Comparison of the Distinct, Host-Specific Response of Three Solanaceae Hosts Induced by Phytophthora infestans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
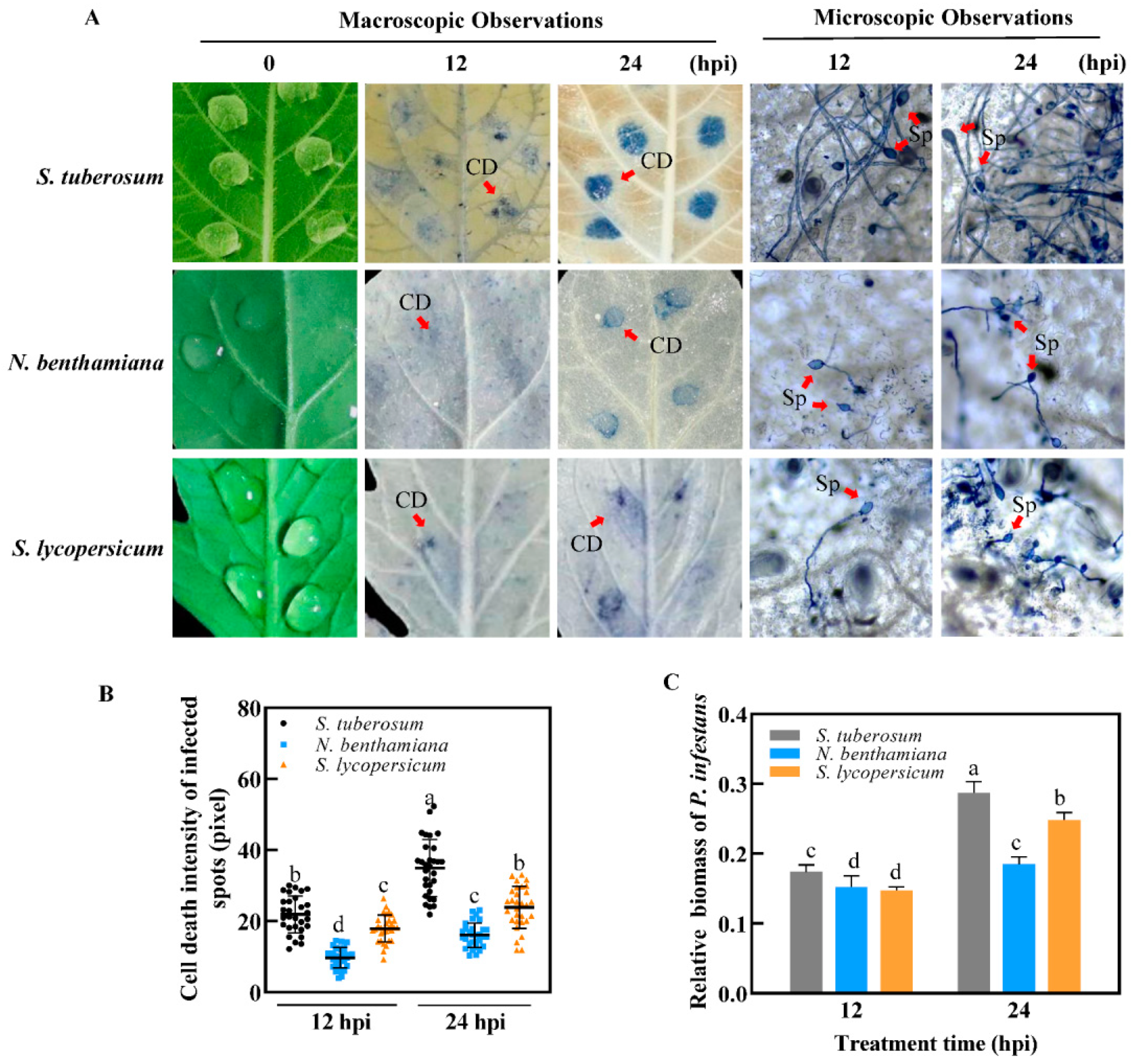
2.1. Comparisons of Infection Process among TSHs
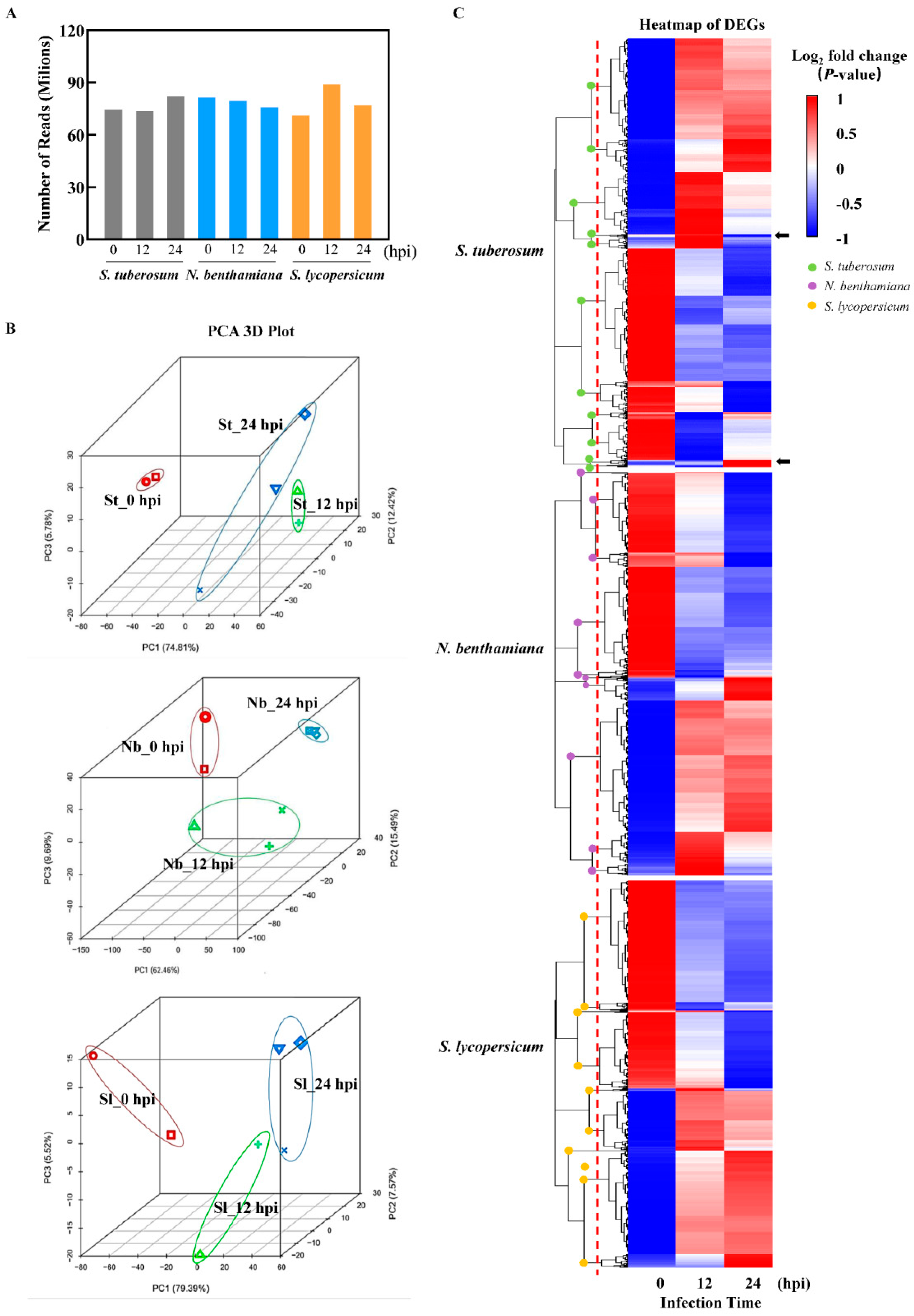
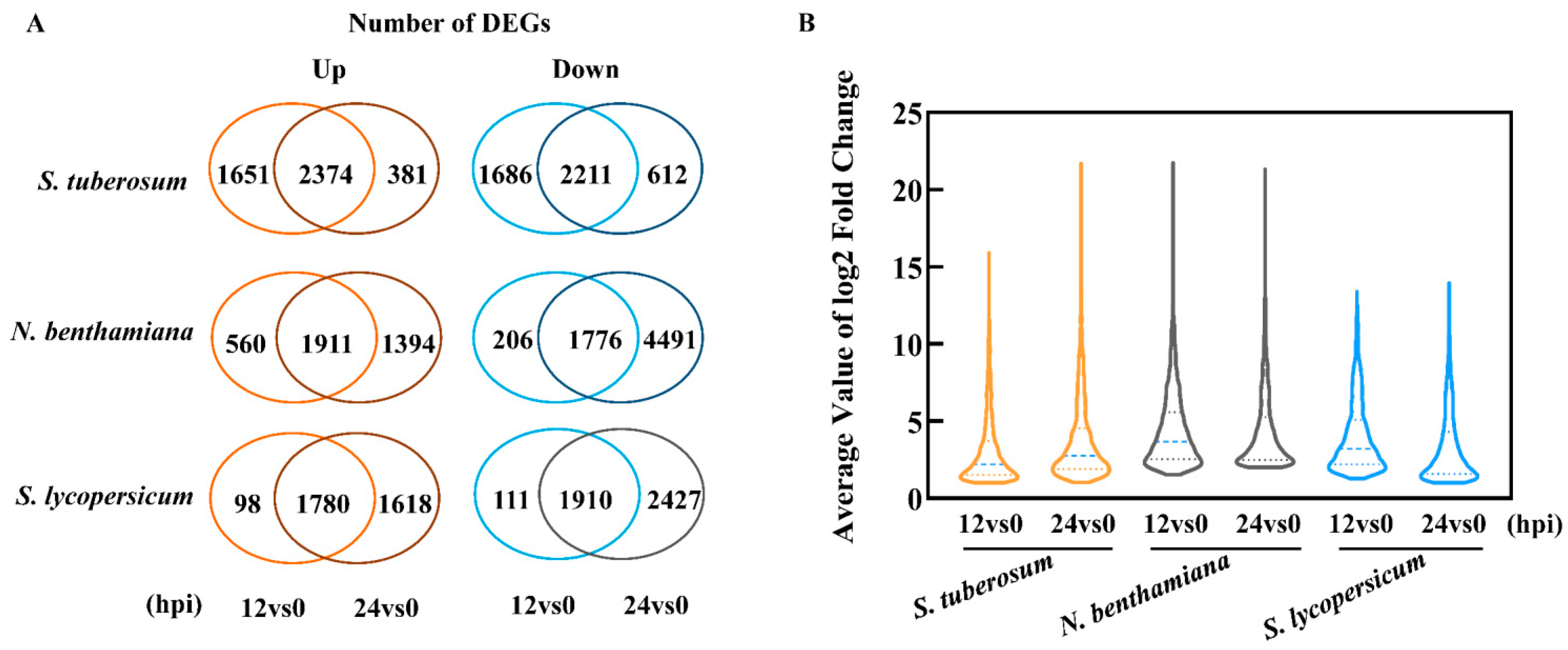
2.2. Initial Analysis of the Infection-Based Transcriptome of Diseased TSHs
2.3. Response Model and Transcript Level of P. infestans Varies with the Solanaceae Host
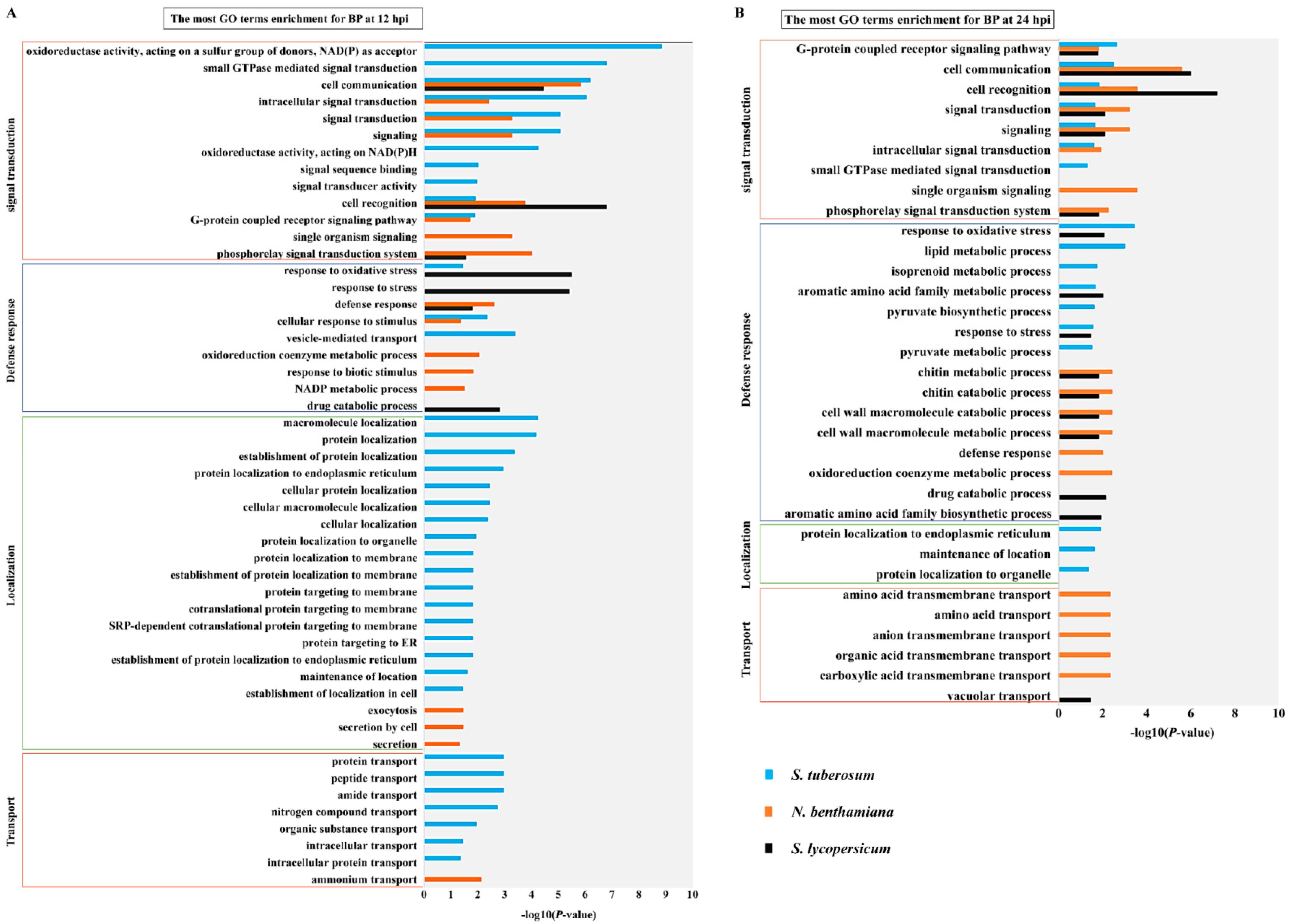
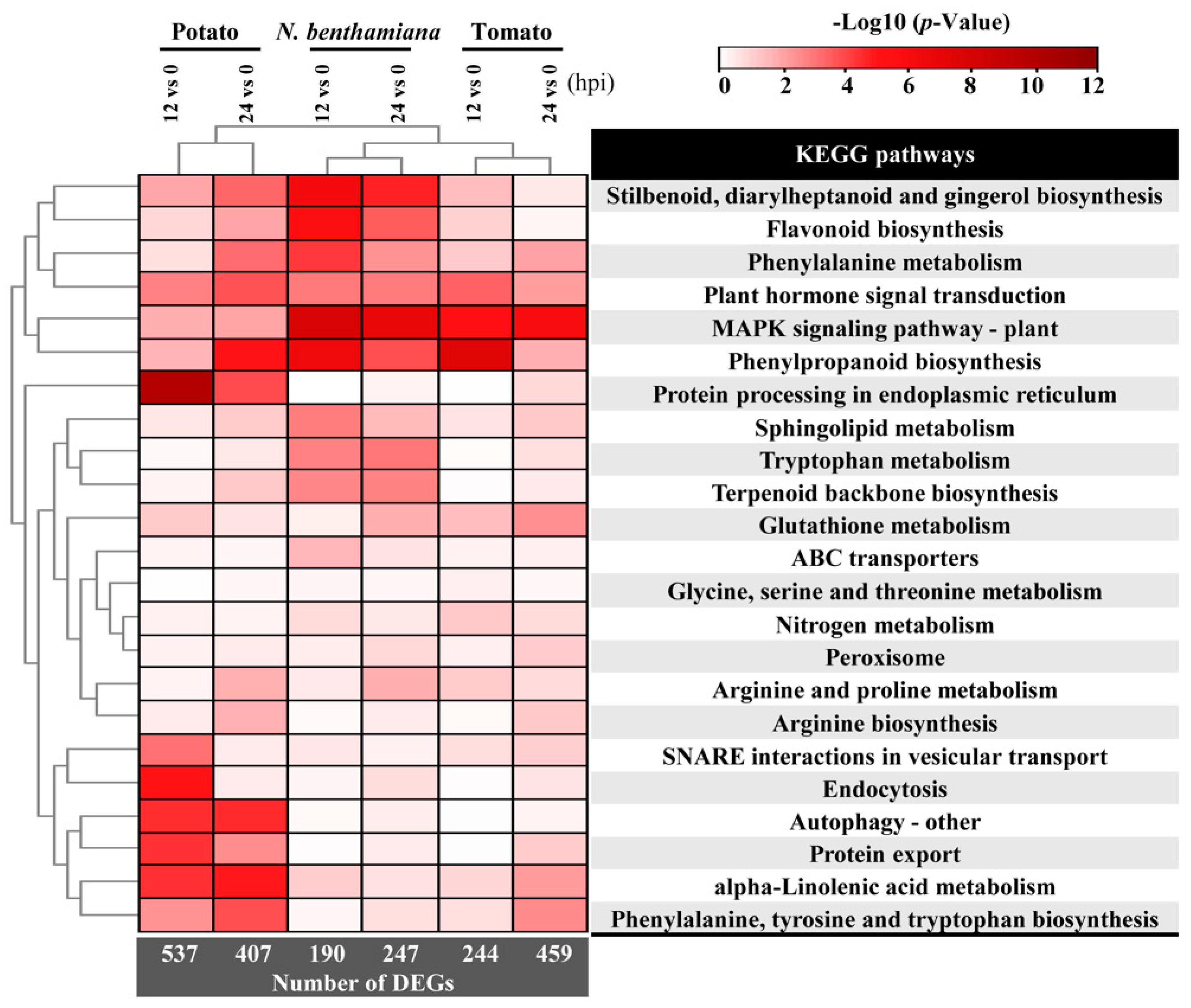
2.4. Distinct Response Influenced by Different Speed of Infection Process among TSHs
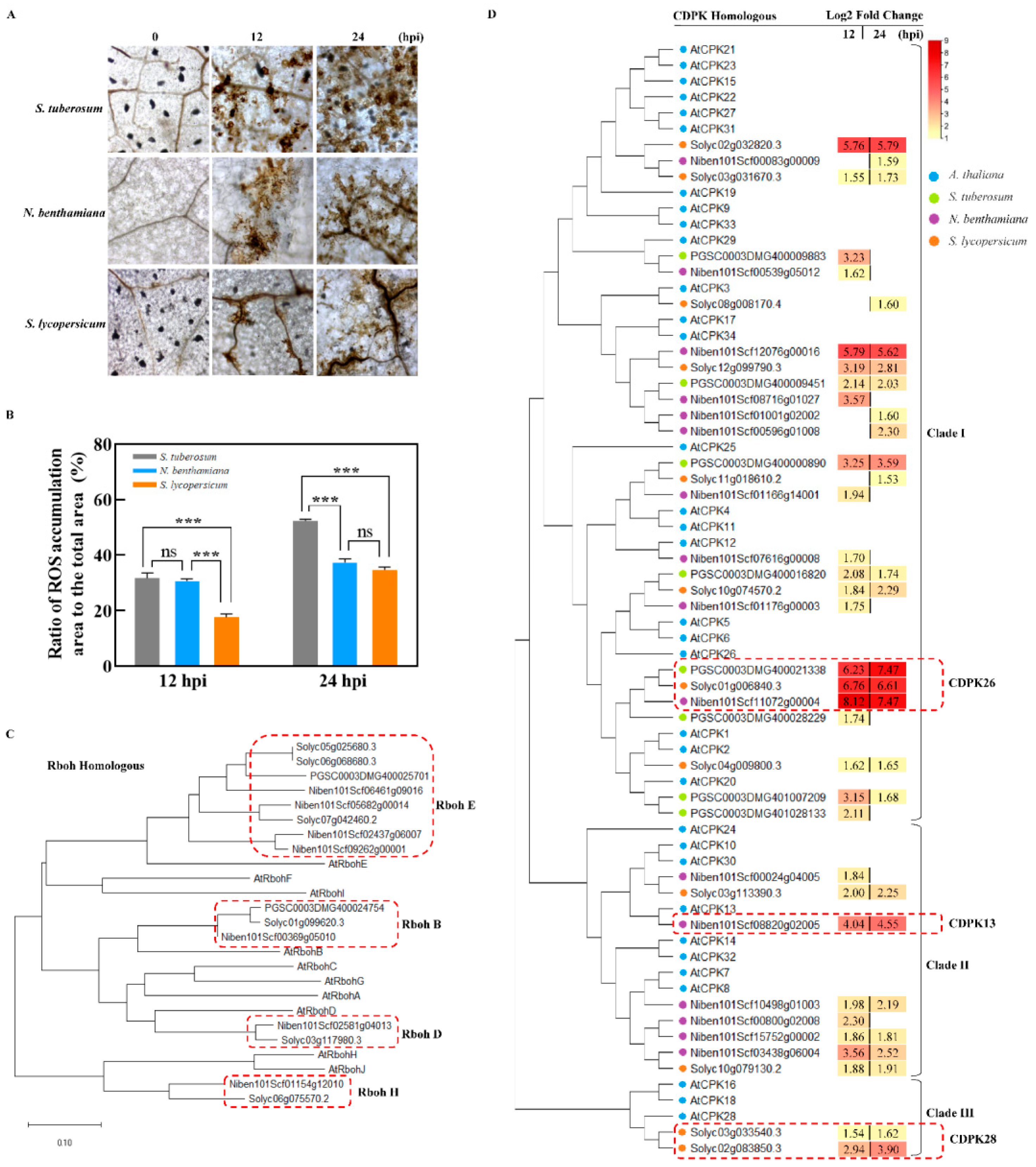
2.5. Differences in ROS Accumulation of the TSHs
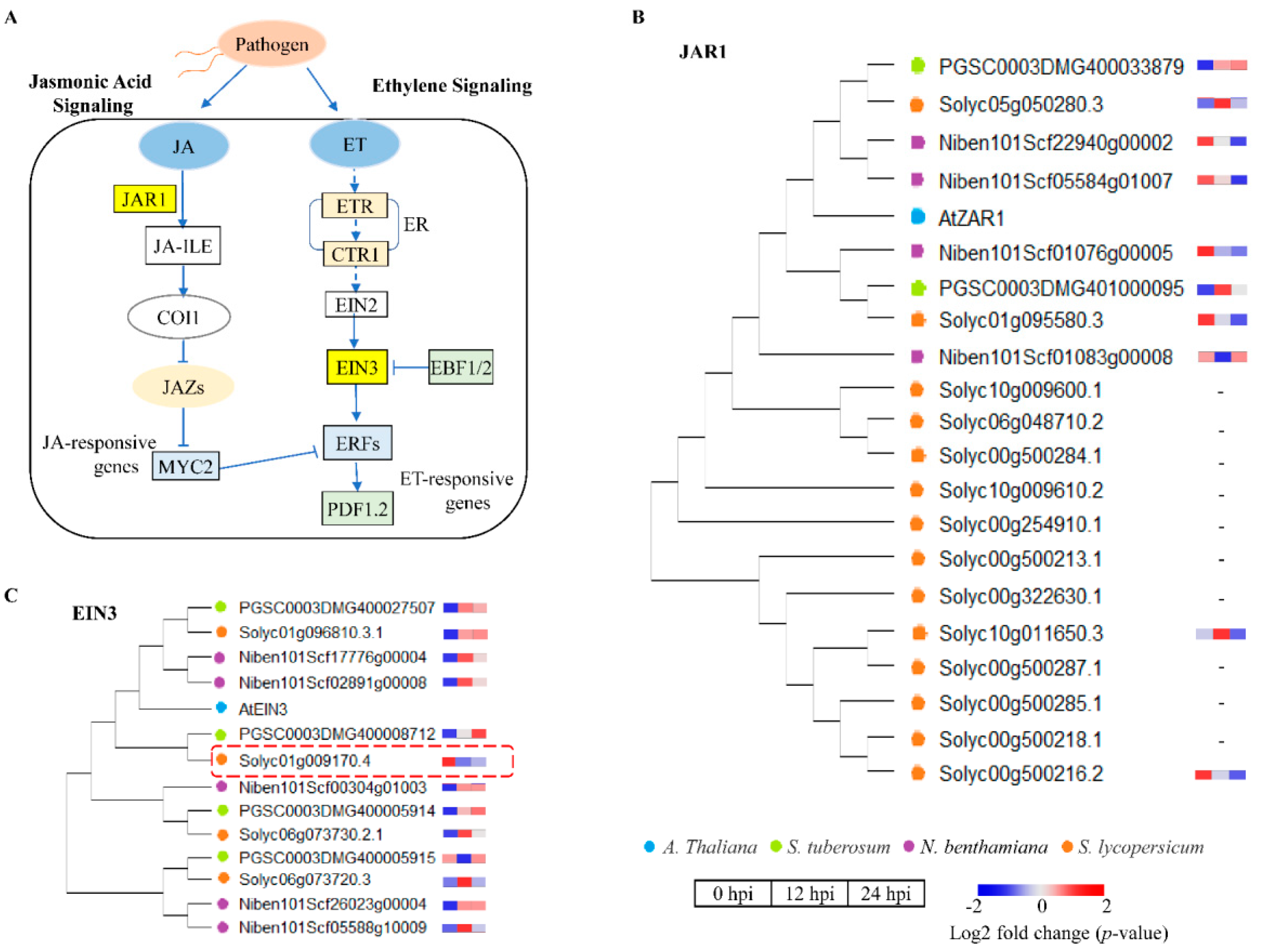
2.6. Differential Gene Expression Related to the Activation of Hormone Signaling Pathways
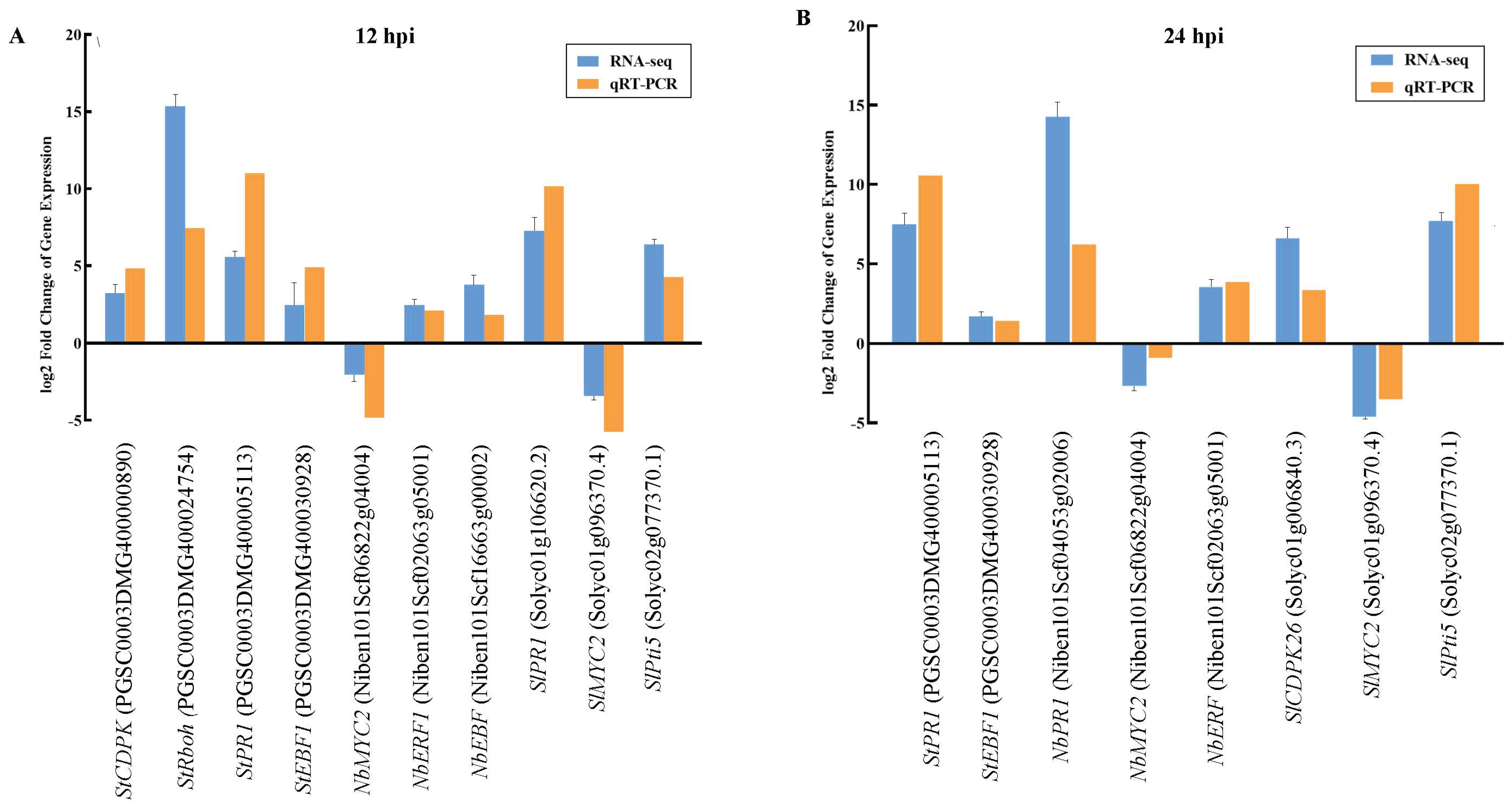
2.7. Expression of Key Genes and qPCR Verification of the Response of the TSHs to P. infestans Infection
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. P. infestans Cultivation and Inoculation Assay
4.3. Sample Production and Total RNA Extraction
4.4. Library Construction and Sequencing
4.5. GO and KEGG Analysis
4.6. Trypan Blue Staining and Microscopic Observation
4.7. Quantification of Cell Death Intensity
4.8. Relative Biomass of P. infestans Determination Assay
4.9. Reactive Oxygen Species Accumulation Assay
4.10. Real-Time qRT–PCR Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weese, T.L.; Bohs, L. A Three-Gene Phylogeny of the Genus Solanum (Solanaceae). Syst. Bot. 2007, 32, 445–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibert, T.; Abel, C.; Wahl, V. Flowering time and the identification of floral marker genes in Solanum tuberosum ssp. andigena. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 23, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derevnina, L.; Petre, B.; Kellner, R.; Dagdas, Y.F.; Sarowar, M.N.; Giannakopoulou, A.; De la Concepcion, J.C.; Chaparro-Garcia, A.; Pennington, H.G.; van West, P.; et al. Emerging oomycete threats to plants and animals. