Structural Insight into the Binding of TGIF1 to SIN3A PAH2 Domain through a C-Terminal Amphipathic Helix
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
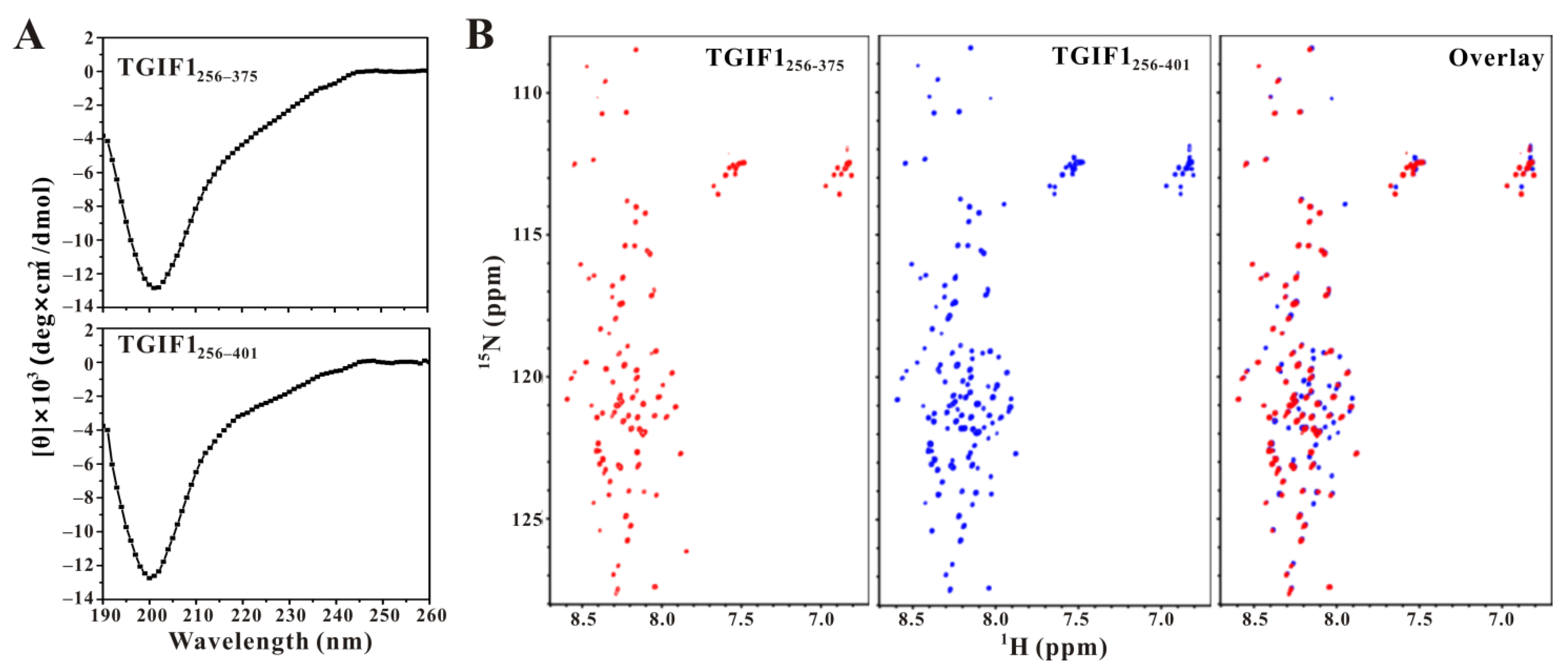
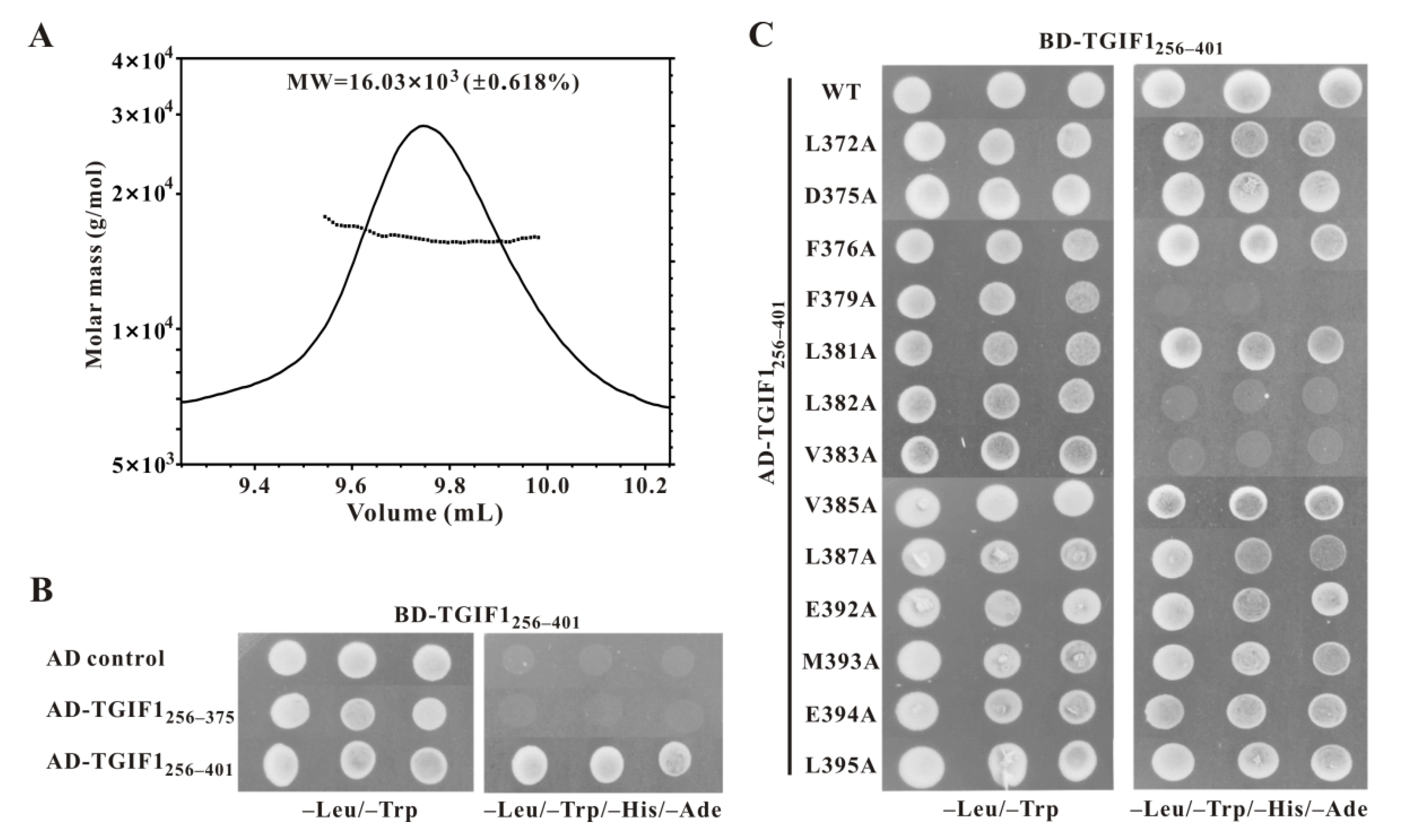
2.1. TGIF1256–401 Adopts an Intrinsically Disordered Structure
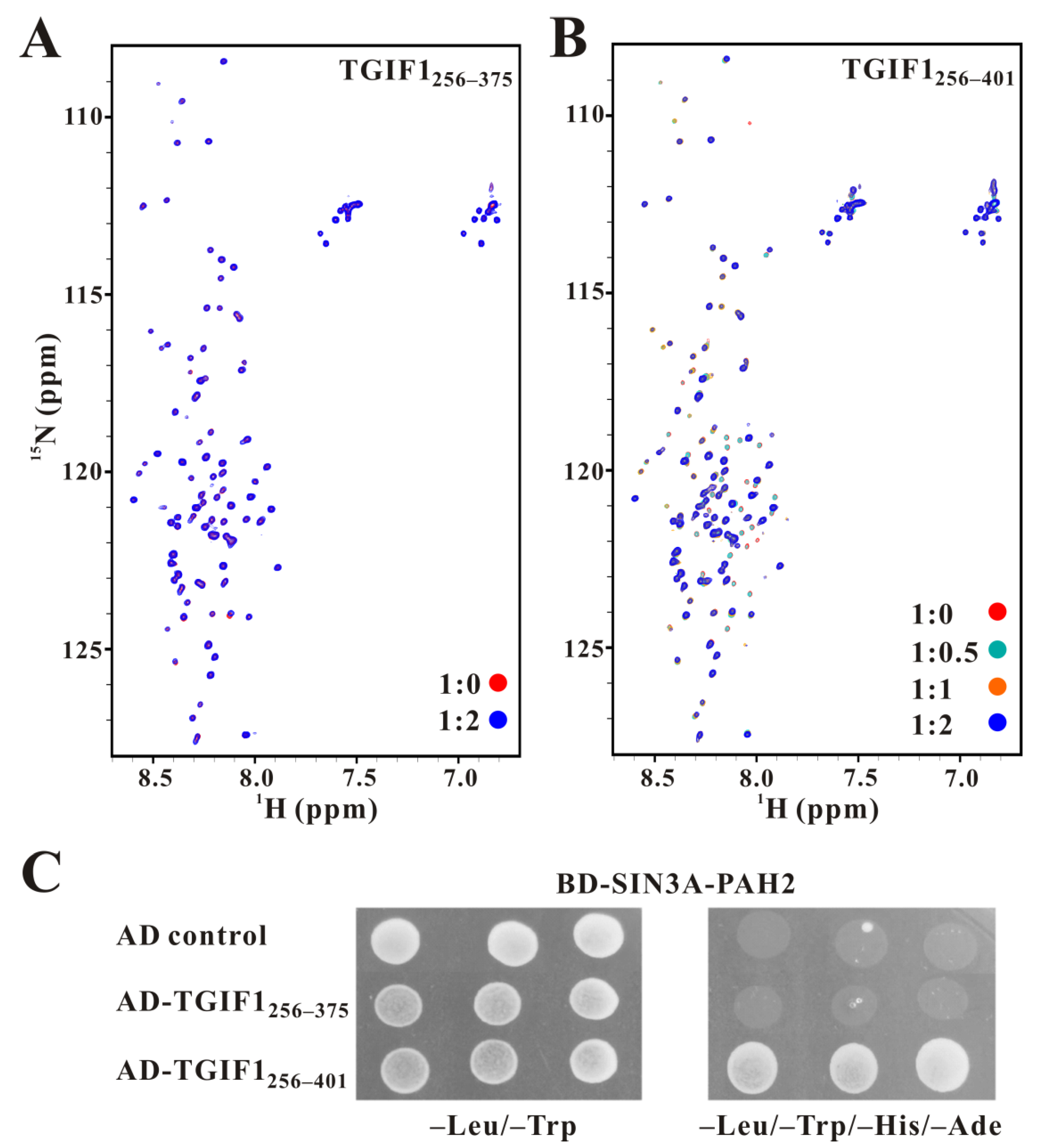
2.2. TGIF1376–401 Plays a Major Role in Binding to SIN3A PAH2
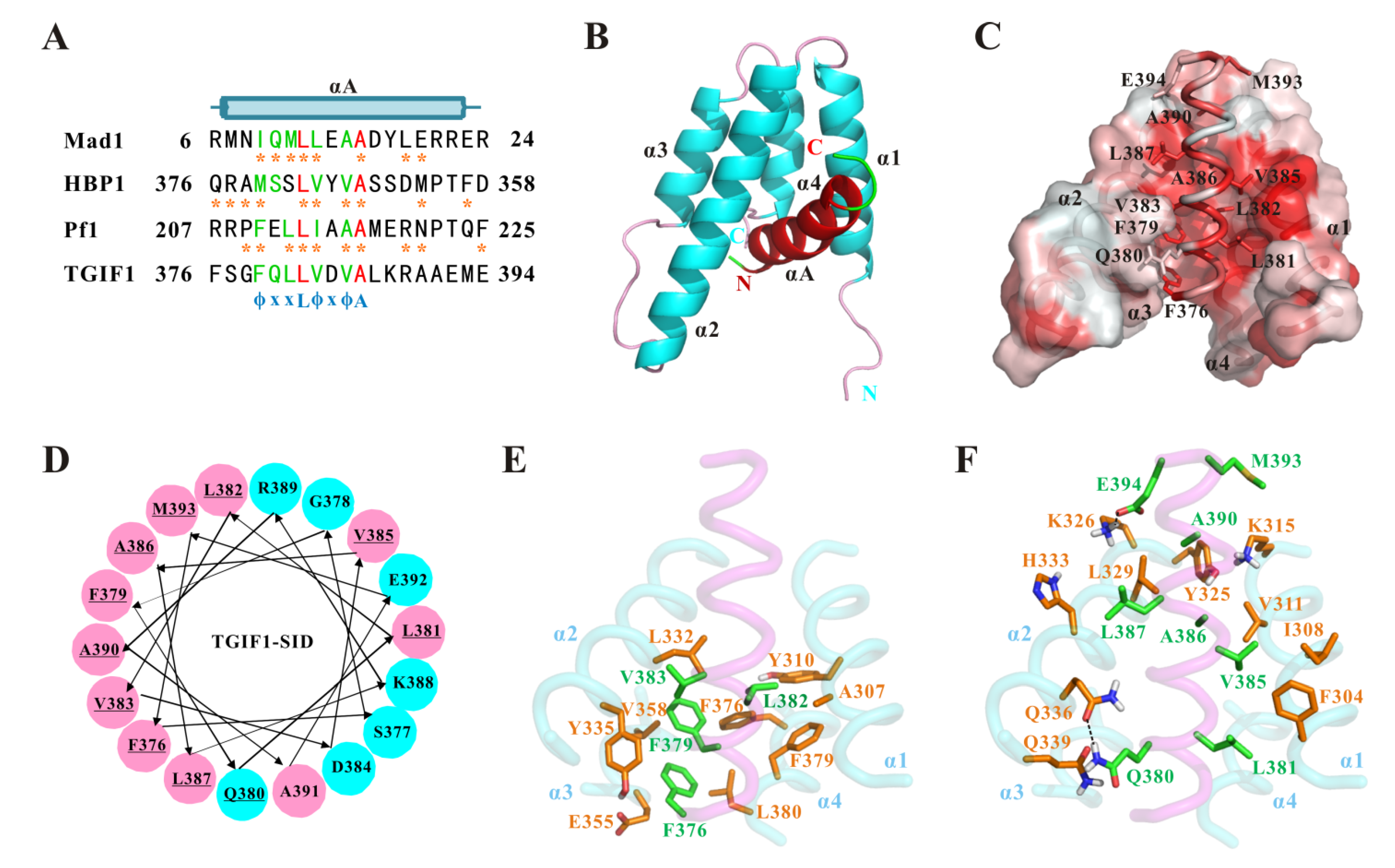
2.3. TGIF1376–401 Sequence Is Conserved among TGIF1 Homologs and Exhibits Similarity to SIDs of Other TFs
2.4. Structure Model of TGIF1-SID/SIN3A-PAH2 Complex Reveals the Interaction Pattern
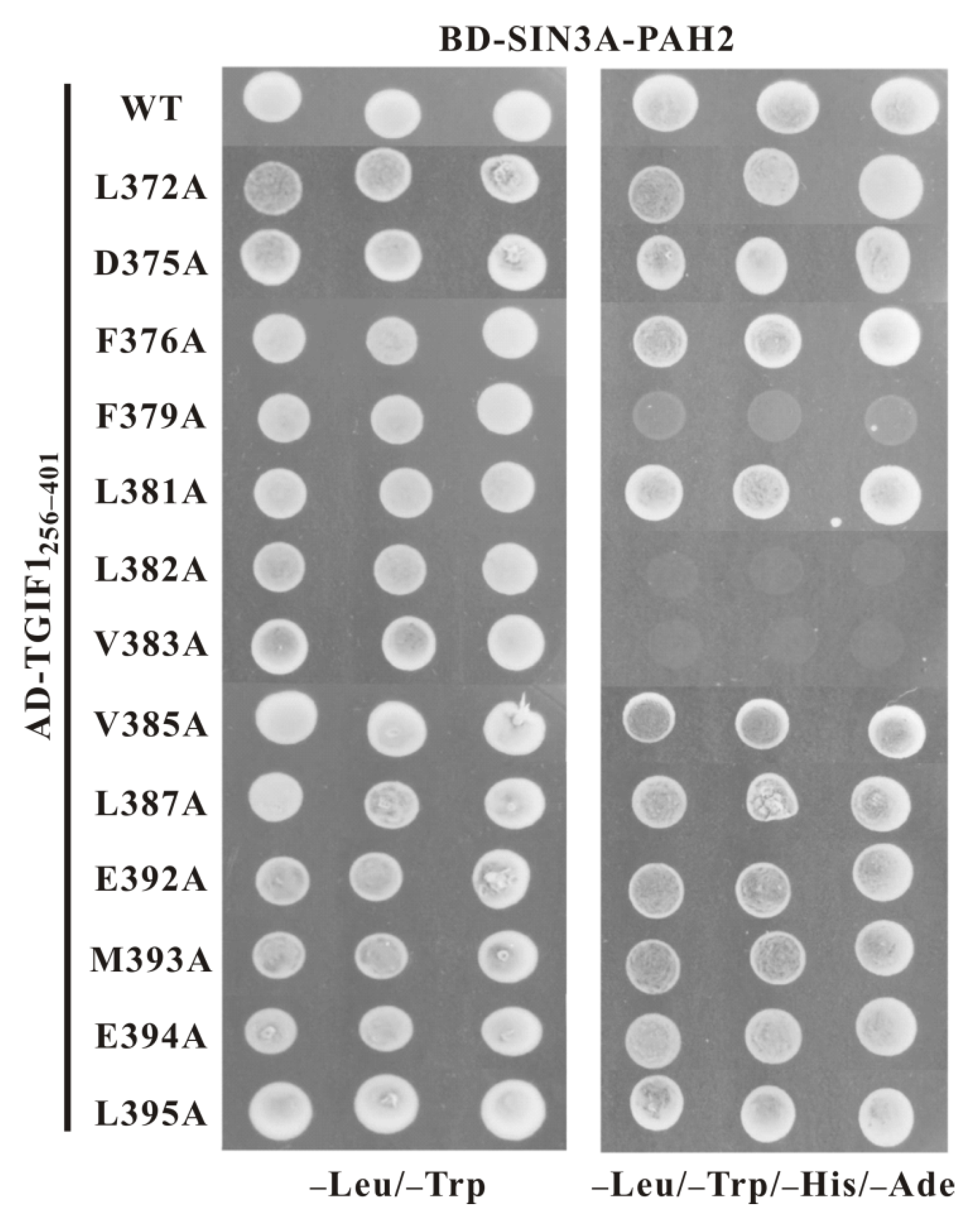
2.5. F379, L382 and V383 Are Key Residues of TGIF1 SID for Binding with Sin3A PAH2
2.6. TGIF1 SID Mediates Homodimerization of TGIF1 in Cell
3. Discussion
3.1. Disorder-to-Order Transition of TGIF1 SID upon Binding to SIN3A PAH2
3.2. Information from the Interaction Pattern of TGIF1 SID with SIN3A PAH2
3.3. Correlation between Homodimerization and SIN3A Binding of TGIF1
3.4. Sequence and Function Comparison of Human TGIF Homologs
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Production of Recombinant Proteins
4.2. Circular Dichroism
4.3. Multi-Angle Light Scattering
4.4. NMR Experiments
4.5. Yeast Two-Hybrid
4.6. Molecular Modeling
4.7. Sequence Alignment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burglin, T.R. Analysis of TALE superclass homeobox genes (MEIS, PBC, KNOX, Iroquois, TGIF) reveals a novel domain conserved between plants and animals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4173–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolino, E.; Reimund, B.; Wildt-Perinic, D.; Clerc, R.G. A Novel Homeobox Protein Which Recognizes a TGT Core and Functionally Interferes with a Retinoid-responsive Motif. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 31178–31188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotton, D.; Lo, R.S.; Lee, S.; Massagué, J. A Smad Transcriptional Corepressor. Cell 1999, 97, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Conway, S.J.; Chen, Y. Intragenic deletion of Tgif causes defectsin brain development. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 3508–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, T.; Ono, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Nishi, H.; Nagao, K.; Kawamura, T.; Abe, Y.; Wada, H.; Shimatsu, A.; Kita, T.; et al. TG-interacting factor is required for the differentiation of preadipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, R.; Brandt, S.J. Transforming growth-interacting factor (TGIF) regulates proliferation and differentiation of human myeloid leukemia cells. Mol. Oncol. 2009, 3, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Gasser, A.; Bolamperti, S.; Maeda, M.; Matthies, L.; Jähn, K.; Long, C.L.; Schlüter, H.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Saini, V.; et al. TG-interacting factor 1 (Tgif1)-deficiency attenuates bone remodeling and blunts the anabolic response to parathyroid hormone. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.; Melhuish, T.A.; Fox, T.E.; Jr, H.F.F.; Wotton, D. TGIF transcription factors repress acetyl CoA metabolic gene expression and promote intestinal tumor growth. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gripp, K.W.; Wotton, D.; Edwards, M.C.; Roessler, E.; Ades, L.; Meinecke, P.; Richieri-Costa, A.; Zackai, E.H.; Massague, J.; Muenke, M.; et al. Mutations in TGIF cause holoprosencephaly and link NODAL signalling to human neural axis determination. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-P.; Chern, S.-R.; Du, S.-H.; Wang, W. Molecular diagnosis of a novel heterozygous 268C?T (R90C) mutation inTGIF gene in a fetus with holoprosencephaly and premaxillary agenesis. Prenat. Diagn. 2002, 22, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilella, C.; Dubourg, C.; Attia-Sobol, J.; Vigneron, J.; Blayau, M.; Pasquier, L.; Lazaro, L.; Odent, S.; David, V. Molecular screening of the TGIF gene in holoprosencephaly: Identification of two novel mutations. Qual. Life Res. 2003, 112, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Jaick, K.; Powers, S.E.; Bartholin, L.; Myers, K.R.; Hahn, J.; Orioli, I.M.; Ouspenskaia, M.; Lacbawan, F.; Roessler, E.; Wotton, D.; et al. Functional analysis of mutations in TGIF associated with holoprosencephaly. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2007, 90, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, K.; Anderson, A.E.; Sutherland, A.; Wotton, D. Loss of Tgif Function Causes Holoprosencephaly by Disrupting the Shh Signaling Pathway. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, B.-W.; Wu, W.-J.; Li, W.-M.; Li, C.-C.; Huang, C.-N.; Kang, W.-Y.; Liu, Z.-M.; Huang, H.-S. Overexpression of TG-Interacting Factor Is Associated with Worse Prognosis in Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, A.; Jakobsen, J.S.; Ohlsson, E.; Rapin, N.; Waage, J.; Billing, M.; Bullinger, L.; Karlsson, S.; Porse, B.T. TGIF1 is a negative regulator of MLL-rearranged acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2014, 29, 1018–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, G.; Yi, Y.; Weiwei, H.U.; Weiming, W. TGIF1 promoted the growth and migration of cancer cells in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 9303–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.-Z.; Ferrigno, O.; Wang, Z.; Ohnishi, M.; Prunier, C.; Levy, L.; Razzaque, M.; Horne, W.C.; Romero, D.; Tzivion, G.; et al. TGIF Governs a Feed-Forward Network that Empowers Wnt Signaling to Drive Mammary Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, P.; Singh, P.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Eragamreddi, S.; Ozkan, S.; Ferrigno, O.; Prunier, C.; Razzaque, M.S.; Xu, K.; et al. TGIF 1 functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.-C.; Hsieh, M.-J.; Wu, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Shan, Y.-S.; Hung, W.-C.; Chen, L.-T.; Cheng, K.-H. Loss of the transcriptional repressor TGIF1 results in enhanced Kras-driven development of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melhuish, T.A.; Wotton, D. The Interaction of the Carboxyl Terminus-binding Protein with the Smad Corepressor TGIF Is Disrupted by a Holoprosencephaly Mutation in TGIF. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 39762–39766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Sun, Z. 5?TG3? Interacting Factor Interacts with Sin3A and Represses AR-Mediated Transcription. Mol. Endocrinol. 2001, 15, 1918–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotton, D.; Knoepfler, P.; Laherty, C.D.; Eisenman, R.N.; Massagué, J. The Smad transcriptional corepressor TGIF recruits mSin3. Cell Growth Differ. Mol. Boil. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2001, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Hamid, R.; Patterson, J.; Brandt, S.J. Genomic structure, alternative splicing and expression of TG-interacting factor, in human myeloid leukemia blasts and cell lines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gene Regul. Mech. 2008, 1779, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wotton, D.; Lo, R.S.; Swaby, L.-A.C.; Massague, J. Multiple Modes of Repression by the Smad Transcriptional Corepressor TGIF. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 37105–37110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojsin, M.; Popovic, J.; Kovacevic Grujicic, N.; Stevanovic, M. TG-interacting factor (TGIF) downregulates SOX3 gene expression in the NT2/D1 cell line. J. Genet Genom. 2012, 39, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramfalk, C.; Melhuish, T.A.; Wotton, D.; Jiang, Z.-Y.; Eriksson, M.; Parini, P. TG-interacting factor 1 acts as a transcriptional repressor of sterol O-acyltransferase. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.E.; Taniguchi, K.; Hao, Y.; Melhuish, T.A.; Shah, A.; Turner, S.D.; Sutherland, A.E.; Wotton, D. Tgif1 and Tgif2 Repress Expression of the RabGAP Evi5l. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00527-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholin, L.; Powers, S.E.; Melhuish, T.A.; Lasse, S.; Weinstein, M.; Wotton, D. TGIF Inhibits Retinoid Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 990–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.R.; Ferrand, N.; Faresse, N.; Prunier, C.; Abecassis, L.; Pessah, M.; Bourgeade, M.F.; Atfi, A. Nuclear retention of the tumor suppressor cPML by the homeodomain protein TGIF restricts TGF-beta signaling. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melhuish, T.A.; Chung, D.D.; Bjerke, G.A.; Wotton, D. Tgif1 represses apolipoprotein gene expression in liver. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 111, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guca, E.; Sunol, D.; Ruiz, L.; Konkol, A.; Cordero, J.; Torner, C.; Aragon, E.; Martin-Malpartida, P.; Riera, A.; Macias, M.J. TGIF1 homeodomain interacts with Smad MH1 domain and represses TGF-beta signaling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 9220–9235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Nie, Y.; Yue, X.; Zhu, J.; Hu, R.; Liu, M.; Yang, Y. Backbone and side chain resonance assignments of the C-terminal domain of human TGIF. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2019, 13, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettahar, A.; Ferrigno, O.; Zhang, M.Z.; Ohnishi, M.; Ferrand, N.; Prunier, C.; Levy, L.; Bourgeade, M.F.; Bieche, I.; Romero, D.G.; et al. Identification of PHRF1 as a tumor suppressor that promotes the TGF-beta cytostatic program through selective release of TGIF-driven PML inactivation. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demange, C.; Ferrand, N.; Prunier, C.; Bourgeade, M.-F.; Atfi, A. A Model of Partnership Co-Opted by the Homeodomain Protein TGIF and the Itch/AIP4 Ubiquitin Ligase for Effective Execution of TNF-α Cytotoxicity. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengoechea-Alonso, M.T.; Ericsson, J. Tumor suppressor Fbxw7 regulates TGFbeta signaling by targeting TGIF1 for degradation. Oncogene 2010, 29, 5322–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadamb, R.; Mittal, S.; Bansal, N.; Batra, H.; Saluja, D. Sin3: Insight into its transcription regulatory functions. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 92, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.E.; Chandru, A.; Cowley, S.M. Co-repressor, co-activator and general transcription factor: The many faces of the Sin3 histone deacetylase (HDAC) complex. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 3921–3932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, N.; David, G.; Farias, E.; Waxman, S. Emerging Roles of Epigenetic Regulator Sin3 in Cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2016, 130, 113–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilers, A.L.; Billin, A.; Liu, J.; Ayer, D. A 13-Amino Acid Amphipathic α-Helix Is Required for the Functional Interaction between the Transcriptional Repressor Mad1 and mSin3A. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 32750–32756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.A.; Knoepfler, P.S.; Huang, K.; Kang, R.S.; Cowley, S.M.; Laherty, C.D.; Eisenman, R.N.; Radhakrishnan, I. HBP1 and Mad1 repressors bind the Sin3 corepressor PAH2 domain with opposite helical orientations. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Garry, D.J. Sin3 interacts with Foxk1 and regulates myogenic progenitors. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 366, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-S.; Moncrieffe, M.C.; Kaczynski, J.; Ellenrieder, V.; Prendergast, F.G.; Urrutia, R.; Haracska, L.; Johnson, R.E.; Unk, I.; Phillips, B.; et al. A Conserved α-Helical Motif Mediates the Interaction of Sp1-Like Transcriptional Repressors with the Corepressor mSin3A. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 7199–7206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farias, E.F.; Petrie, K.; Leibovitch, B.; Murtagh, J.; Chornet, M.B.; Schenk, T.; Zelent, A.; Waxman, S. Interference with Sin3 function induces epigenetic reprogramming and differentiation in breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11811–11816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-J.; Petrie, K.; Leibovitch, B.; Zeng, L.; Mezei, M.; Howell, L.; Gil, V.; Christova, R.; Bansal, N.; Yang, S.; et al. Selective Inhibition of SIN3 Corepressor with Avermectins as a Novel Therapeutic Strategy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1824–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-J.; Leibovitch, B.A.; Bansal, N.; Pereira, L.; Chung, C.