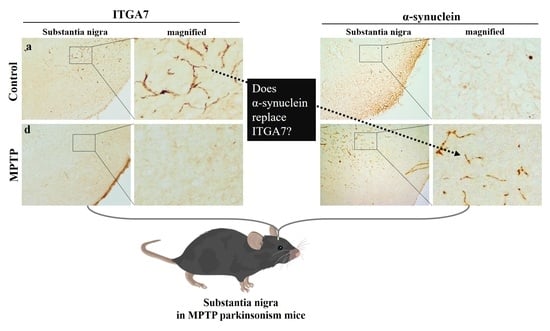
Decrease in ITGA7 Levels Is Associated with an Increase in α-Synuclein Levels in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model and SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Reduction in Tyrosine Hydroxylase Expression in a Mouse Model of Chronic MPTP-Induced PD
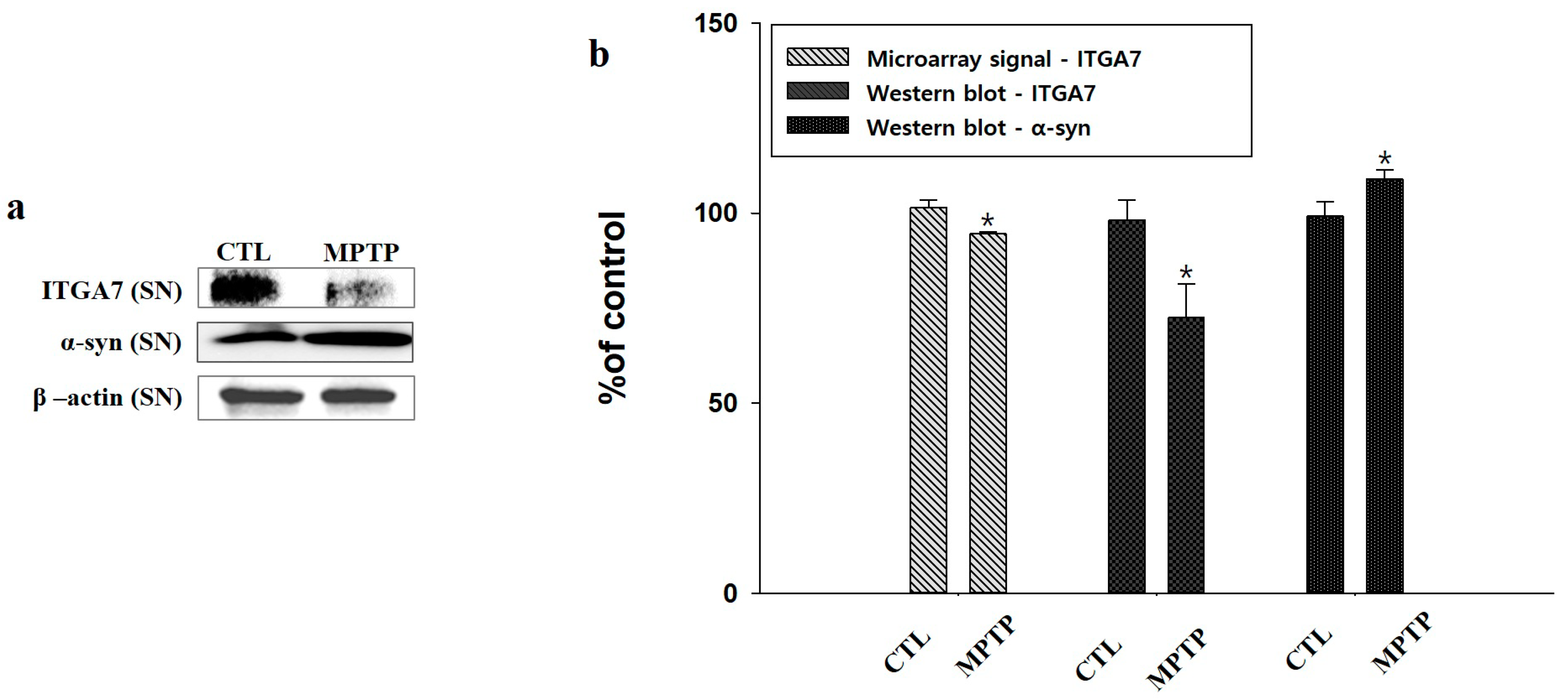
2.2. Microarray Analysis and Western Blot Analysis of ITGA7 in the Substantia Nigra
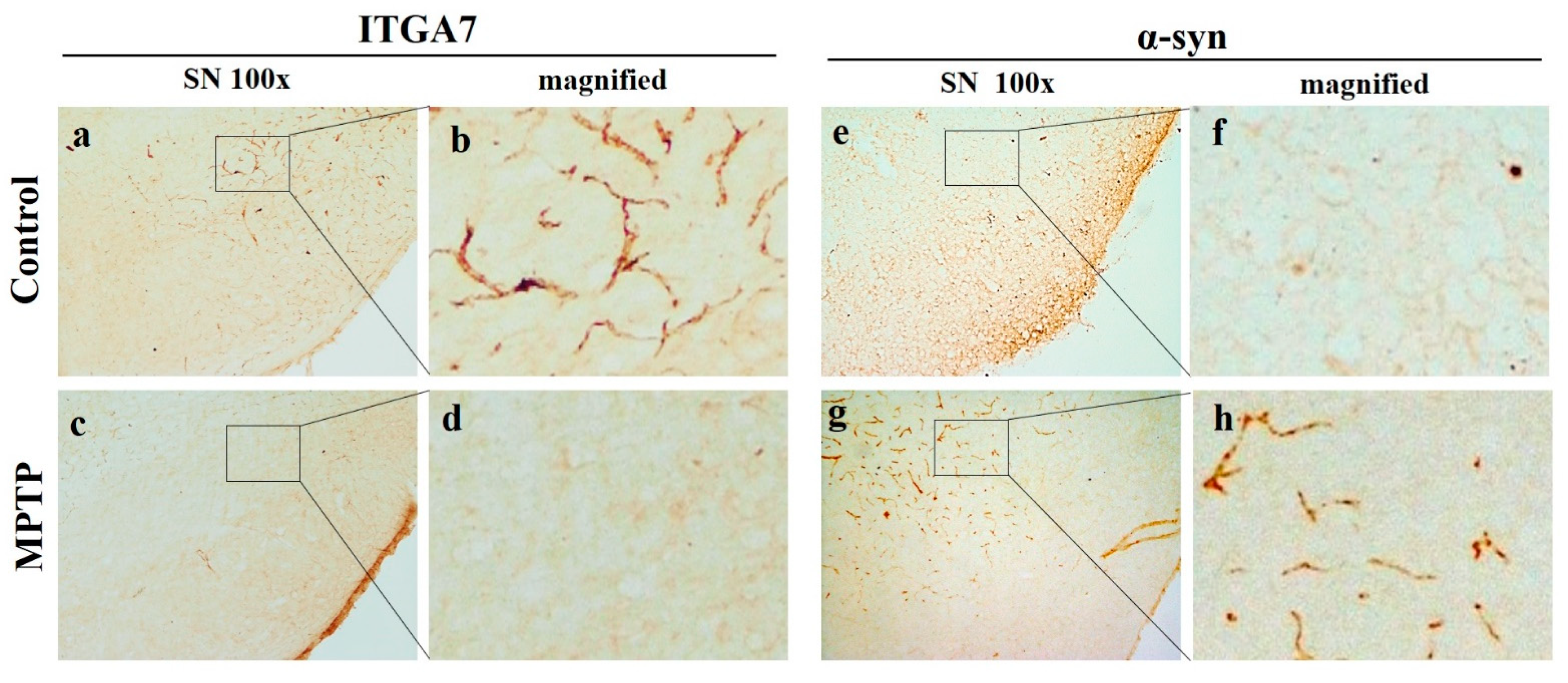
2.3. Reduction in ITGA7 Expression and Increase in α-Syn Expression in the Substantia Nigra in a Mouse Model of Chronic MPTP-Induced PD
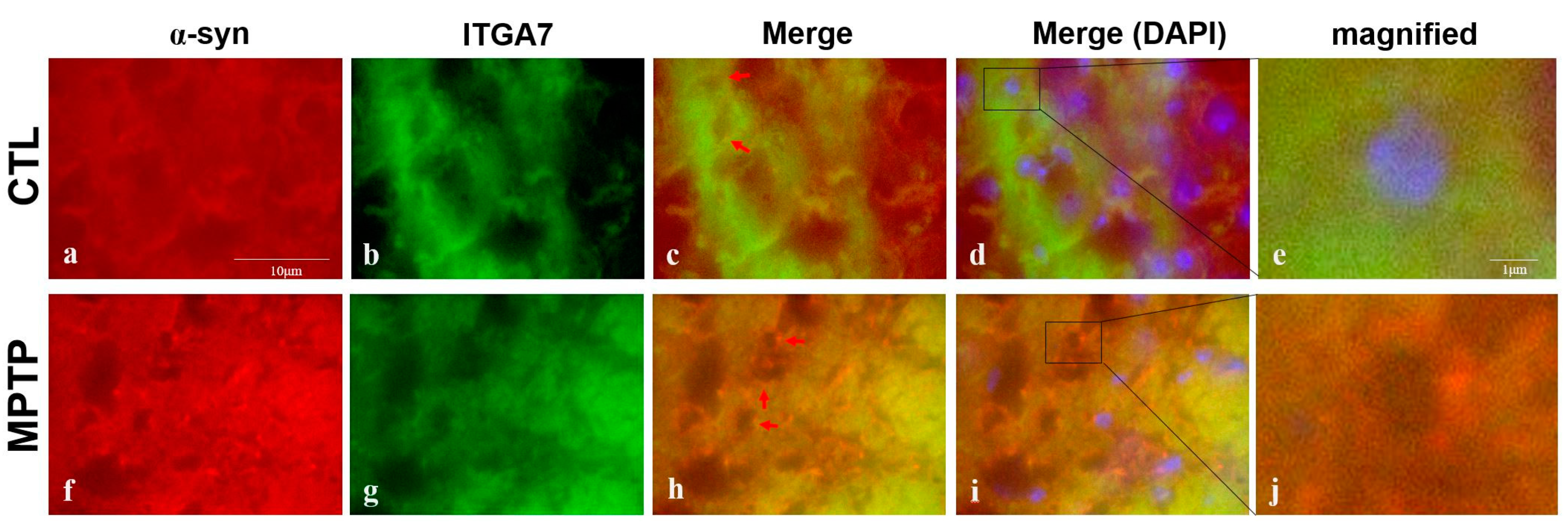
2.4. Immunofluorescence Analysis of ITGA7 Co-Localized with a α-Syn in the Substantia Nigra
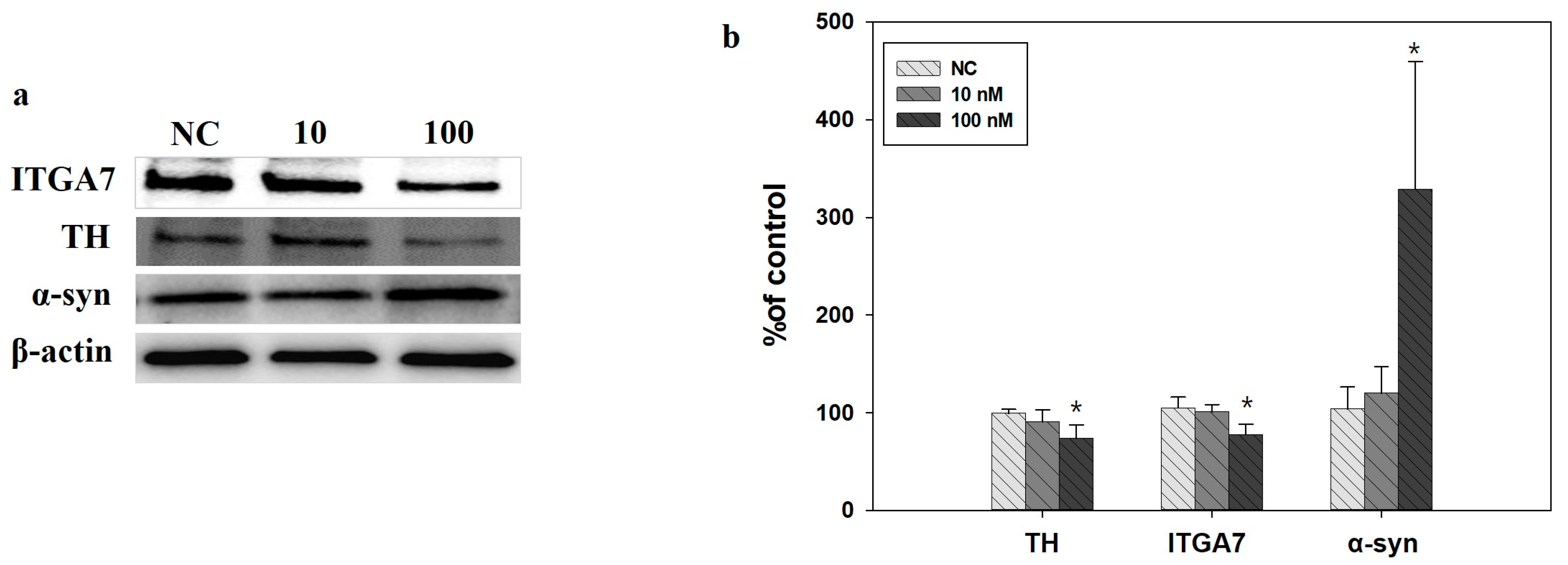
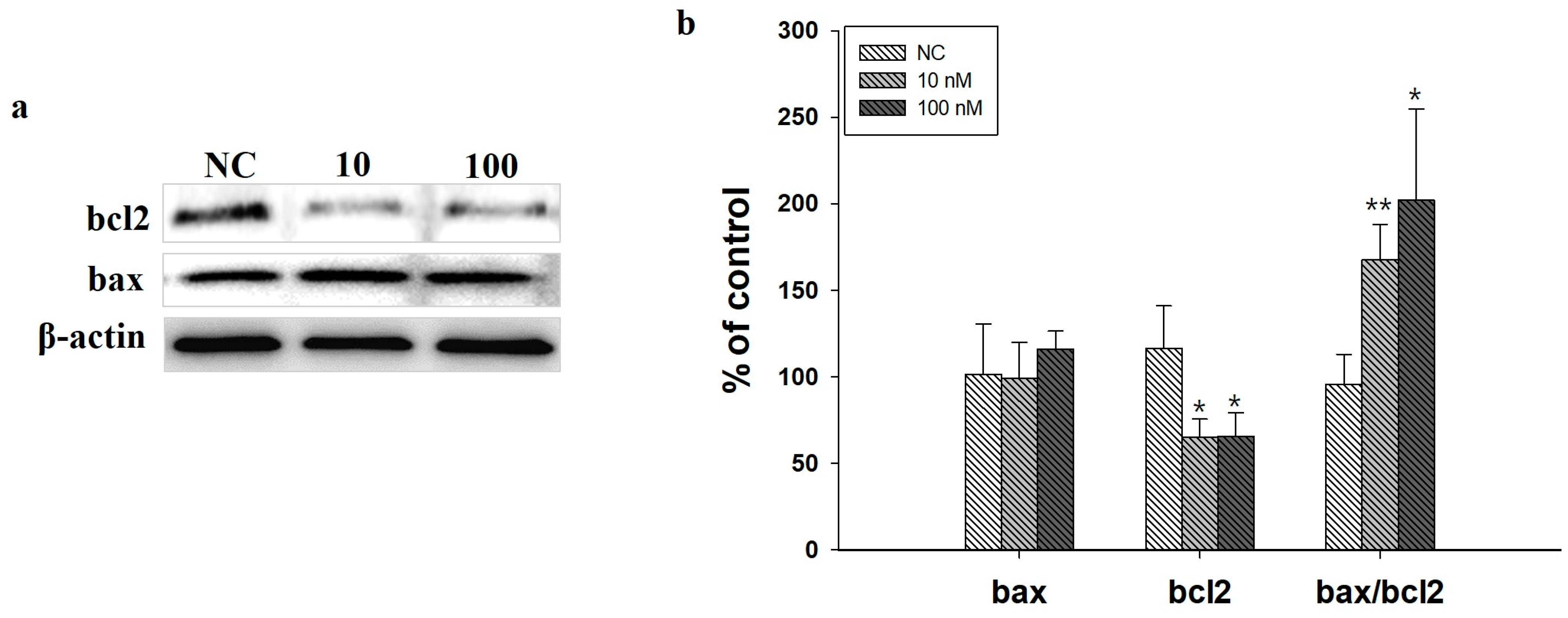
2.5. Western Blot Analysis in SH-SY5Y Cells Induced by ITGA7 siRNA
2.6. Immunofluorescence Analysis of ITGA7 Revealed Co-Localization with α-Syn in SH-SY5Y Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model
4.2. Cell lines and Cultures
4.3. ITGA7 Small Interfering RNA
4.4. MPP+ Treatment
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hattori, N. Etiology and pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: From mitochondrial dysfunctions to familial Parkinson’s disease. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 2004, 44, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J. Parkinson’s disease: Clinical features and diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baba, M.; Nakajo, S.; Tu, P.H.; Tomita, T.; Nakaya, K.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Iwatsubo, T. Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of sporadic Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 879–884. [Google Scholar]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, K. Mechanistic aspects of Parkinson’s disease: Alpha-synuclein and the biomembrane. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 47, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Garcia, E.; Auzmendi-Iriarte, J.; Matheu, A. Integrin α7: A novel promising target in glioblastoma stem cells. Stem Cell Investig. 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Kong, X. Integrin α7 knockdown suppresses cell proliferation, migration, invasion and EMT in hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaffky, E.; Williams, R.; Yao, C.C.; Ziober, B.; Kramer, R.; Sutherland, A. Trophoblast-specific expression and function of the integrin alpha 7 subunit in the peri-implantation mouse embryo. Dev. Biol. 2001, 239, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, L.-Z.; Song, Y.; Nelson, J.; Yu, Y.P.; Luo, J.-H. Integrin α7 Binds Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase 3 to Suppress Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohn, R.D.; Mayer, U.; Saher, G.; Herrmann, R.; van der Flier, A.; Sonnenberg, A.; Sorokin, L.; Voit, T. Secondary reduction of alpha7B integrin in laminin alpha2 deficient congenital muscular dystrophy supports an additional transmembrane link in skeletal muscle. J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 163, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, U.; Saher, G.; Fassler, R.; Bornemann, A.; Echtermeyer, F.; von der Mark, H.; Miosge, N.; Poschl, E.; von der Mark, K. Absence of integrin alpha 7 causes a novel form of muscular dystrophy. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flintoff-Dye, N.L.; Welser, J.; Rooney, J.; Scowen, P.; Tamowski, S.; Hatton, W.; Burkin, D.J. Role for the alpha7beta1 integrin in vascular development and integrity. Dev. Dyn. 2005, 234, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegoraro, E.; Cepollaro, F.; Prandini, P.; Marin, A.; Fanin, M.; Trevisan, C.P.; El-Messlemani, A.H.; Tarone, G.; Engvall, E.; Hoffman, E.P.; et al. Integrin alpha 7 beta 1 in muscular dystrophy/myopathy of unknown etiology. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 2135–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, K.; Grzesiak, J.J.; Bouvet, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Masliah, E.; Shults, C.W. Alpha-synuclein overexpression in oligodendrocytic cells results in impaired adhesion to fibronectin and cell death. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2005, 29, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surguchev, A.A.; Surguchov, A. Integrins-A missing link in synuclein’s pathogenic mechanism. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 97, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surguchev, A.A.; Emamzadeh, F.N.; Surguchov, A. Cell Responses to Extracellular alpha-Synuclein. Molecules 2019, 24, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campos-Sousa, R.N.; Quagliato, E.; da Silva, B.B.; de Carvalho, R.M., Jr.; Ribeiro, S.C.; de Carvalho, D.F. Urinary symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: Prevalence and associated factors. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2003, 61, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, K.; Nemani, V.M.; Azarbal, F.; Skibinski, G.; Levy, J.M.; Egami, K.; Munishkina, L.; Zhang, J.; Gardner, B.; Wakabayashi, J.; et al. Direct membrane association drives mitochondrial fission by the Parkinson