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, S.; Tabata, S.; Hirakawa, H.; Asamizu, E.; Shirasawa, K.; Isobe, S.; Kaneko, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Shibata, D.; Aoki, K.; et al. The tomato genome sequence provides insights into fleshy fruit evolution. Nature 2012, 485, 635–641. [Google Scholar]
- Goodin, M.M.; Zaitlin, D.; Naidu, R.A.; Lommel, S.A. Nicotianabenthamiana: Its history and future as a model for plant-pathogen interactions. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derevnina, L.; Kamoun, S.; Wu, C. Dude, where is my mutant? Nicotiana benthamiana meets forward genetics. New Phytol. 2019, 221, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bombarely, A.; Rosli, H.G.; Vrebalov, J.; Moffett, P.; Mueller, L.A.; Martin, G.B. A draft genome sequence of Nicotiana benthamiana to enhance molecular plant-microbe biology research. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kourelis, J.; Kaschani, F.; Grosse-Holz, F.M.; Homma, F.; Kaiser, M.; van der Hoorn, R.A.L. A homology-guided, genome-based proteome for improved proteomics in the alloploid Nicotiana benthamiana. BMC Genom. 2019, 4, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierro, N.; Battey, J.N.; Ouadi, S.; Bakaher, N.; Bovet, L.; Willig, A.; Goepfert, S.; Peitsch, M.C.; Ivanov, N.V. The tobacco genome sequence and its comparison with those of tomato and potato. Nat. Commun. 2014, 8, 3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomma, B.P.; VAN Esse, H.P.; Crous, P.W.; de Wit, P.J. Cladosporium fulvum (syn. Passalora fulva), a highly specialized plant pathogen as a model for functional studies on plant pathogenic Mycosphaerellaceae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2005, 6, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, E.M. Phytophthora Diseases Worldwide. Plant Pathol. 1998, 47, 224–225. [Google Scholar]