-Y.; Ariztia, E.V.; Zelent, A.; Farias, E.F.; Waxman, S. Targeted interference of SIN3A-TGIF1 function by SID decoy treatment inhibits Wnt signaling and invasion in triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 88421–88436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brubaker, K.; Cowley, S.M.; Huang, K.; Loo, L.; Yochum, G.S.; Ayer, D.E.; Eisenman, R.N.; Radhakrishnan, I. Solution Structure of the Interacting Domains of the Mad–Sin3 Complex: Implications for Recruitment of a Chromatin-Modifying Complex. Cell 2000, 103, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kumar, G.S.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Y.; Radhakrishnan, I. Solution structure of the mSin3A PAH2-Pf1 SID1 complex: A Mad1/Mxd1-like interaction disrupted by MRG15 in the Rpd3S/Sin3S complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferrand, N.; Demange, C.; Prunier, C.; Seo, S.R.; Atfi, A. A mechanism for mutational inactivation of the homeodomain protein TGIF in holoprosencephaly. FASEB J. 2006, 21, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.E.; Taniguchi, K.; Yen, W.; Melhuish, T.A.; Shen, J.; Walsh, C.A.; Sutherland, A.E.; Wotton, D. Tgif1 and Tgif2 regulate Nodal signaling and are required for gastrulation. Development 2010, 137, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melhuish, T.A.; Taniguchi, K.; Wotton, D. Tgif1 and Tgif2 Regulate Axial Patterning in Mouse. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melhuish, T.A.; Gallo, C.M.; Wotton, D. TGIF2 Interacts with Histone Deacetylase 1 and Represses Transcription. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32109–32114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaglio, F.; Grzesiek, S.; Vuister, G.W.; Zhu, G.; Pfeifer, J.; Bax, A. NMRPipe: A multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J. Biomol. NMR 1995, 6, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, T.D.; Kneller, D.G. SPARKY 3; University of California: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server: New development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W174–W181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, B.G.; Wiehe, K.; Hwang, H.; Kim, B.-H.; Vreven, T.; Weng, Z. ZDOCK server: Interactive docking prediction of protein-protein complexes and symmetric multimers. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1771–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Xia, B.; Porter, K.A.; Padhorny, D.; Yueh, C.; Beglov, D.; Vajda, S. The ClusPro web server for protein–protein docking. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 255–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Nie, Y.; Zhou, H.; Hu, R.; Li, Y.; He, T.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, M. Structural Insight into the Binding of TGIF1 to SIN3A PAH2 Domain through a C-Terminal Amphipathic Helix. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312631
He X, Nie Y, Zhou H, Hu R, Li Y, He T, Zhu J, Yang Y, Liu M. Structural Insight into the Binding of TGIF1 to SIN3A PAH2 Domain through a C-Terminal Amphipathic Helix. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(23):12631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312631
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiaoling, Yao Nie, Heng Zhou, Rui Hu, Ying Li, Ting He, Jiang Zhu, Yunhuang Yang, and Maili Liu. 2021. "Structural Insight into the Binding of TGIF1 to SIN3A PAH2 Domain through a C-Terminal Amphipathic Helix" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 23: 12631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312631
APA StyleHe, X., Nie, Y., Zhou, H., Hu, R., Li, Y., He, T., Zhu, J., Yang, Y., & Liu, M. (2021). Structural Insight into the Binding of TGIF1 to SIN3A PAH2 Domain through a C-Terminal Amphipathic Helix. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(23), 12631. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222312631





