers and their corresponding homomers. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14785–14796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komori, S.; Bolton, T.B. Calcium release induced by inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate in single-rabbit intestinal smooth-muscle cells. J. Physiol. Lond. 1991, 433, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benham, C.D.; Bolton, T.B. Spontaneous transient outward currents in single visceral and vascular smooth-muscle cells of the rabbit. J. Physiol. Lond. 1986, 381, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, W.C.; Carl, A.; Sanders, K.M. Muscarinic suppression of Ca2+-dependent K-current in colonic smooth-muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1989, 257, C481–C487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, H.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Muscarinic inhibition of single kca channels in smooth-muscle cells by a pertussis-sensitive G-protein. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261, C1204–C1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonev, A.D.; Nelson, M.T. Muscarinic inhibition of atp-sensitive K+ channels by protein-kinase-C in urinary-bladder smooth-muscle. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, C1723–C1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatakeyama, N.; Wang, Q.; Goyal, R.K.; Akbarali, H.I. Muscarinic suppression of atp-sensitive K+ channel in rabbit esophageal smooth-muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1995, 268, C877–C885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttle, L.C.; Farley, J.M. Muscarinic receptors inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ channels in swine tracheal smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 1997, 273, L478–L484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Murakami, Y.; Ono, N.; Fujikawa, S.; Matsuyama, H.; Unno, T.; Naitou, K.; Tanahashi, Y. Muscarinic suppression of ATP-sensitive K+ channels mediated by the M-3/G(q/11)/phospholipase C pathway contributes to mouse ileal smooth muscle contractions. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2018, 315, G618–G630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.X.; Fleischmann, B.K.; Kotlikoff, M.I. M-2 receptor activation of nonselective cation channels in smooth muscle cells: Calcium and G(i)/G(0) requirements. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1997, 273, C500–C508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Kotlikoff, M.I. Muscarinic signaling pathway for calcium release and calcium-activated chloride current in smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1997, 273, C509–C519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beech, D.J. Inhibitory Effects of histamine and bradykinin on calcium current in smooth-muscle cells isolated from guinea-pig ileum. J. Physiol. Lond. 1993, 463, 565–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, T.; Komori, S.; Ohashi, H. Inhibitory effect of muscarinic receptor activation on Ca2+ channel current in smooth-muscle cells of guinea-pig ileum. J. Physiol. Lond. 1995, 484, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, S.; Bolton, T.B. Inositol trisphosphate releases stored calcium to block voltage-dependent calcium channels in single smooth-muscle cells. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1991, 418, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.C.; Morsy, N.; Shoeb, F.; Zavzavadjian, J.; Akbarali, H.I. Coupling of M-2 muscarinic receptor to L-type Ca2+ channel via c-src kinase in rabbit colonic circular smooth muscle. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, T.B. Depolarizing action of acetylcholine or carbachol in intestinal smooth muscle. J. Physiol. Lond. 1972, 220, 647–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unno, T.; Inaba, T.; Ohashi, H.; Takewaki, T.; Komori, S. Role of Ca2+ mobilization in muscarinic receptor-mediated membrane depolarization in guinea pig ileal smooth muscle cells. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 84, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuyama, H.; Tanahashi, Y.; Kitazawa, T.; Yamada, M.; Komori, S.; Unno, T. Evidence for M-2 and M-3 muscarinic receptor involvement in cholinergic excitatory junction potentials through synergistic activation of cation channels in the longitudinal muscle of mouse ileum. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 121, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zholos, A.V.; Tsytsyura, Y.D.; Philyppov, I.B.; Shuba, M.F.; Bolton, T.B. Voltage-dependent inhibition of the muscarinic cationic current in guinea-pig ileal cells by SK&F 96365. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 129, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itagaki, M.; Komori, S.; Unno, T.; Syuto, B.; Ohashi, H. Possible involvement of a small G-protein sensitive to exoenzyme C3 of clostridium-botulinum in the regulation of myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in beta-escin skinned smooth-muscle of guinea-pig ileum. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somlyo, A.P.; Somlyo, A.V. Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: Modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 1325–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, A.K.; Carty, M.; Singer, C.A.; Yamboliev, I.A.; Gerthoffer, W.T. Coupling of M-2 muscarinic receptors to ERK MAP kinases and caldesmon phosphorylation in colonic smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2000, 278, G429–G437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, E.; Moffat, L.; Ostrander, J.; Walsh, M.P.; MacDonald, J.A. Characterization of protein kinase pathways responsible for Ca2+ sensitization in rat ileal longitudinal smooth muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 293, G699–G710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suguro, M.; Matsuyama, H.; Tanahashi, Y.; Unno, T.; Kitazawa, T.; Yamada, M.; Komori, S. Muscarinic receptor subtypes mediating Ca2+ sensitization of intestinal smooth muscle contraction: Studies with receptor knockout mice. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shehnaz, D.; Ansari, K.Z.; Ehlert, F.J. Acetylcholine-induced desensitization of the contractile response to histamine in guinea pig ileum is prevented by either pertussis toxin treatment or by selective inactivation of muscarinic M-3 receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 297, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Griffin, M.T.; Matsui, M.; Shehnaz, D.; Ansari, K.Z.; Taketo, M.M.; Manabe, T.; Ehlert, F.J. Muscarinic agonist-mediated heterologous desensitization in isolated ileum requires activation of both muscarinic M-2 and M-3 receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, T.B. Role of electrogenic sodium pumping in response of smooth-muscle to acetylcholine. J. Physiol. Lond. 1973, 228, 713–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Unno, T.; Kwon, S.C.; Okamoto, H.; Irie, Y.; Kato, Y.; Matsuyama, H.; Komori, S. Receptor signaling mechanisms underlying muscarinic agonist-evoked contraction in guinea-pig ileal longitudinal smooth muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 139, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wrzos, H.F.; Tandon, T.; Ouyang, A. Mechanisms mediating cholinergic antral circular smooth muscle contraction in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 10, 3292–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.A.; Ehlert, F.J. Pertussis toxin blocks M(2) muscarinic receptor-mediated effects on contraction and cyclic-amp in the guinea-pig ileum, but not M(3)-mediated contractions and phosphoinositide hydrolysis. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1994, 271, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Stengel, P.W.; Gomeza, J.; Wess, J.; Cohen, M.L. M-2 and M-4 receptor knockout mice: Muscarinic receptor function in cardiac and smooth muscle in vitro. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 877–885. [Google Scholar]
- Stengel, P.W.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Cohen, M.L. M-3-receptor knockout mice: Muscarinic receptor function in atria, stomach fundus, urinary bladder, and trachea. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2002, 282, R1443–R1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitazawa, T.; Hashiba, K.; Cao, J.S.; Unno, T.; Komori, S.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Taneike, T. Functional roles of muscarinic M-2 and M-3 receptors in mouse stomach motility: Studies with muscarinic receptor knockout mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 554, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruggieri, M.R.; Braverman, A.S. Gastric body cholinergic contractile signal transduction in M-2 and M-3 receptor knockout mice. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2013, 33, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, M.; Motomura, D.; Karasawa, H.; Fujikawa, T.; Jiang, J.; Komiya, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Taketo, M.M. Multiple functional defects in peripheral autonomic organs in mice lacking muscarinic acetylcholine receptor gene for the M-3 subtype. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 9579–9584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsui, M.; Motomura, D.; Fujiwara, T.; Jiang, J.; Takahashi, S.; Manabe, T.; Taketo, M.M. Mice lacking M-2 and M-3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors are devoid of cholinergic smooth muscle contractions but still viable. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 10627–10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsui, M.; Griffin, M.T.; Shehnaz, D.; Taketo, M.M.; Ehlert, F.J. Increased relaxant action of forskolin and isoproterenol against muscarinic agonist-induced contractions in smooth muscle from M-2 receptor knockout mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 305, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Unno, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Sakamoto, T.; Uchiyama, M.; Izumi, Y.; Okamoto, H.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Komori, S. M-2 and M-3 muscarinic receptor-mediated contractions in longitudinal smooth muscle of the ileum studied with receptor knockout mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, T.; Tanaka, K.; Nakajima, H.; Matsui, M.; Azuma, Y.T. M-2 and M-3 muscarinic receptors are involved in enteric nerve-mediated contraction of the mouse ileum: Findings obtained with muscarinic-receptor knockout mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G154–G164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Griffin, M.T.; Matsui, M.; Ostrom, R.S.; Ehlert, F.J. The guinea pig ileum lacks the direct, high-potency, M-2-muscarinic, contractile mechanism characteristic of the mouse ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2009, 380, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondo, T.; Nakajima, M.; Teraoka, H.; Unno, T.; Komori, S.; Yamada, M.; Kitazawa, T. Muscarinic receptor subtypes involved in regulation of colonic motility in mice: Functional studies using muscarinic receptor-deficient mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 670, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, P.W.; Cohen, M.L. Muscarinic receptor knockout mice: Role of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors M-2, M-3, and M-4 in carbamylcholine-induced gallbladder contractility. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 301, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehlert, F.J.; Griffin, M.T.; Abe, D.M.; Vo, T.H.; Taketo, M.M.; Manabe, T.; Matsui, M. The M2 muscarinic receptor mediates contraction through indirect mechanisms in mouse urinary bladder. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitazawa, T.; Hirama, R.; Masunaga, K.; Nakamura, T.; Asakawa, K.; Cao, J.; Teraoka, H.; Unno, T.; Komori, S.I.; Yamada, M.; et al. Muscarinic receptor subtypes involved in carbachol-induced contraction of mouse uterine smooth muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2008, 377, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, L.; de Haas, N.; Mammen, M.; Stangeland, E.; Steinfeld, T.; Aiyar, J.; Michel, M. Muscarinic receptor subtypes and signalling involved in the attenuation of isoprenaline-induced rat urinary bladder relaxation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2011, 384, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olgart, C.; Iversen, H.H. Nitric oxide-dependent relaxation induced by M-1 muscarinic receptor activation in the rat small intestine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stengel, P.W.; Cohen, M.L. M-1 receptor-mediated nitric oxide-dependent relaxation unmasked in stomach fundus from M-3 receptor knockout mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 304, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unno, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Izumi, Y.; Yamada, M.; Wess, J.; Komori, S. Roles of M-2 and M-3 muscarinic receptors in cholinergic nerve-induced contractions in mouse ileum studied with receptor knockout mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanders, K.M.; Ward, S.M.; Koh, S.D. Interstitial cells: Regulators of smooth muscle function. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 859–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drumm, B.T.; Rembetski, B.E.; Huynh, K.; Nizar, A.; Baker, S.A.; Sanders, K.M. Excitatory cholinergic responses in mouse colon intramuscular interstitial cells of Cajal are due to enhanced Ca(2+)release via M(3)receptor activation. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 10073–10095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.A.; Drumm, B.T.; Skowronek, K.E.; Rembetski, B.E.; Peri, L.E.; Hennig, G.W.; Perrino, B.A.; Sanders, K.M. Excitatory neuronal responses of Ca2+ transients in interstitial cells of cajal in the small intestine. Eneuro 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Groneberg, D.; Lies, B.; Konig, P.; Jager, R.; Seidler, B.; Klein, S.; Saur, D.; Friebe, A. Cell-specific deletion of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase reveals a dual pathway for nitrergic neuromuscular transmission in the murine fundus. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, D.; Han, S.J.; Hamdan, F.F.; Jeon, J.; Li, B.; Li, J.H.; Cui, Y.H.; Mears, D.; Lu, H.Y.; Deng, C.X.; et al. A critical role for beta cell M-3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in regulating insulin release and blood glucose homeostasis in vivo. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostrom, R.S.; Ehlert, F.J. M(2) muscarinic receptor inhibition of agonist-induced cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation and relaxation in the guinea pig ileum. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 280, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roffel, A.F.; Meurs, H.; Elzinga, C.R.S.; Zaagsma, J. Muscarinic M(2) receptors do not participate in the functional antagonism between methacholine and isoprenaline in guinea-pig tracheal smooth-muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1993, 249, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roffel, A.F.; Meurs, H.; Elzinga, C.R.S.; Zaagsma, J. No evidence for a role of muscarinic M(2) receptors in functional antagonism in bovine trachea. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 115, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ehlert, F.J.; Ahn, S.; Pak, K.J.; Park, G.J.; Sangnil, M.S.; Tran, J.A.; Matsui, M. Neuronally released acetylcholine acts on the M-2 muscarinic receptor to oppose the relaxant effect of isoproterenol on cholinergic contractions in mouse urinary bladder. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohta, T.; Kawai, K.; Ito, S.; Nakazato, Y. Ca2+ entry activated by emptying of intracellular Ca2+ stores in ileal smooth-muscle of the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 114, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zholos, A.V. Regulation of TRP-like muscarinic cation current in gastrointestinal smooth muscle with special reference to PLC/InsP(3)/Ca2+ system. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2006, 27, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Jing, R.; Trexler, C.; Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Pan, Z.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, B.; Fang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Deletion of IP(3)R1 by Pdgfrb-Cre in mice results in intestinal pseudo-obstruction and lethality. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Miyakawa, T.; Duttaroy, A.; Yamanaka, A.; Moriguchi, T.; Makita, R.; Ogawa, M.; Chou, C.J.; Xia, B.; Crawley, J.N.; et al. Mice lacking the M3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor are hypophagic and lean. Nature 2001, 410, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanahashi, Y.; Waki, N.; Unno, T.; Matsuyama, H.; Iino, S.; Kitazawa, T.; Yamada, M.; Komori, S. Roles of M2 and M3 muscarinic receptors in the generation of rhythmic motor activity in mouse small intestine. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2013, 25, e687–e697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schworer, H.; Kilbinger, H. Enhancement of guinea-pig intestinal peristalsis by blockade of muscarinic M1-receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 93, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- North, R.; Slack, B.; Surprenant, A. Muscarinic-M1 and Muscarinic-M2 Receptors mediate depolarization and presynaptic inhibition in guinea-pig enteric nervous-system. J. Physiol. Lond. 1985, 368, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B. Pharmacology of transmission and sites of drug action in the enteric nervous system. In The Enteric Nervous System; Blackwell Publishing, Inc.: Malden, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 103–131. [Google Scholar]
- Bulbring, E.; Lin, R.C. The effect of intraluminal application of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxytryptophan on peristalsis; the local production of 5-HT and its release in relation to intraluminal pressure and propulsive activity. J. Physiol. 1958, 140, 381–407. [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa, T.; Misawa, H.; Nakajima, Y.; Takaki, M. Absence of peristalsis in the ileum of W/W(V) mutant mice that are selectively deficient in myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 2005, 41, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Tissue | Protocol/Agonist b | Emax (% of Wild Type) a | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2-KO | M3-KO | M2/M3-KO | M4-KO | |||