- Kamoun, S.; Furzer, O.; Jones, J.D.G.; Judelson, H.S.; Ali, G.S.; Dalio, R.J.D.; Roy, S.G.; Schena, L.; Zambounis, A.; Panabières, F.; et al. The Top 10 oomycete pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 16, 413–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Särkinen, T.; Bohs, L.; Olmstead, R.G.; Knapp, S. A phylogenetic framework for evolutionary study of the nightshades (Solanaceae): A dated 1000-tip tree. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabbadin, F.; Urresti, S.; Henrissat, B.; Avrova, A.O.; Welsh, L.R.J.; Lindley, P.J.; Csukai, M.; Squires, J.N.; Walton, P.H.; Davies, G.; et al. Secreted pectin monooxygenases drive plant infection by pathogenic oomycetes. Science 2021, 373, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlson, E.W.; Ashrafi, H.; Foolad, M.R. Identification and mapping of late blight resistance quantitative trait Loci in tomato accession PI 163245. Plant Genome 2018, 11, 180007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodenburg, S.Y.A.; Seidl, M.F.; Judelson, H.S.; Vu, A.L.; Ridder, G.F. Metabolic model of the Phytophthora infestans tomato interaction reveals metabolic switches during host colonization. mBio 2019, 10, e00454-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, K.K.; Lu, J.; Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, Z.W.; Ismail, O.M.; Wu, J.; Xie, X.J.; Li, X.B.; et al. Efficiency of chitosan application against Phytophthora infestans and the activation of defence mechanisms in potato. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 182, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nobori, T.; Velásquez, A.C.; Wu, J.; Kvitko, B.H.; Kremer, J.M.; Wang, Y.; He, S.Y.; Tsuda, K. Transcriptome landscape of a bacterial pathogen under plant immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3055–E3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, N.; Li, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, X.; Chen, W.; Xing, G.; Zheng, W. The early response during the interaction of fungal phytopathogen and host plant. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Coaker, G.; Zhou, J.M.; Dong, X.N. Plant immune mechanisms: From reductionistic to holistic points of view. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1358–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cejudo, F.J.; Sandalio, F.M.; Van Breusegem, F. Understanding plant responses to stress conditions: Redox-based strategies. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 5785–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhamdi, A.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species in plant development. Development 2018, 145, 164376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanda, A.K.; Andrio, E.; Marino, D.; Pauly, N.; Dunand, C. Reactiveoxygen species during plant-microorganism early interactions. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2010, 52, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.H.; Ngou, B.P.M.; Ding, P.T.; Xin, X.F. PTI-ETI crosstalk: An integrative view of plant immunity. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 62, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.Q.; Xu, J.R. Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in plant pathogenic fungi. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehrotra, S.; Verma, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumari, S.; Mishra, B.N. Transcriptional regulation and signalling of cold stress response in plants: An overview of current understanding. Environ Exp. Bot. 2020, 180, 1042–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, A.A.; Romeis, T.; Jones, J.D.G. CDPK-mediated signalling pathways: Specificity and cross-talk. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.M.; Zhang, Y.L. Plant immunity: Danger perception and signaling. Cell 2020, 181, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.J.; Zhang, Y.L. Short- and long-distance signaling in plant defense. Plant J. 2021, 105, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhao, R.M.; Qiao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.Z.; Sun, H.; Xing, Z.Z.; Wang, X.B. Growth stages classification of potato crop based on analysis of spectral response and variables optimization. Sensors 2020, 20, 3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieterse, C.M.J.; Van der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S.C.M. Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, D. Salicylic acid signaling in disease resistance. Plant Sci. 2014, 228, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesel, L.; Davis, J.L.; Milne, L.; Fernandez, V.R.; Herold, M.B.; Williams, J.M.; Morris, J.; Hedley, P.E.; Harrower, B.; Newton, A.C.; et al. A transcriptional reference map of defence hormone responses in potato. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zuluaga, A.P.; Vega-Arreguín, J.C.; Fei, Z.J.; Ponnala, L.; Lee, S.J.; Matas, A.J.; Patev, S.; Fry, W.E.; Rose, J.K.C. Transcriptional dynamics of Phytophthora infestans during sequential stages of hemibiotrophic infection of tomato. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Restrepo, S.; Myers, K.L.; del Pozo, O.; Martin, G.B.; Hart, A.L.; Buell, C.R.; Fry, W.E.; Smart, C.D. Gene profiling of a compatible interaction between Phytophthora infestans and Solanum tuberosum suggests a role for carbonic anhydrase. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2005, 18, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.L.; Bradeen, J.M. Contrasting potato foliage and tuber defense mechanisms against the late blight pathogen Phytophthora infestans. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Bautista, N.; Dominguez-Nuñez, J.A.; Moreno, M.M.C.; Berrocal-Lobo, M. Plant tissue trypan blue staining during Phytopathogen infection. Bio-Protocol 2016, 6, e2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ray, S.; Mondal, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Kundu, S. Differential responses of resistant and susceptible tomato varieties to inoculation with Alternaria solani. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2015, 90, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.L.; Sun, T.J.; Ao, K.; Peng, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.L. Opposite roles of salicylic acid receptors NPR1 and NPR3/NPR4 in transcriptional regulation of plant immunity. Cell 2018, 31, 1454–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Han, X.; Feng, D.; Yuan, D.Y.; Huang, L.J. Signaling crosstalk between salicylic acid and ethylene/jasmonate in plant defense: Do we understand what they are whispering? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 3, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, M.M.; Zhao, J.H.; Tzeng, D.T.W.; Liu, Y.Y.; Deng, L.; Yang, T.X.; Zhai, Q.Z.; Wu, F.M.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, M. MYC2 orchestrates a hierarchical transcriptional cascade that regulates jasmonate-mediated plant immunity in tomato. Plant Cell 2017, 8, 1883–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camejo, D.; Cedeno, A.G.; Moreno, A. Reactive oxygen species, essential molecules, during plant-pathogen interactions. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2016, 103, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Zhou, W.; Liu, J.; Tan, N.; Zhou, J.M.; Huang, L. A receptor-like protein from Nicotiana benthamiana mediates VmE02 PAMP-triggered immunity. New Phytol. 2021, 4, 2260–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, E.; Carson, M.; May, G. Pathogen and host genotype differently affect pathogen fitness through their effects on different life-history stages. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boevink, P.C.; Birch, P.R.J.; Turnbull, D.; Whisson, S.C. Devastating intimacy: The cell biology of plant-Phytophthora interactions. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolwell, G.P.; Bindschedler, L.V.; Blee, K.A.; Butt, V.S.; Davies, D.R.; Gardner, S.L.; Gerrish, C.; Minibayeva, F. The apoplastic oxidative burst in response to biotic stress in plants: A three-component system. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar]