disease-associated protein alpha-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20710–20726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefanis, L. α-Synuclein in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a009399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burre, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Sudhof, T.C. Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidson, W.S.; Jonas, A.; Clayton, D.F.; George, J.M. Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9443–9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nuscher, B.; Kamp, F.; Mehnert, T.; Odoy, S.; Haass, C.; Kahle, P.J.; Beyer, K. Alpha-synuclein has a high affinity for packing defects in a bilayer membrane: A thermodynamics study. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 21966–21975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- West, A.; Brummel, B.E.; Braun, A.R.; Rhoades, E.; Sachs, J.N. Membrane remodeling and mechanics: Experiments and simulations of alpha-Synuclein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1858 Pt B, 1594–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, N.; Goncalves, N.P.; Jan, A.; Jensen, N.M.; van der Laan, A.; Mohseni, S.; Vaegter, C.B.; Jensen, P.H. Trans-synaptic spreading of alpha-synuclein pathology through sensory afferents leads to sensory nerve degeneration and neuropathic pain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Goncalves, N.P.; Vaegter, C.B.; Jensen, P.H.; Ferreira, N. The Prion-Like Spreading of Alpha-Synuclein in Parkinson’s Disease: Update on Models and Hypotheses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.; Gram, H.; Sorrentino, Z.A.; Gregersen, E.; Schmidt, S.I.; Reimer, L.; Betzer, C.; Perez-Gozalbo, C.; Beltoja, M.; Nagaraj, M.; et al. Multiple system atrophy-associated oligodendroglial protein p25alpha stimulates formation of novel alpha-synuclein strain with enhanced neurodegenerative potential. Acta Neuropathol. 