| Stomach fundus | Cumulative/CCh | 96 | 44 * | 95 | Stengel et al. (2000; 2002) [80,81] | |
| Single dose/CCh | 102 | 66 * | 0 (relax.) | Kitazawa et al. (2007) [82] | ||
| Cumulative/CCh | 114 | 49 * | 0 (relax.) | Kitazawa et al. (2007) [82] | ||
| Stomach antrum | Single dose/CCh | 84 | 64 * | 0 (relax.) | Kitazawa et al. (2007) [82] | |
| Cumulative/CCh | 86 | 57 * | 0 (relax.) | Kitazawa et al. (2007) [82] | ||
| Stomach body | Cumulative/CCh | 95 | 42 * | Ruggieri and Braverman (2013) [83] | ||
| Ileum | Cumulative/CCh | 75 | 25 | 0 | Matsui et al. (2000; 2002) [84,85] | |
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 98 | Matsui et al. (2003) [86] | ||||
| Single dose/CCh | 103 | 62 * | 0 (relax.) | Unno et al. (2005) [87] | ||
| Single dose/ACh | 102 | 43 | Takeuchi et al. (2007) [88] | |||
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 101 | 36 * | Griffin et al. (2009) [89] | |||
| Colon proximal | Single dose/CCh | 66 * | 34 | 0 (relax.) | Kondo et al. (2011) [90] | |
| Colon distal | Single dose/CCh | 65 * | 21 | 0 (relax.) | Kondo et al. (2011) [90] | |
| Trachea | Cumulative/CCh | 86 * | 44 * | 82 | Stengel et al. (2000; 2002) [80,81] | |
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 88 | Matsui et al. (2003) [86] | ||||
| Gallbladder | Cumulative/CCh | 79 | 21 | 100 | Stengel and Cohen (2002) [91] | |
| Urinary bladder | Cumulative/CCh | 95 | 5 | 0 | Matsui et al. (2000; 2002) [84,85] | |
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 84 | Matsui et al. (2003) [86] | ||||
| Cumulative/CCh | 82 | 6 * | 97 | Stengel et al. (2000; 2002) [80,81] | ||
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 89 | 15 * | 0 | Ehlert et al. (2005) [92] | ||
| Single dose/CCh | 77 * | 7 * | 0 | # | ||
| Uterus | Cumulative/CCh | 66 * | 0 | 0 | Kitazawa et al. (2008) [93] | |
| Tissue | Protocol/Agonist | pEC50 | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild Type: M2-KO | Wild Type: M3-KO | Wild Type: M4-KO | |||
| Stomach fundus | Cumulative/CCh | 6.68:6.39 * | 6.54:6.71 | 6.76:6.70 | Stengel et al. (2000; 2002) [80,81] |
| Single dose/CCh | 6.93:6.51 * | 7.03:6.97 | Kitazawa et al. (2007) [82] | ||
| Cumulative/CCh | 6.56:6.18 * | 6.67:6.73 | Kitazawa et al. (2007) [82] | ||
| Stomach antrum | Single dose/CCh | 6.60:6.20 * | 6.50:6.90 | Kitazawa et al. (2007) [82] | |
| Cumulative/CCh | 6.82:6.08 * | 6.92:7.10 | Kitazawa et al. (2007) [82] | ||
| Stomach body | Cumulative/CCh | 6.1:5.7 * | 6.1:6.5 * | Ruggieri and Braverman (2013) [83] | |
| Ileum | Single dose/CCh | 6.39:5.93 * | 6.14:6.18 | Unno et al. (2005) [87] | |
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 6.75:6.26 * | 6.75:6.99 * | Griffin et al., (2009) [89] | ||
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 6.70:6.38 * | Matsui et al. (2003) [86] | |||
| Colon proximal | Single dose/CCh | 6.90:6.34 * | Kondo et al. (2011) [90] | ||
| Colon distal | Single dose/CCh | 5.90:6.03 | Kondo et al. (2011) [90] | ||
| Trachea | Cumulative/CCh | 6.56:6.27 * | 6.52:6.51 | 6.46:6.62 | Stengel et al. (2000; 2002) [80,81] |
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 6.94:6.86 | Matsui et al. (2003) [86] | |||
| Urinary bladder | Cumulative/CCh | 6.27:6.07 * | 6.02:5.71 * | 6.30:6.20 | Stengel et al. (2000; 2002) [80,81] |
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 6.54:6.31 * | 6.54:6.60 | Ehlert et al. (2005) [92] | ||
| Cumulative/Oxo.M | 6.58:6.41 | Matsui et al. (2003) [86] | |||
| Single dose/CCh | 6.22:5.96 | 6.22:6.10 | # | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanahashi, Y.; Komori, S.; Matsuyama, H.; Kitazawa, T.; Unno, T. Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020926
Tanahashi Y, Komori S, Matsuyama H, Kitazawa T, Unno T. Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(2):926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020926
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanahashi, Yasuyuki, Seiichi Komori, Hayato Matsuyama, Takio Kitazawa, and Toshihiro Unno. 2021. "Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 2: 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020926
APA StyleTanahashi, Y., Komori, S., Matsuyama, H., Kitazawa, T., & Unno, T. (2021). Functions of Muscarinic Receptor Subtypes in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscle: A Review of Studies with Receptor-Knockout Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(2), 926. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22020926