- Smart, C.D.; Myers, K.L.; Restrepo, S.; Martin, G.B.; Fry, W.E. Partial resistance of tomato to Phytophthora infestans is not dependent upon ethylene, jasmonic acid, or salicylic acid signaling pathways. Mol. Plant–Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luan, S.; Wang, C. Calcium Signaling Mechanisms across Kingdoms. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 37, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, J.; Tudzynski, P. Reactive oxygen species in phytopathogenic fungi: Signaling, development, and disease. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orłowska, E.; Llorente, B.; Cvitanich, C. Plant integrity: An important factor in plantpathogen interactions. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e22513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, P.; Wang, W.L.; Duan, W.K.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.L. Comprehensive analysis of the CDPK-SnRK superfamily genes in chinese cabbage and its evolutionary implications in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Ji, D.; Chen, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Tian, S. Production, signaling, and scavenging mechanisms of reactive oxygen species in fruit-pathogen interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kunkel, B.N.; Brooks, D.M. Cross talk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berens, M.L.; Berry, H.M.; Mine, A.; Argueso, C.T.; Tsuda, K. Evolution of hormone signaling networks in plant defense. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2017, 55, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borad, V.; Sriram, S. Pathogenesis-related proteins for the plant protection. Asian J. Exp. Sci. 2008, 22, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Bari, R.; Jones, J.D.G. Role of plant hormones in plant defence response. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.C.; Fernando, W.G.D. Hormonal responses to susceptible, intermediate, and resistant interactions in the Brassica napus–Leptosphaeria maculans pathosystem. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepper, C.; Day, B. From perception to activation: The molecular-genetic and biochemical landscape of disease resistance signaling in plants. Arab. Book 2010, 8, e012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solanaceae Genomics Network. Available online: https://solgenomics.net/ (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Zhou, Y.; Jing, M.F.; Levy, A.; Wang, H.Z.; Jiang, S.J.; Dou, D.L. Molecular mechanism of nanochitin whisker elicits plant resistance against Phytophthora and the receptors in plants. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 165, 2660–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Tool for Finding Specific Primers. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/primer-blast (accessed on 10 October 2021).

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Liang, X.; Xu, G.; Jing, M.; Li, Z.; Hein, I.; et al. Comparison of the Distinct, Host-Specific Response of Three Solanaceae Hosts Induced by Phytophthora infestans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011000
Lu J, Liu T, Zhang X, Li J, Wang X, Liang X, Xu G, Jing M, Li Z, Hein I, et al. Comparison of the Distinct, Host-Specific Response of Three Solanaceae Hosts Induced by Phytophthora infestans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(20):11000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011000
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Jie, Tingli Liu, Xiong Zhang, Jie Li, Xun Wang, Xiangxiu Liang, Guangyuan Xu, Maofeng Jing, Zhugang Li, Ingo Hein, and et al. 2021. "Comparison of the Distinct, Host-Specific Response of Three Solanaceae Hosts Induced by Phytophthora infestans" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 20: 11000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011000
APA StyleLu, J., Liu, T., Zhang, X., Li, J., Wang, X., Liang, X., Xu, G., Jing, M., Li, Z., Hein, I., Dou, D., Zhang, Y., & Wang, X. (2021). Comparison of the Distinct, Host-Specific Response of Three Solanaceae Hosts Induced by Phytophthora infestans. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(20), 11000. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222011000