2021, 142, 87–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R.J.; Covell, D.J.; Medellin, C.; Stieber, A.; Robinson, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Pitkin, R.M.; Olufemi, M.F.; Luk, K.C.; et al. Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological alpha-synuclein strains in alpha-synucleinopathies. Nature 2018, 557, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lill, C.M.; Roehr, J.T.; McQueen, M.B.; Kavvoura, F.K.; Bagade, S.; Schjeide, B.M.; Schjeide, L.M.; Meissner, E.; Zauft, U.; Allen, N.C.; et al. Comprehensive research synopsis and systematic meta-analyses in Parkinson’s disease genetics: The PDGene database. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, J.; Yi, K.; Guo, M.; An, X.; Qu, H.; Lin, Q.; Bi, M.; Ma, Q. Analysis of LRRK2, SNCA, and ITGA8 Gene Variants with Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease Susceptibility in Chinese Han Population. Parkinsons Dis. 2016, 2016, 3474751. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, C.; Mehdi, R.N.; Fardell, C.; Xiang, F.; Nissbrandt, H.; Sydow, O.; Wirdefeldt, K.; Belin, A.C. No Association Between rs7077361 in ITGA8 and Parkinson’s Disease in Sweden. Open Neurol. J. 2016, 10, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.C.; Chen, C.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Fung, H.C.; Chang, K.H.; Wu, Y.R. DLG2, but not TMEM229B, GPNMB, and ITGA8 polymorphism, is associated with Parkinson’s disease in a Taiwanese population. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 64, 158.e1–158.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, Y.T.; Wolter, K.G.; Youle, R.J. Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-X(L) during apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3668–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oltvai, Z.N.; Milliman, C.L.; Korsmeyer, S.J. Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 1993, 74, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burre, J.; Sharma, M.; Sudhof, T.C. alpha-Synuclein assembles into higher-order multimers upon membrane binding to promote SNARE complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4274–E4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.; Seo, M.H.; Lim, S.; Yeo, S. Decrease in ITGA7 Levels Is Associated with an Increase in α-Synuclein Levels in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model and SH-SY5Y Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312616
Han S, Seo MH, Lim S, Yeo S. Decrease in ITGA7 Levels Is Associated with an Increase in α-Synuclein Levels in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model and SH-SY5Y Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312616
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Sangeun, Min Hyung Seo, Sabina Lim, and Sujung Yeo. 2021. "Decrease in ITGA7 Levels Is Associated with an Increase in α-Synuclein Levels in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model and SH-SY5Y Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312616
APA StyleHan, S., Seo, M. H., Lim, S., & Yeo, S. (2021). Decrease in ITGA7 Levels Is Associated with an Increase in α-Synuclein Levels in an MPTP-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model and SH-SY5Y Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312616